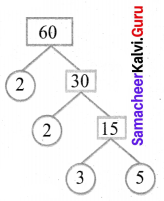
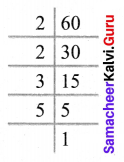
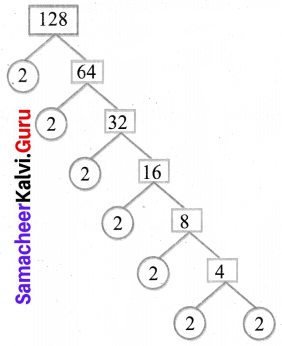
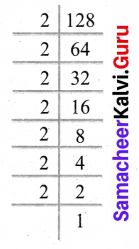
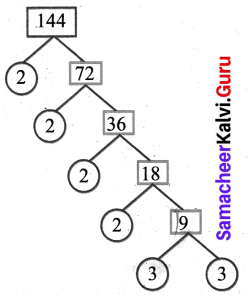
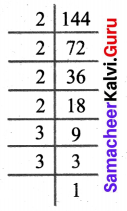
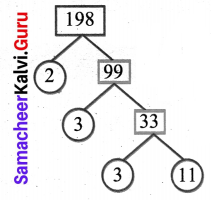
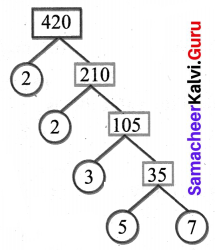
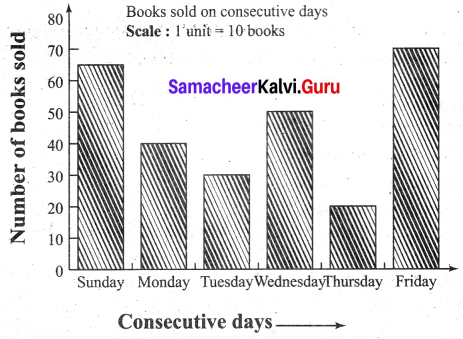
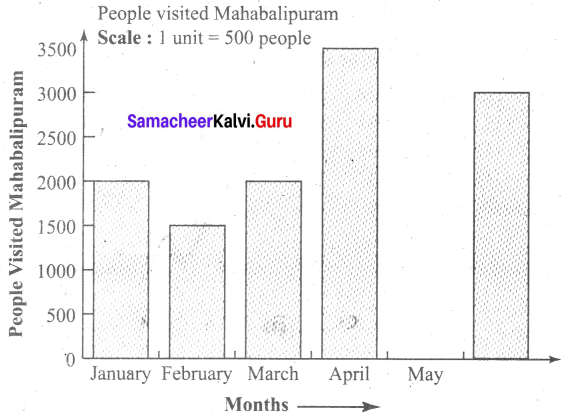
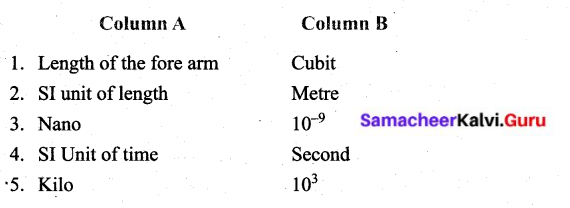
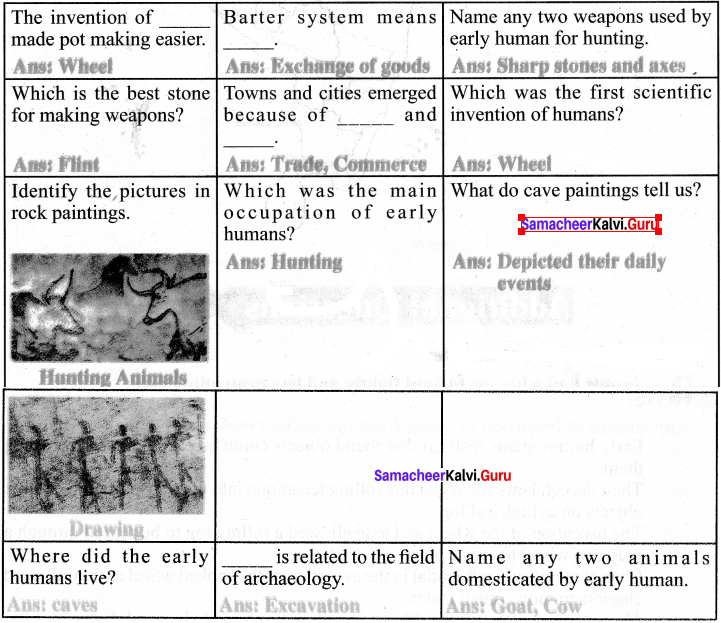
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 4 Our Environment
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Our Environment Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Question 1.
Identify the fresh water ecosystem.
(a) Pond
(b) Lake
(c) River
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
Question 2.
Producers are
a. Animals
b. Birds
c. Plants
d. Snakes
Answer:
c. Plants
Question 3.
It is a biodegradable waste
(a) Plastic
(b) Coconut Shell
(c) Glass
(d) Aluminium
Answer:
(b) Coconut shell
Question 4.
It is an undesirable change that occurs in air and water.
a. Recycling
b. Reuse
c. Pollution
d. Reduce
Answer:
c. Pollution
Question 5.
Usages of chemical pesticides and fertilisers causes pollution.
(a) Air pollution
(b) Water pollution
(c) Noise pollution
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Water pollution

II. Fill in the blanks:
- Primary consumers that eat plants are called _______
- Temperature, light and wind are _______ factors.
- _______ is the process of converting waste materials into new materials.
- Water pollution can spread _______ and chemicals.
- The 3R’s are Reduce, _______ and Recycle.
Answers:
- Herbivores
- Physical
- Recycling
- Diseases
- Reuse

III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement :
Question 1.
The Pacific ocean is an example of an aquatic ecosystem.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Bacteria and fungi are called decomposers.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Human and animal wastes are examples of non-biodegradable waste.
Answer:
False. Human and animal wastes are examples of biodegradable waste.
Question 4.
Excessive use of pesticides leads to air pollution.
Answer:
False. Excessive use of pestides leads to water pollution.
Question 5.
In schools, waste management rules say that we should separate waste in two categories.
Answer:
True

IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
- Biotic factor – Terrestrial Ecosystem
- Sewage – Land pollution
- Fertilizers – Air pollution
- Desert – Water Pollution
- Smoke – Animals
Answer:
- Biotic factor – Animals
- Sewage – Water pollution
- Fertilizers – Land pollution
- Desert – Terrestrial ecosystem
- Smoke – Air pollution

V. Arrange the following in a correct sequence and form a food chain
Question 1.
Rabbit → Carrot → Eagle → Snake
Answer:
Carrot → Rabbit → Snake → Eagle
Question 2.
Human → Insect → Algae → Fish
Answer:
Algae → Insect → Fish → Human

VI. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
Define ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living things that work together.
Question 2.
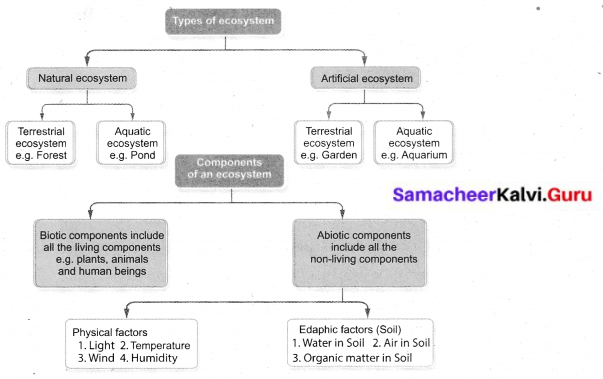
What are the two types of ecosystems?
Answer:
Types of ecosystems:
- Natural ecosystem
- Artificial ecosystem
Question 3.
Write any two things that can be recycled.
Answer:
Recycling things:
- Using old clothes to make paper.
- Melting some plastics to make floor mats, plastic boards, and hose pipes.
Question 4.
What are the types of pollution?
Answer:
There are four major kinds of pollution :
- Air Pollution.
- Water Pollution.
- Land (Soil) Pollution.
- Noise Pollution.
Question 5.
Give one example of a food chain in an aquatic ecosystem.
Answer:
Aquatic plant → Aquatic insect → Larva → fish
Question 6.
Name some pollutants.
Answer:
- Toxic gases and fine particles from burning fossil fuels, chemicals released from factories.
- Sewage, industrial effluents, pesticides and fertilizers
- Plastics and electronics are land pollutants.
Question 7.
What are the pollutions caused by the objects given below?
a. Loud Speaker
b. Plastic
Answer:
a. Loud Speaker – Causes noise pollution.
b. Plastic – Causes land (soil) pollution.

VII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
What is biodegradable waste?
Answer:
The term ‘‘Biodegradable” is used for those things that can be easily decomposed by natural agents like water, oxygen, ultraviolet rays of the sun and microorganisms, etc.
Question 2.
How can we reduce water pollution?
Answer:
- Do not pour left-over oil, old medicines or waste, down the drain or into the toilet.
- Reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers to grow crops.
- Use wastewater for the garden at home.
- Do not litter or dump waste – always use a waste bin.
Question 3.
Write the importance of the food chain.
Answer:
Importance of food chain
- Learning the food chain helps us to understand the feeding relationship and interaction between organisms in any ecosystem.
- Understanding the food chain also helps us to appreciate the energy flow and nutrient circulation in an ecosystem.
- This is important because pollution impacts the ecosystem. The food chain can be used to understand the movement of toxic substances and their impacts.

VIII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Give two examples of how you can avoid or reduce waste?
Answer:
1. Avoid:
- Avoid buying packaged foods.
- Refuse to buy use and throw plastic products.
- The usage of such unwanted materials may create more debris.
2. Reduce:
- Use durable goods that last longer instead of things that are used once and thrown away.
- (Eg.) Write on both sides of paper.
- Instead of unnecessary printing use electronic facilities.
Question 2.
Write a short note on noise pollution.
Answer:
- Noise pollution is caused by loud sounds.
- Loud music, the sounds of motor vehicles, fireworks and machines cause noise pollution which affects the environment.
- We all like a quiet and peaceful place since unpleasant or loud sounds disturb us.
- Continuous noise disturbs our sleep and does not let us study.
- It leads to stress and health impacts such as high blood pressure and hearing loss.
- Loud noise or music can damage our ears.
- It also disturbs animals. For example in noisy areas birds have to communicate louder so they can hear each other.
- Even underwater noise pollution from ships can make whales lose their way as they use sounds to navigate.

IX. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills :
Question 1.
What would happen if an organism is removed from the food chain?
Answer:
- The food chain in a grassland ecosystem is given below.
- Plants 2 Deer 2 Tiger
- Here if any one component of the food chain is harmed, the other living things are affected.
- For example, if the deer populations in a forest is reduced through natural or human activities, the tigers living in the forest will not have enough food to eat and so the number of tigers may get reduced.
Question 2.
Explain the link between waste and dangerous diseases like dengue and malaria?
Answer:
- Dengue and malaria fever are caused by the bite of mosquitoes.
- Accumulation of waste and stagnant water or uncovered containers of stored drinking water are the habitat for breeding mosquitoes.
- In order to control these infectious diseases, people should maintain a clean environment, free from mosquitoes.

X. See the diagram and answer the following questions :

Question 1.
Explain what is happening in the picture?
Answer:
- The atmosphere is polluted in this picture. It is due to the smoke rising from burning garbage.
- Land and water have been polluted because of leaching the toxins into the soil and water.
Questions 2.
What types of pollution are caused by open dumps?
Answer:
Types of pollution caused:
- Air pollution.
- Land pollution.
- Water pollution.

Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Our Environment Intext Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Think of the objects in your home. Just keep in mind, the books, toys, furniture, food materials and even pets of your home. These living and non-living things together make your home. Look at the following picture and list out the living and non-living things.
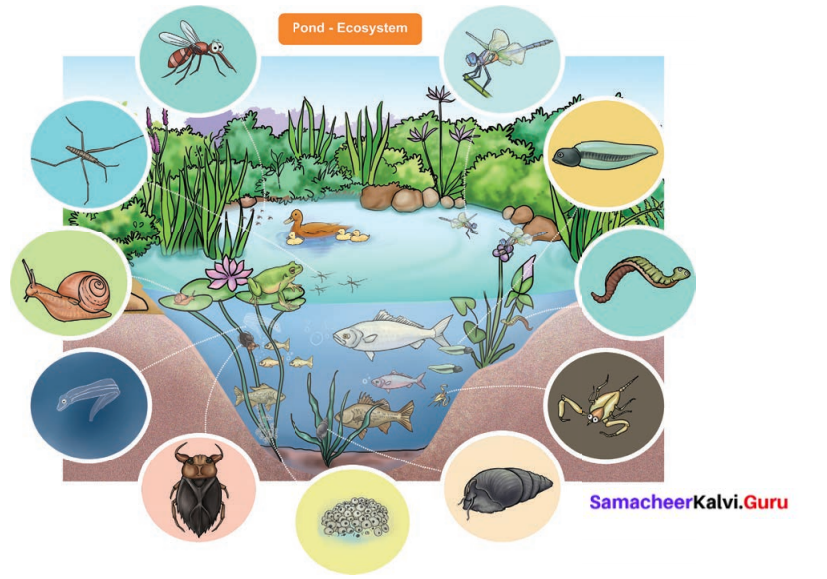
Answer:
Living things: Plants, Beetle, Mosquito, Larva, Water snake, Water scorpion, Snail, Fish, Duck, and Frog, etc.
Non- living things: Sun, Air, Water, Chemicals, Soil, Rocks and Temperature, etc.

Activity 2
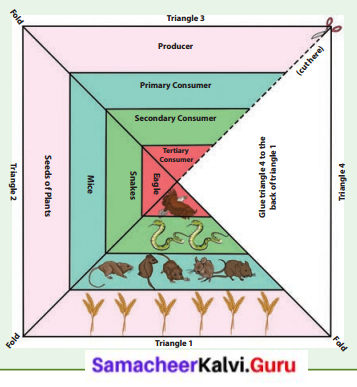
Take a square paper. Fold its diagonals. Draw three lines in three triangles as shown in the picture.
Cut from the edge of the diagonal to the centre as shown in the picture.
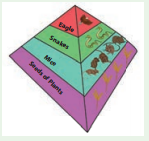
If you fold this triangle and paste behind the third triangle you get a pyramidal shape.
In one of the triangles, draw images of each of the organisms in the different levels.
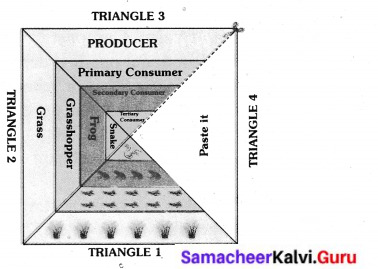
In another triangle write the names of the organisms. In the last triangle, write the energy level of the organism. Have a look at the following example. You must come up with different organisms!
Answer:

Activity 3
Take two mud pots or glass jars and fill them up with garden soil. In the first pot, mix wastes such as banana peel, some vegetable peels and a few tree leaves into the soil. In the second pot, mix a piece of the plastic carry bag, sweet wrapper, and metal foil into the soil.
What happen to the waste materials placed in both pots? Do you notice a difference between the first and second pot? Observe the changes over two weeks and discuss with your classmates.
Answer:
After two weeks, the wastes in the first pot, such as banana peel, some vegetable peel and tree leaves are degraded.
The wastes in the second pot such as carry bag, sweet wrapper and metal foil are not degraded.
Because the first pot has biodegradable wastes. So they are degraded. But the second pot has non-biodegradable wastes. So they are not degraded.

Activity Pg.No : 53
Question 1.
Give some examples for Biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
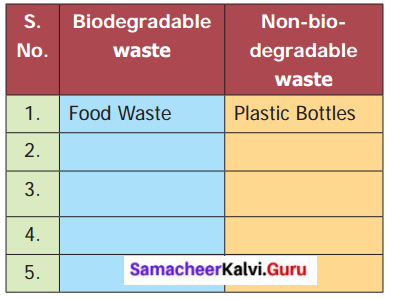
Answer:

Activity 4
Question 1.
Preparation of Vermi Compost

- Dig a pit for about one feet depth in the backyard or garden of your home or school.
- Fill the pit with bio-wastes, paper, and food wastes, place few earthworms in it, sprinkle water, and close the place with jute or cardboard and ensure moisture all the time.
- After 45 days the vermi casting layer formed just above the pit.
- These castings will be applied to the plant.
- This contains water-soluble nutrients.
- This type of compost helps in plant growth as well as sustain the land is fertility.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Classroom Exercise:
Identify who am I?
Question 1.
I am the type of pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels like petrol (or) coal and the smoke of burning garbage. I float around and cause breathing problems. I am _______ pollution.
Answer:
Air.
Question 2.
I am the type of pollution caused by loud sounds and I can cause serious damage to your ears and also affect sleep. In India, I am mainly caused by loudspeakers and the honking of air horns of cars. I am _______ pollution.
Answer:
Noise.
Question 3.
I flow from homes and farms into rivers and lakes. I kill fish and make water unfit for drinking. I am _______ pollution.
Answer:
Water.
Question 4.
I am the type of pollution caused by using too much chemical fertilizers and pesticides by farmers. I lower the quality of soil and even move chemicals into plant parts which are eaten by people. I am _______ pollution.
Answer:
Land.

Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Our Environment Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
These are abiotic factors.
i. Sunlight
ii. Bacteria
iii. Air
iv. Plants
(a) i and ii
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) iii and iv
Answer:
(b) i and iii
Question 2.
Pick out the terrestrial ecosystem
(a) lake
(b) mountain regions
(c) deserts
(d) both b and c
Answer:
(d) both b and c – mountain regions deserts
Question 3.
_______ are organisms that are able to produce their own organic food.
(a) Producers
(b) Consumers
(c) Decomposer
(d) Omnivores
Answer:
(a) Producers
Question 4.
The primary energy production in the world of living things is made by?
(a) aquatic insect
(b) rabbit
(c) plants
(d) deer
Answer:
(c) plants
Question 5.
Natural agents like _______ are the decomposition factors breaking complex forms into the simpler units.
(a) Oxygen
(b) Water
(c) microorganisms
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 6.
The average person in India produces _______ kg of waste everyday
(a) 0.45
(d) 055
(c) 0.40
(d) 0.55
Answer:
(a) 0.45
Question 7.
Most _______ pollution is caused by the burning of these fossil fuels.
(a) Water
(b) Land
(c) Air
(d) Noise
Answer:
(c) Air
Question 8.
Among the following which one is not polluted by noise pollution?
(a) Sounds of motor vehicles
(b) Music from the radio
(c) Firing crackers
(d) Loud music
Answer:
(b) Music from the radio
Question 9.
_______ Pollution has been directly linked to stress and health impacts such as high blood pressure and hearing loss.
(a) Noise
(b) Land
(c) Water
(d) Air
Answer:
(a) Noise

II. Fill in the blanks:
- _______ are called as biotic factors.
- _______ is the best example of a natural terrestrial ecosystem.
- Ecosystem originated without human intervention is called _______
- The ecosystem in water is called the _______ ecosystem.
- _______ obtained energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms.
- The sequence of who eats whom in an ecosystem is called _______
- The food chain begins with the energy given by the _______
- Each level in the food chain is called a _______ level.
- The burning of solid waste in _______ is called incineration.
- Garbage buried inside landfills remain here for a long time as they decompose very slowly and become _______
- Polluted _______ affects the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Land (Soil) pollution happens when toxic change the natural balance in the soil.
Answers:
- Plants
- Forest
- Natural ecosystem
- Aquatic
- Bacterium
- Food chain
- Sun
- Trophic
- Incinerator
- Manure
- Air
- Chemicals

III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
Forest and Mountain regions are the best examples of the artificial terrestrial ecosystem.
Answer:
False. Forest and Mountain regions are the best examples of the natural terrestrial ecosystem.
Question 2.
Fish and other water creatures and plants are maintained in the terrarium.
Answer:
False. Fish and other water creatures and plants are maintained in the aquarium.
Question 3.
Animals that eat both plants and animals are called Carnivores.
Answer:
False. Animals that eat both plants and animals are called Omnivores.
Question 4.
In a food, chain grasshopper gets energy by eating frogs.
Answer:
False. In a food, chain frog gets energy by eating a grasshopper.
Question 5.
If we protect the ecosystem, we can reduce waste by using durable goods.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
The term non-biodegradable is used for those things that can be easily decomposed.
Answer:
False. The term non-biodegradable is used for those things that cannot be easily decomposed.
Question 7.
The process by which waste materials are used to make new products is called recycling.
Answer:
True.
Question 8.
Expired medicines, used batteries are domestic hazardous waste.
Answer:
True.
Question 9.
Lcrud noise or even loud music can damage our eyes.
Answer:
False. Loud noise or even loud music can damage our ears.

IV. Match the following :
A.
| i. |
Abiotic factor |
(a) |
Deer |
| ii. |
Decomposers |
(b) |
Owl |
| iii. |
Herbivores |
(c) |
Heat |
| iv. |
Carnivores |
(d) |
Human |
| v. |
Omnivores |
(e) |
Fungi |
Answers:
i – c
ii – e
iii – a
iv – b
v – d.
B.
| i. |
Avoid the usage |
(a) |
Recycle |
| ii. |
Sharing newspapers |
(b) |
Incinerate |
| iii. |
Using of fountain pens |
(c) |
Buying packaged food |
| iv. |
Using old clothes to make paper |
(d) |
Reducing |
| v. |
Human anatomical waste |
(e) |
Reusing |
Answers:
i – c
ii – d
iii – e
iv – a
v – b.
C.
| i. |
Burning coal |
(a) |
Land pollution |
| ii. |
Throwing plastic |
(b) |
Noise pollution |
| iii. |
Wastewater from factories is mixed with river |
(c) |
Air pollution |
| iv. |
Louder horn of vehicle |
(d) |
Water pollution |
Answers:
i – c
ii – a
iii – d
iv – b.

V. Analogy:
Question 1.
Biotic factor : Animals :: Abiotic factor : _______
Answer:
Air or Water.
Question 2.
Natural terrestrial ecosystem : Forest:: Artificial terrestrial ecosystem : _______
Answer:
Garden.
Question 3.
Primary Consumer : Goat, Cow :: Secondary Consumer : _______
Answer:
Frog, Owl.
Question 4.
Biodegradable waste: Leaves, Garden wastes:: Non-biodegradable waste: _______
Answer:
Plastic cover, glass bottle.
Question 5.
Edaphic factor : Water in soil:: Physical factor : _______
Answer:
Light.

VI. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
List out the following by biotic and abiotic factors. (Sun, plants, animals, air, soil, bacteria, heat, minerals.
Answer:
Abiotic Factors:
Sun, Air
Water, Soil
Heat, Minerals
Biotic Factors:
Plants
Animals
Bacteria
Question 2.
Give a brief account of the landfill.
Answer:
- Land filling is a method in which wastes are dumped into naturally occurring or man-made pits and covered with soil.
- Garbage buried inside landfills remains here for a long time as they decompose very slowly and become man use.
- These places can be converted into parks, gardens, etc.
- The first step should always be to reduce waste.
- The second step is to keep waste separate. So that the waste can be easily reused or recycled.
Question 3.
Define – Aquarium.
Answer:
An aquarium is a place in which fish and other water creatures and plants are maintained.
Example: Fish growing in homes with a small tanks.
Question 4.
What are Autotrophs?
Answer:
Producers are organisms that are able to produce their own organic food. They do not need to eat other organisms, to do this. Producers are also called Autotrophs.
Question 5.
Define – Heterotrophs.
Answer:
Organisms which cannot produce their own food, need to eat other organisms as food. These Organisms are also called consumers. All animals are consumers as they cannot produce their own food. Consumers are also called Heterotrophs.
Question 6.
Differentiate between herbivores and carnivores.
Answer:
Herbivores:
- Animals which eat plants or plant products.
- Ex: Deer, Goat, Cattle, and Rat.
Carnivores:
- Animals that eat other animals..
- Ex: Lion, Tiger, Frog, and Owl.
Question 7.
What are decomposers?
Answer:
Micro-organisms (both plants and animals) that obtain energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms. They break complex organic substances into simple organic substances that go into the soil and are used by plants.
Example: Bacterium, Fungi.

Question 8.
Define Food web.
Answer:
- If we put all the food chains within an ecosystem together, then we end up with many interconnected food chains. This is called a food web.
- A food web is very useful to show the many different feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem.
Question 9.
What is reuse? Give examples.
Answer:
Reusing means using a thing again and again, rather than using and throwing after a single-use.
Example:
- Instead of using plastic bags, use cloth bags.
- Rechargeable batteries and fountain pens.
Question 10.
What is a Landfill?
Answer:
Landfilling is a method in which wastes are dumped into naturally occurring (or) man-made pits and covered with soil.
Question 11.
Give the Solid Waste Management (SWM) rules.
Answer:
The Solid Waste Management (SWM) rules, 2016, say that,
i. Every household should segregate and store the waste generated by them in three separate streams namely bio-degradable, non-biodegradable and domestic hazardous waste in suitable bins and handover the segregated wastes to authorized waste pickers, (or) waste collector as per direction or notification by the local authorities from time to time.
ii. Nobody shall throw, bum, or bury the solid waste on streets, open public spaces outside his premises, or in the drain or water bodies.
Question 12.
List any four domestic hazardous waste.
Answer:
- Discarded paint drums
- Pesticide cans,
- CFL bulbs, tube lights
- Used batteries, used needles, and syringes.
Question 13.
How can we reduce land pollution?
Answer:
- First try to reduce waste, then recycle the rest.
- Always use a waste bin and never litter.
- Do not bum waste, the ash mixes easily with soil.

VII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Give the types of the ecosystem by a flow chart.
Answer:
Question 2.
How can we reduce air pollution?
Answer:
- Cycle or walk short distances instead of using a motor vehicle.
- Travel by public transport (bus or train)
- Do not burn solid waste.
- Avoid fireworks.

Question 3.
Classify the most significant sources of water pollutants.
Answer:
The most significant sources of water pollutants are:
- Sewage (water we use at home for bathing, cleaning, cooking).
- Industrial effluents (liquid wastes from factories).
- Agricultural pollutants (chemical pesticides and fertilisers that get washed from farms).
- Solid waste (when waste gets dumped into water bodies).
Question 4.
How do we reduce noise pollution?
Answer:
- Turn off your electronics when you do not use them.
- Lower the volume when you watch TV or listen to music.
- Remind drivers not to use the horn too much.
- Avoid fireworks.
- Speak, do not shout (try to set an example).
![]()
![]()