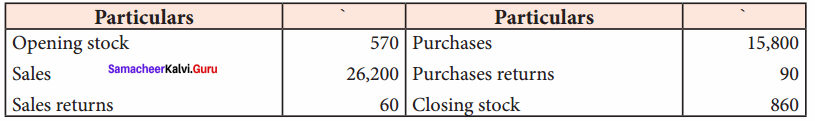
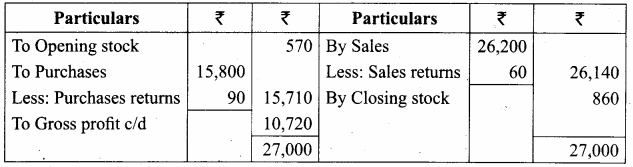
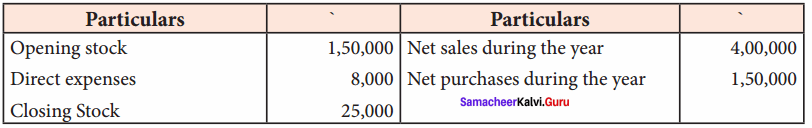
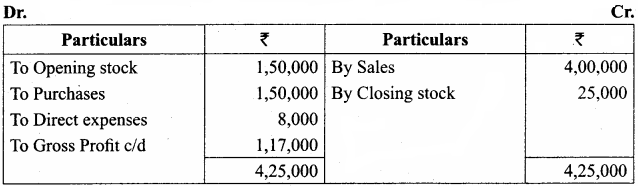
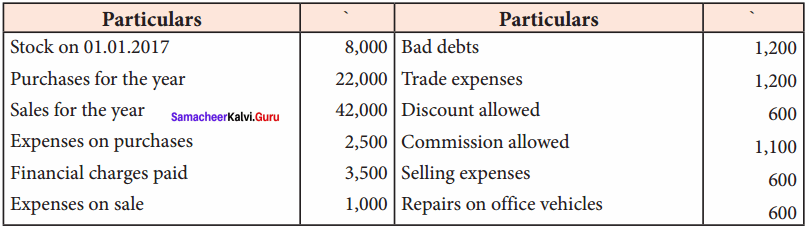
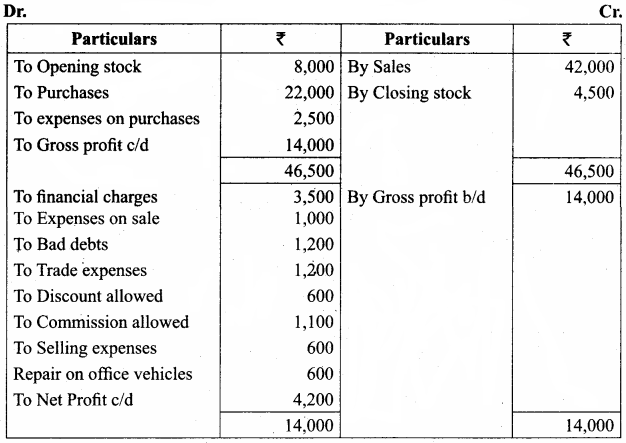
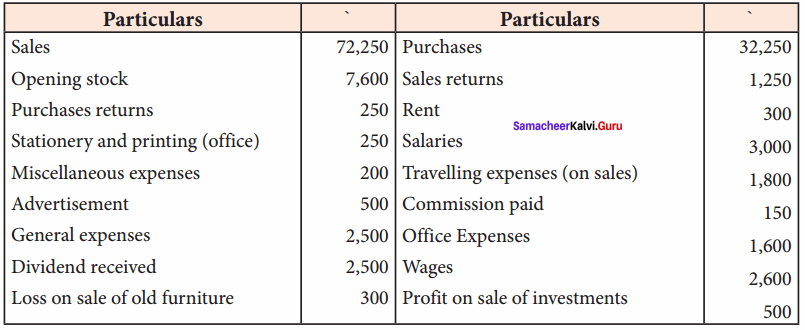
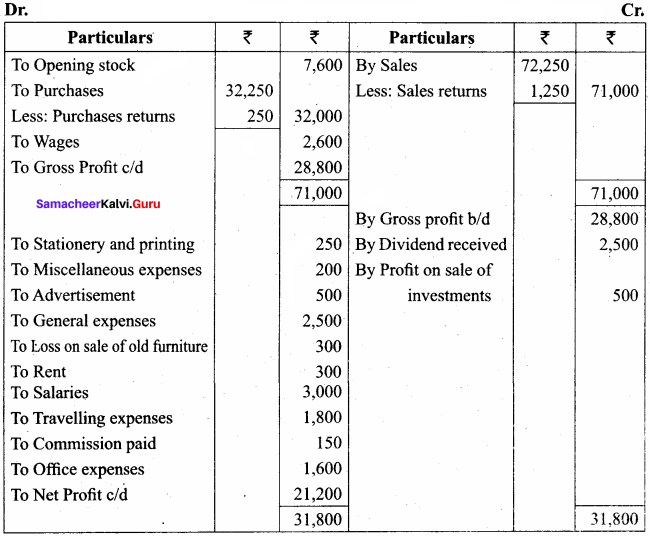
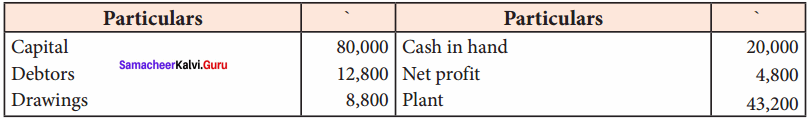
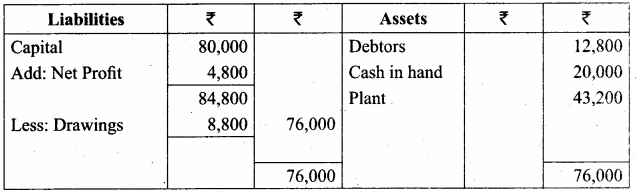
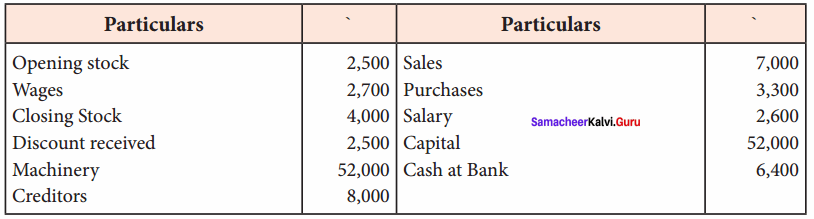
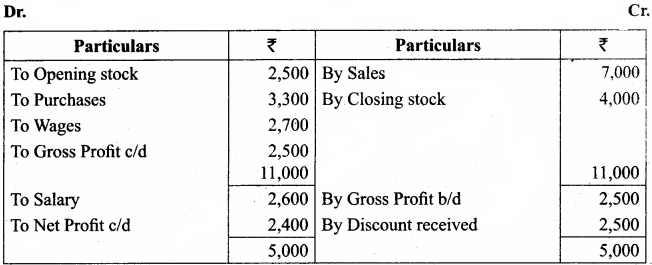
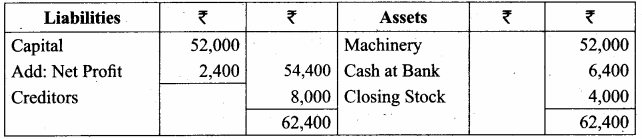
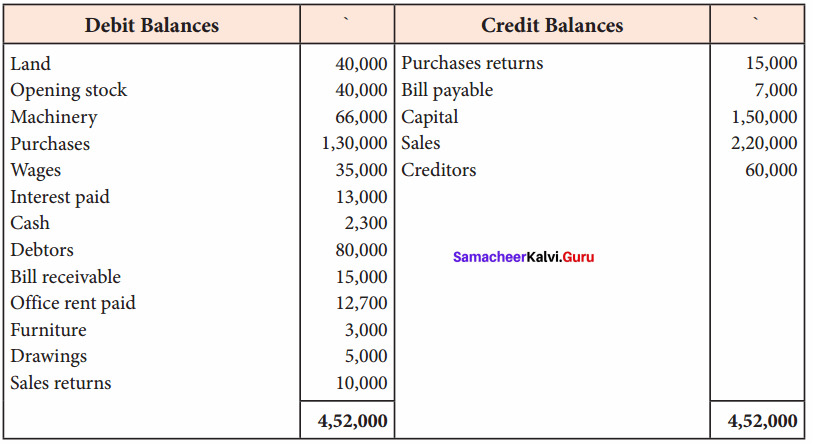
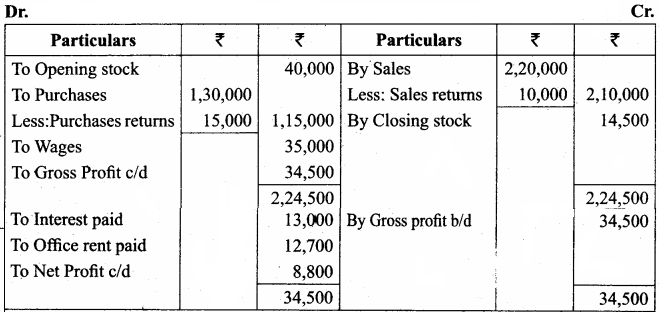
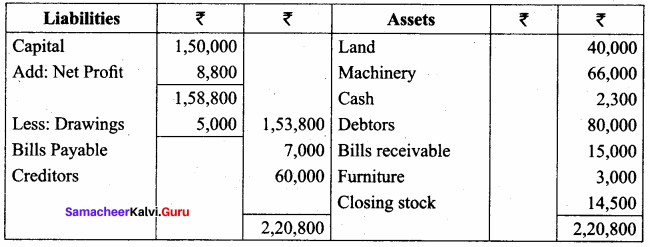
Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 11 Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 11 Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Chapter 11 Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers Textual Evaluation Solved
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
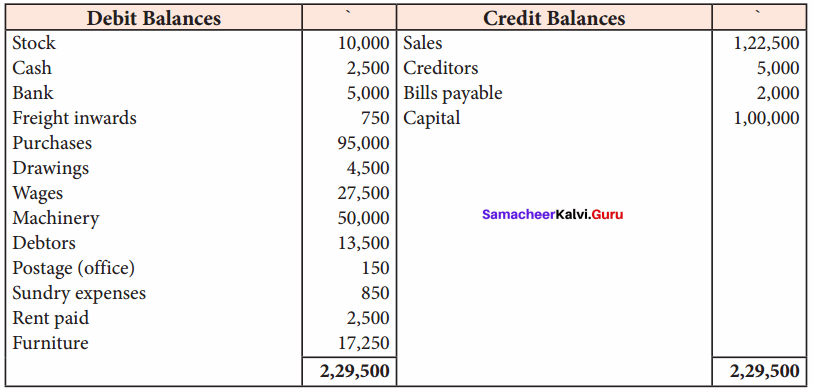
An alcohol (x) gives blue colour in victormayer’s test and 3.7g of X when treated with metallic sodium liberates 560 mL of hydrogen at 273 K and 1 atm pressure what will be the possible structure of X?
(a) CH3 CH (OH) CH2CH3
(b) CH3 – CH(OH) – CH3
(c) CH3 – C (OH) (CH3)2
(d) CH3 – CH2 – CH (OH) – CH2 – CH3
Answer:
(a) CH3 CH (OH) CH2CH3
Hint:
2R – OH + Na → 2RONa + 2H2 ↑ 2 moles of alcohol gives 1 mole of H2 which occupies
22.4L at 273K and 1 atm
number of moles of alcohol = \(\frac{2 \text { moles of } \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{OH}}{22.4 \mathrm{L} \text { of } \mathrm{H}_{2}}\) x 560 mL = 0.05 moles
number of moles = \(\frac{\text { mass }}{\text { molar mass }}\)
= molar mass = \(\frac{3.7}{0.05}\) = 74 g mol-1
General formula for
R – OH Cn H2n+1 – OH
n(12) + (2n+1) (1) + 16 +1 = 74
14n = 74 – 18
14n = 56
n = \(\frac { 56 }{ 4 }\) = 4
The 2° alcohol which contains 4 carbon is CHn CH(OH)CH2 CH3

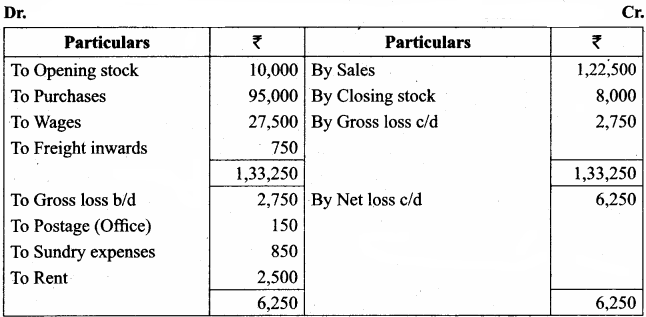
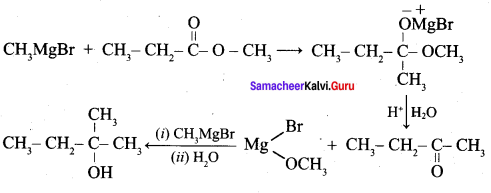
Question 2.
Which of the following compounds on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide will give tertiary alcohol.
(a) benzaldehyde
(b) propanoic acid
(c) methyl propanoate
(d) acetaldehyde
Answer:
(c) methyl propanoate
Hint:
Question 3.
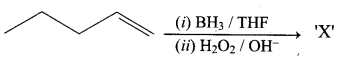
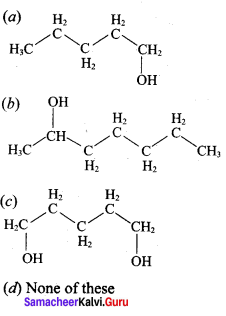
This ‘X’ is …………..
Answer:
Hint:
hydro boration – Anti markownikoff product
i.e CH3 – CH2 – CH – CH2 – CH2 – OH
Question 4.
In the reaction sequence, Ethane

Ethan – 1, 2 – diol. A and X respectively are ………….
(a) Chioroethane and NaOH
(b) ethanol and H2SO4
(c) 2 – chloroethan – 1 – ol and NaHCO3
(d) ethanol and H2O
Answer:
(c) 2 – chloroethan – 1 – ol and NaHCO3
Hint:
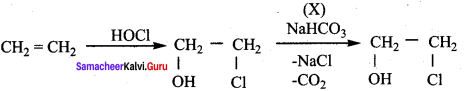
Question 5.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ………..
(a) 2 – nitrophenol
(b) 4 – chlorophenol
(c) 4 – nitrophenol
(d) 3 – nitrophenol
Answer:
(c) 4 – nitrophenol
Question 6.
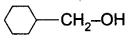
on treatment with Con. H2SO4, predominately gives ……………..
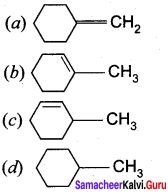
Answer:
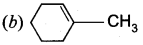
Hint:
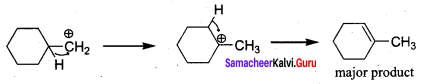
Question 7.
Carbolic acid is …………..
(a) Phenol
(b) Picric acid
(c) benzoic acid
(d) phenylacetic acid
Answer:
(a) Phenol
Question 8.
Which one of the following will react with phenol to give salicyladehyde after hydrolysis …………..
(a) Dichioro methane
(b) trichioroethane
(c) trichloro methane
(d) CO2
Answer:
(c) trichloro methane (Riemer Tiemann reaction)
Hint:
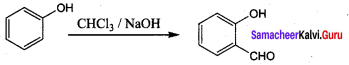
Question 9.
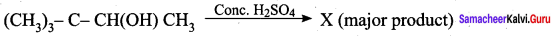
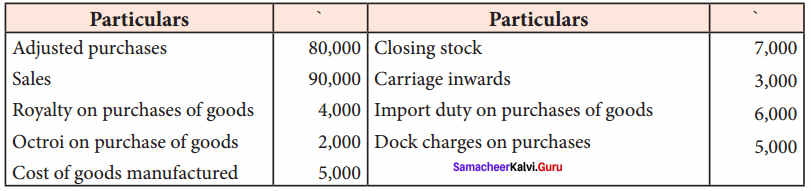
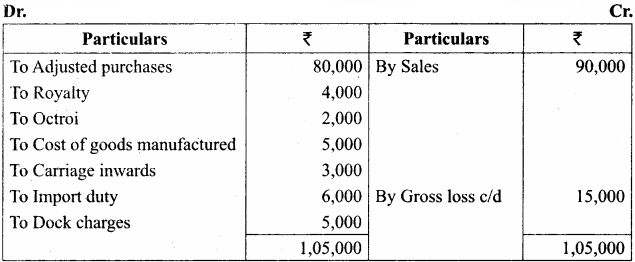
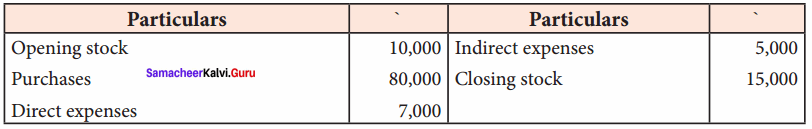
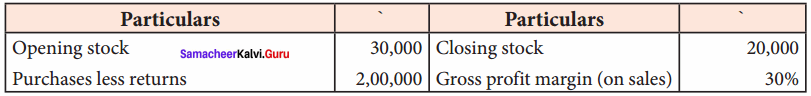
(a) (CH3)3 CCH = CH2
(b) (CH3)2 C = C (CH3)2
(c) CH2 = C(CH3)CH2 – CH2 – CH3
(d) CH2 = C (CH3) – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
Answer:
(b) (CH3)2 C = C (CH3)2
Hint:
Question 10.
The correct IUPAC name of the compound,
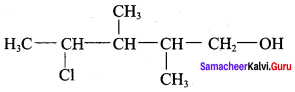
(a) 4 – chloro – 2, 3 – dimethyl pentan – 1 – ol
(b) 2, 3 – dimethyl – 4 – chloropentan – 1 – ol
(c) 2, 3, 4 – trimethyl – 4 – chiorobutan – 1 – ol
(d) 4 – chioro – 2, 3, 4 – trimethyl pentan – 1 – ol
Answer:
(a) 4 – chloro – 2, 3 – dimethyl pentan – 1 – ol
Question 11.
Assertion: Phenol is more acidic than ethanol
Reason: Phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 12.
In the reaction Ethanol
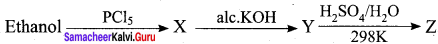 is ………………
is ………………
(a) ethane
(b) ethoxyethane
(c) ethylbisuiphite
(d) ethanol
Answer:
(d) ethanol
Hint:
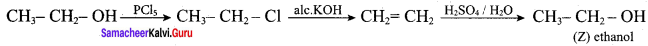
Question 13.
The reaction
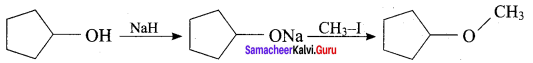
can be classified as
(a) dehydration
(b) Williams on alcoholsynthesis
(c) Williamson ether synthesis
(d) dehydrogenation of alcohol
Answer:
(c) Williamson ether synthesis
Hint: Cyclic alcohol → sodium cyclic alkoxide → williamson ether synthesis
Question 14.
Isoprophylbcnzene on air oxidation in the presence of dilute acid gives …………
(a) C6H5COOH
(b) C6H5COCH3
(c) C6H5COC6H5
(d) C6H5 – OH
Answer:
(a) C6H5 – OH (phenol)
Question 15.
Assertion: Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reaction
Reason: In the case of phenol. the intermediate arenium ion is more stabilized by resonance.
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false,.
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.

Question 16.
HO CH2 CH2 – OH on heating with periodic acid gives ………..
(a) methanoic acid
(b) Glyoxal
(c) methanol
(d) CO2
Answer:
(c) methanol
Question 17.
Which of the following compound can be used as artireeze in automobile radiators?
(a) methanol
(b) ethanol
(c) Neopentyl alcohol
(d) ethan -1, 2-diol
Answer:
(d) ethan -1, 2-diol
Question 18.
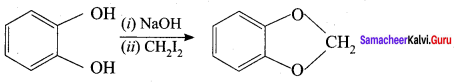
is an example of …………..
(a) Wurtz reaction
(b) cyclic reaction
(c) Williamson reaction
(d) Kolbe reactions
Answer:
(c) Kolbe reactions
Question 19.
One mole of an organic compound (A) with the formula C3H8O reacts completely with two moles of HI to form X and Y. When Y is boiled with aqueous alkali it forms Z. Z answers the iodoform test. The compound (A) is ……………
(a) propan – 2 – ol
(b) propan- 1- ol
(c) ethoxy ethane
(d) methoxy ehane
Answer:
(d) methoxy ehane
Hint:
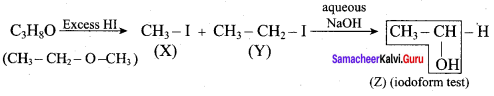
Question 20.
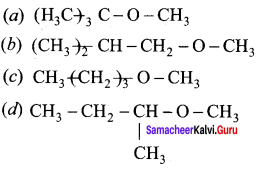
Among the following ethers which one will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot HI?
Answer:
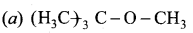
Hint:
Question 21.
Williamson synthesis of preparing dimethyl ether is a / an /
(a) SN1 reactions
(b) SN2 reaction
(c) electrophilic addition
(d) electrophilic substitution
Answer:
(b) SN2 reaction
Question 22.
On reacting with neutral ferric chloride, phenol gives
(a) red colour
(b) violet colour
(c) dark green colour
(d) no colouration
Answer:
(b) violet colour
II. Answer the following questions
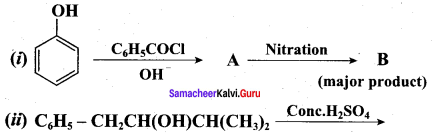
Question 1.
IdentIfy the product (s) is / are formed when 1 – methoxy propane is heated with excess HI. Name the mechanism involved in the reaction
Answer:
1-methoxy propane is heated with excess HI, yields two products named as Methyl iodide and 1- iodo propane.
Step 1:
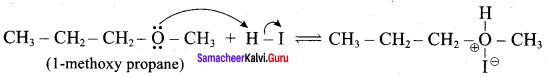
Step 2.
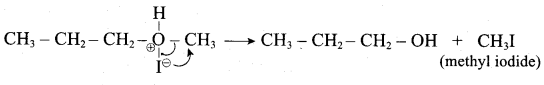
Step 3:
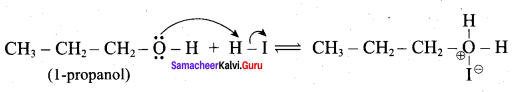
Step 4:
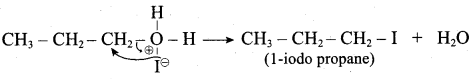
Overall reaction:
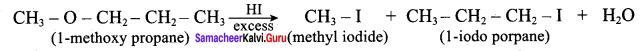
This reaction ivvolves nucleophilic substitution reaction mechanism. (SN1)
Question 2.
Draw the major product formed when 1 – ethoxyprop – 1 – ene is heated with one equivalent of HI
Answer:
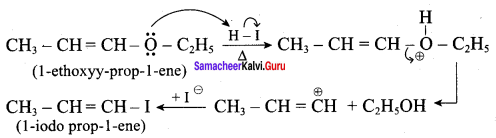
This reaction follows SN1 mechanism because in this reaction the more stable carbocation is formed that is double bonded carbocation. Therefore, the given molecule reacts with HI to form ethanol and 1- iodo prop – 1 – ene.

Question 3.
Suggest a suitable reagent to prepare secondary alcohol with identical group using Grignard reagent.
Answer:
Acetaldehyde reacts with Grignard reagent to give addition product, which on further undergoes acid hydrolysis to yield secondary alcohol, that is isopropyl alcohol.
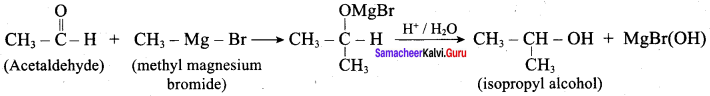
Question 4.
What is the major product obtained when two moles of ethyl magnesium bromide is treated with methyl benzoate followed by acid hydrolysis
Answer:
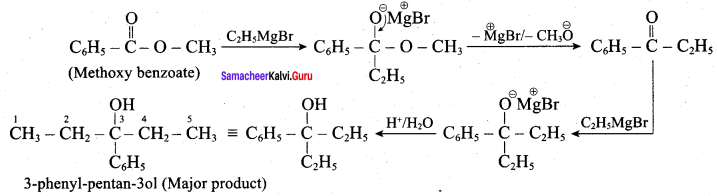
Question 5.
Predict the major product, when 2-methyl but – 2 – ene is converted into an alcohol in each of the following methods.
- Acid catalysed hydration
- Hydroboration
- Hydroylation using bayers reagent
Answer:
1. Acid catalysed hydration:
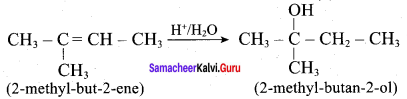
2. Hydroboration.
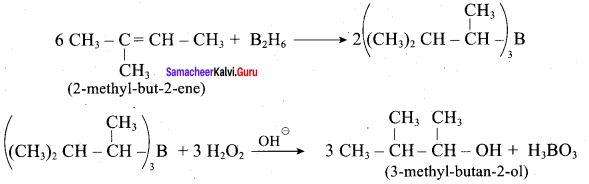
3. Hydroxylation using bayers reagent:
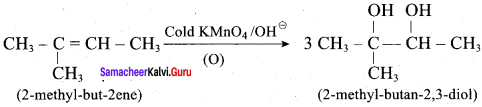
Question 6.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point and give a reason for your ordering
- Butan – 2 – ol, Butan – 1 – SI, 2 – methylpropan – 2 – ol
- Propan – 1 – ol, propan – 1, 2, 3 – triol, propan – 1, 3 – diol, propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
1. Boiling points increases regularly as the molecular mass increases due to a corresponding increase in their Van der waal’s force of attraction. Among isomeric alcohols 2° – alcohols have lower boiling points than 1° – alcohols due to a corresponding decreases in the extent
of H-bonding because of steric hindrance. Thus the boiling point of Butan – 2 – ol is lower than that of Butan – 1 – ol. Overall increasing order of boiling points is, 2 – methylpropan – 2 – ol < Butan – 2 – ol < Butan – 1 – ol
2. 2°-alcohols have lower boiling points than 1° – alcohols due to a corresponding decrease in the extent of H – bonding because of steric hindrance. Therefore Propan – 1 – ol has higher boiling point than Propan – 2 – ol. Hydrogen group increases, boiling point also increases. Overall increasing order of boiling points is, propan – 2 – ol < Propan – 1 – ol < propan – 1, 3 – diol < propan -1, 2, 3 – triol
Question 7.
Can we use nucelophiles such as NH3, CH3O for the Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols
Answer:
1. Increasing order of nucleophilicity,
NH3 < – OH⊕ < CH3O⊖-
2. Higher electron density will increase the nucleophilicity.
3. Negatively charged species are almost always more nucleophiles than neutral species.
4. RO⊖ has an alkyl group attached, allowing a greater amount of polarizability. This means oxygen’s lone pairs will be more readily available to reach in RO⊖ than in OH⊖. Hence CH3O – is the better nucleophile for the nucleophilic substitution of alcohols. NH3 cannot act as nucleophiles for the nucleophilic substitution of alcohols.
Question 8.
Is it possible to oxidise t – butyl alcohol using acidified dichromate to form a carbonyic compound.
Answer:
3° – alcohols do not undergo oxidation reaction under normal conditions, but at elevated temperature, under strong oxidising agent cleavage of C – C bond takes place to give a mixture of carboxylic acid.
Yes, it is possible. t – butyl alcohol is readily oxidsing in acidic solution (K2Cr2O7 / H2SO4) to a mixture of a ketone and an acid each containing lesser number of carbon atoms than the original alcohol. The oxidation presumably occur via alkenes formed through dehydration of alcohols under acidic conditions.
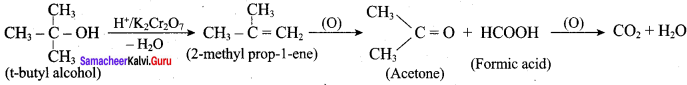
Question 9.
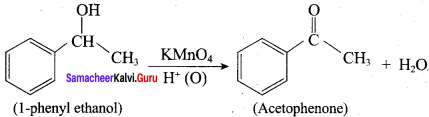
What happens when 1 – phenyl ethanol is treated with acidified KMnO4.
Answer:
1 – phenyl ethanol reacts with acidified KMnO4 to give Acetophenone.
Question 10.
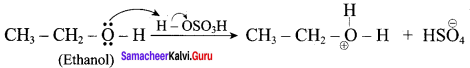
Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to give ethene.
Mechanism of acid catlaysed dehydration of ethanol:
Step1:
Protonation of ethanol.
Step 2:
Elimination of water molecule.
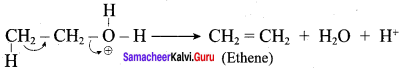
Question 11.
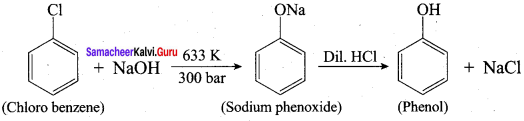
How is phenol prepared form
- chlorobenzene
- isopropyl benzene
Answer:
1. From Chioro benzene:
According to Dow’s process, when Chiorobenzene is hydrolysed with 6 – 8% NaOHat 300 bar and 633K in a closed vessel, sodium phenoxide is formed which on treatment with dilute HCl gives phenol.
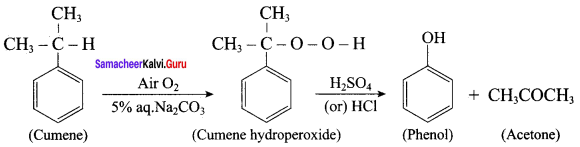
2. For isopropyl benzene:
On passing air to a mixture of cumene (isopropyl benzene) and 5% aqueous sodium carbonate solution, cumene hydroperoxide is formed by oxidation. It is treated with dilute acid to get phenol and acetone.
Question 12.
Explain Kolbe’s reaction
Answer:
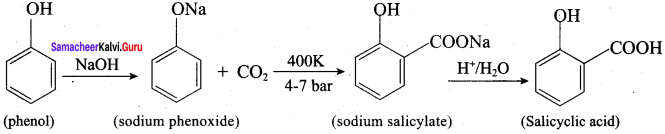
Kolbe’s (or) Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction:
In this reaction, phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide which is more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitution reaction with CO2. Treatment of sodium phenoxide with CO2 at 400K, 4 -7 bar pressure followed by acid hydrolysis gives salicylic acid.
Answer:
Question 13.
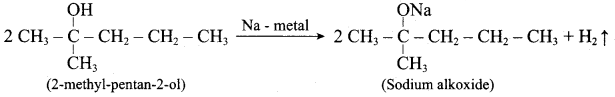
Writes the chemical equation for Williamson synthesis of 2 – ethoxy – 2 – methyl pentane starting from ethanol and 2 – methyl pentan – 2 – ol
Answer:
Step 1:
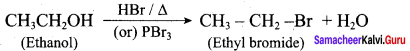
Step 2:
Step 3:
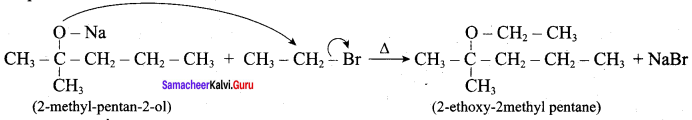
Williamson’s synthesis occurs by SN2 – mechanism and primary alkyl halides are more reactive in SN2 reactions. Therefore ethanol is converted into ethyl bromide.
Question 14.
Write the structure of the aldehyde, carboxylic acid and ester that yield 4 – methylpent – 2 – en – 1 – ol.
Answer:
1. Aldehyde yield 4 – methylpent – 2 – 3n – ol is
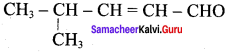
2. Acid yield 4 – methylpent – 2 – en – 1 – ol is
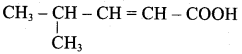
3. Ester yield 4 – methylpent – 2 0 en – 1 – ol is
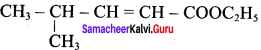
The above-shown compounds undergo a reduction reaction to yield 4 – methylpent – 2 – en – l – ol.
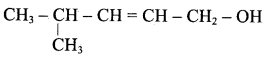
Question 15.
What is metamerism? Give the structure and IUPAC name of metamers of 2 – methoxy propane
Answer:
Metamerism:
It is a special type of isomerism in which molecules with the same formula, same functional group, but different only in the nature of the alkyl group attached to oxygen.
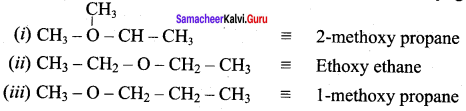
Ethoxy ethane and 1-methoxy propane are metamers of 2-methoxy propane.
Question 16.
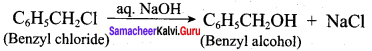
How are the following conversions effected
- benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol
- benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid
Answer:
1. Conversion of benzyl chloride into benzyl alcohol:
2. Conversion of benzyl alcohol into benzoic acid:
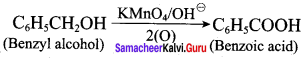
Question 17.
Complete the following reactions
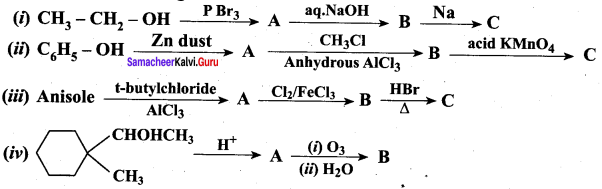
Answer:
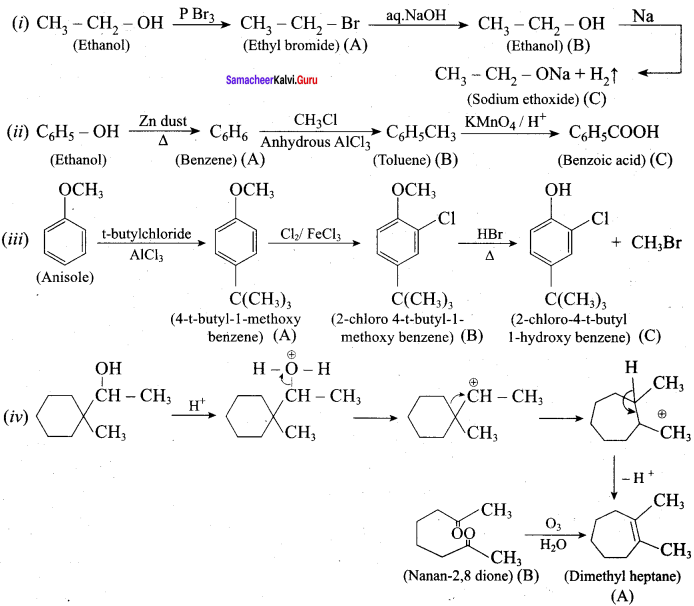
Question 18.
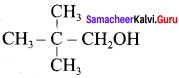
O.44g of a monohydric alcohol, when added to methyl magnesium iodide in ether, liberates at STP 112 cm3 of methane with PCC the same alcohol form a carbonyl compound that answers silver mirror test. Identify the compound.
Answer:
0.44g of monohydric alcohol liberates 112 cm3 of methane.

Mass of monohydric alcohol which gives 22400 cm3 of methane = \(\frac{22400 \times 0.44}{112}\) = 88
C5H12O molecular fórmula has mass number 88 and it shows eight possible isomers. But neopentyl alcohol reacts with PCC to form neopentyl aldehyde, which shows positive silver mirror test. Therefore, compound is. neopentyl alcohol (or) 2, 2 – dimethyl propan – l – ol.
Question 19.
Complete the following reactions
Answer:
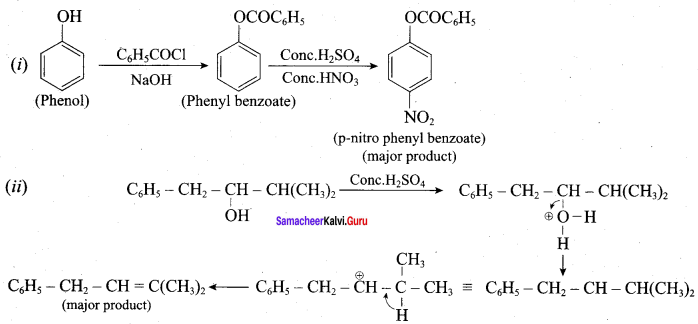
Question 20.
Phenol is distilled with Zn dust gives (A) followed by friedel – crafts alkylation with propyl chloride to give a compound B, B on oxidation gives (C). Identify A,B and C.
Answer:
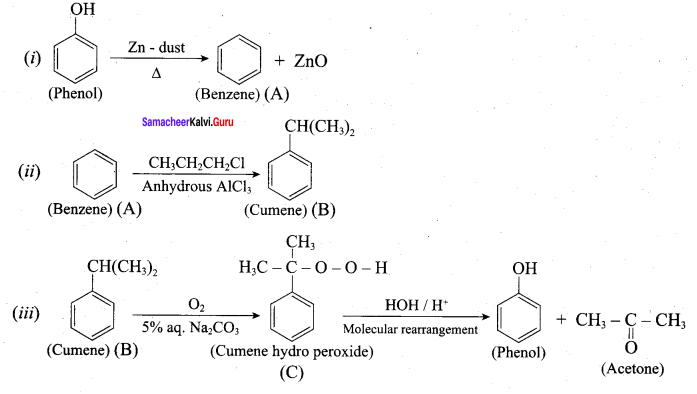
Question 21.
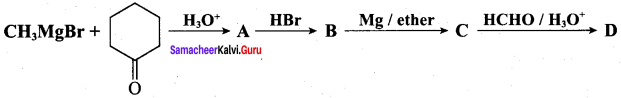
Identify A, B, C, D and write the complete equation.
Answer:
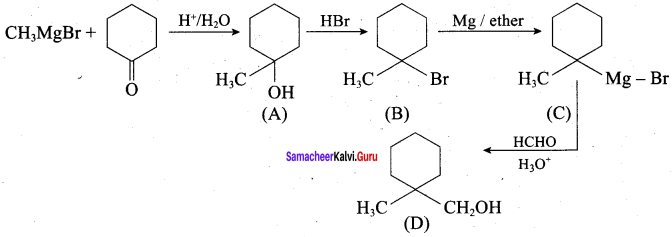
Question 22.
What will be the product for the following reaction
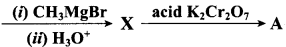
Answer:
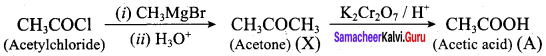
Question 23.
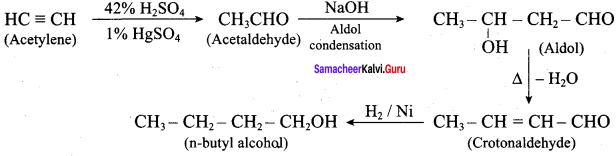
How will you convert acetylene into n – butyl alcohol.
Answer:
Question 24.
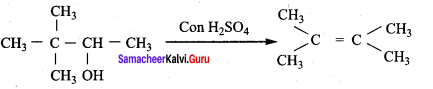
Predict the product A, B, X and Y in the following sequence of reaction
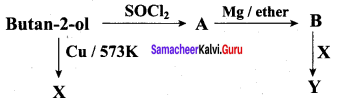
Answer:
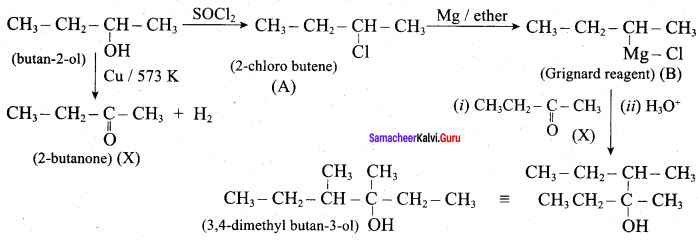
Question 25.
3,3 – dimethylbutan – 2 – ol on treatment with conc. H2SO4 to give tetramethyl ethylene as a major product. Suggest a suitable mechanisms
Answer:
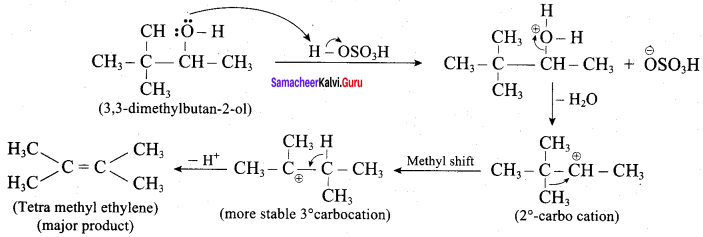
According to Saytzeff’s rule the dehydration of 3,3 – dimethylbutan – 2 – ol gives a mixture of alkenes. But the secondary carbocation formed in this reaction undergoes rearrangement to form a more stable tertiary
carbocation which further, undergoes to 13 – elimination leads more stable product, that is 2,3 – dimethyl but – 2 – ene (more yield). According to Saytzeff’s nile, 2, 3 – dimethyl pent- 2 – ene is the major product.
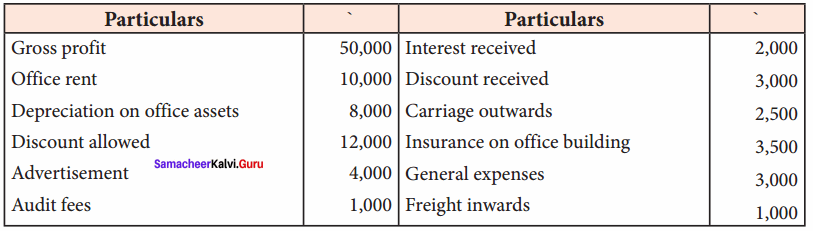
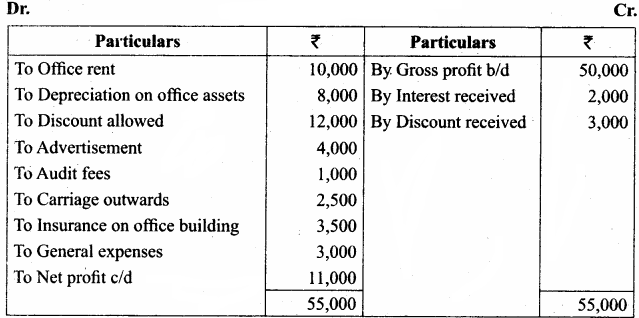
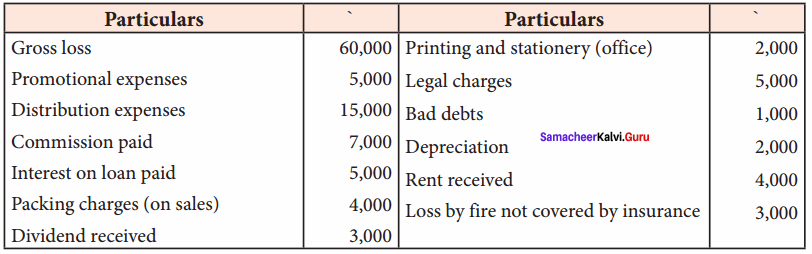
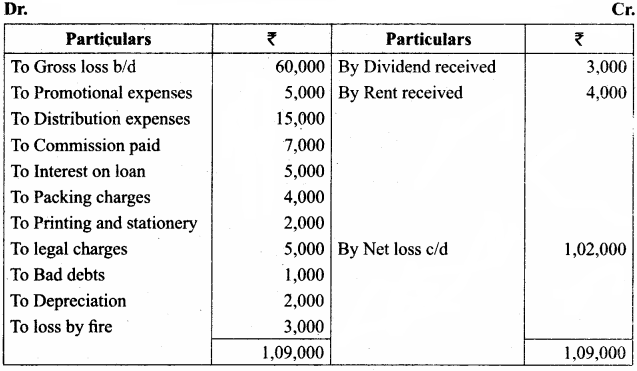
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers Evaluate yourself
Question 1.
Classify the following alcohols as 10, 20, and 30 and give their IUPAC Names.
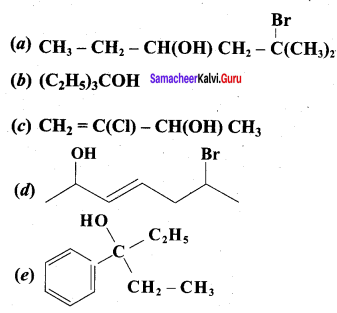
Answer:
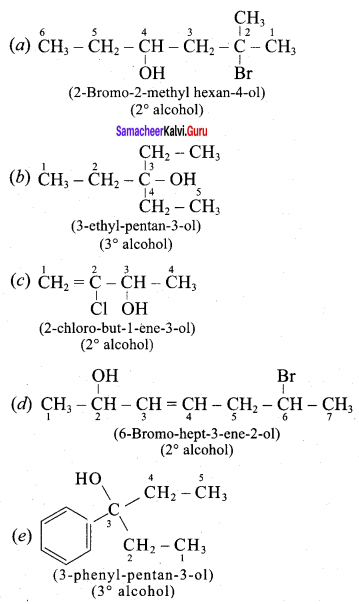
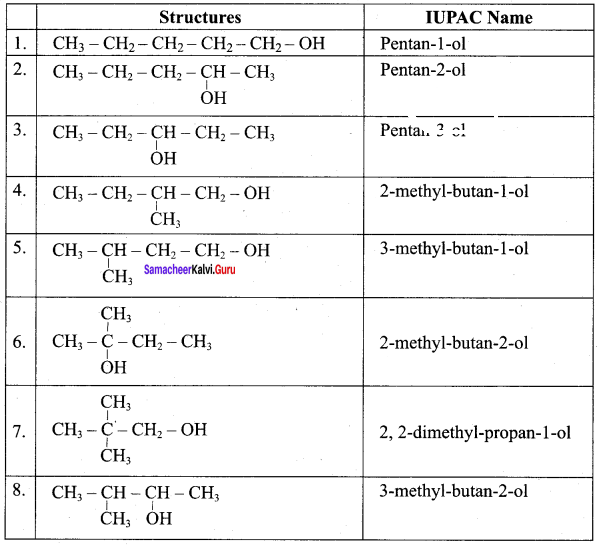
Question 2.
Write all the possible isomers of alcohol having the molecular formula C15H12O and their IUPAC names.
Answer:
Eight isomers are possible for C15H12O. They are,
Question 3.
Suggest a suitable carbonyl compound for the preparation of pent – 2 – en – 1 ol using LiAlH4.
Answer:
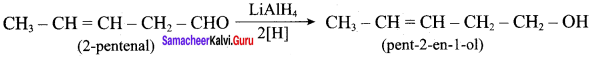
Question 4.
2 – methylpropan – 2 – ene 
Answer:
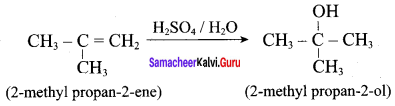
Question 5.
How will you prepare the following using Grignard reagent.
- t – butyl alcohol
- allyl alcohol
Answer:
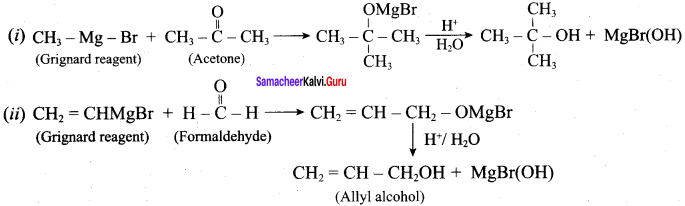
Question 6.
Identify the products in the following reactions. Write their IUPAC names and mention the mechanism involved in the reactions.
Answer:
1. 
This reaction involves E1 – mechanism.
2. 
This reaction ivolves SN2 – mechanims.
3. Step 1:
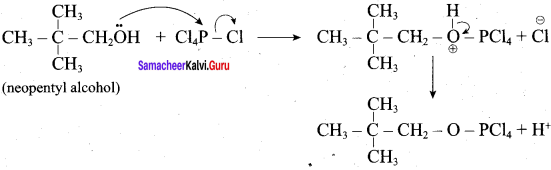
Step 2:
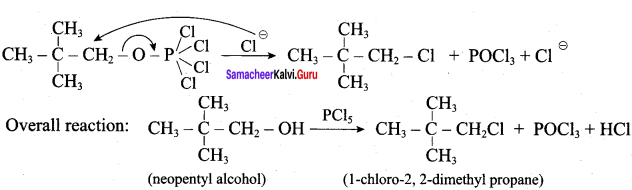
This reaction involves SN2 Mechanims.
Question 7.
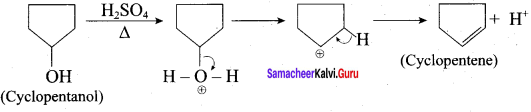
What is the major product obtained when 2,3 – dimethyl pentan – 3 – ol is heated in the presence of H2SO4
Answer:
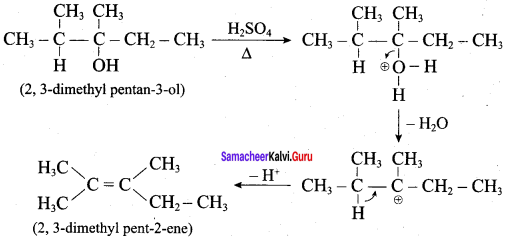
According to Saytzeff’s rule, 2, 3 – dimethyl pent – 2 – ene is the major product.
Question 8.
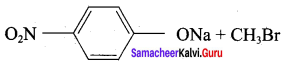
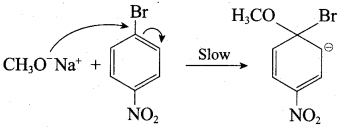
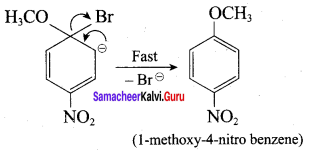
Which of the following set of reactants will give 1 – methoxy – 4 – nitrobenzene.
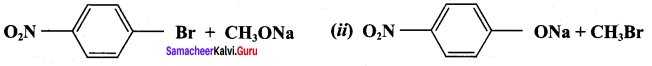
Answer:
Step 1:
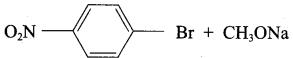
step 2:
Chemically both sets equally possible. In Set – 1, the Br-atom is activated by the electron-withdrawing effect of the – NO2 group. Therefore nucleophilic attack by CH3ONa followed by elimination of NaBr gives the desired ether.
Step 1:
Step 2:
Inset – 2, nucleophilic attack by 4 – nitrosodium phenoxide ion on methyl bromide gives the desired ether.
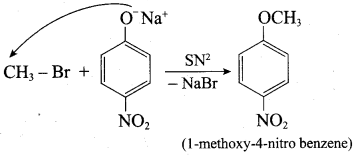
Since alkyl halides (CH3Br) are more reactive than aryl halides in nucleophilic substitution reactions, therefore set – 2 reactants are preferred.
Question 9.
What happens when m – cresol is treated with an acidic solution of sodium dichromate?
Answer:
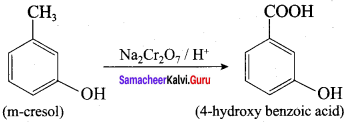
When m – cresol is treated with acidic solution of sodium dichromate it gives 4 – hydroxy benzoic acid.
Question 10.
When phenol is treated with propan – 2 – ol in the presence of HF, Friedel – Craft reaction takes place. Identify the products.
Answer:
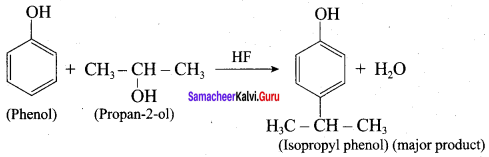
Question 11.
Given the IUPAC name for the following ethers and classify them as simple or mixed.
Answer:
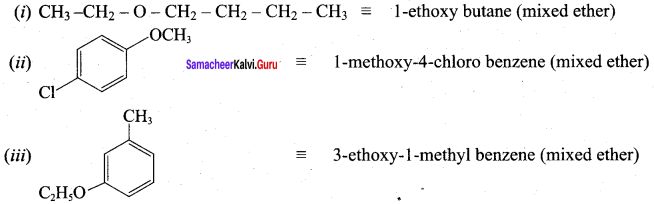
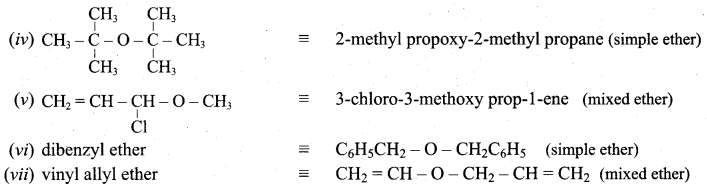
Question 12.
1. Which of the following reaction will give 1 – methoxy – 4 – nitrobenzene.
- 4 – nitro – 1 – bromobenzene + sodium methoxide.
- 4 – nitrosodium phenoxide + bromomethane
Answer:
1. Set – 1:
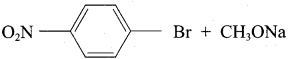
2. set – 2:
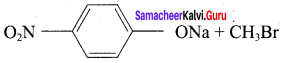
Chemically both sets equally possible. In Set – 1, the Br – atom is activated by electron-withdrawing effect of – NO2 group. Therefore nucleophilic attack by CH3ONa followed by elimination of NaBr gives the desired ether.
Step 1:
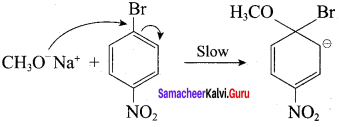
Step 2:
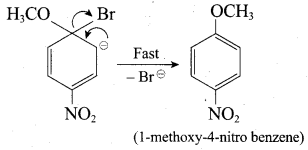
In set – 2, nucleophilic attack by 4 – nitrosodium phenoxide ion on methyl bromide gives the desired ether.
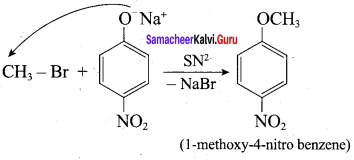
Since alkyl halides (CH3Br) are more reactive than aryl halides in nucleophilic substitution reactions, therefore set – 2 reactants are preferred.
Question 13.
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their acid strength. propan – 1 – ol, 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol, 3 – nitrophenol, 3,5 – dinitrophenol, phenol, 4 – methyiphenol.
Answer:
Phenols are stronger acids than alcohols because the phenoxide ion left after the removal of proton is stabilized by resonance while the alkoxide ion left after the removal of a proton from alcohol is not stabilized. Thus propan – 1 – ol is much weaker acid than any phenol.
Thus propan- 1 – ol is a much weaker acid than any phenol. We know that electron-donating groups decrease the acidic character and stronger is the electron-donating group, weaker is the phenol.
Compare to propan – 1 – ol, 4 – methyl phenol is stronger acidic character. But comparing phenol and 4-methyl phenol, phenol is stronger acidic. Since electron-withdrawing groups increase the acidic character of phenols and the effect is more pronounced at the para position than at the meta position.
Therefore 4 – nitrophenol is a stronger acid than 3 – nitrophenol. Further, as the number of electron-withdrawing groups increases the acidic strength further increases. Therefore 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol is a stronger acid than 3, 5 – dintiro phenol. It may be noted here that although the two nitro groups in 3, 5 – dinitrophenol are at m – position with respect to OH group,
their combined effect is however greater than one nitro group at p – position. Therefore 3, 5 – dinitrophenol is a stronger acid than 4-nitro phenol. Thus, the overall increasing order of acid strength is. Propan – 1 – 01 < 4 – methyl phenol < phenol < 3 – nitrophenol < 3, 5 – dinitrophenol < 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol.
Question 14.
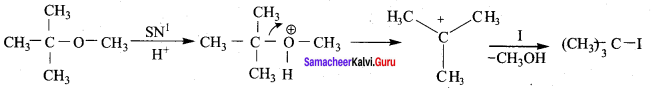
1 mole of HI is allowed to react with t – butyl methyl ether. Identify the product and write down the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer:
Step 1:
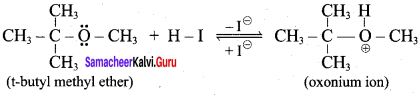
Step 2
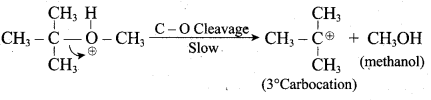
Step 3:

Overall reaction:
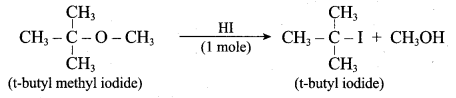
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers Additional Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers 1 Mark Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer.
Question 1.
Which one of the following is trihydric alcohol?
(a) Glycol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Glycerol
(d) Sorbitol
Answer:
(c) Glycerol
Question 2.
Identify the monohydric unsaturated alcohol.
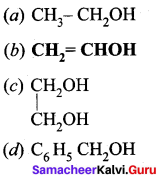
Answer:
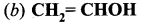
Question 3.
Which one of the following is named as sorbital?
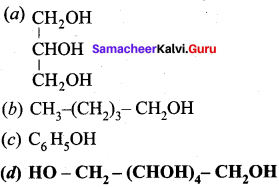
Answer:
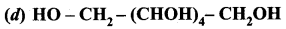
Question 4.
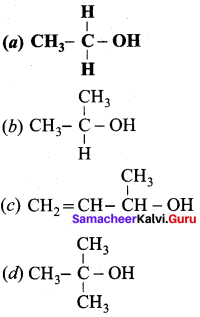
Which one of the following is primary alcohol?
Answer:
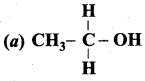
Question 5.
Which of the following is dihydric alcohol?
(a) Ethenol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Ethane – 1, 2 – diol
(d) Propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
(c) Ethane – 1, 2 – diol
Question 6.
Which one of the following is an example of secondary (2°) alcohol?
(a) Propan – 2 – ol
(b) Phenyl methanol
(c) Ethenol
(d) 2 – methyl – propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
(a) Propan – 2 – ol
Question 7.
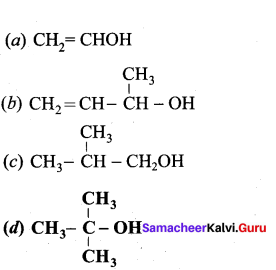
Which one of the following is tertiary alcohol?
Answer:
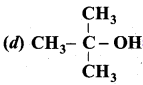
Question 8.
Which of the following is a primary alcohol?
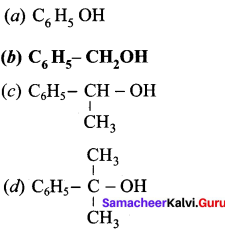
Answer:
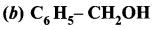
Question 9.
Which one of the following find application in proper functioning of our eyes?
(a) Cholesterol
(b) Retinol
(c) Phenol
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(b) Retinol
Question 10.
Which is the storage of vitamin – A?
(a) Retinol
(b) Benzyl alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) Ascorbic acid
Answer:
(a) Retinol
Question 11.
The important component in our cell membrane is ………….
(a) Retinol
(b) Phenol
(c) Cholesterol
(d) Methanol
Answer:
(c) Cholesterol
Question 12.
Which acts as an additive to petrol?
(a) Glycerol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Phenol
(d) Methanol
Answer:
(b) Ethanol
Question 13.
Which one of the following vitamin is stored in Retinol?
(a) Vitamin – B12
(b) Vitamin – A
(c) Vitamin – C
(a) Vitamin – D
Answer:
(b) Vitamin – A

Question 14.
Which alcohol is used as skin cleanser for injection?
(a) Methanol
(b) Ethanol
(c) 1 -propanol
(d) 2-propanol
Answer:
(d) 2-propanol
Question 15.
Which one of the following is used as an industrial solvent?
(a) Methanol
(b) Benzyl alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) Cholesterol
Answer:
(a) Methanol
Question 16.
2 – methyl but – 3 – en – 2 – ol belongs to which type of alcohol?
(a) 3° alcohol
(b) 2° alcohol
(c) 1° alcohol
(d) Aromatic alcohol
Answer:
(a) 3° alcohol
Question 17.
The IUPAC name of

(a) 1 – methyl – 2 – propanol
(b) 2 – methyl – p ropan – 2 – ol
(c) Tertibutyl alcohol
(d) 2 – propanol
Answer:
(b) 2 – methyl – p ropan – 2 – ol
Question 18.
The TUPAC name of CH2 = CH – CH2OH is …………
(a) Allyl alcohol
(b) Propenc – 2 – ol
(c) Prop – 2 – en – 1 – oI
(d) Isopropyl alcohol
Answer:
(c) Prop – 2 – en – 1 – oI
Question 19.
In methanol, – OH group attached to carbon is ………..
(a) sp hybridised atom
(b) sp3 hybridised atom
(c) sp2 hybridised atom
(d) dsp2 hybridised atom
Answer:
(c) sp2 hybridised atom
Question 20.
Which one of the following is C – O – H bond angle in methanol?
(a) 109.5°
(b) 104°
(c) 90°
(d) 108.9°
Answer:
(d) 108.9°
Question 21.
Primary alkyl halides undergoes substitution by ……….
(a) SN1 reaction
(b) SNi reaction
(c) SN2 reaction
(d) SN reaction
Answer:
(c) SN2 reaction
Question 22.
What is the product formed when propene is hydrolysed in the presence of mineral acid?
(a) Propan – 1 – ol
(b) Propan – 2 – ol
(c) Iso butyl alcohol
(d) 2 – mcthyl – propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
(b) Propan – 2 – ol

Question 23.
The product formed when phenyl magnesium bromide treated with methanal and hydrolysed is ………..
(a) Phenyl methanal
(b) Phenol
(c) Phenyl methanol
(d) Benzyl benzoate
Answer:
(c) Phenyl methanol
Question 24.
To get Butan – 2 – ol, Ethyl magnesium bromide is treated with followed by hydrolysis.
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) CO2
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(d) CH3CHO
Question 25.
Which one of the following is formed when Butyl magnesium bromide is treated with propanone followed by hydrolysis?
(a) Tertiary butyl alcohol
(b) Isopropyl alcohol
(c) 2 – methyl hexan – 2 – ol
(d) Propan – 1 -ol
Answer:
(c) 2 – methyl hexan – 2 – ol
Question 26.
Which one of the following is used to get propan – 2 – ol by the reaction with CH3MgBr?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Ethanal
(c) Ethyl in ethanoate
(d) Propanone
Answer:
(c) Ethyl in ethanoate
Question 27.
Crotanaldehyde on reaction with LiAlH4 and water produces
(a) Ethanol
(b) Propan – 2 – ol
(c) Methanol
(d) But – 2 – en – 1 – ol
Answer:
(d) But – 2 – en – 1 – ol

Question 28.
Which one of the following is used as a catalyst in the conversion of Bcnzoic acid to Benzyl alcohol?
(a) Ni
(b) LiAIH4 / H2O
(c) Sn / HCI
(d) Zn / NaOH
Answer:
(b) LiAIH4 / H2O
Question 29.
What is the product formed when acetone is treated with LiA1H4 and 1120?
(a) Isobutyl alcohol
(b) n – butyl alcohol
(c) Propan – 2 – ol
(d) Propan – 1 – ol
Answer:
(c) Propan – 2 – ol
Question 30.
Which one of the following is formed when ethene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent?
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethylene glycol
(c) Propane – 1, 2 – diol
(d) Glycerol
Answer:
(b) Ethylene glycol
Question 31.
Which one of the following is named as Baeyer’s reagent?
(a) acidified K2Cr2O7
(b) acidified KMnO4
(c) Cold dilute alkaline KMnO4
(d) LiAlH4
Answer:
(c) Cold dilute alkaline KMnO4
Question 32.
The alkaline hydrolysis of fats to give glycerol is known as …………
(a) Esterification
(b) Hydroboration
(c) Hydration
(d) Saponification
Answer:
(d) Saponification

Question 33.
Which one of the following alcohol reacts immediately with Lucas reagent?
(a) Primary alcohol
(b) Tertiary alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) Secondary alcohol
Answer:
(b) Tertiary alcohol
Question 34.
Which one of the following is called Lucas reagent?
(a) Conc. HCl + Anhydrous ZnCl2
(b) Conc. HCl + Anhydrous A1CI3
(c) LiAIH4 + H2O
(d) Cold dilute alkaline KMnO4
Answer:
(a) Conc. HCl + Anhydrous ZnCl2
Question 35.
Which alcohol gives red colour in Victor Meyer’s test?
(a) 2° alcohol
(b) 3° alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) 1° alcohol
Answer:
(d) 1° alcohol
Question 36.
Which colour is given by secondary alcohol in Victor Meyer’s test?
(a) Red
(b) Green
(c) Blue
(d) Yellow
Answer:
(c) Blue
Question 37.
Which mechanism is followed in the reaction of 2 – methyl – 2 – propanol with HBr?
(a) E1 mechanism
(b) E2 mechanism
(c) SN2 mechanism
(d) SN1 mechanism
Answer:
(d) SN1 mechanism
Question 38.
Which mechanism is followed in the conversion of ethanol to bromoethane by HBr?
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) E1 mechanism
(d) E2 mechanism
Answer:
(c) E1 mechanism

Question 39.
Which one of the following is used as a catalyst in the reaction of methanol with thionyl chloride?
(a) Pyridine
(b) pyrrole
(c) THF
(d) Nickel
Answer:
(a) Pyridine
Question 40.
The mechanism of the reaction of ethanol with PCl3 is ……………..
(a) SN1
(b) SN2
(c) E2
(d) E1
Answer:
(b) SN2
Question 41.
Which one of the following reagent is used in the conversion of Ethanol to ethene?
(a) Zn + Hg / H2O
(b) LiAlH4
(c) acidified K2Cr2O7
(d) Conc. H2SO4
Answer:
(d) Conc. H2SO4
Question 42.
Primary alcohol undergoes dehydration by ………
(a) E1 mechanism
(b) E2 mechanism
(c) SN1 mechanism
(d) SN2 mechanism
Answer:
(b) E2 mechanism
Question 43.
Tertiary alcohols undergo dehydration by ……….
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) E2 mechanism
(c) E1 mechanism
(d) SN2 mechanism
Answer:
(c) E1 mechanism

Question 44.
Which one of the following is the correct order of relative reactivities of alcohols in the dehydration reaction?
(a) 1° < 2° < 3°
(b) 2° < 1° < 3°
(c) 3° < 2° < 1°
(d) 3° < 1° < 2°
Answer:
(a) 1° < 2° < 3°
Question 45.
Which of the following is the product formed when 3,3 – dimethyl – 2 – butanol reacts with conc.H2SO4?
(a) 2, 3 – dirnethyl but – 1 – ene
(b) 2,3 – dimethyl but – 2 – ene
(c) 3, 3 – dimethyl but – 1 – ene
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 46.
The oxidising agent used to prepare aldehyde (or) ketone from alcohol, the reagent used is …………..
(a) acidified Na2Cr2O7
(b) alkaline KMnO4
(c) Pyridinium chlorochromate
(d) conc. H2SO4
Answer:
(c) Pyridinium chlorochromate
Question 47.
The product formed when propan – 2 – ol is treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and oxalyl chloride followed by the addition of Et3N is ……….
(a) Oxalyl chloride
(b) Propanal
(c) Ethanoic aicd
(d) Propanone
Answer:
(d) Propanone
Question 48.
Which reaction is used to convert alcohol to ketone/aldehyde in the presence of DMSO?
(a) Lucas test
(b) Swern oxidation
(c) Biological oxidation
(d) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer:
(b) Swern oxidation
Question 49.
Which product is formed when propan- 1 – ol is oxidised by pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)?
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Propane
(d) Propene
Answer:
(a) Propanal

Question 50.
Which one of the enzyme is produced in liver to detoxify the alcohol?
(a) Diastase
(b) Zymase
(c) Invertase
(d) Dehydrogenase alcohol
Answer:
(d) Dehydrogenase alcohol
Question 51.
What is ADH and NAD?
(a) Alcohol dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
(b) Acid dehydration and Nitrogen addition
(c) Alcohol dehydration and Nicotine addiction
(d) Adeninc hydrogenase and Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Answer:
(a) Alcohol dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Question 52.
What is the main reaction takes place when 2 – methyl propan – 2 – ol reacts with Cu at 573 K?
(a) Dehydrogenation
(b) Oxidation
(c) Dehydration
(d) Hydrogenation
Answer:
(c) Dehydration
Question 53.
Name the product formed when tertiary butyl alcohol is treated with Cu at 573 K?
(a) 2 – methyl prop – 1 – ene
(b) 2 – methyl prop – 2 – ene
(c) propene
(d) 1 – butene
Answer:
(a) 2 – methyl prop – 1 – ene

Question 54.
Which one of the following product is formed when propan – 2 – ol is treated with Cu at 573 K?
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Propan – 1 – ol
(d) Propane
Answer:
(b) Propanone
Question 55.
What is the name of the reaction between ethanol and ethanoic acid?
(a) Esterification
(b) Saponification
(c) Ethenfication
(d) Hydroxylation
Answer:
(a) Esterification
Question 56.
Which one of the following is formed when ethan – 1, 2 – diol is treated with PI3?
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethyne
(c) Ethene
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(c) Ethene
Question 57.
Which reagent is used to convert ethylene glycol to ethylene?
(a) HI
(b) I2
(c) PI3
(d) Conc. H2 SO4
Answer:
(c) PI3
Question 58.
What is the product formed when ethylene glycol is heated at 773 K?
(a) Ethanal
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethane
(d) Oxirane
Answer:
(d) Oxirane

Question 59.
Which reagent is used to convert ethan – 1, 2 – diol into Ethanal?
(a) Anhydrous ZnCI2
(b) Dilute. H2SO4
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Conc. H2SO4
Answer:
(c) Either (a) or (b)
Question 60.
Name the product formed when ethan- 1, 2-diol is treated with anhydrous ZnCl2.
(a) Ethanol
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethane
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(d) Ethanal
Question 61.
Which one of the following is formed when ethane – 1, 2 – diol is treated with Conc. H2 SO4?
(a) 1, 4 – dioxane
(b) Ethanal
(c) Ethanoic acid
(d) Ethene
Answer:
(a) 1, 4 – dioxane
Question 62.
Which one of the following is formed when ethylene glycol is treated with periodic acid?
(a) Methanal
(b) Methanol
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(a) Methanal
Question 63.
Identify the product formed when glycerol is treated with nitric acid and conc. H2SO4?
(a) Nitroglycerine
(b) Glyceryl triacetate
(c) Prop – 2 – enal
(d) Glyceric acid
Answer:
(a) Nitroglycerine

Question 64.
What will be the product formed when propan – 1, 2, 3 – triol is treated with KHSO4?
(a) Nitroglycerine
(b) TNG
(c) Prop – 2 – enal
(d) Allyl alcohol
Answer:
(a) Nitroglycerine
Question 65.
Oxidation of glycerol with dil.HNO3 gives ………
(a) Meso oxalic acid
(b) Glyceric acid and tartronic acid
(c) Glycerose
(d) Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone
Answer:
(b) Glyceric acid and tartronic acid
Question 66.
Oxidation of glycerol with Fenton reagent gives ………..
(a) Glyceraldehyde + Dihydroxyacetone
(b) Glyceric acid + Tartronic acid
(c) Meso oxalic acid
(d) Oxalic acid
Answer:
(a) Glyceraldehyde + Dihydroxyacetone
Question 67.
Which one of the following products is formed when glycerol is oxidised with acidified KMnO4?
(a) Meso oxalic acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Formic acid
(d) Glyceric acid
Answer:
(b) Oxalic acid
Question 68.
Which one of the following is used as a solvent for paints, varnishes and gum?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Methanol
(c) Methanal
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(b) Methanol

Question 69.
Which one of the following is used as fuel for aeroplanes?
(a) Methanol + Ethanol
(b) Ethanol + Petrol
(c) Ethanol + Propanol
(d) Butanol + Methanol
Answer:
(b) Ethanol + Petrol
Question 70.
Which one of the following is used as a beverage as well as a preservative for biological specimens?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Methanol
(c) Phenol
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer:
(a) Ethanol
Question 71.
Which one of the following is used as an anti-freezer in automobile radiators?
(a) Glycerol
(b) Phenol
(c) Benzyl alcohol
(d) Ethylene glycol
Answer:
(d) Ethylene glycol
Question 72.
Which one of the following is used as a sweetening agent in confectionery and beverages?
(a) Glycerol
(b) Phenol
(c) Benzyl alcohol
(d) Ethylene glycol
Answer:
(a) Glycerol
Question 73.
Which one of the following is used in the manufacture of cosmetics and transparent soaps?
(a) Methanol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Glycerol
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(c) Glycerol
Question 74.
Which one of the following is used in the manufacture of explosive dynamite and cordite by mixing it with clay?
(a) Glycol
(b) Glycerol
(c) Ethanol
(d) Benzaldehyde
Answer:
(b) Glycerol
Question 75.
Which alcohols is used in making printing inks and stamp pad ink?
(a) Glycol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Glycerol
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(c) Glycerol
Question 76.
Except which alcohol, other alcohols are weaker acid than water?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Phenol
(c) Methanol
(d) Propanol
Answer:
(c) Methanol

Question 77.
Which one of the following is the correct decreasing order of acidity in alcohol?
(a) 1° alcohol > 2° alcohol > 3° alcohol
(b) 3° alcohol > 2° alcohol> 1° alcohol
(c) 2° alcohol> 1° alcohol > 3° alcohol
(d) 3° alcohol > 1° alcohol > 2° alcohol
Answer:
(a) 1° alcohol > 2° alcohol > 3° alcohol
Question 78.
Which one of the following is more acidic?
(a) Benzyl alcohol
(b) Phenol
(c) Ethanol
(d) Methanol
Answer:
(b) Phenol
Question 79.
The JUPAC name of Phioroglucinol is ………….
(a) 4 – methyl phenol
(b) 1, 4 – dihydroxy benzene
(c) 1, 3, 5 – trihydroxy benzene
(d) 1, 2, 3 – trihydroxy benzene
Answer:
(c) 1, 3, 5 – trihydroxy benzene
Question 80.
The other name of 1 , 2, 3 – trihydroxy benzene is called ……….
(a) Phloroglucinol
(b) Quinol
(c) Pyrogallol
(d) Hydroxy quinol
Answer:
(c) Pyrogallol
Question 81.
The other name of 3, 5 – dihydroxy toluene is known as …………
(a) Orcinol
(b) Quinol
(c) Pyrogallol
(d) Resorcinol
Answer:
(a) Orcinol

Question 82.
The IUPAC name of Catechol is known as ………..
(a) 1, 3 – dihydroxy benzene
(b) 1, 2 – dihydroxy benzene
(c) 1, 4 – dihydroxy benzene
(d) 1, 3, 5 – trihydroxy benzene
Answer:
(b) 1, 2 – dihydroxy benzene
Question 83.
The name of
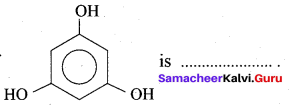
is …………
(a) Phloroglucinol
(b) pyrogallol
(c) Quinol
(d) Resorcinol
Answer:
(a) Phloroglucinol
Question 84.
The name of
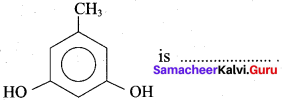
(a) Pyrogallol
(b) Hydroxy cresol
(c) Orcinol
(d) Phloroglucinol
Answer:
(c) Orcinol
Question 85.
The reaction of chiorobenzene with NaOH is known as ………..
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Riemcr – Ticmann reaction
(c) Dow’s process
(d) Cumene synthesis
Answer:
(c) Dow’s process

Question 86.
Which one of the product is formed when benzene and propene is heated at 523K?
(a) Cumene
(b) 2 – ethyl benzene
(c) 2 – propyl benzene
(d) Ethyl enthanoate
Answer:
(a) Cumene
Question 87.
What will be the product formed when phenol is treated with zinc dust?
(a) Cumene
(b) Toluene
(c) Ethyl benzene
(d) Benzene
Answer:
(d) Benzene
Question 88.
The acetylation and benzoylation of phenol are called ……….
(a) Dow’s process
(b) Schotten – Baumann reaction
(c) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
(d) Williamson ether synthesis
Answer:
(b) Schotten – Baumann reaction
Question 89.
Name the product formed when phenol is heated with ammonia in the presence of anhydrous
ZnCl2.
(a) Benzene
(b) Aniline
(c) Anisole
(d) Phenylacetate
Answer:
(b) Aniline

Question 90.
What will be the product formed when phenol is treated with benzoyl chloride in the presence of a base?
(a) Phenylacetate
(b) Phenyl ethanoate
(c) Phenyl benzoate
(d) Benzyl acetate
Answer:
(c) Phenyl benzoate
Question 91.
Which one of the following is formed when phenol is treated with acidified K2Cr2O7?
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) Phenyl amine
(c) Phenylacetate
(d) 1, 4 – benzoquinone
Answer:
(d) 1, 4 – benzoquinone
Question 92.
Hydrogenation of phenol in the presence of Nickel gives ………
(a) cyclo hexane
(b) cyclo hexanol
(c) benzene
(d) cumene
Answer:
(b) cyclo hexanol
Question 93.
Which one of the following is formed when phenol reacts with a mixture of Conc. HNO3 and Conc.H2SO4?
(a) Ortho nitrophenol
(b) Para nitrophenol
(c) 1, 2 – dinitrophenol
(d) 2, 4 , 6 – trinitro phenol
Answer:
(d) 2, 4 , 6 – trinitro phenol
Question 94.
What will be the product formed when phenol reacts with bromine water?
(a) 0 – bromo phenol
(b) P – bromo phenol
(c) 1, 3, 5 – tri bromo phenol
(d) 2, 4, 6 – tri bromo phenol
Answer:
(d) 2, 4, 6 – tri bromo phenol

Question 95.
The conversion reaction of phenol of salicylic acid is known as
(a) Schottan – Baumann reaction
(b) Riemer – Ticmann reaction
(c) Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction
(d) Williamson’s synthesis
Answer:
(c) Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction
Question 96.
The reagent used for the conversion of phenol into salicylaldehyde is ………..
(a) CHCI3 / NaOH
(b) I2 / KOH
(c) Zn
(d) Br2 / CCl4
Answer:
(a) CHCI3 / NaOH
Question 97.
What is the name of the reaction of phenol with chloroform and aqueous alkali?
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Cumene synthesis
(c) Rlemer – Tiemann reaction
(d) Schottan – Baumann reaction
Answer:
(c) Rlemer – Tiemann reaction
Question 98.
Which one of the following is formed when phenol is treated with chloroform and sodium hydroxide.
(a) Chiorobenzene
(b) Salicylaldehyde
(c) Salicylic acid
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(b) Salicylaldehyde
Question 99.
What are the reagents required to prepare phenolphthalein?
(a) Phenol + Phthalic acid
(b) Phenol + Benzene
(c) Phenol + Phthalic anhydride
(d) Phenol + Aniline
Answer:
(c) Phenol + Phthalic anhydride

Question 100.
Which one of the following is formed when Phenol reacts with benzene diazonium chloride?
(a) P – hydroxy diazo phenol
(b) P – hydroxy azobenzene
(c) O – hydroxy benzene
(d) O – hydroxy azobenzene
Answer:
(b) P – hydroxy azobenzene
Question 101.
Which reagent gives purple colouration with phenol?
(a) Anhydrous AlCl3
(b) Anhydrous ZnCl2
(c) Neutral FeCI3
(d) HCI + ZnCI2
Answer:
(c) Neutral FeCI3
Question 102.
Bakelite is formed when phenol reacts with ………..
(a) Methanol
(b) Methanal
(c) Ethanal
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(b) Methanal
Question 103.
Which one of the following is used as an antiseptic – carbolic lotion and carbolic soaps?
(a) Benzyl alcohol
(b) Methanol
(c) Glycol
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(d) Phenol
Question 104.
The product formed when formaldehyde reacts with phenol is ……..
(a) Bakelite
(b) Phenolphthalein
(c) Azodye
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(a) Bakelite
Question 105.
Which one of the following is a simple ether?
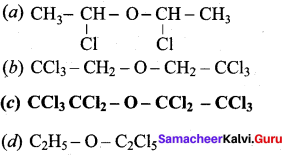
Answer:
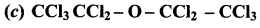
Question 106.
Which one of the following is an example for mixed ether?
(a) Methoxy methane
(b) Phenoxy benzene
(c) Methoxy benzene
(d) Ethoxy ethane
Answer:
(c) Methoxy benzene
Question 107.
The IUPAC name of
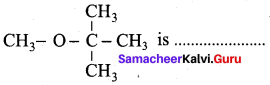
(a) 1 – methoxyl isopropyl ethane
(b) 2 – methoxy – 2 – methyl propane
(c) 2, 2 – dimethyl 2- methoxy ethane
(d) Methoxy tertiary butane
Answer:
(b) 2 – methoxy – 2 – methyl propane
Question 108.
The IUPAC name of C6H5 – O – C6H5 is ……..
(a) Diphenyl ether
(b) Phenoxy methane
(c) Phenoxy benzene
(d) Ethoxy benzene
Answer:
(c) Phenoxy benzene

Question 109.
Which one of the following is not a simple ether?
(a) C6H5 – O – CH2 – CH3
(b) CH3 – O – CH3
(c) C6H5 – O – C6H5
(d) C2H5 – O – C2H5
Answer:
(a) C6H5 – O – CH2 – CH3
Question 110.
What is the name of the reaction when ethanol is treated with Conc.H2SO4 at 413 K?
(a) Intermolecular dehydration
(b) Intramolecular dehydration
(c) Dehydrogenation
(d) Dehydro halogenation
Answer:
(a) Intermolecular dehydration
Question 111.
Identify the product formed when ethanol is treated with Conc.H2SO4 at 413 K?
(a) Ethene
(b) Ethane
(c) 2 – butanol
(d) Diethyl ether
Answer:
(d) Diethyl ether
Question 112.
The reaction of sodium methoxide with ethyl bromide follows
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) E1 reaction
(d) E2 reaction
Answer:
(b) SN2 mechanism
Question 113.
The product formed when tertiary butyl bromide and sodium methode are reacted together is ……….
(a) 2 – methyl – 2 – methoxy propane
(b) ethoxy ethane
(c) 2 – methyl – prop – 1 – ene
(d) 2 – methyl but – 1 – ene
Answer:
(c) 2 – methyl – prop – 1 – ene

Question 114.
Identify the product formed when diazomethane reacts with Ethanol in the presence of HBF4?
(a) Methoxy ethane
(b) Ethoxy ethane
(c) Diethyl ether
(d) Ethyl isopropyl ether
Answer:
(a) Methoxy ethane
Question 115.
What arc the products formed when methoxy ethanc is treated with hydroiodic acid?
(a) Phenol + iodomethane
(b) Todomethane + Ethanol
(c) lodoethane + Methanol
(d) lodobenzene + Methane
Answer:
(b) Todomethane + Ethanol
Question 116.
What are the products formed when methoxy benzene is treated with HI?
(a) C6H5OH + CH4
(b) CH3I + C6H6
(c) C6H5 OH + CH3I
(d) C2H5I + C6H6
Answer:
(c) C6H5 OH + CH3I
Question 117.
The mechanism involved in Williamson’s synthesis is …………
(a) E1
(b) E2
(c) SN2
(d) SN1
Answer:
(c) SN2
Question 118.
When diethyl ether is exposed to excess oxygen, the reaction taken place is …………
(a) reduction
(b) hydrogenation
(c) dehydrogenation
(d) auto oxidation
Answer:
(d) auto oxidation
Question 119.
Which one of the following is formed when Diethyl ether is treated with dil.H2SO4?
(a) CH3CH2HSO4
(b) CH3 – CH2OH
(c) CH2 = CH2
(d) CH3 – CH3
Answer:
(b) CH3 – CH2OH
Question 120.
Which one of the following is formed when diethyl ether reacts with Cl2 in the presence of light?
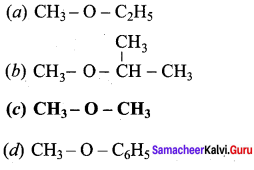
Answer:
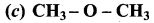
Question 121.
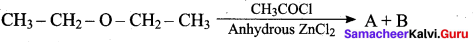
In the above reaction A and B are
(a) CH3 CH2 OH + CH3 – CH2 Cl
(b) CH3 – CH2Cl + CH3 COOH
(c) CH3 COOH + CH3 COOCH3
(d) CH3 – CH2CI + CH3COOCH2CH3
Answer:
(d) CH3 – CH2CI + CH3COOCH2CH3
Question 122.
Anisole undergoes bromination with Br2 in acetic acid in the absence of catalyst, the major product formed is ………..
(a) O – bromoan isole
(b) P – bromoan isole
(c) Benzyl bromide
(d) Bromo benzene
Answer:
(b) P – bromoan isole
Question 123.
Anisole reacts with methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AICI3 and CS2 to give ……..
(a) 2 – methoxy toluene
(b) 4 – methoxy toluene
(c) either (a) or (b)
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b)
Question 124.
Which one of the following is used as a surgical anesthetic agent in surgery?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Ethoxy ethane
(c) Methoxy ethane
(d) Methoxy propane
Answer:
(b) Ethoxy ethane
Question 125.
Which one of the following is a precursor to the synthesis of perfumes and insecticide pheromones?
(a) Phenol
(b) Benzyl alcohol
(c) Anisole
(d) Diethyl ether
Answer:
(c) Anisole
Question 126.
Among the alkenes which one produces tertiary butyl alcohol on acid hydration?
(a) (CH3)2C CH2
(b) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
(c) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2
(d) CH3 – CH = CH2
Answer:
(a) (CH3)2C CH2

Question 127.
Ether is more volatile than an alcohol having the same molecular formula. This is due to
(a) the dipolar character of ethers
(b) alcohols having resonance structures
(c) intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ethers
(d) intermolecular hydrogen bonding in alcohols
Answer:
(d) intermolecular hydrogen bonding in alcohols
Question 128.
An organic compound A containing C, H and O has a pleasant odour. On boiling A with Conc.H2SO4, colourless gas is produced which decolourises bromine water and alkaline KMnO4. The organic liquid A is ………..
(a) C2H5COOCH3
(b) C2HOH
(c) C2H5CI
(d) C2H6
Answer:
(b) C2HOH
Question 129.
Chloroethane reacts with X to form diethyl ether. What is X?
(a) NaOH
(b) H2SO4
(c) C2H5ONa
(d) C2H5Cl
Answer:
(c) C2H5ONa
Question 130.
In the following sequence of reactions,
the compound D is ……….
(a) Butanal
(b) n-butyl alcohol
(c) propan – 1 – ol
(d) Propanal
Answer:
(c) propan – 1 – ol
Question 131.
Propan – 1 – ol and Propan – 2 – ol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?
(a) PCI5
(b) Reduction
(c) Oxidation with K2 Cr207
(d) Ozonolysis
Answer:
(c) Oxidation with K2 Cr207
Question 132.
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the following reagents except
(a) Sodium
(b) NaOH / I2
(c) Neutral FeCI3
(d) Br2 / H2O
Answer:
(a) Sodium
Question 133.
in cold countries, ethylene glycol is added to water in the radiators to …………
(a) bring down the specific heat of water
(b) lower the viscosity
(c) reduce the viscosity
(d) make water a better lubricant
Answer:
(a) bring down the specific heat of water
(i.e.) lowering down the freezing point of water.
Question 134.
Main constituent of dynamite is ………..
(a) nitro benzene
(b) nitroglycerine
(c) Picric acid
(d) TNT
Answer:
(b) nitroglycerine
Question 135.
Diethyl ether finds use in medicine as …………
(a) a pain killer
(b) a hypnotic
(c) an antiseptic
(d) an anaesthetic
Answer:
(d) an anaesthetic

Question 136.
Benzene diazonium chloride on reaction with phenol in weakly basic medium gives
(a) Diphenyl ether
(b) P – hydroxy azo benzene
(c) Chlorobenzene
(d) Benzene
Answer:
(b) P – hydroxy azo benzene
Question 137.
The alcohol that produces turbidity immediately with ZnCl2 + Conc.HCl at room temperature is ………..
(a) Rutan – 1- ol
(b) Butan – 2- ol
(c) 2 – methyl – propan – 1 – ol
(d) 2 – methyl – propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
(d) 2 – methyl – propan – 2 – ol
Question 138.
Propanone is the product obtained by dehydrogenation of …………
(a) Propan – 2 – ol
(b) Propan – 1 – ol
(c) Propanal
(d) n – propyl alcohol
Answer:
(a) Propan – 2 – ol
Question 139.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Phenol is less acidic than ethanol
(b) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol
(c) Phenol is more acidic than carboxylic acid
(d) Phenol is less acidic than carboxylic acid
Answer:
(b) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol
Question 140.
The reaction of ethylene glycol with Pl3 gives ………..
(a) CH2 = CHI
(b) ICH2 – CH2I
(c) CH2 = CH22
(d) CH = CH
Answer:
(a) CH2 = CHI
Question 141.
During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with Conc. H2SO4, the initiation step is ………..
(a) protonatlon of alcohol
(b) formation of carbocation
(c) elimination of water
(d) formation of carbanion
Answer:
(a) protonatlon of alcohol
Question 142.
Sodium phenoxide reacts with CO2 at 400 K and 4 – 7 bar pressure to give ………
(a) Sodium salicylate
(b) Salicylaldehyde
(c) Catechol
(d) Pyrogallol
Answer:
(a) Sodium salicylate

Question 143.
The reaction of C2 H5OH with Cone. H2 SO4 does not give ………..
(a) Ethylene
(b) Diethyl ether
(c) Acetylene
(d) Ethyl hydrogen sulphate
Answer:
(c) Acetylene
Question 144.
Which of the following gives ketone on oxidation?
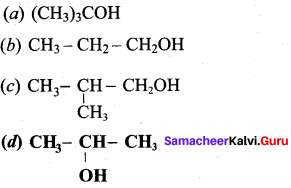
Answer:
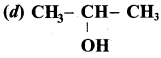
Question 145.
Phenol is treated with Br2 /H2O and shaken well. The white precipitate formed during the process is …………
(a) m – bromo phenol
(b) 2,4 – dibromo phenol
(c) 2, 4, 6 – tribromo phenol
(d) 1, 2 – dibromo benzene
Answer:
(c) 2, 4, 6 – tribromo phenol
Question 146.
Which compound has the highest boiling point?
(a) Acetone
(b) Diethyl ether
(c) Methanol
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(d) Ethanol
Question 147.
When phenol reacts with NH3 in the presence of ZnCl2 at 300°C, it gives ………..
(a) 1° amine
(b) 2° amine
(c) 3° amine
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(a) 1° amine

Question 148.
Azo dyes are prepared from …………
(a) Aniline + Phenol
(b) Phenol + Phthalic anhydride
(c) Phenol + Benzene diazonium chloride
(d) Aniline + Phthalic anhydride
Answer:
(c) Phenol + Benzene diazonium chloride
Question 149.
A compound that easily undergoes bromination is ………….
(a) Phenol
(b) Toluene
(c) Benzene
(d) Diethyl ether
Answer:
(a) Phenol
Question 150.
When glycerol is treated with P2O5 (or) KHSO4 the product formed is ……….
(a) CH2 = CH – CH3
(b) CH2 = CH – CH2OH
(c) CH2 = CH – CHO
(d) CH2 = C = CH2
Answer:
(c) CH2 = CH – CHO
Question 151.
The ether that undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions is ………….
(a) CH3 – O – C2H5
(b) C6H5 – O – CH3
(c) C2H5 – O – C2H5
(d) CH3 – O – CH3
Answer:
(b) C6H5 – O – CH3
Question 152.
With anhydrous ZnCl2, ethylene glycol gives …………
(a) Formaldehyde
(b) Acetylene
(c) Acetaldehyde
(d) Dioxan
Answer:
(c) Acetaldehyde
Question 153.
Fats on alkaline hydrolysis give …………
(a) Oil + Soap
(b) Soap + Glycol
(c) Soap + Ester
(d) Soap + Glycerol
Answer:
(d) Soap + Glycerol
Question 154.
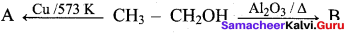
B. in this reaction A and B are respectively
(a) Alkene, Alkyne
(b) Alkanal, Alkene
(c) Alkyne, Alkanal
(d) Alkyne, Alkene
Answer:
(b) Alkanal, Alkene
Question 155.
The oxygen atom in ether is …………
(a) very active
(b) replaceable
(c) comparatively inert
(d) less active
Answer:
(c) comparatively inert

Question 156.
Chlorination of toluene in the presence of light and heat followed by treatment with aqueous NaOH gives ………….
(a) O – cresol
(b) P – cresol
(c) Phioroglucinol
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer:
(c) Phioroglucinol
Question 157.
Primary alcohols can be obtained from the reaction of RMgX with …………
(a) CO2
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3CHO
(d) H2O
Answer:
(b) HCHO
Question 158.
The dehydration of alcohol is an example of ………….
(a) Bimolecular elimination reaction
(b) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(c) Unimolecular elimination reaction
(d) internal substitution reaction
Answer:
(c) Unimolecular elimination reaction
Question 159.
Ethanol is converted into Ethoxy ethane ………….
(a) by heating with cone. H2SO4 at 443 K
(b) by heating with conc. H2SO4 at 413 K
(c) by heating with excess oxygen
(d) by heating with hydrogen
Answer:
(b) by heating with conc. H2SO4 at 413 K
Question 160.
Which of the following is not the product of dehydration of
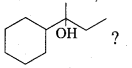
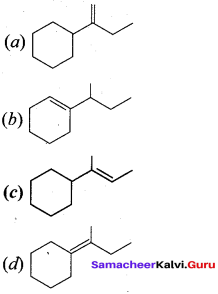
Answer:
II. Fill in the blanks
- Cholesteryl alcohol commonly known as …………. is an important component in our ………….
- …………. the storage form of vitamin A, finds application in proper functioning of our eyes.
- Methanol s used as an …………. solvent.
- Isopropyl alcohol is used as …………. for injection.
- CH2CHOH is called as ………….
- An example of hexahydric alcohol is ………….
- The IUPAC name of glycerol is ………….
- The TUPAC name of Neopentyl alcohol is ………….
- The TUPAC name of CH2 CH – CHOH is ………….
- In methanol, the – OH group attached to …………. hybridised carbon atom.
- The bond angle C – OH in methanol is ………….
- alkyl halides undergo substitution by SN2 reaction whereas …………. and …………. alkyl halides undergo substitution by SN1 reaction.
- Addition of H2O to an unsymmetric alkene in the process of sulphuric acid follows ………….
- Nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to aldehydes/ketones take place in the presence …………. followed by acid hydrolysis gives .
- With RMgx …………., …………. gives l°alcohol.
- Butyl Magnesium bromide reacts with propanone to give ………….
- …………. is used to prepare a secondary alcohol with identical group.
- Hydroboration yields an …………. product.
- …………. is the best reagent to prepare unsaturated alcohol by reduction reaction of carbonyl compound.
- …………. occurs in natural fats and in long chain fatty acids in form of triglycerides.
- The alkaline hydrolysis of fats gives glycerol and the reaction is known as ………….
- In Lucas test …………. alcohol do not react at room temperature.
- In Victor Meyer’s test no colouration will be observed in case of ………….
- Alkyl halide formation from primary alcohol follows …………. mechanism.
- Alkyl halide formation from tertiary alcohol follows …………. mechanism.
- The reaction between methanol and thionyl chloride in the presence of pyridine follows…………. mechanism.
- …………. alcohols undergo dehydration by E2 mechanism whereas alcohols undergo dehydration by E1 mechanism.
- To stop the oxidation reaction of alcohol at aldehyde / ketone stage …………. is used as an oxidising agent.
- In …………. oxidation dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is used as an oxidising agent.
- The fermentation of food consumed by an animal produces …………..
- The detoxify the alcohol, the liver produces an enzyme called ………….
- …………. present in the animals act as an oxidising agent and …………. catalyses the oxidation of toxic alcohol into non-toxic aldehydes.
- Ethylene glycol, when heated to 773 K, it forms ………….
- The reagent used to convert ethane 1, 2 -diol to ethanal is ………….
- When Ethane – 1, 2 -diol is treated with conc.H2S04, it forms ………….
- The intermediate product formed when ethylene glycol is treated with periodic acid is ………….
- The final product formed when glycol reacts with periodic acid is ………….
- The IUPAC name of Acrolein (or) CH2 = CH – CHO is ………….
- Oxidation of glycerol with dilute nitric acid gives …………. and ………….
- Oxidation of glycerol with bismuth nitrate gives ………….
- Oxidation of glycerol with Fenton’s reagent gives ………….
- LTA is known as ………….
- Oxidation of glycerol with acidified KMnO4 gives ………….
- FeSO4 + H2O2 is called ………….
- …………. is used as a substitute for petrol under the name and used as fuel for aeroplane.
- …………. is used as an anti-freezer in automobile radiators.
- …………. is used as a sweetening agent in confectionery and beverages.
- …………. is used in the manufacture of transparent soap, printing ink and stamp pad ink.
- Glycerol is used in the manufacture of explosives like and by mixing with ………….
- Except …………. all other alcohols are weaker acid than water.
- The electron withdrawing groups such as – NO2, – Cl enhances the acidic nature of phenol especially when they are present at …………. positions.
- The LUPAC name of hydroxy quinol is ………….
- The IUPAC name of orcinol is ………….
- The other name of 1, 2, 3 – trihydroxy benzene is ………….
- The reaction of chioro benzene with aqueous NaOH to give phenol is known as ………….
- The product formed when benzene diazonium chloride is boiled with hot water is ………….
- The IUPAC name of curnene is ………….
- Phenol is converted to benzene on heating with ………….
- The acetylation and benzoylation of phenol are called ………….
- The reagent used in the conversion of phenol to 1, 4 – benzo quinone is ………….
- When phenol is treated with Conc.HNO3 and Conc.H2SO4, the product formed is ………….
- Phenol reacts with bromine water to give a precipitate of ………….
- The conversion reaction of phenol to salicylic acid is known as ………….
- The conversion reaction of phenol into salicylaldehyde is known as ………….
- The product formed when phenol is treated with phthalic anhydride in the presence of Conc.H2SO4 is ………….
- …………. dye is Ibmied when phenol couples with benzene diazonium chloride in an alkalin
solution.
- Phenol gives …………. colouration with neutral FeCI3.
- Phenol formaldehyde is known as ………….
- The IUPAC name of tertiary butyl methyL ether is known as ………….
- C6H5O – CH2 – CH3 is known as ………….
- The mechanism take place when alkyl halide is treated with alcohol solution of sodiunalkoxide is ………….
- The dipole moment of diethyl ether is ………….
- The reaction take place when ethers are exposed to oxygen is ………….
- …………. is used as a surgical anesthetic agent in surgery.
- …………. is used as a refrigerant.
Answer:
- cholesteroL, cell membrane
- Retinol
- industrial
- skin cleanser
- vinyl alcohol (or) ethenol
- Sorbitol
- propan – 1, 2, 3 – tnol,
- 2, 2 – ditnethyl propan – 1 – ol
- prop – 2 – en – 1 – ol
- sp3
- 108.9°
- 1°, 2°, 3°
- Markownikoff’s rule
- dry ether, alcohol
- formaldehyde, HCHO
- 2-methyl hexan – 2 – ol
- Formate ester
- Anti-Markownikoft’s
- LiAlH4
- Glycerol
- Saoinufucatuib
- Primary
- Tertiary alcohol
- SN2
- SN1
- SN2
- Pnmary, Tertiary
- pyridinium chlorochromate
- Swer
- alcohol
- alcohol dehydrogenase ALH
- NAD,ADH
- epoxide (or) 1,2-epoxy ethane (or) oxirane
- dil.H2SO (or) anhydrous ZnCI2
- 1,4 – dioxane
- cyclic periodate ester
- formaldehyde
- prop – 2 – enal
- glycenc acid, Tartronic acid
- Meso oxalic acid
- glycerose (or) a mixture of glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone
- Lead tetraacetate
- Oxalic acid
- 44. Fenton’s reagent
- Ethanol, Power alcohol
- Ethylene glycol
- Glycerol
- Glycerol
- dynamite, cordite, china clay
- Methanol
- ortho and para
- 1, 2, 4 – trihydroxy benzene
- 3, 5 – dihydroxy toluene
- Pyrogallol
- Dows process
- Phenol
- 2 – phenyl propane
- Zinc dust
- Schotten-Baumann reaction
- acidified K2Cr2O7
- 2,4, 6 – trinitro phenol (or) Picric acid
- white, 2,4, 6-tribromo phenol
- Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction
- Riemer-Tiemann Reaction
- Phenolphthalein
- P-hydroxy azobenzene (or) Red-orange dye
- Purple
- Bakelite
- 2-methoxy – 2 – methyl propane
- Phenatole (or) Ethoxy benzene
- SN2
- 1.18 D
- auto oxidation
- Diethyl ether
- Diethyl ether
III. Match the following Colum – I with Column – II ysubg tge cide guveb below.
Question 1.

Answer:
(a) 3 4 1 2
Question 2.
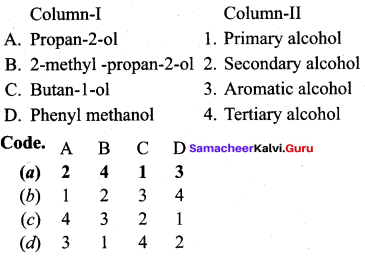
Answer:
(a) 2 4 1 3
Question 3.
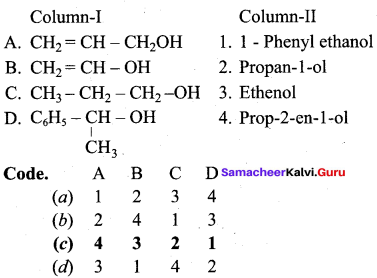
Answer:
(c) 4 3 2 1
Question 4.
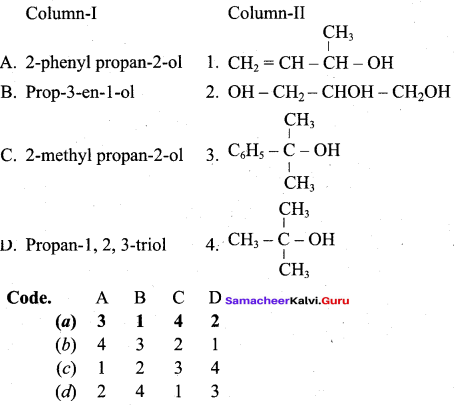
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 5.

Answer:
(b) 4 3 1 2
Question 6.
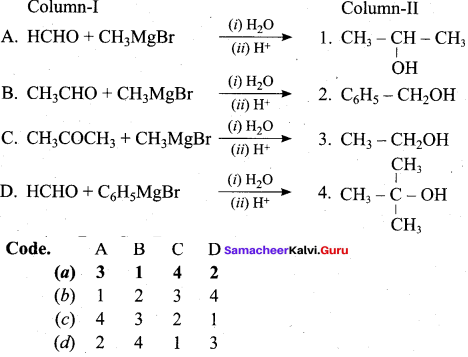
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 7.
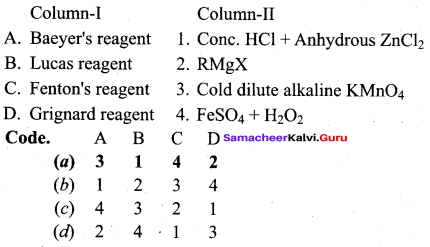
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 8.
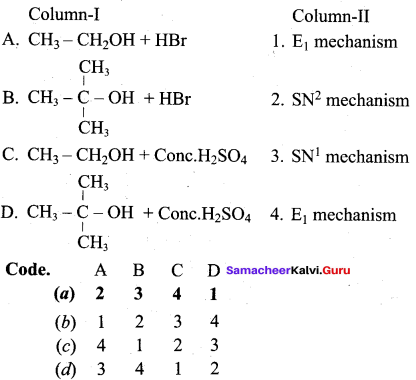
Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 9.
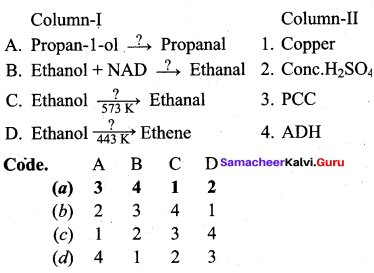
Answer:
(a) 3 4 1 2
Question 10.
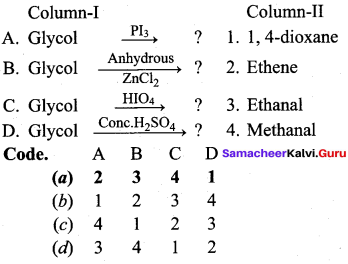
Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 11.
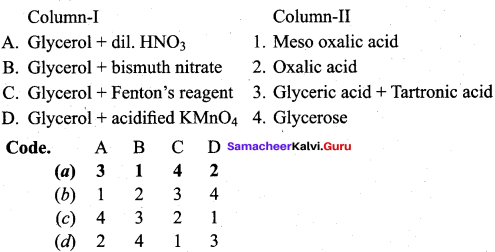
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 12.

Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 13.
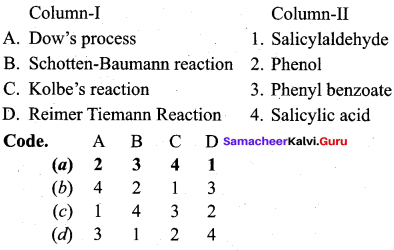
Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 14.
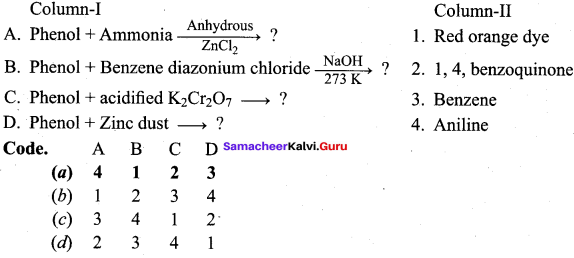
Answer:
(a) 4 1 2 3
Question 15.
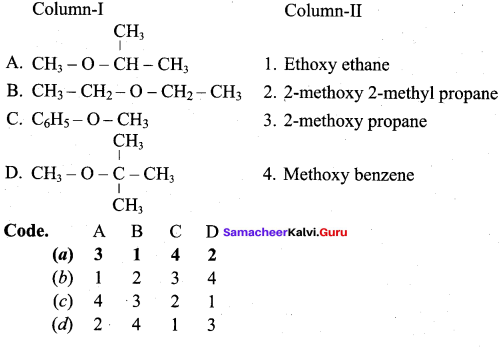
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 16.
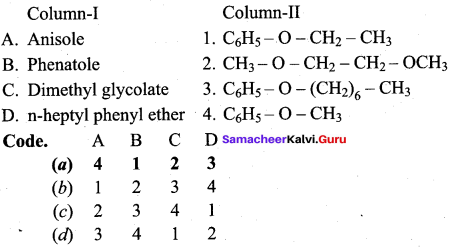
Answer:
(a) 4 1 2 3
Question 17.
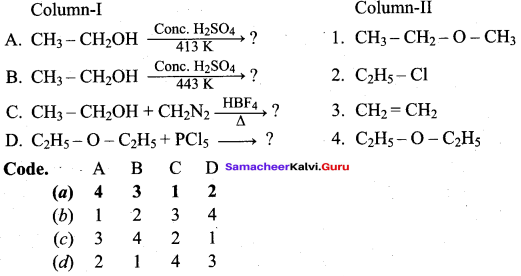
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
IV. Assertion and reasons.
Question 1.
Assertion(A): P – nitro phenol is having lower pKa value than phenol.
Reason (R): The electron with drawing group – NO2 at para position enhances the acidic nature.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b)BothAand Rare wrong
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Assertion(A): Alcohols cannot be used as solvent for Grignard reagent.
Reason (R): Alcohols are decomposed by Grignard reagents to give alkane.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct but R is wrong
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
Assertion(A): Phenols are soluble in alcohols.
Reason (R): Phenols are soluble in alcohol due to the formation of inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong .
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
Assertion(A): Phenol is insoluble in NaHCO3 solution but acetic acid is soluble.
Reason (R): Phenols are weakly acidic and hence they dissolve only in strong base and insoluble in weak base like NaHCO3. But acetic acid is a stronger acid than phenol and so it is soluble in weak base NaHCO3.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are correct
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.

Question 5.
Assertion(A): Glycol is more viscous than ethanol.
Reason (R): Glycol contains two hydroxyl groups and the inter molecular hydrogen bonding is made much stronger resulting in a polymeric structure. This leads to high viscosity than ethanol.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion(A): Ethanol is a weaker acid than Phenol.
Reason (R): Sodium ethoxidc may be prepared by the reaction of ethanol with sodium metal but phenol reacts with NaOH.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R ¡s the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R ¡s the correct explanation of A
Question 7.
Assertion(A): Both alcohol and ether have higher boiling point.
Reason (R): Both are having intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are wrong
Question 8.
Assertion(A): Bond angle in ethers is slightly less than the tetra hedral angle.
Reason (R): There is a repulsion between the two bulkier R groups.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and arc wrong
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 9.
Assertion(A): P-nitro phenol is a stronger acid than o – nitro phenol.
Reason (R): Intra molecular hydrogen bonding in o – nitro phenol make it as a weaker acid.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 10.
Assertion(A): Phenol is more reactive towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Reason (R): In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbo cations is more resonance stabilized.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 11.
Assertion(A): Phenol forms 2, 4, 6 – tribromo phenol on treatment with Br2 in CS2 at 273 K.
Reason (R): Bromine polarizes in CS2.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are incorrect
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and are incorrect

Question 12.
Assertion(A): Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
Reason (R): Phenoxide ion is more stable than ethoxide due to resonance.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Assertion(A): Boiling point of ethanol is higher in comparison to methoxy methane.
Reason (R): Ethanol is associated with inter molecular hydroxide bonding whereas in methoxy methane, inter molecular hydrogen bonding is not present.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 14.
Assertion(A): (CH3)3 C – O – CH3 on reaction with HI gives CH3OH and (CH3)3C – I as the main products and not (CH3)3 C – OH and CH3I.
Reason (R): (CH3)3 C + (Tertiary carbo cation) is more stable and reacts with HI to form (CH3)3 C – I as main product.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 15.
Assertion(A): The bond angle (C – O – H) in methanol is reduced to 108.9° from the regular tetra hedral bond angle of 109.5°.
Reason (R): In methanol, two lone pairs of electrons are present in oxygen atom and due to lone pair – lone pair repulsion, the bond angle is reduced.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.

Question 16.
Assertion(A): LiAlH4 is the best reagent to prepare unsaturated alcohols from carbonyl compounds.
Reason (R): LiAlH4 does not reduce the carbon – carbon double bond present in the carbonyl carbon compound.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 17.
Assertion(A): Primary alcohols are more acidic than tertiary alcohol.
Reason (R): Alkyl groups (electron releasing group) increases the electron density on oxygen and decreases the polar nature of – OH bond. Hence it results in the decrease in acidity.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are not correct
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 18.
Assertion(A): P – cresol is less acidic than phenol.
Reason (R): Alkyl substituted phenols show a decreased acidity due to the electron releasing + I effect of alkyl group.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 19.
Assertion(A): O – nitro phenol is slightly soluble in water whereas P – nitro phenol is more soluble in water.
Reason (R): O – nitro phenol has intra molecular hydrogen bonding whereas P – nitro phenol has inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wiong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 20.
Assertion(A): Inter molecular dehydration of alcohol is not a suitable method of prepare mixed ethers.
Reason (R): When a mixture of two different alcohols are used, mixture of different ethers are formed and they are difficult to separate.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers 2 Mark Questions and Answers
V. Answer the following
Question 1.
Write the molecular formula and IUPAC name of the following compounds.
- Vinyl alcohol
- Sorbitol
Answer:
1. Vinyl alcohol
CH2 = CHOH
IUPAC name: Ethenol
2. Sorbitol
HO – CH2 – (CHOH)4 – CH2OH
IUPAC name : Hexan – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 – hexol
Question 2.
Write the structural formula of the following compounds.
- Prop – 2 – en – 1 – ol
- Prop – 3 – en – 1 – ol
Answer:
1. Prop – 2 – en – 1 – ol : CH2 = CH – CH2OH
2. Prop – 3 – en – 1 – oI :
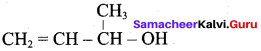
Question 3.
Write the structural formula of the following compound.
- Phenyl methanol
- 2 – methyl – but – 3 – en – 2 – ol
Answer:
1. Phenyl methanol : C6H5 – CH2OH
2. 2 – methyl – but – 3 – en – 2 – ol :
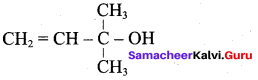
Question 4.
Write the possible isomers for the formula
- C2H6O
- C3H8O
Answer:
1. C2H6O
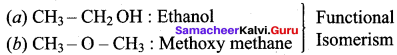
2. C3H8O
(a) CH3 CH2 – CH2 OH : Propan – 1 – ol
(b) 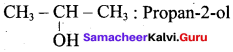
Propan – 1 – ol
(a) and (b) – Position isomerism
(a) and (c) – Functional isomerism
Question 5.
Explain about the structure of methanol.
Answer:
1. In methanol, one of the sp3 hybridised orbital of oxygen linearly overlap with the sp3 hybridised orbital of carbon to form a C – O, a bond and another sp3 hybridised orbitai linearly overlap with 1s orbital of hydrogen atom to form a O – H a bond.
2. 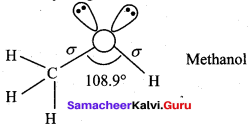
3. The remaining two sp3 hybridised orbitais of oxygen are occupied by two lone pairs of electrons. Due to the lone pair – lone pair repulsion, the C – O – H bond angle in methanol is reduced to 108.9° from the regular tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°.
Question 6.
Convert phenyl magnesium bromide to phenyl methanol (or) How would you prepare phenyl methanol from Grignard reagent?
Answer:
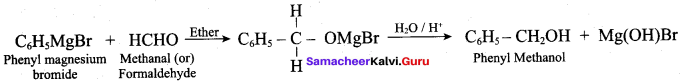
Question 7.
How will you prepare Butan-2-ol from ethanal? (or) Convert Ethyl Magnesium bromide into 2 – Butanol (or) Starting from acetaldehyde, how would you obtain butan – 2 – ol?
Answer:
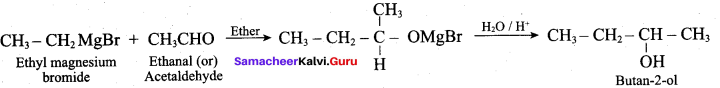
Question 8.
Convert propanone into 2 – methyl – propan – 2 – ol.
Answer:
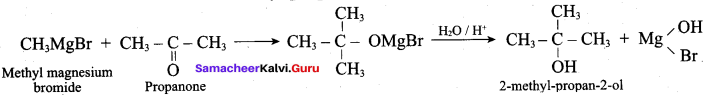
Question 9.
Starting from butyl magnesium bromide, how would you obtain 2 – methyl bexan – 2 – ol?
Answer:
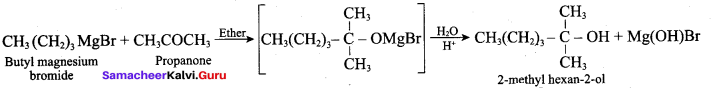
Question 10.
What happens when methyl magnesium bromide reacts with ethl methanoate followed by acid hydrolysis?
Answer:
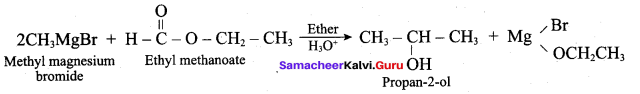
Question 11.
LiAlH4 is a best reagent to prepare unsaturated alcohol. Prove it.
Answer:
LiAIH4(Lithium Aluminium Hydride) does not reduce the carbon – carbon double bond present in the carbonyl compound and hence it is the best reagent to prepare unsaturated alcohol.
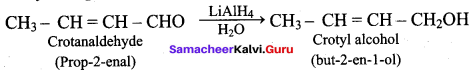
Question 12.
Convert acetone into propan – 2 – ol.
Answer:
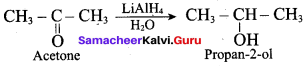
Question 13.
How would you get Benzyl alcohol from Benzoic acid.
Answer:
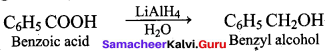
Question 14.
Starting from ethyl ethanoate, how would you prepare ethanol?
Answer:
Question 15.
How will you prepare 4 – alkyl – 4 – hydroxy butanoic acid?
Answer:
When two or more functional groups are present in a molecule a less vigorous sodium borohydride is used as a reducing agent to reduce the more reactive group. For example, if a compound contains both carbonyl and carboxyl group, NaBH4 reduces the carbonyl group.
Question 16.
What is saponification? Explain with equation.
Answer:
The alkaline hydrolysis of fats gives glycerol and soap then the reaction is known as saponification.
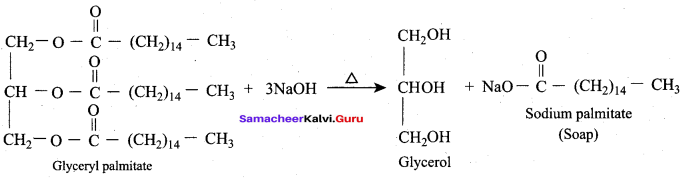
Question 17.
What happens when thionyl chloride is treated with methanol?
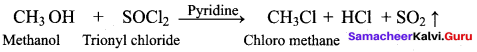
The above reaction follows SN2 mechanism in the presence of pyridine.
Question 18.
Answer:
1. In Swern oxidation method, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is used as the oxidising agent and it converts alcohols to ketones / aldehydes.
2. When propan – 2 – ol is treated with DMSO and oxalyl chloride followed by the addition of triethylamine, it produces Propanone.
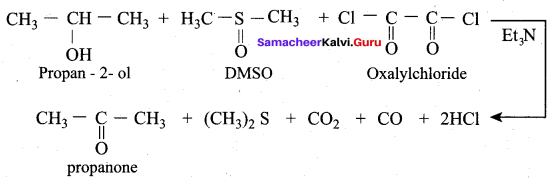
Question 19.
Explain biological oxidation with an example.
Answer:
Biological oxidation is the fermentation of the food consumed by an animal produces alcohol. To detoxify the alcohol, the liver produces an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) present in the animals acts as a oxidising agent and ADH catalyses the oxidation of toxic alcohols into non-toxic aldehyde.

Question 20.
What is esterificatloin? Explain with equation.
Answer:
Alcohols react with carboxylic acids in the presence of an acid to give esters. This reaction is known as Esterification.
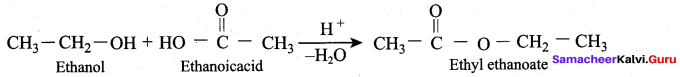
Question 21.
How would you convert ethylene glycol into ethene?
Answer:
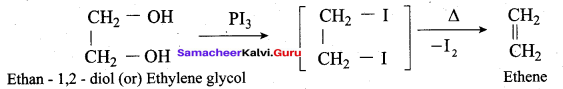
Question 22.
Explain the action of conc.HNO3 and conc.H2SO4 with ethan – 1, 2 – diol.
Answer:
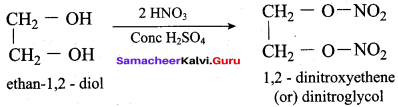
Question 23.
What happens when ethylene glycol is treated with periodic acid?
Answer:
Ethylene glycol on treatment with periodic acid gives formaldehyde. This reaction is selective for vicinal 1, 2 – diols and it proceeds through a cyclic periodate ester intermediate.
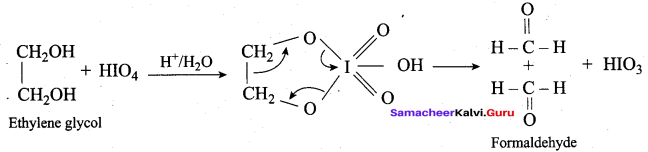
Question 24.
How is glycerol reacts with fuming nitric acid? (or) How would you convert glycerol into nitroglycerine?
Answer:
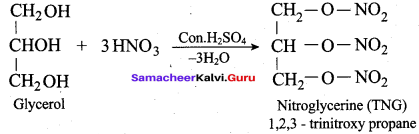
Question 25.
What happens when conc.H2SO4 or KHSO4 is heated with glycerol?
Answer:
Dehydration:
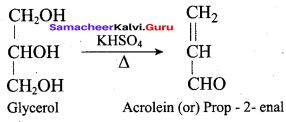
Question 26.
Mention the uses of methanol.
Answer:
- Methanol is used as a solvent for paints, varnishes, shellac, gums, cement, etc.
- Methanol is used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs, perfumes and formaldehyde.
Question 27.
What are the uses of ethylene glycol?
Answer:
- Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze in automobile radiator
- Its dinitrate is used as an explosive with DNG.

Question 28.
Write a note about acidity of aliphatic alcohols.
Answer:
1. According to Bronsted theory, an acid is defined as a proton donor and the acid strength is the tendency to give up a proton. Alcohols are similarly acidic when compared with water. Except methanol, all other alcohols are weaker acid than water. The Ka value for water is 1.8 x 10-16 where as for alcohols the Ka value in the order 10-18 to 10-16.
2. 2C2H5 – OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2 ↑
This reaction explains the acidic nature of alcohol as it liberates H2 gas with Na metal.
Question 29.
Alcohol can act as Bronsted base. Prove this statement.
Answer:
Alcohols can also act as a Bronsted bases. It is due to the presence of unshared electron pairs on oxygen which make them to accept proton. So proton acceptor are Bronsted bases. i.e., alcohols are Bronsted bases.
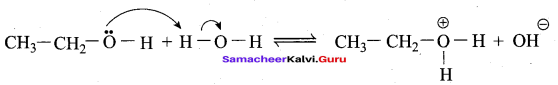
Question 30.
What are cresols? Give examples.
Answer:
Methyl Phenols are called cresols.
They are
Question 31.
How is phenol obtained from benzene suiphonic acid?
Answer:
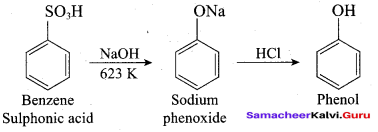
Question 32.
How is Aniline converted into Phenol?
Answer:
Aniline is diazotized with nitrous acid (NaNO2 + HCI ) at 273 – 278K to give benzene diazonium chloride which on further treatment with hot water in the presence of mineral acid gives phenol.
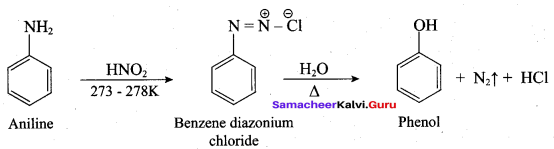
Question 33.
How will you convert phenol into benzene?
Answer:
Phenol is converted to benzene on heating with Zinc dust.
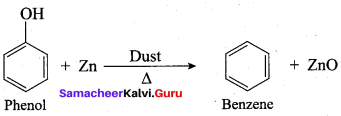
Question 34.
What happens when phenol is heated with NH3?
Answer:
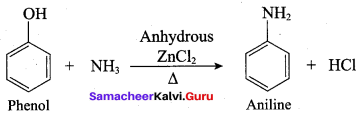
Question 35.
What happens when phenol is heated with acidified K2Cr2O7?
Answer:
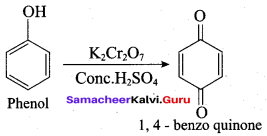
Question 36.
How is phenol treated with Nickel?
Answer:
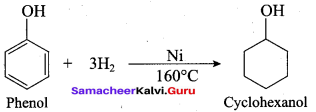
Question 37.
O – nitro phenol is slightly soluble ¡n water where as P-nitro phenol is more soluble. Cive reason.
Answer:
O-nitro phenol is slightly soluble in water and more volatile due to intra molecular hydrogen bonding, whereas P-nitro phenol is more soluble in water and less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 38.
Explain Reimer Tiemann reaction.
Answer:
On treating phenol with CHCl3 / NaOH, a – CHO group is introduced at ortho position. This reaction proceeds through the formation of substituted benzal chloride intermediate.
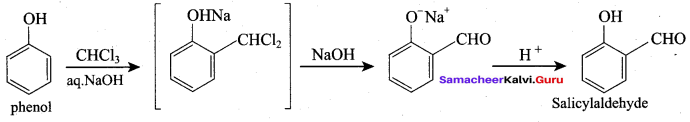
Question 39.
How is phenolphthalein prepared from phenol?
Answer:
On heating phenol with phthalic anhydride in presence of con.H2SO4, phenolphthalein is obtained,
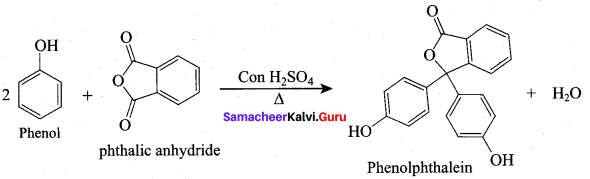
Question 40.
What is Coupling reaction? Give equation.
Answer:
Phenol couples with benzene diazonium chloride in an alkaline solution to form p-hydroxy azobenzene(a red orange dye).
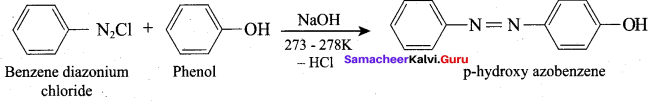
Question 41.
Write a note about the structure of ethereal oxygen.
Answer:
The structure of ethereal oxygen which is attached to two alkyl groups is similar to the structure of – OH group of alcohol. The oxygen atom is sp3 hybridized. Two sp3 hybridized orbitals of oxygen linearly overlap with two sp3 hybrid orbitais of the carbon which are directly attached to the oxygen forming two
C – O ‘σ’ bonds.
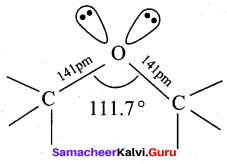
The C – O – C bond angle is slightly greater than the tetrahedral bond angle due to the repulsive interaction between the two bulkier alkyl groups.
Question 42.
Write the structure and common name of
- Ethoxy benzene
- Phenoxy benzene
Answer:
1. C6H5 – O – CH2 – CH3 : Ethoxy benzene (or) Phenetole (or) Ethyl phenyl ether
2. C6H5 – O – C6H5 : Phenoxy benzene (or) Diphenyl ether (or) Phenyl ether
Question 43.
What happens when ethanol reacts with conc. H2SO4 Sulphuric acid at 413 K?
Answer:
When ethanol reacts with con.H2SO4 at 413 K, inter molecular dehydration take place and diethyl ether is formed as product.

Question 44.
Explain the action of diazomethane with ethanol.
Answer:
Methyl ethers can be prepared when ethanol is treated with diazomethane in presence of fluoro boric acid.

Question 45.
Ether are miscible with water. Justify this statement.
Answer:
1. Oxygen of ether can also form Hydrogen bond with water and hence they are miscible with water.
2. Ethers dissolve wide range of polar and non-polar substances.
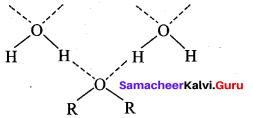
Question 46.
Ether bottle should not be kept open. Why?
Answer:
1. When ether bottle is kept open, they are exposed to atmospheric oxygen and slowly oxidised to form hydroperoxides and dialkyl peroxides. These are explosive in nature. Such a spontaneous oxidation by atmospheric oxygen is called autooxidation.
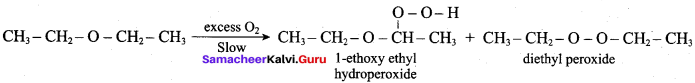
Question 47.
Explain the action of hydrogen iodide with anisole (or) methoxy benzene. –
Answer:
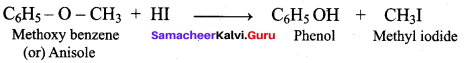
Question 48.
What are the uses of anisole?
Answer:
- Anisole is a precursor to the synthesis of perfumes and insecticide pheromones,
- It is used as a pharmaceutical agent.
Question 49.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Alcohols can form H-bond with water molecules and break the H-bond already existing between the water molecules. Therefore, they are soluble in water.
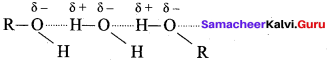
On the other hand hydrocarbons do not have the ability to form H-bond with water molecules. Hence they are insoluble in water.
Question 50.
Explain why is ortho nitrophenol more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol?
Answer:
Ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol because nitro group is an electron withdrawing and it will increase +ve charge on the oxygen atom to make it more acidic whereas – OCH3 group is an electron releasing group and it will decrease +ve charge on the oxygen atom, thus making it less acidic and hence the O – H bond will not break easily.
Question 51.
Give reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
Answer:
Ethanol undergoes intermolecular H-bonding due to the presence of a hydrogen atom attached to the electronegative oxygen atom. As a result, ethanol exists as associated molecules.
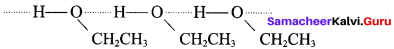
Consequently, a large amount of energy is required to break these hydrogen bonds. Therefore, the boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxymethane which does not form H-bonds.
Question 52.
What happens when phenol is treated with ¡ce cold bromine dissolved in CS2?
Answer:
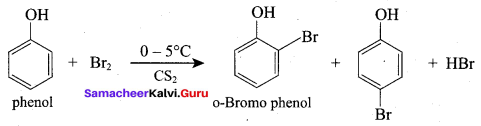
Question 53.
What happens when phenol is treated with excess of nitrating mixture? (Give equation only).
Answer:
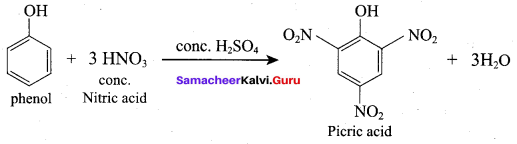
Question 54.
Describe the mechanism by which the hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic ring is more acidic than the hydroxyl group attached to an alkyl group. How does the presence of nitro group in phenol affects its acidic character?
Answer:
1. The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution indicates that phenol is a stronger acid than alcohols in water.
2. Because phenoxide ion formed is stabilised by resonance whereas alkoxide ion formed is destabilised by positive inductive effect of alkyl group.
3. Presence of electron withdrawing group such as nitro group enhances the acidic strength of phenol. lt is due to the effective delocalisation of the negative charge in phenoxide ion.
Question 55.
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare the acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
Answer:
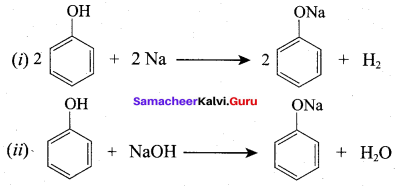
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers 3 Mark Questions and Answers
VI. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Give one example for each of the following with their structure and IUPAC name.
- 1° alcohol
- 2° alcohol
- 3° alcohol
Answer:
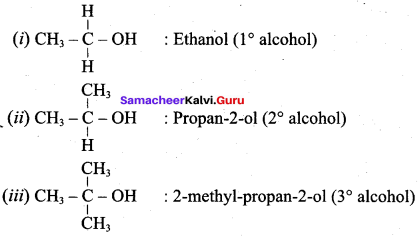
Question 2.
Write the structure of the following compounds.
- Phenyl methanol
- 1 – Phenyl ethanol
- 2 – Phenyl propan – 2 – ol
Answer:
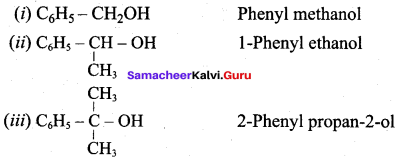
Question 3.
Write the structures and IUPAC names of the following compounds.
- Tertiary butyl alcohol
- Neopentyl alcohol
- Isobutyl alcohol
Answer:
1. 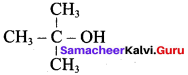
2 – methyl propan – 2 – ol (Tertiary butyl alcohol)
2. 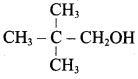
2, 2 – dimethyl propan – 1 – ol (Neopentyl alcohol)
3. 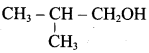
2 – methyl propan – 1- ol (Isobutyl alcohol)
Question 4.
Draw the structures and write the IUPAC name of the following compounds.
- Benzyl alcohol
- Allyl alcohol
- Cyclohexyl alcohol
Answer:
1. 
Phenyl methanol (Benzyl alcohol)
2. CH2 = CH – CH2OH Prop – 2 – en – 1 – ol (Allyl alcohol)
3. 
Cyclo hexanol (Cyclohexyl alcohol)
Question 5.
Describe Lucas test used to distinguish Primary, Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.
Answer:
When alcohols are treated with Lucas agent (conc. HCI + anhydrous ZnCl2) at room temperature, tertiary alcohols react immediately to form a turbidity due to the formation of alkyl chloride which is insoluble in the medium. Secondary alcohols react within 10 minutes to form a turbidity of alkyl chloride where primary alcohols do not react at room temperature.
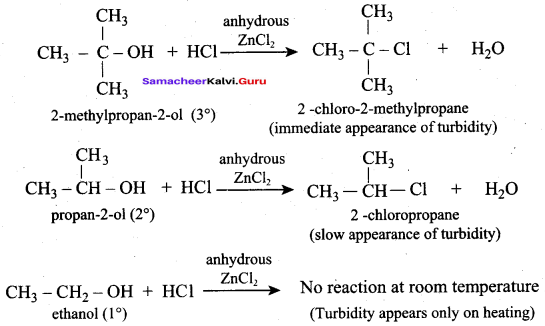
Question 6.
Explain the mechanism of the reaction of alkyl halide formation from primary alcohol.
Answer:
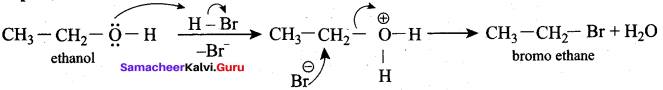
Question 7.
Explain SN1 mechanism of Tertiary alcohols reaction with HBr.
Answer:
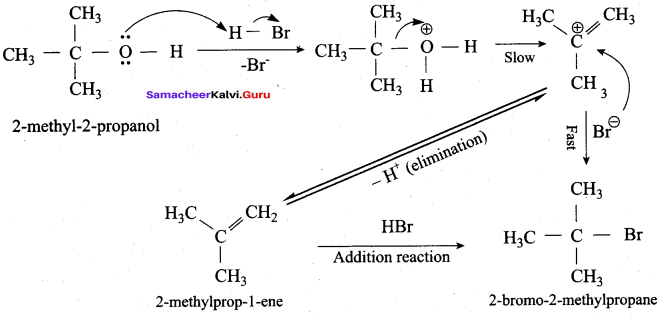
Question 8.
Explain the mechanism involved in the reaction of phosphorous trichloride with Ethanol. SN2 reaction of Ethanol with PCl3
Answer:
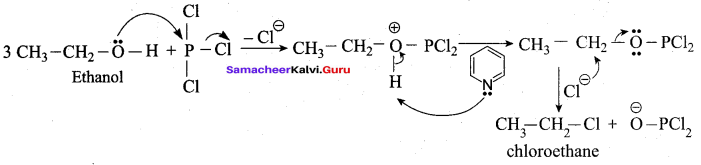
Question 9.
Describe Saytzeff’s rule with example.
Answer:
1. During intramolecular dehydration, if there is a possibility to form a carbon – carbon double bond at different locations, the preferred location is the one that gives the more (highly) substituted alkene i.e., the stable alkene.
2. For example, the dehydration of 3, 3 – dimethyl – 2 – butanol gives a mixture of alkenes. The secondary carbocation formed in this reaction undergoes rearrangement to form a more stable tertiary carbocation.
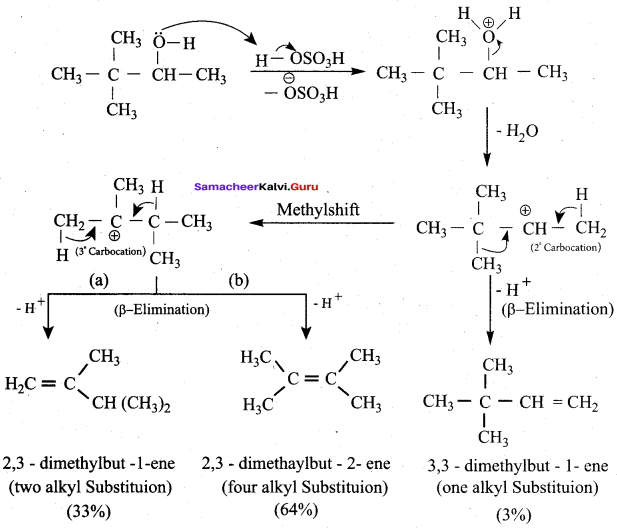
Question 10.
Explain the following reactions.
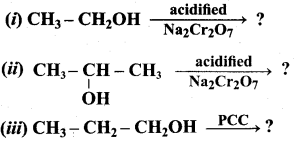
Answer:
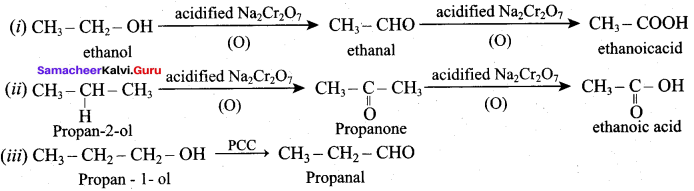
Question 11.
Explain about catalytic dehydrogenation of 10, 20 and 30 alcohols
Answer:
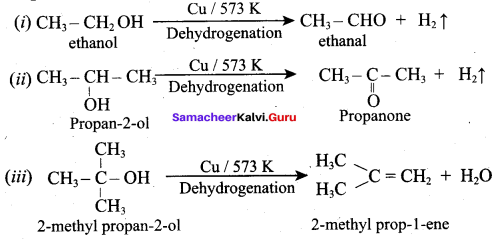
Question 12.
Describe about the oxidation reaction of ethylene glycol with dilute nitric acid.
Answer:
When dilute nitric acid (or) alkaline KMnO4 is used as the oxidizing agent, the following products are formed.
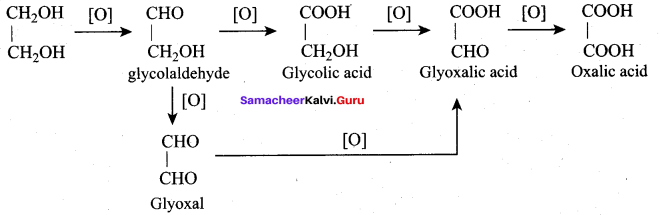
Question 13.
Explain about the oxidation reaction of Glycerol with different oxidising reagents.
Answer:
- Oxidation of glycerol with dii. FINO3 gives glyceric acid and tartronic acid.
- Oxidation of glycerol with Conc. HNO3 gives mainly glyceric acid.
- Oxidation of glycerol with bismuth nitrate gives as meso oxalic acid.
- Oxidation of glycerol with Br2 /H2O (or) NaOBr (or) Fenton reagent (FeSO4 + H2O2)
- gives a mixture of glyceraldehyde and dihydroxy acetone(glycerose).
- On oxidation with HIO4 or Lead tetra acetate (LTA) it gives formaldehyde and formic acid.
- Acidified KMnO4 oxidises glycerol into oxalicacid.
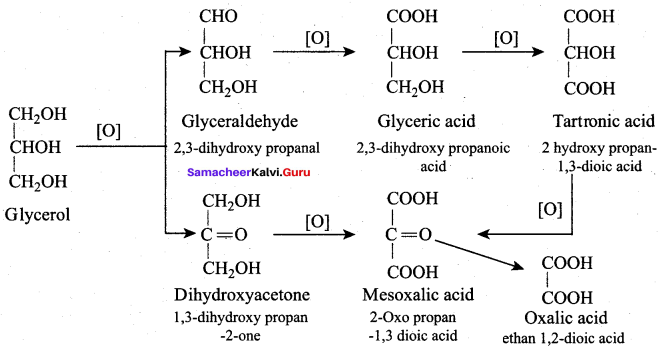
Question 14.
What are the uses of ethanol.
Answer:
- Ethanol is used as an important beverage.
- It is also used in the preparation of
- Paints and varnishes
- Organic compounds like ether, chloroform, iodoform, etc.,
- Dyes, transparent soaps.
- As a substitute for petrol under the name power alcohol used as fuel for aeroplane.
- It is used as a preservative for biological specimens.
Question 15.
Mention the uses of Glycerol.
Answer:
- Glycerol is used as a sweetening agent in confectionery and beverages.
- It is used in the manufacture of cosmetics and transparent soaps.
- It is used in making printing inks and stamp pad ink and lubricant for watches and clocks.
- It is used in the manufacture of explosive like dynamite and cordite by mixing it with china clay.

Question 16.
Compare the acidity of 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols.
Answer:
1. The acidic nature of the alcohol is due to the polar nature of O – H bond. When an electron withdrawing -I groups such as – Cl, – F etc… is attached to the carbon bearing the OH group, it withdraws the electron density towards itself and thereby facilitating the proton donation.
2. In contrast, the electron releasing group such as alkyl group increases the electron density on oxygen and decreases the polar nature of 0 – H bond, I lence it results in the decrease in acidity.
3. On moving from primary to secondary and tertiary alcohols, the number of alkyl groups which attached to the carbon bearing -OH group increases, which results in the following order of acidity.
1°alcohol > 2° alcohol > 3° >alcohol
For example
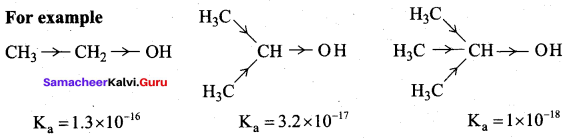
Question 17.
What are dihydric phenols? Give three examples.
Answer:
When benzene ring has 2 – OH groups, it is called Dihydric phenol.
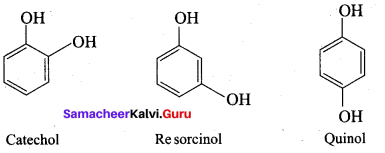
Question 18.
What are Trihydric phenols. Give example.
Answer:
When 3 – OH groups are present in benzene ring, it is called trihydric phenol.
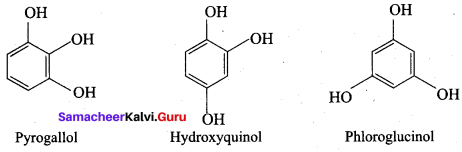
Question 19.
Write the possible isomers for the formula C7H8O with their names C7H8O
Answer:
1. C6H5 – CH2OH : Benzyl alcohol
2. C6H5 – O – CH3 : Anisole
3. 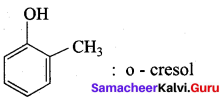
4. 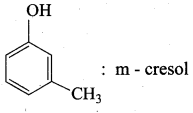
5. 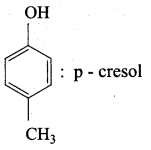
Question 20.
Explain about the bromination of phenol.
Answer:
1. Phenol reacts with bromine water to give a white precipitate of 2, 4, 6 – tri bromo phenol.
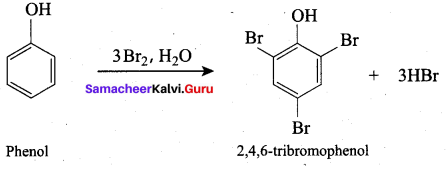
2. When phenol reacts with Br2 in the presence of CS2 or CCl4 at 278K. a mixture of ortho and para bromo phenols are formed.
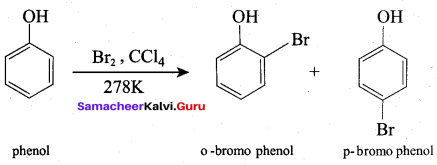
Question 21.
Differentiate phenols from alcohol.
Answer:
Test to differentiate alcohols and phenols:
1. Phenol react with benzene diazonium chloride to form a red orange dye, but ethanol has no reaction with it.
2. Phenol gives purple colouration with neutral feme chloride solution, alcohols do not give such coloration with FeCI3.
3. Phenol reacts with NaOH to give sodium phenoxide. Ethyl alcohol does not react with NaOH
Question 22.
What are the uses of phenol?
Answer:
- About half of world production of phenol is used for making phenol formaldehyde resin. (Bakel ite).
- Phenol is a starting material for the preparation of
- drugs such as phenacetin, Salol, aspirin, etc.
- phenolphthalein indicator.
- explosive like picric acid.
- It is used as an antiseptic – carbolic lotion and carbolic soaps.
Question 23.
Write the structure formula and IUPAC name of the following.
- n – heptyl phenyl ether
- Isopentyl phenyl ether
- Dimethyl glycolate
Answer:
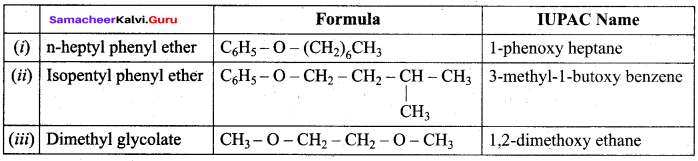
Question 24.
ExplaIn about the mechanism of intermolecular dehydration of ethanol with conc.H2SO4 at 413 K.
Answer:
When ethanol reacts with conc.H2SO4 at 413 K, inter molecular dehydration takes place and the product formed is Ethoxy ethane.
Mechanism:
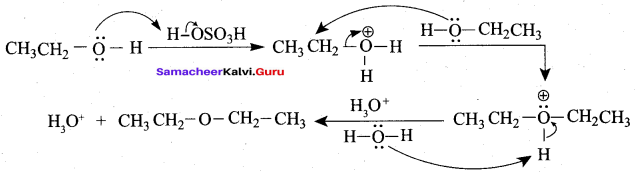
Question 25.
Explain about the mechanism involved in Williamson’s synthesis.
Answer:
When an alkyl halide is heated with an alcoholic solution of sodium alkoxide, the corresponding ether is formed. This reaction involves SN2 mechanism.
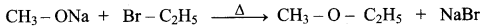
Mechanism:
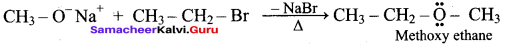
Question 26.
Explain the mechanism involved in the reaction between Tertiary alkyl halide and primary alkoxide with eample.
Answer:
When tertiary alkyl halide reacts with primary alkoxide, elimination dominates and succeeds over substitution to form an alkene.
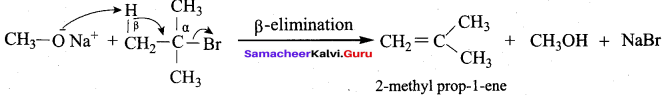
Question 27.
Explain about the reaction mechanism of methoxy ethane with HI.
Answer:
Ethers can undergo nucleophilic substitútion reactions with HI.

Ethers having primary alkyl group undergo SN2 reaction whereas tertiary alkyl ether undergo SN1 reaction. Protonation of ether is followed by the attack of halide ion. The halide ion preferentially attacks the less sterically hindered of the two alkyl groups which are attached etherial oxygen.
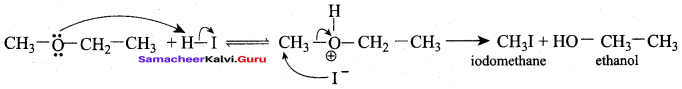
Question 28.
What are the uses of diethyl ether.
Answer:
- Diethyl ether is used as a surgical anesthetic agent in surgery.
- It is a good solvent for organic reactions and extraction.
- It is used as a volatile starting fluid for diesel and gasoline engine.
- It is used as a refrigerant.
Question 29.
Classify the following as primary secondary and tertiary alcohols.
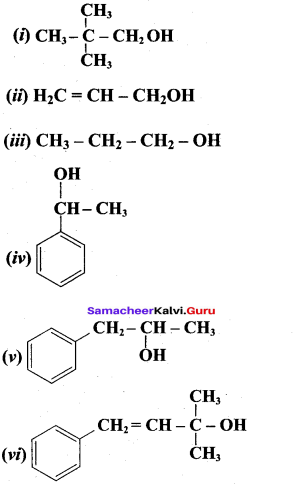
Answer:
Primary alcohols:
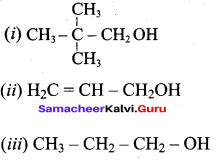
Secondary alcohols:
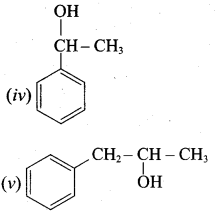
Tertiary alcohols:
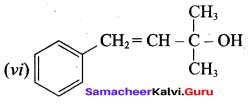
Question 30.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
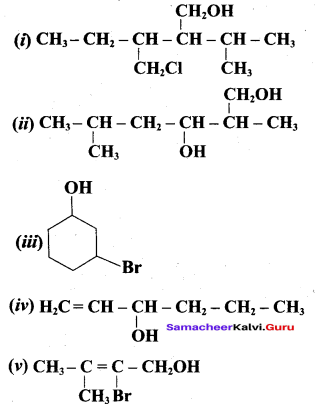
Answer:
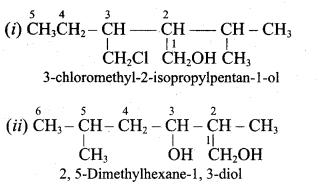
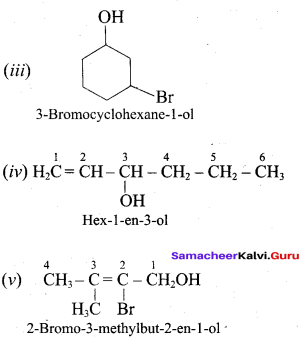
Question 31.
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal?

Answer:
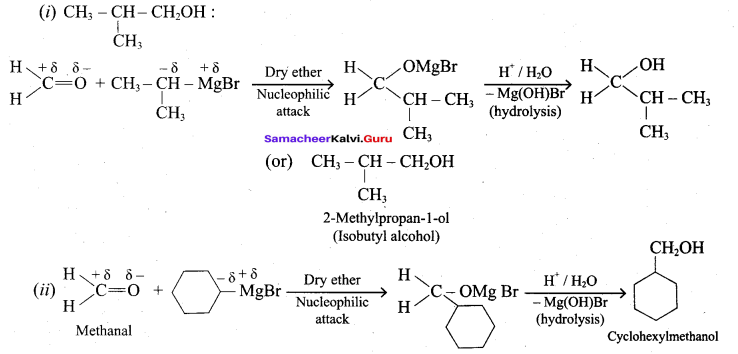
Question 32.
You are given benzene, conc H2SO4 and NaOH. Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using these reagents.
Answer:
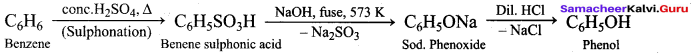
Question 33.
How will you convert ethanol to acetone ?
Answer:
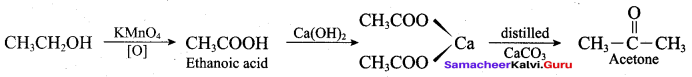
Question 34.
How are the following conversions carried out?
- Phenol to Toluene
- Ethanol to 1, 1 – dichloroethane.
Answer:
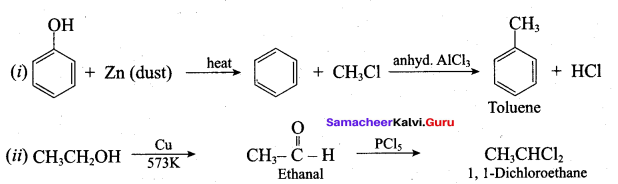
Question 35.
How are the following conversions carried out ? (Write the reactions and conditions in each case):
- Ethanol to 2 – propanol
- Phenol to Acetophenone
Answer:
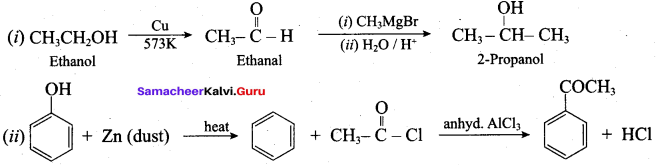
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers 5 Mark Questions and Answers
II. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Explain Victor Meyer’s test used to distinguish 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols.
Answer:
Victor Meyer’s test :
This test is based on the behaviour of nitro alkanes formed by the three types of alcohols with nitrous acid and it consists of the following steps.
- Alcohols are converted into alkyl iodide by treating with I2/P.
- Alkyl iodides so formed is then treated with AgNO2 to form nitro alkane.
- Nitro alkanes are finally treated with HNO2 (mixture of NaNO2/HCl) and the resultant solution is made alkaline with KOH.
Result:
- Primary alcohol gives red colour
- Secondary alcohol gives blue colour.
- No colouration will be observed in tertiary alcohol.
1° alcohol:

2°alcohol:
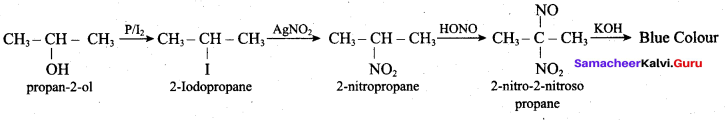
3°alcohol:
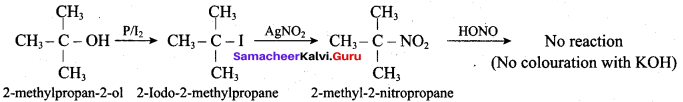
Question 2.
Write the possible isomers for the formula C4H10O, write their IUPAC names and structures.
Answer:
C4H10O – 7 Isomers
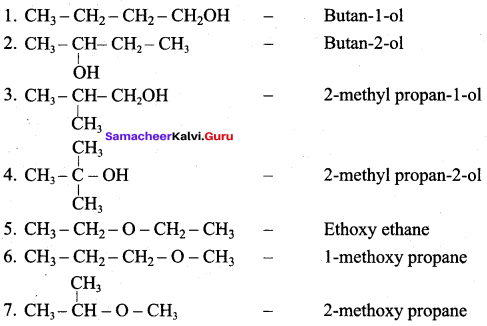
Question 3.
Explain about mechanism involved in the dehydration of tertiary alcohols.
Answer:
Tertiary alcohols undergo dehydration by E1 mechanism. It involves the formation of a carbocation.
Step 1:
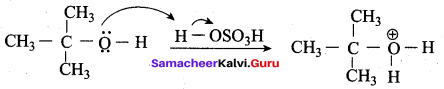
Step 2:
Dissociation of oxonium ion to form a carbocation
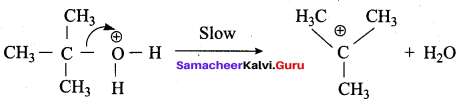
Step 3:
Deprotonation of carbocation to form an alkene
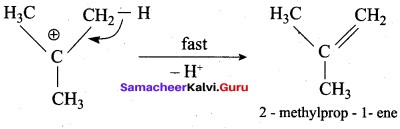
Question 4.
Explain about the various dehydration reactions of ethylene glycol.
Answer:
Ethylene glycol undergoes dehydration reaction under different conditions to form different products.
1. When ethylene glycol is heated to 773K, it forms epoxides.
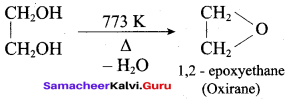
2. When heated with dilute sulphuric acid (or) anhydrous ZnCl2 under pressure in a sealed tube, it gives acetaldehyde.
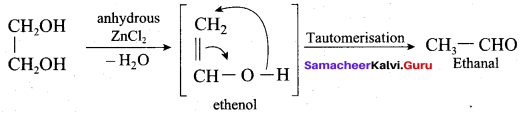
3. When distilled with Conc. H2SO4, glycol forms 1, 4 – dioxane
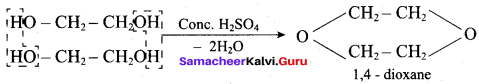
Question 5.
Explain the following reactions.
- Schotten-Baumann reaction
- Kolbe’s reaction
- Reimer – Tiemann reaction
Answer:
1. Schotten – Baumann reaction:
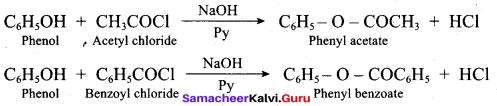
2. Kolbe’s reaction:
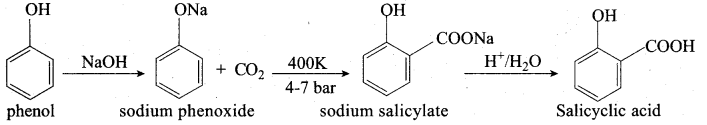
3. Reimer – Tiemann reaction.
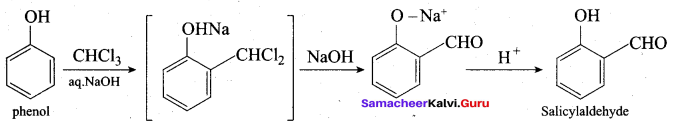
Question 6.
Describe the following electrophilic substitution reaction using phenol.
- Nitrosation
- Nitration
- Sulphonation
Answer:
1. Nitrosation:
Phenol can be readily nitrosoated at low temperature with nitrous acid.
2. Nitration:
Phenol can be nitrated using 20% nitric acid at room temperature, a mixture of ortho and para nitro phenols are formed.
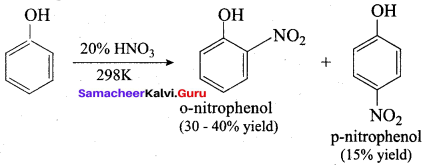
3. Phenol when treated with Conc.HNO3 and Conc.H2SO4, picric acid is formed.
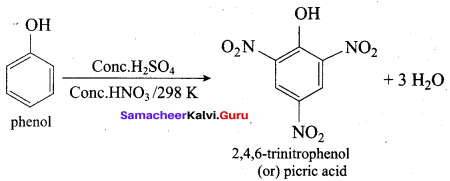
4. Sulphonation:
Phenol when reacts with Conc.H2SO4 at 280K, o – phenol suiphonic acid is formed as major product. But when the reaction is carried out at 313K, the major product is p – phenol suiphonic acid.
Question 7.
What happens when diethyl ether reacts with following reagents.
- excess O2
- Cl2 / light
- PCI5
- dil.H2SO4 / H2O
- CH2COCI /Anhydrous ZnCI2.
Answer:
Auto – oxidation:
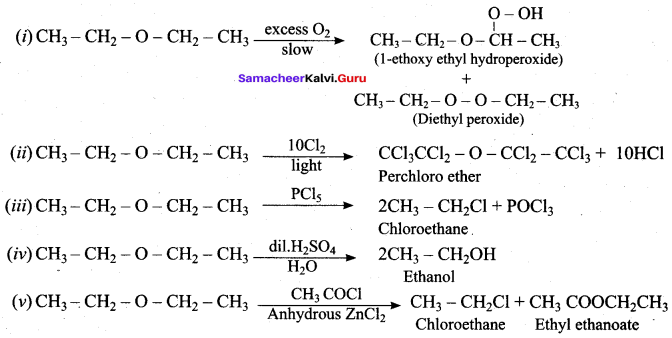
Question 8.
Explain the aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions of anisole with equations. Aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions:
Answer:
1. Halogenation:
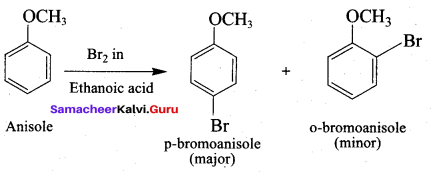
2. Nitration.
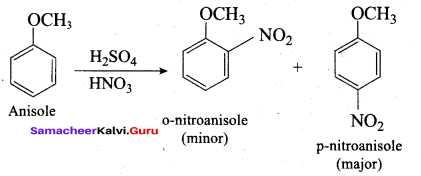
3. Friedel Craft’s alkylation.
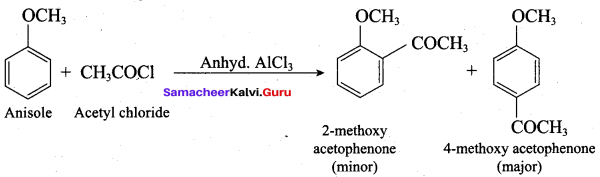
4. Friedel Craft’s acylation.
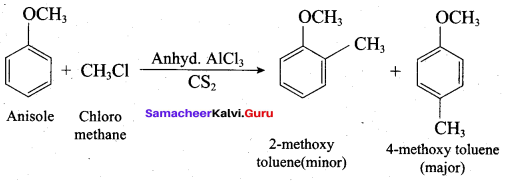
Question 9.
Starting from phenol, how would you prepare the following compounds.
- Benzene
- Aniline
- Anisole
- 1, 4, benzoqulnone
- Cyclohexanol
Answer:
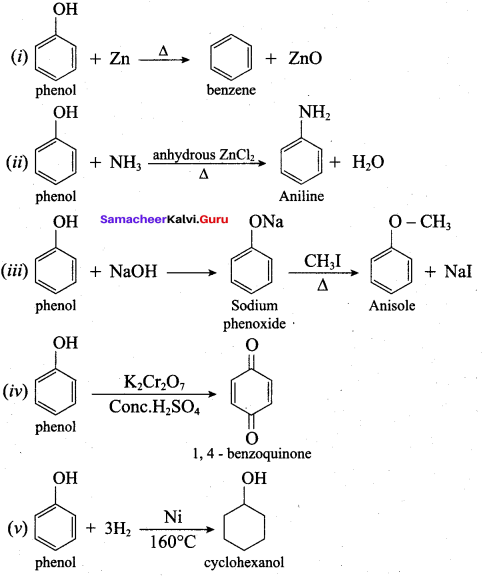
Question 10.
A compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H10O is unreactive towards sodium metal. it does not add Bromine water and does not react with NaHSO3 solution. On refluxing ‘A’ with excess of HI, it gives ‘B’ which reacts with aqueous NaOH to form ‘C’. ‘C’ can be converted into ‘B’ by reacting with red P and I3. ‘C, on treating with conc. H2SO4 forms ‘D’. ‘D’ decolounses bromine water. Identify A to D and write the reactions involved.
Answer:
‘A’ is not an alcohol therefore it does not react with sodium metal. ‘A’ is also not an aldehyde or a ketone as it does not react with NaHSO3. ‘A’ is not an unsaturated hydrocarbon as it does not add Br2 (aq). So, it is likely to be a ether.
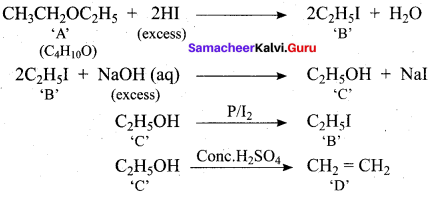
Question 11.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O on reaction with conc.H2SO4 at 443 K gives an unsaturated hydrocarbon (B). (B) on reaction with Baeyer’s reagent produces (C) of molecular formula C2H6O2. (C) on reaction with anhydrous ZnCI2 produces (D) of molecular formula C2H4O. (D) reduces Tollen’s reagent. Identify A, B, C and D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) reacts with Conc.H2SO4 at 443 K produces ethene by intermolecular dehydration. So, (A) is ethanol – CH3CH2OH.
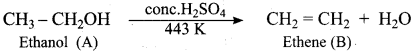
2. Ethene on reaction with Baeyer’s reagent (cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4) produces ethylene glycol as product (C).
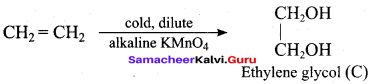
3. Ethylene glycol on reaction with anhydrous ZnCI2 dehydration and tautomerisation take place to give actaldehyde as product (D).
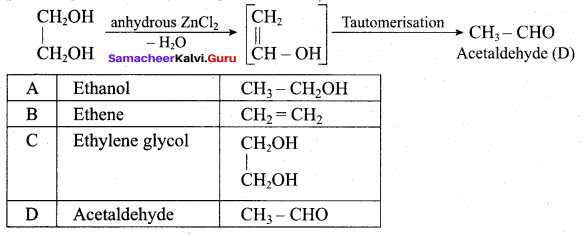
Question 12.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O liberates H2 gas with metallic sodium and gives (B). (B) on reaction with methyl bromide produces (C) of molecular formula C3H8O. (C) on reaction with excess III produces (D) and (E). Identify A, B, C, D and E and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) reacts with Na metal and liberates H2 gas means it must be an alcohol. From the molecular formula it is identified as ethanol – CH3 – CH2OH (A).
2. Ethanol on reaction with Na metal to produce sodium ethoxide as (B) with liberation of H2 gas.

3. Sodium ethoxide on reaction methyl bromide undergo Williamson’s synthesis to produce methoxy ethane as (C).

4. Methoxy ethane on reaction with excess HI will give Ethyl iodide and Methyl iodide as (D) and (E).
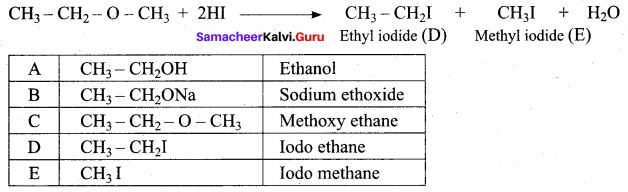
Question 13.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula CH4O on mild oxidation gives (B) of formula CH2O that reduces tollen’s reagent. (B) on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide followed by acid hydrolysis will give (C) of molecular formula C2H6O which liberates H2 gas with metallic sodium. Identify A, B, C and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. (A) is identified from the molecular formula as methanol (CH3OH).
2. CH3OH – methanol on mild oxidation will give formaldehyde as (B). Aldehydes reduce Tollen’s reagent to silver mirror. So, (B) is HCHO (methanal)
3. Formaldehyde reacts with CH3MgBr, followed by acid hydrolysis produces primary alcohol and (C) is identified from the formula as CH3 – CH2OH – Ethanol. Ethanol liberates H2 gas with metallic sodium.
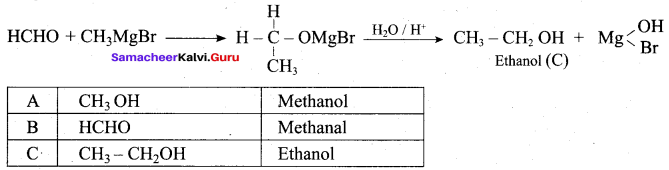
Question 14.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O reacts with metallic Na and liberates H2 gas. (A) on mild oxidation with Cu at 573 K gives (B) of molecular formula C2H4O. (B) on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide followed by acid hydrolysis gives (C) of molecular formula C3H5O. (C) gives Blue colour in Victor Meyer’s test. (C) on mild oxidation with Cu at 573 K gives (D) of formula C3H6O. identify A, B, C, D and
explain the reactions.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) reacts with Na metal and liberates H2 gas means it must be alcohol. From the molecular formula it is identified as Ethanol (CH3 – CH2OH).
2. Ethanol on oxidation with Cu at 573 K undergoes catalytic dehydrogenation and produces Acetaldehyde as product (B).

3. Acetaldehyde on reaction with CH3MgBr followed by hydrolysis will give Isopropyl alcohol as (C).
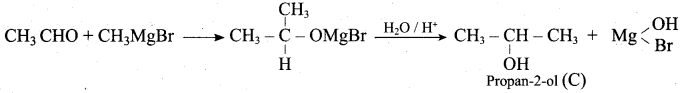
4. Propan – 2 – ol is secondary alcohol and so it gives blue colour in Victor Meyer’s test. (C) on reaction with Cu at 573 K will give Propanone as (D).
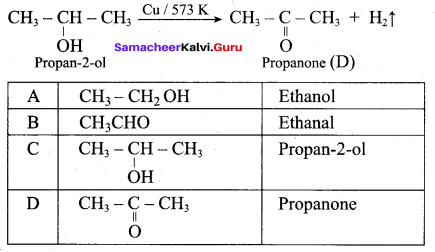
Question 15.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C3H8O gives blue colour in Victor Meyer’s test. (A) on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives (B) which further reacts with Methyl magnesium bromide followed by acid hydrolysis yields (C) of molecular formula C4H10O. (C) on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives (D) of formula C4H8. Identify A, B, C, D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound gives blue colour in Victor Meyer’s test means it must be a secondary alcohol. From the formula, it is identified as
 Propan – 2- ol (A)
Propan – 2- ol (A)
2. Propan – 2 – ol on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives Propanone as (B).
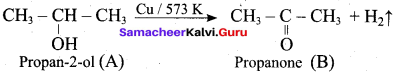
3. Propanone on treatment with CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis will yield Tertiary butyl alcohol (CH3)3C – OH as (C).
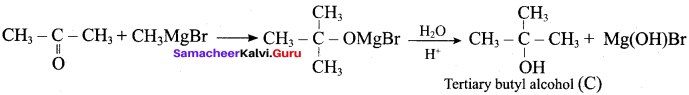
4. Tertiary butyl alcohol on reaction with copper at 573 K undergoes dehydration reaction to
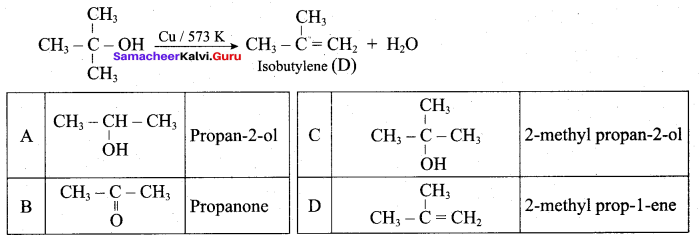
Question 16.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C3H6 on reaction with Conc. H2SO4 and H2O gives ClH5O as (B) as a MarkownikoWs product. (B) on oxidation with Cu at 573 K gives (C) of formula C3H6O. (C) on reaction with CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis yields (D) as C4H10O which will not give any colour in Victor Meyer’s test. Identify A, B, C, D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) is identified from the molecular formula as CH3 – CH = CH2 propene.
2. Propene on hydrolysis in acid medium, Markownikoff’s rule is followed and the product formed is
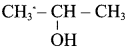 Propan – 2- ol as (B)
Propan – 2- ol as (B)
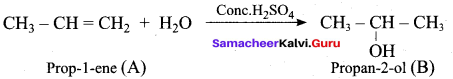
3. Propan – 2 – ol on reaction with Cu at 573 K undergoes dehydrogenation reaction to produce Propanone as (C).
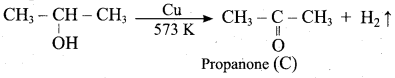
4. Propanone on reaction with CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis gives tertiary butyl alcohol (D). It will not give any colouration in Victor Meyer’s test.
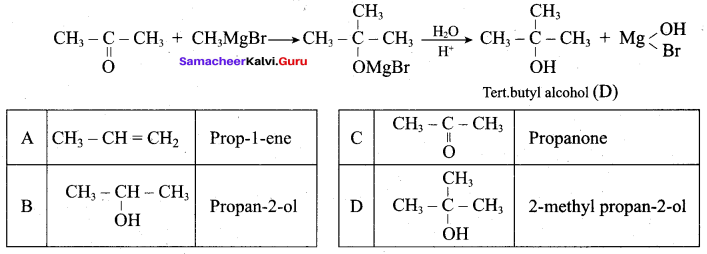
Question 17.
An aromatic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H5Cl on reaction with aqueous NaOH gives (B) of formula C6H60 that give violet colouration with neutral FeCI3. (B) on reaction with ammonia in presence of anhydrous ZnCI2 gives (C) of formula C6H7N. Identify A, B, C and explain the reactions.
Answer:
1. An aromatic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H5Cl is identified as chioro benzene.
2. Chioro benzene on reaction with aqueous NaOH produces phenol as (B).

3. Phenol gives violet colour with neutral FeCI3. Phenol on treated with NH3 in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl2 gives Aniline as (C).
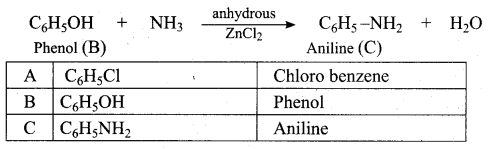
Question 18.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H6O gives white precipitate with bromine water. (A) on reaction with NaOH gives (B). (B) reacts with methyl iodide in presence of dry ether gives (C) of molecular formula C7H8O which will not liberate H2 gas with metallic Na. (C) on reaction with acetvl chloride gives (D) and (E) of formula which are position isomers. Identify A, B, C, D & E and explain the reaction.
Answer:
1. An organic compound gives white precipitate with bromine water means it must be a phenol. From the molecular formula it is identified as C6H5OH.
2. Phenol on reaction with NaOH gives (B) as sodium phenoxide C6H5ONa.
3. Sodium phenoxide on reaction with methyl iodide in the pressure of dry ether undergo Williamsons synthesis and gives Anisole as (C).
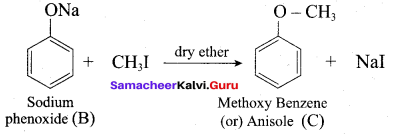
4. Anisole on reaction with acetyl chloride undergoes Fnedel Craft’s acetylation and yield O – methoxy acetophenone and p-methoxy acetophenone as (D) and (E).
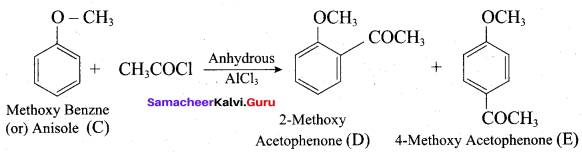
Question 19.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H5CI on reaction with aqueous NaOH gives (B) of formula C6H6O. (B) on reaction with NaOH gives (C) of formula C6H5ONa. (C) on treatment with CO2, followed by acid hydrolysis yield (D) of formula C7H6O3 an aromatic hydroxy acid. Identify A, B, C, D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
- (A) is identified from the formula as C6H5CI – Chloro benzene.
- Chloro benzene on treatment with aqueous NaOH yeilds C6H5OH – phenol as (B).
- Phenol on reaction with NaOH produces sodium phenoxide C6H5ONa as (C).
- Sodium phenoxide on reaction with CO2, followed acid hydrolysis, Kolbe’s reaction takes place to give Salicylic acid as (D).
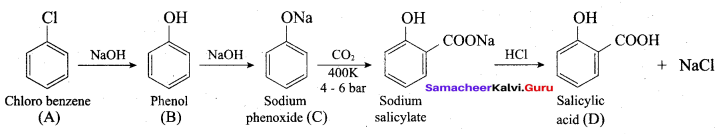
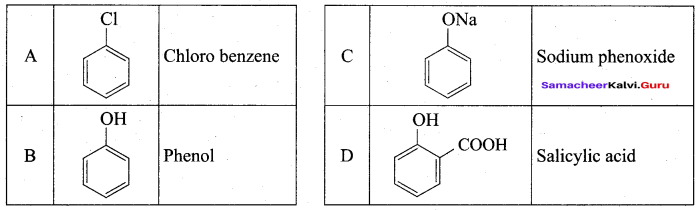
Question 20.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6HN2Cl on boiling with hot water gives (B) of molecular formula C6H6O. (B) on reaction with Zinc dust gives (C) a simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. (C) on reaction with methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AICI2 gives (D) of molecular formula C7H8. Identify A, B, C, D and explain the reaction.
Answer:
1. (A) is identified from the formula as Benzene diazonium chloride – C6H5N2Cl.
2. Benzene diazonium chloride when boiled with hot water produces phenol as (B).
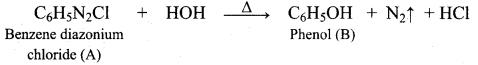
3. Phenol on reaction with Zinc dust gives Benzene as (C) which is simplest aromatic hydrocarbon.
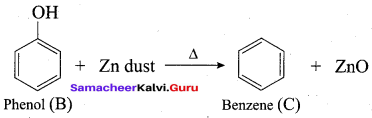
4. Benzene on treatment with (C) methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, Friedel Crafts reaction take place and the product formed is Toluene as (D).
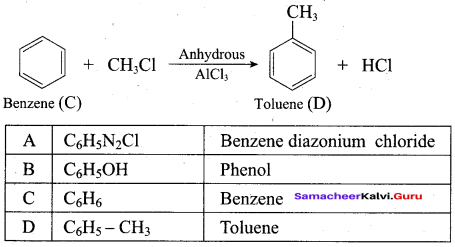
Question 21.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H6O gives violet colour with neutral FeCI3. (A) reacts benzene diazoniurn chloride in basic medium to give (B) as an azo dye. (A) reacts with acidified K2Cr2O7 gives (C) of formula C6H4O2. (A) on reaction with H2 in the presence of nickel gives (D) of formula C6H12O. Identify A, B, C, D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. (A) of molecular formula C6H6O gives violet colour with neutral FeCI3 means it must be Phenol – C6H5OH.
2. Phenol couples with benzene diazonium chloride in the presence of basic medium to produce p-hydroxy azo benzene, a red orange dye as (B).
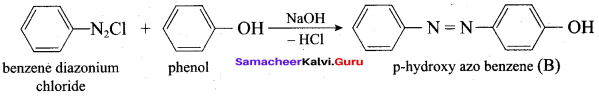
3. Phenol on reaction with acidified K2Cr2O7 undergoes oxidation reaction to give 1, 4 – benzo quinone as (C).
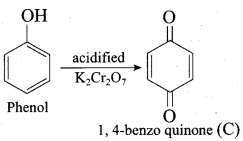
4. Phenol on reaction with H2, in the presence of Nickel gives cyclohexanol as (D).
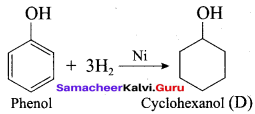
Question 22.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H6 reacts with propylene in the presence of H3PO4 at 532 K gives (B) of formula C9H12 . (B)on air oxidation gives C9H12O2 as (C). (C) on acidification with H2SO4 gives (D) of formula C6H6O and (E) of formula C3H6O. Identify A, B, C, D and E and explain the reactions.
Answer:
1. (A) is identified as benzene from the molecular formula.
2. Benzene reacts with propylene in the presence of H3PO4 gives cumene as (B).
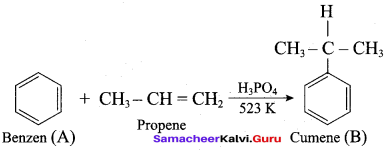
3. Cumene on air oxidation produces cumene hydroperoxide as (C).
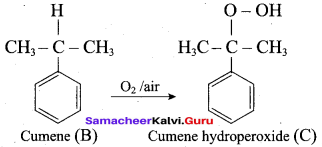
4. Cumene hydroperoxide on treatement with H2SO4 yield phenol as (D) and acetone as (E).
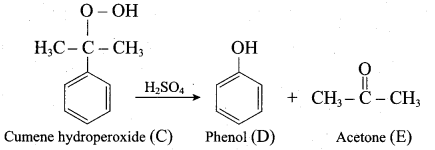
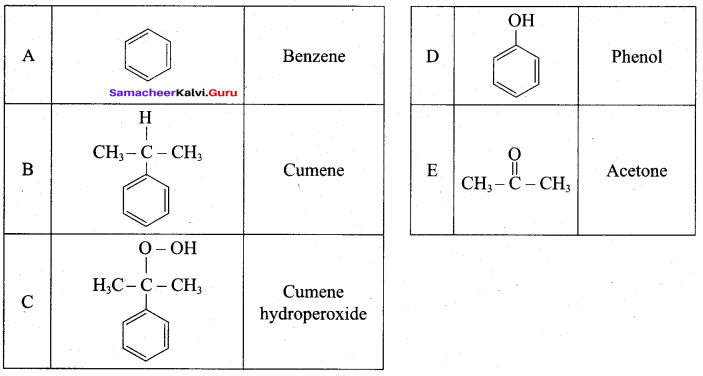
Question 23.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O reacts P/I2 gives (B) which on further reaction with silver nitrite gives (C) of formula C2H5NO2. (C) on treatment with nitrous acid yield (D) of formula C2H4N2O3. (D) on reaction with KOH give red color product (E). Identify A, B, C, D and E. From the final product (E) red colour product, it is identified these reactions are the reactions of primary alcohols in Victor Meyer’s test.
Answer:
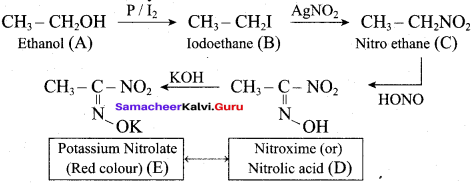
Question 24.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C3HO on reaction P/I2 gives C3H7I as (B). (B) on reaction with AgNO2 produces (C) with formula C3H7NO2. (C) on reaction with nitrous acid gives (D) of molecular formula C3H6N2O3. (D) on reaction with KOH produces blue colour. Identify A, B. C, D and explain the reaction.
Answer:
From the final colour blue, this reaction are considered as reactions of secondary alcohol in Victory Meyer’s. (A) is identified as  2 – propanol.
2 – propanol.
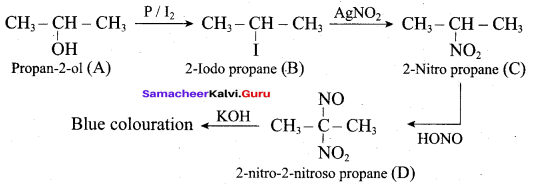
Question 25.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C4H10O gives no colouration in Victor Meyer’s test. (A) on reaction with P / I2 gives (B) of formula C4H9I. (B) on treatment with nitrous acid gives (C) of formula C3H9NO2. (C) does not react with KOH. Identify A, B, C and explain.
Answer:
C4H10O gives no colouration in Victor Meyer’s test means it must be tertiary alcohol. So (A) is tertiary butyl alcohol. The reactions involved are,
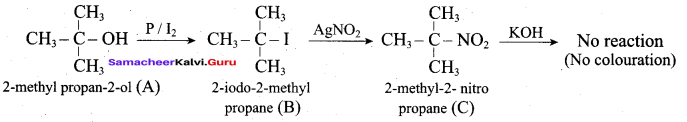
Common Errors
- Writing IUPAC names may be difficult and students may get confused.
- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary alcohols functional groups may get confused. Phenol, aromatic alcohols are differenet.
- Benzene ring should be drawn properly.
- Skeleton carbon chain may be a problem to students.
Rectifications
1. Parent hydrocarbon – longest carbon chain. Lowest number of the carbon having functional group. Arrangement of substitutents in alphabetical order. Alcohol – Name should end in the word ol.
2. Primary alcohol – CHI2OH, Secondary alcohol > CHOH, Tertiary alcohol > COH – OH gp/ directly attached to benzene ring is
Phenol 
It is not aromatic alcohol
– OH gp/ is attached to the side chain of the benzene ring is an aromatic alcohol.
Benzyl alcohol
3. Altemat double bond along with regular hexagon is ben zeane.
 Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane.
Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane.
 Cyclohexane (C6H12)
Cyclohexane (C6H12)
4. 
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
n-heptane

CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH = CH2
Pent – 1 – ene
![]()
![]()
![]()
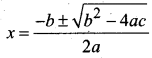
![]()
![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

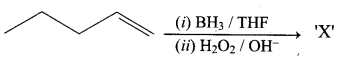


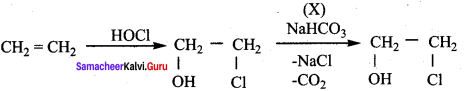







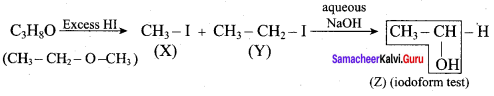



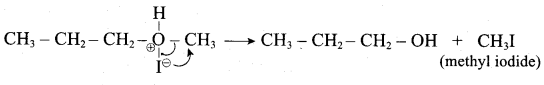

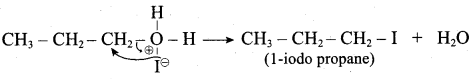
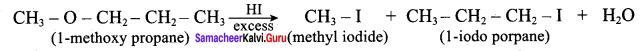













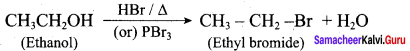


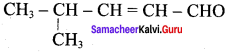
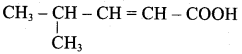
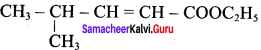
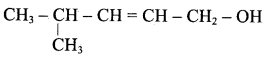


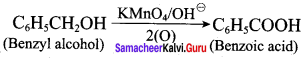








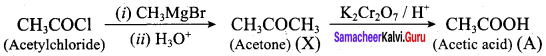







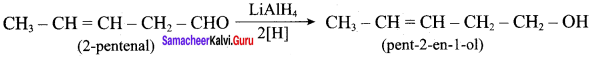




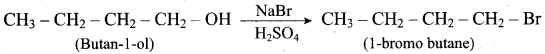



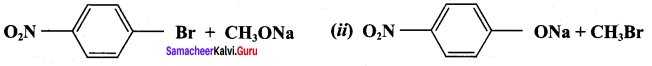














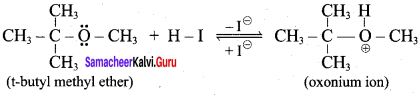


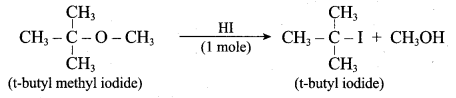



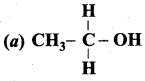

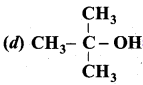








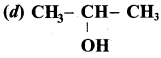





















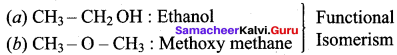
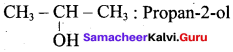

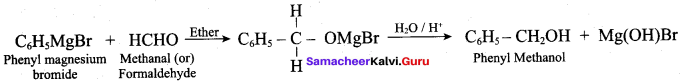


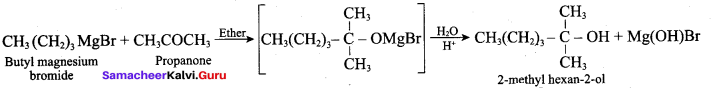



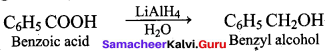
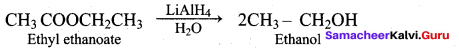
































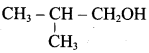







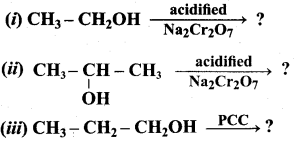

























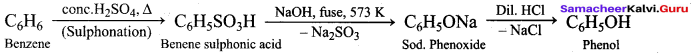
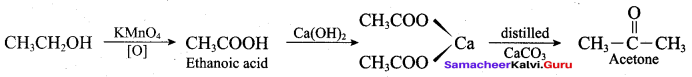


























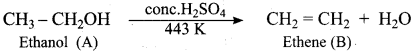






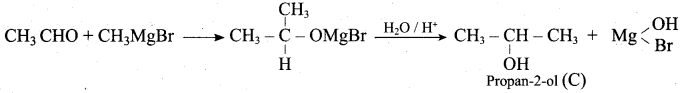


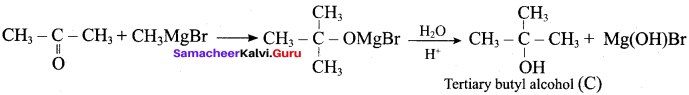

 Propan – 2- ol as (B)
Propan – 2- ol as (B)






















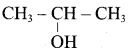 2 – propanol.
2 – propanol.



 Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane.
Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane. Cyclohexane (C6H12)
Cyclohexane (C6H12)
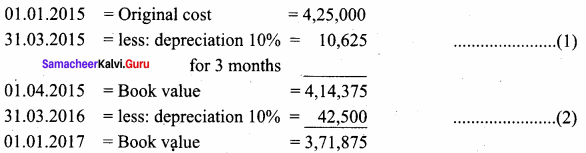
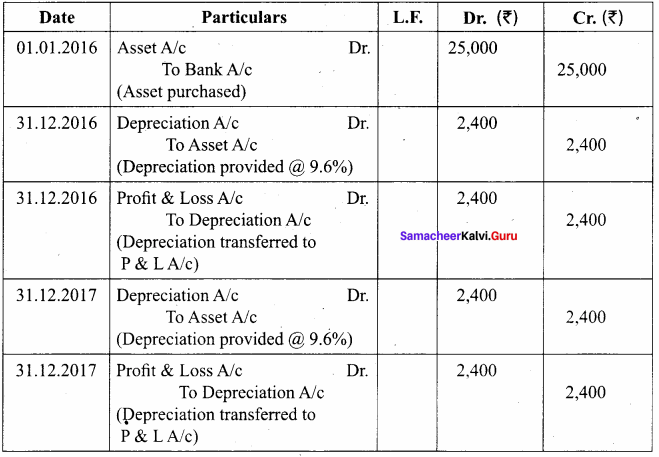
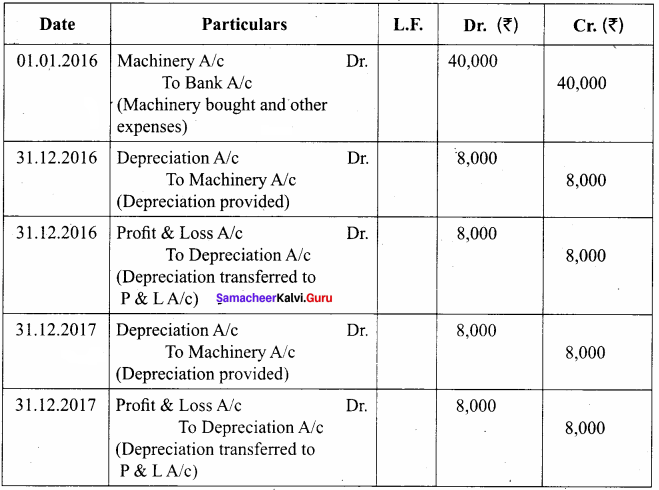
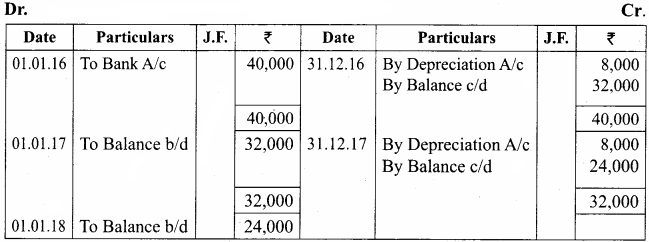
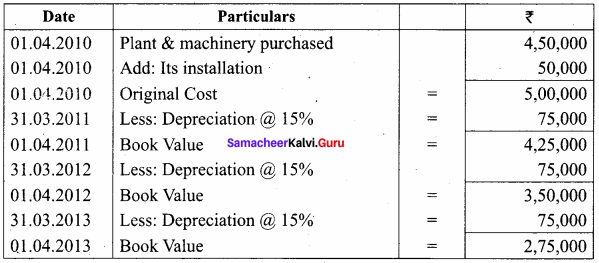
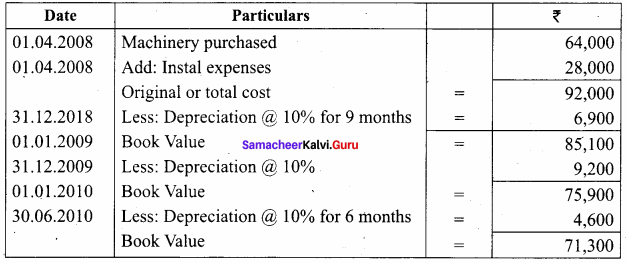
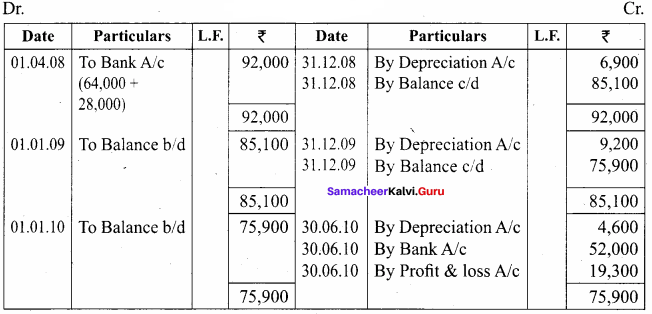
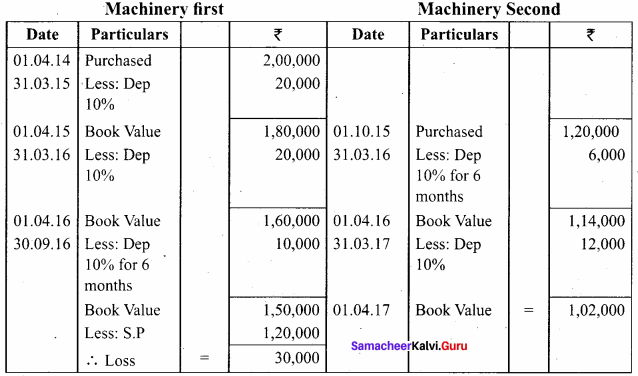
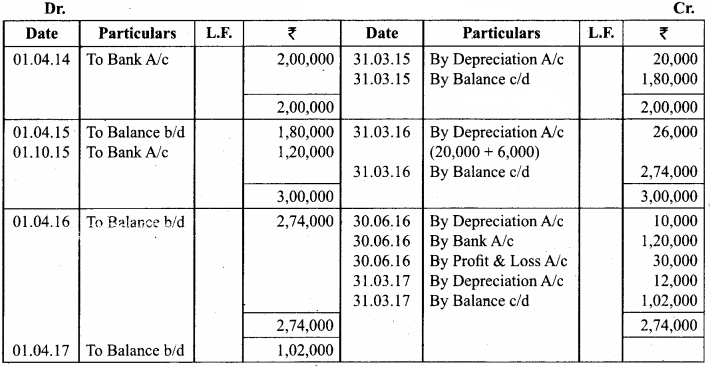
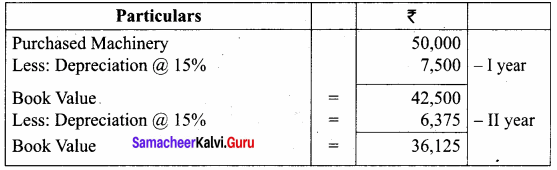
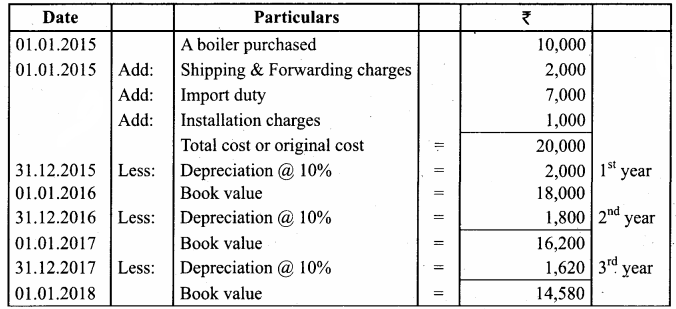
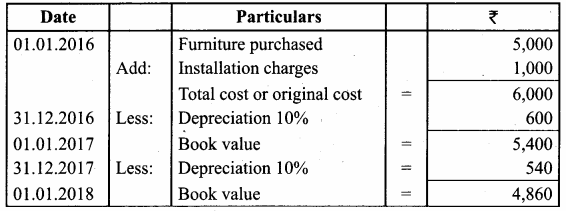
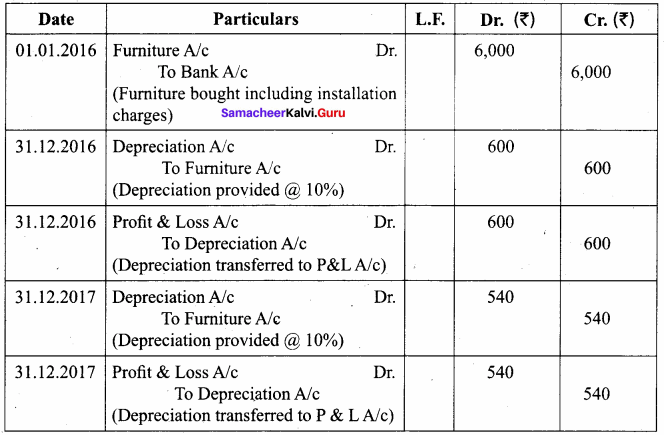
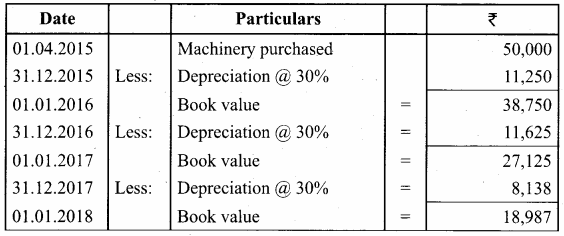
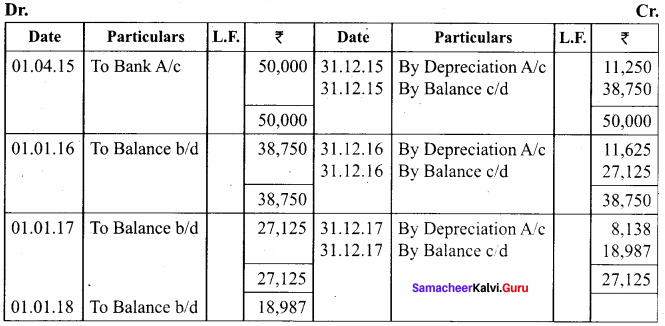
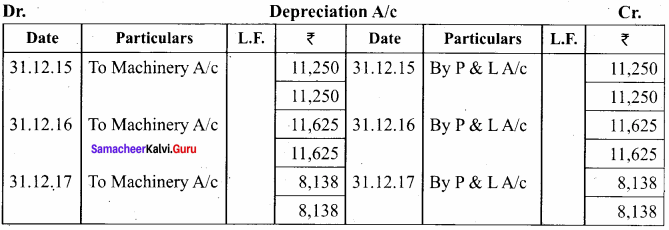
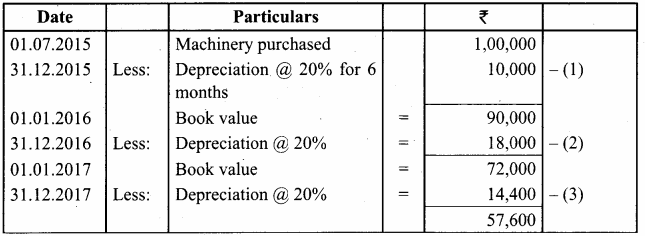
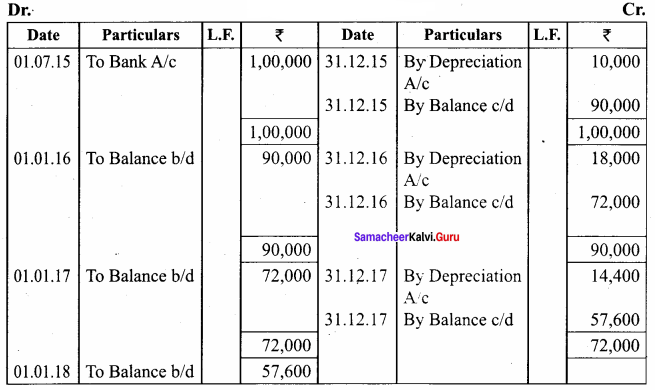
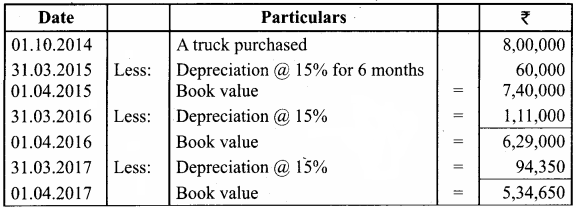
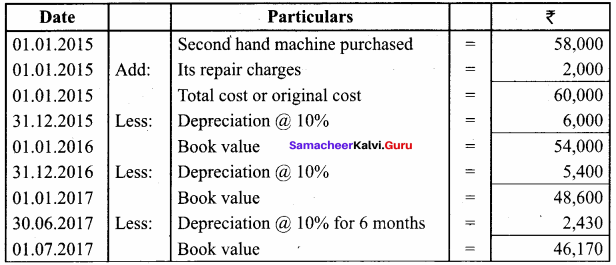
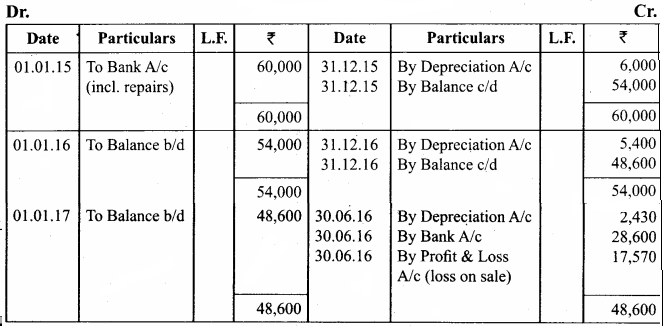
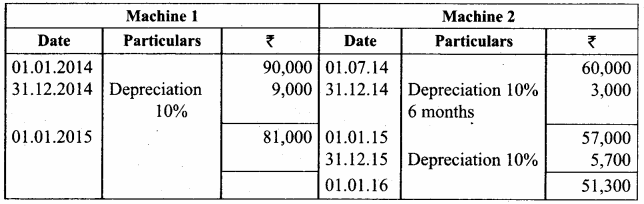
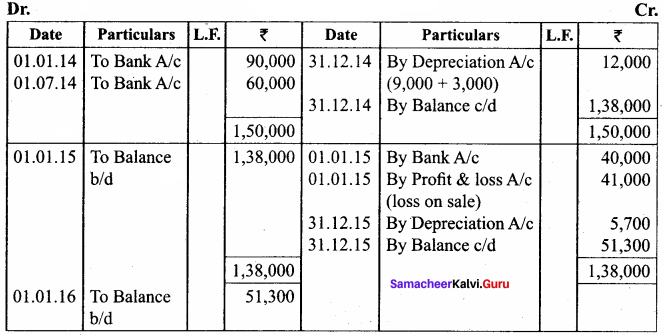
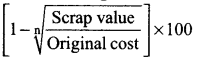 ……………….
……………….