Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 18 Electronic Data Interchange – EDI Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 18 Electronic Data Interchange – EDI
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Electronic Data Interchange – EDI Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
EDI stands for ……………………
(a) Electronic Details Information
(b) Electronic Data Information
(c) Electronic Data Interchange
(d) Electronic Details Interchange
Answer:
(c) Electronic Data Interchange
Question 2.
Which of the following is an internationally recognized standard format for trade, transportation, insurance, banking and customs?
(a) TSLFACT
(b) SETFACT
(c) FTPFACT
(d) EDIFACT
Answer:
(d) EDIFACT
![]()
Question 3.
Which is the first industry-sjpecific EDI standard?
(a) TDCC
(b) VISA
(c) Master
(d) ANSI
Answer:
(a) TDCC
Question 4.
UNSM stands for:
(a) Universal Natural Standard message
(b) Universal Notations for Simple message
(c) United Nations Standard message
(d) United Nations Service message
Answer:
(c) United Nations Standard message
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is a type of EDI?
(a) Direct EDI
(b) Indirect EDI
(c) Collective EDI
(d) Unique EDI
Answer:
(a) Direct EDI
Question 6.
Who is called as the father of EDI?
(a) Charles Babbage
(b) Ed Guilbert
(c) Pascal
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Ed Guilbert
![]()
Question 7.
EDI interchanges starts with ……………………. and ends with ……………………..
(a) UNA, UNZ
(b) UNB, UNZ
(c) UNA, UNT
(d) UNB, UNT
Answer:
(b) UNB, UNZ
Question 8.
EDIFACT stands for ………………………
(a) EDI for Admissible Commercial Transport
(b) EDI for Advisory Committee and Transport
(c) EDI for Administration, Commerce and Transport
(d) EDI for Admissible Commerce and Trade
Answer:
(c) EDI for Administration, Commerce and Transport
Question 9.
The versions of EDIFACT are also called as ……………………….
(a) Message types
(b) Subsets
(c) Directories
(d) Folders
Answer:
(c) Directories
![]()
Question 10.
Number of characters in an single EDIFACT messages ……………………..
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(b) 6
PART – II
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
Define EDI?
Answer:
The Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the exchange of business documents between one trade partner and another electronically. It is transferred through a dedicated channel or – through the Internet in a predefined format without much human intervention.
![]()
Question 2.
List few types of business documents that are transmitted through EDI?
Answer:
- Direct EDI EDIviaVAN
- EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS
- Web EDI
- Mobile EDI
Question 3.
What are the 4 major components of EDI?
Answer:
There are four major components of EDI. They are:
- Standard document format
- Translator and Mapper
- Communication software
- Communication network
![]()
Question 4.
What is meant by directories in EDIFACT?
Answer:
The versions of EDIFACT are also called as directories. These EDIFACT directories will be revised twice a year; on 1 st April and 1 st October to include new or update, existing EDIFACT messages. EDIFACT directories have names like D. 18B (D stands for Directory, 18 is the year and A/B indicates the month of release)
Question 5.
Write a note on EDIFACT subsets?
Answer:
Due to the complexity, branch-specific subsets of EDIFACT have developed. These subsets of EDIFACT include only the functions relevant to specific user groups.
Example:
- CEFIC – Chemical industry
- EDIFURN – furniture industry
- EDIGAS – gas business
PART – III
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Write a short note on EDI?
Answer:
- The Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the exchange of business documents between one trade partner and another electronically.
- It is transferred through a dedicated channel or through the Internet in a predefined format without much human intervention.
- It is used to transfer documents such as delivery notes, invoices, purchase orders, advance ship notice, functional acknowledgements etc.
- These documents are transferred directly from the computer of the issuing company to that of the receiving company, with great time saving and avoiding many errors of traditional “on paper” communications.
![]()
Question 2.
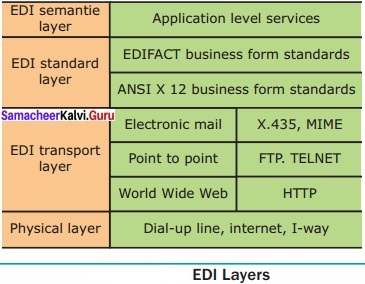
List the various layers of EDI?
Answer:
Electronic data interchange architecture specifies four different layers namely –
- Semantic layer
- Standards translation layer
- Transport layer
- Physical layer
These EDI layers describes how data flows from one computer to another.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on UN/EDIFACT?
Answer:
- United Nations / Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport
- (UN / EDIFACT) is an international EDI – standard developed under the supervision of the United Nations.
- In 1987, the UN / EDIFACT syntax rules were approved as ISO: IS09735 standard by the International Organization for Standardization.
- EDIFACT includes a set of internationally agreed standards, catalogs and guidelines for electronic exchange of structured data between independent computer systems.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on EDIFACT message?
Answer:
The basic standardization concept of EDIFACT is that there are uniform message types called United Nations Standard Message (UNSM). In so-called subsets, the message types can be specified deeper in their, characteristics depending on the sector. The message types, all of which always have exactly one nickname consisting of six uppercase English alphabets. The message begins with UNH and ends with UNT.
Service messages
To confirm / reject a message, CONTRL and APERAK messages are sent.
- CONTRL – Syntax Check and Confirmation of Arrival of Message
- APERAK – Technical error messages and acknowledgment
- Data exchange
- CREMUL – multiple credit advice
- DELFOR-Delivery forecast
- IFTMBC – Booking confirmation
![]()
Question 5.
Write about EDIFACT separators?
EDI Separators:
Answer:
EDIFACT has the following punctuation marks that are used as standard separators.
Character:
- Apostrophe
- Plus sign +
- Colon:
- Question mark ?
- Period
Uses:
- Segment terminator
- Segment tag and data element separator
- Component data element separator
- Release character
- Decimal point
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Briefly explain various types of EDI?
Answer:
The types of EDI were constructed based on how EDI communication connections and the conversion were organized. Thus based on the medium used for transmitting EDI documents the following are the major EDI types.
- Direct EDI
- EDI via VAN
- EDI via-FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS
- Web EDI
- Mobile EDI
- Direct EDI/Point-to-Point
It is also called as Point-to-Point EDI. It establishes a direct connection between various business stakeholders and partners individually. This type of EDI suits to larger businesses with a lot of day to day business transactions.
EDI via VAN:
EDI via VAN (Value Added Network) is where EDI documents are transferred with the support of third party network service providers. Many businesses prefer this network model to protect them from the updating ongoing complexities of network technologies.
EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS:
When protocols like FTP/VPN, SFTP and FTPS are used for exchange of EDI based documents through the Internet or Intranet it is called as EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS.
Web EDI:
Web based EDI conducts EDI using an web browser via the Internet. Here the businesses are allowed to use any browser to transfer data to their business partners. Web based EDI is easy and convenient for small and medium organizations.
Mobile EDI:
When smartphones or other such handheld devices are used to transfer EDI documents it is called as mobile EDI. Mobile EDI applications considerably increase the speed of EDI transactions.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the advantages of EDI?
Answer:
Advantages of EDI:
EDI was developed to solve the problems inherent in paper-based transaction processing and in other forms of electronic communication. Implementing EDI system offers a company greater control over its supply chain and allow it to trade more effectively. It also increases productivity and promotes operational efficiency. The following are the other advantages of EDI.
- Improving service to end users
- Increasing productivity
- Minimizing errors
- Slashing response times
- Automation of operations
- Cutting costs
- Integrating all business and trading partners
- Providing information on process Status
- Optimizing financial ratios
EDI Layers:
Electronic data interchange architecture specifies four different layers namely;
- Semantic layer
- Standards translation layer
- Transport layer
- Physical layer
These EDI layers describes how data flows from one computer to another.

![]()
Question 3.
Write about structure of EDIFACT?
Answer:
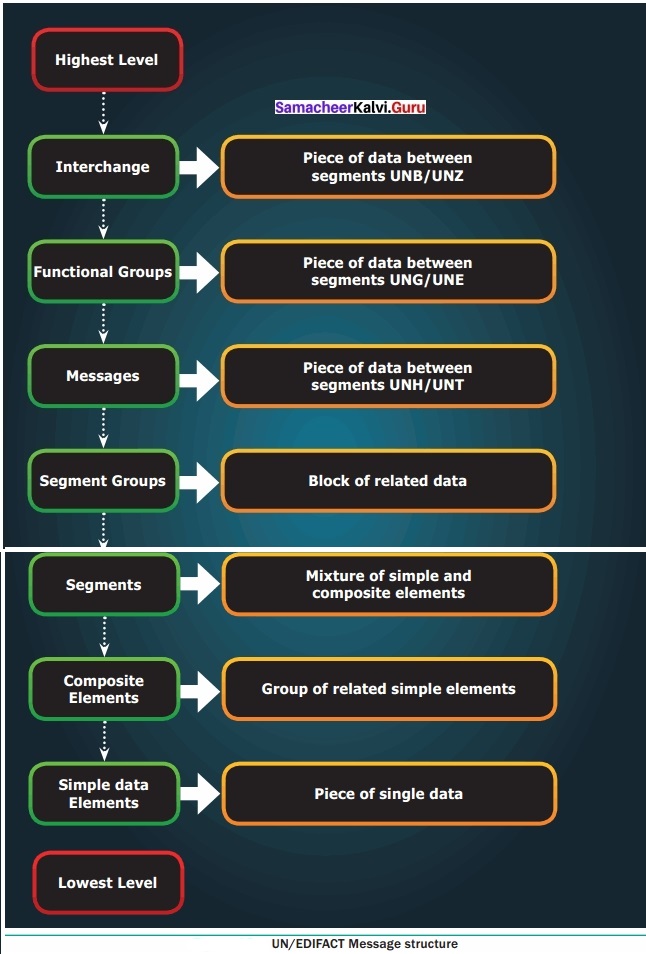
EDIFACT Structure:
EDIFACT is a hierarchical structure where the top level is referred to as an interchange, and lower levels contain multiple messages. The messages consist of segments, which in turn consist of composites. The final iteration is a data element.
Segment Tables:
Segment table lists the message tags. It contains the tags, tag names, requirements designator and repetition field. The requirement designator may be mandatory (M) or conditional (C). The (M) denotes that the segment must appear at least once. The (C) denotes that the segment may be used if needed. e.g. C10 indicates repetitions of a segment or group between 0 and 10.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Electronic Data Interchange – EDI Additional Questions and Answers
1. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
……………………. is the exchange of business documents between one trade partner and another electronically.
(a) EDI
(b) UDI
(c) FDI
(d) DDI
Answer:
(a) EDI
![]()
Question 2.
Identify which one of the following is not a EDI standard?
(a) EDIFACT
(b) XML
(c) ANSI ASC X12
(d) HTML
Answer:
(d) HTML
Question 3.
……………………. is a paperless trade.
(a) EDI
(b) XML
(c) EDIF
(d) EFT
Answer:
(a) EDI
Question 4.
…………………… is a paperless payment.
(a) EDI
(b) EFT
(c) XML
(d) EDIFAC
Answer:
(b) EFT
![]()
Question 5.
TDCC stands for ………………………
Answer:
Transportation Data Coordinating Committee
Question 6.
TDCC was formed in the year …………………….
(a) 1964
(b) 1966
(c) 1968
(d) 1970
Answer:
(c) 1968
Question 7.
The first EDI standard was released by TDCC in the year
(a) 1972
(b) 1975
(c) 1976
(d) 1978
Answer:
(b) 1975
![]()
Question 8.
Expand EDIA
(a) Electronic Data Interchange Authorigy
(b) Electronic Data Information Association
(c) Electronic Data Interchange Association
(d) Electronic Device Interface Amplifier
Answer:
(c) Electronic Data Interchange Association
Question 9.
The TDCC is renamed as EDIA in the year ……………………….
(a) 1972
(b) 1975
(c) 1976
(d) 1978
Answer:
(d) 1978
Question 10.
ANSI stands for …………………….
Answer:
American National Standards Institute
![]()
Question 11.
EDIA has become …………………….. committee.
(a) ANSIXI2
(b) ANSIXI3
(c) ANSIXI4
(d) ANSIX15
Answer:
(a) ANSIXI2
Question 12.
EDIFACT is created by …………………..
(a) UN
(b) WHO
(c) UNESCO
(d) UNICEF
Answer:
(a) UN
![]()
Question 13.
EDIFACT was created in ……………………..
(a) 1982
(b) 1978
(c) 1981
(d) 1985
Answer:
(d) 1985
Question 14.
Identify the statement which is not true?
(a) The first EDI message was sent from the Holland – American Streamship line to Trans-Atlantic Shipping Company
(b) It is send usign telex
(c) It took 2 minutes to send a full page
(d) These messages were written on the CD to load into another computer
Answer:
(d) These messages were written on the CD to load into another computer.
![]()
Question 15.
The first EDI message was sent in ………………………
(a) 1955
(b) 1965
(c) 1975
(d) 1985
Answer:
(b) 1965
Question 16.
How many major classifications of EDI are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
Question 17.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Direct EDI
(b) Web EDI
(c) Android EDI
(d) Mobile EDI
Answer:
(c) Android EDI
![]()
Question 18.
…………………… is also called as point-to-point EDI.
Answer:
Direct EDI
Question 19.
Which EDI is better for day to day business transactions?
(a) Direct EDI
(b) EDI via VAN
(c) Web EDI
(d) Mobile EDI
Answer:
(a) Direct EDI
Question 20.
Expand VAN?
(a) Value Added Network
(b) Voice Added Network
(c) Vast Area Network
(d) Value Area Network
Answer:
(a) Value Added Network
![]()
Question 21.
A …………………….. acts as an intermediary between trading partners.
(a) VAN
(b) Web
(c) Mobile
(d) FTPs
Answer:
(a) VAN
Question 22.
……………………… is convenient for small and medium organizations.
Answer:
web based EDI
![]()
Question 23.
Match the following
(i) point to point EDI – 1. easy for small and medium organizations.
(ii) EDI via VAN – 2. Speed Transactions.
(iii) EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS – 3. Large day to day business transactions
(iv) Web EDI – 4. Third party Network service providers.
(v) Mobile EDI – 5. Uses protocols
(a) (i)-3 (ii)-4 (iii)-5 (iv)-1 (v) 2
(b) (i)-1 (ii)-2 (iii)-3 (iv)-4 (v)-5
(c) (i)-5 (ii)-4 (iii)-3 (iv)-2 (v)-1
(d) (i)-4 (ii)-3 (iii)-2 (iv)-1 (v)-5
Answer:
(a) (i)-3 (ii)-4 (iii)-5 (iv)-1 (v) 2
Question 24.
How many layers are there in EDI?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 25.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Semantic layer
(b) Transport layer
(c) Session layer
(d) Physical layer
Answer:
(c) Session layer
Question 26.
Identify the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Semantic layer – application level services
(b) Standard layer – ANSI XI2
(c) Transport layer – FTP, TELNET
(d) Physical layer – Electronic mail
Answer:
(d) Physical layer – Electronic mail
![]()
Question 27.
MIME, HTTP, FTP comes under …………………….. layer.
(a) Semantic
(b) Standard
(c) Transport
(d) Physical
Answer:
(c) Transport
Question 28.
How many major components of EDI are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 29.
Which one of the following is not a major component of EDI?
(a) Standard document
(b) Standard translation
(c) Translator and Mapper
(d) Communication Software
Answer:
(b) Standard translation
Question 30.
………………………. is the EDI standard for warehousing Industry.
Answer:
WINS
Question 31.
GTDI means …………………………
Answer:
Guideline for Trade Data Interchange
![]()
Question 32.
ECE stands for
(a) Economic Commission for Europe
(b) Electronic and Communication Engineering
(c) Electrical and Communication Engineering
(d) Easy control Edges
Answer:
(a) Economic Commission for Europe
Question 33.
UN/EDIFACT is officially proposed in the year ………………………
(a) 1986
(b) 1987
(c) 1988
(d) 1989
Answer:
(a) 1986
![]()
Question 34.
The EDIFACT directories will be revised …………………….
(a) twice a year
(b) once in a year
(c) thrice a year
(d) cannot be revised
Answer:
(a) twice a year
Question 35.
In EDIFACT directories A/B indicates the ……………………… of release.
Answer:
month
![]()
Question 36.
Find the wrongly matched pair.
(a) EDICHEM – Chemical Industry
(b) EDIFURN – Furniture Industry
(c) EDIGAS – Gas Business
Answer:
(a) EDICHEM – Chemical Industry
Question 37.
Which one of the following is a hierarchical structure with multiple messages?
(a) CEFIC
(b) EDIFACT
(c) EDIFURN
(d) EDIGAS
Answer:
(b) EDIFACT
![]()
Question 38.
The top level in EDIFACT is referred to as ………………………..
(a) Subsets
(b) Segment
(c) interchange
(d) data
Answer:
(c) interchange
Question 39.
In EDIFACT, the messages consist of which in turn consist of …………………….. which in turn consist of ……………………….
Answer:
segments and composites
Question 40.
The final iteration in EDIFACT is
(a) data element
(b) control variable
(c) interchange
(d) subset
Answer:
(a) data element
![]()
Question 41.
………………………. indicates the repetitions of a segment or group between 0 and 10.
(a) A10
(b) BIO
(c) C1O
(d) D1O
Answer:
(c) C1O
Question 42.
……………………. lists the tags, tag names, requirements designator and repetitation fields.
Answer:
Segment Table
Question 43.
The interchange is also called as …………………..
Answer:
envelope
![]()
Question 44.
The EDIFACT message begins and ends with …………………….
(a) UNH, UNT
(b) UNB, UNZ
(c) UNH, UNZ
(d) UNB, UNT
Answer:
(a) UNH, UNT
Question 45.
………………….. show technical error messages in EDIFACT.
Answer:
APERAK
![]()
Question 46.
A segment is a …………………….. character alphanumeric code.
Answer:
3
Question 47.
In EDIFACT message ………………………… is the format for century, year, month, date, hour, minute.
Answer:
CCYYMMDDHHMM
Question 48.
……………………. is date/time information in the segment.
Answer:
DTM
![]()
Question 49.
Which is the release character?
(a) :
(b) ?
(c) .
(d) +
Answer:
(b) ?
Question 50.
Which punctuator is segment tag?
(a) ,
(b) +
(c) :
(d) !
Answer:
(b) +
Question 51.
Which is used for component data element separator?
(a) :
(b) +
(c) ?
(d) ?
Answer:
(a) :
![]()
Question 52.
…………………… is the segment terminator.
(a) :
(b) +
(c) ‘
(d) ?
Answer:
(c) ‘
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is VAN?
Answer:
A value-added network is a company, that is based on its own network, offering EDI services to other businesses. A value-added network acts as an intermediary between trading partners. The principle operations of value- added networks are the allocation of access rights and providing high data security.
![]()
Question 2.
Write note on EDI Via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS?
Answer:
EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS:
When protocols like FTP/VPN, SFTP and FTPS are used for exchange of EDI based documents through the Internet or Intranet it is called as EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS. .
Question 3.
Write a short note on Segment Table?
Answer:
Segment Tables:
Segment table lists the message tags. It contains the tags, tag names, requirements designator and repetitation field. The requirement designator may be mandatory (M) or conditional (C). The (M) denotes that the segment must appear atleast once. The (C) denotes that the segment may be used if needed.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention Some examples for FDIFACT subset?
Answer:
- GEFIC – Chemical industry
- EDIFURN – furniture industry
- EDIGAS – gas business
Question 5.
Write note on EDIFACT Segment?
Answer:
EDIFACT Segment
It is the subset of message. A segment is a three-character alphanumeric code. These segments are listed in segment tables. Segments may contain one, or several related user data elements.
![]()
Question 6.
Mention service messages in EDIFACT?
Answer:
- CONTRL- Syntax Check and Confirmation of Arrival of Message
- APERAK – Technical error
Question 7.
Mention data exchange in EDIFACT message?
Answer:
Data exchange:
CREMUL – multiple credit advice DELFOR-Delivery forecast IFTMBC – Booking confirmation.
![]()
Question 8.
Write note on EDI Interchange?
Answer:
EDI Interchange:
Interchange is also called as envelope. The top level of EDIFACT structure is Interchange. An interchange may contain multiple messages. It starts with UNB and ends with UNZ.
III. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain EDI standards?
Answer:
EDI Standards:
- The standard is the most critical part of the entire EDI. Since EDI is the data transmission and information exchange in the form of an agreed message format, it is important to develop a unified EDI standard.
- The EDI standard is mainly divided into the following aspects: basic standards, code-standards, message standards, document standards, management standards, application standards, communication standards and security standards.
- The first industry-specific EDI standard was the TDCC published by the Transportation Data coordinating Committee in 1975.
- Then other industries started developing unique standards based on their individual needs. E.g. WINS in the warehousing industry.
- Since the application of EDI has become more mature, the target of trading operations is often not limited to a single industry.
- In 1979, the American National Standards Institute Accredited Standard Committee (ANSI ASC) developed a wider range of EDI standard called ANSI XI2.
- On the other hand, the European region has also developed an integrated EDI standard. Known as GTDI (Guideline for Trade Data Interchange).
- ANSI X12 and GTDI have become the two regional EDI standards in North America and Europe respectively.
- After the development of the two major regional EDI standards and a few years after trial, the two standards began to integrate and conduct research and development of common EDI standards.
- Subsequently, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UN/ECE/WP.4) hosted the task of the development of international EDI standards. In 1986, UN/EDIFACT is officially proposed. The most widely used EDI message standards are the United Nations EDIFACT and the ANSI X12.