Students can Download Maths Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.3 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.3
Question 1.
Construct the following rhombuses with the given measurements and also find their area.
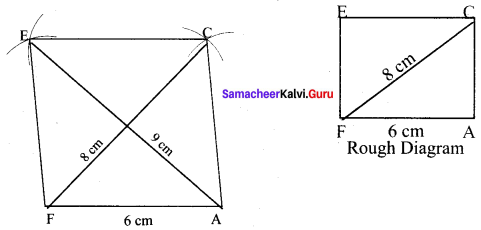
(i) FACE, FA = 6 cm and FC = 8 cm
Solution:
Given FA = 6 cm and FC = 8cm
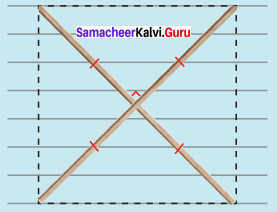
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment FA = 6 cm.
(ii) With F and A as centres, drawn arcs of radii 8 cm and 6 cm respectively and let them cut at C.
(iii) Joined FC and AC.
(iv) With F and C as centres, drawn arcs of radius 6 cm each and let them cut at E. Joined FE and EC.
(v) FACE is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 × 9 sq.units = 36 cm²

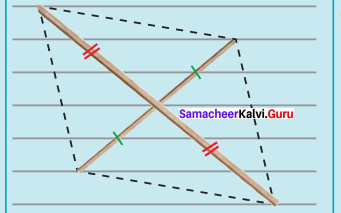
(ii) RACE, RA = 5.5 cm and AE = 7 cm
Solution:
Given RA = 5.5 cm and AE = 7 cm
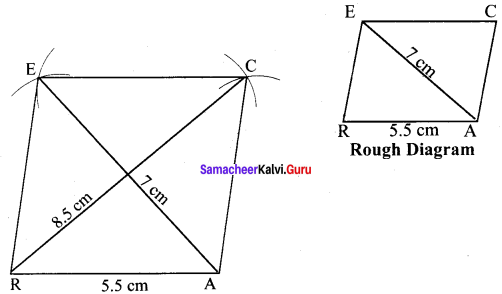
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment RA = 5.5 cm.
(ii) With R and A as centres, drawn arcs of radii 5.5 cm and 7 cm respectively and let them cut at E.
(iii) Joined RE and AE.
(iv) With E and A as centres, drawn arcs of radius 5.5 cm each and let them cut at C.
(v) Joined AC and EC.
(vi) RACE is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 7 × 8.5 cm² = 29.75 cm²
(iii) CAKE, CA = 5 cm and ∠A = 65°
Solution:
Given CA = 5 cm and ∠A = 65°
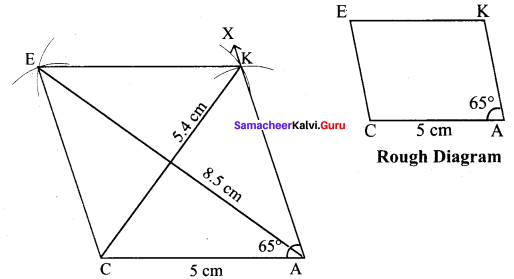
(i) Drawn a line segment CA = 5 cm.
(ii) At A on AC, made ∠CAX = 65°
(iii) With A as centre, drawn arc of radius 5 cm. Let it cut AX at K.
(iv) With K and C as centres, drawn arcs of radius 5 cm each and let them cut at E. Joined KE and CE.
(v) CAKE is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5.4 × 8.5 cm² = 22.95 cm²
(iv) MAKE, MA= 6.4 cm and ∠M = 80°
Solution:
Given MA = 6.4 cm and ∠M = 80°
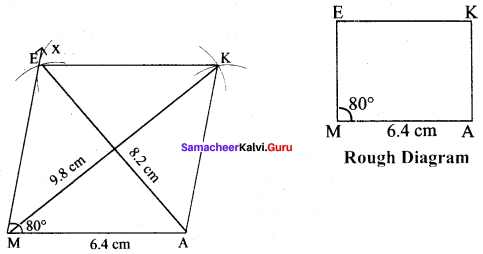
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment MA = 6.4 cm.
(ii) At M on MA, made ∠AMX = 80°
(iii) With M as centres, drawn arc of radius 6.4 cm. Let it cut MX at E.
(iv) With E and A as centres, drawn arcs of radius 6.4 cm each and let them cut at K.
(v) Joined EK and AK.
(vi) MAKE is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8.2 × 9.8 cm² = 40.18 cm²
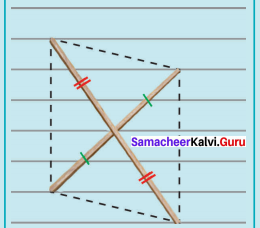
(v) LUCK, LC = 7.8 cm and UK = 6 cm
Solution:
Given LC = 7.8 cm and UK = 6 cm
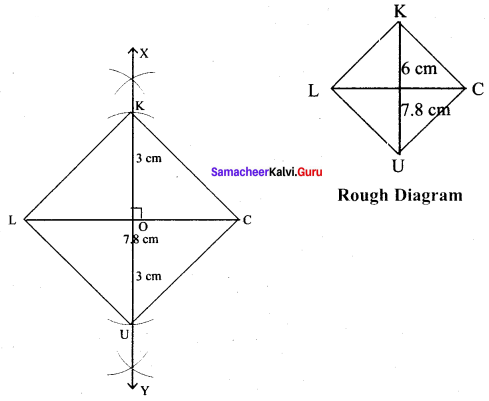
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment LC = 7.8 cm.
(ii) Drawn the perpendicular bisector XY to LC. Let it cut LC at ‘O’
(iii) With O as centres, drawn arc of radius 3 cm on either side of O which cut OX at K and OY at U.
(iv) Joined LU, UC, CK and LK.
(v) LUCK is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 7.8 × 6 cm² = 23.4 cm²
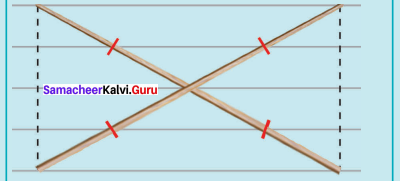
(vi) DUCK, DC = 8 cm and UK = 6 cm
Solution:
Given DC = 8 cm and UK = 6 cm
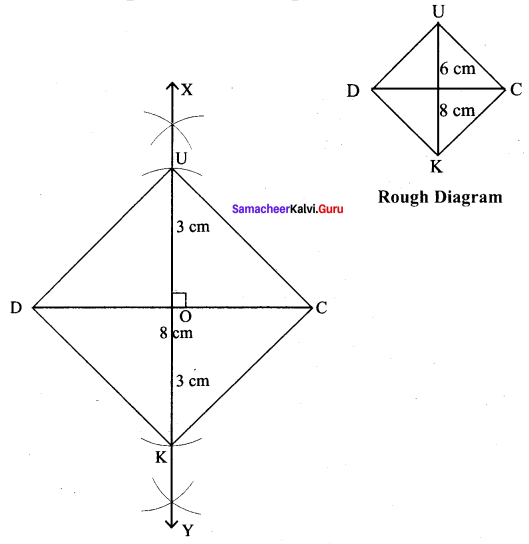
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment DC = 8 cm.
(ii) Drawn the perpendicular bisector XY to DC. Let it cut DC at ‘O’
(iii) With O as centres, drawn arc of radius 3 cm on either side of O which cut OX at U and OYat K.
(iv) Joined DK, KC, CU and DU.
(v) DUCK is the required rhombus.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 × 6 cm² = 24 cm²

(vii) PARK, PR = 9 cm and ∠P = 70°
Solution:
Given PR = 9 cm and ∠P = 70°
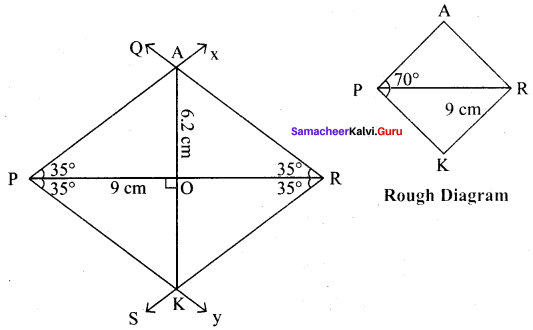
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment PR = 9 cm.
(ii) At P, made ∠RPX = ∠RPY = 35° on either side of PR.
(iii) At R, made ∠PRQ = ∠PRS = 35° on either side of PR
(iv) Let PX and RQ cut at A and PY and RS at K.
(v) PARK is the required rhombus
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 9 × 6.2 cm² = 27.9 cm²
(viii) MARK, AK =7.5 cm and ∠A = 80°
Solution:
Given AK = 7.5 cm and ∠A = 80°
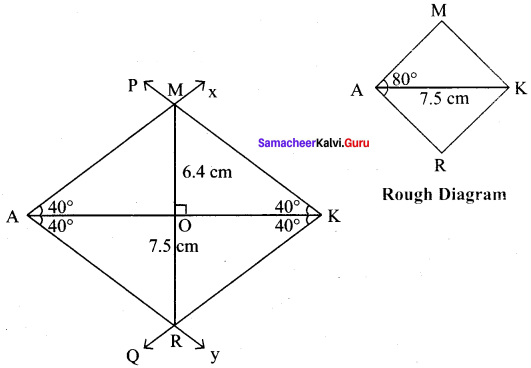
(i) Drawn a line segment AK = 7.5 cm.
(ii) At A, made ∠KAX = ∠KAY = 40° on either side of AK.
(iii) At K, made ∠AKP = ∠AKQ = 40° on either side of AK
(iv) Let AX and KP cut at M and AY and KQ at R.
(v) MARK is the required rhombus
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 sq.units = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 7.5 × 6.4 cm² = 24 cm²
Question 2.
(i) Construct the following rectangles with the given measurements and also find their area.
(i) HAND, HA = 7 cm and AN = 4 cm
Solution:
Given HA = 7 cm and AN = 4 cm
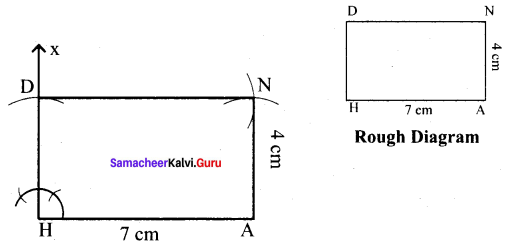
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment HA = 7 cm.
(ii) At H, constructed HX ⊥ HA.
(iii) With H as centre, drawn an arc of radius 4 cm and let it cut at HX at D.
(iv) With A and D as centres, drawn arcs of radii 4 cm and 7 cm respectively and let them cut at N.
(v) Joined AN and DN.
(vi) HAND is the required rectangle.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rectangle HAND = l × b sq.units = 7 × 4 cm² = 28 cm²
(ii) SAND, SA = 5.6 cm and SN = 4.4 cm
Solution:
Given SA = 5.6 cm and SN = 4.4 cm
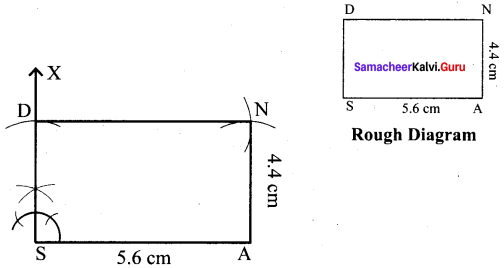
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment SA = 5.6 cm.
(ii) At S, constructed SX ⊥ SA.
(iii) With S as centre, drawn an arc of radius 4.4 cm and let it cut at SX at D.
(iv) With A and D as centres, drawn arcs of radii 4.4 cm and 5.6 cm respectively and let them cut at N.
(v) Joined DN and AN.
(vi) SAND is the required rectangle.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rectangle SAND = l × b sq.units = 5.6 × 4.4 cm² = 26.64 cm²
(iii) LAND, LA = 8 cm and AD = 10 cm
Solution:
Given LA = 8 cm and AD = 10 cm
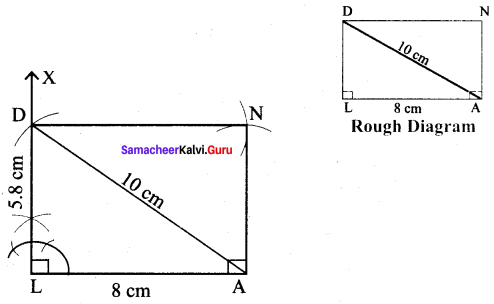
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment LA = 8 cm.
(ii) At L, constructed LX ⊥ LA.
(iii) With A as centre, drawn an arc of radius 10 cm and let it cut at LX at D.
(iv) With A as centre and LD as radius drawn an arc. Also with D as centre and LA as radius drawn another arc. Let then cut at N.
(v) Joined DN and AN.
(vi) LAND is the required rectangle.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rectangle LAND = l × b sq.units = 8 × 5.8 cm² = 46.4 cm²

(iv) BAND, BA = 7.2 cm and BN = 9.7 cm
Solution:
Given = 7.2 cm and BN = 9.7 cm
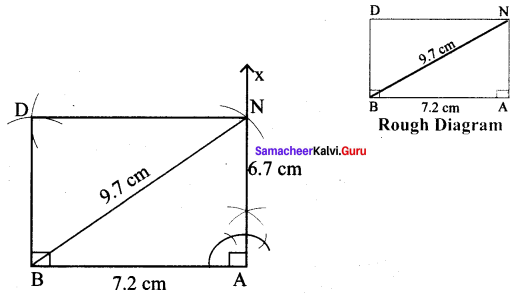
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment BA = 7.2 cm.
(ii) At A, constructed NA ⊥ AB.
(iii) With B as centre, drawn an arc of radius 9.7 cm and let it cut at AX at N.
(iv) With B as centre and AN as radius drawn an arc. Also with N as centre and BA as radius drawn another arc. Let then cut at D.
(v) Joined ND and BD.
(vi) BAND is the required rectangle.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the rectangle BAND = l × b sq.units = 7.2 × 6.7 cm² = 48.24 cm²
Question 3.
Construct the following squares with the given measurements and also find their area.
(i) EAST, EA = 6.5 cm
Solution:
Given side = 6.5 cm
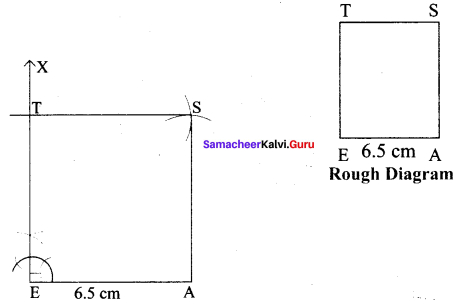
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment EA = 6.5 cm.
(ii) At E, constructed EX ⊥ EA.
(iii) With E as centre, drawn an arc of radius 6.5 cm and let it cut EX at T.
(iv) With A and T as centre drawn an arc of radius 6.5 cm each and let them cut at S.
(v) Joined TS and AS.
(vi) EAST is the required square.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the square EAST = a² sq.units = 6.5 × 6.5 cm² = 42.25 cm²
(ii) WEST, ST = 6 cm
Solution:
Given side of the square = 6 cm
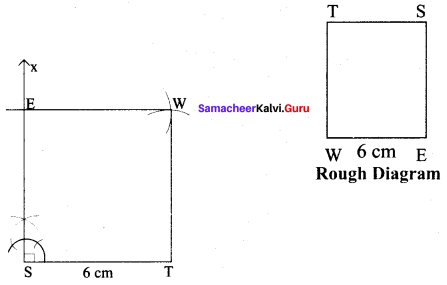
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment ST = 6 cm.
(ii) At S, constructed SX ⊥ ST.
(iii) With S as centre, drawn an arc of radius 6 cm and let it cut SX at E.
(iv) With E and T as centre drawn an arc of radius 6 cm each and let them cut at W.
(v) Joined TW and EW.
(vi) WEST is the required square.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the square WEST = a² sq.units = 6 × 6 cm² = 36 cm²

(iii) BEST, BS = 7.5 cm
Solution:
Given diagonal = 7.5 cm
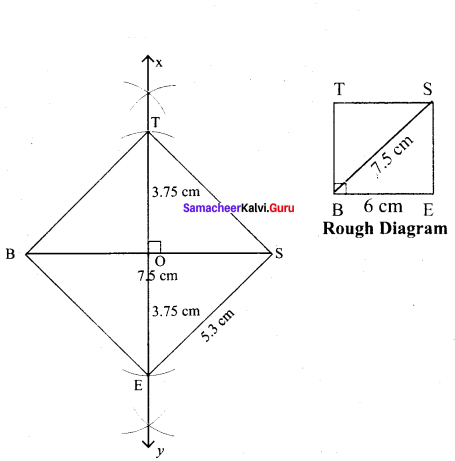
Steps :
(i) Drawn a line segment BS = 7.5 cm.
(ii) Drawn the perpendicular bisector XY to BS. Let it bisect BS at O.
(iii) With O as centre, drawn an arc of radius 3.7 cm on either side of O which cut OX at T and OY at E
(iv) Joined BE, ES, ST and BT.
(v) BEST is the required square.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the square BEST = a² sq.units = 5.3 × 5.3 cm² = 28.09 cm²
(iv) REST, ET = 8 cm
Solution:
Given diagonal = 8 cm
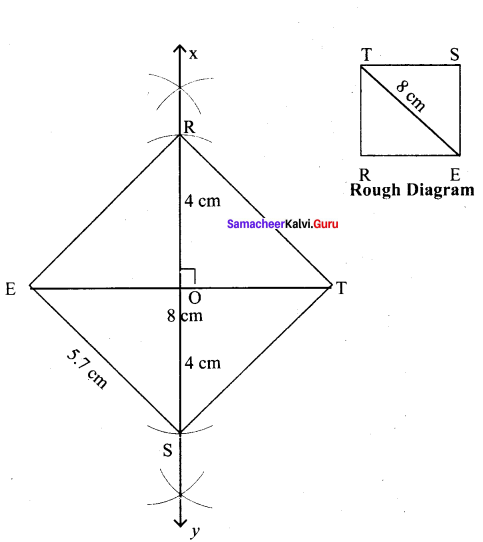
Steps:
(i) Drawn a line segment ET = 8 cm.
(ii) Drawn the perpendicular bisector XY to ET. Let it bisect ET at O.
(iii) With O as centre, drawn an arc of radius 4 cm on either side of O which cut OX at R and OY at S
(iv) Joined ES, ST, TR and ER.
(v) REST is the required square.
Calculation of Area :
Area of the square REST = a² sq.units = 5.7 × 5.7 cm² = 32.49 cm²
![]()
![]()

























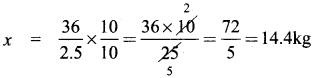
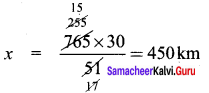

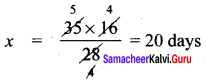
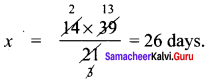







 +
+