Students can Download Economics Chapter 11 Tamil Nadu Economy Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Tamil Nadu Economy
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Tamil Nadu Economy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In health index, Tamil Nadu is ahead of
(a) Kerala
(b) Punjab
(c) Gujarat
(d) all the above
Answer:
(c) Gujarat
![]()
Question 2.
In sex ratio, Tamil Nadu ranks
(a) first
(b) second
(c) third
(d) fourth
Answer:
(c) third
Question 3.
Tamil Nadu is rich in
(a) Forest resource
(b) human resource
(c) mineral resource
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) human resource
Question 4.
The main source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu is
(a) river
(b) tank
(c) well
(d) canals
Answer:
(c) well
Question 5.
Knitted garment production is concentrated in
(a) Coimbatore
(b) Tiruppur
(c) Erode
(d) Karur
Answer:
(b) Tiruppur
Question 6.
Which of the following is wrongly matched?
(a) Gateway of Tamil Nadu – Thoothukudi
(b) Home textile city – Erode
(c) Steel city – Salem
(d) Pump city – Coimbatore
Answer:
(b) Home textile city – Erode
Question 7.
Which of the following cities does not have international airport?
(a) Madurai
(b) Tiruchirappalli
(c) Paramakudi
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(c) Paramakudi
Question 8.
TN tops in the production of the following crops except
(a) Banana
(b) Coconut
(c) plantation crops
(d) cardamom
Answer:
(d) cardamom
Question 9.
Largest area of land is used in the cultivation of
(a) Paddy
(b) sugarcane
(c) Groundnut
(d) Coconut
Answer:
(a) Paddy
![]()
Question 10.
In literacy rate, TN ranks
(a) second
(b) fourth
(c) sixth
(d) eighth
Answer:
(d) eighth
Question 11.
In investment proposals filed by MSMEs, TN ranks
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(a) I
Question 12.
Which district in TN has the highest sex ratio?
(a) Nagapattinam
(b) Nilgiris
(c) Tiruchirapalli
(d) Thanjavur
Answer:
(b) Nilgiris
Question 13.
Which district has the lowest child sex ratio?
(a) Madurai
(b) Theni
(c) Ariyalur
(d) Cuddalore
Answer:
(c) Ariyalur
Question 14.
Which Union Territory has the highest sex ratio?
(a) Chandigarh
(b) Pondicherry
(c) Lakshadeep
(d) Andaman Nicobar
Answer:
(b) Pondicherry
Question 15.
The largest contribution to GSDP in Tamil Nadu comes from
(a) agriculture
(b) industry
(c) mining
(d) services
Answer:
(d) services
Question 16.
In human development index, TN is ranked
(a) Second
(b) fourth
(c) sixth
(d) third
Answer:
(d) third
Question 17.
SPIC is located in
(a) Chennai
(b) Madurai
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Pudukottai
Answer:
(c) Tuticorin
Question 18.
The TICEL park is
(a) Rubber Park
(b) Textile park
(c) Food park
(d) Bio
Answer:
(d) Bio
Question 19.
In India’s total cement production, Tamil Nadu ranks
(a) third
(b) fourth
(c) first
(d) second
Answer:
(a) third
![]()
Question 20.
The Headquarters of Southern Railway is at
(a) Tiruchirappalli
(b) Chennai
(c) Madurai
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(b) Chennai
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
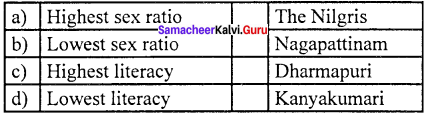
State any two districts with favourable sex ratio. Indicate the ratios.
Answer:
Population Growth in Tamil Nadu: At a glance (2011 census)
1. Sex Ratio (per 1000 males) District with highest:
The Nilgiris (1041 females) Thanjavur (1031 females) Nagapattinam (1025 females)
2. Sex Ratio (per 1000 males) District with Lowest:
Theni (900 females) Dharmapuri (946 females)
Question 22.
Define GSDP.
Answer:
The Gross State Domestic Product refers to the total money value of all the goods and services produced annually in the state.
Question 23.
Mention any four food crops which are favourable to Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Rice: Tamil Nadu is India’s second-biggest producer of rice.
- Banana and Coconut: Tamil Nadu ranks first in the production of Banana and coconut.
- Cashewnut: Tamil Nadu ranks second in the production of cashew nut.
- Pepper: Tamil Nadu ranks third in the production of pepper.
- Sugarcane: Tamil Nadu ranks fourth in the production of Sugarcane.
Question 24.
What are major ports in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Major ports at Chennai, Ennore and Tuticorin Intermediate port in Nagapattinam.
Question 25.
What is heritage tourism?
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu has since ancient past been a hub for tourism.
- In recent years, the state has emerged as one of the leading tourist destinations for both domestic and foreign tourists.
- Tourism in Tamil Nadu is promoted by Tamil Nadu Tourism Development Corporation (TTDC), a Government of Tamil Nadu undertaking.
- The State currently ranks the highest among the Indian States with about 25 crore arrivals (in 2013). Approximately 28 lakh foreign and 11 crore domestic tourists visit the State.
Question 26.
What are the nuclear power plants in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
The Kalpakkam Nuclear power plant and the Koodankulam Nuclear power plant.
![]()
Question 27.
Define Micro industry.
Answer:
- Micro, small and medium Enterprises are MSMEs that produce a wide variety of products in almost all sectors.
- The prominent among them are the engineering, electrical, chemicals, plastics, steel, paper, matches, textiles, hosiery, and garments sector.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 28.
Write a note on mineral resources in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Mineral resources in Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu has a few mining projects based on Titanium, Lignite, Magnesite, Graphite, Limestone, Granite and Bauxite.
- The first one is the Neyveli Lignite Corporation that has led the development of large industrial complex around Neyveli in the Cuddalore district with Thermal Power Plants, Fertilizer and carbonization plants.
- Magnesite mining is at Salem from which mining of Bauxite ores are carried out at Yercaud and this region is also rich in Iron ore at Kanjamalai.
- Molybdenum is found in Karadikuttam in Madurai district.
Question 29.
Explain GSDP in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) refers to the total money value of all the goods and services produced annually in the state.
- Tamil Nadu is the second-largest economy in India with a GSDP of $ 207.8 billion in 2016 – 2017 according to the Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Tamil Nadu.
- The GSDP of Tamil Nadu is equal to the GDP of Kuwait on nominal terms and the GDP of UAE on PPP terms. Per capita, GSDP would be better for intercountry or interstate comparisons.
- Tamil Nadu GSDP = $207.8 billion in 2016 – 17.
Question 30.
Describe development of textile industry in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Development of textile industry in Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu is the largest textile hub of India. Tamil Nadu is known as the “Yam Bowl” of the country.
- Tamil Nadu accounts for 41% of India’s cotton yam production.
- It produce direct employment to 35 million people.
- It contributes 4% of GDP and 35% of gross export earnings.
- The textile sector contributes to 14% of the manufacturing sector.
![]()
Question 31.
Compare productivity of any two food crops between Tamil Nadu and India.
Answer:
- Asia result of Government’s efforts Tamil Nadu tops in productivity, in food crops as well as non-food crops, among the states in India.
- Among Indian states Tamil Nadu ranks first in maize, Kambu, Groundnut, Oil seeds and Cotton.
- Second in rice and coconut.
- Third in Sugarcane, Sunflower and Jowar.
Question 32.
Explain the prospect for the development of tourism.
Answer:
- Tourism in Tamil Nadu is promoted by Tamil Nadu Tourism Development Corporation (TTDC), a Government of Tamil Nadu undertaking.
- Tamil Nadu has since ancient past been a hub for tourism. In recent years, the state has emerged as one of the leading tourist destinations for both domestic and foreign tourists.
- The state currently ranks the highest among Indian states with about 25 crore arrivals in 2013.
- Approximately 28 lakh foreign and 11 crore domestic tourists visit the State.
Question 33.
What are the renewable sources of power in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Renewable sources of power in Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu is the fore front of all other Indian States in installed capacity.
- Muppandal wind farm is a renewable energy source, supplying the villagers with electricity for work.
- Wind farms were built in Nagercoil and Tuticorin apart from already existing ones around Coimbatore, Pollachi, Dharapuram, and Udumalaipettai.
- Wind energy contributes 2% of the total power output of India.
- Tamil Nadu tops in solar power generation in India.
- There are about 20 hydro electric units in Tamil Nadu.
Question 34.
Describe the performance of Tamil Nadu economy in health.
Answer:
Performance of Tamil Nadu economy in health:
- Tamil Nadu has a three-tier health infrastructure comprising hospitals, primary health centres, health units, community health centres and sub-centres.
- Tamil Nadu has placed third in health index as per the NITIAAYOG report.
- The neo natal mortality rate is 14 which is lower than many other states.
- The under 5 mortality has dropped from 21 in 2014 to 20 in 2015.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 35.
Describe the qualitative aspects of population.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu stands sixth in population with 7.21 crore against India’s 121 crores as per 2011 census. Tamil Nadu’s population is higher than that of several countries according to UN Report. Tamil Nadu population 7.2 [crores] in 2017.
Density:
- The density of population which measures population per sq.km is 555 [2011] against 480 [2001].
- Tamil Nadu ranks 12th in density among the Indian States and overall it is 382 for India.
Urbanization:
- Tamil Nadu is the most urbanized state with 48.4% of urban population against 31.5% for India as a whole.
- The State accounts for 9.61% of total urbanites in India against 6% share of total population.
Sex Ratio [Numbers of females per 1000 males].
- A balanced sex ratio implies improvement in the quality of life of the female population.
- The sex ratio in Tamil Nadu is nearing balance with 995 which is far better compared to most of the States and all India level.
- Tamil Nadu stands third next only to Kerala State and Puducherry Union Territory in sex ratio.
Question 36
Explain the various sources of energy in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu tops in power generation among the southern states. Tamil Nadu is in the forefront of all other Indian states in installed capacity.
Muppandal wind farm is a renewable energy source, Supplying the villagers with electricity for work.
1. Nuclear energy : The Kalpakkam and the Koddankulam Nuclear Power Plants are the major nuclear energy plants for the energy grid.
2. Thermal power: In Tamil Nadu the share of thermal power in total energy sources is very high and the thermal power plants are at Athippattu, Ennore, Mettur, Neyveli and Thoothukudi.
3. Hydel energy : There are about 20 hydro electric units in Tamil Nadu. The prominent units are Hundah, Mettur, Periyar, Maravakandy, Parson valley etc.
4. Solar energy : Tamil Nadu tops in solar power generation in India. Southern Tamil Nadu is considered as one of the most suitable regions the country for developing solar power projects.
5. Wind energy : Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India.
The state has very high quality of off shore wind energy potential off the Tirunelveli coast and Southern Thoothukudi and Rameswaram coast.
![]()
Question 37.
Explain the public transport system in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Transport: Tamil Nadu has a well-established transportation system that connects all parts of the State. This is partly responsible for the investment in the State.
Tamil Nadu is served by an extensive road network in terms of its spread and quality, providing links between urban centers, agricultural market-places, and rural habitations in the countryside. However, there is scope for improvement.
Road Transport:
- There are 28 national highways in the State, covering a total distance of 5,036 km.
- The State has a total road length of 167,000 km, of which 60,628 km are maintained by the Highways Department.
Rail Transport:
- Tamil Nadu has a well-developed rail network as part of Southern Railway, headquartered in Chennai.
- Tamil Nadu has a total railway track length of 6,693 km and there are 690 railway stations in the State.
- Main rail junctions in the State include Chennai, Coimbatore, Erode, Madurai, Salem, Tiruchirapalli, and Tirunelveli.
- Chennai has a well-established suburban railway network, a Mass Rapid Transport system, and is currently developing a Metro System, with its first underground stretch operational since May 2017.
Air Transport:
- Tamil Nadu has four major international airports.
- Chennai International Airport is currently the third-largest airport in India.
- Other international airports in Tamil Nadu include Coimbatore International Airports, Madurai International Airport, and Tiruchirapalli International Airport.
- It also has domestic airports at Tuticorin, Salem, and Madurai.
- Increased industrial activity has given rise to an increase in passenger traffic as well as freight movement which has been growing at over 18% per year.
Ports:
- Tamil Nadu has three major ports; one each at Chennai, Ennore, and Tuticorin, as well as one intermediate port in Nagapattinam, and 23 minor ports.
- The ports are currently capable of handling over 73 million metric tonnes of cargo annually (24% share of India).
- All the minor ports are managed by the Tamil Nadu Maritime Board, Chennai Port.
- This is an artificial harbour and the second principal port in the country for handling containers.
- It is currently being upgraded to have a dedicated terminal for cars capable of handling 4,00,000 vehicles.
- Ennore Port was recently converted from an intermediate port to a major port and handles all the coal and ore traffic in Tamil Nadu.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Tamil Nadu Economy Additional Questions and Answers
Part-A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
Molybdenum is found in the _____ district of Tamil Nadu.
(a) Chennai
(b) Madurai
(c) Tirunelveli
(d) Vellore
Answer:
(b) Madurai
Question 2.
Tamil Nadu has _____ Population as against 121 crores of India.
(a) 7.12 crore
(b) 1.72 crore
(c) 7.21 crore
(d) 1.27 crore
Answer:
(c) 7.21 crore
![]()
Question 3.
Tamil Nadu’s per capital income is _____
(a) 1100 dollar
(b) 2200 dollar
(c) 3360 dollar
(d) 4400 dollar
Answer:
(d) 4400 dollar
Question 4.
Gross state domestic product is
(a) GSDP
(b) MMR
(c) GDP
(d) IMF
Answer:
(a) GSDP
Question 5.
The Detroit of Asia is _____
(a) Bengaluru
(b) Madurai
(c) Coimbatore
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(d) Chennai
Question 6.
_____ is Tamil Nadu’s steel city
(a) Chennai
(b) Karur
(c) Salem
(d) Namakkal
Answer:
(c) Salem
Question 7.
_____ is famous for the bus body building.
(a) Karur
(b) Trichy
(c) Vellore
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(a) Karur
Question 8.
_____ is the yarn bowl of India.
(a) Orissa
(b) Kerala
(c) Andhra
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(d) Tamil Nadu
![]()
Question 9.
Gateway of Tamil Nadu is _____
(a) Thoothukudi
(b) Chennai
(c) Coimbatore
(d) Ranipet
Answer:
(a) Thoothukudi
Question 10.
_____ is the knitting city.
(a) Erode
(b) Karur
(c) Namakkal
(d) Tirupur
Answer:
(d) Tirupur
Question 11.
Which of the following is wrongly matched?
(a) SAIL – Salem
(b) The Pumpcity – Coimbatore
(c) BHEL – Trichy
(d) Knitting City – Karur
Answer:
(d) Knitting City – Karur
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
Question 1.
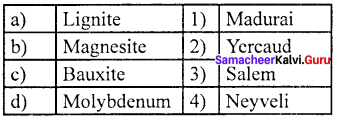
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 3 4 2 1
Answer:
(a) 4 3 2 1
Question 2.
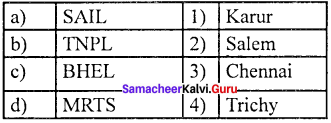
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 2 1 3 4
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 3.
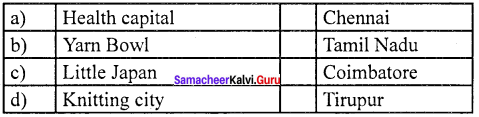
Answer:
(c) Little japan (iii) Coimbatore
Question 4.
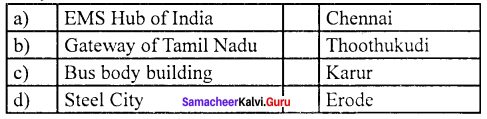
Answer:
(d) Steel City (iv) Erode
Choose the correct statement
Question 5.
(a) Tamil Nadu is the third largest contributor to India’s GDP
(b) Tamil Nadu ranks second in coconut production.
(c) Tamil Nadu ranks first in cement production
(d) Chennai is called as Detroit of Asia.
Answer:
(d) Chennai is called as Detroit of Asia.
![]()
Question 6.
(a) The population density of T.N is 480 as per 2011 census,
(b) There are 30 national highways in Tamil Nadu.
(c) Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India
(d) The headquarters of southern railway is at Trichy.
Answer:
(c) Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 7.
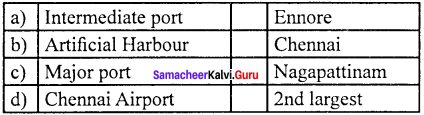
Answer:
(b) Artificial Harbour (ii) Chennai
Question 8.
Answer:
(a) Highest sex ratio (i) The Nilgiris
Question 9.
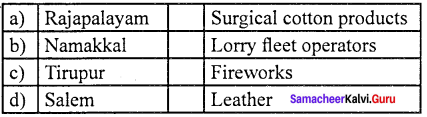
Answer:
(a) Rajapalayam (i) Surgical cotton product
Pick the odd one out
Question 10.
(a) Coimbatore
(b) Erode
(c) Madurai
(d) Trichy
Answer:
(b) Erode
Question 11.
(a) Coconut
(b) Groundnut
(c) Rice
(d) Sugarcane
Answer:
(c) Rice
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 12.
(a) Chennai is referred as banking capital of India.
(b) Tamil Nadu ranks first in maize production.
(c) Tamil Nadu ranks 3rd in human development Index.
(d) Tamil Nadu is the third-largest contributor to India’s GDP
Answer:
(d) Tamil Nadu is the third-largest contributor to India’s GDP
Question 13.
(a) Tamil Nadu has eight agro-climatic zones
(b) There are 17 river basins in Tamil Nadu.
(c) The tertiary sector is the major contributor to Tamil Nadu’s GSDP.
(d) Tamil Nadu is the second-largest economy in India.
Answer:
(d) Tamil Nadu is the second-largest economy in India.
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 14.
Tamilnadu has _______ population as against 121 crore of India
(a) 7.12 crore
(b) 1.72 crore
(c) 7.21 crore
(d) 1.27 crore
Answer:
(c) 7.21 crore
![]()
Question 15.
Tamil Nadu’s per capita income is ______
(a) 1100 dollar
(b) 2200 dollar
(c) 3360 dollar
(d) 4400 dollar
Answer:
(b) 2200 dollar
Question 16.
Gross state domestic product is ______
(a) GSDP
(b) MMR
(c) GDP
(d) IMF
Answer:
(a) GSDP
Question 17.
IMR is the number of mortality before completing
(a) 1 year of age
(b) 5 years of age
(c) 3 years of age
(d) 10 years of age
Answer:
(a) 1 year of age
Question 18.
The world’s biggest bagasse based paper mill is at ______
(a) Trichy
(b) Karur
(c) Coimbatore
(d) Erode
Answer:
(b) Karur
Question 19.
Every year India international leather fair is hosted at ______
(a) Coimbatore
(b) Madurai
(c) Chennai
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(c) Chennai
Question 20.
______ wind farm is a renewable energy source
(a) Nagapattinam
(b) Valapandal
(c) Nagercoil
(d) Muppandal
Answer:
(d) Muppandal
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
How can you calculate per capita income?
Answer:
Percapita income = ![]()
Question 2.
Define infant mortality rate
Answer:
IMR is the number of mortality before completing 1 year of age.
Question 3.
What is cash – deposit ratio?
Answer:
C-D ratio is the ratio of bank advances to deposits.
Question 4.
What is the position of Tamil Nadu in automotives?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu has 28% share each in automotive and auto components industries, 19% in the trucks segment and 18% each in passenger cars and two-wheelers.
Question 5.
Why is Sivakasi called Little Japan?
Answer:
Sivakasi is a leader in the areas of printing, fireworks, and safety matches. It contributes 80% of India’s fireworks production and 60% of India’s total offset printing solution. As there are too many industries in Sivakasi it is called Little Japan.
Question 6.
Name the cement manufacturing places of Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Ariyalur, Virudhunagar, Coimbatore, and Tirunelveli.
Question 7.
What is the measure of unemployment in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu ranks 22nd with unemployment rate of 42 per 1000.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in one Paragraph
Question 1.
Explain about unemployment and poverty in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Unemployment: Tamil Nadu ranks 22nd with unemployment rate of 42 per 1000 as against national average of 50.
Poverty:
- Tamil Nadu is one of India’s richest states.
- Since 1994, the state has seen a steady decline in poverty.
- Tamil Nadu has lower levels of poverty than most other states in the country.
Question 2.
Explain about water resources of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Water resources of Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu is not endowed with rich natural resources compared to other states.
- It accounts for three percent of water sources, four percent of land area against six percent of population.
- North east monsoon is the major source of rainfall followed by the south west monsoon.
- There are 17 river basins in Tamil Nadu. The main rivers are Palar, Cheyyar, Ponnaiyar, Cauvery, Bhavani, Vaigai, Chittar, Tamiraparani, Vellar, Noyyal, Siruvani, Gundar, Vaipar etc.
- Wells are the largest source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the water resources of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Water resources of Tamil Nadu:
- Ranipet, Ambur, Vaniyambadi – Leather
- Salem . – Powerlooms, Home textiles, Steel, Sago
- Sankagiri – Lorry fleet operators
- Tiruchengode – Borewell drilling services
- Naakkal – Transportation Poultry
- Karur – Coach-building, Powerlooms
- Erode – Powerlooms, Turmeric
- Coimbatore – Spinning mills, Engineering industries
- Tirupur – Knitwear, Readymade garments
- Rajapalayam – Surgical cotton products
- Sivakasi – Safety matches, Fireworks, Printing
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 1.
Elaborate the highlights of Tamil Nadu economy.
Answer:
Highlights of Tamil Nadu economy:
- Growth of GSDP in Tamil Nadu has been among the fastest in India since 2005.
- Poverty reduction is faster than that in many other states.
- It contains a smaller proportion of India’s poor population.
- Second largest contributor to India’s GDP.
- 3rd in Human Development Index.
- Ranks 3rd in terms of invested capital and value of total industrial output.
- Ranks first among the states in terms of invested capital and value of total industrial output.
- Third in the health index
- Has highest Gross Enrollment Ratio in higher education.
- Has the largest number of engineering colleges.
- Has emerged as a major hub for renewable energy.
- Has highest credit deposit ratio in commercial and cooperative banks.
- Ranks first on investment proposals filled by MSMEs.
Question 2.
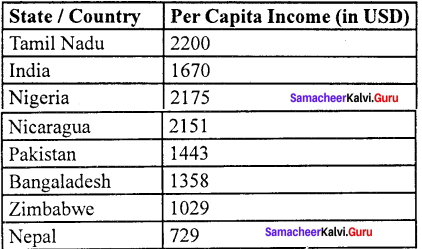
Compare the per capital income of Tamil Nadu with other countries.
Answer:
- The per capita GSDP of Tamil Nadu is $ 2200 which is higher than that of many other states in India.
- Per capita, the GSDP of Tamil Nadu is nearly 1.75 times higher than the national average, as per 2018 data.
- In terms of the per capital income in Tamil Nadu was Rs. 1,03,600 in 2010-11 and it has increased to Rs. 1,88,492 in 2017-18 as per the budget figures 2018.
Question 3.
Explain the role of MSMEs in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Role of MSMEs in Tamil Nadu:
- The MSME enterprises are classified as manufacturing and service enterprises based on the investment in plant, machinery and equipment MSMED act 2006.
- Tamil Nadu accounts of 15,07% micro, small and medium enterpriser which is highest in the country.
- There are 6.89 lakhs registered MSMEs producing over 8000 varieties of product for investment more than Rs. 32,008 crore.
- The prominent products of MSMEs are the engineering, electrical, chemicals, plastics, steel paper, matches, textiles, hosiery and garments sector.
- Around 15.61 lakh entrepreneurs have registered, providing employment opportunities to about 99.7 lakhs persons with a total investment of Rs. 1,68,331 crore.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain about banks in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
In Tamil Nadu, Nationalised banks account for 52% with 5,337 branches, private commercial banks 30% (3060) branches, state bank of India and its associates 13% (1,364) RRBs 5% (537) branches and the remaining 22 foreign bank branches.
Deposits of the banks:
- Total deposits of the banks in Tamil Nadu increased by 14.32% by March 2017 and touched Rs. 6,65,068.59 crores.
- Total credits of the banks increased by 13.50% by March 2017 and touched Rs. 6,95,500.31 crores.
Advances of the banks:
- The share of priority sector advances stands at 45.54% as against the national average of 40%
- Primary sector advances stand at 45.54%
- Agricultural advances stands at 19.81% on March 2017.
- Banks in Tamil Nadu has the highest credit deposit ratio of 119.15% in the country.