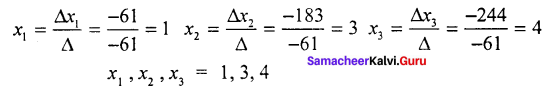Students can Download Economics Chapter 12 Mathematical Methods for Economics Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 12 Mathematical Methods for Economics
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Mathematical Methods for Economic Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Mathematical Economics is the integration of ____________
(a) Mathematics and Economics
(b) Economics and Statistics
(c) Economics and Equations
(d) Graphs and Economics
Answer:
(a) Mathematics and Economics
Question 2.
The construction of demand line or supply line is the result of using ____________
(a) Matrices
(b) Calculus
(c) Algebra
(d) Analytical Geometry
Answer:
(d) Analytical Geometry
![]()
Question 3.
The first person used the mathematics in Economics is ____________
(a) Sir William Petty
(b) Giovanni Ceva
(c) Adam Smith
(d) Irving Fisher
Answer:
(a) Sir William Petty
Question 4.
Function with single independent variable is known as ____________
(a) Multivariate Function
(b) Bivariate Function
(c) Univariate Function
(d) Polvnomial Function
Answer:
(c) Univariate Function
Question 5.
A statement of equality between two quantities is called ____________
(a) Inequality
(b) Equality
(c) Equations
(d) Functions
Answer:
(c) Equations
Question 6.
An incremental change in dependent variable with respect to change in independent variable is known as ____________
(a) Slope
(b) Intercept
(c) Variant
(d) Constant
Answer:
(a) Slope
![]()
Question 7.
(y – y1) = m (x – x1) gives the ____________
(a) Slope
(b) Straight line
(c) Constant
(d) Curve
Answer:
(b) Straight line
Question 8.
Suppose D = 50 – 5P. When D is zero then ____________
(a) P is 10
(b) P is 20
(c) P is 5
(d) Pis-10
Answer:
(a) Pis 10
Question 9.
Suppose D = 150 – 50P. Then, the slope is
(a) -5
(b) 50
(c) 5
(d) – 50
Answer:
(d) – 50
Question 10.
Suppose determinant of a matrix A = 0, then the solution ____________
(a) Exists
(b) Does not exist
(c) Is infinity
(d) Is zero
Answer:
(b) Does not exist
Question 11.
State of rest is a point termed as ____________
(a) Equilibrium
(b) Non – Equilibrium
(c) Minimum Point
(d) Maximum Point
Answer:
(a) Equilibrium
![]()
Question 12.
Differentiation of constant term gives ____________
(a) one
(b) zero
(c) infinity
(d) non – infinity
Answer:
(b) zero
Question 13.
Differentiation of xn is ____________
(a) nx (n – 1)
(b) nx (n + 1)
(c) zero
(d) one
Answer:
(a) nx (n – 1)
Question 14.
Fixed Cost is the ____________ term in cost function represented in mathematical form.
(a) Middle
(b) Price
(c) Quantity
(d) Constant
Answer:
(d) Constant
Question 15.
The first differentiation of Total Revenue function gives ____________
(a) Average Revenue
(b) Profit
(c) Marginal Revenue
(d) Zero
Answer:
(c) Marginal Revenue
Question 16.
The elasticity of demand is the ratio of ____________
(a) Marginal demand function and Revenue function
(b) Marginal demand function to Average demand function
(c) Fixed and variable revenues
(d) Marginal Demand function and Total demand function
Answer:
(b) Marginal demand function to Average demand function
![]()
Question 17.
If x + y = 5 and x – y = 3 then, Value of x ____________
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 16
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 18.
Integration is the reverse process of
(a) Difference
(b) Mixing
(c) Amalgamation
(d) Differentiation
Answer:
(d) Differentiation
Question 19.
Data processing is done by ____________
(a) PC alone
(b) Calculator alone
(c) Both PC and Calculator
(d) Pen drive
Answer:
(c) Both PC and Calculator
Question 20.
The command Ctrl + M is applied for ____________
(a) Saving
(b) Copying
(c) getting new slide
(d) deleting a slide
Answer:
(c) getting new slide
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
If 62 = 34 + 4x what is x?
solution:
If 62 = 34 + 4x what is x
Given:
62 = 34 + 4x
34 + 4x = 62
4x = 62 – 34
4x = 28
x = \(\frac { 28 }{ 4 }\)
x = 7
![]()
Question 22.
Given the demand function q = 150 – 3p, derive a function for MR.
Solution:
Given:
q = 150 – 3p
\(\frac { dq }{ dq }\) = 0 – 3 (1)
\(\frac { dq }{ dq }\) = – 3
Revenue = price × quantity = p (150 – 3p)
= p (150 – 3p)
= 150p – 3p2
MR = \(\frac { dq }{ dq }\) = 150 \(\frac { dq }{ dq }\) -6p \(\frac { dq }{ dq }\)
= 150 (\(\frac { – 1 }{ 3 }\)) – 6p (\(\frac { – 1 }{ 3 }\))
= – 50 + 2p
= – 50 = 2 (\(\frac { 150 – q }{ 3 }\))
= 50 + 100 + \(\frac { – 2 q }{ 3 }\)
= 50 – \(\frac { 2 q }{ 3 }\)
= 50 – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) (150 – 3p)
MR = 2p – 50
Question 23.
Find the average cost function where TC = 60 + 10x +15x2
Solution:
Given:
Formula = \(\frac{TC}{x}\)
Average cost function = \(\frac{60}{x}\) + \(\frac{10x}{x}\) + \(\frac { 15x^{ 2 } }{ x } \)
Average cost = \(\frac{60}{x}\) + 10 + 15x
Question 24.
The demand function is given by x = 20 – 2p – p2 where p and x are the price and the quantity respectively. Find the elasticity of demand for p = 2.5.
Solution:
Given:
x = 20 – 2p – p2
p = 2.5
ed = (\(\frac { p }{ x }\)) (\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\))
If p = 2.5 then x,
x = 20 – 2 (2.5) – (2.5)2
= 20 – 5 – (6.25)
= 15 – 6.25
x = 8.75
Here x = 20 – 2p – p2
\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\) = 0 – 2 (1) – 2p
= -2 – 2p
If P = 2.5 then
\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\) = -2 – 2 (2.5)
= -2 – 5
\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\) = – 7
ed = \(\frac { -2.5 }{ 8.75 }\) × – 7
= 0.2857 × – 7
ed = 2
![]()
Question 25.
Suppose the price p and quantity q of a commodity are related by the equation q = 30 – 4p – p2
find :
- ed at p = 2
- MR
Solution:
Given:
q = 30 – 4p – p2
1. ed = (\(\frac { p }{ x }\))(\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\))
If P = 2 then
x = 30 – 4 (2) – 22
= 30 – 8 – 4
=20 – 12
x = 18
\(\frac { dx }{ dp }\) =30 – 4p – p2
= 0 – 4 – 2p
= 0 – 4 – 2 (2)
= -4 -4
= -8
ed = \(\frac { 2 }{ 18 }\) (-8)
x = – \(\frac { 16 }{ 18 }\)
ed = – 0.88
2. MR
TR = p ×q
TR = p (30 – 4p – p2)
= 30p – 4p2 – p3
MR = \(\frac { d(TR) }{ dp }\)
= 30 – 8p – 3p2
If p = 2
MR = 30 – 8 (2) – 3 (2)2
= 30 – 16 12
MR = 2
Question 26.
What is the formula for elasticity of supply if you know the supply function?
Solution:
Elasticity of supply = (\(\frac { p }{ q }\)) (\(\frac { dq }{ dp }\))
Question 27.
What are the main menus of MS Word?
Answer:
- Home menu
- Insert
- Page layout
- Reference
- Review
- View
- Print layout
- Outline
- Task pane
- Toolbars
- Header and footer
- Footnotes
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 28.
Illustrate the uses of Mathematical Methods in Economics.
Answer:
- Mathematical Methods help to present the economic problems in a more precise form.
- Mathematical Methods help to explain economic concepts.
- Mathematical Methods help to use a large number of variables in economic analyses.
- Mathematical Methods help to quantify the impact or effect of any economic activity implemented by the Government or anybody. There are of course many other uses.
![]()
Question 29.
Solve for A: quantity demanded if 16x – 4 = 68 + 7x.
Solution:
Given:
16x – 4 = 68 + 1x
16x – 7x = 68 + 4
9x = 72
x = (\(\frac { 72 }{ 9 }\))
x = 8
Question 30.
A firm has the revenue function R = 600q – 0.03q2 and the cost function is C = 150q + 60,000, where q is the number of units produced. Find AR, AC, MR and MC.
Solution:
Given:
(I) Average Revenue = \(\frac{R}{q}\)
\(\frac { 600q-0.03q^{ 2 } }{ q } \) = \(\frac{600q}{q}\) – \(\frac { 0.03q^{ 2 } }{ q } \)
AR = 600 – 0.03q
(II) Average Cost = \(\frac{C}{q}\)
= \(\frac{150q}{q}\) + \(\frac{60000}{q}\)
AC = 150 + \(\frac{60000}{q}\)
(III) Marginal Revenue = \(\frac{dR}{dq}\)
R = 600q – 0.03q2
\(\frac{dR}{dq}\) = 600 – (0.03) (2q)
MR = 600 – 0.06q
(IV) Marginal Cost = \(\frac{dC}{dq}\)
C = 150q + 60000
MC = 150
Question 31.
Solve the following linear equations by using Cramer’s rule.
x1 – x2 + x3 = 2
– x1 – x2 – x3 = 0
– x1 – x2 – x3 = – 6
Solution:
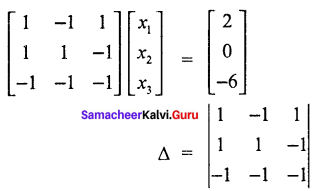
= 1 (- 1 – 1) + 1 (- 1 – 1) + 1 (- 1 + 1)
= 1(- 2) + 1 (0)
∆ = – 2 – 2
∆ = – 2 – 2
∆ = – 4
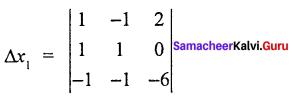
= 2 (- 1 – 1) + 1 (0 + 6) + 1 (0 – 6)
= 2 (- 2) + 1(6) + 1 (- 6)
= – 4 + 6 – 6
∆ = – 4
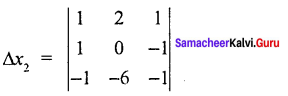
= 1 (0 – 6) – 2 (- 1 – 1)+1(- 6 + 0)
= 1 (- 6) – 2 (- 2) + 1 (- 6)
= – 6 + 4 – 6
= – 12 + 4
∆x3 = -8
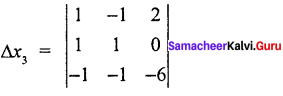
1 (- 6 + 0) + 1 (- 6 + 0) + 2 (- 1 + 1)
= 1 (- 6) + 1 (- 6) + 2 (0)
= – 6 – 6
∆x3 = – 12
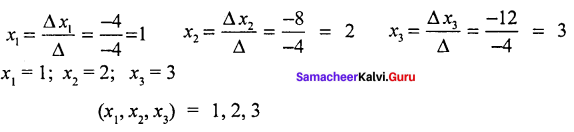
![]()
Question 32.
If a firm faces the total cost function TC = 5+ x2 where x is output, what is TC when x is 10?
Solution:
Given:
TC = 5 + x2
If x = 10
TC = 5 + 102
= 5 + 100
TC = 105
Question 33.
If TC = 2.5q3 – 13q2 + 50q + 12 derive the MC function and AC function.
solution:
Given:
TC= 2.5q3 – 13q2 + 50q + 12
Marginal cost function
MC = \(\frac { d(TC) }{ dQ }\)
= \(\frac { d }{ dq }\) [2.5q3 – 13q2 + 50q + 12]
= 2.5 (3q2) – 13 (2q) + 50 (1) + 0
MC = 7.5q – 26q + 50
Average cost AC =\(\frac { TC }{ q }\)
= \(\frac{2.5 q^{3}-13 q^{2}+50 q+12}{q}\)
= \(\frac{2.5 q^{3}}{q}\) – \(\frac{13 q^{2}}{q}\) + \(\frac { 50q }{ q }\) + \(\frac { 12 }{ q }\)
AC = 2.5q – 13q + 50 + \(\frac { 12 }{ q }\)
Question 34.
What are the steps involved in executing an MS Excel Sheet?
Answer:
MS Excel is used in data analysis by using formulas. A spreadsheet is a large sheet of paper which contains rows and columns.
To start an excel there are various options.
Click Start → Program → Microsoft Excel
Double click the MS Excel Icon from the Desktop.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 35.
A Research scholar researching the market for fresh cow milk assumes that Qt = f (Pt, Y, A, N, Pc) where Qt is the quantity of milk demanded, Pt is the price of fresh cow milk, Y is average household income, A is advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk, N is population and Pc is the price of processed pocket milk.
- What does Qt= f (Pt, Y,A,N, Pc) mean in words?
- Identify the independent variables.
- Make up a specific form for this function. (Use your knowledge of Economics to deduce whether the coefficients of the different independent variables should be positive or negative.)
Solution:
1. Qt is the function of Pt, Y, A, N, Pc
The determinants of demand are
Pt = Price of fresh cow milk.
Y = Average household income
A = Advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk
N = Population
Pc = Price of processed pocket milk.
2. Y and N are independent variables
3. Average household income and population are directly proportional to quantity demanded of cow’s milk (ie if Y and N increases Qt also increase)
Price of fresh cow milk, advertising expenditure on pocket milk and price of processed pocket milk are inversely proportional to Qt.
There
Qt = – aPt + by – CA + dN – ePc
Question 36.
Calculate the elasticity of demand for the demand schedule by using differential calculus method P = 60 – 0.2 Q where price is
- zero
- Rs.20
- Rs.40
Solution:
P = 60 – 0.2 Q
0.2 Q = 60 – P
(0.2 Q) 10 = (60 – p) 10
2 Q = 600 – 10p
Q = 300 – 5p
Given demand function Q = 300 – 5p
1. If P = 0 then Q = 300 – 5 (0)
= 300
\(\frac { dq }{ dp }\) = 300 – 5p
= 0 – 5
\(\frac { dq }{ dp }\) = – 5
ed = \(\frac { p }{ p }\)(\(\frac { dq }{ dp }\))
= \(\frac { 0 }{ 300 }\)(-5)
ed = 0
![]()
2. If p = 20 then Q = 300 = 5 (20)
= 200
ed = \(\frac { 20 }{ 200 }\) (-5)
= – \(\frac { 100 }{ 200 }\)
ed = – 0.5
3. If = 40 then Q = 300 – 5 (40)
= 300 – 200
Q = 100
ed = \(\frac { p }{ q }\)(\(\frac { dq }{ dp }\))
= \(\frac { 40 }{ 100 }\) (-5)
ed = – \(\frac { 200 }{ 100 }\)
ed = -2
Question 37.
The demand and supply functions are pd=1600 – x2 and ps = 2x2 + 400 respectively. Find the consumer’s surplus and producer’s surplus at an equilibrium point.
Answer:
At equilibrium pd = ps
1600 – x2 = 2x2 + 400
– x2 – 2x2 = 400 – 1600
– 3x2 = – 1200
x2 = \(\frac { 1200 }{ 3 }\)
x2 = 400
x = 20
If x = 20 po = 1600 – (20)2
= 1600 – 400
po = 1200
po xo = 1200 × 20
= 24000
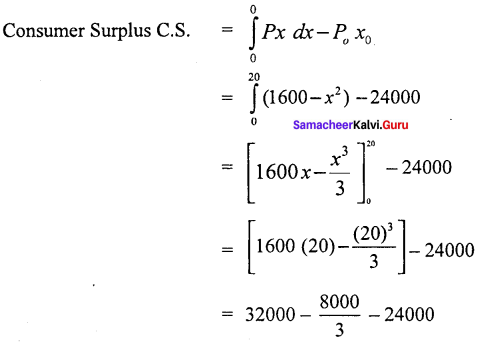
= 8000 – \(\frac { 8000 }{ 3 }\)
= \(\frac { 24000 – 8000 }{ 3 }\)
= \(\frac { 16000 }{ 3 }\)
C.S = 5333.3

Question 4.
What are the ideas of information and communication technology used in economics?
Answer:
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is the infrastructure that enables computing faster and accurate
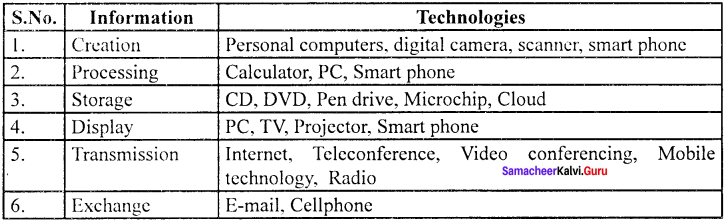
In economics the uses of mathematical and statistical tools need the support of ICT for data compiling, editing, manipulating and presenting the results.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Introduction To Micro-Economics Additional Questions and Answers
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
Question 1.
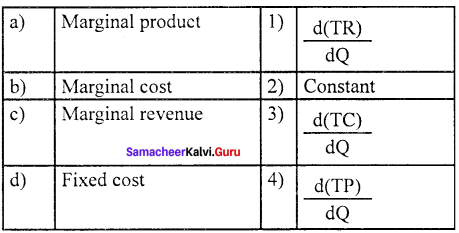
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 4 3 1 2
Answer:
(c) 3 4 2 1
![]()
Question 2.
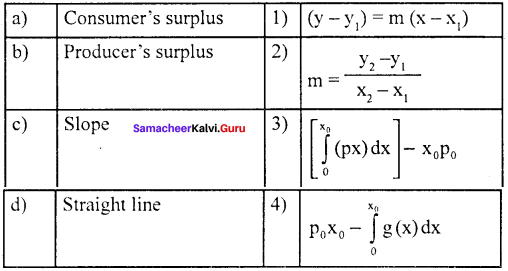
(a) 4 3 1 2
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 2 1 4
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 3.
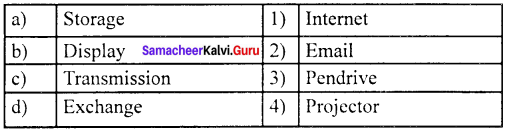
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 4 3 1 2
(d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
(b) 3 4 1 2
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 4.
(a) Differentiation of constant is zero
(b) Differentiation of xn is x
(c) Constant value is known as fixed cost
(d) x° = 1 when x = 0
Answer:
(d) x° = 1 when x = 0
Question 5.
(a) The population density of T.N is 480 as per 2011 census.
(b) There are 30 national highways in Tamil Nadu.
(c) Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India.
(d) The headquarters of southern railway is at Trichy
Answer:
(b) There are 30 national highways in Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Pick the odd one out
Question 6.
(a) Arithmetic
(b) Comparison
(c) Text concatenation
(d) Foot note
Answer:
(d) Foot note
Question 7.
(a) X = independent variable
(b) Y = dependent variable
(c) X = f (y)
(d) M – slope
Answer:
(c) X = f (y)
Choose the correct statement
Question 8.
(a) X + Y = 6 and X – Y = 2 then X = 4
(b) If D = 60 – 6P when D is 0 then P is 20
(c) In the equation 0.1 X2 + 1 OX + 100 constant = 10
(d) If Y = 6X3 then slope is 9X:
Answer:
(a) X + Y = 6 and X – Y = 2 then X = 4
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 9.
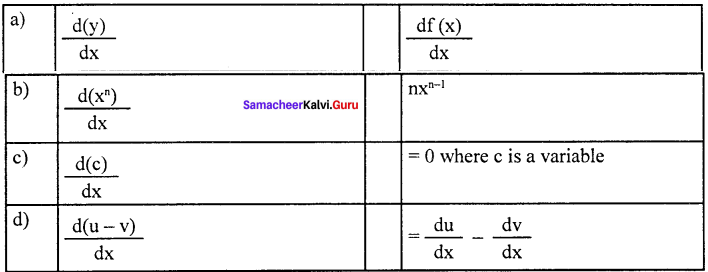
Answer:
(c) \(\frac { d(c) }{ dx }\) = 0 where c is a variable
Question 10.
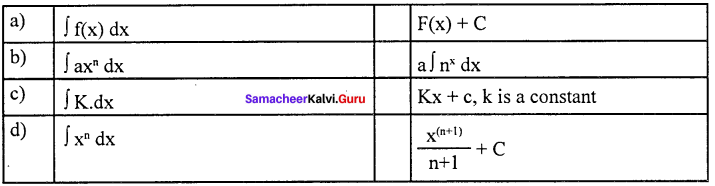
Answer:
(a) ∫f(x) dx – (i) F (x) + C
Fill in the blanks with suitable option given below
Question 11.
__________ is the first to use mathematics in economics.
(a) Giovanni Ceva
(b) William petty
(c) J.M.Keynes
(d) None
Answer:
(b) William petty
![]()
Question 12.
The formula for constructing a straight line is __________
(a) \(\mathrm{m}=\frac{\mathrm{y}_{2}-\mathrm{y}_{1}}{\mathrm{x}_{2}-\mathrm{x}_{1}}\)
(b) y = mx
(c) \(\frac { Change in x }{ Change in y }\)
(d) (y -y1) = m (x – x1)
Answer:
(d) (y -y1) = m (x – x1)
Question 13.
If the determinant ∆ = ?, then solution does not exist
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 2
(d) -1
Answer:
(b) 0
Question 14.
Power rule ∫xdx ______
(a) \(\frac{x^{2}}{n+1}\) + C
(b) \(\frac { pq }{ n + 1 }\) + C
(c) \(\frac{\mathrm{x}^{(\mathrm{n}+1)}}{\mathrm{n}+1}\) + C
(d) None
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{\mathrm{x}^{(\mathrm{n}+1)}}{\mathrm{n}+1}\) + C
Question 15.
______ is a rectangular array of numbers systematically arranged in rows and columns within brackets.
(a) Matrix
(b) Determinants
(c) Function
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Matrix
Choose the best option
Question 16.
__________ provides the solution of a system of linear equations with ‘n’ variables and ‘n’ equations
(a) Demand function
(b) Consumer’s surplus
(c) Equilibrium
(d) Cramer’s rule
Answer:
(d) Cramer’s rule
Question 17.
The first known writer to apply the mathematical method to economic problems was __________
(a) Giovanni Ceva
(b) William petty
(c) Keynes
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Giovanni ceva
Question 18.
In y = f (x) which is the independent variable
(a) f
(b) y
(c) x
(d) None
Answer:
(c) x
![]()
Question 19.
Formula for marginal cost is
(a) MC = \(\frac { d(TC) }{ dQ }\)
(b) MC = \(\frac { d(TC) }{ dP }\)
(c) MC = \(\frac { d(TC) }{ dQ }\)
(d) None
Answer:
(a) MC = \(\frac { d(TC) }{ dQ }\)
Question 20.
Function with a single independent variable are called _____
(a) Multivariate function
(b) Consumption function
(c) Simple univariate function
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Simple univariate function
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What is economic analysis?
Answer:
Economic analysis is a systematic approach to determine the optimum use of scare resources and choose available alternatives and select the best alternative to achieve a particular objective.
Question 2.
What is the slope of a straight line ?
Answer:
Slope or gradient of the line represents the ratio of the changes in vertical and horizontal lines
Question 3.
State the phases of evolution of ICT?
Answer:
- Computer
- PC
- Micro Processor
- Internet and
- Wireless links.
Question 4.
What are determinants?
Answer:
The determinant is an arrangement of the same elements of the corresponding matrix into rows and columns by enclosing vertical lines.
![]()
Question 5.
State the application of differential calculus.
Answer:
- To find the rate of change in demand with respect to price.
- To find the rate of change in income with respect to the investment.
Question 6.
What is ICT?
Answer:
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is the infrastructure that enables computing faster and accurate.
Question 7.
What is a worksheet?
Answer:
A worksheet is a table like a document containing rows and columns with data and formula
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
The marginal cost function for producing x units is y = 23 + 16.x – 3.x2 and the total cost for producing zero unit is Rs. 40. Obtain the total cost function and the average cost function.
Solution:
Given Marginal cost functions
y = 23 + 16x – 3x2
C = 40
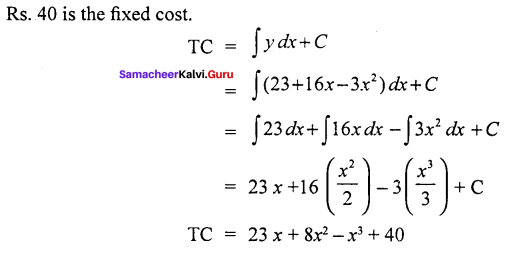
Average cost function = \(\frac { TC }{ x }\)
= \(\frac{23 x+8 x^{2}-x^{3}+40}{x}\)
AC = 23 + 8x – x + \(\frac { 40 }{ x }\)
![]()
Question 2.
Find the solution of the system of equations
5x1 + 3x2 = 30
6x1 – 2X2 = 8
Solution :
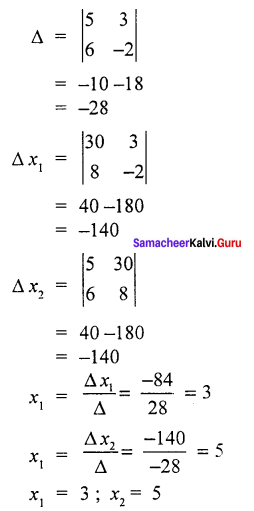
Question 3.
If the demand function is p = 35 – 2x – x2 and the demand xo is 3, what will be the consmer’s surplus
Solution:
Given:
p = 35 – 2x – x2
If x = 3 then
p = 35-2 (3) – 32
= 35 – 6 – 9
p = 20
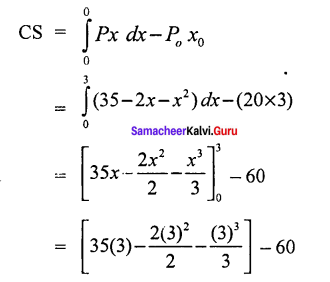
= 35 (3) – 9 – 9 – 60
= 105 – 9 – 9 – 60
CS = 27 units
Question 4.
Given the total cost function TC = 15 + 3Q2 + 7Q3 drive the marginal cost function.
Solution:
Given:
TC = 15 + 3Q2 + 7Q2
MC = \(\frac { d(15) }{ dQ }\) + \(\frac{\mathrm{d}\left(3 \mathrm{Q}^{2}\right)}{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{Q}}\) + \(\frac{\mathrm{d}\left(7 \mathrm{Q}^{3}\right)}{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{Q}}\)
= 0+ 3 (2) Q + 7 (3) Q + (3) Q2
MC = 6Q + 21 Q2
Question 5.
Find the value of the determinant of the matrix
Solution:
Given:
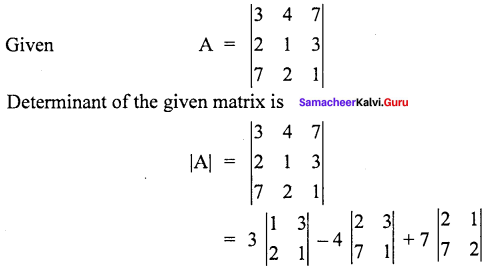
= 3 (-5) -4 (-19) +7 (-3)
= -15 + 76 – 21
A = 40
![]()
Question 6.
Find the value of the determinant of the matrix A =.
Solution:
Given:
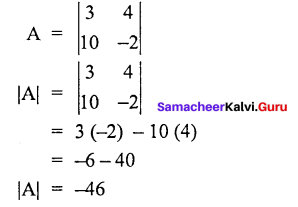
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 1.
Find the equation of a straight line which passes through two points (2,2) and (4, -8) which are (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) respectively.
Note: For drawing a straight line, at least two points are required. Many straight lines can pass through a single point.
Solution:
Here x1 = 2 y1- = 2 and x2 = 4 y2 = – 8
Formula for constructing a straight line.

Slope (m) = -5
y intercept = 12
Constant = C
This is of this from y = mx + C
y = 12 – 5x
When x = 0
y = 12
When y = 0
x = \(\frac { 12 }{ 5 }\) = 2.4
![]()
Question 2.
Find the solution of the equation system
Solution:
7x1 – x2 – x3 = 0
10x1 – 2x2 + x3 = 8
6x1 + 3x2 – 2x3 = 7
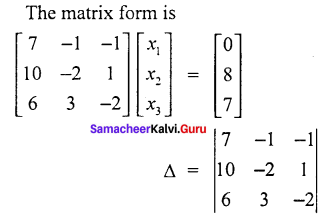
= 7 (4 – 3) + 1 (-20 -6) -1 (30 + 12)
= 7 (1) + 1 (-26) -1 (42)
+ 7 -26 – 42
∆ = – 61
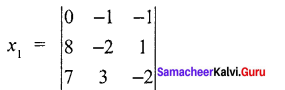
= 0 (4 -3) + 1 (-16 -7) – 1 (24+14)
= 0 + 1 (-23) – 1 (38)
= -23 – 38
= -61
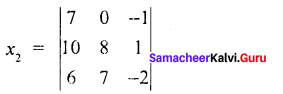
= 7 (-16 – 7) – 0 (- 20 – 6) – 1 (70 – 48)
= 7 ( -23) + 0 (-20 – 6) – 1(70 – 48)
= – 161 – 22
= – 183
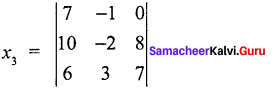
= 7(-14 -24) + 1 (70 – 48) + 1 (30 + 12)
= 7 (-38) + 1 (22) + 0
= – 266 + 22
= – 244