Students can Download English Lesson 1 The Nose-Jewel Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Solutions Term 3 Prose Chapter 1 The Nose-Jewel
The Nose Jewel Lesson Plan Read And Understand
A. Choose the correct synonyms for the italicized words
Question 1.
Nice fun indeed.
(a) in fact
(b) doubtedly
(c) fine
Answer:
(a) in fact
Question 2.
The poor woman is in a panic.
(a) fear
(b) grid
(c) crash
Answer:
(a) fear

Question 3.
The mother consoled her little girl.
(a) pretended
(b) comforted
(c) left
Answer:
(b) comforted
Question 4.
You are always self-centered.
(a) egoistic
(b) generous
(c) heroic
Answer:
(a) egoistic
Question 5.
What is the secret you are whispering?
(a) rumour
(b) murmur
(c) louder
Answer:
(b) murmur
B. Find the antonym for the following words.
- Delight × displease
- Disgrace × glory
- Careless × careful
- Secret × public
- confine × release
C. The Nose Jewel Question Answer
Question 1.
Where did the sparrows build the nest?
Answer:
The sparrows built the nest in a nice spot on the roof of Ramayya’s house.
Question 2.
Why did the birds drop the diamond stud?
Answer:
The wife bird shouted at the male bird to go in search of food. So it dropped the diamond stud.
Question 3.
What were the words of Meenakshi Ammal to her daughter?
Answer:
Meenakshi Ammal consoled her little girl saying that they would search and found out the jewel. You should not tell their anything to her father or else he would go into a rage.

Question 4.
Who was suspected of stealing the diamond nose stud?
Answer:
The maid-servant Kuppayi was suspected of stealing the diamond nose stud.
Question 5.
What did Ramayya’s wife do with the stud?
Answer:
Ramayya’s wife found the diamond stud. She took it and wore it.
Question 6.
What happened to Ramayya’s wife at the end?
Answer:
Ramayya’s wife developed a severe fever and was confined to her bed.
D. Answer the following in about 100 words.
Question 1.
Why did the sparrow throw the nose jewel into Ramayya’s house?
Answer:
The male sparrow wanted to help Ramayya. It felt pity for Ramayya. Ramayya was facing harsh words from his wife often. One day, somewhere in the muck-heap laid a diamond nose jewel. The male bird picked it up and came to the nest with the shining stud in his beak. The male sparrow asked his wife if she liked the jewel. The wife bird replied that the jewel was useless for her. She also said that it would be better for the male sparrow if he went out to find some grub for the hungry young ones. Then the male bird dropped the diamond stud on the floor and went out in search of little worms for the young ones.

Question 2.
Explain how Ramayya’s wife reacted when she saw the nose jewel?
Answer:
When Ramayya’s wife was sweeping the floor she found the diamond nose stud. She picked it up with delight and wore it. Her husband told her that it was a mistake to keep the jewel. She did not bother about it. She knew that the jewel belonged to her neighbour’s daughter. Yet she did not reveal about it to anyone. The maid servant of the neighbour was suspected. The police searched her hut, but could not find it. Ramayya’s wife put the stud away in her box. She soon developed a server fever and was confined to her bed.
The Nose-Jewel Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct Synonyms for the Italicized words :
Question 1.
The female sparrow said with disdain, “Let me see what help you can do for him”.
(a) respect
(b) scorn
(c) value
(d) admire
Answer:
(b) scorn
Question 2.
Find some grub; the young ones are hungry.
(a) food
(b) smoothen
(c) poison
(d) task
Answer:
(a) food
Question 3.
She is very careless and ignorant,
(a) educated
(b) unaware
(c) polite
(d) humble
Answer:
(b) unaware
Question 4.
If tomorrow the police should come and search our house, it will be disgrace to us.
(a) honour
(b) glory
(c) praise
(d) dishonour
Answer:
(d) dishonour

Question 5.
The maid-servant Kuppayi was suspected by everyone to have stolen it.
(a) knew
(b) doubted
(c) amazed
(d) believed
Answer:
(b) doubted
Question 6.
Ramayya’s heart was in aflutter.
(a) calm
(b) still
(c) steady
(d) flap
Answer:
(d) flap
Question 7.
She was confined to her bed.
(a) invasive
(b) restricted
(c) released
(d) freed
Answer:
(b) restricted
Question 8.
The loss of the jewel had to be admitted.
(a) dismissed
(b) excluded
(c) accepted
(d) refused
Answer:
(c) accepted
Question 9.
“And a good thing too”, said the cruel male sparrow.
(a) merciful
(b) kind
(c) merciless
(d) compassionate
Answer:
(c) merciless

Question 10.
The male bird answered gravely, “Did I tell her to steal the thing?”
(a) seriously
(b) cheerfully
(c) joyfully
(d) happily
Answer:
(a) seriously
II. Choose the correct antonyms for the Italicized words,
Question 1.
“Why does the lady of this house always quarrel with her husband?”
(a) fight
(b) argue
(c) agree
(d) shout
Answer:
(c) agree
Question 2.
“Please do not talk about what does not concern us.”
(a) anxiety
(b) worry
(c) uneasiness
(d) disregard
Answer:
(d) disregard

Question 3.
The male bird went out in search of little worms for the young ones.
(a) ignore
(b) seek
(c) find
(d) quest
Answer:
(a) ignore
Question 4.
We should go and deliver it to the village magistrate.
(a) bring
(b) hand over
(c) collect
(d) give
Answer:
(c) collect
Question 5.
He would go into a rage if he knew that you had lost the diamond nose-stud.
(a) anger
(b) fury
(c) passion
(d) peace
Answer:
(d) peace
Question 6.
The loss of the jewel had to be admitted.
(a) confessed
(b) denied
(c) allowed
(d) entered
Answer:
(b) denied
Question 7.
Everyone thought that Kuppayi had stolen it.
(a) sacked
(b) swiped
(c) donated
(d) robbed
Answer:
(c) donated

Question 8.
She soon developed a severe fever and was confined to her bed.
(a) minor
(b) great
(c) intense
(d) harsh
Answer:
(a) minor
Question 9.
The lady of the house is scared and is down with fever.
(a) afraid
(b) frightened
(c) confident
(d) timid
Answer:
(c) confident
Question 10.
This is bound to happen when humans are beings greedy.
(a) generous
(b) self-centered
(c) grabby
(d) miserly
Answer:
(a) generous
III. Choose the right answer (MCQ):
Question 1.
He was not rich but could take care of his _________
(a) wife
(b) children
(c) mother
(d) family
Answer:
(d) family
Question 2.
_________ sparrows built a nest in a nice spot in the roof of Ramayyas house.
(a) Four
(b) Five
(c) Two
(d) Three rerca
Answer:
(c) Two

Question 3.
The female sparrow said with _________, “Let me see what help you can do for him”.
(a) disdain
(b) contempt
(c) hatred
(d) love
Answer:
(a) disdain
Question 4.
The bird dropped the _________ stud on the floor.
(a) gold
(b) diamond
(c) silver
(d) metal
Answer:
(b) diamond
Question 5.
_________ questioned her angrily.
(a) Meenakshi Ammal
(b) Ramayyas wife
(c) Ramayya
(b) Kuppayi
Answer:
(c) Ramayya
Question 6.
She is verv careless and _________ .
(a) silly
(b) ignorant
(c) innocent
(d) foolish
Answer:
(b) ignorant
Question 7.
She picked it up with _________
(a) joy
(b) sorrow
(c) delight
(d) disgrace
Answer:
(c) delight

Question 8.
The loss of the jewel had to be _________
(a) accepted
(b) announced
(c) told
(d) admitted
Answer:
(d) admitted
Question 9.
The _________ came and searched her hut.
(a) thief
(b) Ramayya
(c) Meenakshi Ammal
(d) police
Answer:
(d) police
Question 10.
Ramayya’s wife put the _________ away in her box.
(a) ring
(b) stud
(c) chain
(d) bangle
Answer:
(b) stud
IV. Very Short Questions and Answers :
Question 1.
Where did Ramayya live?
Answer:
Ramayya was a simple man who lived in a town.
Question 2.
What did the male-bird find?
Answer:
The male-bird found a diamond stud in a heap.
Question 3.
What did Ramavva’s wife notice?
Answer:
Ramayya’s wife noticed the diamond stud, as she was sweeping the floor.
Question 4.
Who was Kuppavi?
Answer:
Kuppayi was the maid-servant of Meenakshi Ammal.
Question 5.
Did the police find anything?
Answer:
The police could not find anything
V. Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What did the male-bird say to the female-bird about Ramayya’s wife?
Answer:
The male-bird complained to his wife that Ramayya’s wife always quarreled with his wife.
Question 2.
What was the state of Ramayya, when the police were searching the stud?
Answer:
Ramayya’s heart was in a flutter. He was frightened that the police would come to his house and search for the stud.
VI. Paragraph Question and Answer
Question 1.
What is the moral of the story ‘The Nose-Jewel’?
Answer:
The moral of The Nose Jewel Story In English is that ‘we should never be greedy for what belongs to others’. Greediness will cause pain. Mrs. Ramayya found the diamond nose stud when she was sweeping the floor. It didn’t belong to her. But she was delighted to find it and wore it. She did not feel guilty, that she was wearing someone else’s jewel. Her husband warned her not to take it. But she did not pay heed to his words. After some time, she developed a severe fever and was confined to her bed. The couple spent the rest of their life in fear.
Vocabulary
Eponymous Words
E. Fill in the blanks with correct Meaning and Eponym for the given words.
Answer:
| Word |
Meaning |
Eponym |
| saxophone |
A woodwind instrument made of brass and played with a single-reed mouthpiece. |
Adolphe Sax, a Belgian – born inventor, was the designer of the saxophone. |
| volcano |
A rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object. |
Vulcan, the god of fire in Roman mythology. |
| Eiffel Tower |
It is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the champ de Mars in Paris, France. |
Gustave Eiffel, an Engineer. His company designed and built the tower. |
| Boycott |
At act of voluntary absence from using, buying or dealing with a person or organization. |
Captain Charles C. Boycott, an Irish land agent. |
| Mount Everest |
The world’s highest mountain above sea-level. |
Sir George Everest the surveyor General of India. |
Euphemistic Words
F. Fill in the blanks with correct Euphemisms for the given words.
Answer:
| Deaf, or hard of hearing |
Hearing-impaired |
| Mentally ill |
Intellectually impaired |
| Fat |
Big-boned |
| Blind |
Visually impaired |
| liar |
Spinning a yarn |
Grammar Additional
Eponymous Words
An eponym refers to a person or thing after which something else is named. Words whose origin is traced to individuals are known as eponymous words.
A. Fill in the blanks with correct Meaning and Eponym for the given words
| Word |
Meaning |
Eponym |
| Atlas |
|
|
| Braille |
|
|
| Celsius |
|
|
| Fahrenheit |
|
|
Answer:
| Word |
Meaning |
Eponym |
| Atlas |
A book of maps |
In Greek mythology, Atlas was the God of astronomy. He was forced to support the heavens upon his shoulders. |
| Braille |
A writing system which allows blind or visually impaired people to read. |
Louis Braille (1809-1852) suffered an eye injury as a small child and went blind. He developed his own writing system of raised dots. |
| Celsius |
a temperature scale (0°C – 100°C) |
Anders Celsius (1701-1744), a Swedish professor, developed the idea behind the temperature scale. The Celsius temperature scale was named after him. |
| Fahrenheit |
One method of measuring temperature. |
Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit (1686-1736) was a German physicist. The Fahrenheit temperature scale was named after him. |
Euphemistic Words
Euphemisms are polite, mild phrases which substitute unpleasant ways of saying something sad or uncomfortable.
B. Fill in the blanks with correct Euphemisms for the given words.
| Word |
Euphemisms |
| Housewife |
|
| Old people |
|
| Short |
|
| Prison |
|
| Toilet |
|
| Homeless |
|
| Lazy |
|
| Lunatic asylums |
|
Answer:
| Word |
Euphemisms |
| Housewife |
homemaker |
| Old people |
senior citizen |
| Short |
vertically challenged |
| Prison |
correctional facility |
| Toilet |
restroom |
| Homeless |
on the street |
| Lazy |
couch potato |
| Lunatic asylums |
mental institutions |
Greetings In Informal Conversations
Practicing Dialogue
C. complete the following dialogue
Amala: Sanjay,_____(i)_____
Sanjay: Hi Amala_____(ii)_____I’m just hanging out. What’s up with you?
Amala: It’s a good day. I’m feeling fine.
Sanjay: How is your sister?
Amala: Oh, fine. Not much has changed.
Sanjay: Well, I have to go _____(iii)_____
Amala: Later!
Answer:
(i) what’s up
(ii) Nothing much
(iii) Nice seeing you!
Greetings In Formal Conversations
Practicing Dialogue
C. Complete the following dialogue :
Cecily : Good morning.
Prabu : Good morning _____(i)_____
Cecily : I’m very well thank you. And you?
Prabu : _____(ii)_____Thank you for asking.
Cecily : Do you have a meeting this morning?
Prabu : Yes, I do. Do you have a meeting as well?
Cecily: Yes. Well. It was _____(iii)_____
Prabu : Goodbye.
Answer:
(i) How are you?
(ii) I’m fine
(iii) a pleasure seeing you
Listening
G. Listen to the passage carefully and choose the right answer.
“Why Do Birds Sing?”
Why do birds sing? You might assume that birds sing because they are happy. While birds might be happy, they sing in order to communicate. One reason they sing is to stake a claim on the territory. Birds sing to warn other birds to stay off their property. For example, a robin might stake a claim on a piece of land which measures about 200 feet wide by 200 feet long. This amount of land provides enough worms for the robin to feed its family. A bird maintains singing perches around the outside edges of its territory. The perches are high in the trees, so other birds can see and hear them. Birds also sing to find a mate. The length and complexity of the mating song gives information about the fitness of the bird. Healthy birds can sing longer, more complicated songs. Birds call to one another in shorter vocalizations in order to warn of danger and to locate one another. Birds sing instinctively. Young birds learn to perfect their songs by listening to adult birds and interacting with other birds. Birds in a local area might learn variations in the basic song which help them recognize other members of their group.
Question 1.
Why do birds sing?
(A) To locate one another
(B) To warn other birds
(C) To find a mate
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above

Question 2.
Birds perch very high so _____?
(A) other birds can hear them
(B) other birds can see them
(C) they can hide there
(D) Both A and B are correct.
Answer:
(D) Both A and B are correct.
Question 3.
health Of a bird can be determined _____
(A) by the length of its song
(B) by the complexity
(C) by the volume of its Song
(D) Both A and B are correct
Answer:
(D) Both A and B are correct
Question 4.
Shorter bird vocalizations are _____
(A) territorial songs
(B) mating songs
(C) warnings
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) warnings
Question 5.
Young birds perfect their songs by _____
(A) natural instinct
(B) by the complexity of its song.
(C) practice
(D) Both A and B are correct.
Answer:
(B) by the complexity of its song.
Question 6.
Fitness is _____
(A) health
(B) danger
(C) a song
(D) a warning.
Answer:
(A) health
Question 7.
What help does a basic song do?
(A) recognize other members
(B) Maintain health
(C) Increase the length of their song
(D) Communicate with one another.
Answer:
(A) recognize other members
Writing
Forms
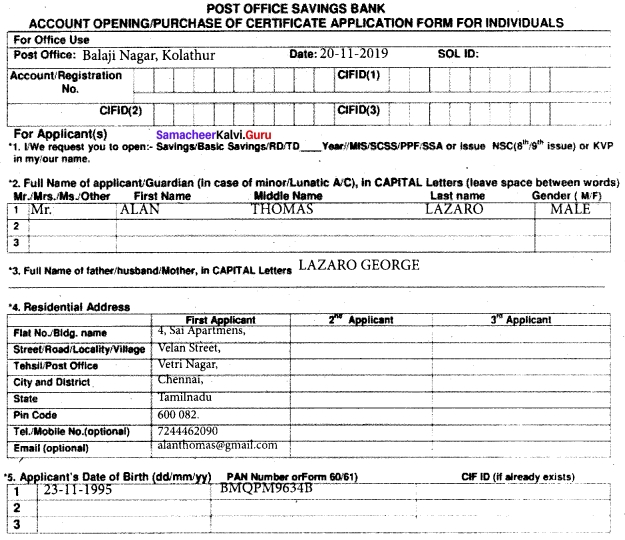
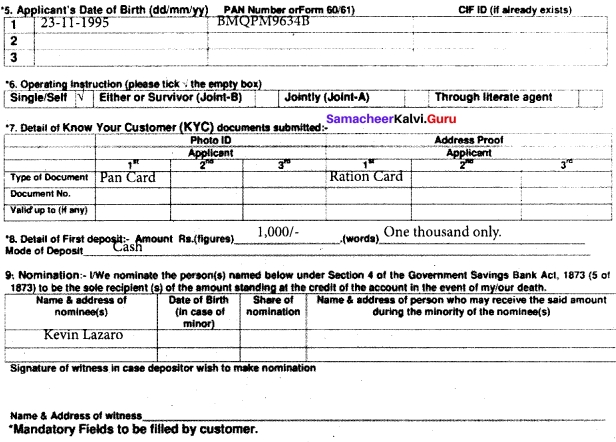
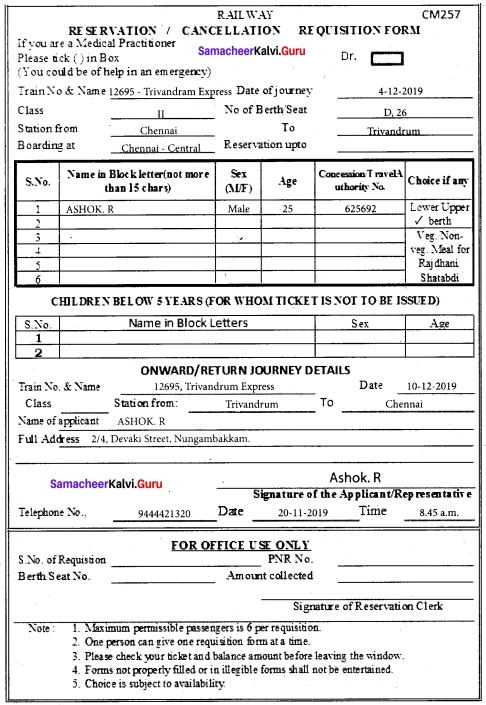
H. Fill in the form given below.
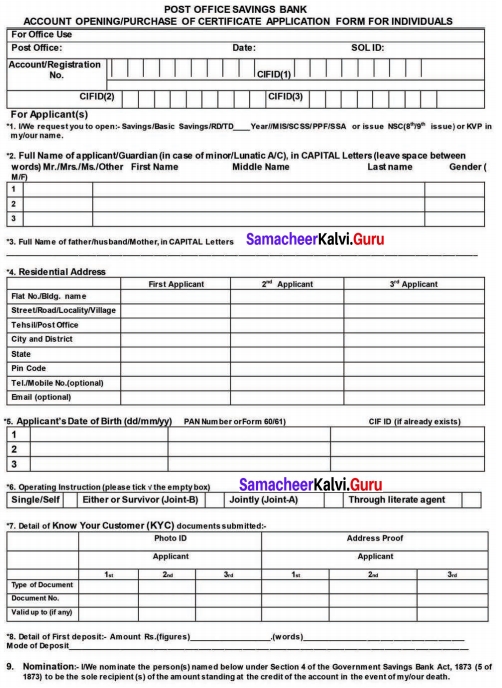
Answer:
I. Fill in the form given below.
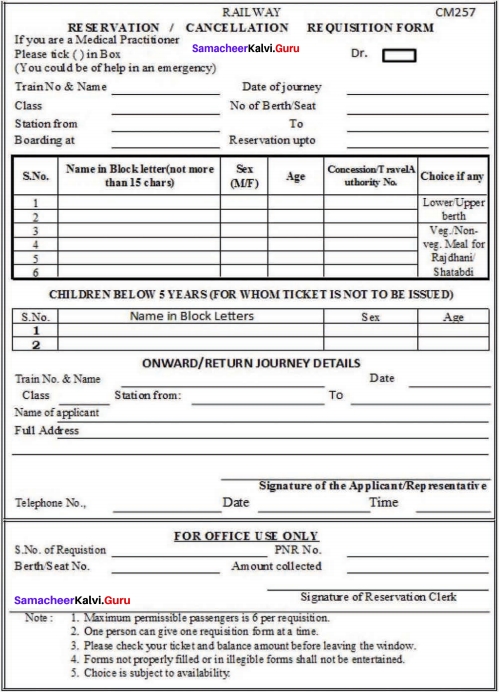
Answer:
Grammar
Direct And Indirect Speech
A. Change the following into Indirect Speech:
Question 1.
“What do you want?” he said to her.
Answer:
He asked her what she wanted.
Question 2.
He said, “How’s your father?”
Answer:
He enquired how his father was.
Question 3.
“Are you coming home with me?” he asked.
Answer:
He asked him whether he was coming home with him.

Question 4.
The poor man exclaimed, “Will none of you help me?”
Answer:
The poor man asked in despair whether none of them would help him.
Question 5.
“Don’t you know the way home?” asked I.
Answer:
I asked whether he knew the way home.
B. Change the following into Indirect Speech
:
Question 1.
“Bring me a glass of milk,” said the swami to the villagers.
Answer:
The swami commanded the villages to bring him a glass of milk.
Question 2.
Sit down, boys,” said the teacher.
Answer:
The teacher ordered the boys to sit down.
Question 3.
“Halt!” shouted the officer to his men.
Answer:
The officer shouted to his men to halt.
Question 4.
“Take off your hat,” the king said to the Hatter.
Answer:
The king ordered the Hatter to take off his hat.
Question 5.
The teacher said to him, “Do not read so fast.”
Answer:
The teacher commanded him not to read very fast.
Question 6.
He said to me, “Wait until I come.”
Answer:
He urged me to wait until he came.
Question 7.
“Hurry up,” he said to his servant, “do not waste time.”
Answer:
He ordered his servant to hurry up and not to waste time.
Question 8.
“Runaway, children,” said their mother.
Answer:
Their mother urged the children to run away.
Question 9.
He said, “Daughter, take my golden jug, and fetch me some water from the Well.”
Answer:
He requested his daughter to take his golden jug and fetch him some water from the well.

Question 10.
“Go down to the bazaar. Bring me some oil and a lump of ice,” ordered his master.
Answer:
His master ordered him to go down to the bazaar and bring him some oil and a lump of ice.
C. Change the following into Indirect Speech :
Question 1.
He said, “My God! I am ruined.”
Answer:
He exclaimed sadly that he was ruined.
Question 2.
He said, “Alas! our foes are too strong.”
Answer:
He exclaimed sorrowfully that their foes were too strong.
Question 3.
“How smart you are!” she said.
Answer:
She exclaimed that he was very smart.
Question 4.
He said. “Oh ! that’s a nuisance.”
Answer:
He exclaimed with disgust that it was a nuisance.
Question 5.
He said, “What a pity you did not come!”
Answer:
He exclaimed with sorrow that he did not come.
D. What were the actual words used in each instance below? The sentences containing the actual words are listed afterwards in the wrong order. Write them out in the same order as the others.
- Punitha asked Pushpa what she was reading.
- Pushpa told her that he was reading Robinson Crusoe.
- Punitha asked her what it was all about.
- Pushpa said it was about a man wrecked on an island.
- Punitha then asked her friend who gave her the book.
- Pushpa answered that her uncle gave it to her at Christmas.
- Finally, Punitha inquired if she could borrow it.
- Pushpa replied that she would certainly lend it to her.
(a) “May I borrow it?” inquired Punitha.
(b) “What are you reading, Pushpa?” asked Punitha.
(c) “It is about a man wrecked on an island,” Pushpa said.
(d) “Of course I will lend it to you,” replied Pushpa.
(e) “Uncle gave it to me at Christmas,’ answered Pushpa.
(f) “What is it all about?” Punitha asked.
(g) “I am reading Robinson Crusoe, Pushpa told her.
(h) “Who gave you the book, Pushpa?” Punitha then asked.
Answer:
(b) “What are you reading, Pushpa?” asked Punitha.
(g) “I am reading Robinson Crusoe”, Pushpa told her.
(f) “What is it all about?” Punitha asked.
(c) “It is about a man wrecked on an island,” Pushpa said.
(h) “Who gave you the book, Pushpa?” Punitha then asked.
(e) “Uncle gave it to me at Christmas,’ answered Pushpa.
(a) “May I borrow it?” inquired Punitha.
(d) “Of course I will lend it to you,” replied Pushpa.
E. Change the following into Direct Speech :
Question 1.
Nevin asked his father when the next letter would come.
Answer:
Nevin asked his father, “When will the next letter come?”
Question 2.
I wrote that I would visit him the next day.
Answer:
I wrote, “I will visit you tomorrow”.
Question 3.
I told them to be quiet.
Answer:
I said to them, “Be quiet”.
Question 4.
Lakshan asked me if I had anything to say.
Answer:
He asked me, “Do you have anything to say”.

Question 5.
An old mouse asked who would bell the cat.
Answer:
An old mouse asked, “Who will bell the cat?”
Question 6.
Mervin said that he wanted to be a soldier.
Answer:
Mervin said, “I want to be a soldier”.
Question 7.
Elwin asked me what I wanted.
Answer:
He asked me, “What do you want?”
Question 8.
Bhagya said that she had seen that picture.
Answer:
Bhagya said, “I have seen this picture”.
Question 9.
The stranger asked Nasrin where she lived.
Answer:
The stranger asked Nasrin, “Where do you live?”
Question 10.
I asked Mary if she would lend me a pencil.
Answer:
I asked Mary, “Will you lend me a pencil?”.
F. Sherlyn receives a postcard from her friend Pushpa who is holidaying in Sri Lanka. She calls her friend Galen and tells him what Pushpa has written. Help her by filling in the blanks, using reported speech.

Answer:
Hello, Galen Today I received a postcard from Pushpa. Remember I had told you that She has gone to Sri Lanka on a holiday? Well, she has written from Colombo. She has written that she had visited Pinnawala Elephant Orphanage. It had 84 elephants. She said that it is the biggest herd of elephants in the world that is living under human supervision. She also added that she was glad that they had come there because she was learning a lot. The Elephant Orphanage was truly worth visiting. She said that next day, they are going to the national park. She would be returning next week and added that she was looking forward to meeting me then.
G. Convert the following into indirect speech.
a. Sharun said to me, ‘Are you coming to school tomorrow?’
Answer:
Sharun asked me if I am coming to school, the next day.
b. “We must visit the historical buildings of Delhi since we are here,’ said Ashok.
Answer:
Ashok said that they had to visit the historical building of Delhi since they were there.
c. ‘Have you read The Wind in the Willows?’ asked Amutha.
Answer:
run Amutha asked whether he had read ‘The Wind in the Willows’.
d. Teacher said to us, ‘You must conduct the experiment very carefully.’
Answer:
The teacher told us that we had to conduct the experiment very carefully.

e. ‘Wow! That is great news!’ said Tejeswar.
Answer:
Tejaswar exclaimed happily that it was great news.
The Nose-Jewel Grammar Additional
Direct And Indirect Speech
A. Change the following into indirect speech :
Question 1.
Ramu says, “I am busy”.
Answer:
Ramu says that he is busy.
Question 2.
Suresh said, “I like dancing”.
Answer:
Suresh said that he liked dancing.

Question 3.
He said, “I am going to the cinema”.
Answer:
He said that he was going to the cinema.
Question 4.
Ravi said, “I have bought a cycle”.
Answer:
Ravi said that he had bought a cycle.
Question 5.
Ram said, “Visu came at night”.
Answer:
Ram said that Visu had come at night. I
Question 6.
He said, “Honesty is the best policy”.
Answer:
He said that honesty is the best policy.
Question 7.
She said, “I have done my homework”.
Answer:
She said that she had done her homework.
Question 8.
He says, “I am happy”.
Answer:
He says that he is happy.
Question 9.
The teacher said, “Hari will definitely pass”.
Answer:
The teacher said that Hari would definitely pass.
Question 10.
Raju said, “I shall be here this evening”.
Answer:
Raju said that he would be there that evening.
B. Change the following into direct speech :
Question 1.
The teacher ordered the boys to leave that place.
Answer:
The teacher said to the boys, “Leave this place”.
Question 2.
I requested him to give me a glass of water.
Answer:
I said to him, “Please give me a glass of water”.

Question 3.
The captain ordered the soldiers to stand at ease.
Answer:
The captain said, “Stand at ease”.
Question 4.
My brother said that he might go to Kolkata.
Answer:
My brother said, “I may go to Kolkata”.
Question 5.
He said that the earth moves around the sun.
Answer:
He said, “The earth moves around the sun”.
Question 6.
Ravi asked Ganesh when he was going to the library.
Answer:
Ravi said to Ganesh, “When are you going to the library?”
Question 7.
The policeman ordered the boy to show him his licence.
Answer:
The policeman said to the boy, “Show me your licence”.
Question 8.
She told him that she was going to the market then.
Answer:
She said to him, “I am going to the market now”.
Question 9.
He said that he was buying a cell phone that day.
Answer:
He said, “I am buying a cell phone today”.
Question 10.
He asked who I was.
Answer:
He said, “Who are you?”
Warm-Up
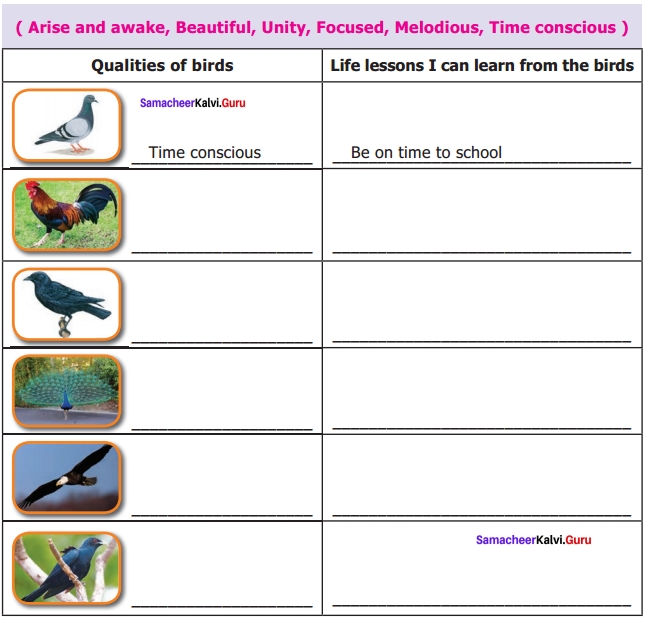
What are the life lessons that you can learn from the birds? Match the birds with the characters given in the box and fill in the blanks.
Answer:


The Nose Jewel Summary By C Rajagopalachari
Ramayya was a simple man, who lived in a town. His house was made of tiled roots He lived with ‘made his wife. He was not rich. But take good care of his family. On the roof of his house, two sparrows built a nest. The mother-bird laid her eggs in it. The male-bird wanted to help Ramavya, as he noticed Ramayyas wife always quarreling with him. But the female bird advised her male bird not to bother about others. But to mind their own business.
One day, the male-bird found a diamond nose-jewel in a heap. When he showed it to his wife, she replied that it was of no use to her. So she asked him to find some food for the young ones. The bird dropped the diamond stud on the floor and went out in search of food.
Ramayyas wife noticed the jewel as she was sweeping the floor. She picked it with delight and wore it. Her husband shouted at her and told her that they should go and deliver it to the magistrate. But his wife wouldn’t want to part with it.
This nose-stud belonged to their neighbour, Meenakshi Ammal’s daughter. She forgot and left it in the bathroom. Kuppayi, their servant woman would have swept it out. Meenakshi Ammal consoled her daughter. She also advised her not to inform her father Ramanathan about the lost stud. He would become very angry. But her husband Ramanathan and the whole village knew about it. The maidservant was suspected to have stolen it. The police came and searched for her hut. But they could not find it.
Ramayyas wife put the stud away in her box. She soon developed a severe fever and was always in her bed. The two birds witnessed all this and thought that “we should never be greedy for what belongs to others.” Ramayya and his wife spent the rest of their lives in fear of being caught.

![]()
![]()
![]()