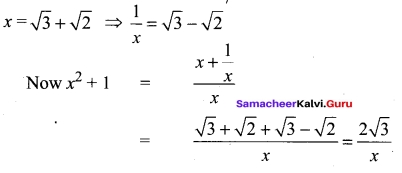
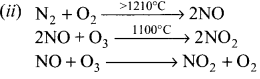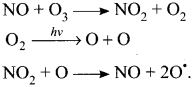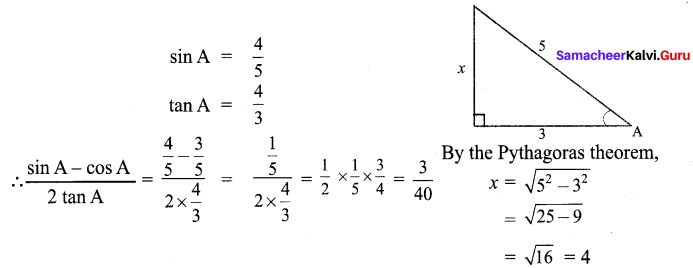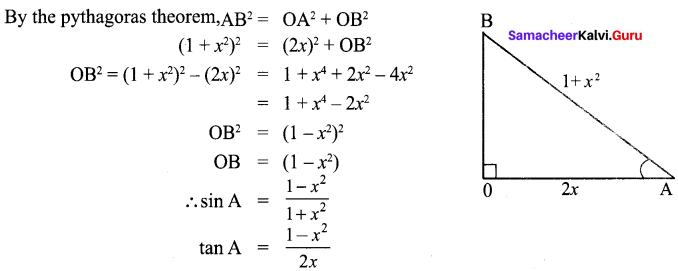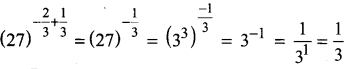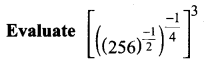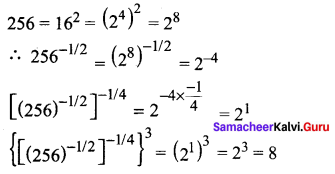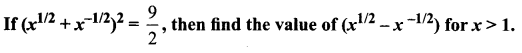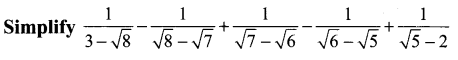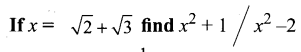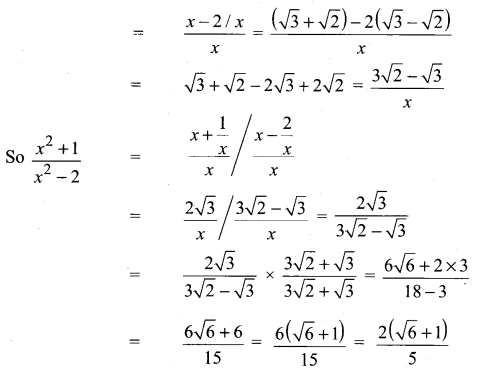Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions
Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 12 Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions Chemistry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose The Best Answer:
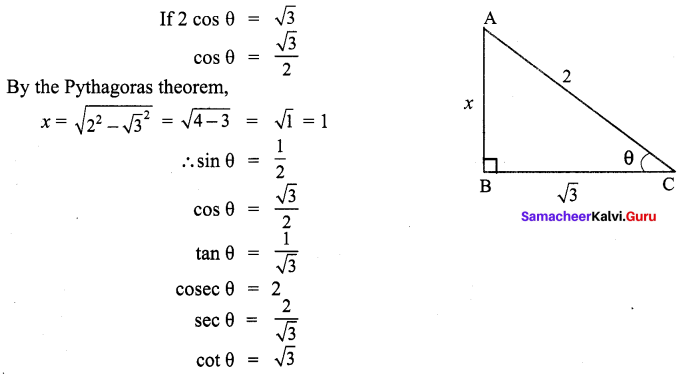
Question 1.
For the Following reactions –
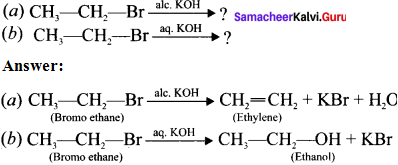
(A) CH3 CH2 CH2 Br + KOH → CH3 – CH + KBr + H2O
(B) (CH3 )3 CBr + KOH → (CH3 )3 COH + KBr
(C) 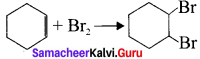
Which of the following statement is correct’?
(a) (A) is elimination, (B) and (C) are substitution
(b) (A) is substitution, (B) and (C) are elimination
(c) (A) and (B) are elimination and (C) is addition reaction
(d) (A) is elimination, B is substitution and (C) is addition reaction.
Answer:
(d) (A) is elimination, B is substitution and (C) is addition reaction.
Question 2.
What is the hybridisation state of benzyl carbonium ion?
(a) sp2
(b) spd2
(c) sp3
(d) sp2d
Answer:
(a) sp2
Question 3.
Decreasing order of nucleophilicity is –
(a) OH–> RNH2– > –OCH3> RNH2
(b) NH2–> OH–> –OCH3> RNH2
(c) NH,> CH3O >OH–> RNH2
(d) CH3O–> NH2–> OH–> RNH2
Answer:
(b) NH2–> OH–> –OCH3> RNH2+
![]()
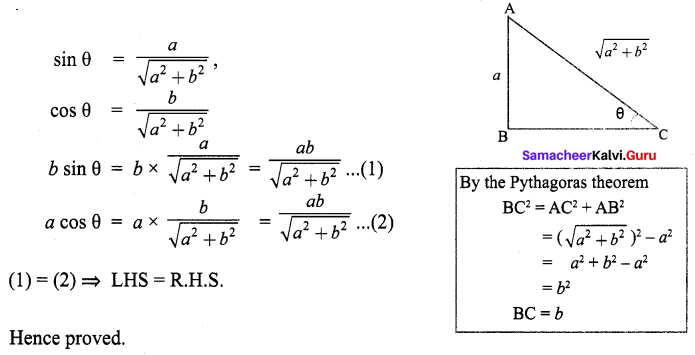
Question 4.
Which of the tòllowing species is not eLectrophilic in nature?
(a) Cl+
(b) BH3
(c) H3O+
(d) +NO2
Answer:
(c) H3O+
Question 5.
Homolytic fission of covalent bond leads to the formation of –
(a) electrophile
(b) nucicophile
(c) Carbocation
(d) free radical
Answer:
(d) free radical
Question 6.
Hyper Conjugation is also known as –
(a) no bond resonance
(b) Baker – nathan effect
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 7.
Which of the group has highest +I effect?
(a) CH3–
(b) CH3CH2–
(c) (CH3)2 -CH-
(d) (CH3)3-C-
Answer:
(d) (CH3)3-C-
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following species does not exert a resonance effect?
(a) C6H5OH
(b) C6H5Cl
(c) C6H5NH2
(d) C6H5NH3
Answer:
(d) C6H5NH3
Question 9.
-I effect is shown by –
(a) -Cl
(b) -Br
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) -CH3
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 10.
Which of the following carbocation will be most stable?
(a) \({ PH }_{ 3 }\overset { + }{ C- } \)
(b) CH3–\(\overset { + }{ C{ H }_{ 2 } } \)
(c) (CH3)2–\(\overset { + }{ C{ H } } \)
(d) CH2 = CH-CH3
Answer:
(a) \({ PH }_{ 3 }\overset { + }{ C- } \)
Question 11.
Assertion : Tertiary Carbocations are generally formed more easily than primary Carbocations.
Reason : Hyper conjugation as well as inductive effect due to additional alkyl group stabilize tertiary carbonium ions.
(a) both assertion and reason arc true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
(d) Both assertion and reason are false
Answer:
(a) both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 12.
Heterolytic fission of C-C bond results in the formation of –
(a) free radical
(b) Carbanion
(c) Carbocation
(d) Carbanion and Carbocation
Answer:
(e) Carbocation
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following represent a set of nucleophiles?
(a) BF3, H2O, NH2-
(b) AlCl3, BF3, NH3
(c) CN–, RCH–2, ROH
(d) H+, RNH+2, CCl2
Answer:
(c) CN–, RCH–2, ROH
Question 14.
Which of the following species does not acts as a nucleophile?
(a) ROH
(b) ROR
(c) PCl3
(d) BF3
Answer:
(d) BF3
Question 15.
The geometrical shape of carbocation is
(a) Linear
(b) tetrahedral
(c) Planar
(d) Pyramidal
Answer:
(c) Planar
II. Write brief answer to the following questions.
Question 16.
Write short notes on:
(a) Resonance
(b) Hyper conjugation
Answer:
(a) Resonance:
1. Certain organic compounds can be represented by more than one structure and they differ only in the position of bonding and lone pair of electrons. Such structures are called resonance structure and this phenomenon is called as resonance. This phenomenon is also called as mesomerism or mesomeric effect.
2. For example, the structure of aromatic compounds such as benzene and conjugated system like 1,3 butadiene cannot be represent by a single structure and their observed properties can be explained on the base of a resonance hybrid.
3. Resonance structure of benzene.
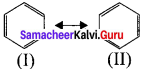
(I) and (II) are called as resonance hybridš of benzcnc.
4. For 1,3 butadiene:
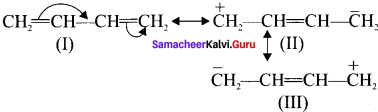
(I), (II) and (III) are called as resonance hybrids of 1,3 butadiene.
(b) Hyper conjugation:
1. The denationalization of electrons of σ bond is called as hyper conjugation. it is a special stabilizing effect that results due to the interaction of electrons of a σ bond with the adjacent empty non-bonding P-orbitais resulting in an extended molecular orbital.
2. Hyper conjugation is a permanent effect.
3. For example, in propane. the σ- electrons of C-H bond of methyl group can be delocalised into the it- orbital of doubly bonded carbon as represented below.
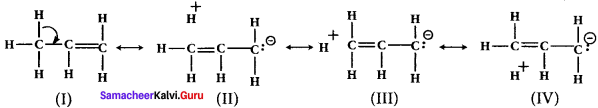
Question 17.
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Give suitable examples for each.
Answer:
Nucleophiles are reagents that has high affinity for electron positive centers. They possess an atom that has an unshared pair of electrons, and hence it is in search for an electro-positive centre where it can have an opportunity to share its electrons to form a covalent bond, and gets stabilised. They are usually negatively charged ions or electron-rich neutral molecules (contains one or more lone pair of electrons). All Lewis bases act as nucleophiles.
Example :
Ammonia(NH3) and amines (RNH2), water (H2O), alcohols (ROH) and ethers ((R-O-R)
Electrophiles:
Electrophiles are reagents that are attracted towards negative charge or electron-rich center. They are either positively charged ions or electron-deficient neutral molecules. All Lewis acids acts as electrophiles. Neutral molecules like SnCl4 can also act as an electrophile, as it has vacant d – orbitals which can accommodate the electrons from others.
Example:
Carbon dioxide (CO2), dichlorocarbene (: CCl2), Aluminium chloride (AlCl3), boron trifluoride (BF3) and Ferric Chloride (FeCl3)
![]()
Question 18.
Show the heterolysis of the covalent bond by using curved arrow notation and complete the following equations. Identify the nucleophile In each case.
1. CH3-Br+KOH →
2. CH3-OCH3+HI →
Answer:
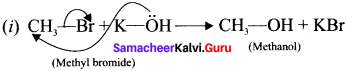
In this case, \(\overset { \ominus }{ Br } \) and \(\overset { \ominus }{ OH } \) are nucleophiles.
Another mechanism:
Step – I
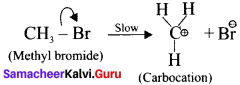
Step-II
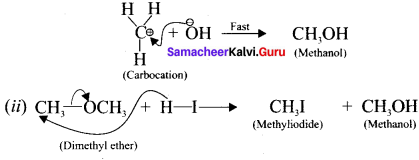
In this case, OCH3 and -I are nucleophiles
Another mechanism:
Step – I
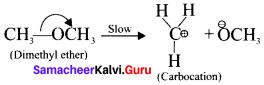
Step – II
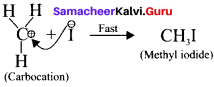
Question 19.
Explain inductive effect with suitable example.
Inductive effect:
Answer:
1. it is defined as the change ¡n the polarization of a covalent bond due to the presence of adjacent bonded atoms or groups in the molecule. It is denoted as I-effect.
2. Atoms or groups which lose electron towards a carbon atom are said to have a +I effect.
Example:
CH3-,(CH3)2 CH-,(CH3)2 C- etc.
3. Atoms or groups which draw electrons away from a carbon atom are said to have a -I effect.
Example:
-NO2. -I, -Br, -OH, C6H5 etc.
4. For example, consider ethane and ethyl chloride. The C-C bond in ethane is non polar while the C-C bond in ethyl chloride is polar. We know that chlorine is more electronegative than carbon and hence it attracts the shared pair of electrons between C-Cl in ethyl chloride towards it self.
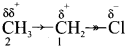
This develops a slight negative charge on chlorine and a slight positive charge on carbon to which chlorine is attached. To compensate it, the C1 draws the shared pair of electron between itself and C2. This polarization effect is called inductive effect.
![]()
Question 20.
Explain the electromeric effect.
Electromeric effect:
Answer:
1. The electromeric effect refers to the polarity produced in a multiple bonded compound when it is attacked by a reagent when a double or a triple bond is exposed to an attack by an electrophile the two π electrons which from the π bond are completely transferred to one atom or the other.
2. When a nucleophile approaches the carbonyl compound, the π-electrons between C and O is instantaneously shifted to the more electronegative oxygen. This makes the carbon electron-deficient and thus facilitating the formation of a new bond between the incoming nucleophile and the carbonyl carbon atom.
![]()
3. When an electrophile such as H approaches an alkene molecule their electrons are instantaneously shifted to the electrophile and a new bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen. This makes the other carbon electron-deficient and hence it acquires a positive charge.
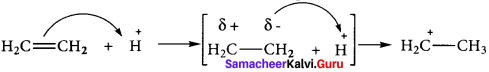
4. This effect denotes as E-effect.
Question 21.
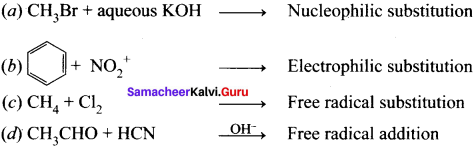
Give examples for the following types of organic reactions
1. – elimination
2. Electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
1. β-elimination:
Elimination reactions involve the cleavage of a bond and tórmation of an air bond. A nucleophilic pair of electrons heads into a new it bond as a leaving group departs. This process is called 3-elimination because the bond Í to the nucleophilic pair of electrons breaks.
Example:
(a) n-propyl bromide on reaction with alcoholic KOH give propene. in this reaction hydrogen and Br are eliminated.
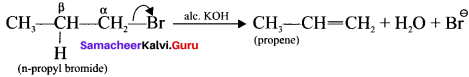
(b) Acid-catalysed dehydration of alcohols
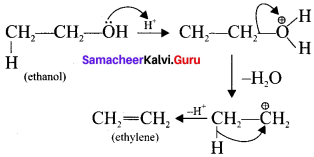
2. Electrophilic substitution:
Substitution reactions when are brought about by electrophiles are called electrophilic substitution reaction.
Example:
(a) Nitration of benzene
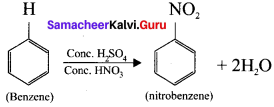
(b) Bromination of benzene:
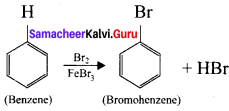
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Organic ReactionsAdditional Questions Solved
I. Choose The Correct Answer.
Question 1.
Statement-I: All the organic molecules contain covalent bonds.
Statement-II: Organic molecules are formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms.
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is the correct explanation of statement-I.
(b) Statement-I and II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation of statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but statement-II is wrong.
(d) Statement-I is wrong but statement-II is correct.
Answer:
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
Question 2.
Statement-I: Homolytic cleavage is an asymmetrical one.
Statement-II: A single covalent bond breaks and each of the bonded atoms retains one electron.
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
(b) Statement-I and II are correct but statement-II is not correct explanation of statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but statement-II is wrong.
(d) Statement-I is wrong but statement-II is correct.
Answer:
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-Il is correct explanation of statement-I.
Question 3.
Heterolysis of propane gives
a) Methyl and ethyl free radicals
b) Methyl carbocation and ethyl free radicals
c) Methyl anion and ethyl carbocation
d) Methyl free radical and ethyl carbocation
Answer:
c) Methyl anion and ethyl carbocation
Question 4.
Which one of the following ¡s correct order of stability of alkyl free radicals?
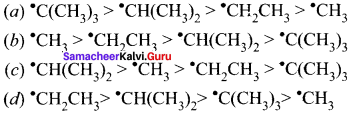
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
Statement-I: Ileterolytic cleavage is unsymmetrical one.
Statement-II: A covalent bond breaks and one of the bonded atom retains the bond pair of electrons.
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
(b) Statement-I and II are correct but statement-II is not correct explanation of statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but statement-II is wrong.
(d) Statement-I is wrong but statement-II is correct
Answer:
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
Question 6.
The shape of methyl free radicals is
a) Planar
b) Pyramidal
c) Tetrahedral
d) Linear
Answer:
a) Planar
Question 7.
Which one of the following is correct order of the stability of carbanions?
(a) –C(CH3)3> –CH(CH3)2> –CH2-CH3> –CH3
(b) –CH3> –CH2-CH3> –CH(CH3)2> –C(CH3)3
(c) –CH(CH3), > –CH3> –CH2-CH3 > –C(CH3)3
(d) –CH2-CH3 > –CH(CH3)2> –CH3> –C(CH3)3
Answer:
(b) CH3> CH2-CH3> CH(CH3)2> C(CH3)3
Question 8.
Which of the following contains only three pairs of electrons
a) Carbocation
b) Carbanion
c) Free radical
d) All of these
Answer:
a) Carbocation
Question 9.
Which one of the following is not nucleophile
(a) H2O
(b) NH3
(c) R-OH
(d) FeCl3
Answer:
(d) FeCl3
![]()
Question 10.
In carbonium ion the carbon bearing the positive charge is
a) sp hybridized
b) sp2 hybridized
c) sp3 hybridized
d) un hybridized
Answer:
b) sp2 hybridized
Question 11.
Which one of the following is nucleophile?
(a) BF3
(b) AlCl3
(c) CO2
(d) R-SH
Answer:
(d) R-SH
Question 12.
The geometry of a methyl carbanion is likely to be
a) Pyramidal
b) Tetrahedral
c) Planar
d) Linear
Answer:
a) Pyramidal
Question 13.
Which one of the following species has a tendency to show +I effect?
(a) -NH2
(b) -Cl
(c) -C6H5
(d) -CH3
Answer:
(d) -CH3
Question 14.
Which one of the following has the strongest acidic character?
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH2ClCOOH
(d) CCl3COOH
Answer:
(d) CCl3COOH
Question 15.
Which one of the following has the least acidic character?
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH2ClCOOH
(d) CCl3COOH
Answer:
(b) CH3COOH
![]()
Question 16.
Electrophiles are
a) Electron loving species
b) Electron hating species
c) Nucleus loving reagents
d) Nucleus hating reagents
Answer:
a) Electron loving species
Question 17.
Statement-I: Fluoro acetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid
Statement-II: Fluorine has high electronegativity and it is facilitate to dissociate the OH bond easily.
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
(b) Statement-I and II are correct but statement-II is not correct explanation of statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but statement-II is wrong.
(d) Statement-I is wrong but statement-Il is correct
Answer:
(a) Statement-I and II are correct and statement-II is correct explanation of statement-I.
Question 18.
Which one of the following is an example for negative mesomeric effect?
(a) -SH
(b) -SR
(c) -NH2
(d) -NO2
Answer:
(d) -NO2
Question 19.
Methyl carbanium ion is
a) Electrophile
b) Lewis acid
c) Nucleophile
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
c) Nucleophile
![]()
Question 20.
Identify the one which does not come under the organic addition reaction
(a) Hydration
(b) Dehydration
(c) Halogenation
(d) Hydro halogenation
Answer:
(b) Dehydration
Question 21.
Primary alcohols undergo which type of reaction to form alkenes?
(a) Elimination
(b) Oxidation
(c) Reduction
(d) Hydrolysis
Answer:
(a) Elimination
Question 22.
![]() Identify the type of reaction
Identify the type of reaction
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Elimination reaction
(c) Reduction reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Answer:
(d) Oxidation reaction
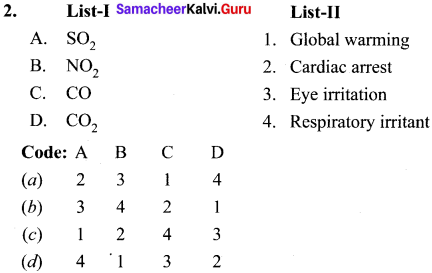
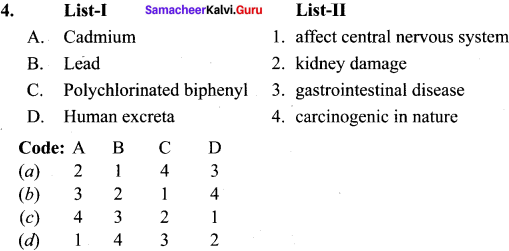
II. Match the following.

Answer:
![]()
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The slowest step in the mechanism determines ………..
Answer:
Rate of reaction
Question 2.
Homolytic cleavage occurs under the conditions of ………….
Answer:
High temperature.
Question 3.
During the cleavage of Azobisisobutyronitrile produces species ……….
Answer:
Free radical
Question 4.
The cleavage of C-Br bond in tert-butyl bromide leads to formation of ………..
Answer:
Carbocation
Question 5.
The cleavage of C-H bond in aldehydes Leads to formation of ………….
Answer:
Carbanion
![]()
Question 6.
Electron displacement occurring in saturated compounds along a carbon chain is termed as …………
Answer:
Inductive effect
Question 7.
The addition of H to alkene is an example of effect ……….
Answer:
+E
Question 8.
Example for positive mesomeric effect is ………..
Answer:
-OH
Question 9.
Acidity of phenol was explained by …………
Answer:
R-effect
Question 10.
Hydrolysis of alkyl halide is an example for ……….
Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution
Question 11.
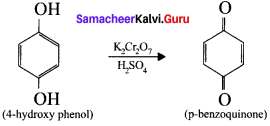
4-hydroxy phenol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate to gives
Answer:
p-Benzoquinone
Question 12.
Enzyme present in apple is
Answer:
Polyphenol oxidase
Question 13.
Benzene reacts with H2 in the presence of Pt to give
Answer:
Cyclohexane
Question 14.
Alcohol on refluxing with K2Cr2O7 gives……..
Answer:
Carboxylic acid
Question 15.
Carbonyl compounds especially ketones undergo reduction to form ………..
Answer:
Secondary alcohols
Question 16.
Ethane undergoes thrombolytic cleavage to form ………..
Answer:
Methyl free radical
![]()
IV. Choose the odd one out.
Question 1.
(a) NH3
(b) H2O
(c) CN–
(d) RSH
Answer:
(c) CN– It is a negatively charged nucleophile whereas others are neutral nucleophiles.
Question 2.
(a) CO2
(b) RX
(c) MCl3
(d) FeCl3
Answer:
(b) RX. It is a positive charged electrophiles whereas others are neutral electrophiles.
Question 3.
(a) -F
(b) – Cl
(c) – COOH
(d) CH3O–
Answer:
(d) CH3O–. It is a group carrying negative charge one electron-donating (or) +I group whereas others are -I group.
Question 4.
(a) – C(CH3)3
(b) – COOK
(c) – CH(CH3)2
(d) – COO–
Answer:
(b) – COOH. It has -I effect whereas others have a +I effect.
Question 5.
(a) -OH
(b) -NH2
(c) -SH
(d) -COOH
Answer:
(d) – COOH. It has a negative mesomeric effect whereas others have a positive mesomeric effect.
![]()
V. Choose the correct pair.
Question 1.
(a) Homolytic clevage : carbocation
(b) Homolytic clevage : carbanion
(c) Homolytic clevage : free radicals
(d) Heterolytic clevage : free radicals
Answer:
(c) Homolytic clevage : free radicals
Question 2.
(a) + C(CH3)3 > +CH(CH3)2> +CH2-CH3 > +CH3 : Relative stability of carbocations.
(b) – C(CH3)3 > –CH(CH3)2 > –CH2-CH3 > –CH3 : Relative stability of carbanion.
(c) OH–,RO–, RCOO– : Neutral nucleophile
(d) AlCl3, BF3, FeCl3 : Positively charged nucleophile
Answer:
(a) + C(CH3)3 > +CH(CH3)2> +CH2-CH3 > +CH3 : Relative stability of carbocations.
Question 3.
(a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2Br + Alcoholic KOH : Substitution reaction
(b) CH3 – CH2 – CH2Br + Alcoholic KOH : Elimination reaction
(c) CH3CHO + Acidic dichromate : Reduction reaction
(d) Benzene + Pt + H2 : Oxidation reaction
Answer:
(b) CH3 – CH2 – CH2Br + Alcoholic KOH : Elimination reaction
VI. Choose the incorrect pair.
Question 1.
(a) – OH,- SH, -NH2 : Positive mesometic effect
(b) – NO2 >CO, – COOH : Negative mesomeric effect
(c) – F, – Cl, – NO2 : Electron withdrawing group
(d) – C(CH3)3, – CH(CH3)3 – CH2 – CH3 : Electron withdrawing group
Answer:
(c) – F, – Cl, – NO2 : Electron withdrawing group
Question 2.
(a) NH3 andAmines : Neutral nucleophile
(b) OH– and RCOO– : Negative nucleophile
(c) RX and H3O3 : Positive electrophile
(d) MCl3, BF3 : Negative electrophile
Answer:
(d) AlCl3, BF3 : Negative electrophile
Question 3.
Answer:
![]()
VII. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Neutral molecule SnCl4 can act as an electrophile.
Reason (R): it has vacant ‘d’ orbitais which can accommodate the electrons from others.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : The C-C bond in ethane is non-polar while the C-C bond in ethyl chloride is polar.
Reason (R) : Chlorine is more electronegative than carbon and hence it attracts the shared pair of electron between C-C in ethyl chloride and it develops a negative charge on Cl and positive charge on Carbon.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Phenol is more acidic than aliphatic alcohols.
Reason (R): The phenoxide ion is more stabilized than phenol by resonance effect and hence resonance favours ionization of phenol to form H and shows acidity.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of(A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of(A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of(A).
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The cut apple turns brown.
Reason (R): Cut apple exposes its cells to atmospheric oxygen and the oxidizes the phenolic compound present in it. Due to this enzymatic browning, the cut apple turns brown.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions 2 Marks Question and Answers
II. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
What is the mechanism of reaction?
Answer:
Many chemical reactions are depicted in one or more simple steps. Each step passes through an energy barrier, leading to the formation of short-lived intermediates or transition states. The series of simple steps which collectively represent the chemical change, from the substrate to product is called the mechanism of the reaction. The slowest step in the mechanism determines the overall rate of the reaction.
Question 2.
What is the mechanism of the reaction?
Answer:
In organic reactions, that series of simple steps collectively represent the chemical change, from the substrate to product, this is called as the mechanism of the reaction. The slowest step in the mechanism determines the overall rate of the reaction.
Question 3.
What is the Negative Mesomeric effect? Give example.
Answer:
The negative resonance effect occurs when the electrons move towards the substituent attached to the conjugated system. It occurs if the electron-withdrawing substituents are attached to the conjugated system. In such cases, the attached group has a tendency to withdraw electrons through resonance. These electron-withdrawing groups are usually denoted as -R or -M groups.
Example:
NO2, > C = O, – COOH, – C ≡ N etc..
Question 4.
Explain the homolytic fission of a covalent bond?
Answer:
- Homolytic cleavage is the process in which a covalent bond breaks symmetrically in such way that each of the bonded atoms retains one electron.
- This type of cleavage occurs under high temperatures or in the presence of UV light.
- in a compound containing a non-polar covalent bond formed between atoms of similar electronegativity, in such molecules the cleavage of bonds results in free radicals.
- For example, ethane undergoes homolytic fission to produce, two methyl free radicals.
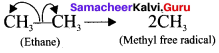
Question 5.
What are free radical initiators?
Answer:
The types of reagents that promote homolytic cleavage in substrate are called as free radical initiators. They are short lived and are highly reactive.
![]()
Question 6.
Mention any two examples for free radical initiators?
Answer:
Two examples for free radical initiators
- Azobisisobutyronitnie (AIBN)
- Benzoyl peroxide
Question 7.
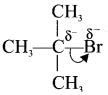
Explain the heterolytic fission of a covalent bond?
Answer:
- Heterolytic cleavage is the process in which a covalent bond breaks unsymmetrically such that one of the bonded atom retains the bond pair of electron.
- It results in the formation of a cation and an anion of the two bonded atoms the most electronegative.
- For example in tert-butyibromide, the C-Br bond is polar as bromine is more electronegative than carbon. Hence the C-Br undergoes heterolytic cleavage to form a terl-butyl carbocation and bromide anion.
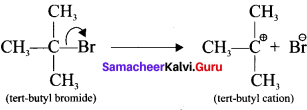
Question 8.
What are carbocations?
Answer:
1. Let us consider the heterolytic fission of the bond C-X present in organic molecule. If atom X has a greater electronegativity than the carbon atom, the former takes away the bonding electron pair and becomes negatively charged while the carbon will lose its electron and thus acquire a positive charge.
2. Such a cationic species carrying a positive charge on carbon are known as carbocation or carhonitim ion.

Question 9.
What are carbanions?
Answer:
Let us consider the heterolytic fission of the bond C-X present in an organic molecule. if the carbon atom has greater electronegativity than the atom X, the former takes away the bonding electron pair and acquires a negative charge. The resulting carbon anion is known as carbanion.

Question 10.
After cutting an apple it turns brown. Why?
Answer:
Apples contain an enzyme called polyphenol oxidase (PPO), also known as tyrosinase. Cutting an apple exposes its cells to atmospheric oxygen and oxidizes the phenolic compounds present in apples. This is called the enzymatic browning that turns a cut apple brown. In addition to apples, enzymatic browning is also evident in bananas, pears, avocados and even potatoes.
Question 11.
Identify which of the following are electrophiles and nucleophiles?
- NH3
- AlCl3
- R-SH
- R-X
- R-O-R
- BF3
Answer:
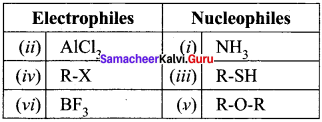
Question 12.
How will you distinguish between electrophiles and nucleophiles?
Answer:
Electrophiles:
- They are electron deficient.
- They are cations.
- They are lewis acids.
- Accept an electron pair.
- Attack on electron-rich sites.
Nucleophites:
- They are electron-rich.
- They are anions.
- They are lewis bases.
- Donate an electron pair.
- Attack on electron-deficient sites.
Question 13.
What are all the sources for the human body that produces free radicals?
Answer:
Sources for the human body produces free radicals,
- The human body is exposed to X-rays.
- Cigarette smoke.
- Industrial chemicals.
- Air pollutants.
Question 14.
In what way free radicals affect the human body?
Answer:
- Free radicals can disrupt cell membranes.
- Increase the risk of many forms of cancer.
- Damage the interior lining of blood vessels.
- leads to a high risk of heart disease and stroke.
Question 15.
How to reduce the effect of free radicals?
Answer:
- Use vitamins and minerals to counter the effects of free radicals.
- Fruits contain antioxidants which decrease the effects of free radicals.
Question 16.
Identify which of the following shows the +I and -I effect?
- -NO2
- -SO2H
- -I
- -OH
- CH2O-
- CH2–
Answer:
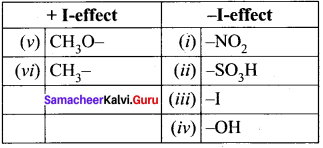
Question 17.
Why chloro acetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid?
Chioro acetic acid:
Answer:
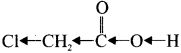
Chioro acetic acid has Cl-group and it has high electronegativity and shows -I effect. Therefore Cl-atom to faciLitate the dissociation of O-H bond very fastly, whereas in the case of acetic acid, has CH3 group and it shows +I effect, theretòre dissociation of O-H bond will be more difficult. Thus chloro acetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid.
![]()
Question 18.
Explain the positive and negative electromeric effects?
Answer:
1. When an electrophile such as W approaches an alkene molecule, the π electrons are instantaneously shifted to the electrophile and a new bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen. This makes the other carbon electron deficient and hence it acquires a positive charge.
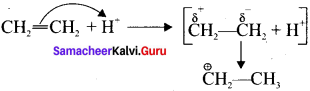
2. When the it electron is transferred towards the attacking reagent, it is called the positive electromeric (+E) effect.
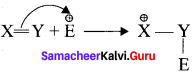
3. Whèn the t electron is transferred away from the attacking reagent it is called the negative electromeric (-E) effect.
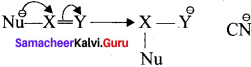
For example : The attack of C\({ N }^{ \ominus }\) on a carbonyl carbon.
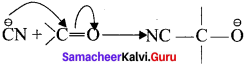
Question 19.
Write short notes on the positive mesomeric effect?
Answer:
- The positive mesomeric effect occurs, when the electrons move away from substituent attached to the conjugated system.
- It occurs if the electron releasing substituents are attached to the conjugated system.
- The attached group has a tendency to release electrons through resonance, these electron releasing groups are usually denoted as +R or +M groups.
- Examples: -OH, -SH, -OR, -SR, -NH2 etc.
Question 20.
Write short notes on the negative mesomeric effect?
Answer:
- The negative mesomeric effect occurs when the electrons move towards the substituent attached to the conjugated system.
- It occurs if the electron-withdrawing substituents are attached to the conjugated system.
The attached group has a tendency to withdraw electrons through resonance, these electron-withdrawing groups are usually denoted as -R or -M groups. - Examples:
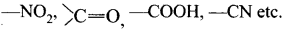
Question 21.
What are addition reactions? Give an example.
Answer:
All organic compounds having double or triple bond adopt addition reactions in which two substances unite to form a single compound. During the addition reaction the hybridization of the substrate changes as only one bond breaks and two new bonds are formed.
Example:
![]()
Question 22.
What are elimination reactions? Give an example.
Answer:
In these reactions, two atoms or groups are removed from a molecule without being substituted by other atoms or groups. A new C-C double bond is formed between the carbon atoms to which the eliminated atoms or groups are previously attached. It is always accompanied with change in hybridization.
Example:
![]()
Question 23.
What are organic oxidation reactions? Give an example.
Answer:
Most of the oxidation reaction of organic compounds involves gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
Example:
![]()
![]()
Question 24.
What are organic reduction reactions? Give an example.
Answer:
Most of the reduction reaction of organic compounds involves the gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen.
Example:
Question 25.
Why cut apple turns a brown colour?
Answer:
- Apples contain an enzyme called polyphenol oxidase (PPO) also known as tyrosinase.
- Cutting an apple exposes its cells to atmospheric oxygen and oxidizes the phenolic compounds present in apples. This is called the “enzymatic browning” that turns a cut apple brown.
- In addition to apples, enzymatic browning is also evident in bananas, pears, avocados, and even potatoes.
Question 26.
What are the different types of organic reactions?
Answer:
Organic compounds undergo many reactions, however, in the actual sense, we can fit all those reactions into the below-mentioned six categories.
- Substitution reactions
- Addition reactions
- Elimination reactions
- Oxidation and reduction reactions
- Rearrangement reactions
- Combination of the above
Question 27.
How will you convert alcohol into aldehyde?
Answer:
When primary alcohol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate to gives aldehyde.
![]()
Question 28.
What happen when nitrile undergoes acid hydrolysis?
Answer:
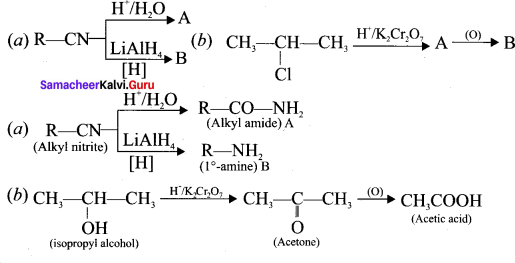
When alkyl nitrile undergoes acid hydrolysis to give amide, which on further hydrolysis to give carboxylic acid.
![]()
Question 29.
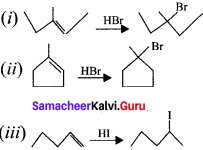
Complete the following reactions and identify the products?
Answer:
Question 30.
Predict the product for the following reaction.
Answer:
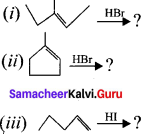
Answer:
Question 31.
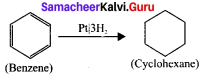
How will you convert benzene into cyclohexane?
Answer:
Benzene undergo catalytic hydrogenation in presence of platinum to give cyclohexane.
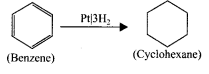
Question 32.
Complete the reaction and name the product
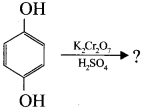
Answer:
Question 33.
Identify the product and mention the type of organic reaction.
Answer:
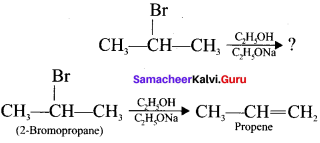
This is one of the elimination reaction.
Question 34.
Complete the following reaction and identify the product.
Answer:
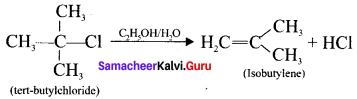
Question 35.
What are substitution reaction?
Answer:
In this reaction an atom or a group of atoms attached to a carbon atom is replaced by a new atom or a group of atoms.
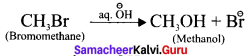
Here, -Br is replaced by -OH group.
![]()
Question 36.
How will substitution reactions are classified?
Answer:
Substitution reactions can be classified as,
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction.
- Electrophilic substitution reaction.
- Free radical substitution reaction.
Question 37.
Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds?
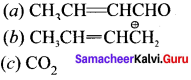
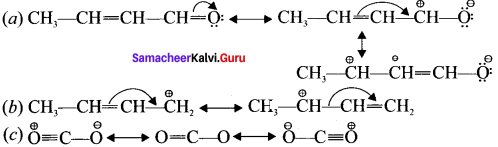
Answer:
Question 38.
Identify the reagents shown in box in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles.
Answer:
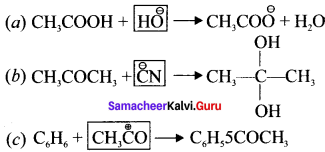
In (a) \(\overset { \ominus }{ OH } \) is nucleophile
In (b) \(\overset { \ominus }{ CN } \) is nucleophile
In (c) CH3\(\overset { \ominus }{ CO } \) is electrophile
Question 39.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type of organic reaction.
Answer:
(a) CH3CH2Br + \({ SH }^{ \ominus }\) → CH3CH2SH + \({ Br }^{ \ominus }\)
(b) (CH3)2C = CH2 + HCI (CH3)2CCl – CH3
(c) CH3CH2Br + \({ OH }^{ \ominus }\) → CH2 = CH2 + H2O + \({ Br }^{ \ominus }\)
(a) Nucleophilic substitution reaction.
(b) Electrophilic addition reaction.
(c) Elimination reaction.
Question 40.
Which electron displacement effect explain the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids?
Answer:
CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2 CHCOOH > (CH3)3C COOH
As the number of alkyl group increases, +I effect increases and it strengthen the O-H bond. i.e., O-H bond dissociation is very difficult.
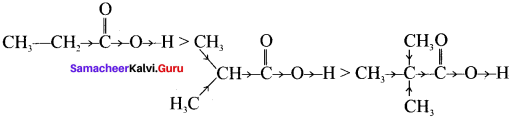
Therefore +I effect explain the correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids.
Question 41.
Which of the two, NO2CH2CH2\({O}^{ \ominus }\) or CH3CH2\({O}^{ \ominus }\) is expected to be more stable and why?
Answer:
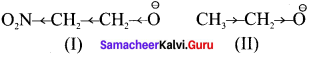
(I) is more stable than (II) because NO2 group has -I effect and hence it tends to disperse the -ve charge on the 0-atom. In contrast., CH3CH, has +I effect. It therefore, tends to intensify the -ve charge and hence destabilizes it.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions 5 Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain electron movement in organic reactions.
Answer:
All organic reactions can be understood by following the electron movements.
- Lone pair becomes a bonding pair.
- Bonding pair becomes a lone pair.
- A bond breaks and becomes another bond.
The electron movement depends on the nature of the substrate, reagent and the prevailing conditions.
Type – 1.
A lone Pair to a bonding pair
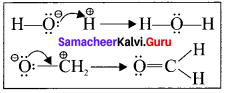
Type – 2.
A bonding pair to a lone Pair
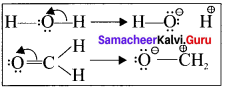
Type – 3.
A bonding pair to an another bonding pair
Question 2.
How does inductive effect influence the reactivity and acidity of carboxylic acids?
Answer:
(a) Reactivity:
- When a highly electronegative atom such as halogen is attached to a carbon then it makes the C—X bond polar.
- In such cases the -I effect of halogen facilitates the attack of an incoming nucleophile at the polarized carbon and hence increases the reactivity.
- If a -I group is attacher neared to a carbonyl carbon, it decreases the availability of electron density on the carbonyl carbon and hence increases the rate of the nucleophilic addition reaction.
(b) Acidity of carboxylic acid:
- When a halogen atom is attached to the carbon which is neared to the carboxylic acid group, its -I effect withdraws the bonded electrons towards itself and makes the ionization of H+ easy.
- The acidity of various chioro acetic acid is in the following order. Cl3C-COOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2COOH The strength of the acid increases with increase in the effect of the group attached to the carboxyl group.
- Similarly the following order of acidity in the carboxylic acids is due to the +1 effect of alkyl group. (CH3)3CCOOH < (CH3)2CHCOOH <CH3COOH
Question 3.
Explain the acidic nature of phenol.
Answer:
- Resonance is useful in explaining certain properties such as acidic of phenol.
- The phenoxide ion is more stabilized than phenol by resonance effect.
- The resonance favours ionisation of phenol to form H+ and shows acidity.
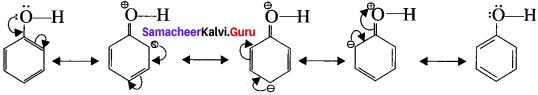
phenoxide ion resonance structures.
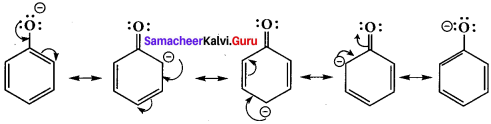
- The above structures shows that there is a charge separation in the resonance structure of phenol which needs energy whereas there is no such hybrid structures in the case of phenoxide ion. This increases stability accounts for the acidic character of phenol.
Question 4.
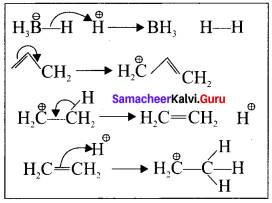
How does the hyperconjugation effect explain the stability of alkenes?
Answer:
- The relative stability of various classes of carhonium ions may be explained by the number of no-bond resonance structures that can be written for them.
- Such structures are arrived by shifting the bonding electrons from an adjacent C-H bond to the electron-deficient carbon.
- in this way, the positive charge originally on carbon is dispersed to the hydrogen. This manner of electron release by assuming no bond character in the adjacent C-H bond is called hyperconjugation or Baker- Nathan effect.
- The greater the hyperconjugation, the greater will be the stability of the compound. The increasing order of stability can be shown as:
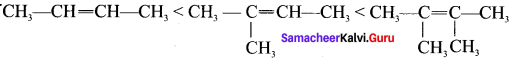
- Alkyl group increases in the C=C double bond carbon, hyperconjugation increases, and stability of that organic compound also increases.
Question 5.
Explain the types of addition reactions?
Answer:
Addition reactions are classified into three types. They are,
- Electrophilic addition reaction
- Nucleophilic addition reaction
- Free radical addition reaction
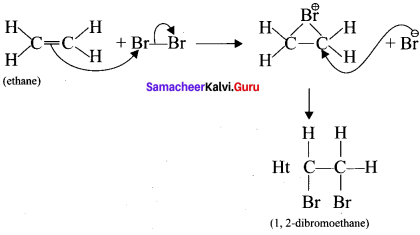
1. Electrophilic addition reaction:
An electrophilic addition reaction can be described as an addition reaction in which a reactant with multiple bonds as in a double or triple bond undergoes has it air bond broken and two new a bond are formed.
2. Nucleophilic addition reaction:
A nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electron-deficient or electrophilic double or triple bond, reacts with a nucleophilic which is an electron-rich reactant with the disappearance of the double bond and creation of two new single or bonds.
3. Free radical addition reaction:
it is an addition reaction in organic chemistry involving free radicals. The addition may occur between a radical and a non radical or between two radicals.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the types of substitution reaction?
Answer:
Substitution reactions are classified into three types. They are,
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction.
- Electrophilic substitution reaction.
- Free radical substitution reaction.
1. Nucleophilic substitution reaction:
A nucleophilic substitution reaction in organic chemistry is a type of reaction where a nucleophilic gets attached to the positive charged atoms or molecules of the other substance. A good example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction is the hydrolysis of alkyl bromide, under the basic conditions where in the nucleophile is nothing but the base H. whereas the leaving group is the Br°. The reaction for the following is as give below.
![]()
2. Electrophilic substitution reaction:
The electrophilic substitution reaction involves the electrophiles. The electrophilic reactions occur mostly with the aromatic compounds. This types of substitution reaction arc basically defined as those chemical reactions where the electrophile replaces the functional group in a compound but not the hydrogen atom, sometimes hydrogen atom can be also replaced by electrophiles.
For example:
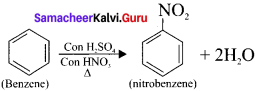
3. Free radical substitution reaction:
Free radical substitution reaction involving free radicals arc a reactive intermediate.
A – X + Y → A – Y + X
CH4 + Cl → CH + HCl
CH3 + Cl → CH3Cl (methyl chloride)
Question 7.
For the following bond cleavages use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify each as homolytic or heterolytic fission. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical,, carbocation and carbanion?
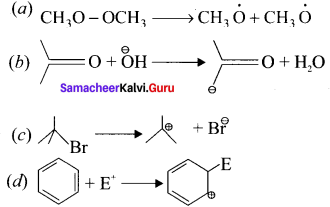
Answer:
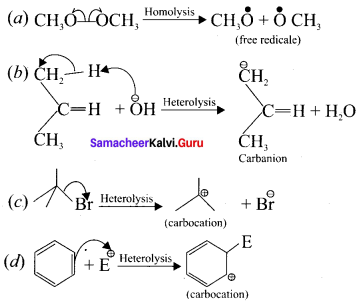
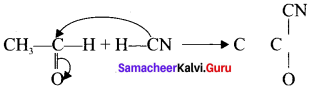
Question 8.
An organic compound (A) has a molecular formula C2H6O it is one of the primary alcohol. A reacts with acidified potassium dichromate to give B. B on further undergoes to oxidation reaction to give C. C on reacts with SOCl3 to give D which ¡s chlorinated product. Identify A,B,C and D, explain with equation.
Answer:
1. C2H6O is CH3-CH2-OH which is a primary alcohol (A)
2. CH3-CH2-OH (A) reacts with H+/ K2Cr2O7 to give acetaldehyde (B)
![]()
3. CH3CHO (B) which on further oxidation to give acetic acid (C).
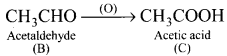
4. Acetic acid reacts with SOCl2 to give acetyl chloride (D).
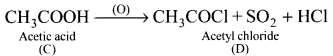
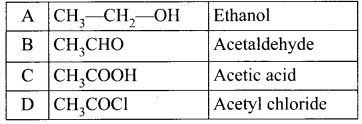
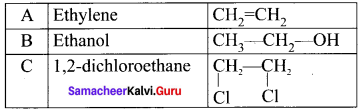
Question 9.
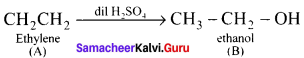
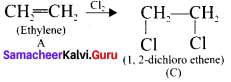
An organic compound (A) of a molecular formula C2H4 which is a simple alkene. A reacts with dil H2S04 to give B. A again reacts with Cl2 to give C. Identify AB and C and write the equations.
Answer:
1. C2H2 is CH2=CH2 is a simple alkene. A is ethylene.
2. Ethylene (A) reacts with dii H2SO4 to give ethanol (B)
3. Ethylene (A) reacts with Cl, to give 1.2 dichloro ethane (C)
Question 10.
Complete the reactions and identify the products.
Answer: