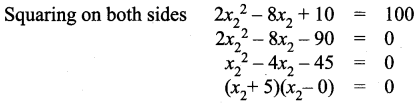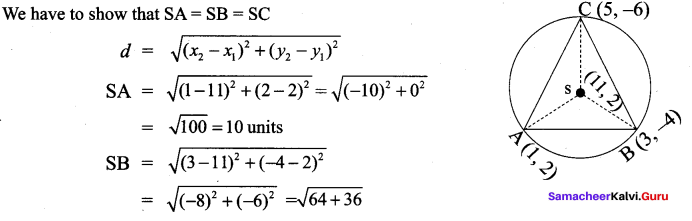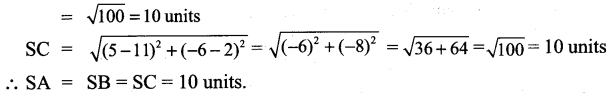You can Download From Zero to Infinity Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf Prose Chapter 6 help you to revise complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Exploring the textbook concepts is not enough for students who dreamt to do a cakewalk in English grammar. Consistently do your learning and practicing session with Samacheer Kalvi 9th English Grammar study material and achieve all your dreams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th English Solutions Prose Chapter 6 From Zero to Infinity
From Zero To Infinity 9th Standard English Warm Up:
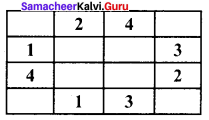
Answer:
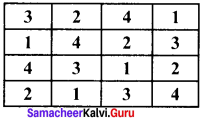
Question 1.
Did you enjoy solving this?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 2.
Was it easy or hard to solve?
Answer:
It was very easy to solve.
Question 3.
Do you like Mathematics? Give reasons.
Answer:
I like mathematics because it is fun to solve and find the right solutions. It is very useful in our daily lives.
OR
I do not like mathematics because it is complicated and too hard to understand.
From Zero to Infinity Intext Questions
Question 1.
What was the reaction of the classmates to Ramanujan’s question?
Answer:
There was a roar of laughter in the class when Ramanujan asked a question. The boys exclaimed that it was a silly question to ask.
Question 2.
What did the Indian mathematician Bhaskara prove?
Answer:
The Indian mathematician Bhaskara proved that zero divided by zero is infinity.
Question 3.
Where did Ramanujan get S.L. Loney’s book on Trigonometry?
Answer:
Ramanujan got the book “Loney’s Trignometry” from a college library.
Question 4.
Where did Ramanujan do his mathematical problems?
Answer:
Ramanujan did his mathematical problems on loose sheets of paper or on a slate.
Question 5.
What were the subjects neglected by Ramanujan in college?
Answer:
The subjects neglected by Ramanujan in college were History, English, and Physiology.
Question 6.
Which University granted him a fellowship of H75 a month?
Answer:
University of Madras granted him a fellowship of? 75 a month.
Question 7.
What did Ramanujan send to G.H. Hardy?
Answer:
Ramanujan sent a letter to G.H. Hardy in which he set out 120 theorems and formulae.
Question 8.
Who discovered a rare mathematical genius in Ramanujan?
Answer:
G.H Hardy and his colleague J.E. Littlewood discovered a rare mathematical genius in Ramanujan.
From Zero to Infinity Textual Questions
A. Answer the following questions in a sentence or two.
Question 1.
Why did the students laugh at Ramanujan?
Answer:
The teacher complimented Ramanujan because he had asked a question that had taken mathematicians several centuries to answer.
Question 2.
Why did the teacher compliment Ramanujan?
Answer:
The teacher complimented Ramanuj for asking a question that took centuries for mathematicians to answer.
Question 3.
Question What did Ramanujan do after reading the book on Trigonometry?
Answer:
Ramanujan mastered the book and also began his own research.
Question 4.
What disappointed Ramanujan’s father?
Answer:
Ramanujan failed twice in his first-year arts examination in college as he neglected other subjects such as History, English and Physiology. This disappointed his father.
Question 5.
How did Ramanujan manage his paper crisis?
Answer:
Ramanujan started using even scraps of paper he found lying on the streets. Thus he managed his paper crisis.
Question 6.
Why was Ramanujan’s application for jobs rejected?
Answer:
Ramanujan would show his frayed notebooks to every officer. But no one could understand what was written in the notebooks. So, his applications for jobs were rejected.
Question 7.
Why was Ramanujan sent back to India?
Answer:
Ramanujan was being devoured by Tuberculosis, then an incurable disease. So he was sent back to India.
Additional Questions:
Question 1.
Who asked the intriguing question to the arithmetic teacher? What do you know about him?
Answer:
The intriguing question was asked by Srinivasa Ramanujan. He was a native of Kumbakonam. Both during his school and research work at Cambridge, he was always ahead of his mathematics teachers.
Question 2.
Where and when was Ramanujan born? What do you know of his father?
Answer:
Ramanujan was born in Erode in Tamil Nadu on December 22, 1887. His father was a petty clerk in a cloth shop.
Question 3.
What was the most significant turn in Ramanujan’s life?
Answer:
The most significant turn came when one of Ramanujan’s senior friends showed him Synopsis of Elementary> Results in Pure Applied Mathematics by George Shoobridge Carr. Ramanujan was delighted than intimidated. This book triggered the mathematical genius in him and he began to work on the problems given in it.
Question 4.
What was Hardy’s opinion of Ramanujan?
Answer:
According to Hardy, Ramanujan was an unsystematic mathematician, similar to one who knows the Pythagorus theorem but does not know what a congruent triangle means. He felt that many discrepancies in his research could be due to his lack of formal education.
Question 5.
How can you say that Ramanujan was multi-talented?
Answer:
Besides Ramanujan being a mathematician, he was a reputed astrologer. He was also an excellent orator and many were eager to listen to his practical and intellectual talks. He used to give lectures on subjects like “God, Zero and Infinity”, topics that no ordinary man can easily indulge in. Hence we can surely say he was multi-talented.
B. Answer the following questions in about 80 -100 words.
Question 1.
Describe the life of Srinivasa Ramanujan in India.
Answer:
Ramanujan was born in Erode in Tamilnadu on December 22,1887. From early childhood, it was evident that he was a prodigy. Senior students used to get his assistance in solving math problems. At the age of 13, he began his own research on Trigonometry. The book “Elementary Results in Pure Applied Mathematics” by George Shoobridge Carr triggered the genius in Ramanujan. He used to do problems on loose sheets and enter the results in notebooks which are now famous as “Ramanujan’s Frayed Notebooks”.
Although Ramanujan secured a first class in Mathematics in the matriculation examination and was awarded the Subramanyan Scholarship, he failed twice in his first year arts examination in college as he neglected other subjects such as History, English and Physiology. He searched for job for food and papers to do calculations. The Director of Madras Port Trust gave a clerical job to Ramanujan on a monthly salary of Rupees 25.
Question 2.
Narrate the association of Ramanujan with G.H. Hardy.
Answer:
Ramanujan sent a letter to the great Mathematician G.H. Hardy of Cambridge University, in which he set out 120 theorems and formulae which included the Reimann Series. Hardy and his colleague Littlewood realized that they had discovered a rare mathematical genius.
They invited him to Britain.Despite the cold weather and food, Ramanujan continued his research with determination in the company of Hardy and Littlewood. Hardy found an unsystematic mathematician in Ramanujan due to his lack of formal education. Ramanujan’s achievements include the Hardy-Ramanujan-Littlewood circle method in number theory.
Additional Questions:
Question 1.
What prompted Ramanujan to ask an intriguing question?
Answer:
The Mathematics teacher was teaching and solving concepts in division. She drew three bananas on the blackboard and she pointed to three boys who were there and asked them how many each would get. A smart student quickly answered that each would get one. After appreciating the students’ answer, the teacher introduced a similar instance of 1,000 bananas distributed among 1,000 boys where each would again get one. While the teacher was explaining, a boy seated in one comer who was none other than Ramanujan asked an intriguing question wherein if no banana was distributed among no one, would everyone still get one banana?
Question 2.
Mention the achievements of Srinivasa Ramanujan.
Answer:
Ramanujan was elected Fellow of the Royal Society on February 28, 1918. In October, 1918 he became the first Indian to be elected Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge. His achievements at Cambridge include the Hardy-Ramanujan-Littlewood circle method in number theory.
He is also popular with Roger-Ramanujan’s identities in partition of integers. A long list of the highest composite numbers, besides work on the number theory and the algebra of inequalities are also his noted achievements. In algebra his work on continued fractions is considered on par with great mathematicians like Leonard Euler and Jacobi.
Question 3.
What did Ramanujan do when his mind was flooded with ideas?
Answer:
Mathematical ideas flooded Ramanujan’s mind. He was not able to write all of them down. ‘He solved problems on loose sheets of paper, slate and jotted the results down in notebooks. Before he went abroad he had filled three notebooks, later known as Ramanujan’s Frayed Notebooks.
His father who found him scribbling, mistook him to be mad. He had to find money for food and papers to do calculations. Every month, he needed at least 2,000 sheets of paper. He started using scraps of paper found lying on the streets. Sometimes, he even wrote using red ink over used papers found on the streets.
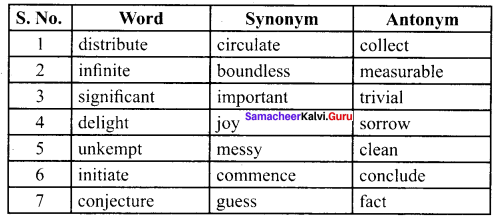
C. Match the words with correct Synonym and Antonym from the table.
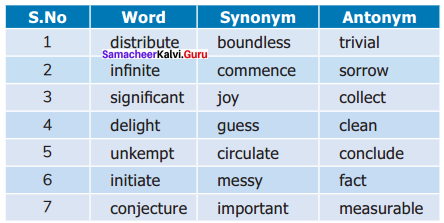
Answer:
Listening:
D. Listen to the anecdote “Two Geniuses” and narrate it in your own words.
Answer:
Narration of “Two Geniuses”
There’s a story about how Dr. Albert Einstein was travelling to Universities in his car, delivering lectures on his theory of relativity. During one tired journey, his driver Hans remarked “Dr. Einstein, I have heard you deliver that lecture about 30 times. ,t I know it by heart and bet I could give it myself.”
“Well, I’ll give you the chance”, said the Dr. “They don’t know me at the next University, so when we get there, I’ll put on your cap, and you introduce yourself as Dr. Einstein and give the lecture.”
The driver delivered Einstein’s lecture without any mistakes. When he finished, he started to leave, but one of the professor stopped him and asked a complex question filled with mathematical equations and formulae. The driver thought fast. “The answer to that problem is so simple,” he said,” I’m surprised you have to ask me. In fact, to show you just how simple it is, I’m going to ask my driver Hans to come up here and answer your question”.
Speaking:
E. Divide the students into groups of five and conduct a group discussion on the topic “Importance of Mathematics in Our Everyday Life” The teacher will act as a moderator.
Answer:
Group Discussion on Importance of Mathematics
Teacher: Good morning students! We have just learnt the life of the great mathematician Ramanujan. Now let’s have a group discussion on “Importance of Mathematics in Our Everyday Life”. Divide yourselves into groups of five.
Harsha (Group A) : The importance of maths in everyday life. Mathematics is a methodical application of matter. It is so said because the subject makes a man methodical or systematic. Mathematics makes our life orderly and prevents chaos.
Varsha (Group B) : In Hebrew, it’s root is “thinking.” They tell us that mathematics gives us the critical ability to learn and think logically in any field of endeavor. The skills of learning today are more important than knowledge, which is so readily available on the Internet.
Yusuf (Group C) : Math is an important part of our lives, because in the future you will get a job that deals with math. Math is pretty much in everything you do, really. Math is important because it is the most widely used subject in the world. Every career uses some sort of math.
Adhira (Group D) : Maths improves problem-solving abilities. Teaches clearer logical reasoning. Sharpens concentration and observance. Develops confidence and self-esteem.
Danny (Group E) : Knowing basic math principles keeps you from having to carry around a calculator because good use of math allows you to do many calculations in your head.
Reading:
F. Answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Question 1.
What made John Shepherd-Barron to come up with the idea of ATM?
Answer:
It was then John’s habit to withdraw money on a Saturday, but on this particular weekend he had arrived one minute late and found the bank doors locked against him. This made him to come up with idea of ATM.
Question 2.
When and where was the first ATM installed?
Answer:
The first ATM was installed at a branch in the North London suburb of Enfield on June 27, 1967.
Question 3.
Who was the first person to withdraw cash from the ATM?
Answer:
The first person to withdraw cash from the ATM was Reg Varney, a celebrity resident of Enfield known for his part in the number of popular television series.
Question 4.
Why did Shepherd-Barron reduce the PIN number from six digits to four?
Answer:
Shepherd-Barron’s wife said that she could only remember four figures, because of her, four figures became the world standard.
Question 5.
Which theory of Ramanujan helps the ATMs to dispense cash?
Answer:
Ramanujan’s Partition theory helps the ATMs to dispense cash.
Writing:
G. Paragraph Writing
Question 1.
Write a paragraph of 100-120 words about a memorable anecdote / incident of your life.
Answer:
A memorable anecdote/incident in my life:
I was then a student of class four. One day, I was left at home with my grandmother. It was in the afternoon, my grandmother was taking a nap. I was a very restless one. The toys soon bored me and I looked around for something new. The unique thing which caught my attention was my Grandma’s spectacles.
I put it on my nose just in the style of my Grandma and looked around. Soon my eyes got tired. As I felt pain in my eyes, I removed the specs and threw them away. They struck the wall and landed on the ground broken. Now I got worried and afraid. I started trying to repair it. As I was holding these glass pieces I felt a severe pain in the middle finger of my right hand, I looked at it .
Blood was trickling down from a deep cut in my finger. I started crying loudly. On hearing my loud wailing my Grandma woke up. She hurriedly came out of her room, took a quick glance at my adventure and detecting the source of my trouble, she pressed her hand on my cut finger for some time and then she took me to the doctor for bandaging. I was very much afraid of punishment but my Grandma forgave me although she had to suffer difficulty in seeing until the glasses were repaired. However I was naturally punished as I could neither eat my meals nor do my homework for three days.
Question 2.
Write a paragraph of 100-120 words about your favorite personality.
Answer:
My favorite personality:
There are many people all around the world who are very famous and celebrities. But my favourite personality is my father. My father is my hero. He is kind, polite and really friendly to everyone. He is a teacher by profession and is very good in teaching. He is always ready to help and support the needy and helpless. He is a God fearing person and always teaches us to remember the God’s gifts and God’s love for the world.
I am so proud to have a father like him. He is a simple man with kind rules. He is handsome, my favourite and my ideal man. He is my friend and always ready to encourage, appreciate me for success and always ready to help me wherever I need a friend or a support of my father. I am proud of my father and wish him good health forever.
Grammar:
A. Complete the following sentences using appropriate Connectors from the box.

1. She felt cold _________ she was wearing a winter coat.
Answer:
although
2. This restaurant has some of the best chefs in the town.__________ their service is excellent.
Answer:
Moreover
3. I’m not going to the party tonight __________ I didn’t get an invitation.
Answer:
because
4. You can set the table. __________, I’ll start making dinner.
Answer:
Meanwhile
5. I can play quite a few instruments __________ , the flute, the guitar and the piano.
Answer:
For instance
6. The store was out of chocolate chips; __________ they would need to make a different type of cookies.
Answer:
therefore
7. The stores are open daily __________ Sundays.
Answer:
except
8. I’ll stay __________ you need me.
Answer:
as long as
9. This detergent is highly concentrated and __________ you will need to dilute it.
Answer:
thus
10. It was the thing he prized __________ .
Answer:
above all
Active Voice and Passive Voice:
B. Convert the following active sentences into passive sentences by supplying an appropriate passive verb form.
Question 1.
She will not recognize us. / We__________ by her.
(a) will not recognize
(b) will not being recognized
(c) will not be recognized
Answer:
(c) will not be recognized
Question 2.
They didn’t invite me, but I went anyway. /I __________ but I went anyway.
(a) wasn’t invited
(b) wasn’t being invited
(c) wasn’t inviting
Answer:
(a) wasn’t invited
Question 3.
They broke up the table for firewood. / The table __________ up for firewood.
(a) broke
(b) had broken
(c) was broken
Answer:
(c) was broken
Question 4.
She has won the first prize. / The first prize __________ by her.
(a) has won
(b) has been won
(c) had been won
Answer:
(b) has been won
Question 5.
A friend of mine is repairing the car. / The car __________ by a friend of mine.
(a) is repairing
(b) is repaired
(c) is being repaired
Answer:
(c) is being repaired
Question 6.
Begin the work tomorrow. / Let the work __________ tomorrow.
(a) be begun
(b) begin
(c) is beginning
Answer:
(a) be begun
Question 7.
They speak English in New Zealand. / English __________ in New Zealand.
(a) is speaking
(b) is spoken
(c) is being spoken
Answer:
(b) is spoken
Question 8.
His attitude shocked me. / I __________ by his attitude.
(a) had shocked
(b) had been shocked
(c) was shocked
Answer:
(c) was shocked
Question 9.
She had already sent the parcel. / The parcel __________ by her.
(a) has already been sent
(b) had already been sent
(c) was already sent
Answer:
(b) had already been sent
Question 10.
Her silence worries me / I __________ her silence.
(a) am worrying by
(b) am worried by
(c) have worried by
Answer:
(b) am worried by
C. Match the following Active voice sentences with Passive voice.
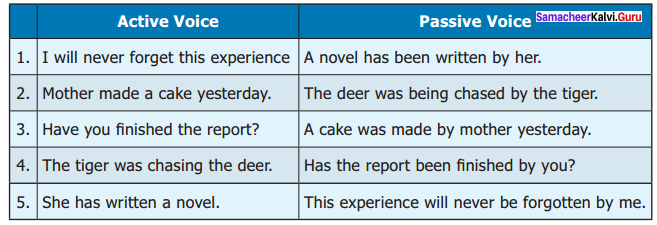
Answers:
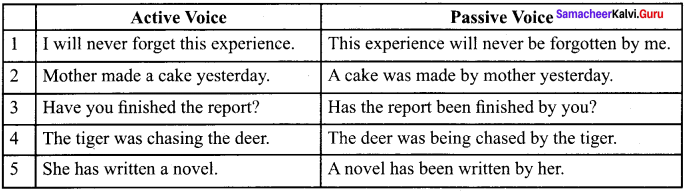
D. Change the following into passive voice.
Question 1.
Stanley will inform you later.
Answer:
You will be informed by Stanley later.
Question 2.
People speak Portuguese in Brazil.
Answer:
Portuguese is spoken by people in Brazil.
Question 3.
My grandfather built this house in 1943.
Answer:
This house was built by my grandfather in 1943.
Question 4.
Do not hurt the animals.
Answer:
You are warned not to hurt the animals.
Question 5.
You must not drop litter in the streets.
Answer:
You are warned not to drop litter in the streets.
Question 6.
Carry it home.
Answer:
Let it be carried to home.
Question 7.
They are decorating the wall.
Answer:
The wall is being decorated by them.
Question 8.
He has already mended the TV set.
Answer:
The TV set has already been mended by him.
E. Make a scrapbook of’Famous Biographies’ by collecting at least five biographies of famous scientists, mathematicians, inventors, artists etc., of your choice. You may also collect the pictures related to their achievements, inventions etc.
Answer :
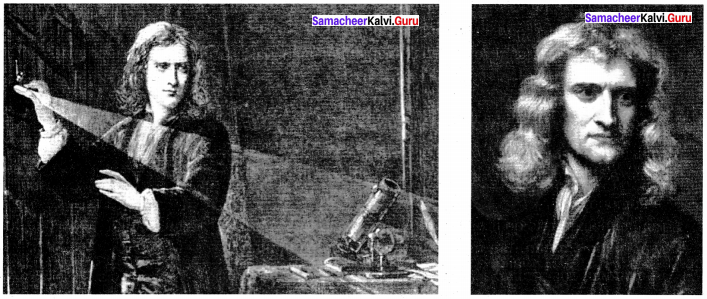
Sir Isaac Newton (Scientist):
Sir Isaac Newton was born on Christmas day, 1642. He was an English physicist and mathematician, who was the culminating figure of the scientific revolution of the 17th century. Born in the hamlet of Woolsthorpe, Newton was the only son of a local yeoman. Newton would eventually pick up his idea of a mathematical science of motion and bring his work to full fruition.
A tiny and weak baby, Newton was not expected to survive his first day of life, much less 84 years. Deprived of a father before birth, he soon lost his mother as well, for within two years she married a second time. He was left with his grandmother and moved to a neighbouring village.
For nine years, Isaac was effectively separated from his mother, and his pronounced psychotic tendencies have been ascribed to this traumatic event. Like thousands of other undergraduates, Newton began his higher education by immersing himself in Aristotle’s work. Even though the new philosophy was not in the curriculum, it was in the air.
Sometime during his undergraduate career, Newton discovered the works of the French natural philosopher Rene Descartes and the other mechanical philosophers. Newton had also begun his mathematical studies. Within little more than a year, he had mastered the literature; and, pursuing his own line of analysis, he began to move into new territory.
Despite the. fact that only a handful of savants were even aware of Newton’s existence, he had arrived at the point where he had become the leading mathematician in Europe.
Leonardo da Vinci (Artist):
Leonardo da Vinci was a leading artist and intellectual of the Italian Renaissance who’s known for his enduring works ‘ The Last Supper’ and the ‘Mona Lisa’. Leonardo da Vinci was born on April 15, 1452, in a farmhouse nestled amid the undulating hills of Tuscany outside the village of Anchiano, in present-day Italy. Born out of wedlock to respected Florentine notary Serpiero and a young peasant woman named Caterina.
Leonardo da Vinci was raised by his father and his stepmother. At the age of five, he moved to his father’s family estate in nearby Vinci, the Tuscan town from which the surname associated with Leonardo derives, and lived with his uncle and grandparents. Young Leonardo received little formal education beyond basic reading, writing and mathematics instruction, but his artistic talents were evident from an early age.
Around the age of 14, da Vinci began a lengthy apprenticeship with the noted artist Andrea del Verrocchio in Florence. He learned a wide breadth of technical skills including metalworking, leather arts, carpentry, drawing, painting and sculpting. His earliest known dated work, a pen-and-ink drawing of a landscape – the Amo Valley – was sketched in 1473. With a curious mind and keen intellect, da Vinci studied the laws of science and nature, which greatly improved his work. His ideas and body of work have influenced countless artists and made da Vinci a leading light of the Italian Renaissance.

Pythagoras (Mathematician):
Pythagoras is often known as the first pure mathematician. born on the island of Samos, Greece in 569 BC, his father, Mnesarchus, was a gem merchant. His mother’s name was Pythais and Pythagoras lived with his two or three brothers. Pythagoras was well educated, and played the lyre. He knew poetry and recited Homer. He was interested in mathematics, philosophy, astronomy and music.
Pythagoras believed:
- The sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to two right angles.
- The theorem of Pythagoras – for a right-angled triangle the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
- Constructing figures of a given area and geometrical algebra. For example they solved various equations by geometrical means.
- Pythagoras taught that Earth was a sphere in the center of the Universe, that the planets, stars, and the universe were spherical because the sphere was the most perfect solid figure.
- Pythagoras recognized that the morning star was the same as the evening star, Venus.
The Pythagorean Theorem is a cornerstone of mathematics, and continues to be so interesting to mathematicians that there are more than 400 different proofs of the theorem, including an original proof by President Garfield.

Michael Joseph Jackson (Singer and Dancer):

Michael Joseph Jackson was an American singer, songwriter and dancer. Dubbed the “King of Pop”, he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural icons of the 20th century and is also regarded as one of the greatest entertainers of all time. Jackson’s contributions to music, dance, and fashion, along with his publicized personal life, made him a global figure in popular culture for over four decades.
The eighth child of the Jackson family, Michael made his professional debut in 1964 with his elder brothers Jackie, Tito, Jermaine and Marlon as a member of the Jackson 5. He began his solo career in 1971 while at Motown Records.
In the early 1980s, Jackson became a dominant figure in popular music. His music videos, including “Beat It”, “Billie Jean”, and “Thriller” from his 1982 album Thriller, are all time favourites. Through stage and video performances, Jackson popularized a number of complicated dance techniques, such as the robot and the moonwalk, to which he gave the name.
His distinctive sound and style has influenced numerous artists of various genres. While preparing for his comeback concert series, This Is It, Jackson died of acute propofol and benzodiazepine intoxication in 2009, after suffering from cardiac arrest.
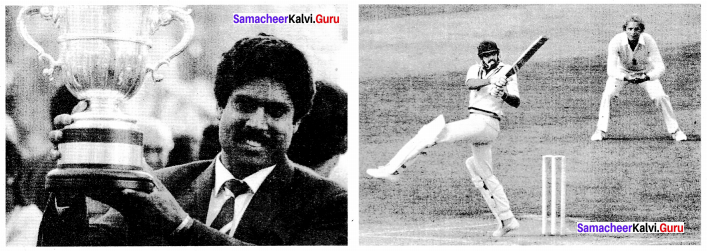
Kapil Dev (Cricketer):

Dev was born as Kapil Dev Nikhanj to Ram Lai Nikhanj, a prominent timber merchant and his wife Raj Kumari Ram Lai Nikhanj in Chandigarh on 6 January 1959. His mother was born in Pakpattan, in the town of the Sufi Saint Baba Farid. His father was from Dipalpur. They lived in Shah Yakka which is now in Okara district, Pakistan. His four sisters were born there before partition and his two brothers in Fazilka, where they moved after partition. His father spent his early life after the partition in Fazilka. They moved to the capital city Chandigarh.
Dev was a student at D.A.V. School and joined Desh Prem Azad in 1971. Dev captained the Indian cricket team that won the 1983 Cricket World Cup. He was India’s national cricket coach between October 1999 and August 2000. He retired in 1994, holding the world record for the most number of wickets taken in Test cricket, a record subsequently broken by Courtney Walsh in 2000.
He is the first player to take 200 ODI wickets. He is the only player in the history of cricket to have taken more than 400 wickets (434 wickets) and scored more than 5000 runs in Tests, making him one of the greatest all-rounders to have played the game. On 11 March 2010, Dev was inducted into the ICC Cricket Hall of Fame.
From Zero to Infinity Lesson Summary By Biography Of Srinivasa Ramanujan
Ramanujan was born in Erode in Tamil Nadu on December 22, 1887. His father was a petty clerk in a cloth shop. From early childhood it was evident that he was a prodigy. Mathematical ideas flooded in his mind for which he did not find enough papers to note it down. Hence he started writing them in loose sheets which was later known as Ramanujan’s Frayed Notebook. At the age of 13, he was not only able to master the Loney’s Trigonometiy, but also started his own research and came up with many mathematical theorems and formulae.
At the age of 15, the book Synopsis of Elementary Results in Pure Applied Mathematics by George Shoobridge Carr given by his senior friends triggered the mathematical genius in him. Though Ramanujan was a mathematical genius and was awarded the Subramanyan Scholarship, he failed twice in his first-year arts examination in college, which disappointed his father.
Then Ramanujan started looking for a job as he needed money not only for food but also for papers to do his calculations. His applications were rejected as no one could understand what he had scribbled in his notebooks. Luckily, Director of Madras Port Trust, Francis Spring, understood his capability and he gave Ramanujan a clerical job on a monthly salary of ?25. Later on, some teachers and educationists helped him to get a research fellowship. Thus, on 1st May 1913, the University of Madras granted him a fellowship of ?75 a month, though he had no qualifying degree.
Meanwhile, he had sent a letter to the great mathematician G.H. Hardy of Cambridge University, in which he set out 120 theorems and formulae. Among them was what is known as the Reimann Series, a topic in the definite integral of Calculus. These letters made G.H. Hardy and his colleague J.E. Littlewood realize that they bad discovered a rare mathematical genius. They made quick arrangements for his passage and stay at Cambridge University. Ramanujan sailed to Britain on March 17, 1914.
Even though he found it difficult to adapt to the new environment, he continued his research in Mathematics with determination. He forgot his hardships in the company of Hardy and Littlewood. Ramanujan was elected Fellow of the Royal Society on February 28, 1918. He was the youngest Indian to receive this distinguished fellowship. In October that year, he became the first Indian to be elected Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge.
Ramanujan continued his works even though Tuberculosis, then an incurable disease, was devouring him. When his friends found him pale, exhausted and emaciated, they sent him back to India. He continued to play with numbers until his death. Apart from a mathematician, Ramanujan was an astrologer of repute and a good speaker.
From Zero to Infinity Glossary:

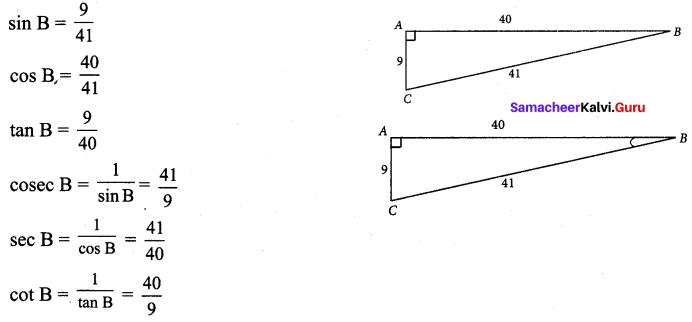
![]()
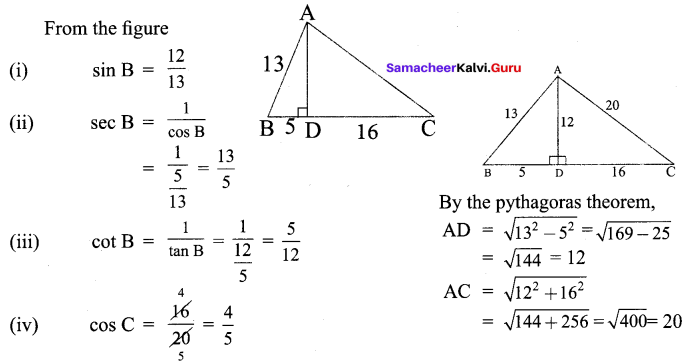
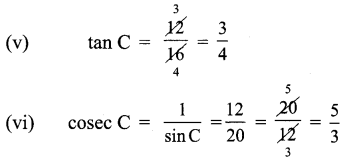
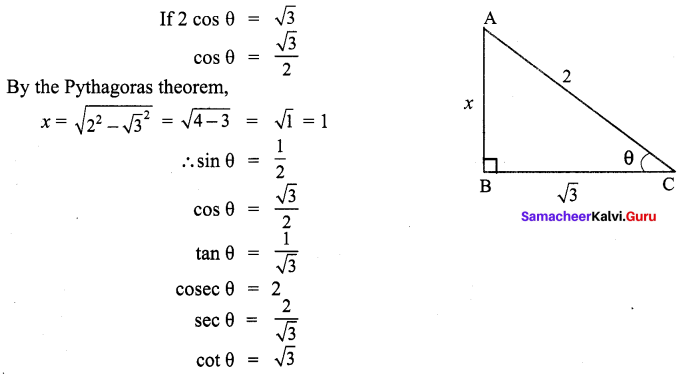
![]()


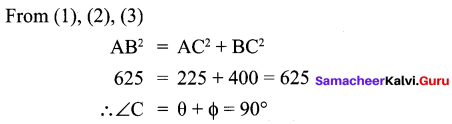
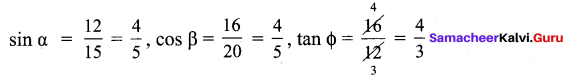
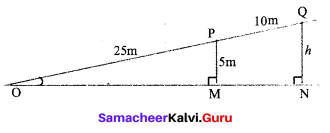
![]()
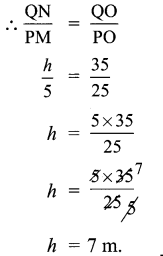
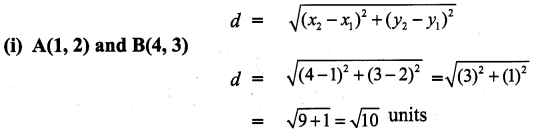
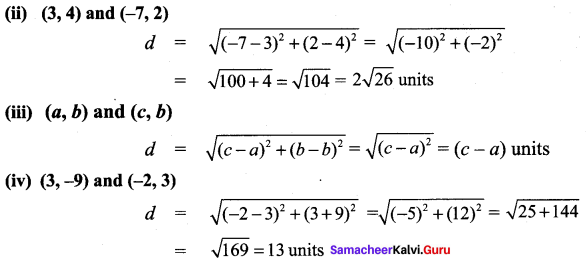
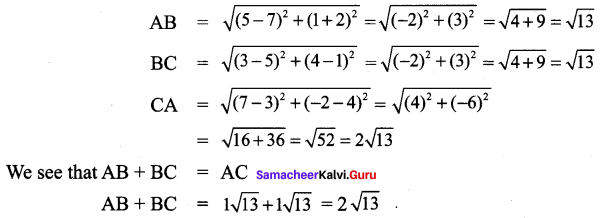
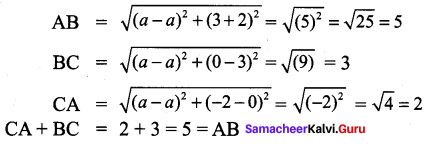
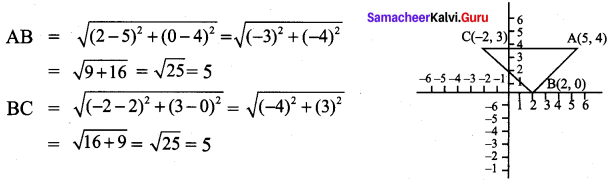
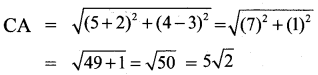
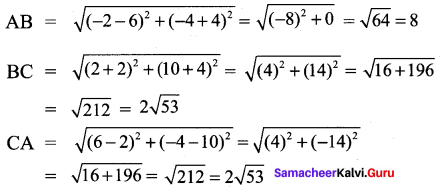
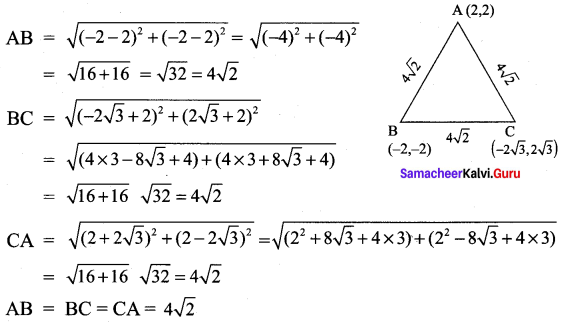
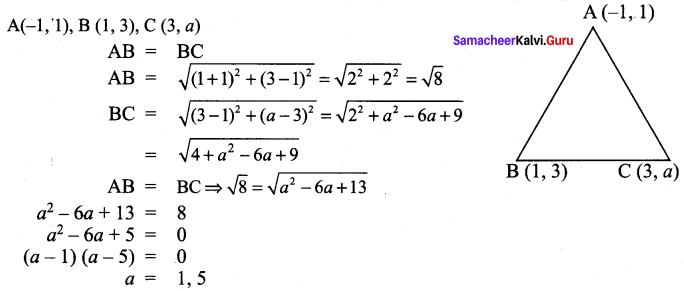
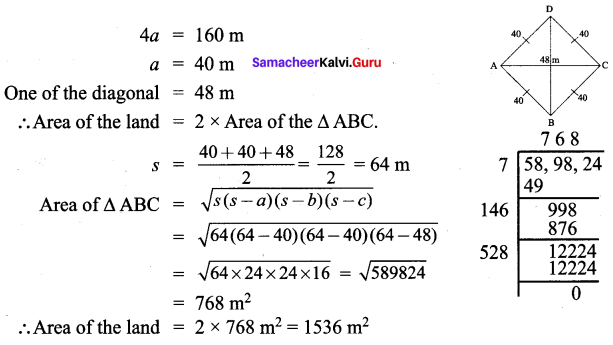
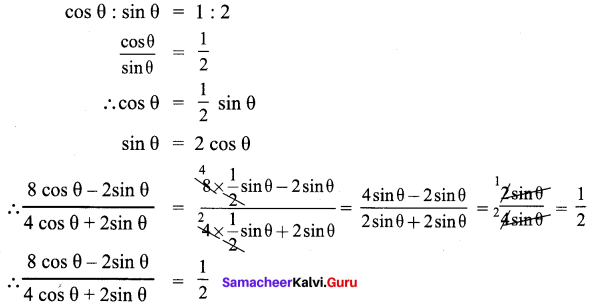
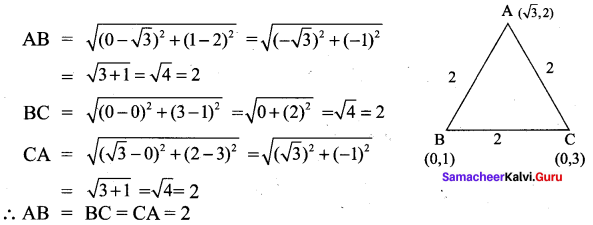 All the 3 sides of ∆ABC are equal. Hence ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.
All the 3 sides of ∆ABC are equal. Hence ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.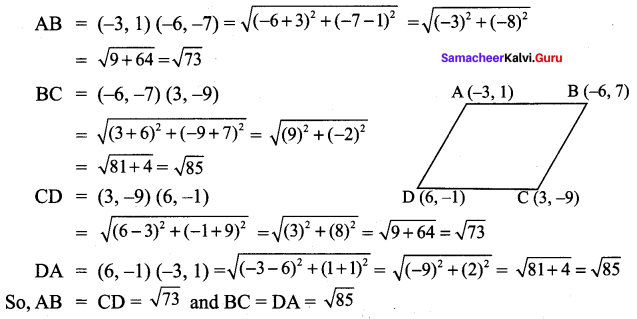
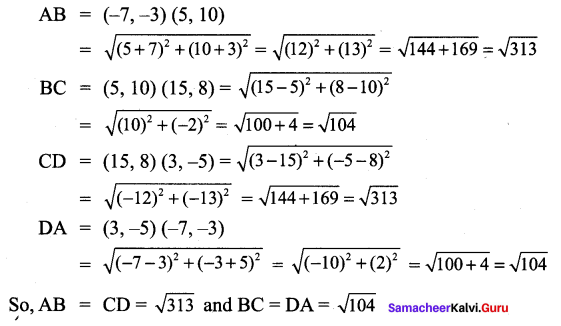
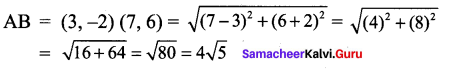
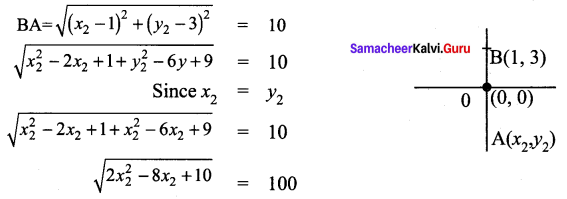
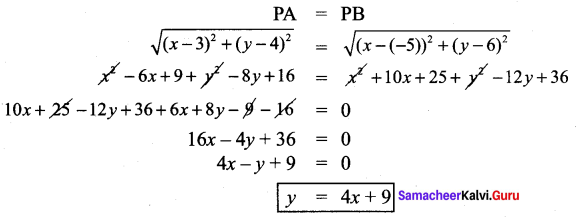
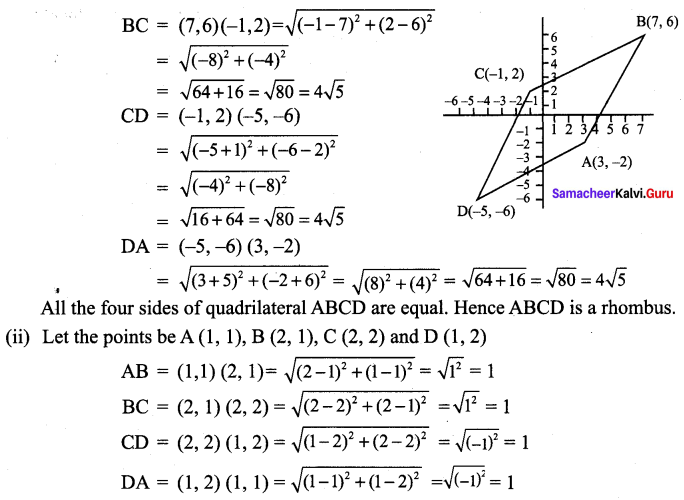 ∴ All the four sides of quadrilateral ABCD are equal. Hence ABCD is a rhombus.
∴ All the four sides of quadrilateral ABCD are equal. Hence ABCD is a rhombus.