Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 24 Environmental Science
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 24 Environmental Science
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Environmental Science Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
All the factors of biosphere which affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce are called as ………………
(a) biological factors
(b) abiotic factors
(c) biotic factors
(d) physical factors
Answer:
(b) abiotic factors
Question 2.
The ice sheets from the north and south poles and the icecaps on the mountains, get converted into water vapour through the process of …………….
(a) evaporation
(b) condensation
(c) sublimation
(d) infiltration
Answer:
(a) evaporation
![]()
Question 3.
The atmospheric carbon dioxide enters into the plants through the process of …………………….
(a) photosynthesis
(b) assimilation
(c) respiration
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(a) photosynthesis
Question 4.
Increased amount of …………….. in the atmosphere, results in greenhouse effect and global warming.
(a) carbon monoxide
(b) sulphur dioxide
(c) nitrogen dioxide
(d) carbon dioxide
Answers
(d) carbon dioxide
II. Match the Following:
| S.No. | Microorganism | S.No. | Role Played |
| 1. | Nitrosomonas | a | Nitrogen fixation |
| 2. | Azotobacter | b | Ammonification |
| 3. | Pseudomonas species | c | Nitrification |
| 4. | Putrefying bacteria | d | Denitrification |
Answer:
- (b) Ammonification
- (d) Denitrification
- (a) Nitrogen fixation
- (c) Nitrification
III. State whether the statements are true or false. Correct the false statements.
- Nitrogen is a greenhouse gas – False
Correct statement: Atmosphere is a rich source of nitrogen and contains about 78% nitrogen. - Poorly developed root is an adaptation of mesophytes – False
Correct statement: The roots of mesophytes are well developed and are provided with root caps. - Bats are the only mammals that can fly – True
- Earthworms use the remarkable high frequency system called echoes – False
Correct statement: Bats use the remarkable high frequency system called echoes. - Aestivation is an adaptation to overcome cold condition – False
Correct statement: Aestivation is an adaptation to overcome hot and dry condition.
IV. Answer in brief.
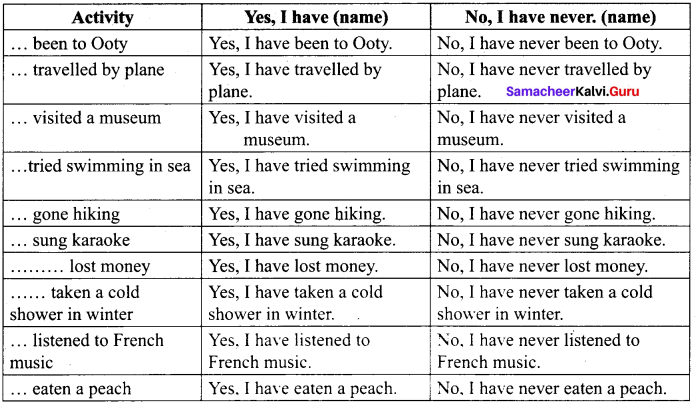
Question 1.
What are the two factors of the biosphere?
Answer:
- Biotic (or) living factors, which include plants, animals and all other living organisms.
- Abiotic (or) non-living factors, which include temperature, pressure, air, water, sunlight etc.
![]()
Question 2.
How do human activities affect the nitrogen cycle?
Answer:
Burning fossil fuels, application of nitrogen-based fertilizers and other activities can increase the amount of biologically available nitrogen in an ecosystem.
Question 3.
What is adaptation?
Answer:
Any feature of an organism or its part that enables it to exist under conditions of its habitat is called adaptation.
Question 4.
What are the challenges faced by hydrophytes in their habitat?
Answer:
Hydrophytes face certain challenges in their habitat. They are:
- Availability of more water than needed.
- Water current may damage the plant body.
- Water levels may change regularly.
- Maintain buoyancy in water.
Question 5.
Why is it important to conserve water?
Answer:
- Water is one of the precious natural resources.
- Clean and fresh water is essential for almost every human activity.
Question 6.
List some of the ways in which you could save water in your home and school?
Answer:
- When washing dishes, don’t let the tap be open. Fill one sink with wash water and another with rinse water.
- Adjust sprinklers so that only the plants are watered.
- Install rainwater tanks.
- Use hose water once a week to clean the driveway and sidewalk.
- Be sure to turn off the tap while not in use.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the uses of recycled water?
Answer:
Recycled water can be used for
- Agriculture
- Landscape
- Public parks.
- Cooling water for power plants and oil refineries
- Toilet flushing
- Dust control
- Construction activities.
Question 8.
What is IUCN? What is the vision of IUCN?
Answer:
IUCN is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
The vision of IUCN is ‘A just world that values and conserves nature’.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Describe the processes involved in the water cycle?
Answer:
Process of the water cycle
1. Evaporation:
- Conversion of liquid into gas (vapour) before reaching its boiling point.
- Water evaporates from the surface of the earth and water bodies such as the oceans, seas, lakes, ponds and rivers turn into water vapour.
2. Sublimation:
Direct conversion from solid to gas.
- Ice sheets and Ice caps from north and south pole,
- Ice caps on mountains converted into water vapour.
3. Transpiration :
The process in which plants release water vapour to atmosphere through small pores ‘ in leaves and stems.
4. Condensation :
Change from gas phase into liquid phase.
(e.g) Formation of clouds and fog.
5. Precipitation:
- Clouds combine to make bigger droplets and pour down as precipitation (rain) due to change in wind or temperature.
- Precipitation includes drizzle, rain, snow and hail.
6. Run off : Rain water runs over the earth to form rivers, lakes and ends up into seas and Oceans.
7. Infiltration: Water moves down the soil to increase ground water level.
8. Percolation : Water moves through porous or fractured rock.
Question 2.
Explain carbon cycle with the help of a flow chart?
Answer:
Carbon occurs in various forms on earth. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are elemental forms of carbon. Combined forms of carbon include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonate salts. All living organisms are made up of carbon-containing molecules like proteins and nucleic acids. The atmospheric carbon dioxide enters into the plants through the process of photosynthesis to form carbohydrates.
From plants, it is passed on to herbivores and carnivores. During respiration, plants and animals release carbon into atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is also returned to the atmosphere through decomposition of dead organic matter, burning fossil fuels and volcanic activities. Contribution of carbon to the atmosphere could be reduced by aforestation and lesser use of fossil fuels.
![]()
Question 3.
List out the adaptations of xerophytes?
Answer:
Adaptations of xerophytes:
- Well developed roots, (e.g) Calotropis.
- Water storing parenchymatous tissues, (e.g) Aloe vera, Opuntia.
- Small-sized leaves with waxy coating, (e.g) Acacia. In some plants, leaves are modified into spines, (e.g) Opuntia.
- Complete life span in a very short period on availing the moisture.
Question 4.
How does a bat adapt itself to its habitat?
Answer:
Mostly, bats live in caves. Caves provide them protection during the day from most predators and the temperature here is very stable. Apart from caves, bats also live in trees, hollowed logs and rock crevices. They are extremely important to humans as they reduce the insect population and help to pollinate plants.
Bats are active at night. This is a useful adaptation for them, as flight requires a lot of energy during day. Their thin, black wing membrane (Patagium) may cause excessive heat absorption during the day. This may lead to dehydration.
Question 5.
What is water recycling? Explain the conventional wastewater recycling treatment?
Answer:
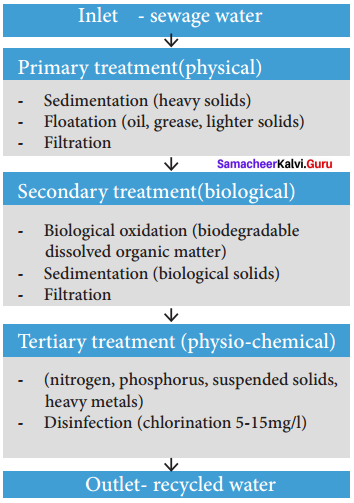
Water recycling is reusing treated wastewater for beneficial purposes such as agricultural and landscape irrigation, industrial processes, flushing in toilets and groundwater recharge. Conventional wastewater treatment consists of a combination of physical, chemical and biological processes which remove solids, organic matter, and nutrients from wastewater.
Wastewater treatment involves the following stages:
Primary treatment:
Primary treatment involves the temporary holding of the wastewater in a tank. The heavy solids get settled at the bottom while oil, grease and lighter solids float over the surface. The settled and floating materials are removed. The remaining liquid may be sent for secondary treatment.
Secondary treatment:
Secondary treatment is used to remove the biodegradable dissolved organic matter. This is performed in the presence of oxygen by aerobic microorganisms (Biological oxidation). The microorganisms must be separated from treated wastewater by sedimentation. After separating the sediments of biological solids, the remaining liquid is discharged for tertiary treatment.
Tertiary treatment:
Tertiary or advanced treatment is the final step of sewage treatment. It involves removal of inorganic constituents such as nitrogen, phosphorus and microorganisms. The fine colloidal particles in the sewage water are precipitated by adding chemical coagulants like alum or ferric sulphate.
VI. Give reason.
Question 1.
Roots grow very deep and reach the layers where water is available. Which type of plants develops the above adaptation? Why?
Answer:
Xerophytes are the type of plants that grow deep roots so as to reach the water source as they exist in a dry habitat.
![]()
Question 2.
Why streamlined bodies and the presence of setae is considered adaptations of earthworms?
Answer:
Stream-lined bodies help them to live in narrow burrows underground and for easy penetration into the soil.
Setae help the earthworm to move through the soil and provide an anchor in the burrows. Therefore these are considered to be adaptations of earthworm.
Question 3.
Why is it impossible for all farmers to construct it in their fields?
Answer:
All farmers may not be able to contact a pond in their fields as they occupy a large portion of farmer’s lands.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Environmental Science Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
……………… includes plants, animals and all other living organisms.
(a) Physical factors
(b) biotic factors
(c) abiotic factors
(d) biological factors
Answer:
(b) biotic factors
Question 2.
……………… is a type of vapourization, where liquid is converted to gas before reaching its boiling point.
(a) Evaporation
(b) Sublimation
(c) Condensation
(d) Transpiration
Answer:
(a) Evaporation
Question 3.
When there is a change in wind or temperature, clouds combine to make bigger droplets and pour down as ……………….
(a) percolation
(b) infiltration
(c) precipitation
(d) runoff
Answer:
(c) precipitation
![]()
Question 4.
……………… is the changing of the gas phase into the liquid phase.
(a) Transpiration
(b) Percolation
(c) Sublimation
(d) Condensation
Answer:
(d) Condensation
Question 5.
During …………….. microorganisms must be separated from treated wastewater by sedimentation.
(a) water recycling
(b) primary treatment
(c) secondary treatment
(d) tertiary treatment
Answer:
(c) secondary treatment
Question 6.
Which of the following is not an adaptation of xerophytes?
(a) the well developed root system
(b) store water
(c) small sized leaves with a waxy coating
(d) straight and branched stems
Answer:
(d) straight and branched stems
Question 7.
…………….. helps earthworm to live in narrow burrows underground and easy penetration into the soil.
(a) Aestivation
(b) Setae
(c) Stream-lined body
(d) Skin
Answer:
(c) Stream-lined body
Question 8.
……………. is a state of inactivity in which the body temperature drops with a lowered metabolic rate during winter.
(a) Hibernation
(b) Noctumality
(c) Echolocation
(d) Aestivation
Answer:
(a) Hibernation
![]()
Question 9.
…………… provides the primary nutrient important for the survival of all living organisms.
(a) Water cycle
(b) Nitrogen cycle
(c) Carbon cycle
(d) Oxygen cycle
Answer:
(b) Nitrogen cycle
Question 10.
……………….. is the process by which plants absorb nitrate ions and use them for making organic matter.
(a) Ammonification
(b) Nitrification
(c) Nitrogen assimilation
(d) Denitrification
Answer:
(c) Nitrogen assimilation
II. Match the Following:
| S.No. | Column A | Column B | |
| 1. | Water recycling | a | Living factors |
| 2. | Abiotic | b | Management of water resources |
| 3. | Water conservation | c | Non-living factors |
| 4. | Biotic | d | Landscape irrigation |
Answer:
- d. Landscape irrigation
- c. Non-living factors
- b. Management of water resources
- a. Living factors
III. State whether True or false. If false, write the correct statement.
- Water cycle is an essential component of proteins, DNA and chlorophyll – False
Correct statement: Nitrogen cycle is an essential component of proteins, DNA and chlorophyll. - Well developed root is an adaptation of hydrophytes – False
Correct statement: Well developed root is an adaptation of xerophytes. - Noctumality is a useful adaptation for them, as flight requires a lot of energy during day – True
- Hibernation is a state of inactivity in which the body temperature drops with a lowered metabolic rate during winter – True
- The ability to tolerate temperature depends on the surrounding moisture in the environment – True
IV. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
What are the types of biogeochemical cycles?
Answer:
Some of the important biogeochemical cycles are:
- Water cycle
- Nitrogen cycle
- Carbon cycle
Question 2.
Write the human impacts on carbon cycle.
Answer:
More carbon moves into the atmosphere due to burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. By increasing the amount of carbon dioxide, earth becomes warmer. This leads to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
![]()
Question 3.
Define ‘Cindrella of the plant kingdom’.
Answer:
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is a very charming plant. It is called as ‘Cindrella of the plant kingdom’. It covers entire surface of the water resources.
Question 4.
What are the strategies to support water conservation?
Answer:
Some of the strategies to support water conservation are:
- Rainwater harvesting.
- Improved irrigation techniques.
- Active use of traditional water harvesting structures.
- Minimising domestic water consumption.
- Awareness on water conservation.
- Construction of farm ponds.
- Recycling of water.
Question 5.
Write a short note on water conservation.
Answer:
Water conservation is the preservation, control and management of water resources.
- Industrial conservation
Water conservation measures that can be taken by industries are:- using dry cooling systems.
- if water is used as cooling agent, reusing the water for irrigation or other purposes.
- Agricultural conservation
Agricultural water is often lost due to leaks in canals, run off and evaporation. Some of the water conserving methods are:- using lined or covered canals that reduce loss of water and evaporation.
- using improved techniques such as sprinklers and drip irrigation.
- encouraging the development of crops that require less water and are drought resistant.
- mulching of soil in vegetable cultivation and in horticulture.
Question 6.
What are the limitations of farm ponds?
Answer:
Limitations of farm ponds
- Farm ponds reduce water flow to other tanks and ponds situated in lower-lying areas.
- They occupy a large portion of farmer’s lands.
Question 7.
Why are earthworms called as “farmers friend”?
Answer:
Earthworms are referred to as farmers friends as after digesting organic matter, they excrete nutrient rich Waste product called castings. These are useful to the plant and also as the earthworms burrow the soil, there is sufficient aeration which is useful for the roots.
Question 8.
Explain nocturnality in Bat and Earthworm.
Answer:
- Nocturnality in Bat
Bats are active at night which is a useful adaptation for them, as flight requires a lot of energy during day. The thin, black wing membrane called patagium may cause excessive heat absorption during the day leading to dehydration. - Nocturnality in Earthworm
Earthworms have no eyes, instead, they can sense light through the light-sensitive cells called photoreceptors present in their skin. They are very sensitive to bright light and therefore stays in burrows during the day and comes out only at night.
![]()
Question 9.
Why is Water Hyacinth responsible for the death of aquatic plants arid animals?
Answer:
Water Hyacinth is called as ‘Cindrella of the plant kingdom’. It covers entire surface of the water resources like ponds and lakes. It will not allow the light to penetrate into the water and increases the Biological Oxygen Demand leading to the death of aquatic plants and animals.3
Question 10.
What is vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost is the manure prepared by using earthworms to speed up the process of decomposition of plant and animal wastes. Vermicomposting is the fundamental practise of organic gardening. Vermicompost helps better plant growth and crop yield, improves physical structure of soil, increases the water-holding capacity of soil and is useful in elimination of biowaste.
Question 11.
Describe methods of water conservation in agriculture.
Answer:
Ways of water conservation in agriculture:
Agricultural water is often lost due to leaks in Canals, run off and evaporation. Some Of the water-conserving methods are:
- using lined or covered canals that reduce loss of water and evaporation.
- using improved techniques such as sprinklers and drip irrigation.
- encouraging the development of crops that require less water and are drought resistant.
- mulching of soil in vegetable cultivation and in horticulture.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
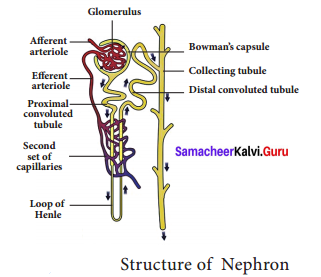
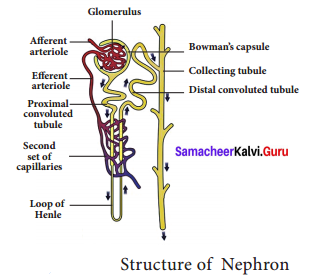
Explain Nitrogen cycle with a diagram.
Answer:
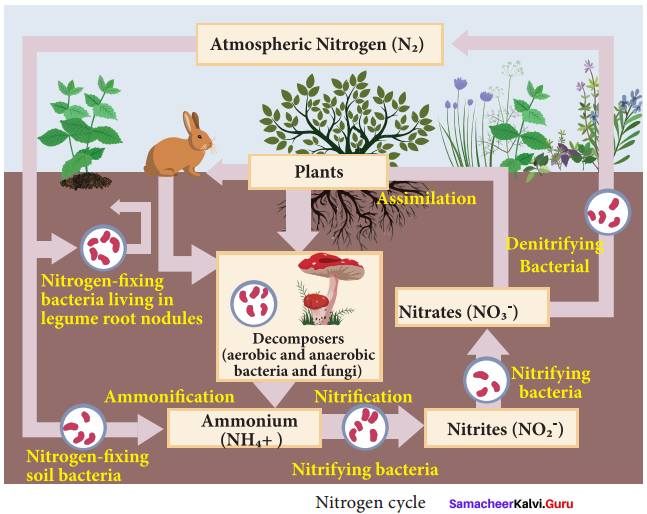
Nitrogen is primary nutrient important for survival of all living organisms. It is an essential component of proteins, DNA and chlorophyll. Atmosphere is a rich source of nitrogen and contains about 78% nitrogen. Plants and animals cannot utilize atmospheric nitrogen. They can use it only if it is in the form of ammonia, amino acids or nitrates. Processes involved in nitrogen cycle are:
- Nitrogen fixation: Nitrogen fixation is the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen, which is inert, into reactive compounds available to living organisms. This conversion is done by a number of bacteria and blue green algae (Cyanobacteria).
- Nitrogen assimilation: Plants absorb nitrate ions and use them for making organic matter like proteins and nucleic acids.
- Ammonification: The process of decomposition of nitrogenous waste by putrefying bacteria and fungi into ammonium compounds is called ammonification.
- Nitrification: The ammonium compounds formed by ammonification process are oxidised to soluble nitrates. This process of nitrate formation is known as nitrification. The bacteria responsible for nitrification are called as nitrifying bacteria.
- Denitrification: Free-living soil bacteria such as Pseudomonas sp. reduce nitrate ions of soil into gaseous nitrogen which enters the atmosphere.
Question 2.
Write in detail the adaptations of bat.
Answer:
Mostly, bats live in caves. Caves provide them protection during the day from most predators and the temperature here is very stable. Apart from caves, bats also live in trees, hollowed logs and rock crevices. They are extremely important to humans as they reduce insect population and help to pollinate plants.
The adaptations of a bat in relation to their habitat are;
- Nocturnality
Bats are active at night. This is a useful adaptation for them, as flight requires a lot of energy during day. Their thin, black wing membrane (Patagium) may cause excessive heat absorption during the day. This may lead to dehydration. - Flight adaptation
Bat wings are entirely different from those of birds or insects. Modified forelimbs serve as wings. The bones in the wings of bats are elongated fingers and are connected by the flaps of skin on either side of the body known as Patagia. Tail supports and controls movements during flight. Muscles are well developed and highly powerful and achieve in beating of wings. Tendons of hind limbs provide a tight grasp when the animals are suspended upside down at rest. - Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of inactivity in which the body temperature drops with a lowered
metabolic rate during winter. Bats are warm-blooded animals but unlike other mammals, they let their internal temperature reduce when they are resting. They go to a state of decreased activity to conserve energy. - Echolocation
Bats are not blind. But to fly around and hunt for insects in the dark, they use a remarkable high-frequency system called echolocation. Bats give out high-freqUeney sounds (ultrasonic sounds). These sounds are reflected back from its prey and perceived by the ear. Bats use these echoes to locate and identify the prey.
Question 3.
Write the advantages of farm ponds.
Answer:
The advantages of farm ponds are:
- They provide water to growing crops, without waiting for rainfall.
- They provide water for irrigation, even when there is no rain.
- They reduce soil erosion.
- They recharge groundwater.
- They improve drainage.
- The excavated soil can be used to enrich the soil in fields and levelling lands.
- They promote fish rearing.
- They provide water for domestic purposes and livestock.
![]()
Question 4.
Write in detail about IUCN.
Answer:
International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It provides public, private and non-governmental organizations with the knowledge to enable human progress, economic development, and nature conservation to take place together.
1. Vision of IUCN: The vision of IUCN is ‘A just world that values and conserves nature’.
2. Mission of IUCN: The mission of IUCN is to influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve the integrity and diversity of nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable. It tries to influence the actions of governments, businesses and other stakeholders by providing information and advice. The organization is best known to the wider public for compiling and publishing the IUCN red list of threatened species, which assesses the conservation status of species worldwide.
India became a state member of IUCN in 1969, through the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change (MOEFCC). Four of 34 globally identified biodiversity hotspots are found in India. They are:
- The Himalayas
- The Western Ghats
- The North-East
- The Nicobar islands