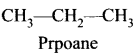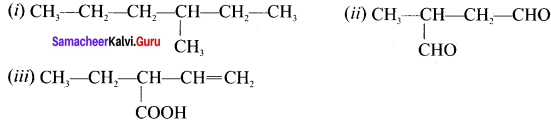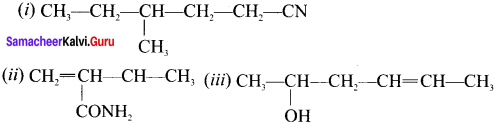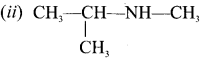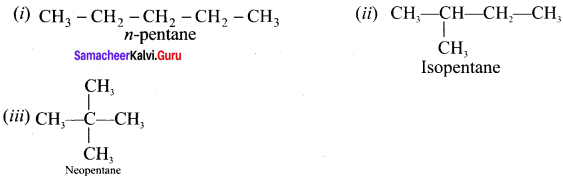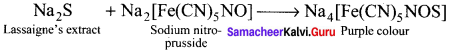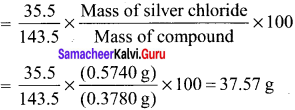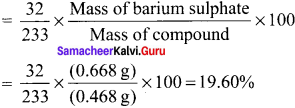Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 11 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 11 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Textual Evaluation Solved
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Select the molecule which has only one ir bond.
(a) CH3-CH=CH-CH3
(b) CH3-CH=CH-CHO
(c) CH3-CH=CH-COOH
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) CH3-CH=CH-CH3
Question 2.
In the hydrocarbon 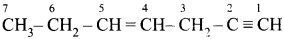 the state of hybridisation of carbon 1,2,3,4 and 7 are in the following sequence.
the state of hybridisation of carbon 1,2,3,4 and 7 are in the following sequence.
(a) sp, sp, sp3, sp2, sp3
(b) sp2, sp, sp3, sp2, sp3
(c) sp, sp, sp2, sp, sp3
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) sp, sp, sp3, sp2, sp3
Question 3.
The general formula for alkadiene is ……….
(a) CnH2n
(b) CnH2n-1
(c) CnH2n-2
(d) CnHn-2
Answer:
(c) CnH2n-2

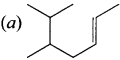
Question 4.
Structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 5, 6 – dimethylhept-2-ene is ……….
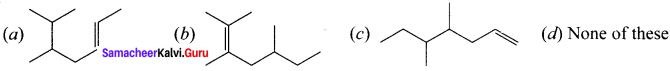
Answer:
Question 5.
The IUPAC name of the compound is …………
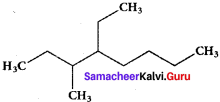
(a) 2,3 – Diemethyiheptane
(b) 3 – Methyl – 4 – ethyloctane
(c) 5 – ethyl – 6 – methyloctanc
(d) 4 – Ethyl -3 – methyloctane.
Answer:
(d) 4 – Ethyl – 3 – methyloctane.
Question 6.
Which one of the following names does not fit a real name?
(a) 3 – Methyl – 3 – hexanone
(b) 4- Methyl – 3 – hexanone
(c) 3 – Methyl – 3 – hexanol
(d) 2 – Methyl cyclo hexanone.
Answer:
(a) 3 – Methyl – 3 – hexanone
Question 7.
The TUPAC name of the compound CH3— CII = CH -C CH is ……………
(a) Pent – 4 – yn – 2 – ene
(b) Pent -3-en – 1- yne
(c) pent – 2 – en – 4 – yne
(d) Pent – 1 – yn – 3 – ene
Answer:
(b) Pent -3-en – 1- yne

Question 8.
IUPAC name of 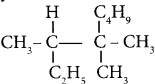 is ……….
is ……….
(a) 3, 4, 4 – Trimethylheptane
(b) 2 – Ethyl – 3, 3 – dimethyl heptane
(c) 3, 4, 4 – Trimethyloctane
(d) 2 Butyl – 2 -methyl – 3 – ethyl-butane.
Answer:
(c) 3, 4, 4 – Trimethyloctane
Question 9.
The IUPAC name of 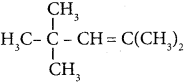 is ………
is ………
(a) 2 – Hydroxypropionic acid
(b) 2, 4. 4 – Trimethylpent -3-ene
(c) Propan – 2 – ol 1 – oie acid
(d) 2, 2, 4 – Trimethylpent -2-ene
Answer:
(b) 2 – Hydroxy Propanoic acid
Question 10.
The IUPAC name of the compound 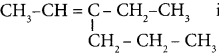 is ………
is ………
(a) 3 – Ethyl – 2- hexene
(b) 3 – Propyl – 3. hexene
(c) 4 – Ethyl – 4 – hexene
(d) 3 – Propyl -2-hexenc
Answer:
(a) 3 – Ethyl – 2- hexene
Question 11.
The IUPAC name of the compound 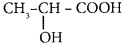 is ……..
is ……..
(a) 2 – Hydroxypropionic acid
(b) 2 – Hydroxy Propanoic acid
(c) Propan 2 – ol – 1 – oic acid
(d) 1 – Carboxyethanol.
Answer:
(b) 2 – Hydroxy Propanoic acid
Question 12.
The IUPAC name of 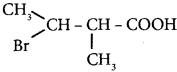 is ………
is ………
(a) 2 – Bromo – 3 – methylbutanoic acid
(b) 2 – methyl – 3 – bromobutanoic acid
(c) 3 – Bromo – 2 – methylbutanoic acid
(d) 3 – Bromo – 2. 3 – dimethyl propanoic acid.
Answer:
(c) 3 – Bromo – 2 – methylbutanoic acid
Question 13.
The structure of isobutyl group in an organic compound is ………

Answer:
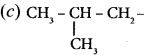
Question 14.
The number of stereoisomers of 1, 2-dihydroxycyclopentane is ……..
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3

Question 15.
Which of the following is optically active?
(a) 3 – Chioropentane
(b) 2 – Chioropropane
(c) Meso – tat-tat-ic acid
(d) Glucose
Answer:
(d) Glucose
Question 16.
The isomer of ethanol is ……….
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) dimethylether
(c) acetone
(d) methyl carbinol
Answer:
(b) dimethylether
Question 17.
How many cyclic and acyclic isomers are possible for the molecular formula C3H6O?
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 9
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 9
Question 18.
Which one of the following shows functional isomerism?
(a) ethylene
(b) Propane
(c) ethanol
(d) CH2Cl2
Answer:
(c) ethanol
Question 19.
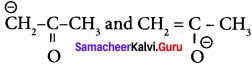 are ………
are ………
(a) resonating structure
(b) taulomers
(c) optical isomers
(d) conformers
Answer:
(b) tautomers

Question 20.
Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is earned out by Lassaigne’s test. The blue colour formed is due to the formation of ………….
(a) Fe3[Fe(CN)6]2
(b) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
(c) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]2
(d) Fe3[Fe(CN)6]3
Answer:
(b) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Question 21.
Lassaigne’s test for the detection of nitrogen fails in ………..
(a) H2N -CO – NH. NH2. HCl
(b) NH2 – NH2. HCl
(c) C6H5 – NH – NH2. HCl
(d) C6H5CONH2
Answer:
(c) C6H5 – NH – NH2. HCl
Question 22.
Connect pair of compounds which give blue colouration/precipitate and white precipitate respectively, when their Lassaigne’s test is separately done.
(a) NH2NH2HCl and CICH2 – CHO
(b) NH2CS NH2 and CH3 – CH2Cl
(c) NH2CH2 COOH and NH2CONH2
(d) C6H5NH2 and ClCH2 – CHO
Answer:
(d) C6H5NH2 and ClCH2 – CHO
Question 23.
Sodium nitropruside reacts with suiphide ion to give a purple colour due to the formation of ………..
(a) [Fe(CN)5N0]3-
(b) [Fe(NO)5CN]+
(c) [Fe(CN)5NOS]4-
(d) [Fe(CN)5NOS]3-
Answer:
(c) [Fe(CN)5NOS]4-
Question 24.
An organic compound weighing 0.15 g gave on carius estimation, 0.12 g of silver bromide. The percentage of bromine in the compound will be close to ……….
(a) 46%
(b) 34%
(c) 3.4%
(d) 4.6%
Answer:
(b) 34%
Question 25.
A sample of 0.5g of an organic compound was treated according to Kjeldahl’s method. The ammonia evolved was absorbed in 50 mL of 0.5M H2SO4. The remaining acid after neutralisation by ammonia consumed 80 mL of 0.5 M NaOH, The percentage of nitrogen in the organic compound is ……….
(a) 14%
(b) 28%
(c) 42%
(d) 56%
Answer:
(b) 28%

Question 26.
In an organm compound, phosphorus is estimated as ……….
(a) Mg2P2O7
(b) Mg3(PO4)2
(c) H3PO4
(d) P2O5
Answer:
(a) Mg2P2O7
Question 27.
Ortho and para-nitro phenol can be separated by ………….
(a) azeotropic distillation
(b) destructive distillation
(c) steam distillation
(d) cannot be separated
Answer:
(c) steam distillation
Question 28.
The purity of an organic compound is determined by …………
(a) Chromatography
(b) Crystallisation
(c) melting or boiling point
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (c)
Question 29.
A liquid which decomposes at its boiling point can be purified by …………
(a) distillation at atmospheric pressure
(b) distillation under reduced pressure
(c) fractional distillation
(d) steam distillation
Answer:
(b) distillation under reduced pressure
Question 30.
Assertion: 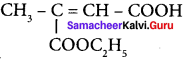 is 3-carbethoxy -2- butenoicacid.
is 3-carbethoxy -2- butenoicacid.
Reason: The principal functional group gets lowest number followed by double bond (or) triple bond.
(a) both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d both the assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Short Answer Questions
Question 31.
Give the general characteristics of organic compounds.
Answer:
- All organic compounds are covalent compounds of carbon and are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
- They are inflammable (except CCl4).
- They possess low boiling and melting points due to their covalent nature.
- They are characterized by functional groups.
- They exhibit isomerism.
Question 32.
Describe the classification of organic compounds based on their structure.
classification of organic compounds based on the structure
Answer:
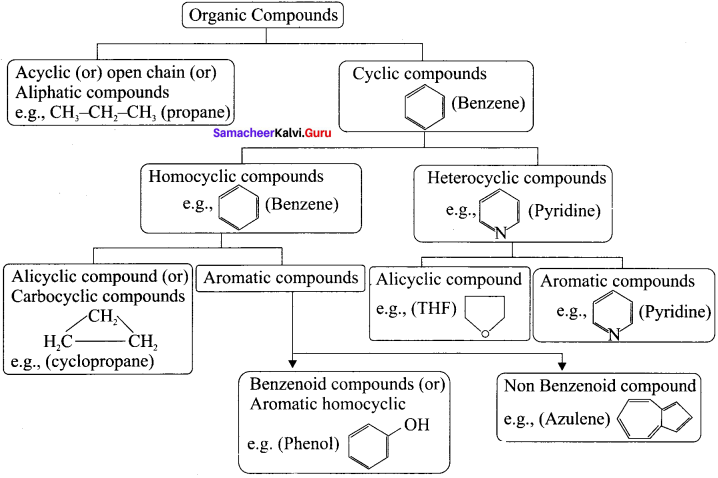
Question 33.
Write a note on the homologous series.
Answer:
- A series of organic compounds each containing a characteristic functional group and the successive members differ from each other in molecular formula by a CH2 group is called homologous series.
- e.g., Alkanes, Methane (CH4) ethane (C2H6), Propane (C3H8) etc.
- Compounds of the homologous series are represented by a general formula. e.g., Alkanes: C2H2nAlkene: CnH2n
- They can be prepared by general methods.
- They show regular gradation in physical properties but have almost similar chemical properties.
Question 34.
What is meant by a functional group? Identify the functional group in the following compounds.
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) oxalic acid
(c) dimethyl ether
(d) methylamine
Answer:
1. A functional group ¡s an atom or a specific combination of bonded atoms that react in a characteristic way, irrespective of the organic molecule in which it is present.
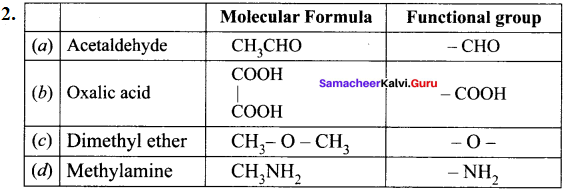
Question 35.
Give the general formula for the following classes of organic compounds
(a) Aliphatic monohydric alcohol
(b) Aliphatic ketones
(c) Aliphatic amines.
Answer:
(a) Aliphatic monohydric alcohol – CnH2n+1 + OH
(b) Aliphatic ketones – CnH2nO
(c) Aliphatic amines – C2H2n+1NH2

Question 36.
Write the molecular formula of the first six members of homologous series of nitroalkanes.
Nitroalkanes:
Answer:
- CH2NO2 Nitromethane
- CH2-CH2NO2 Nitroethane
- CH3-CH2-CH2NO2 1- nitropropane
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-NO2 1- nitrobutane
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NO2 1 – nitropentane
- CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NO2 1- nitrohexane
Question 37.
Write the molecular and possible structural formula of the first four members of homologous series of carhoxylic acids.
Answer:
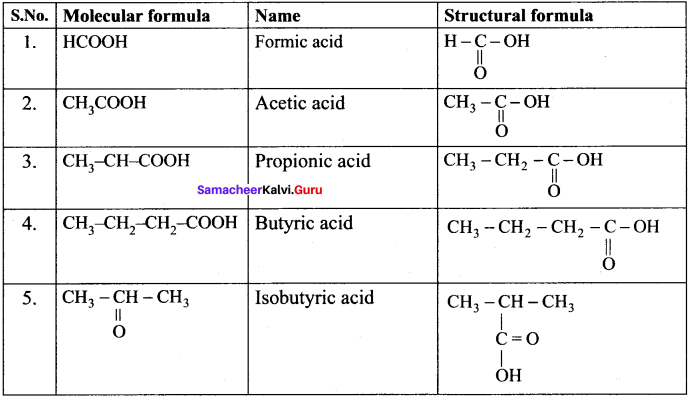
Question 38.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
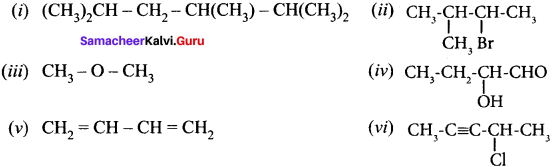
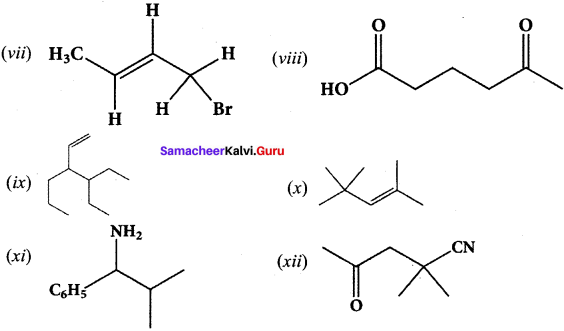
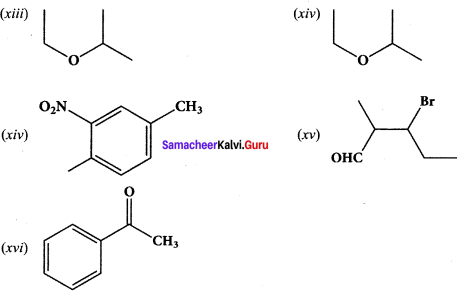
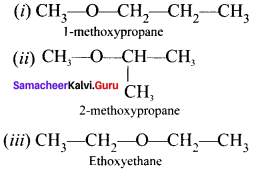
Answer:
(i) 2,3,5-tnmethylhexane
(ii) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
(iii) methoxymethane
(iv) 2-hydroxybutanal
(v) buta-1,3-diene
(vi) 4-chioropent-2-yne
(vii) 1 -bromobut-2-ene
(viii) 5-oxohexanoic acid
(ix) 3-ethyl-4-ethenylheptane
(x) 2, 4, 4-trimethylpent-2-ene
(xi) 2- methyl-I -phenyipropan- I -amine
(xii) 2,2- dimethyl-4-oxopentanenitrile
(xiii) 2-ethoxypropane
(xiv) I -fluoro-4-methyl-2-nitrobenzene
(xv) 3-bromo-2-methylpentanal
Question 39.
Give the structure for the following compound.
(i) 3 – ethyl – 2 methyl -1 – pentene
(ii) 1, 3, 5 – Tnmethyl cyclohex – 1 – ene
(iii) tertiary butyl iodide
(iv) 3 – Chlorobutanal
(y) 3 – Chlorobutanol .
(vi) 2 – Chloro – 2 – methyl propane
(vii) 2, 2-dimethyl- 1 – chioropropane
(viii) 3 – methylbut – 1 – ene
(ix) Butan – 2, 2 – diol
(x) Octane – 1 ,3 – diene
(xi) 1 ,5 – Dimethylcyclohexane
(xii) 2 – Chlorobut – 3 – ene
(xiii) 2 – methylbutan – 3 – ol
(xiv) acetaldehyde
Answer:

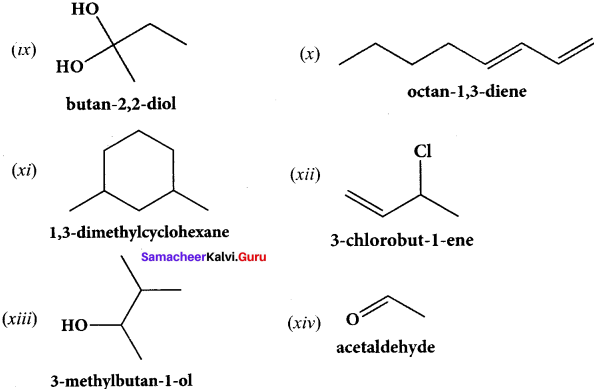
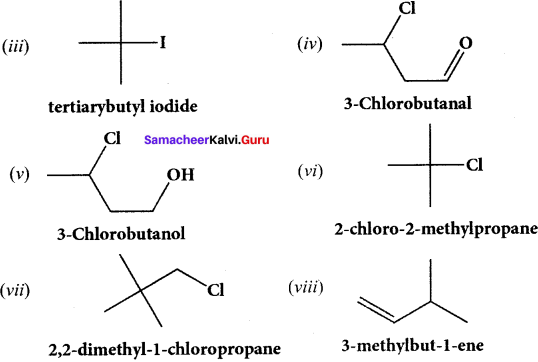
Question 40.
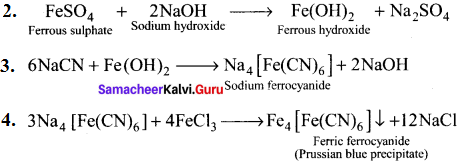
Describe the reactions involved in the detection of nitrogen in an organic compound by Lassaigne method.
Answer:
Detection of Nitrogen:
The following reactions are involved in the detection of nitrogen with formation of prussian blue precipitate conforming the presence of nitrogen in an organic compound.

Question 41.
Give the principle involved in the estimation of halogen in an organic compound by Carius method.
Estimation of halogens:
Answer:
carius method:
1. A known mass of the organic compound is heated with fuming HNO3 and AgNO3.
2. C, H and S gets oxidised to CO2, H2O and SO2 and halogen combines with AgNO3 to form a precipitate of silver halide
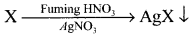
3. The precipitate AgX is filtered, washed, dried and weighed.
4. From the mass of AgX and the mass of organic compound taken, the percentage of halogens are calculated.
Question 42.
Give a brief description of the principles of:
1. Fractional distillation
2. Column Chromatography
Answer:
1. Fractional distillation:
This is one method to purify and separate liquids present in the mixture having their boiling point close to each other. In the fractional distillation, a fractionating column is fitted with distillation flask and a condenser. A thermometer is fitted in the fractionating column near the mouth of the condenser. This will enable to record the temperature of vapour passing over the condenser.
The process of separation of the components in a liquid mixture at their respective boiling points in the form of vapours and the subsequent condensation of those vapours is called fractional distillation. The process of fractional distillation is repeated, if necessary. This method finds a remarkable application in the distillation of petroleum, coal-tar and crude oil.
2. Column Chromatography:
This is the simplest chromatographic method carried out in long glass column having a stop cock near the lower end. This method involves the separation of a mixture over a column of adsorbent (Stationery phase) packed in a column. In the column a plug of cotton or glass wool is placed at the lower end of the column to support the adsorbent powder. The tube is uniformly packed with suitable adsorbent constitutes the stationary phase. (Activated aluminum oxides (alumina), Magnesium oxide, starch are also used as adsorbents).
The mixture to be separated is placed on the top of the adsorbent column. Eluent which is a liquid or a mixture of liquids is allowed to flow down the column slowly. Different components depending upon the degree to which the components are adsorbed and complete separation takes place. The most readily adsorbed substances are retained near the top and others come down to various distances in the column.

Question 43.
Explain paper chromatography.
Answer:
Paper chromatography:
1. It is an example of partition chromatography. A strip of paper acts as an adsorbent. This method involves continues differential partitioning of components of a mixture between stationary and mobile phase. In paper chromatography, a special quality paper known as the chromatographic paper is used. This paper act as a stationary phase.
2. A strip of chromatographic paper spotted at the base with the solution of the mixture is suspended in a suitable solvent which acts as the mobile phase. The solvent rises up and flows over the spot. The paper selectivity retains different components according to their different partition in the two phases where a chromatograrn is developed.
3. The spots of the separated coloured components are visible at different heights from the position of initial spots on the chromatogram. The spots of the separated colourless compounds may be observed either under ultraviolet light or by the use of an appropriate spray reagent.
Question 44.
Explain various types of constitutional isomerism (structural isomerism) in organic compounds.
Answer:
Constitutional isomers:
These isomers having the same molecular formula but differ in their bonding sequence. It is classified into 6 types:
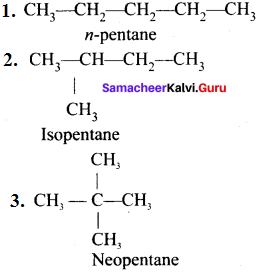
1. Chain (or) nuclear (or) skeletal isomerism:
The phenomenon in which the isomers have similar molecular formula but differ in the nature of carbon skeleton (i.e., straight (or)
branched)
e.g., C5H12:
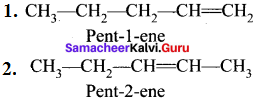
2. Position isomerism:
If different compounds belonging to same homologous series with the same molecular formula and carbon skeleton but differ in the position of substituent or functional group or an unsaturated linkage are said to exhibit position isomerism.
e.g., C5H10:
3. Functional isomerism:
Different compounds having same molecular formula but different functional groups are said to exhibit functional isomerism.
e.g., C3H6O:
(i) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH=CH2 propanal (Aldehyde group)

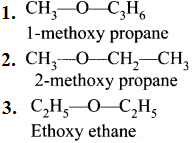
4. Metamerism:
This isomerism anses due to the unequal distribution of carbon atoms on either side of the functional group or different alkyl groups attached to either side of the same functional group and having same molecular formula.
e.g., C4H10O:
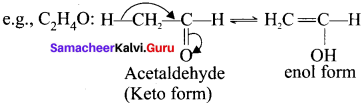
5. Tautomerism:
It is an isomerism in which a single compound exists in two readily inter convertible structures that differ markedly in the relative position of atleast one atomic nucleus generally hydrogen.
e.g., C2H4O:
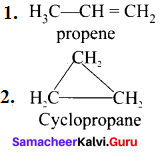
6. Ring chain isomerism:
It is an isomerism in which compounds having same molecular formula but differ in terms of bonding of carbon atom to form open chain and cyclic structures.
e.g., C2H6:
Question 45.
Describe optical isomerism with a suitable example.
Answer:
Compounds having same physical and chemical property but differ only in the rotation of plane of the polarized light are known as optical isomers and the phenomenon is known as optical isomerism.
Example:
Some organic compounds such as glucose have the ability to rotate the plane of the plane-polarized light and there called are said to be optically active compounds and this property of a compound is called optical activity. The optical isomer, which rotates the plane of the plane polarised light to the right or in clockwise direction is said to be dextrorotary (dexter means right) denoted by the sign (+), whereas the compound which rotates to the left or anticlockwise is said to be leavorotatory (leavues means left) denoted by sign (-). Dextrorotatory compounds are represented as ‘d’ or by sign (+) and laevorotatory compounds are represented as ‘l’ or by sign (-).

Question 46.
Briefly explain geometrical isomerism in alkenes by considering 2- butene as an example.
Answer:
2-butene: Geometrical isomerism : CH3 -CH = CH – CH3
1. Geometrical isomers are the stereoisomers which have different arrangement of groups or atoms around a rigid framework of double bonds. This type of isomerism occurs due to restricted rotation of double bonds or about single bonds in cyclic compounds.
2. In 2-butene, the carbon-carbon double bond is sp2 hybridised. The carbon-carbon double bond consists of a a bond and a it bond. The presence of it bond lock the molecule in one position. Hence, rotation around C = C bond is not possible.

4. These two compounds are termed as geometrical isomers and are termed as cis and trans form.
5. The cis-isomer is the one in which two similar groups arc on the same side otthe double bond. The trans-isomer is that in which two similar groups are on the opposite side of the double bond. Hence, this type of isomerism is called cis-Irans isomerism.
Question 47.
0.30 g of a substance gives 0.88 g of carbon dioxide and 0.54 g of water calculate the percentage of carbon and hydrogen in it.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.30 g
Weight of carbon-dioxide = 0.88 g
Weight of water = 0.54 g
Percentage of hydrogen:
18 g of water contains 2 g of hydrogen
0.54 g of water contain = \(\frac {2}{18}\) × 0.54 g of hydrogen
% of hydrogen = \(\frac {2}{18}\) × \(\frac {0.54}{0.30}\) × 100 = \(\frac {2}{18}\) × \(\frac {54}{0.3}\)
% of H = 0.111 × 180 = 19.888 ≈ 20%
Percentage of carbon:
44 g of CO2 contains 12 g of carbon
0.88 g of CO2 contains = \(\frac {12}{44}\) × 0.88 g of carbon
% of carbon = \(\frac {12}{44}\) × \(\frac {0.88}{0.30}\) × 100 = \(\frac {12}{44}\) × \(\frac {88}{0.3}\) = \(\frac {24}{0.3}\)
% of carbon = 80 % .
Question 48.
The ammonia evolved form 0.20 g of an organic compound by kjeldahl method neutralised 15m1 of N/20 Sulphuric acid solution. Calculate the percentage of Nitrogen.
Answer:
weight of organic compound = 0.20 g
Normality of acid = \(\frac{\mathrm{N}}{20}\)
Volume of standard acid neitralized by ammonia = 15 ml
1000 ml of N ammonia contains = 14 g of nitrogen
15 ml of ammonia of normality \(\frac{\mathrm{N}}{20}\) contains nitrogen = \(\frac{14 \times 15 \times 1}{1000 \times 20}\)
0.20 g of compound contains nitrogen = \(\frac{14 \times 15}{1000 \times 20}\)
100 g of compound contains nitrogen = \(\frac{14 \times 15 \times 100}{1000 \times 20 \times 0.20}\) = 5.25 g
Percentage of nitrogen = 5.25 %

Question 49.
0.32 g of an organic compound. after heating with fuming nitric acid and barium nitrate crystals is a scaled tube gave 0.466 g of barium sulphate. Determine the percentage of sulphur in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.32 g
Weight of BaSO4 formed = 0.466 g
233 g of BaSO4 contains = 32 g of sulphate
0.466 g of l3aSO4 contain = \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {0.466}{2.32}\) x 100
= \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {46.6}{0.32}\) = 19.999 g of sulphur
% of sulphur = 20 %
Question 50.
024 g of an organic compound gave 0.287 g of silver chloride in the carius method. Calculate the percentage of chlorine in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.24 g
Weight of silver chloride = 0.287 g
143.5 g of AgCl contains = 35.5 g of Cl
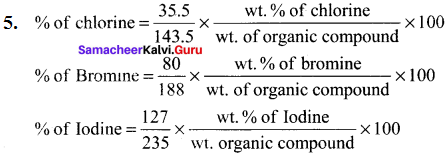
0.287 g of AgCl contains = \(\frac {35.5}{143.5}\) x 0.287 g of Cl
% of chlorine = \(\frac {35.5}{143.5}\) x \(\frac {0.287}{0.24}\) x 100 = 29.58 %
Question 51.
In the estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Dumas method 0.35 g yielded 20.7 mL of nitrogen at 15°C and 760 mm Hg pressure. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen ¡n the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.35 g
Volume of moist nitrogen (V1) = 20.7 ml = 20.7 x 10-3 L
Temperature = T1 = 15°C = 273 + 15°C = 288K
Pressure of moist nitrogen P1 = 760 mmHg

V0 = 19.62 x 10-3L
Percentage of nitrogen = \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x \(\frac{\mathrm{V}_{0}}{\mathrm{W}}\) x 100
= \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x \(\frac{19.62 \times 10^{-3}}{0.35}\) x 100
= \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x = \(\frac {19.62}{0.35}\) x 10-1
= 56.05 x 10-3 x 100 = 7.007%
Percentage of nitrogen = 7.007%

In Text Questions – Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
Give two examples for each of the following type of organic compounds.
1. non-benzonoid aromatic
2. aromatic heterocyclic
3. alicycic
4. aliphatic open chain.
Answer:
1. Non benzenoid aromatic compounds
2. Aromatic heterocyclic compounds

3. Alicyclic compounds

4. Aliphatic open chain compounds
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 n-pentane
- CH3-CH2-CH2OH 1-propanol
Question 2.
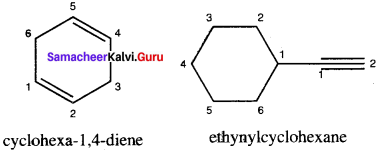
Write structural formula for the following compounds
1. Cyclohexa-1, 4-diene
2. Ethynykyclohexane
Question 3.
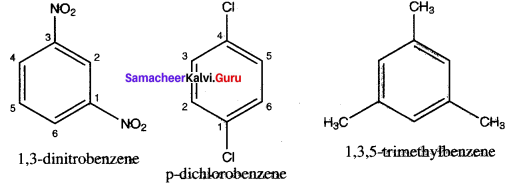
Write structural formula for the following compounds
1. m – dinitrobenzene
2. p-dichlorobenzene
3. 1, 3, S- Trimethytbeuzene
Answer:
Question 4.
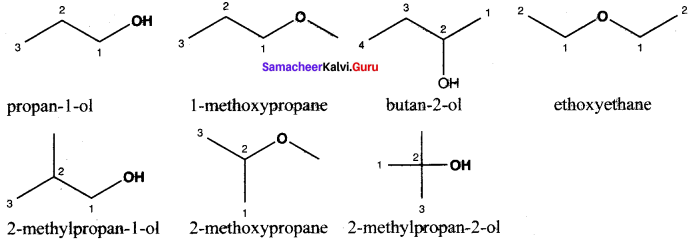
Write all the possible isomers of molecular formula C4H10O and identify the isomerisms found in them.
Answer:
C4H10O isomers:
Question 5.
0.2346 g of an organic compound containing C, H & O, o comhution giweb 0.2754 g of H2O and 0.4488 g CO2. Calculate the % composition of C, H & O in the organic compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic substance (w) = 0.2346 g
Weight of water (x) = 0.2754 g
Weight of CO2 (y) = 0.4488 g
Percentage of carbon = \(\frac {12}{44}\) x \(\frac {y}{w}\) x 100
= \(\frac {12}{44}\) – \(\frac {0.4488}{0.2346}\) x 100 = 52.17%
Percentage of hydrogen = \(\frac {2}{18}\) x \(\frac {y}{w}\) x 100
= \(\frac {2}{18}\) x \(\frac {0.2754}{0.2346}\) x 100 = 13.04%
Percentage of oxygen = [100- (52.17 +13.04)] = 100 – 65.21 = 34.79%

Question 6.
0.16 g of an organic compound was heated in a carlus tube and H2SO4 acid formed was precipitated with BaCl4. The mass of BaSO4 was 0.35 g. Find the percentage of sulphur.
Answer:
Weight of organic substance (w) = 0.16 g
Weight of Barium sulphate (x) = 0.35 g
Percentage of Sulphur = \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {x}{w}\) x 100
= \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {0.35}{0.16}\) x 100 = 30.04%
Question 7.
0.185 g of an organic compound when treated with Conc. HNO3 and silver nitrate gave 0.320 g of silver bromide. Calculate the % of bromine in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic substance (w) 0.185 g ;
Weight of silver bromide (x) = 0.320 g
Percentage of bromine = \(\frac {80}{188}\) x \(\frac {x}{w}\) x 100 = \(\frac {80}{188}\) x \(\frac {0.32}{0.185}\) x 100 = 73.6%
Question 8.
0.40 g of an iodo-substituted organic compound gave 0.235 g of Agi by carius method. Calculate the percentage of iodine in the compound. (Ag = 108, I = 127).
Answer:
Weight of organic substance (w) = 0.40 g
Weight of silver iodide (x) = 0.235 g
127 x 127 0.235
Percentage of iodine = \(\frac {127}{235}\) x \(\frac {x}{w}\) x 100
= \(\frac {x}{w}\) x \(\frac {0.235}{0.40}\) x 100 = 31.75%
Question 9.
0.33 g of an organic compound containing phosphorous gave 0.397 g of Mg2P2O7 by the analysis. Calculate the percentage of P in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.33g ;
Weight of Mg,P,07 = 0.397g
222 g of Mg2P2O7 contains 62 g of phosphorous.
0.397 g of Mg2P2O7 will contain \(\frac {62}{222}\) x 0.397 g of P.
0.33 g of organic compound contains \(\frac {62}{222}\) x 0.397 g of P
100 g of organic compound will contain \(\frac {62}{222}\) x \(\frac {0.397}{0.33}\) x 100
= \(\frac {2,461.4}{73.26}\) = 33.59 %
Percentage of phosphorous = 33.59 %

Question 10.
0.3 g of an organic compound on Kjeldahl’s analysis gave enough ammonia to just neutralise 30 mL of 0.1N H2SO4. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound (w) = 0.3 g
Strength of sulphuric acid used (N) = 0.1 N
Volume of sulphuric acid used (V) = 30 mL
30 ml of 0.1 N sulphuric acid 30 ml of 0.1 N ammonia
Percentage of nitrogen = \(\left(\frac{14 \times \mathrm{NV}}{1000 \times w}\right)\) x 100
= \(\left(\frac{14 \times 0.1 \times 30}{1000 \times 0.3}\right)\) x 100 = 14%
Example Problems
Question 1.
Classify the following compounds based on the structure
1. CH≡C-CH2-C≡CH
2. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
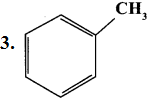
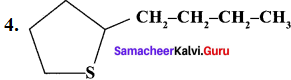
Answer:
- Unsaturated open chain compound
- Saturated open chain compound
- Aromatic benzenoid compound
- Alicyclic compound
Question 2.
0.26 g of an organic compound gave 0.039 g of water and 0.245 g of carbon dioxide on combustion. Calculate the percentage of C & H.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.26 g
Weight of water = 0.039 g
Weight of CO2 = 0.245 g
Percentage of hydrogen:
18 g of water contains 2 g of hydrogen
0.039 g of water contains = \(\frac {2}{18}\) x \(\frac {0.039}{0.26}\) of H
% of hydrogen = \(\frac {0.039}{0.26}\) x \(\frac {2}{18}\) x 100 = 1.66%
Percentage of carbon:
44 g of CO2 contains 12 g of C
0.245 g of CO2 contains = \(\frac {12}{44}\) x \(\frac {0.245}{0.26}\) g of C
% of Carbon = \(\frac {12}{44}\) x \(\frac {0.245}{0.26}\) x 100 = 25.69%

Question 3.
In an estimation of sulphur by Carius method, 0.2 175 g of the substance gave 0.5825 g of BaSO4, calculate the percentage composition of S ¡n the compound.
Answer:
Weight of organic compound = 0.2 175 g
Weight of BaSO4 = 0.5825 g
233 g of BaSO4 contains = 32 g of S
0.5825 g of BaSO4 contains = \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {0.5825}{0.2175}\) g of S
Percentage of S = \(\frac {32}{233}\) x \(\frac {0.5825}{0.2175}\) x 100 = 36.78%
Question 4.
0.284 g of an organic substance gave 0.287 g AgCl in Carius method for the estimation of halogen. Find the percentage of Cl in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of the organic substance = 0.284 g
Weight of AgCl = 0.287 g
143.5 g of AgCl contains 35.5 g of chlorine
0.287 g of AgCl Contains = \(\frac {35.5}{143.5}\) x \(\frac {0.287}{0.284}\)
% of chlorine = \(\frac {35.5}{143.5}\) x \(\frac {0.287}{0.284}\) x 100 = 24.98%
Question 5.
0.24 g of organic compound containing phosphorous gave 0.66 g of Mg2P2O7 by the usual analysis. Calculate the percentage of phosphorous ¡n the compound
Answer:
Weight of an organic compound = 0.24 g
Weight of Mg2P2O7 = 0.66 g
222 g of Mg2P2O7 contains = 62 g of P
o. 66 g contains = \(\frac {62}{222}\) x 0.66 g of P
Percentage of P = \(\frac {62}{222}\) x \(\frac {0.66}{0.24}\) x 100 = 76.80%

Question 6.
0.1688 g when analysed by the Dumas method yield 31.7 mL of moist nitrogen measured at 14°C and 758mm mercury pressure. Determine the % of N in the substance (Aqueous tension at 14°C =12 mm of Hg).
Answer:
Weight of Organic compound = 0.168 g
Volume of moist nitrogen (V1) = 31.7 ml. = 31.7 x 10-3 L
Temperature (T1) = 14°C = 14 + 273 = 287 K
Pressure of Moist nitrogen (P) = 758 mm Hg
Aqueous tension at 14°C = 12 mm of Hg
\(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{P_{0} V_{0}}{T_{0}}\)
V0 = \(\frac{746 \times 31.7 \times 10^{-3}}{287} \times \frac{273}{760}\)
V0 = 29.58 x 10-3 L
Percentage of nitrogen:

= 21.90 %
Question 7.
0.6 g of an organic compound was Kjeldhalised and NH3 evolved was absorbed into 50 mL of semi-normal solution of H2SO4. The residual acid solution ws diluted with distilled water and the volume made up to 150 mL. 20 mL of this diluted solution required 35 mL of \(\frac {N}{2}\) NaOH solution for complete neutralisation. Calculate the % of N in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of Organic compound = 0.6 g
Volume of sulphuric acid taken = 50 mL
Strength of sulphuric acid taken = 0.5 N
20 ml of diluted solution of unreacted sulphuric acid was neutralised by 35 mL of 0.05 N Sodium hydroxide
Strength of the diluted sulphuric acid = \(\frac {35 x 0.05}{20}\) = 0.0875 N
Volume of the sulphuric acid remaining after reaction with ammonia = V1 mL
Strength of H2SO4 = 0.5 N
Volume of the diluted H2SO4 = 150 mL
Strength of the diluted sulphuric acid = 0.0875 N
V1 = \(\frac {150 x 0.087}{0.5}\) = 26.25 mL
Volume of H2SO2consumed by ammonia = 50 – 26.25 = 23.75 mL
23.75 mL of 0.5 N H2SO4 = 23.75 mL of 0.5N NH3
The amount of Nitrogen present in the 0.6 g of organic compound
= \(\frac{14 \mathrm{g}}{1000 \mathrm{mL} \times 1 \mathrm{N}}\) x 23.75 x 0.5 N = 0.166 g
Percentage of Nitrogen \(\frac {0.166}{0.6}\) x 100 = 27.66%
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Additional Questions Solved
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Statement 1. The tendency of an atom to form a chain of bonds with the atoms of the same element is called catenation.
Statement 2. The high strength of C-C bond is responsible for its catenation property.
(a) Statement 1 & 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
(b) Statement 1 & 2 arc correct but statement 215 not the correct explanation of statement 1.
(c) Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is wrong.
(d) Statement 1 is wrong but statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
(a) Statement 1 & 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
Question 2.
Generally, organic compounds are
a) Amorphous
b) Complexes
c) Covalent
d) Electrovalent
Answer:
c) Covalent

Question 3.
Which of the following is an example of an organic reaction?
(a) Rusting of iron
(b) Combustion of magnesium
(c) Biochemical reactions
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Biochemical reactions
Question 4.
The first carbon compound prepared from its elements is
a) Urea
b) Acetic acid
c) Methane
d) benzene
Answer:
b) Acetic acid
Question 5.
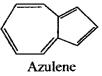
Which of the following is an example of the non-benzenoid aromatic compound?
(a) Tolucnc
(b) Phenol
(c) Benzyl alcohol
(cl) azulene
Answer:
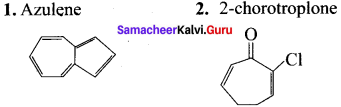
(d) azulene
Question 6.
The first organic compound synthesized in the laboratory from an inorganic compound is
a) NH4NCO
b) NH2 – CO – NH2
c) CH3COOH
d) CH4
Answer:
b) NH2 – CO – NH2

Question 7.
Which of the following is an example of carbocyclic alicyclic compound?
(a) Pyrrole
(b) Thiophene
(c) Cyclopropane
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(c) Cyclopropane
Question 8.
Which one of the following is the functional group of ketone?
(a)-CHO
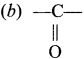
(c) -O-
(d)-OH
Answer:
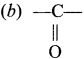
Question 9.
Which one of the following indicates isothiocyanate functional group?
(a) -NC
(b) -NCS
(c) -SCN
(d) -NCO
Answer:
(b) -NCS
Question 10.
n – Butane and isobutane are a pair of
a) chain isomers
b) position isomers
c) metamers
d) functional isomers
Answer:
a) chain isomers
Question 11.
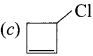
Which structure ¡s named as 3-chlorocyclobut-1-ene?

Answer:
Question 12.
Which one of the following is called 2-cyclobutyipropanal?
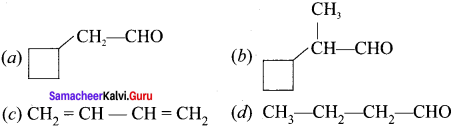
Answer:
Question 13.
Which one of the following is called cyclopentyl benzene’s?

Answer:
Question 14.
Which one of the following is commonly called mesitylene?
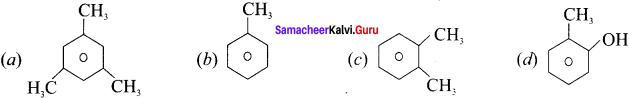
Answer:
Question 15.
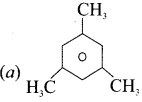
The number of possible monochloro benzenes is
a) 1
b) 3
c) 5
d) 6
Answer:
a) 1
Question 16.
Which of the following pair are called functional isomers?
(a) methyl propyl ether and diethyl ether
(b) 2-pentanone & 3-pentanone
(c) propanoic acid and methyl acetate
(d) I -butanol and 2-butanol
Answer:
(c) propanoic acid and methyl acetate

Question 17.
Which of the following does not show optical isomerism’?
(a) Glucose
(b) Tartane acid
(c) Lactic acid
(d) Methane
Answer:
(d) Methane
Question 18.
Which metal is used to prepare Lassaigne’s extract?
(a) Copper
(b) Sodium
(c) Aluminium
(d) Iron
Answer:
(b) Sodium
Question 19.
The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether is
a) n – propyl methyl ether
b) Butan – 1 – ol
c) 2 – Methylpropan – 2 – ol
d) Butanone
Answer:
d) Butanone
Question 20.
Which one of the following is called feme ferrocyanide?
(a) Na4[Fe(CN)6]
(b) Na4[Fe(CN)6]3
(c) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]
(d) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Answer:
(d) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Question 21.
What is the colour formed in Lassaigne’s test of an organic compound containing N and S?
(a) Prussian blue colour
(b) Blood red colour
(c) Purple colour
(d) Canary yellow colour
Answer:
(b) Blood red colour
Question 22.
Which one of the following is the formula of sodium nitroprusside?
(a) Na4[Fe(CN)5N05]
(b) Na4[Fe(CN)5SON]
(c) Na4[Fe(CN)6]
(d) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Answer;
(a) Na4[Fe(CN)5N05]
Question 23.
According to Huckel’s rule, a compound is said to be aromatic if’ it contains
a) 4n bonds
b) 4n atoms
c) (4n + 2) atoms
d) (4n + 2) π electrons
Answer:
d) (4n + 2) π electrons

Question 24.
Which one of the following solutions are added to Lassaigne’s extract to identify halogens?
(a) Acetic acid + Lead acetate
(b) dil HNO3 + AgNO3
(c) Fe(OH)2 + FeCl3
(d) Na2CO3 + KNO3
Answer:
(b) dil HNO3 + AgNO3
Question 25.
Which is a saturated compound?
a) alkanes
b) alkenes
c) alkynes
d) cyclo alkenes
Answer:
a) alkanes
Question 26.
Which one of the following test is used to detect phosphorous in an organic compound?
(a) Silver nitrate test
(b) Copper oxide test
(c) Ammonium molybdate test
(d) Lassaigne’s test
Answer:
(c) Ammonium molybdate test
Question 27.
Identify the colour formed in the test kr phosphorous using ammonium molybciate.
(a) Crimson red colour
(b) Deep violet colour
(c) Prussian blue colour
(d) Canary yellow colour
Answer:
(d) Canary yellow colour
Question 28.
Which of the following will absorb CO2?
(a) Conc. H2SO4
(b) KOH
(c) HCl
(d) Copper
Answer:
(b) KOH
Question 29.
IUPAC name of ester is
a) Alkoxy alkane
b) Alkyl alkanoate
c) Alkanoyl halide
d) Alkanoic anhydride
Answer:
b) Alkyl alkanoate

Question 30.
Which method is used to estimate sulphur?
(a) Lassaigne’s test
(b) Oxide test
(c) Carius method
(d) Kjedahl’s method
Answer:
(c) Cari us method
Question 31.
Which method is used to estimate nitrogen?
(a) Dumas method and Kjeldahl’s method
(b) Carius method & Oxide method
(c) Lassaignes test & Copper oxide test
(d) Ammonium molybdate test & Silver nitrate test
Answer:
(a) Dumas method and Kjeldahl’s method
Question 32.
IUPAC name of CH2OH – CH2OH is
a) 1, 2 – dihydroxy ethane
b) ethylene glycol
c) ethane – 1, 2 – diol
d) ethane – 1, 2 – dial
Answer:
c) ethane – 1, 2 – diol
Question 33.
Which of the following is used to decolourise the organic compounds?
(a) Chlorine
(b) Bleaching powder
(c) Animal charcoal
(d) Iodine
Answer:
(c) Animal charcoal
Question 34.
Which method is used to extract essential oils from plants and flowers?
(a) Crystallization
(b) Sublimation
(c) Steam distillation
(d) Differential extraction
Answer:
(c) Steam distillation
Question 35.
Which of the following is used as adsorbent?
(a) silica gel and alumina
(b) glass wool and cotton
(c) glass plate and paper
(d) glucose and fructose
Answer:
(a) silica gel and alumina
Question 36.
Which of the following compounds gives prussian blue colour in Lassaigne’s test?
(a) CH4 and CH3OH
(b) CH3NH2 and CH3NO2
(c) CH3Cl and CHCl3
(d) CH3CHO and CH3COCH3
Answer:
(b) CH3NH2 and CH3NO2
Question 37.
Which of the following is the functional isomer of methyl acetate?
a) Ethyl acetate
b) Propanoic acid
c) Ethyl formate
d) Propanone
Answer:
b) Propanoic acid
Question 38.
Which one of the following is not used as air adsorbent in chromatography?
(a) Alumina
(b) Silica gel
(c) Magnesia
(d) Sucrose
Answer:
(d) Sucrose

Question 39.
The IUPAC name of 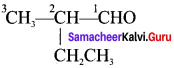 ……..
……..
(a) 2-methyl butanal
(b) butan-2-aldehyde
(c) 2-ethyipropanal
(d) 3-methyl isobutraldehyde
Answer:
(c) 2-ethyipropanal
Question 40.
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans isomerism?
Answer:
(a) 2-Buiene
(b) 2-Butyne
(c) 1-Butene
(d) 2-Butanol
Answer:
(a) 2-Butene
Question 41.
Which of the following sodium fusion extract of organic compound gives brilliant violet colour with sodium nitroprusside solution?
(a) Urea
(b) Thiourea
(c) Benzoic acid
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(b) Thiourea
Question 42.
The IUPAC name of Cinnamaldehyde is
a) 3 – Phenyl prop – 2 – enal
b) 1 – Phenyl – prop – 1 – enal
c) 1 – Phenyl – prop – 2 – enal
d) 3 – Phenyl – prop – 1 – enal
Answer:
a) 3 – Phenyl prop – 2 – enal
Question 43.
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
(a) Alcohols
(b) Aldehydes
(c) Alkyl halides
(d) Cyanides
Answer:
(c) Alkyl halides
Question 44.
Which one of the following is used as a column in the separation of pigments of chlorophyll by chromatography technique?
(a) Petroleum ether
(b) CaCO3
(c) Activated charcoal
(d) Ethanoic acid
Answer:
(b) CaCO3
Question 45.
Which one of the following compound does not give Prussian blue colour in Lassaigne’s test?
(a) C6H5NH2
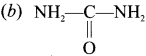
(c) C6H5CONH2
(d) C6H5COCl
Answer:
(d) C6H5COCl
Question 46.
Which one of the following shows geometrical isomerism?
(a) n-Butane
(b) 1-butene
(c) 2-butene
(d) butyne
Answer:
(c) 2-butene
Question 47.
Which one of the following shows functional group isomerism?
(a) Ethene
(b) Acetone
(c) Ethane
(a) Propane
Answer:
(b) Acetone
Question 48.
Which of the following pair gives curdy white precipitate and yellow precipitate respectivety in their Lassaignes test?
(a) C2H5I and C2H5Br
(b) C2H5NO2 and C2H5NH2
(c) C6H5Cl and CH3
(d) CH4 and CH3OH
Answer:
(c) C6H5Cl and CH3
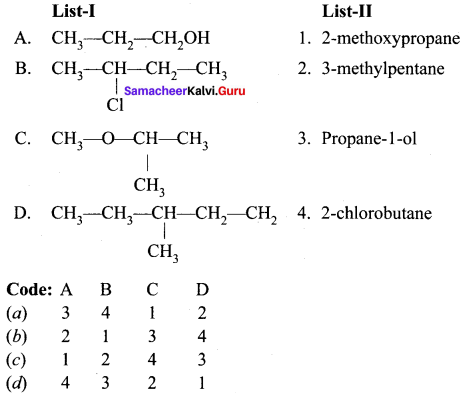
II. Match the following.
Question 1.
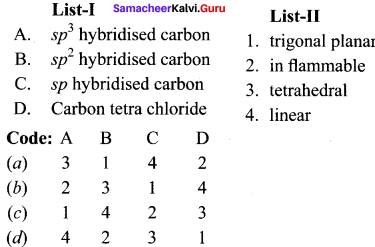
Answer:
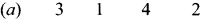
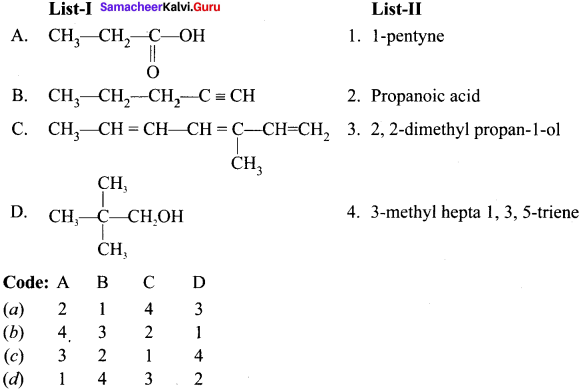
Question 2.
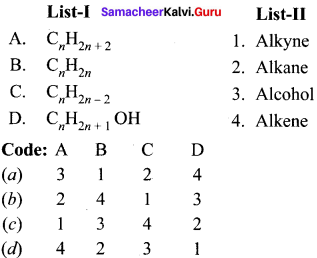
Answer:
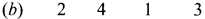
Question 3.
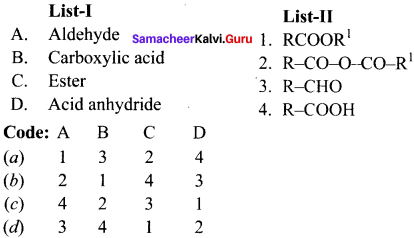
Answer:
Question 4.
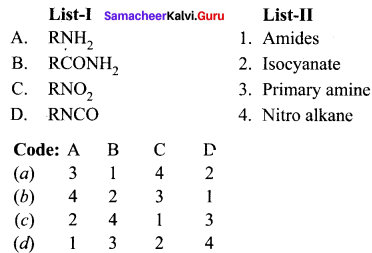
Answer:
Question 5.
Answer:

Question 6.
Answer:
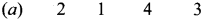
Question 7.
Answer:
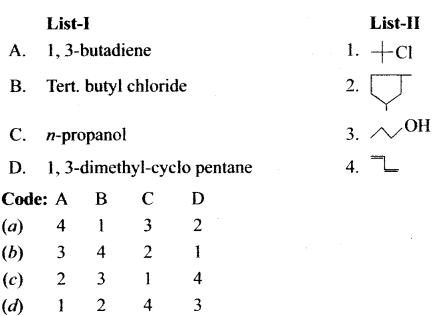
Question 8.
Answer:
III. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The property catenation is possible in ……..
Answer:
Carbon.
Question 2.
Acetic acid was synthesised by ………
Answer:
Kolbe
Question 3.
Methane was synthesised in laboratory by ………
Answer:
Berthiot
CH3

Question 4.
 is an example of ………
is an example of ………
Answer:
aromatic benzenoid compound
Question 5.
2-butene is an example of compound.
Answer:
unsaturated open chain
Question 6.
The IUPAC name of 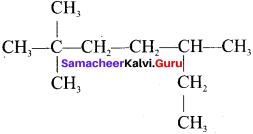 is …….
is …….
Answer:
2, 2, 5-trimethyl heptane
Question 7.
The IUPAC name of 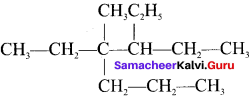 is ……..
is ……..
Answer:
3, 4-diethyl, 4-methylheptane
Question 8.
The name of 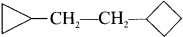 is ……….
is ……….
Answer:
1-cyclobutyl-2-cyclopropylethene
Question 9.
The name of 
Answer:
2-(cyclobut-2-en-1-yl)-propanal
Question 10.
The name of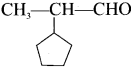 is …………
is …………
Answer:
2-cyclopentyipropanal
Question 11.
Esopentane and neopentane are the examples for ………
Answer:
chain isomerism
Question 12.
 are called ……….
are called ……….
Answer:
functional isomers

Question 13.
Copper oxide test is used to detect ………..
Answer:
Carbon & Hydrogen
Question 14.
The formula of feme suiphocyanide is ………
Answer:
Fe(CNS)3
Question 15.
In Lassaigne’s test for halogens, if colour of the precipitate is curdy white, the halogen present is ……….
Answer:
chlorine
Question 16.
The formula of ammonium phospho molybate is ……….
Answer:
(NH4)3.PO4. MO3
Question 17.
Silver nitrate test is used to detect the presence of ……….
Answer:
Halogens
Question 18.
During the estimation of carbon and hydrogen, presence of nitrogen can be avoided by using ………
Answer:
a spiral of copper
Question 19.
In Carius method, the sulphur in an organic compound is oxidised to ……….
Answer:
H2SO4
Question 20.
The method used to estimate nitrogen in foods and fertilisers is ………
Answer:
Kjeidahl’s method
Question 21.
The mixture of diethyl ether and ethanol can he purified by ………
Answer:
simple distillation
Question 22.
The method used to purify petroleum. coal-tar and crude oil is ………
Answer:
fractional distillation
Question 23.
The method used in the manufacture of aniline and turpentine is ……….
Answer:
steam distilation

Question 24.
The mixture of exhanol and water are separated by ………..
Answer:
azeotropic distillation
Question 25.
The different coloured constituents of chlorophyll are separated by ………
Answer:
chromatography
Question 26.
The large number of organic compounds is due to of carbon ………..
Answer:
catenation
Question 27.
The IUPAC name of the compound shown below is:
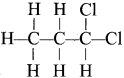
Answer:
1, 1-dichloropropane
Question 28.
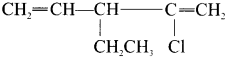 name of this compound is ………..
name of this compound is ………..
Answer:
2-chloro-3-ethyl- 1, 4-pentadiene
Question 29.
Carboxylic acids are isomenc with ……….
Answer:
esters
Question 30.
Alcohols are isomeric with ……….
Answer:
ethers
Question 31.
The correct IUPAC name for the following structure is ……….

Answer:
5-hex-i -en-3-ol
Question 32.
The Prussian blue colour confirms the presence of nitrogen in an organic compound is due to the formation of ………
Answer:
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]I
Question 33.
The principle involved in paper chromatography is ……….
Answer:
partition

Question 34.
Steam distillation is used for the extraction of ……..
Answer:
essential oils
Question 35.
In chromatography, if the stationary phase is solid, the basis is ……….
Answer:
adsorption
Question 36.
In chromatography, if the stationary phase is liquid, the basis is ………
Answer:
partition
Question 37.
The isomer of acetaldehyde is ……….
Answer:
acetone
Question 38.
The general formula of alkyne is ……….
Answer:
CnH2n-2
Question 39.
The IUPAC name of (CH3)2CH-CH2-CH(CH3)2-CH(CH3)2 is ……..
Answer:
2, 3, 5-trimethyl hexane
IV. Choose the odd one out.
Question 1.
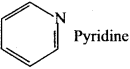
(a) THF
(b) Pyridine
(c) Phenol
(d) Thiophene
Answer:
(c) Phenol. ft is a homocyclic compound whereas others are heterocyclic compounds.
Question 2.
Answer:
Question 3.
(a) Azulene
(b) Propane
(c) Butane
(d) Ethene
Answer:
(a) Azulene. It is a non-benzenoid aromatic homocyclic compound whereas others are aliphatic compounds.

Question 4.
(a) Dyes
(b) Polymers
(c) Cosmetics
(d) Common salt
Answer:
(d) Common salt. It is an inorganic compound whereas others are organic compound.
Question 5.
(a) Renzene
(b) Water
(c) Ether
(d) Chloroform
Answer:
(b) Water. It is a polar solvent whereas others are non-polar solvents.
V Choose the correct pair.
Question 1.
(a) Benzene: Aliphatic compound
(b) Propane: Aromatic compound
(c) Pyridine: Heterocyclic compound
(d) Cyclohexane: Polycyclic compound
(c) Pyridine: Heterocyclic compound
Question 2.
(a)-OH : Ketone
(b)-CHO : Carboxylic acid
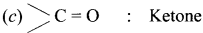
(d)-NO2 : Amine
Answer:
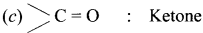
Question 3.
(a) Organic compounds: inflammable
(b) Organic compounds: ionic compound
(c) Organic compounds: high boiling point and high melting point
(d) Organic compounds: soluble in water
Answer:
(a) Organic compounds: inflammable
Question 4.
(a) CnH2n+2 : C2H4
(b) CnH2n : C3H6
(c) CnH2n-2 : C2H6
(d) CnH2n+2 : C3H4
Answer:
(b) CnH2n : C3H6
Question 5.

Answer:

Question 6.
(a) n-pentane and iso pentane : position isomerism
(b) neopentane and n-pentane : chain isomerism
(c) propanal and propanone : position isomerism
(d) propañoic acid and methyl acetate : chain isomerism
Answer:
(b) neopentane and n-pentane : chain isomerism
VI. Choose The incorrect pair.
Question 1.
(a) Dumas method : Estimation of nitrogen
(b) Kjeldahls method : Estimation of nitrogen
(c) Carius method : Estimation of halogens
(d) Dumas method : Estimation of sulphur
Answer:
(d) Dumas method : Estimation of sulphur
Question 2.
(a)-CHO : Aldehyde
(b)-COOH : Carboxylic acid
(c)-NH2 : Nitro group
(d)-O- : Ether
Answer:
(c)-NH2 : Nitro group

Question 3.
(a) Benzene and nitro benzene : Distillation
(b) Coal tar and crude oil : Fractional distillation
(c) Aniline and turpentine : Steam distillation
(d) Naphthalcne and benzoic acid : Crystallization
Answer:
(d) Naphthalene and benzoic acid: Crystallization
Question 4.
(a) BaSO4 : White colour precipitate
(b) Ag2S : Black colour precipitate
(c) Fe(CNS)3 : Prussian blue colour
(d) PbS : Black colour precipitate
Answer:
(c) Fe(CNS)3 : Prussian blue colour
Question 5.
(a) propanal and propropane : Functional isomerism
(b) Nitrite fòrrn and nitro form : Tautomerism
(c) Pent- 1-ene and pcnt-2-ene : Chain isomerism
(d) Propanoic acid and methyl acetate: Functional isomerism
Answer:
(c) Pent-1-ene and pent-2-ene : Chain isomerism
VII. Assertion & Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Carbon cannot form ionic bond.
Reason (R) : It is not possible for the carbon to form either C4t or C ions, as it requires large amount of energy.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct hut R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is.correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but Ris correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Simple distillation can help in separating a mixture of propan-1-ol (boiling point 97°C) and propanone (boiling point 56°C).
Reason (R) : Liquids with a dîftèrence of more than 30°C in their boiling points can be separated by simple distillation.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.

Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Pent-1 -ene and pent-2-ene are position isomers.
Reason (R) : Position isomers ditTer in the position of functional group or substituent.
(a) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
VIII. Choose the correct statement.
Question 1.
(a) All organic compounds are ionic compounds.
(b) All organic compounds have high boiling point and high melting point.
(c) Many of the organic compounds are inflammable.
(d) Organic compounds are mostly soluble in water.
Answer:
(c) Many of the organic compounds are inflammable.
Question 2.
(a) Propane is heterocyclic compound.
(b) Azulene is a non benzenoid and aromatic homocyclic compound.
(c) Pyridine is a homocyc lic compound.
(d) Cyclopropane is an aromatic compound.
Answer:
(b) Azulene is a non henzenoid and aromatic homocyclic compound.
Question 3.
(a) CH≡CH-CH2-C≡CH is a saturated open chain compound.
(b) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
 is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
Answer:
 is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
Question 4.
(a) Organic compounds are covalent and generally insoluble in water.
(b) Organic compounds are ionic but generally soluble in water.
(c) Organic compounds non-inflammable
(d) Organic compounds do not show catenation.
Answer:
(a) Organic compounds are covalent and generally insoluble in water.

Question 5.
(a) Fe4[Fe(CN)6] is prussian blue precipitate.
(b) Ag2S is a white precipitate.
(c) PbS is a blood red colour precipitate.
(d) BaSO4 is a black colour precipitate.
Answer:
(a) Fe4[Fe(CN)6] is prussian blue precipitate.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry 2 Mark Question and answers
Write brief answer to the following questions:
Question 1.
What is catenation?
Answer:
The tendency of an atom to form a chain of bonds with the atoms of the same element is called catenation. The high strength of C-C bond is responsible for its catenation property.
Question 2.
Explain the following terms in IUPAC system of nomenclature. of organic compounds.
(i) Root word
(ii) prefix
(iii) suffix
Answer:
(i) Root word:
Root word denotes the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous chain in molecules.
(ii) prefix:
Prefix denotes the group(s) attached to the main chain which is placed before the root.
(iii) suffix:
Suffix denotes the functional group and is paced after the root word.
Question 3.
What is meant by functional group? Give two example.
Answer:
A functional group is an atom or a specific combination of bonded atoms that react in a characteristic way. irrespective of organic molecule in which it is present. The reaction of an organic compound takes place at the functional group.
e.g.. Alcohol -OH group
Ether -O- group

Question 4.
Classify the following compounds based on the structure.
(i) CH2=CH-CH=CH2
(ii) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
Answer:
(i) Unsaturated open chain compound
(ii) Saturated open chain compound
(iii) Aromatic benzenoid compound
(iv) Alicylic compound
Question 5.
Give one example for each of the following type of organic compounds.
- Non-benzeoid
- Aromatic heterocclic
- Alicyclic
- Aliphatic open chain
Answer:
1. Non-benzenoid aromatic compound
2. Alicyclic compound
3. Aromatic heterocyclic Compound
4. Atiphatic open chain compound
Question 6.
Give two examples for each of the following type of organic compounds.
- Aromatic homocyclic compound
- Aromatic heterocyclic compound
Answer:
1. Aromatic homocyclic compound
2. Aromatic heterocyclic compound
Question 7.
Write the functional group of the following compounds
- Aldehyde
- Ester
- Ether
- alcohol
Answer:
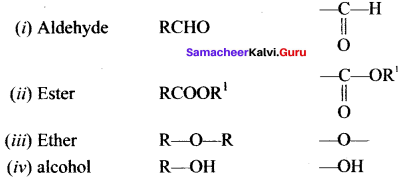
Question 8.
Write the functional group of –
- cyanide
- socyanide
- cyanate
- isocyanate
Answer:
- cyanide -CN
- isocyanide -NC
- cyanate -CNO
- isocyanate -NCO
Question 9.
Write the functional group of –
- thiocyanate
- isothiocyanate
- thiols
- thioether
Answer:
- Thio cyanale -SCN
- Isothiocyanate -NCS
- thiols -SH
- thicethers -S-
Question 10.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
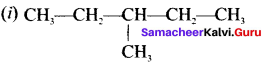
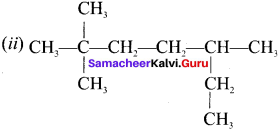
Answer:
- 3-methylpentane
- 2, 2, 5-trimethylheptane
Question 11.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
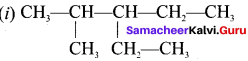
Answer:
- 3-ethyl-2-methyl pentane
- 2-methylbutanal
Question 12.
What are the IUPAC names of the following compounds?
Answer:
- 2-ethyl-but-4-ene-oic acid
- 2, 2-dimethyl-hexanoic acid
Question 13.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
Answer:
- 2-ethyl-3-propyl pentane-dioic acid
- 3-methy-1 hexane
Question 14.
Predict the IUPAC names of the following compounds

Answer:
- cyclobutane
- cyclopentane
- cyclobutene
- cyclo octane
Question 15.
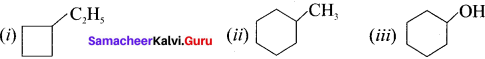
Answer:
- Ethyl cyclobutane
- Methylcyclohexane
- Cyclohexanol
Question 16.
Write the ¡UPAC names of the following compounds.
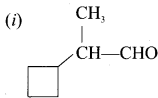
Answer:
- 2-cyclobutyl propanol
- 3-cyclohexyl pentan-2-one
Question 17.
Write the structural formula for the following compounds.
(i) cyclohexa- 1, 3-diene
(ii) methyl cyclopentane
Answer:
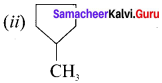
Question 18.
Draw the structures of –
(i) o-xylene
(ii) m-xylene
(iii) p-xylene
Answer:
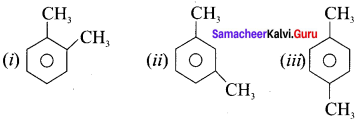
Question 19.
Draw the structure of –
(i) Mesitylene
(ii) 1,2, 3-trimethyl benzene
Answer:
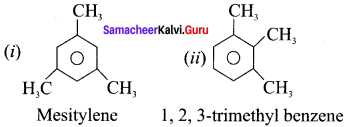
Question 20.
Write the structure of –
(i) p-dinitrobenzene
(ii) o-dichlorobenzene
Answer:
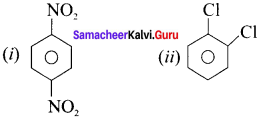
Question 21.
Draw the structure of –
(i) 2-cyclopentyl propanal
(ii) 2-(cyclo-but-cnyl) propanal
Answer:
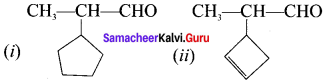
Question 22.

Answer:
- N, N-dimethylbenzene amine
- N-ethyl-N-methylpropan-I-amine
Question 23.
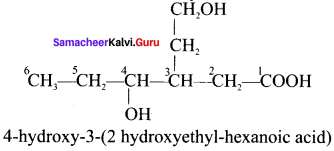
Draw the structure of 4-hydroxy-3(2-hydroxy ethyl) hexanoic acid.
Answer:
Question 24.
Explain about dash line structure with a suitable example.
Answer:
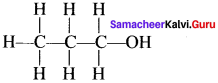
The line bond structure is obtained by representing the two electron covalent bond by a dash or line (-) in a lewis structure. A single line or dash represents a single covalent bond.
e.g., n- propanal:
Question 25.
What ¡s meant by condensed structure? Explain with an example.
Answer:
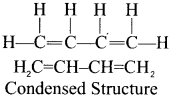
The bond line structure can be further abbreviated by omitting all these dashes representing covalent bonds and by indicating the number of identical groups attached to an atom by a subscript. The resulting expression of the compound is called a condensed structural formula.
e.g., 1, 3-butadiene.
Question 26.
What are bond-line structures? Give one example.
Answer:
The condensed structural formula is simplified in which only lines are used. In this type of representation of organic compounds, carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown and the lines representing carbon-carbon bond are shown in zig-zag fashion. The only atoms are specially written are oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen etc. Example, Ten. butyl chloride
condensed structure
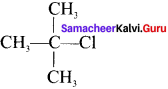
bond line structure
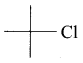
Question 27.
Define isomerism. Give example.
Answer:
Isomerism represents the existence of two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure and properties. Compounds exhibiting this isomerism are called isomers.
e.g., C2H6O:
- CH3-CH2OH Ethanol
- CH3-O-CH3 Methoxyrnethane
Question 28.
Write the possible isomers for the formula C5H10 with their name and type of isomerism present in it.
Answer:
C5H10:
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH = CH2 (Pent-1-ene)
- CH3-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 (Pent-2-ene)
The type of isomerism present above is position isomerism.
Question 29.
Write the possible isomers for the formula C5H10O with their name indicating position isomerism.
Answer:
Question 30.
Draw the functional isomers for the formula C3H6O2 with their names.
Answer:
C3H6O2:
- CH3-CH2-COOH (Propanoic acid)
- CH3-COOCH2 (Methyl acetate)
Question 31.
What is metamerism? Give an example.
Answer:
Metamerism is one kind of structural isomerism which arises due to the unequal distribution of carbon atoms on either side of the functional group or diffèrent alkyl groups attached to the either side of the same functional group and having the same molecular formula.
e.g., C4H10O:
Question 32.
What is tautomerism?
Answer:
It is a special type of functional isomerism in which single compound exists in two readily interconvertible structures that differ markedly in the relative position of atleast one atomic hydrogen. The two different structures are known as tautomers.

Question 33.
What ¡s meant by dyad system? Explain with example.
Answer:
In this system, hydrogen atom oscillates between two directly linked polyvalent atoms.
Question 34.
What is triad system? Give example.
Answer:
1. In this system hydrogen atom oscillates between three polyvalent atoms. It involves 1. 3-migration of hydrogen atom from one polyvalent atom to other with in the molecule.
2. The most important type of triad system is keto-enol tautomerism and the two groups of tautomers are keto form and enol form.
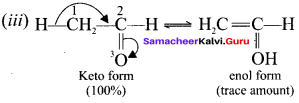
Question 35.
What is enolisation? What is labile form?
Answer:
Enolisation is a process in which keto form is converted into eno! form. Both tautomeric forms are equally stable. The less stable form is known as labile form.
Question 36.
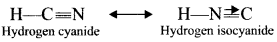
Give the structures of Nitro-aci tautomerism.
Answer:

Question 37.
Explain ring chain isomerism with the formula C4H8.
Answer:
In ring chain isomerism, compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in terms of bonding of carbon atoms to form open chain and cyclic structures.
C4H8:
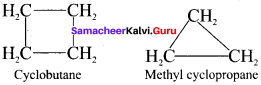
Question 38.
Define stereo-isomerism.
Answer:
The isomers which have same bond connectivity but different arrangement of groups or atoms in space are known as stereoisomers. This phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism.
Question 39.
Define geometrical isomerism with an example.
Answer:
Geometrical isomers are the stereoisomers which have different arrangement of groups or atoms around a rigid framework of double bonds. This type of isomerism occurs due to restricted rotation of double bonds or about single bonds in cyclic compounds.
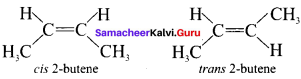
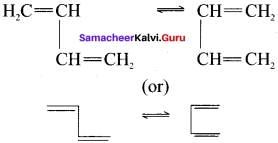
Question 40.
Trans isomer is more stable than cis isomer. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Trans isomer is more stable than cis isomer. This is because in the cis isomer, the bulky groups are on the same side of the double bond. The steric repulsion of the groups makes the cis isomers less stable than the trans isomers in which bulky groups are on the opposite side.

Question 41.
Draw the cis, trans isomeric structures of 1, 3-butadiene.
Answer:
Question 42.
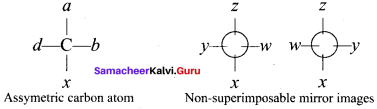
What are the condition for optical isomerism (or) enantiomerism.
Answer:
1. A carbon atom whose tetravalency in satisfied by four different substituents (atoms (or) groups) is called asymmetric carbon (or) chiral carbon. The optical isomer should have one or more chiral carbon to show optical activity.
2. The molecule possessing chiral carbon atom and is non-superimposable its own mirror image is said to be chiral ntolecule and the property is called chirality or dissymmetry.
Question 43.
How will you prepare Lassaigne’s extract?
Lassagine’s extract preparation:
Answer:
- A small piece of Na dried by pressing between the folds of filter paper is taken in a fusion tube and it is gently heated. When it melts to a shining globule, a pinch of organic compound is added.
- The tube is heated till reaction ceases arid become red hot. Then it is plunged in 50 ml of distilled water taken in a china dish and the bottom of the tube is broken by striking it against the dish.
- The contents of the dish is boiled for 10 minutes and then it is filtered. The filtrate is known as Lassaigne’s extract.
Question 44.
What Is the need for purification of organic compounds?
Answer:
In order to study the structure, physical properties, chemical properties and biological properties of organic compounds, they must be in the pure state. So organic compounds must be purified.
Question 45.
Define sublimation. Give two examples.
Answer:
The process of conversion of solid to vapour without melting or heating and on cooling the vapours getting back solids, such phenomenon is known as sublimation.
e.g., Naphthalene, Camphor.

Question 46.
Explain the process of chromatography in chlorophyll.
Answer:
The separation of different coloured constituents of chlorophyll is done by chromatography by M.S. Tswelt. He achieved it by passing a petroleum ether solution of chlorophyll present in leaves through a column of CaCO3 firmly packed into a narrow glass tube. Different components of the pigments got separated and lands to form zones of different colours.
Question 47.
Draw the first six members of the carboxylic acid homologous series.
Answer:
- HCOOH
- CH3COOH
- CH3-CH2-COOH
- CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2COOH
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH
Question 48.
Give the condensed formula and bond line formula of 2, 2,4- trimethylpentane.
Answer:
2, 2, 4 – irimethylpentane
(CH3)3CCH2CH(CH3)2-Condensed formula

Question 49.
Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an organic compound by
- Dumas method
- Kjeldahl’s method.
Answer:
1. Dumas method:
The organic compound is heated strongly with excess of CuO (Cupic Oxide) in an atmosphere of CO2 where free nitrogen, CO2 and H2O are obtained.
2. Kjeldahl’s method:
A known mass of the organic compound is heated strongly with conc. H2SO4, a little amount of potassium sulphate and a little amount of mercury (as catalyst). As a result of reaction, the nitrogen present in the organic compound is converted to ammonium sulphate.

Question 50.
Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Answer:
This is the simplest form of chromatography. Here a strip of paper acts as an adsorbent. It is based on the principle which is partly adsorption. The paper is made of cellulose fibres with molecules of water adsorbed on them. This acts as stationary phase. The mobile phase is the mixture of the components to be identified whose solution is prepared in a suitable solvent.
Question 51.
Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound with metallic sodium for testing nitrogen, sulphur and halogens.
Answer:
Organic compound is fused with sodium metal so as to convert organic compounds into NaCN, Na2S, NaX and Na3PO4. Since these are ionic compounds and become more reactive and thus can be easily tested by suitable reagents.
Question 52.
Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixture of calcium, sulphate and camphor.
Answer:
Sublimation. Because camphor can sublime whereas CaSO4 does not.
Question 53.
Explain, why an organic liquid vapourises at a temperature below its boiling point on steam distillation?
Answer:
It is because in steam distillation the sum of vapour pressure of organic compound and steam should be equal to atmospheric pressure.
Question 54.
Will CCl4give white precipitate of AgCl on heating it with silver nitrate? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
No. CCl4 is a completely non-polar covalent compound whereas AgNO3 is ionic in nature. Therefore they are not expected to react and thus a white ppt. of silver chloride will not be formed.

Question 55.
Why is a solution of potassium hydroxide used to absorb carbon dioxide evolved during the estimation of carbon present in an organic compound?
Answer:
CO2 is acidic in nature and therefore it reacts with the strong base KOH to form K2CO3:
2KOH + CO2 – K2CO2 + H2O
Question 56.
Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acidification of sodium extract for testing sulphur by lead acetate test?
Answer:
Sulphur sodium extract is acidified with acetic acid because lead acetate is soluble and does not interfere with the test.
Pb(OCOCH3)2 + H2SO4 → PbSO4-+ 2CH3COOH
Question 57.
Why is an organic compound fused with sodium for testing nitrogen, halogens and sulphur?
Answer:
On Ilising with sodium metal the elements present in an organic compound are converted into sodium salts which are water soluble which can be filtered and detected by the respective tests.
Question 58.
Under what conditions can the process of team distillation is used?
Answer:
Steam distillation is used to purify the Liquids which are steam volatile and not miscible with water.
Question 59.
Answer:
1, 2-dichloropropane

Question 60.
Write bond-line formulas for: Isopropyl alcohol, 2, 3-dimethvlbutanal, Heptan-4-one.
Answer:
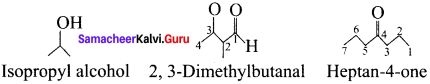
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry 3-Mark Questions
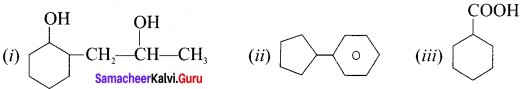
Question 1.
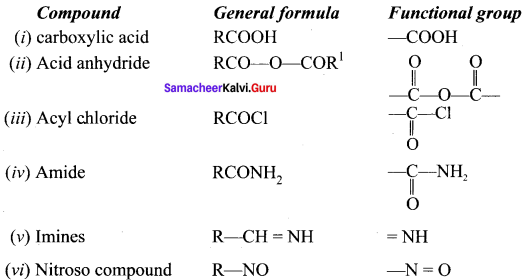
Write the functional group of the following compounds:
(i) carboxylic acid
(ii) Acid anhydride
(iii) Acyichioride
(iv) Amide
(v) imines
(vi) Nitroso compound
Answer:
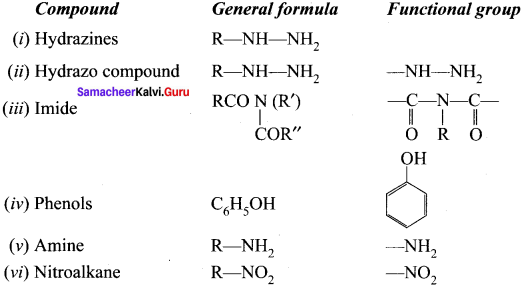
Question 2.
What are the general molecular formula and functional group of the following compounds?
Answer:
(i) Ilydrazines
(ii) Hydrazo compound
(iii) Imide
(iv) Phenols
(v) Amine
(vi) Nitroalkane
Answer:
Question 3.
Write the tUPAC names of the following compounds.
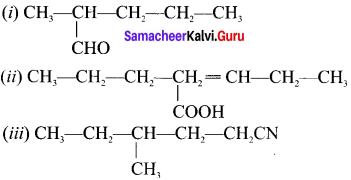
Answer:
(i) Pentan-2a1
(ii) Pentan-(2-ene-2-propyl)- i -oic acid
(iii) 4-methyl-i -cyanohexane
Question 4.
Answer:
(I) Hex-4-ene-2-oI
(ii) 3-ethyl-5-methyl heptane
Question 5.
Draw the structure of
(i) 1-ethyl-2-methyl cyclopentane
(ii) 1-ethyl-2, 3-dimethyl cyclohexane
(iii) 5-ethyl-2-methylcyclohcx- I -ene
Answer:
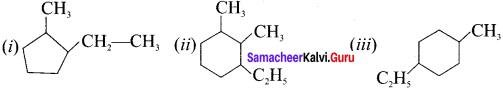
Question 6.
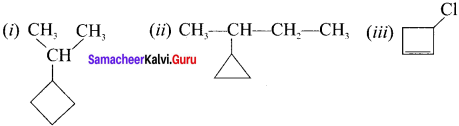
Draw the structures of:
(i) 2-cyclobutyl propane
(ii) 2-cyctopropyl butane
(iii) chiorocyclo but-2-eue
Answer:
Question 7.
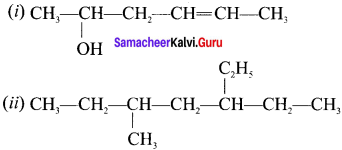
Give the IUPAC name of the following compounds:
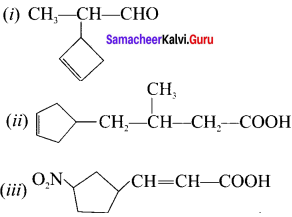
Answer:
(i) 2-(cyclo but-2-en-1-yl)-propanal
(ii) 4-(cyclopent-3-en- 1-yl )-3-methylbutanoic acid
(iii) 3-(3-nitro cyclopenryl)-prop-2-enoic acid
Question 8.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds
Answer:
(I) 2-(2-hydroxypropyl) cyclohexan- 1-01
(ii) CyclopentyÍ benzene
(iii) Cyclohexane carboxyl Ic acid
Question 9.
Draw the structure
(i) 1-(cyclo bytyl)-2 (cylopropyl) ethane
(ii) 2-carbamyl cyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid
Answer:
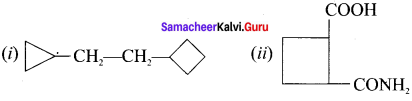
Question 10.
Draw the structures of:
(i) Bromohenzene
(ii) 1, 2-dichlorobenzene
(iii) 1-chloro-3-methvlbenzene
Answer:
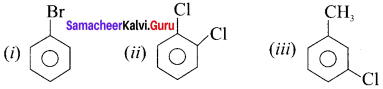
Question 11.
Draw the structures of –
(i) Benzvl chloride
(ii) Benzal dichloride
(iii) Benzotrichloride
Answer:
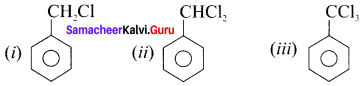
Question 12.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
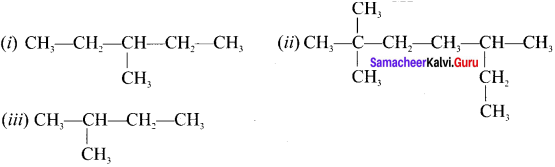
Answer:
(i) 3-methylpentane
(ii) 2, 2. 5-trimethylheptane
(iii) 2-methylbutanal
Question 13.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
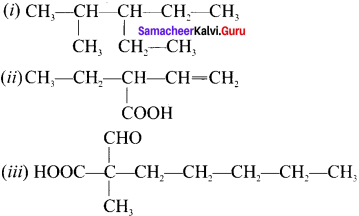
Answer:
(i) 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane
(ii) 2-ethyl but-3-enoic acid
(iii) 2-forrnyl-2-methylheptanoic acid
Question 14.
Draw the structures of
(i) 3-methylpentanal
(ii) 5-hydroxy 2,2-dimethyl heptanoic acid
(iii) 2-ethyl-4-propy Ipentane-d ioic acid
Answer:
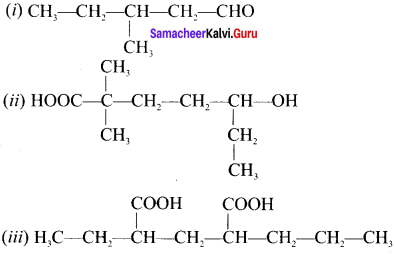
Question 15.
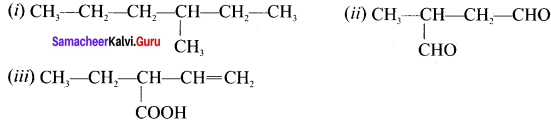
Answer:
(i) 3-methylhexane
(ii) 2-methylbutanal
(iii) 2-ethylbut-3-enoic acid
Question 16.
Give the IUPAC name Of –
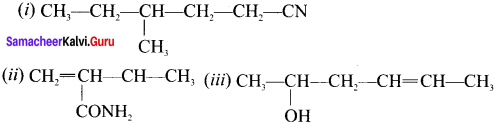
Answer:
(i) 4-methyl/hexanenitrite
(ii) 2-methyl but-3-en-amide
(iii) I-Iex-4-en-2-ol
Question 17.
Draw the structures of –
(i) 3-ethyl-5-methylheptane
(ii) 3-ethyl-2-methylhexane
(iii) 2, 4-dimethylpent-2-ene
Answer:
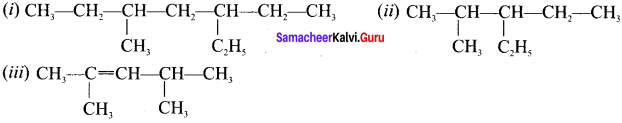
Question 18.
Draw the structures of:
(i) 3-methylhcpta 1, 3, 5-triene
(ii) pent-1-yne
(iii) 2-methylpropan-2-oI
Answer:
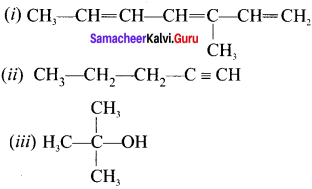
Question 19.
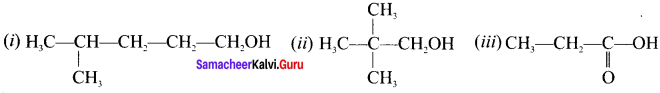
Give the IUPAC name of the following compounds.
Answer:
(i) 4-mcthylpcntan-1-ol
(ii) 2, 2-dimethylpropan-1-ol
(iii) Propanoic acid
Question 20.
Draw the structural formula of:
(i) 4-methylpent-3-en-2rone
(ii) pent-1-yne-3-one
Answer:

Question 21.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
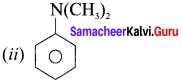
CH3-CH2-CH2-NH-CH3
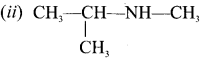
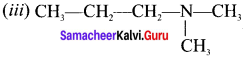
Answer:
(i) N-methylpropan- 1 -amine
(ii) N-rnethylpropan-2-amine
(iii) N, N-dimethylpropan- 1-amine
Question 22.
Draw the structurai formula of the following compounds.
(i) N-cthyl-N-methylpropan-1-amine
(ii) N, N-dimethyl benzenamine
Answer:
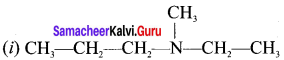
Question 23.
Draw the complete structural formula, condensed structure and bond line structure of
(i) n-propanol
(ii) 1, 3-butadiene.
Answer:
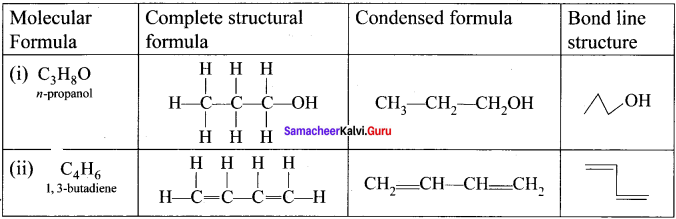
Question 24.
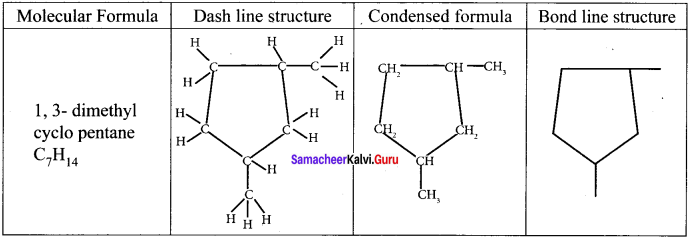
Draw the dash line structure, condensed structure and bond line structure of 1, 3-dimethyl cyclopentane.
Answer:
Question 25.
What is wedge formula? Explain with suitable example.
Answer:
1. The simplest convention is solid and dashed wedge formula in which 3-D image of a molecule can be perceived from two dimensional picture.
2. In this representation, a tetrahedral molecule with four atoms or groups a, b, e and d bonded to it can be represented by wedge formula as follows.
3. A solid wedge 
or a heavy line is used to indicate a bond projecting above the plane of the paper and dashed wedge 
or a dashed line is used to depict the bond below the plane. The bonds lying in the plane of the paper are shown by normal lines.
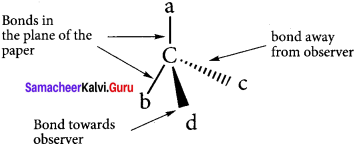
Question 26.
Draw the fisher projection formula for tartaric acid.
Answer:
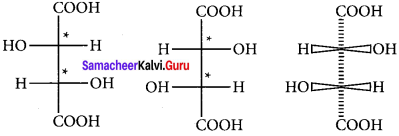
Question 27.
Explain the advantage of sawhorse projection formula over the fisher projection formula with an example.
Answer:
1. The fisher projection fonnula inadequately portrays the spatial relationship between ligands attached to the atoms. The sawhorse projection attempts to clarify the relative location of the groups.
2. In sawhorse projection formula, the bond between two carbon atoms ¡s drawn diagonally and slightly elongated. The lower left hand carbon is considered lying towards the front and the upper right hand carbon towards the back.
Question 28.
Explain about the Newmann projection formula with an example.
Answer:
1. In this method, the molecules are viewed from the front along the carbon-carbon bond axis.
2. The two carbon atom forming the G bond is represented by two circles. One behind the other so that only the front carbon is seen. The front carbon atom is shown by a point where as the carbon lying farther from the eye is represented by the origin of the circle.
3. Therefore the C-H bonds of the front carbon are depicted from the circle while the C H bonds of the back carbon are drawn from the circumferance of the circle with an angle of 120 to each other.
Question 29.
Write the possible isomers for the formula C5H12 with their names and structures.
Answer:
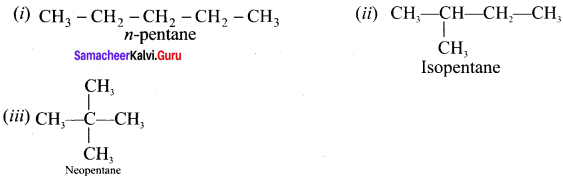
(i), (ii) and (iii) are chain isomers.
Question 30.
What are the possible isomers for the formula C4H9Cl? Give their structures and IUPAC names.
Answer:
C4H9Cl:
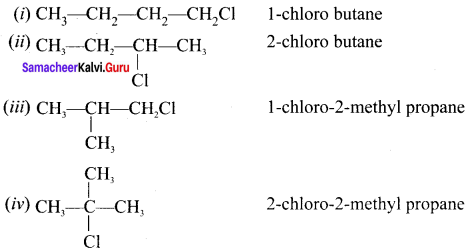
Question 31.
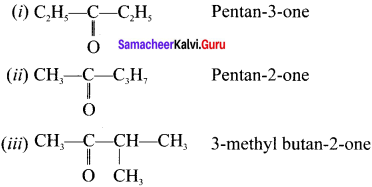
Write the metamers for the formula C5H10O with their IUPAC names.
Answer:
Question 32.
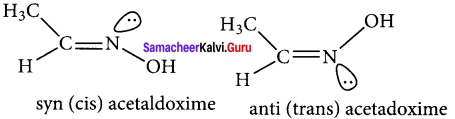
Explain about the geometrical isomerism possible in oximes.
Answer:
1. Restricted rotation around C = N (oximes) gives rise to geometrical isomerism in oximes. Here syn and anti are used instead of cis and trans respectively.
2. In the syn isomer the H atom of a doubly bonded carbon and OH group of doubly bonded nitrogen lie on the same side of the double bond, while in the anti isomer, they lie on the opposite side of the double bond.
3. for e.g.,
Question 33.
What are enantiomers?
Answer:
1. An optically active substance may exist in two or more isomeric forms which have same physical and chemical properties but diflèr in terms of direction of rotation of plane polarised light, such optical isomers which rotate the plane polarised light with equal angle but in opposite directions are known as enantiomers and (he phenomenon is known as enantiomerism.
2. Isomers which are non-super impossible mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Question 34.
How would you detect sulphur?
Answer:
1. To a portion of the Lassaigne’s extract, freshly prepared sodium nitroprusside solution is added. If deep violet or purple colour is formed, the presence of sulphur is confirmed.
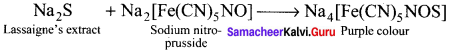
2. To another portion of Lassaignes extract, acetic acid and lead acetate solution are added. If black precipitate is formed, sulphur presence is confirmed.

Question 35.
Explain about the oxidation test for sulphur.
Answer:
1. Oxidation test:
The organic substances are fused with a mixture of KNO3 and Na2CO3. The sulphur if present is oxidised to sulphate.
Na2CO3 + S + 3(O) Na2SO4 + CO2
2. The fused mass is extracted with water, acidified with HCl and the BaCl2 solution is added to it. A while precipitate indicates the presence of sulphur.
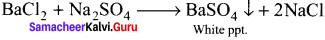
Question 36.
How would you detect the halogens in an organic compound?
Answer:
- To a portion of the Lassaigne’s filtrate. dii. HNO3 is added, warmed gently and AgNO3 solution is added.
- Appearance of curdy white precipitate soluble in ammonia solution indicates the presence of chlorine.
- Appearance of pale yellow precipitate sparingly soluble in ammonia solution indicates the presence of bromine.
- Appearance of yellow precipitate insoluble in ammonia solution indicates the presence of iodine.

Question 37.
Why nitric acid is added in the Lassaigne’s test for halogens?
Answer:
1. if N (or) S is present in the organic compound along with the halogen, we might obtain Na2S and NaCN in the solution which interfere with the detection of the halogen in the AgNO3 test.
2. Therefore we boil the Lassiagne’s extract with HNO3 which decomposes NaCN and Na2 S as follows:
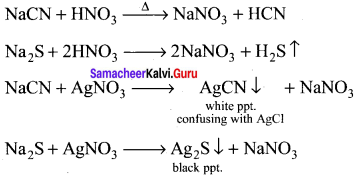
Question 38.
Explain about the test for phosphorous in an organic compound.
Answer:
- A solid organic compound is strongly heated with a mixture of Na2CO3 and KNO3. Phosphorous present in the compound is oxidised to sodium phosphate.
- The residue is extracted with water and boiled with cone. HNO3. A solution of ammonium molyixiate is added to this solution.
- A canary yellow precipitate shows the presence of phosphorous.
Question 39.
Explain about principle and reactions involved in carius method of estimation of sulphur. Carius method:
Answer:
1. Principle:
A known mass of the organic substance is heated strongly with fuming HNO3. C and H get oxidized to CO2. and H2O while sulphur is oxidised to sulphuric acid as follows.
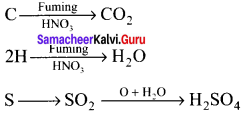
2. The resulting solution is treated with excess of BaCl2 solution, H2SO4 present in the solution is converted into BaSO4. From the mass of BaSO4, the percentage of sulphur can be calculated.
Question 40.
Explain about the procedure and calculation behind the carius method of estimation of sulphur.
Answer:
Carius method:
(I) Procedure:
A known mass of the organic compound is taken in a clean carius tube and few mL of fuming HNO3 is added and then the tube is sealed. It is then placed in an iron tube and bcatcd for 5 hours. The tube is allowed to cool and a hole is made to allow gases to escape. The carius tube is broken and the content collected in a beaker. Excess of BaCl, is added to the beaker. BaSO4 furmed is converted to BaSO4 (white ppt.) The precipitate is filtered. washed, dried and weight. From the mass of BaSO4, percentage of S is calculated.
(ii) Calculation:
Mass of organic compound = Wg
Mass of BaSO4 formed = r g
233 g of BaSO4 contains 32 g of sulphur
∴ x g of BaSO4 contain \(\frac {32}{233}\) x x g of sulphur
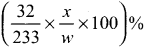
Question 41.
What is Homologous Series? Give a suitable example.
Answer:
Homologous series:
It is a series of compounds in which the adjacent members differ by a – CH2 unit. Individual members of such series are called homologues, and the phenomenon is called homology. All the members of such a series of alkane have the general formula CnH2n + 2. Few members of this family are
CH4 – Methane
C2H6 – Ethane
C3H8 – Propane
C4H10 – Butane
C5H12 – Pentane

Question 42.
Explain the copper oxide test for the detection of carbon and hydrogen present in the given organic compound.
Answer:
Copper oxide test:
The organic substance is mixed intimately with about three times its weight of dry copper oxide by grinding. The mixture is then placed in a hard glass test tube fitted with a bent delivery tube. The other end of which is dipping into lime water in another test tube. The mixture is heated strongly and the following reaction take place.
C + 2CuO → CO2 + 2CuO
2H + CuO → H2O + Cu
Thus if carbon is present, it is oxidized to CO2 which turns lime water millcy. If hydrogen is also present, it will be oxidized to water which condenses in small droplets on the cooler wall of the test tube and inside the bulb. Water collected in the bulb is separated on anhydrous CuSO4 which turn blue. This confirms the presence of C and H in the compound. If however, H is not present water droplet is not obtained in the bulb.
Question 43.
Explain differential extraction.
Answer:
- The process of removing a substance from its aqueous solution by shaking with a suitable organic solvent is termed extraction.
- When an organic substance present as solution in water can be recovered from the solution by means of a separating funnel.
- The aqueous solution is taken in a separating funnel with little quantity of ether or chloroform (CHCl3). The organic solvent immiscible with water will form a separate layer and the contents are shaken gently.
- The solute being more soluble in the organic solvent is transferred to it.
- The solvent layer is then separated by opening the tap of separating funnel and the substance is recovered.
Question 44.
Explain about the principle involved in chromatography. Give its types.
Answer:
- The principle behind chromatography is selective distribution of the mixture of organic substances between two phases-a stationary phase and a moving phase. The stationary phase can be a solid or liquid while the moving phase is a liquid or a gas.
- if the stationary phase is solid, the basis is adsorption and when it is a liquid, the basis is partition.
- Chromatography is defined as technique for the separation of a mixture brought about by differential movement of the individual compound through porous medium under the influence of moving solvent.
- The various methods of chromatography are:
- Column chromatography (CC)
- Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- Paper chromatography (PC)
- Gas liquid chromatography (GLC)
- Ion exchange chromatography
Question 45.
Describe about adsorption chromatography.
Answer:
- The principle involved is different compounds are adsorbed on an adsorbent to different degree.
- Silica gel and alumina are the commonly used adsorbent. The components of the mixture move by varying distances over the stationary phase.
Question 46.
What are hybridisation states of each carbon atom ¡n the following compounds?
Answer:
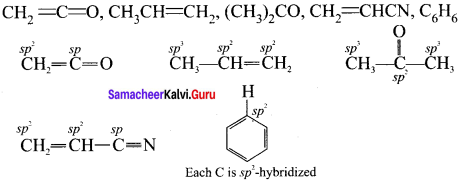
Question 47.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
Answer:
(a) Propylbenzene
(b) Methylpentanenitrile
(c) 2, 5-Dimethyllieptanc
(d) 3-Bromo-3-chloroheptane
(e) 3-Chioropropanal
(f) 2, 2-Dichloroethanol
Question 48.
Write the formulas for the first five members of each homologous series beginning with the following compound. CH3COCH3
Answer:
CH3COCH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3CO(CH2)4CH3

Question 49.
Write the formulas for the first five members of each homologous series beginning with the following compound: H-CH=CH2
Answer:
H-CH=CH2
CH3CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH=CH2
Question 50.
Identify the functional groups ¡n the following compounds.
Answer:
Question 51.
What is the difference between distillation, distillation under reduced pressure and steam distillation?
Answer:
Distillation:
it is used in case of volatiLe liquid mixed with a non-volatile impurities.
Distillation under reduced pressure:
This method is used to purify such liquids which have very high boiling points and which decompose at or below their boiling points.
Steam distillation:
it is used to purify steam volatile liquids associated with water immiscible impurities.

Question 52.
(a) What is Lassaigne’s extract? Will NaCN give a positive Lassaigne’s test for nitrogen?
(b) Which colour will appear in the Lassaigne’s test if the compound contains both nitrogen and sulphur.
(c) Why is Lassaigne’s extract prepared in distilled water? Can we detect oxygen iii a compound by Lassaigne’s test?
Answer:
(a) When organic compounds is fused with sodium metal and then extracted by water it is called Lassaigne’s extract. Yes.
(b) Blood red colour.
(c) Lassaigne’s extract is prepared in distilled water since ta water contains Cl’ ions. No, oxygen cannot be detected by Lassaigne’s test.
Question 53.
0.3780 g of an organic compound gave 0.5740 g of silver chloride in Carius estimation. Calculate the percentage of chlorine in the compound.
Answer:
Mass of the compound = 0.3780
Mass of silver chloride 0.5740 g
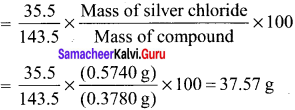
Question 54.
In an estimation of sulphur by Carius method, 0.468 of an organic sulphur compound gave 0.668 g of barium sulphate. Find the percentage of sulphur in the compound.
Answer:
Percentage of sulphur
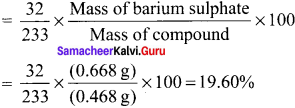
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry 5 marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain about the steps involved in naming an organic compound as per IUPAC nomenclature.
Answer:
The following steps should be followed for naming an organic compound as per IUPAC nomenclature.
- Choose the longest carbon chain (Root word). Consider all other groups attached to this chain as substituents.
- Numbering of the longest carbon chain.
- Naming the substituents (prefixes) or (suffixes).
- Arrange the substituents in the alphabetical order.
- Write the name of the compound as below.
Prefix + Root word Primary suffix + r Secondary suffix

Question 2.
How will you detect the presence of carbon and hydrogen in an organic compound?
Answer:
Copper oxide test:
1. The organic substance is mixed with three times its weight of dry copper oxide by grinding. The mixture is placed in a hard glass test rube fitted with a bent delivery tube. The other end of which is dipping into lime water in an another test tube. The mixture is heated strongly.
2. 2CuO + C → CO2 + 2Cu
CuO + 2H → H2O + Cu
3. Thus if carbon is present, it is oxidized to CO2 which turns lime water milky. If hydrogen is also present, it will be oxidized to water and condenses in small droplets on the cooler wall of the test tube and inside the bulb. Water is collected on white anhydrous CuSO4 which turns blue.
4. This confirms the presence of C and H in the compound.
Question 3.
Explain lassaigne’s test for detection of nitrogen ¡n an organic compound.
Answer:
I step:
Preparation of sodium fusion extract:
A small piece of Na dried by pressing between the folds of filter paper is taken in a fusion tube and it is heated. When it melts to a shining globule, a pinch of organic compound is added to it. The tube is then heated till the reaction ceases and becomes red hot.
Then the test tube is plunged in about 50 ml of distilled water taken in a china dish and break the bottom of the tube by striking against the dish. The contents of the dish is boiled for about 10 minutes and then filtered. This filtrate is known as lassaigne’s extract (or) sodium fusion extract.
II step :
Test for Nitrogen:
If Nitrogen is present, it gets converted to sodium cyanide which reacts with freshly prepared ferrous sulphate and ferric ion followed by cone. HCl and gives a Prussian blue colour (or) green coloured precipitate, it confirms the presence of nitrogen. HCl is added to dissolve the greenish precipitate of ferrous hydroxide produced by the action of NaOH on FeSO4 which would otherwise mark the Prussian blue precipitate.
Reactions involved:
Na + C + N → NaCN
FeSO4 + 2NaOH → Fe(OH)2 + Na2SO4
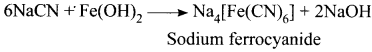
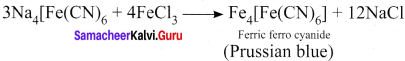
if both N & S are present. a blood red colour is obtained due to the following reactions
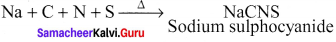
Question 4.
Explain about the estimation of carbon and hydrogen.
1. Principle:
A known weigIt of organic substance is brunt in excess of oxygen and the carbon and hydrogen present in it are oxidised to CO2 and H2O respectively.

The weight of carbon dioxide and water thus formed are determined and the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the organic substance are calculated.
2. Description of the apparatus:
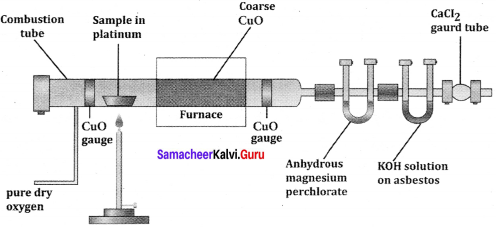
(a) The oxygen supply (b) combustion tube (c) Absorption tube
Oxygen supply:
To remove the moisture from oxygen. it is allowed to bubble through sulphuric acid and then passed through a U-tube containing sodalime to remove CO2. The oxygen gas free from moisture and CO2 enters the combustion tube.
Combustion tube:
A hard glass tube open at both ends used for the combustion. It contains (i) an oxidized copper gauze to prevent the backward diffusion of the products of combustion (ii) a porcelain boat containing a known weight of the organic substance (iii) coarse copper oxide on either side and (iv) an oxidized copper gauze placed towards the end of the combustion tube. The combustion tube is heated by a gas burner.
Absorption apparatus:
The combustion products containing moisture and CO2 are then passed through the absorption apparatus which consists of(i) a weighed U-tube packed with pumice soaked in conc. H2SO4 to absorb water (ii) a set of bulbs containing a Strong solution of KOH to absorb CO2 and finally (iii) a guard tube filled with anhydrous CaCl2 to prevent the entry of moisture from atmosphere.
3. Procedure:
The combustion tube is heated strongly to dry its content. It is then cooled and connected to absorption apparatus. The other end of the combustion tube is open for a while and the boat containing weighed organic substance is introduced. The tube is again heated strongly till all the substance in the boat is burnt away. This takes about 2 hours. Finally a strong current of oxygen is passed. Then the U-tube and potash bulbs are then
detached and increase in weight of each of them is determined.
4. Calculation:
Weight of organic substance = W g
Increase in weight of H2O = x g
Increase in weight of CO2 = y g
18g of H2O contains 2 g of hydrogen
∴ x g of H2O contain \(\frac {1}{2}\) × x g of hydrogen.
∴ Percentage of hydrogen = (\(\frac {2}{18}\) x \(\frac {x}{w}\) x 100
44g of CO2 contains 12 g of carbon
∴ y g of CO2 contain \(\frac {12}{44}\) × y g of carbon
∴ Percentage of carbon = (\(\frac {12}{44}\) × \(\frac {12}{44}\) × 100)%

Question 5.
Explain about the estimation of halogens by carius method.
Answer:
Carius method:
A known mass of the substance is taken along with fuming HNO3 and AgNO3 taken in a clean carius tube. The open end of the carius tube is sealed and placed in a iron tube for 5 hours in a range at 530 to 540 K. Then the tube is allowed to cool and a small hole is inade in the tube to allow the gases to excape. The tube is broken and the precipitate is filtered, washed, dried and weighed. From the mass of AgX produced percentage of halogen in the organic compound is calculated.
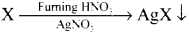
Calculation:
Weight of the organic compound = Wg
Weight of AgCl = a g
143.5 g AgCl contains 35.5g of Cl
a g of AgCl contain \(\frac {35}{143.5}\) x 9 g of Cl
Wg of organic compound contains \(\frac {35}{143.5}\) × 9 g of Cl
% of chlorine = (\(\frac {35}{143.5}\) × \(\frac {a}{w}\) × 100)%
Weight of silver bromide = b g
188 g of AgBr contains 80 g of Br
b g of AgBr contain = \(\frac {80}{188}\) × b g of Br
% of Bromine = (\(\frac {80}{188}\) × \(\frac {b}{w}\) × 100)
Weight of silver iodide = c g
235 g of AgI contains 127 g of I
c g of AgI contain = \(\frac {80}{188}\) × c g of I
% of Iodine = (\(\frac {80}{188}\) × \(\frac {c}{w}\) × 100)
Question 6.
How will you estimate phosphorous in an organic compound?
Answer:
Carius method:
Procedure:
A known mass of organic compound (wg) containing phosphorus is heated with fuming HNO3 in a sealed tube where C is converted into CO2 and H to H2O. Phosphorous present in the organic compound is oxidised to phosphoric acid which is precipitated as ammonium phospho molybdate by heating with conc. HNO3 and by adding ammonium molybdate.
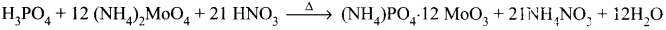
The precipitate of ammonium phrospho molybdate is filtered, washed, dried and weighed.
Calculation:
Mass of organic compound = Wg
Mass of ammonium phospho molybdate = x g
Molar mass of ammonium phospho molybdate 1877 g
1877 g of ammonium phospho molybdate contains 31 g of phosphorous
x g of ammonium phospho molybdate contain = \(\frac {31}{1877}\) × x g of phosphorous
% of phosphorous = (\(\frac {31}{1877}\) × \(\frac {x}{w}\) × 100)% of phosphorous
In an alternate method, phosphoric acid is precipitated as magnesium-ammoniumphosphate by adding magnesia mixture. The ppt. is washed dried and ignited to get magnesium pyrophosphate which is washed, dried and weighed.
Weight of magnesium pyrophosphate = y g
Molar mass of magnesium pyrophosphate = 222 g
222 g of magnesium pyrophosphate contains 62 g of P
y g of magnesium pyrophosphate contain = \(\frac {62}{222}\) × y g of P
% of phosphorous = (\(\frac {31}{1877}\) × \(\frac {y}{w}\) × 100)%

Question 7.
Explain Dumas method of estimation of nitrogen.
Answer:
Dumas method:
Principle:
This method is based on the fact that nitrogeneous compound when heated with cupric oxide in an atmosphere of CO2 yields free nitrogen.
Traces of nitrogen are reduced to elemental nitrogen by passing over heated copper spiral.
Description of the apparatus:
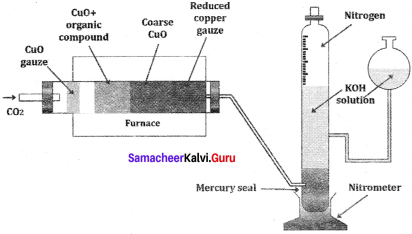
CO2 Generator:
CO2 needed in this process’is prepared by heating magnetite or sodium bicarbonate contained in a hard glass tube (or) by the action of dil. HCl on marble in a kipps apparatus. The gas is passed through the combustion tube after dried by bubbling through cone. H2SO4.
Combustion tube:
The combustion tube is heated in a furnace is charged with (a) A roll of oxidised copper gauze to prevent the back diffusion of products of combustion and to heat the organic substance mixed with CuO by radiation (b) a weighed amount of organic substance mixed with excess of CuO (c) a layer of CitO packed in about 2/3 length of the tube and kept in position by loose asbestos plug on either side and (d) a reduced copper piral which reduces any oxides of nitrogen formed during combustion of nitrogen.
Schiff’s nitromctc:
The nitrogen gas obtained by the decomposition of the substance in the combustion tube is mixed with considerable excess of CO2. It is estimated by passing nitro meter when CO2 is absorbed by KOH and the nitrogen gas gets collected in the upper part of the graduated tube.
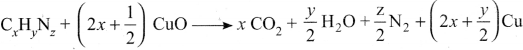
Calculation:
Weight of the substance taken Wg
Volume of nitrogen = V1L
Room temperature = T1K
Atmospheric pressure = p mm Hg
Aqueous tension al room temperature P’ nun of Hg
Pressure of dry nitrogen = P—P’ = P’1 mm Fig
P0, V0 and T0 be the pressure, volume and temperature respectively of dry nitrogen at S.T.P.
Then, \(\frac{P_{0} V_{0}}{T_{0}}=\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{T_{1}}\)
V0 = \(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{T_{1}} \times \frac{T_{0}}{P_{0}}\)
V0 = \(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{T_{1}} \times \frac{273 \mathrm{K}}{760 \mathrm{mm} \mathrm{Hg}}\)
22.4 L of N2 at STP weigh 28 g of N2
V0L of N2 at STP weigh \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x V0
W g of organic compound contain \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x V0 g of N2
100 g of organic contain \(\frac {28}{22.4}\) x \(\frac{V_{o}}{w}\) x 100 = % of Nitrogen

Question 8.
Explain Kjeldahl’s method.
Answer:
Principle:
This method is based on the fact that an organic compound containing nitrogen is heated with cone. H2SO4. the nitrogen is conerted Lo ammonium sulphate. The resultant liquid is heated with excess of alkali and then liberated ammonia gas is absorbed in excess of standard acid. The amount of ammonia (nitrogen) is determined by finding the amount of acid neutralised by back titration with same standard alkali.
Procedure:
A weighed quantity of the substance 0.3 to 0.5g is placed in a special long necked Kjeldahl flask made of pyrex glass. About 25 ml of cone. H2SO4 together with a little K2SO4 and CuSO4 [catalyst] are added to il. the flask is loosely stoppered by a glass bulb and heated gently in an inclined position.
The heating is continued till the brown colour of the liquid disappears leaving the content clear as before. At this point all the nitrogen is converted to ammonium sulphate. The kjeldahl flask is cooled aiid its contents are diluted with distilled water and carefully transferred into a I litre round bottom flask. An excess NaOH is poured down the side of the flask and it is filled with a kjeldhals trap and a water condenser.
The lower end of the condenser dips in a measured volume of excess of \(\frac {N}{20}\) H2SO4 solution. The liquid in the round bottom flask is heated and liberated ammonia is distilled to sulphuric acid. When no more ammonia passes over (test the distillate with red litmus) the receiver is removed. The excess of acid is then determined by titration with alkali, using phenolphthalein as the indicator.
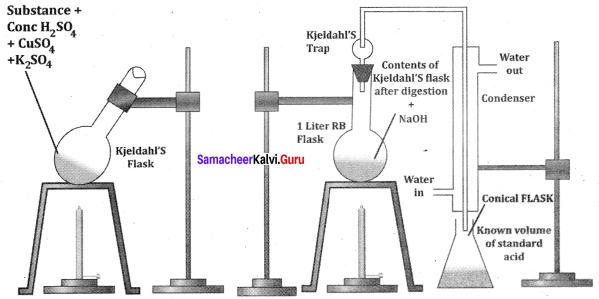
Calculation:
Weight of the substance = Wg
Volume of H2SO4 required for the complete neutralisation of evolved NH3 = V ml
Strength H2SO4 used to neutralise NH3 = N.
Let the volume and strength of NH3 formed are V1 and N1 respectively.
V1N1 = VN
The amount of nitrogen present in W g of organic compound = \(\frac{14 \times \mathrm{NV}}{1 \times 1000 \times w}}\)
Percentage of nitrogen = \(\frac{14 \times \mathrm{NV}}{1000 \times w} \times 100\) = \(\frac {1.4NV}{w}\) %

Question 9.
How will you estimate carbon and hydrogen present in the given organic compound?
Answer:
Both carbon and hydrogen are estimated by the same method. A known weight of the organic substance is burnt in excess of oxygen and the carbon and hydrogen present in it are oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, respectively.
CXHY + O2 + XCO2 + \(\frac{\mathrm{y}}{2}\)H2O
The weight of carbon dioxide and water thus formed are determined and the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the original substance is calculated. The apparatus employed for the purpose consists of three units (1) oxygen supply (2) combustion tube (3) absorption apparatus.
Oxygen supply:
To remove the moisture from oxygen it is allowed to bubble through sulphuric acid contained in a drech gel bottle and then passed through a U-tube charged with soda lime to remove CO2. The oxygen gas free from moisture and carbon dioxide enters the combustion tube.
Combustion tube:
A hard glass tube open at both end is used for the combustion of the organic substance. It is filled with
(i) a role of oxidized copper gauze to prevent the backward diffusion of the product of combustion
(ii) a porcelain boat containing a known weight of the organic substance
(iii) coarse copper oxide packed in about 2/3 of the entire length of the tube, and kept in position by loose asbestos plugs on either side and
(iv) a roll of oxidized copper gauze placed towards the end of the combustion tube to prevent any vapours of the organic substance having the tube unoxidized. The combustion tube is enclosed in a furnace, and heated by a gas burner.
Absorption Apparatus:
The products of combustion containing moisture and carbon dioxide are then passed through the absorption apparatus which consists of
(i) a weighed U-tube packed with pumice soaked in Conc. H2SO4 to absorb water
(ii) a set of bulbs containing strong solution of KOH to absorb CO2 and finally
(iii) a guard tube filled with anhydrous CaCl2 to prevent the entry of moisture from atmosphere.
Procedure:
To start with, before loading it with the boat, the combustion tube is detached from the absorption unit. The tube is heated strongly to dry its content and CO2 present in it is removed by passing a current of pure, dry oxygen through it. It is then cooled slightly and connected to the absorption apparatus. The other end of the combustion tube is open for a while and the boat containing weighed organic substance is introduced.
The tube is again heated strongly till the substance in the boat is burnt away. This takes about 2 hours. Finally, a strong current of oxygen is passed through the combustion tube to sweep away any traces of carbon dioxide or moisture which may have been left in it. The U-tube and the potash bulbs are then detached and the increase in weight of each of them is determined.
Calculation:
Weight of the organic substance taken = w g
Increase in weight of H2O = x g
Increase in weight of CO2 = y g
18 g of H2O contain 2 g of hydrogen
∴ x g of H2O contain = \(\left(\frac{2}{18} \times \frac{x}{w}\right)\)
% of hydrogen = \(\left(\frac{2}{18} \times \frac{x}{w} \times 100\right)\) %
44 g of CO2 contains = 12 g of carbon
∴ y g of CO2 contain = \(\left(\frac{12}{44} \times \frac{y}{w}\right)\) g of carbon
Percentage of carbon = \(\left(\frac{12}{44} \times \frac{y}{w} \times 100\right)\) %

Question 10.
Explain steam distillation (or) How is essential oils are recovered from plants and flowers.
Steam distillation:
This method is applicable for solids and liquids. If the compound to be steam distilled and it should not decompose at any steam temperature should have a fairly high vapour pressure at 273 K, it should be insoluble in water and the impurities present should be non-volatile.
The impure liquid along with little water is taken in a round-bottomed flask which is connected to a boiler on one side and water condenser on the other side, the flask is kept in a slanting position so that no droplets of the mixture will enter into the condenser on the brisk boiling and bubbling of steam.
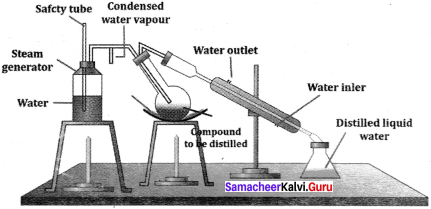
The mixture in the flask is heated and then a current of steam passed into it. The vapours of the compound mix up with the steam and escape into the condenser. The condensate obtained is a mixture of water and organic compound which can be separated. This method is used to recover essential oils from plants and flowers also in the manufacture of aniline and turpentine oil.
Question 11.
Explain about azeotropic distillation.
Answer:
The mixture of liquids that cannot be separated by fractional distillation can be purified by azeotropic distillation. The mixture are called azeotropes. These azeotropes are constant boiling mixture which distill as a single component at a fixed temperature for example ethanol and water in the ratio of 95.87: 4.13. In this method, the presence of a third component C6H6, CCl4, ether, glycol glycerol which act as dehydrating agent depress the partial pressure of one component of azeotropic mixture and raises the boiling point of that component and thus the other component will distil over. Substance like C6H6, CCl4 have low b.pt. and reduce the partial vapour pressure of alcohol more than that of water while substance like glycerol and glycol have high boiling point and reduce the partial vapour pressure of water more than that of alcohol.
Question 12.
Explain about thin layer chromatography.
Answer:
A sheet of glass is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent (cellulose, silica gel (or) Alumina). This sheet of glass is called chromplate or thin layer chromatography plate. After drying the plate, a drop of the mixture is placed just above one edge and the plate is then placed in a closed jar containing eluant (solvent) .
The eluant is drawn up the adsorbent layer by capillary action. The components of the mixture move up along with the eluent to different distances depending upon their degree of adsorption of each component of the mixture. It is expressed in terms of its retention factor (Rf) value.
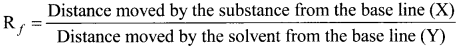
The spots of coloured compounds are visible on TLC plate due to their original colour. The colourless compounds are viewed under Uy light or in another method using Iodine crystals or by using appropriate reagent.
Question 13.
An organic compound contains 69% carbon and 4.9% hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen. Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this compound is subjected to complete combustion.
Answer:
Step I.
Calculation of mass of CO2 produced
Mass of compound = 0.20 g
Percentage of carbon = 69 g
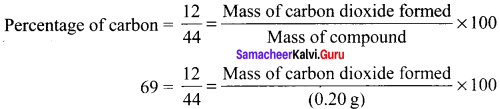
Mass of CO2 formed = \(\frac{69 \times 44 \times(0.20 \mathrm{g})}{12 \times 100}\) = 0.506g
Step II.
Calculation of mass of H2O produced
Mass of compound = 0.20 g
Percentage of hydrogen = 4.8%
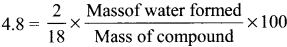
Mass of H2O formed = \(\frac{4.8 \times 18 \times(0.20 \mathrm{g})}{2 \times 100}\) = 0.0864 g
Question 14.
0.50 g of an organic compound was Kjeldahlished. The ammonia eolved was passed in 50cm3 of IN H2SO2. The residual acid required 60 cm3 of N/2 NaOH solution. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
Answer:
Step 1.
Calculation of volume of unused acid
Volume of NaOli solution required = 60 cm3
Normality of NaOH solution = \(\frac {1}{2}\) N
Normality of H2SO4 solution = \(\frac {1}{N}\)
Volume of unused acid can be calculated by applying normality equation
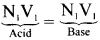
1 x V = \(\frac {1}{2}\) x 60 = 30cm3
Step II.
Calculation of volume of acid used
Volume of acid added = 50 cm3
Volume of unused acid = 30 cm3
Volume of acid used = (50 – 30) = 20 cm3
Step III.
Calculation of percentage of nitrogen
mass of compound = 0.05 g
Volume of acid used = 20 cm3
Normality of acid used = 1 N
percentage of nitrogen = \(\frac{1.4 \times 20 \times 1}{0.50}=56 \%\)
Question 15.
In a Dumas nitrogen estimation method, 0.30 g of an organic compound gave 50 cm3 of N2 collected at 300 K and 715 mm Hg pressure. Calculate the percentage composition of nitrogen ¡n the compound. (‘apour pressure of water at 300 K is 15 mm Hg)
Answer:
P1 = 715 – 15 = 700mm Hg, P1 = 760 mm Hg
\(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{P_{2} V_{2}}{T_{2}}\)
T1 = 300 K, T2 = 273K, V1 = 50 cm3, V2 = ?
V2 = \(\frac{700 \times 50 \times 273}{300 \times 760}\) = 41.9 cm3
% of N = \(\frac {28}{22400}\) x 41.9 x \(\frac {100}{W}\) = 17.46%
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
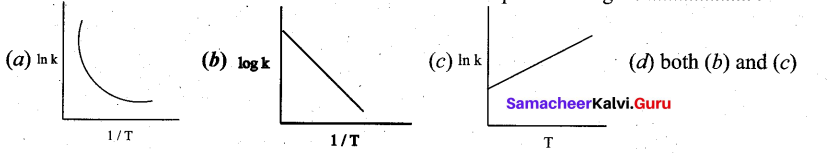
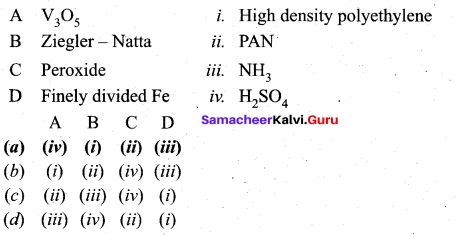
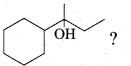
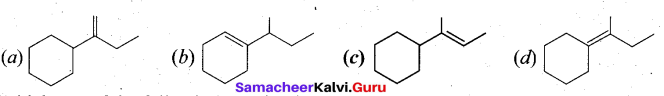

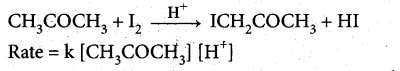
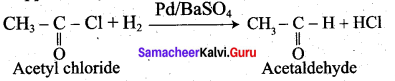
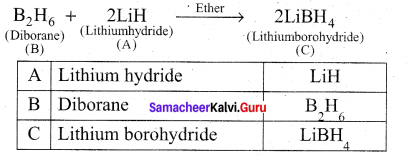
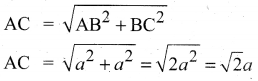 In∆ACG,
In∆ACG,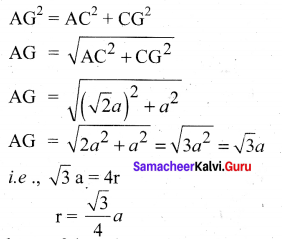
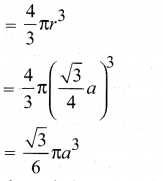
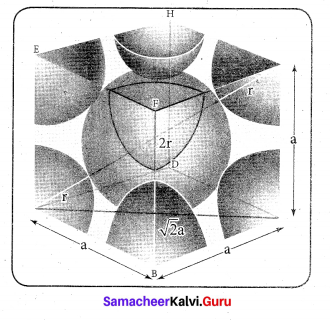
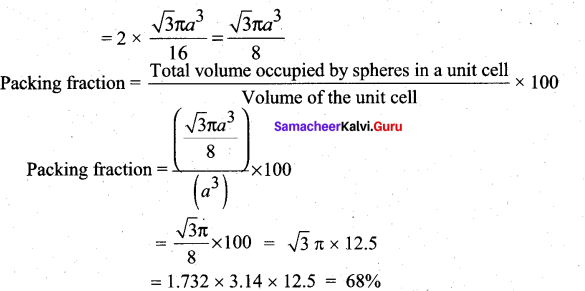
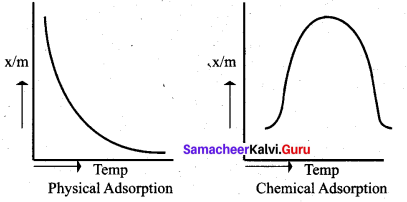
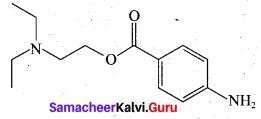
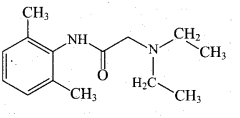
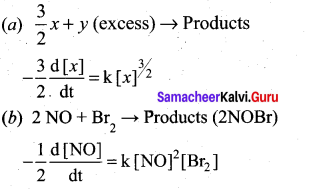
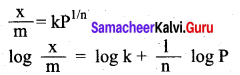
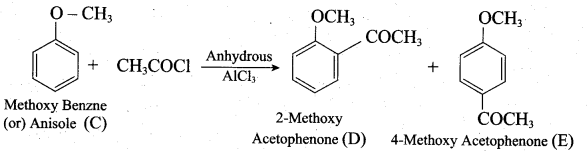
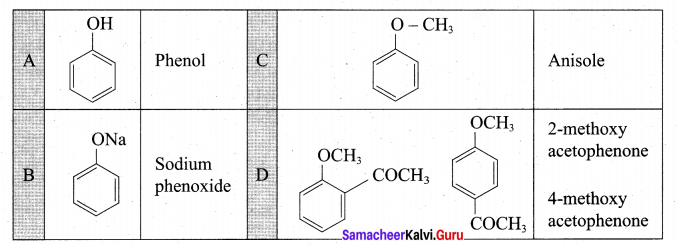
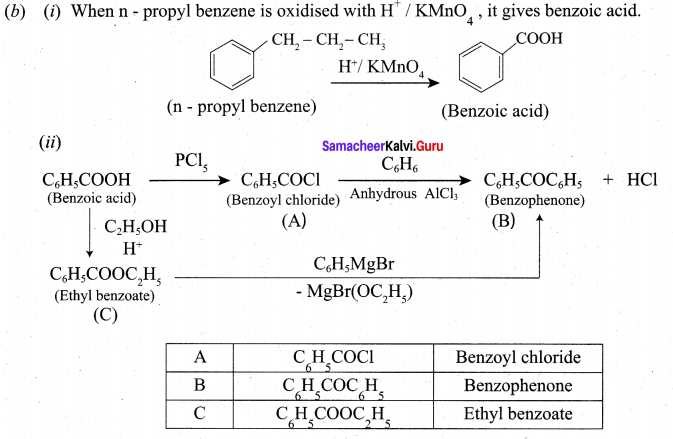
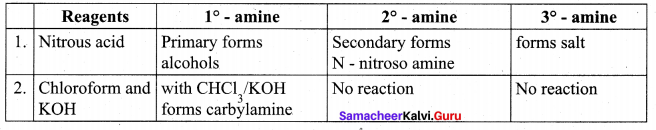

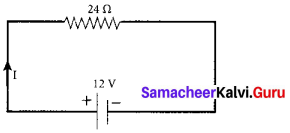
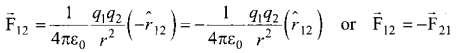
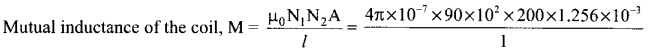
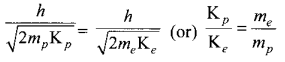
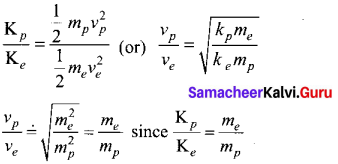


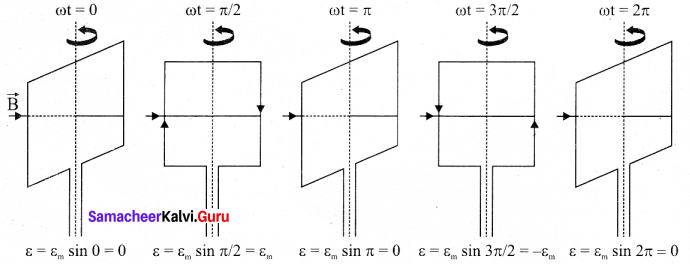
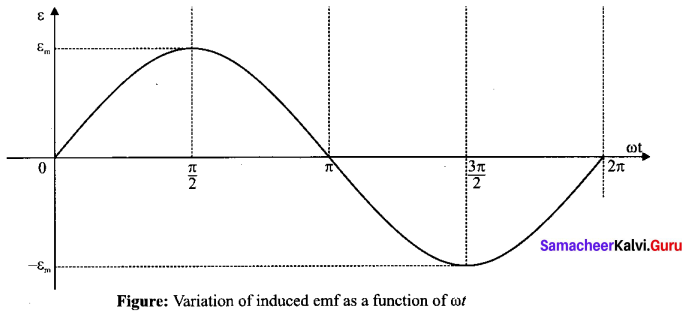
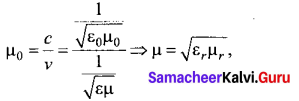
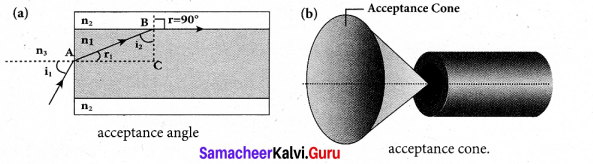
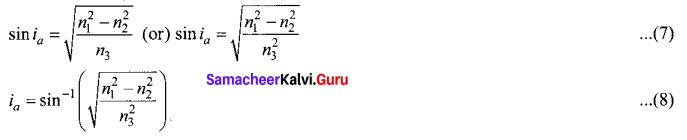

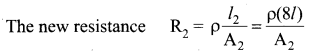
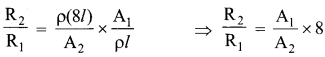
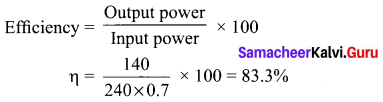
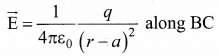



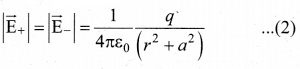
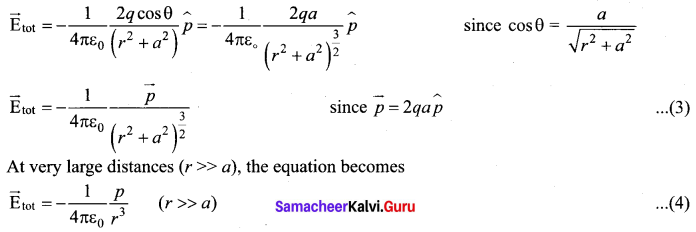
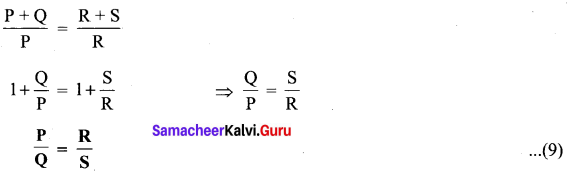
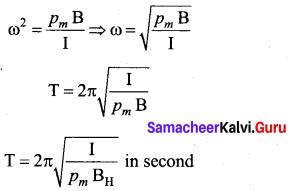
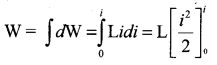
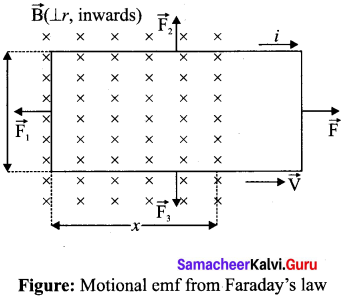
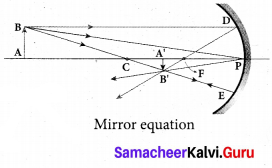

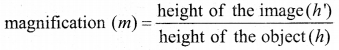
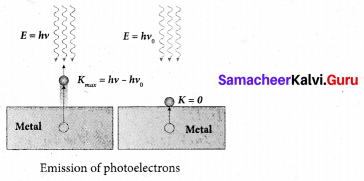
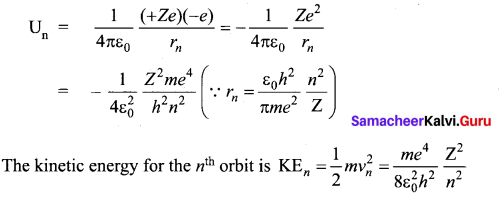
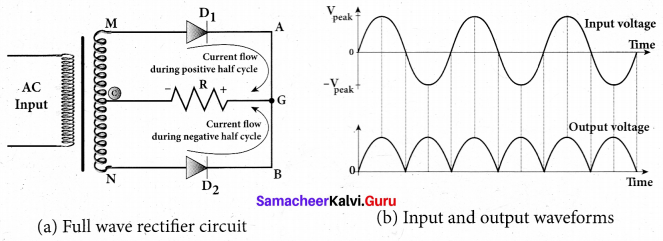





















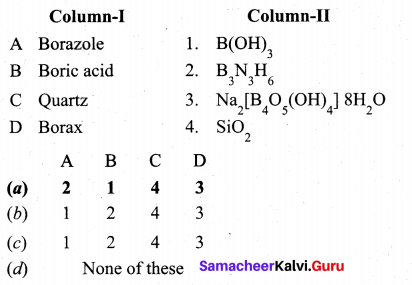
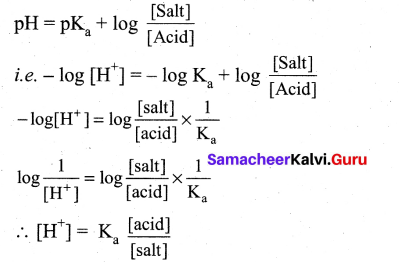
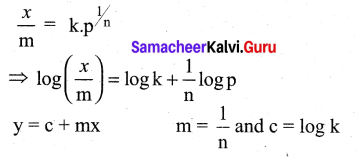
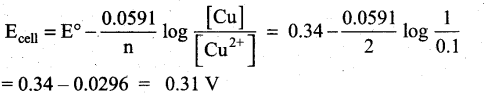
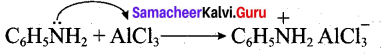
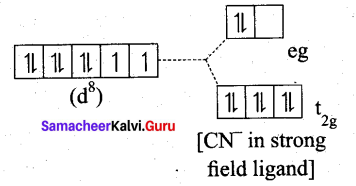
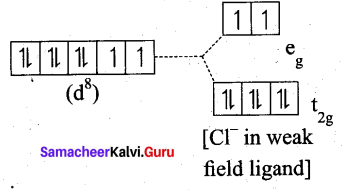
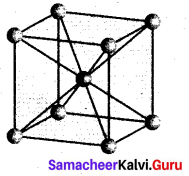
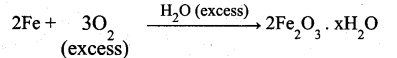
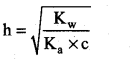
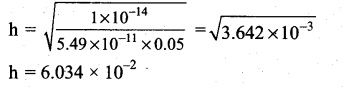
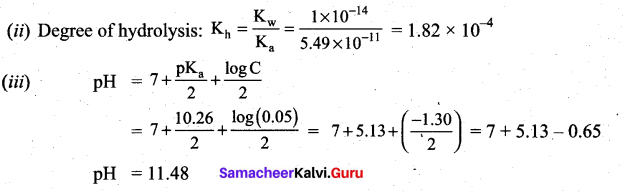
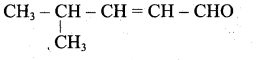
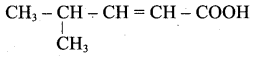
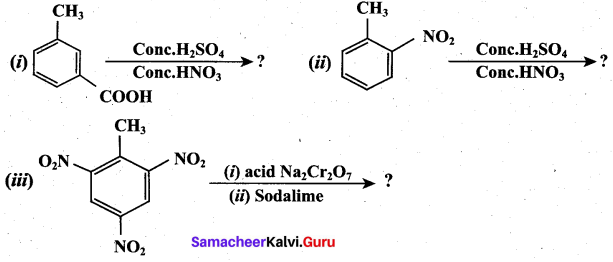
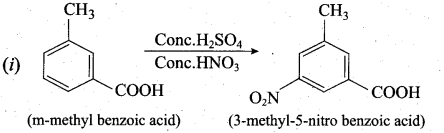
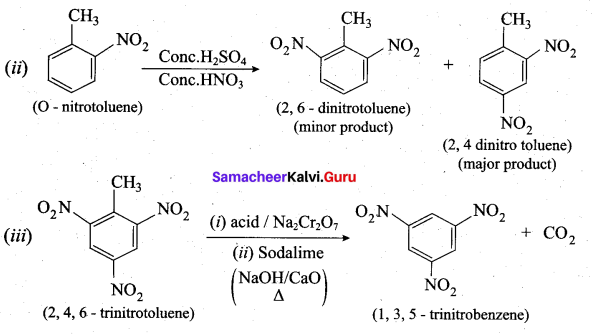
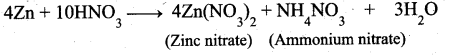
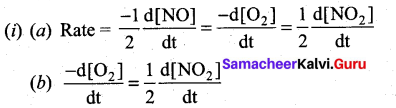
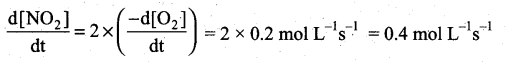
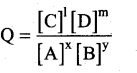
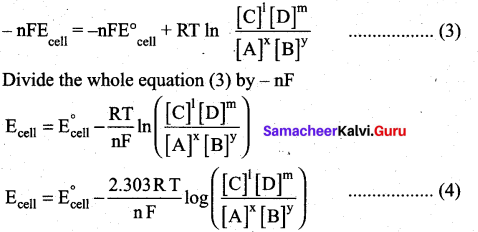
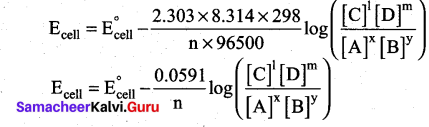
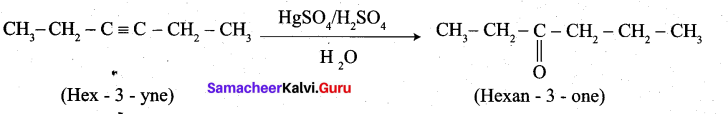
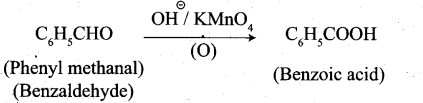
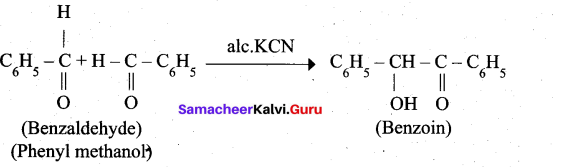
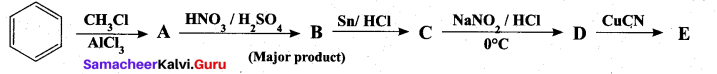
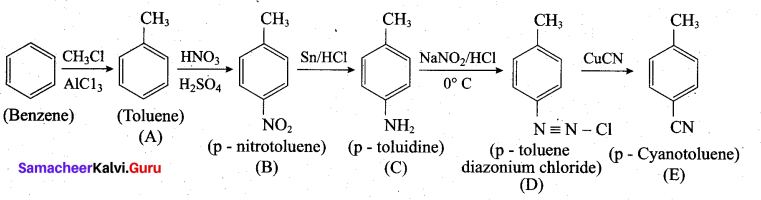
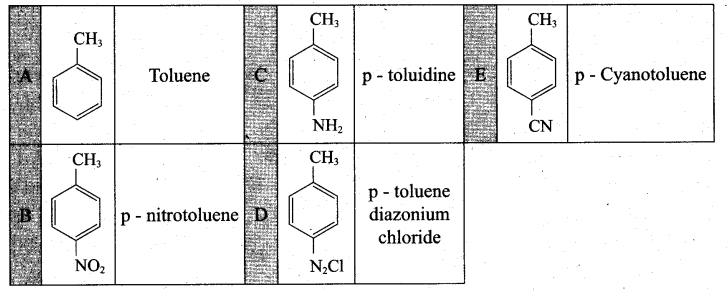




















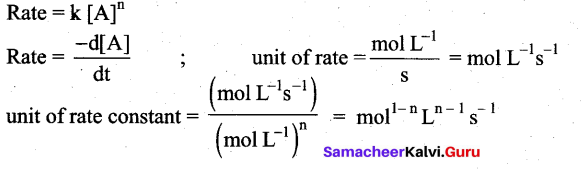
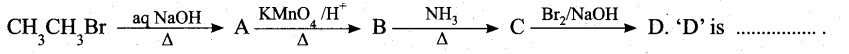
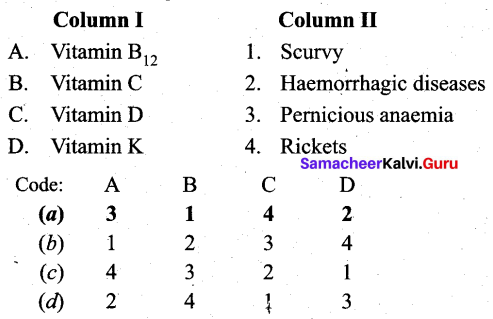
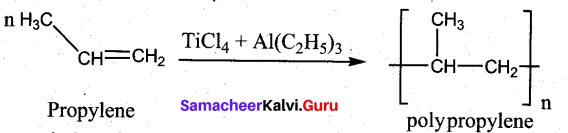
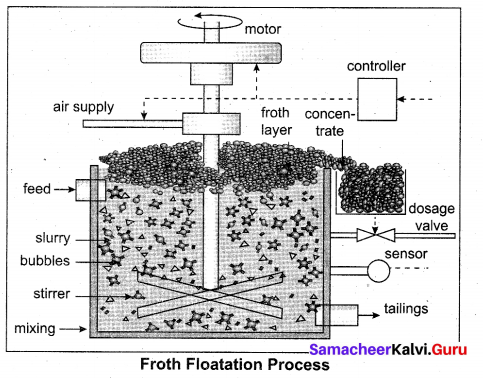
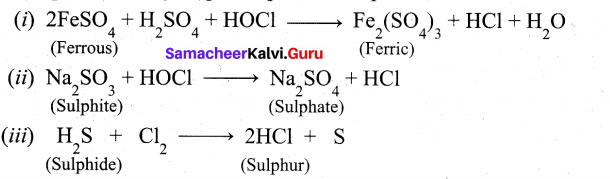
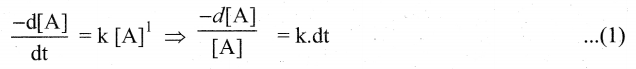
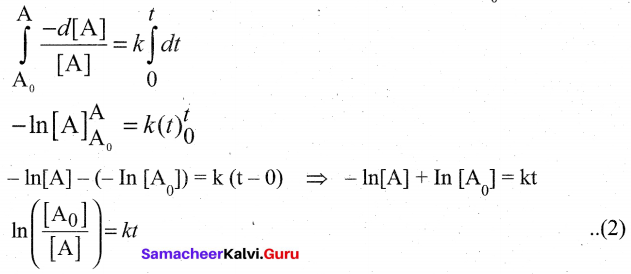
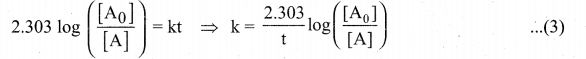
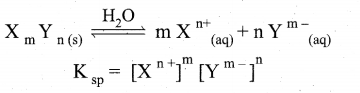
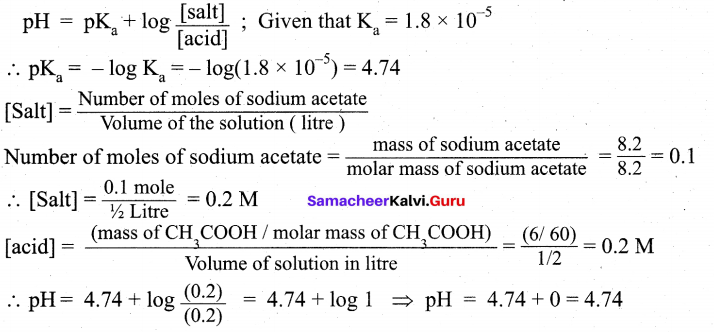
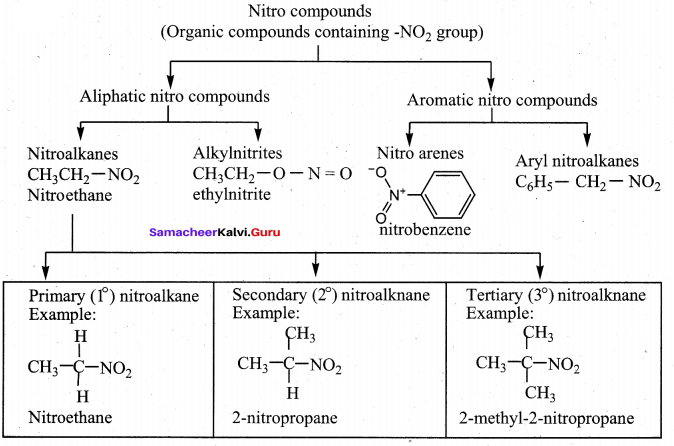
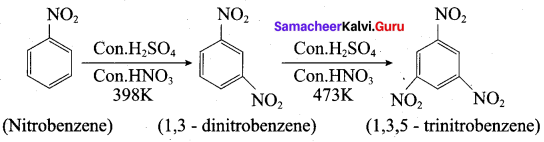
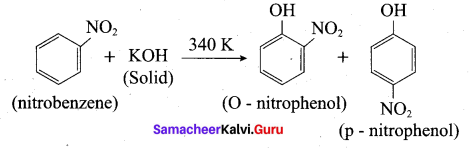


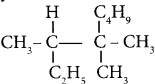 is ……….
is ……….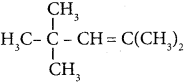 is ………
is ………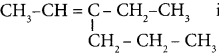 is ………
is ………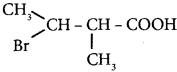 is ………
is ………
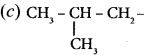
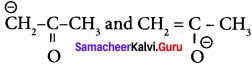 are ………
are ………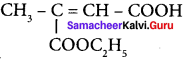 is 3-carbethoxy -2- butenoicacid.
is 3-carbethoxy -2- butenoicacid.


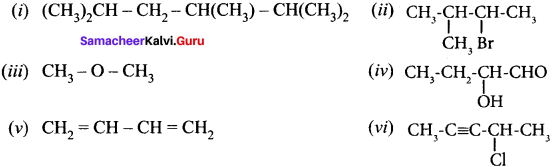



























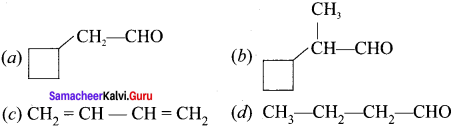




 ……..
……..








 is an example of ………
is an example of ……… is …….
is ……. is ……..
is ……..
 is …………
is ………… are called ……….
are called ……….
 name of this compound is ………..
name of this compound is ………..



 is an aromatic benzenoid compound.
is an aromatic benzenoid compound.