Students can Download Bio Botany Chapter 1 Living World Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 1 Living World
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Living World Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which one of the following statement about virus is correct?
(a) Possess their own metabolic system
(b) They are facultative parasites
(c) They contain DNA or RNA
(d) Enzymes are present
Answer:
(c) They contain DNA or RNA
Question 2.
Identify the incorrect statement about the Gram positive bacteria.
(a) Teichoic acid absent
(b) High percentage of peptidoglycan is found in cell wall
(c) Cell wall is single layered
(d) Lipopolysaccharide is present in cell wall
Answer:
(a) Teichoic acid absent

Question 3.
Identify the Archaebacterium.
(a) Acetobacter
(b) Erwinia
(c) Treponema
(d) Methanobacterium
Answer:
(d) Methanobacterium
Question 4.
The correct statement regarding Blue green algae is
(a) lack of motile structures
(b) presence of cellulose in cell wall
(c) absence of mucilage around the thallus
(d) presence of floridean starch
Answer:
(a) lack of motile structures
Question 5.
Identify the correctly matched pair
(a) Actinomycete – 1. Late blight
(b) Mycoplasma – 2. Lumpy jaw
(c) Bacteria – 3. Crown gall
(d) Fungi – 4. Sandal spike
Answer:
(c) Bacteria – 3. Crown gall

Question 6.
Differentiate Homoiomerous and Heteromerous lichens.
Answer:
Homoiomerous and Heteromerous Lichens:
| Homoiomerous |
Heteromerous |
| 1. Algal cells evenly distributed in the thallus |
1. A distinct layer of algae and fungi present |
Question 7.
Write the distinguishing features of Monera.
Answer:
Distinguishing Features of Monera:
- This kingdom includes all prokaryotic organisms. Example: Mycoplasma, bacteria, actinomycetes and cyanobacteria.
- These are microscopic. They do not have a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
- Many other bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter and Clostridium can fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
- Some bacteria are parasites and others live as symbionts.
Question 8.
Why do farmers plant leguminous crops in crop rotations/mixed cropping?
Answer:
Rotations / Mixed Cropping:
- Legumes have bacteria on nodules which are on the roots of the plants. The bacteria on the nodules takes nitrogen from the air and fixes it into the soil, so that other plants that require nitrogen can use it as well.
- Rotation of crops improves the fertility of the soil and hence brings about an increase in the production of food grains.
- Rotation of crops helps in saving on nitrogenous fertilizers, because leguminous plants grown during the rotation of crops can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil with the help of nitrogen fixing bacteria.
- Crop rotation adds diversity to an operation.

Question 9.
Briefly discuss on five kingdom classification. Add a note on merits and demerits.
Answer:
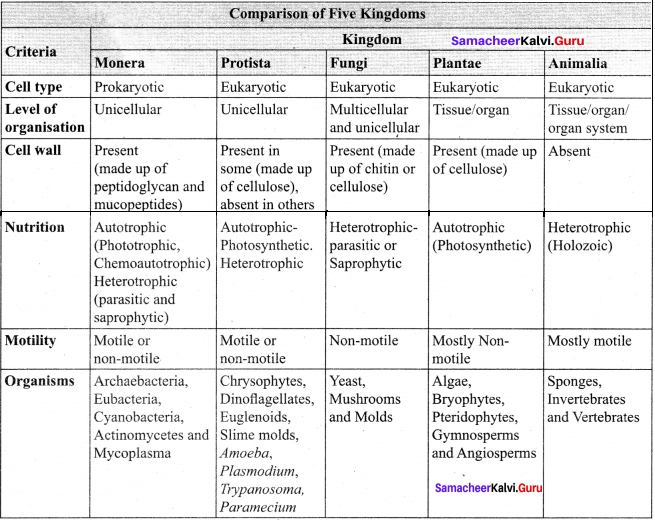
R.H. Whittaker, an American taxonomist proposed five kingdom classification in the year 1969. The kingdoms include Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. The criteria adopted for the classification include cell structure, thallus organization, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationship. A comparative account of the salient features of each kingdom is given in table.
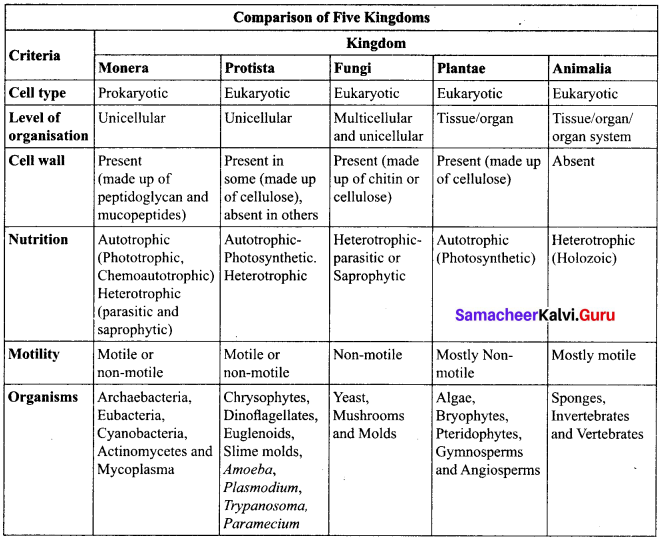
Merits:
- The classification is based on the complexity of cell structure and organization of thallus.
- It is based on the mode of nutrition.
- Separation of fungi from plants.
- It shows the phylogeny of the organisms
Demerits:
- The kingdom monera and protista accommodate both autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms, cell wall lacking and cell wall bearing organisms thus making these two groups more heterogeneous.
- Viruses were not included in the system.
Question 10.
Give a general account on lichens.
Answer:
The symbiotic association between algae and fungi is called lichens. The algal partner is called Phycobiont and the fungal partner is called Mycobiont. Algae provide nutrition for fungal partner and also help in fixing the thallus to the substratum through rhizinae. Asexual reproduction takes place through fragmentation, Soredia and Isidia. Phycobionst reproduce by akinetes, hormogonia, aplanospore, etc. Mycobionts undergo sexual reproduction and produce ascocarps.
Classification:
- Based on the habitat lichens are classified into following types: Corticolous (on bark) Lignicolous (on wood) Saxicolous (on rocks) Terricolous (on ground) Marine (on siliceous rocks of sea) and Fresh water (on siliceous rock of fresh water).
- On the basis of morphology of the thallus they are divided into Leprose (a distinct fungal layer is absent) Crustose – crust like; Foliose – leaf like; Fruticose – branched pendulous shrub like.
- The distribution of algal cells distinguishes lichens into two forms namely Homoiomerous (Algal cells evenly distributed in the thallus) and Fleteromerous (a distinct layer of algae and fungi present).
- If the fungal partner of lichen belongs to ascomycetes, it is called Ascolichen and if it is basidiomycetes it is called Basidiolichen.
Textbook Activity Solved
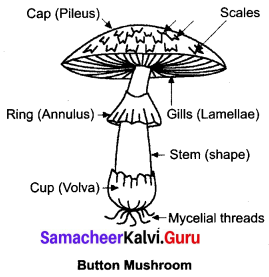
Get a button mushroom. Draw diagram of the fruit body. Take a thin longitudinal section passing through the gill and observe the section under a microscope. Record your observations.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Living World Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Earth was formed around billion years ago …………… .
(a) 3.3
(b) 5.6
(c) 4.6
(d) 5.9
Answer:
(c) 4.6

Question 2.
According to Mora et al., in 2011, the number of estimated species on Earth is …………… .
(a) 8.7 million
(b) 9.7 million
(c) 7.7 million
(d) 9.7 billion
Answer:
(a) 8.7 million
Question 3.
Which of the following is NOT a prokaryote?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Blue green algae
(c) Oedogonium
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(c) Oedogonium
Question 4.
Which of the following organism undergoes regeneration?
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Planaria
(c) Yeast
(d) Aspergillus
Answer:
(b) Planaria
Question 5.
Vaccination for small pox was discovered by …………… .
(a) W.M. Stanley
(b) Adolf Mayer
(c) Robert Koch
(d) Edward Jenner
Answer:
(d) Edward Jenner

Question 6.
Who coined the term ‘Bacteriophage’?
(a) F.W. Twort
(b) d’Herelle
(c) Ivanowsky
(d) Robert Gallo
Answer:
(b) d’Herelle
Question 7.
The size of TMV is …………… .
(a) 300 × 20 mm
(b) 300 × 200 µm
(c) 300 × 20 nm
(d) 300 × 20 Å
Answer:
(c) 300 × 20 nm
Question 8.
One nanometer equals to metres …………… .
(a) 10-9
(b) 10-6
(c) 10-5
(d) 10-12
Answer:
(a) 10-9
Question 9.
Which is a non – living character of viruses?
(a) Undergoes mutation
(b) Host – specific
(c) Crystallized
(d) Irritability
Answer:
(c) Crystallized

Question 10.
According to David Baltimore, the viruses are classified …………… into classes.
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 7
Question 11.
Identify the criteria not used in classifying viruses by Baltimore …………… .
(a) ss (or) ds
(b) use of RT
(c) capsid
(d) sense or antisense
Answer:
(c) capsid

Question 12.
Viruses with dsRNA is …………… .
(a) Toga viruses
(b) Retro viruses
(c) Reo viruses
(d) Rhabdo viruses
Answer:
(c) Reo viruses
Question 13.
Which of the plant virus contains DNA as genome?
(a) Tobacco mosaic virus
(b) Cauliflower mosaic virus
(c) Sugarcane mosaic virus
(d) Cucumber mosaic virus
Answer:
(b) Cauliflower mosaic virus
Question 14.
Parvo viruses have …………… .
(a) ssDNA
(b) dsDNA
(c) ssRNA
(d) dsRNA
Answer:
(a) ssDNA
Question 15.
Molecular weight of TMV is dalton …………… .
(a) 39 × 106
(b) 39 × 10-6
(c) 39 × 109
(d) 39 × 10-9
Answer:
(a) 39 × 106

Question 16.
Approximate number of capsomeres in TMV is …………… .
(a) 3120
(b) 1203
(c) 2130
(d) 3021
Answer:
(c) 2130
Question 17.
The empty protein coat left outside after penetration is …………… .
(a) host
(b) ghost
(c) capsid
(d) capsomeres
Answer:
(b) ghost
Question 18.
The genome of viroid is …………… .
(a) linear ssRNA
(b) dumb – bell shaped ssRNA
(c) circular ssRNA
(d) linear dsRNA
Answer:
(c) circular ssRNA
Question 19.
Viroids were discovered by …………… .
(a) Ivanowsky
(b) Robert Gallo
(c) Diener
(d) d’Herelle
Answer:
(c) Diener
Question 20.
Mad cow disease is caused by …………… .
(a) viroids
(b) virusoids
(c) prions
(d) viruses
Answer:
(c) prions

Question 21.
Match the Following:
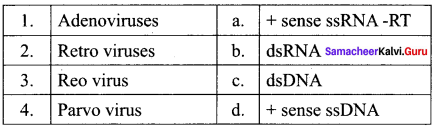
(a) 1- d, 2 – b, 3 – a, 4 – c
(b) 1 – c, 2 – d, 3 – a, 4 – b
(c) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – d
(d) 1 – d, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – c
Answer:
(c) 1- c, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – d
Question 22.
Identify the correct sequence regarding lytic cycle of viruses …………… .
(A) Penetration
(B) Adsorption
(C) Assembly
(D) Synthesis
(a) BADC
(b) CABD
(c) BDAC
(d) ADBC
Answer:
(a) BADC
Question 23.
Mycophages infect …………… .
(a) blue green algae
(b) bacteria
(c) fungi
(d) cyanobacteria
Answer:
(c) fungi
Question 24.
Rice tungro is caused by …………… .
(a) fungi
(b) bacteria
(c) mycoplasma
(d) viruses
Answer:
(d) viruses

Question 25.
Father of Botany …………… .
(a) Aristotle
(b) Theophrastus
(c) Lederberg
(d) Whittaker
Answer:
(b) Theophrastus
Question 26.
Three kingdom classification was proposed by …………… .
(a) Copeland
(b) Theophrastus
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Haeckel
Answer:
(d) Haeckel
Question 27.
Which Is not a part of five kindgom classification?
(a) Viruses
(b) Monera
(c) Protista
(d) Mycoplasma
Answer:
(a) Viruses

Question 28.
Six kingdom classification was proposed by …………… .
(a) Haeckel
(b) Copeland
(c) Woese
(d) Cavalier – Smith
Answer:
(d) Cavalier – Smith
Question 29.
Ruggerlo et al., in 2015 proposed …………… kingdom classification.
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 7
Question 30.
…………… is a new kingdom in seven kingdom classification.
(a) Eubactena
(b) Plantae
(c) Chromista
(d) Archaebacteria
Answer:
(c) Chromista
Question 31.
Actinomycetes comes under …………… kindgom.
(a) fungi
(b) chromista
(c) monera
(d) protista
Answer:
(c) monera
Question 32.
The sourness of curd is due to …………… .
(a) acetic acid
(b) galactic acid
(c) lactic acid
(d) lactone
Answer:
(c) lactic acid

Question 33.
Who is the founder of Modern Bacteriology …………… ?
(a) Aristotle
(b) Robert Koch
(c) Pasteur
(d) Linnaeus
Answer:
(b) Robert Koch
Question 34.
The term bacterium was coined by …………… .
(a) Stanley
(b) Ehrenberg
(c) Gram
(d) Koch
Answer:
(b) Ehrenberg
Question 35.
Plasmids were discovered by …………… .
(a) Ehrenberg
(b) H.Bergy
(c) Joshua Lederberg
(d) Koch
Answer:
(c) Joshua Lederberg
Question 36.
Genophore is seen in …………… .
(a) Amoeba
(b) Cyanobacteria
(c) Chlamydomonas
(d) Euglena
Answer:
(b) Cyanobacteria
Question 37.
Number of domains of life are there according to Carl Woese …………… .
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 3

Question 38.
Which is not a component of bacterial cell?
(a) Mesosomes
(b) Glycocalyx
(c) Polysomes
(d) Histones
Answer:
(d) Histones
Question 39.
The most abundant polypeptide in bacterial cell wall is …………… .
(a) chitin
(b) amylopectin
(c) porin
(d) pectin
Answer:
(c) porin
Question 40.
Extra chromosomal element in bacterial cells are …………… .
(a) plasmids
(b) mesosomes
(c) histones
(d) genophores
Answer:
(a) plasmids
Question 41.
Bacteriocins are found in …………… .
(a) genophore
(b) plasmids
(c) nucleoids
(d) mesosomes
Answer:
(b) plasmids
Question 42.
Colour revealed by Gram positive bacteria after Gram staining is …………… .
(a) red
(b) indigo
(c) dark violet
(d) blue
Answer:
(c) dark violet

Question 43.
How many number of basal body rings seen in the flagella of Gram negative bacteria?
(a) 2
(b) 9
(c) 4
(d) 1
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 44.
Capnophilic bacteria require for growth …………… .
(a) C2
(b) CO
(c) CO2
(d) O3
Answer:
(c) CO2

Question 45.
The pigment present in green sulphur bacteria is …………… .
(a) bacterioviridin
(b) bacteriochlorophyll
(c) chlorophyll a
(d) xanthophyll
Answer:
(b) bacteriochlorophyll
Question 46.
The hydrogen donor of purple sulphur bacteria is …………… .
(a) H2S
(b) thiosulphate
(c) ethanol
(d) acetic acid
Answer:
(b) thiosulphate
Question 47.
Campylobacter is a …………… .
(a) obligate aerobe
(b) obligate anaerobe
(c) capnophilic
(d) aerobe
Answer:
(c) capnophilic

Question 48.
Mycobacterium is a …………… .
(a) parasite
(b) symbiont
(c) saprophyte
(d) free – living
Answer:
(a) parasite
Question 49.
Which is the most common mode of asexual reproduction in bacteria?
(a) Endospore formation
(b) Fission
(c) Budding
(d) Conidia
Answer:
(b) Fission

Question 50.
…………… are thick walled resting spores.
(a) Aplanospores
(b) Endospores
(c) Conidia
(d) Zoospores
Answer:
(b) Endospores
Question 51.
In which of the following method genetic recombination does not occur?
(a) Generalised transduction
(b) Conjugation
(c) Transformation
(d) Fission
Answer:
(d) Fission
Question 52.
During conjugation in bacteria, which of the following is transferred from donor to recipient cell?
(a) R factor
(b) F factor
(c) Ti factor
(d) Ri factor
Answer:
(b) F factor

Question 53.
Griffith used …………… for his experiment.
(a) rat
(b) rabbit
(c) mice
(d) monkey
Answer:
(c) mice
Question 54.
Transformation in bacteria was demonstrated by …………… .
(a) Lederberg
(b) Zinder
(c) Edward
(d) Griffith
Answer:
(d) Griffith
Question 55.
Lederberg studied transduction in bacterium …………… .
(a) Diplococcus pneumoniae
(b) Streptococcus
(c) Salmonella typhi
(d) Escherichia coil
Answer:
(c) Salmonella typhi
Question 56.
Bacteria used in the curing of tea is …………… .
(a) Mycococcus candisans
(b) Eseherichia coli
(c) Acetobacter aceti
(d) Streptococcus lactis
Answer:
(a) Mycococcus candisans

Question 57.
Syphilis k caused by …………… .
(a) Mycococcus candisans
(b) Treponema pallidum
(c) Yersinia pestis
(d) Mycohacterium leprae
Answer:
(b) Treponema pallidum
Question 58.
Methanobacterium is …………… .
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Malobacteria
(c) Eubacteria
(d) Archaebacteria
Answer:
(d) Archaebacteria
Question 59.
…………… is NOT a phycobiont in lichens.
(a) Gloeocapsa
(b) Dermacarpa
(c) Scytonema
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(b) Dermacarpa
Question 60.
Red sea is red colour due to …………… .
(a) Dermacarpa sps.
(b) Trichodesmium sps.
(c) Scytonema sps.
(d) Gloeocapsa sps.
Answer:
(b) Trichodesmium sps.
Question 61.
Filamentous trichome is the plant body of …………… .
(a) Chroococcus
(b) Gloeocapsa
(c) Nostoc
(d) Oscillatoria
Answer:
(c) Nostoc
Question 62.
Stromatolites are the colonies of cyanobacteria bind with …………… .
(a) calcium carbonate
(b) calcium hydroxide
(c) magnesium sulphate
(d) calcium silicate
Answer:
(a) calcium carbonate

Question 63.
…………… sps. is an endophyte in coralloid roots of Cycas.
(a) Gioeocapsa
(b) Scytonerna
(c) Nostoc
(d) Azolla
Answer:
(c) Nosloc
Question 64.
Myxophyceae refers to …………… .
(a) Algae
(b) Fungi
(c) Archaebacteria
(d) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
(d) Cyanobacteria
Question 65.
…………… is used in single cell protein.
(a) Spirulina
(b) Azolla
(c) Dermacarpa
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(a) Spirulina
Question 66.
…………… is a pleomorphic organism.
(a) Fungi
(b) Mycoplasma
(c) Bacteria
(d) Algae
Answer:
(b) Mycoplasma
Question 67.
Pleuropneumonia is caused by …………… .
(a) bacteria
(b) fungi
(c) mycoplasma
(d) viruses
Answer:
(c) mycoplasma

Question 68.
…………… is also called as Ray fungi.
(a) Basidiomycetes
(b) Ascomycetes
(c) Actinomycetes
(d) Deuteromycetes
Answer:
(c) Actinomycetes
Question 69.
Earthy odour of soil after rain is due to …………… .
(a) Basidiomycetes
(b) Ascomycetes
(c) Actinomycetes
(d) Deuteromycetes
Answer:
(c) Actinomycetes
Question 70.
Viruses that attack blue green algae are called as …………… .
(a) Mycophages
(b) Phycophages
(c) Cyanophages
(d) Bacteriophages
Answer:
(c) Cyanophages
Question 71.
Cell membrane of Archaebacteria has …………… .
(a) glycine and isopropyl ethers
(b) glycerol and isobutyl ethers
(c) glycerol and isopropyl ethers
(d) cellulose and isobutyl ethers
Answer:
(c) glycerol and isopropyl ethers
Question 72.
Which is a true bacteria?
(a) Halobacterium
(b) Thermoplasma
(c) Methanobacteriurn
(d) Azotobacter
Answer:
(d) Azolobacter
Question 73.
Study of fungus is called as …………… .
(a) phycology
(b) mycology
(c) algology
(d) biology
Answer:
(b) mycology
Question 74.
Who is considered as the founder of mycology?
(a) K.C.Mehta
(b) G.C.Ainsworth
(c) P.A.Micheli
(d) T.S.Sadasivan
Answer:
(c) P.A.Micheli
Question 75.
Asexual phase of fungi is called as …………… .
(a) telomorph
(b) holomorph
(c) metamorph
(d) anamorph
Answer:
(d) anamorph
Question 76.
In which mycelium, the hyphae are arranged loosely?
(a) Prosenchyma
(b) Plectenchyma
(c) Pseudoparenchyrna
(d) Arenchyma
Answer:
(a) Prosenchyma

Question 77.
Number of nuclei in coenocytic mycelium …………… .
(a) 2
(b) many
(c) nil
(d) 9
Answer:
(b) many
Question 78.
Thallospores are produced by …………… .
(a) Aspergillus
(b) Erysiphe
(c) Saccharomyces
(d) Fusarium
Answer:
(b) Erysiphe
Question 79.
In Agaricus, …………… type of sexual reproduction occurs.
(a) spermatization
(b) somatogamy
(c) oogamy
(d) isogamy
Answer:
(b) somatogamy
Question 80.
Albugo belongs to …………… .
(a) oomycetcs
(b) zygomycetes
(c) ascomycetes
(d) deuteromycetes
Answer:
(a) oomycetes

Question 81.
Fungi growing on dung is called as …………… .
(a) Mold fungus
(b) Saprophytes
(c) Capnophilous
(d) Coprophilous
Answer:
(d) Coprophilous
Question 82.
Coprophilous belongs to …………… group.
(a) basidiomycetes
(b) ascomycetes
(c) zygomycetes
(d) oomycetes
Answer:
(c) zygomycetes
Question 83.
Which of the following is a coprophilous fungi?
(a) Albugo
(b) Entomophthora
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Pilobolus
Answer:
(d) Pilobolus
Question 84.
Cup fungus belongs to …………… .
(a) zygomycetes
(b) oomycetes
(c) ascomycetes
(d) actinomycetes
Answer:
(c) ascomycetes
Question 85.
Which group of fungus is called as Sac fungi?
(a) Deuteromycetes
(b) Zygomycetes
(c) Ascomycetes
(d) Oomycetes
Answer:
(c) Ascomycetes
Question 86.
Number of ascospores in an asci is …………… .
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer:
(d) 8

Question 87.
Shape of perithecium is …………… .
(a) cup shaped
(b) flask shaped
(c) completely closed
(d) open type
Answer:
(b) flask shaped
Question 88.
…………… are called as Club fungi.
(a) Ascomycetes
(b) Zygomycetes
(c) Basidiomycetes
(d) Deuteromycetes
Answer:
(c) Basidiomycetes
Question 89.
Parasexual cycle is observed in …………… .
(a) basidiomycetes
(b) zygomycetes
(c) deuteromycetes
(d) ascomycetes
Answer:
(c) deuteromycetes
Question 90.
Which is called as imperfect fungi?
(a) Basidiomycetes
(b) Zygomycetes
(c) Deuteromycetes
(d) Ascomycetes
Answer:
(c) Deuteromycetes
Question 91.
In basidiomycetes, clamp connections are formed to maintain …………… condition.
(a) monokaryotic
(b) coenocytic
(c) dikaryotic
(d) zygotic
Answer:
(c) dikaryotic

Question 92.
…………… is a single celled fungus used in dairy industry.
(a) Volvariella
(b) Agaricus
(c) Penicillin
(d) Yeast
Answer:
(d) Yeast
Question 93.
Ergot alkaloids are produced by …………… .
(a) Penicillium notatum
(b) Acremonium chrysogenum
(c) Claviceps purpurea
(d) Penicillium griseofulvum
Answer:
(c) Claviceps purpurea
Question 94.
Kojic acid is produced by …………… .
(a) Aspergillus terreus
(b) Aspergillus niger
(c) Aspeigillus oryzae
(d) Agaricus hisporus
Answer:
(c) Aspergillus oryzae
Question 95.
…………… infest dried foods and produce carcinogenic toxin.
(a) Aspergillus flavus
(b) Amanita verna
(c) Amanita phalloides
(d) Rhizopus
Answer:
(a) Aspergillus flavus
Question 96.
Rust of wheat is produced by …………… .
(a) Albugo candida
(b) Puccinia graminis tritici
(c) Candida albicans
(d) Colletotrichum sps
Answer:
(b) Puccinia graminis tritici
Question 97.
VAM is a type of …………… .
(a) Endomycorrhiza
(b) Ectomycorrhiza
(c) Ectendomycorrhiza
(d) Endectomycorrhiza
Answer:
(a) Endomycorrhiza

Question 98.
Algal partner of lichen is …………… .
(a) phycobiont
(b) phytobiont
(c) mycobiont
(d) both (a) & (c)
Answer:
(a) phycobiont
Question 99.
Asexual reproduction by Soredia is seen in …………… .
(a) fungi
(b) lichen
(c) mycorrhiza
(d) algae
Answer:
(b) lichen
Question 100.
Saxicolous lichen grow on …………… .
(a) ground
(b) bark
(c) wood
(d) rock
Answer:
(d) rock

Question 101.
In leprose form of lichen distinct …………… layer is absent.
(a) fungal
(b) algal
(c) both
(d) none
Answer:
(a) fungal
Question 102.
…………… are used as pollution indicators.
(a) Algae
(b) Lichen
(c) Fungi
(d) Mycorrhiza
Answer:
(b) Lichen
Question 103.
…………… acid is obtained from lichen acting as antibiotics.
(a) Alginic
(b) Acetic
(c) Oxalic
(d) Usnic
Answer:
(d) Usnic.
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate plant growth from animal growth.
Answer:
Plant Growth From Animal Growth:
| S. No. |
Plant growth |
Animal growth |
| 1. |
1. Growth is indefinite. |
1. Growth is definite. |
| 2. |
2. It occurs throughout life. |
2. It occurs for some period. |
Question 2.
Define Growth.
Answer:
Growth is an intrinsic property of all living organisms through which they can increase cells both in number and mass.

Question 3.
Growth of living thing is an intrinsic property – Justify.
Answer:
Living cells grow by the addition of new protoplasm within the cells. Therefore, growth in living thing is intrinsic.
Question 4.
Define reproduction and Mention its types.
Answer:
Reproduction is the tendency of a living organism to perpetuate its own species. There are two types of reproduction namely asexual and sexual.
Question 5.
What is metabolism? Mention its types.
Answer:
The sum total of all the chemical reactions taking place in a cell of living organism is called metabolism. It is broadly divided into anabolism and catabolism.

Question 6.
What is consciousness and irritability?
Answer:
Animals sense their surroundings by sense organs. This is called consciousness. Respond of plants to the stimuli is called irritability.
Question 7.
List out few attributes of living organisms.
Answer:
The attributes of living organisms are growth, metabolism, movement, reproduction, nutrition, excretion, etc.
Question 8.
Define cyclosis.
Answer:
The movement of cytoplasm inside the cell is called cytoplasmic streaming or cyclosis.

Question 9.
How will you define viruses?
Answer:
Viruses are sub – microscopic, obligate intracellular parasites. They have nucleic acid core surrounded by protein coat.
Question 10.
Mention the size of Bacteriophage and tobacco mosaic virus (TMV).
Answer:
Bacteriophage measures about 10 – 100 nm in size. The size of TMV is 300 × 20 nm.
Question 11.
Classify viruses based on nature of nucleic acid with example.
Answer:
On the basis of nature of nucleic acid viruses are classified into four categories. They are viruses with ssDNA (Parvo viruses), dsDNA (Bacteriophages), ssRNA (TMV) and dsRNA (wound tumour virus).
Question 12.
Distinguish between deoxyviruses and riboviruses.
Answer:
Deoxyviruses and Riboviruses:
- Deoxyviruses: Viruses having DNA are called deoxyviruses. E.g. Animal viruses except HIV
- Riboviruses: Viruses having RNA are called riboviruses. E.g. Plant viruses except cauliflower mosaic virus (CMV)

Question 13.
Write the constituents of virions.
Answer:
The virion is made up of two constituents, a protein coat called capsid and a core called nucleic acid.
Question 14.
What are capsomeres?
Answer:
The protein coat of viruses is made up of approximately 2130 identical protein subunits called capsomeres.
Question 15.
Name the two types of phage multiplication.
Answer:
Phages multiply through two different types of life cycle:
- Lytic or Virulent cycle
- Lysogenic or Avirulent life cycle
Question 16.
What do you mean by a ‘ghost’ in virology?
Answer:
The empty protein coat left outside by the phage after penetrating the host cell is called as ghost.
Question 17.
What do you understand by “pinning” of phage?
Answer:
Once the contact is established between tail fibres of phase and bacterial cell, tail fibres bend to anchor the pins and base plate to the cell surface. This step is called pinning.

Question 18.
What is prophage?
Answer:
As soon as the phage injects its linear DNA into the host cell, it becomes circular and integrates into the bacterial chromosome by recombination. The integrated phage DNA is now called prophage.
Question 19.
When does a prophage enters lytic cycle?
Answer:
On exposure to UV radiation and chemicals the excision of phage DNA may occur and results in lytic cycle.
Question 20.
Define virion?
Answer:
Virion is an intact infective virus particle which is non – replicating outside a host cell.
Question 21.
What are viroids?
Answer:
Viroid is a circular molecule of ssRNA without a capsid. RNA is of low molecular weight.
Question 22.
Name any two disease caused by viroids.
Answer:
Two Disease:
- Citrus exocortis
- Potato spindle tuber disease
Question 23.
What are virusoids?
Answer:
Virusoids are the small circular RNAs which are similar to viroids but they are always linked with larger molecules of the viral RNA.

Question 24.
Who discovered viroids and virusolds?
Answer:
Viroids were discovered by T.O. Diener in 1971. Virusoids were discovered by J.W.Randles in 1981.
Question 25.
Name the causative organism for mad cow disease.
Answer:
Prions are the causative organisms for mad cow disease, Prions are the proteinaceous infectious particles.
Question 26.
What are cyanophages? Who reported it first?
Answer:
Viruses infecting blue green algae are called Cyanophages and are first reported by Safferman and Morris in the year 1963.
Question 27.
Name any two disease caused by Prions.
Answer:
Two Disease:
- Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) (mad cow disease)
- Creutzfeldt – Jakob Disease (CJD)
Question 28.
What are mycophages? Who first reported it?
Answer:
Viruses infecting fungi are called mycophages or mycoviruses. Mycophages were first reported by Hollings in 1962.

Question 29.
Expand the following acronyms: (a) SARS and (b) AIDS.
Answer:
Acronyms:
(a) SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
(b) AIDS: Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Question 30.
Name the two groups of aninmals according to Aristotle.
Answer:
Two Groups of Aninmals:
- Enaima – animals with red blood.
- Anaima – animals without red blood.
Question 31.
Which are the major setbacks of Linnaeus classification?
Answer:
Linnaeus classification faced major setback because prokaryotes and eukaryotes were grouped together. Similarly fungi, heterotrophic organisms were placed along with the photosynthetic plants.

Question 32.
Name the viruses which are employed as potential insecticides?
Answer:
Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis Granulo viruses and Entomopox virus were employed as potential insecticides.
Question 33.
Who proposed five kingdom classification? Mention the five kingdoms.
Answer:
R.H. Whittaker proposed the five kingdom classification. It includes Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
Question 34.
List out the criteria undertaken for Whittaker’s classification.
Answer:
The criteria adopted for the classification include cell structure, thallus organization, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationship.

Question 35.
Point out the demerits of five kingdom classification.
Answer:
(a) The kingdom Monera and Protista accommodate both autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms, cell wall lacking and cell wall bearing organisms thus making these two groups more heterogeneous.
(b) Viruses were not included in the system.
Question 36.
Who proposed six kingdom classification? Mention the kingdoms.
Answer:
Thomas Cavalier – Smith proposed six kingdom classification.
The kingdom includes:
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae and
- Animalia.
Question 37.
How milk is changed into curd, if a few drops of curd is added to it? What is the reason for its sourness?
Answer:
The change is brought by Lactobacillus lactis, a bacterium present in the curd. The sourness is due to the formation of lactic acid.
Question 38.
Define bacteria and bacteriology.
Answer:
Bacteria are prokaryotic, unicellular, ubiquitous, microscopic organisms. The study of bacteria is called bacteriology.

Question 39.
What is Porin? How it helps the bacteria?
Answer:
Porin is an abundant polypeptide present in bacterial cell walls. It helps in the diffusion of solutes.
Question 40.
List out the cytoplasmic inclusions of bacterial cell.
Answer:
Glycogen, poly-β-hydroxybutyrate granules, sulphur granules and gas vesicles.
Question 41.
Define Genophore.
Answer:
The bacterial chromosome is a single circular DNA molecule, tightly coiled and is not enclosed in a membrane as in Eukaryotes. This genetic material is called nucleoid or genophore.
Question 42.
Write the chemical composition of bacterial cell wall.
Answer:
The chemical composition of cell wall is rather complex and is made up of peptidoglycan or mucopeptide (N – acetyl glucosamine, N – acetyl muramic acid and peptide chain of 4 or 5 aminoacids).
Question 43.
What are polysomes?
Answer:
During protein synthesis, the ribosomes are held together by mRNA and form the polysomes.

Question 44.
What are Pili?
Answer:
Pili or fimbriae are hair like appendages found on surface of cell wall of gram – negative bacteria.
Question 45.
What are capnophilic bacteria? Give an example.
Answer:
Bacteria which require CO2 for their growth are called as capnophilic bacteria.
Example: Campylobacter.
Question 46.
Distinguish between Photolithotrophs and Photoorganotrophs.
Answer:
Between Photolithotrophs and Photoorganotrophs:
- Photolithotrophs: In photolithotrophs, the hydrogen donor is an inorganic substance. E.g. Chlorobium
- Photoorganotrophs: In Photoorganotrophs, the hydrogen donor is an organic acid or alcohol. E.g. Rhodospirillum
Question 47.
Name the hydrogen donor of green sulphur bacteria and purple sulphur bacteria.
Answer:
Hydrogen donor of green sulphur bacteria is H2S. Hydrogen donor of purple sulphur bacteria is thiosulphate.
Question 48.
Name the bacterial pigment of green sulphur bacteria and purple sulphur bacteria.
Answer:
Bacteria’s:
- Green sulphur bacteria – Bacterioviridin
- Purple sulphur bacteria – Bacteriochlorophyll
Question 49.
What are endospores?
Answer:
Endospores are thick walled resting spores developed by bacteria during unfavourable condition.
E.g. Clostridium tetani produces endospores.

Question 50.
Mention the various ways by which genetic recombination occurs.
Answer:
Genetic recombination in bacteria occurs by conjugation, transduction and transformation.
Question 51.
Name the eminent persons who demonstrated the conjugation process.
Answer:
J. Lederberg and Edward L. Tatum.
Question 52.
What is transformation? Name the bacteriologist who described it.
Answer:
The Bacteriologist Who Described it:
- Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another is called transformation.
- Fredrick Griffith demonstrated the transformation process.
Question 53.
Which organism and bacterial species was used in Griffith’s transformation experiment?
Answer:
Mice and Diplococcus pneumoniae.
Question 54.
List out the asexual modes of reproduction of bacteria.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction in bacteria includes binary fission, conidia formation and endospore formation.
Question 55.
Who discovered transduction? Define it.
Answer:
Zinder and Lederberg (1952) discovered transduction in Salmonella typhimurum. Phage mediated DNA transfer is called transduction.
Question 56.
Name any two bacterial species and the antibiotic produced by them.
Answer:
| Bacteria |
Antibiotic |
| 1. Streptomyces griseus |
1. Streptomycin |
| 2. Bacillus polymyxa |
2. Polymyxin |
Question 57.
How bacteria helps in vinegar production?
Answer:
Acetobacter aceti bacteria oxidises ethanol obtained from molasses by fermentation to form vinegar.

Question 58.
Name any two ammonifying bacteria.
Answer:
Two Ammonifying Bacteria:
- Bacillus ramosus and
- Bacillus mycoides.
Question 59.
What do you mean by retting of fibres?
Answer:
The fibres from the fibre yielding plants are separated by the action of Closiridium is called retting of fibres.
Question 60.
Name any two plant disease caused by the bacteria and mention the host.
Answer:

Question 61.
Name any four animal disease caused by bacteria.
Answer:
Four Animal Disease:
- Anthrax
- Brucellosis
- Bovine tuberculosis and
- black leg.
Question 62.
Name any four human disease caused by bacteria.
Answer:
Four Human Disease:
- Cholera
- Typhoid
- Tuberculosis and
- Leprosy.
Question 63.
What are Archaebacteria?
Answer:
Archaebacteria are primitive prokaryotes and are adapted to thrive in extreme environments like hot springs, high salinity and low pH.
E.g., Thermoplasma.

Question 64.
How stromatolites are formed?
Answer:
Stromatolites are deposits formed when colonies of cyanobacteria bind with calcium carbonate.
Question 65.
What is the reason for the colour of Red Sea?
Answer:
A cyanobacteria called Trichodesmium erythraeum imparts red colour to sea.
Question 66.
Mention the cyanobacteria leading endophytic relation with Cycas roots.
Answer:
Nostoc and Anabaena.
Question 67.
Define Cyanobacteria.
Answer:
Cyanobacteria are popularly called as ‘Blue green algae’ or ‘Cyanophyceae’. They are photosynthetic, prokaryotic organisms. Cyanobacteria are primitive forms and are found in different habitats.
Question 68.
Blue green algae can also be called as Myxophyceae. How?
Answer:
The presence of mucilage around the thallus is characteristic feature of cyanobacteria group. Therefore, this group is also called Myxophyceae.
Question 69.
Define mycoplasma?
Answer:
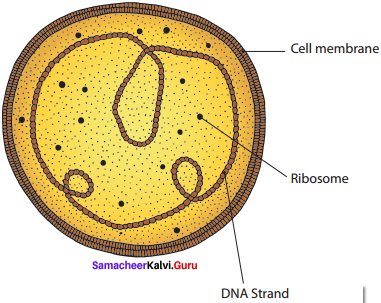
The mycoplasma are very small (0.1 – 0.5 μm), pleomorphic gram negative microorganisms.

Question 70.
Name few plant disease caused by mycoplasma.
Answer:
Little leaf of brinjal, witches broom of legumes, phyllody of cloves and sandal spike are some plant diseases caused by mycoplasma.
Question 71.
Draw and label the structure of mycoplasma.
Answer:
The Structure of Mycoplasma:
Question 72.
What is the reason behind the earthy odour after raining?
Answer:
Streptomyces is a mycelial forming Actinobacteria which lives in soil, they impart “earthy odour” to soil after rain which is due to the presence of geosmines (volatile organic compound).
Question 73.
When and by whom the penicillin was discovered?
Answer:
Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Flemming in 1928.
Question 74.
Define Fungi.
Answer:
Fungi are ubiquitous, eukaryotic, achlorophyllous heterotrophic organisms. They exist in unicellular or multicellular forms.
Question 75.
Define mycology. Who is the founder of mycology?
Answer:
Study of fungi is called mycology. P.A. Micheli is considered as the founder of mycology.

Question 76.
Name few eminent Mycologists.
Answer:
John Webster, G.C. Ainsworth, T.S. Sadasivan and C.V. Subramanian.
Question 77.
With example define coenocytic mycelium.
Answer:
In lower fungi the hypha is aseptate, multinucleate and is known as coenocytic mycelium (Example: Albugo).
Question 78.
What is plectenchyma? Mention its types.
Answer:
The mycelium is organised into loosely or compactly interwoven fungal tissues called plectenchyma. It is further divided into two types: prosenchyma and pseudoparenchyma.
Question 79.
Distinguish between Anamorph and Telomorph.
Answer:
Between Anamorph and Telomorph:
| Anamorph |
Telomorph |
| The asexual phase of fungi is called anamorph. |
The sexual phase of fungi is called telomorph. |
Question 80.
What is holomorph?
Answer:
Fungi showing both sexual and asexual phases are called holomorph.

Question 81.
What is planogametic copulation? Mention its types.
Answer:
Fusion of motile gamete is called planogametic copulation.
Types:
- Isogamy
- Anisogamy and
- Oogamy.
Question 82.
List out the asexual spores produced by fungus.
Answer:
Zoospores, conidia, oidia and chlamydospores.
Question 83.
What are coprophilous fungi? Give an example.
Answer:
Fungi growing on dung are called coprophilous fungi.
Example: Pilobolus.

Question 84.
Ascomycetes are called sac fungi. Give reason.
Answer:
In ascomycetes the ascospores are found inside a bag like structure called ascus. Due to the presence of ascus, this group is popularly called “Sac fungi”.
Question 85.
Name the four types of ascocarps produced by ascomycetes.
Answer:
Four Types Of Ascocarps Produced By Ascomycetes:
- Cleistothecium
- Perithecium
- Apothecium and
- Pseudothecium.
Question 86.
Basidiomycetes are called club fungi. Give reason.
Answer:
In basidiomycetes the basidium is club shaped with four basidiospores, thus this group of fungi is popularly called “Club fungi”. The fruit body formed is called Basidiocarp.
Question 87.
Name the special structures in deuteromycetes that produces conidia.
Answer:
Pycnidium, acervulus, sporodochium and synnemata.
Question 88.
Deuteromycetes are imperfect fungi – Justify.
Answer:
The fungi belonging to deuteromycetes lack sexual reproduction and are called imperfect fungi.
Question 89.
List out the antibiotics produced by fungi.
Answer:
Penicillin, cephalosporins and griseofiilvin.

Question 90.
Name some toxins produced by Fungus.
Answer:
Alfatoxin, Patulin and Ochratoxin – A.
Question 91.
Name 2 fungal species employed as Biopesticides.
Answer:
Two Fungal Species Employed As Biopesticides:
- Beauveria bassiana and
- Metarhizium anisopliae.
Question 92.
Name few fungal diseases in plants.
Answer:
Blast of paddy, rust of wheat, red rot of sugarcane and white rust of crucifers.
Question 93.
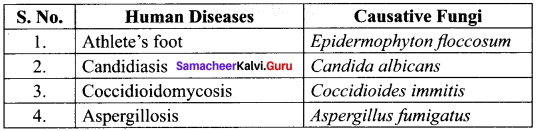
Name few fungal diseases in Humans?
Answer:
Fungal Diseases in Humans:
| S. No. |
Human Diseases |
Causative Fungi |
| 1. |
Athlete’s foot |
Epidermophyton floccosum |
| 2. |
Candidiasis |
Candida albicans |
| 3. |
Coccidioidomycosis |
Coccidioides immitis |
| 4. |
Aspergillosis |
Aspergillus fumigatus |
Question 94.
What is mycorrhiza?
Answer:
The symbiotic association between fungal mycelium and roots of plants is called as mycorrhiza.
Question 95.
What are 3 types of mycorrhiza?

Answer:
3 types of mycorrhiza:
- Ectomycorrhiza
- Endomycorrhiza and
- Ectendomycorrhiza
Question 96.
Define lichen.
Answer:
Lichen is a symbiotic association between algae and fungi.
Question 97.
What is a phycobiont and mycobiont?
Answer:
Fungal partner of lichen is called as mycobiont. Algal partner of lichen is called as phycobiont.
Question 98.
How symbiosis workout in lichen?
Answer:
In lichens, algae provide nutrition for fungal partner in turn fungi provide protection and also help to fix the thallus to the substratum through rhizinae.
Question 99.
Classify lichens based on morphology.
Answer:
Morphology:
- Leprose – Absence of distinct fungal layer
- Crustose – Crust-like
- Foliose – Leaf-like
- Fruticose – Branched pendulous shrub-like
Question 100.
What is homoiomerous and heteromerous?
Answer:
In homoiomerous (algal cells evenly distributed in the thallus) and heteromerous (a distinct layer of algae and fungi present).
Question 101.
Define ascolichen and basidiolichen.
Answer:
If the fungal partner of lichen belongs to ascomycetes, it is called ascolichen and if it is basidiomycetes it is called basidiolichen.

Question 102.
Lichens are pollution indicators. How?
Answer:
Lichens are sensitive to air pollutants especially to sulphur-di-oxide. Therefore, they are considered as pollution indicators.
Question 103.
Classify lichens based on habitat.
Answer:
III. Short Answer Type Questions (3 Marks)
Question 1.
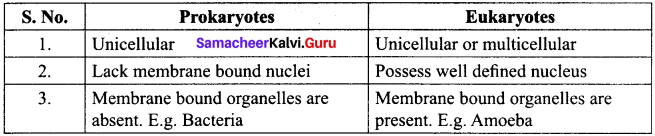
Distinguish between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Answer:
Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes:
Question 2.
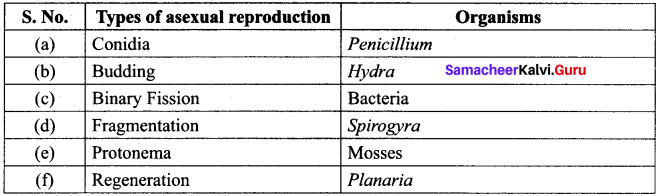
List out various types of asexual reproduction in living organisms.
Answer:
Reproduction in Living Organisms:
Question 3.
Define Homeostasis. Why it is essential?
Answer:
Property of self – regulation and tendency to maintain a steady state within an external environment which is liable to change is called homeostasis. It is essential for the living organism to maintain internal condition to survive in the environment.
Question 4.
Viruses are considered as biological puzzle – Justify.
Answer:
Viruses are considered as biological puzzle since they exhibit both living and non – living characters.

Question 5.
State the 3 types of viral symmetry.
Answer:
3 Types Of Viral Symmetry:
- Cuboid symmetry – Example: Adenovirus and Herpes virus.
- Helical symmetry – Example: Influenza virus and TMV.
- Complex or Atypical – Example: Bacteriophage and Vaccinia virus.
Question 6.
List out the non – living characters of viruses.
Answer:
The non – living characters of viruses:
- Can be crystallized.
- Absence of metabolism.
- Inactive outside the host.
- Do not show functional autonomy.
- Energy producing enzyme system is absent.
Question 7.
Name any one RNA animal virus and DNA plant virus.
Answer:
RNA animal virus and DNA plant virus:L
- RNA animal virus is HIV.
- DNA plant virus is Cauliflower mosaic virus.
Question 8.
What are the prominent symptoms of TMV affected tobacco plants?
Answer:
The first visible symptom of TMV is discoloration of leaf colour along the veins and show typical yellow and green mottling which is the mosaic symptom. The downward curling and distortion of young apical leaves occurs, plant becomes stunted and yield is affected.
Question 9.
What are bacteriophages? Where can we find it?
Answer:
Viruses infecting bacteria are called bacteriophages. It literally means ‘eaters of bacteria’. Phages are abundant in soil, sewage water, fruits, vegetables and milk.
Question 10.
Sequencely mention the types of lytic cycle.
Answer:
Types of Lytic Cycle:
- Adsorption
- penetration
- synthesis
- assembly
- maturation and
- release.
Question 11.
Why classification of organisms is important?
Answer:
Classification is essential to achieve following needs:
- To relate things based on common characteristic features.
- To define organisms based on the salient features.
- Helps in knowing the relationship amongst different groups of organisms.
- It helps in understanding the evolutionary relationship between organisms.
Question 12.
List out the merits of five kingdom classification.
Answer:
Five kingdom Classification:
- The classification is based on the complexity of cell structure and organization of thallus.
- It is based on the mode of nutrition.
- Separation of fungi from plants.
- It shows the phylogeny of the organisms.
Question 13.
Who is called as founder of modern bacteriology? Mention his contribution?
Answer:
Robert Heinrich Hermann Koch is considered as the founder of modern bacteriology. He identified the causal organism for Anthrax. Cholera and Tuberculosis. He proved experimental evidence for the concept of infection (Koch’s postulates).

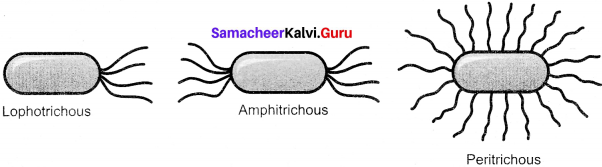
Question 14.
Draw Amphitrichous, Lophotrichous and Peritrichous flagellation in bacteria.
Answer:
Amphitrichous, Lophotrichous and Peritrichous flagellation in bacteria:
Question 15.
What are the three layers of bacterial cell?
Answer:
The bacterial cell reveals three layers:
- capsule / glycocalyx
- cell wall and
- cytoplasm.
Question 16.
What is a capsule? Mention its role.
Answer:
Some bacteria are surrounded by a gelatinous substance which is composed of polysaccharides or polypeptide or both. A thick layer of glycocalyx bound tightly to the cell wall is called capsule. It protects cell from desiccation and antibiotics. The sticky nature helps them to attach to substrates like plant root surfaces, Human teeth and tissues. It helps to retain the nutrients in bacterial cell.
Question 17.
What are plasmids? How it helps the bacteria?
Answer:
Plasmids are extrachromosomal double stranded, circular, self-replicating, autonomous elements. They contain genes for fertility, antibiotic resistant and heavy metals. It also help in the production of bacteriocins and toxins which are not found in bacterial chromosome.
Question 18.
Classfiy plasmids based on function.
Answer:
Plasmids are classified into different types based on the function. Some of them are F (Fertility) factor, R (Resistance) plasmids, Col (Colicin) plasmids, Ri (Root inducing) plasmids and Ti (Tumor inducing) plasmids.
Question 19.
Give a brief note on Mesosomes.
Answer:
Mesosomes are localized infoldings of plasma membrane produced into the cell in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae. They are clumped and folded together to maximize their surface area and helps in respiration and in binary fission.

Question 20.
How Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria react on Gram staining process?
Answer:
The Gram positive bacteria retain crystal violet and appear dark violet, whereas Gram negative type loose the crystal violet and when counterstained by safranin appear red under a microscope.
Question 21.
Name the three components of gram negative cell wall.
Answer:
Three Components Of Gram Negative Cell Wall:
- Lipoprotein
- outermembrane and
- lipopolysaccharide.
Question 22.
What are Magnetosomes?
Answer:
Intracellular chains of 40 – 50 magnetite (Fe3O4) particles are found in bacterium Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum and it helps the bacterium to locate nutrient rich sediments.
Question 23.
Write a note on binary fission.
Answer:
Under favourable conditions the cell divides into two daughter cells. The nuclear material divides first and it is followed by the formation of a simple median constriction which finally results in the separation of two cells.
Question 24.
How do archaebacteria thrive at extreme temperatures and against lytic agents?
Answer:
The unique feature of archaebacteria is the presence of lipids like glycerol and isopropyl ethers in their cell membrane. Due to the unique chemical composition the cell membrane show resistance against cell wall antibiotics and lytic agents.
E.g. Methanobacterium.
Question 25.
Name few members of cyanobacteria which act as phycobiont in lichen thalli.
Answer:
Gloeocapsa, Nostoc and Scytonema.

Question 26.
Describe in brief about Actinomycetes.
Answer:
Actinomycetes are also called ‘Ray fungi’ due to their mycelia like growth. They are anaerobic or facultative anaerobic microorganisms and are Gram positive. They do not produce an aerial mycelium. Their DNA contain high guanine and cytosine content (E.g., Streptomyces).
Question 27.
Mention few antibiotics produced by Streptomyces group of fungi.
Answer:
Streptomycin, Chloramphenicol and Tetracycline.
Question 28.
Explain in brief about the plant body of fungi?
Answer:
Majority of fungi are made up of thin, filamentous branched structures called hyphae. A number of hyphae get interwoven to form mycelium. The cell wall of fungi is made up of a polysaccharide called chitin (polymer of N – acetyl glucosamine).
Question 29.
Point out the steps involved in sexual reproduction of fungi.
Answer:
Sexual reproduction in fungi includes three steps:
- Fusion of two protoplasts (plasmogamy)
- Fusion of nuclei (karyogamy) and
- Production of haploid spores through meiosis.
Question 30.
Differentiate between Anisogamy and Oogamy with an example of fungus.
Answer:
Between Anisogamy and Oogamy with an example of fungus:
| Anisogamy |
Oogamy
|
Fusion of morphologically or physiologically dissimilar gametes.
E.g. Allomyces |
Fusion of both morphologically and physiologically dissimilar gametes.
E.g. Monoblepharis |
Question 31.
Define Spermatization.
Answer:
In spermatization method a uninucleate pycniospore / microconidium is transferred to receptive hyphal cell (Example: PuccinialNeurospora).
Question 32.
Draw a simple diagram showing the budding of yeast.
Answer:
Diagram showing the budding of yeast:
Question 33.
Write a simple note on Oomycetes.
Answer:
Coenocytic mycelium is present. The cell wall is made up of glucan and cellulose. Zoospore with one whiplash and one tinsel flagellum is present. Sexual reproduction is Oogamous.
Example: Albugo.
Question 34.
Give a brief account on fungal food.
Answer:
Mushrooms like Lentinus edodes. Agaricus bisporus and Volvariella volvaceae are consumed for their high nutritive value. Yeasts provide vitamin B and Eremothecium ashbyii is a rich source of vitamin B12

Question 35.
List out the importance of mycorrhiza.
Answer:
The Importance Of Mycorrhiza:
- Helps to derive nutrition in Monotropa, a saprophytic angiosperm.
- Improves the availability of minerals and water to the plants.
- Provides drought resistance to the plants.
- Protects roots of higher plants from the attack of plant pathogens.
Question 36.
How symbiotic relationship is executed in mycorrhiza?
Answer:
In mycorrihiza, relationship fungi absorbs nutrition from the root and in turn the hyphal network of mycorrhiza forming fungi helps the plant to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Question 1.
Define metabolism. List out the differences between the types of metabolism.
Answer:
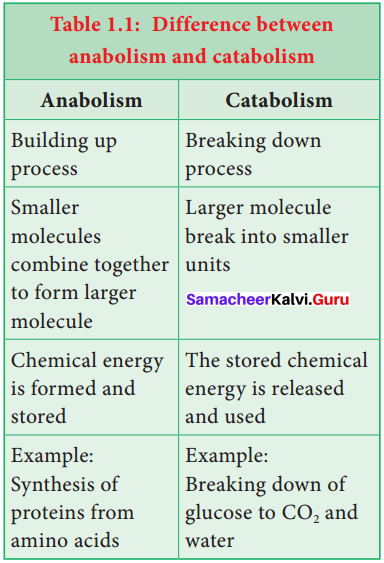
Metabolism: The sum total of all the chemical reactions taking place in a cell of living organism is called metabolism. It is broadly divided into anabolism and catabolism. The difference between anabolism and catabolism is given in table.
Question 2.
Draw a flow chart representing the various levels of organisation and integration in living organisms.
Answer:
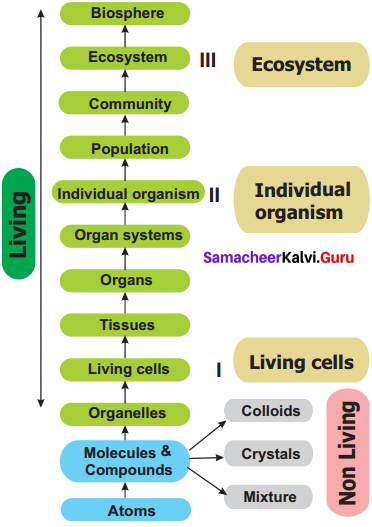
A flow chart representing the various levels of organisation and integration in living organisms:
Question 3.
Enumerate the living and non – living characters of viruses.
Answer:
Living characters:
- Presence of nucleic acid and protein.
- Capable of mutation.
- Ability to multiply within living cells.
- Able to infect and cause diseases in living beings.
- Show irritability.
- Host – specific.
Non – living characters:
- Can be crystallized.
- Absence of metabolism.
- Inactive outside the host.
- Do not show functional autonomy,
- Energy producing enzyme system is absent.
Question 4.
Draw and describe the structure of tobacco mosaic virus.
Answer:
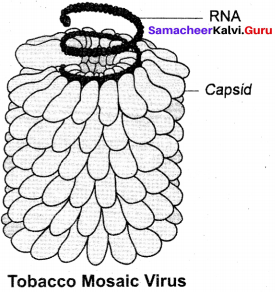
Electron microscopic studies have revealed that TMV is a rod shaped helical virus measuring about 280 × 150 pm with a molecular weight of 39 × 106 Daltons. The virion is made up of two constituents, a protein coat called capsid and a core called nucleic acid. The protein coat is made up of approximately 2130 identical protein subunits called capsomeres which are present around a central single stranded RNA molecule. The genetic information necessary for the formation of a complete TMV particle is contained in its RNA. The RNA consists of 6,500 nucleotides.

Question 5.
Write a note on David Baltimore’s classification of viruses.
Answer:
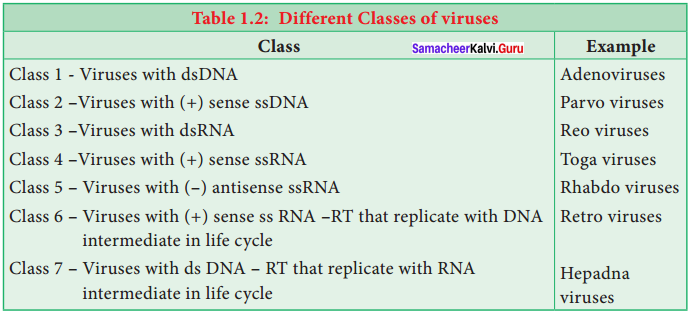
David Baltimore (1971) classification is based on mechanism of RNA production, the nature of the genome (single stranded -ss or double stranded – ds ), RNA or DNA, the use of reverse transcriptase (RT), ss RNA may be (+) sense or (-) antisense. Viruses are classified into seven classes.
Question 6.
Give an account of viral genome.
Answer:
Each virus possesses only one type of nucleic acid either DNA or RNA. The nucleic acid may be in a linear or circular form. Generally nucleic acid is present as a single unit but in wound tumour virus and in influenza virus it is found in segments. The viruses possessing DNA are called ‘Deoxyviruses’ whereas those possessing RNA are called ‘Riboviruses’.
Majority of animal and bacterial viruses are DNA viruses (HIV is the animal virus which possess RNA). Plant viruses generally contain RNA (Cauliflower Mosaic virus possess DNA). The nucleic acids may be single stranded or double stranded. On the basis of nature of nucleic acid viruses are classified into four categories. They are viruses with ssDNA (Parvo viruses), dsDNA (Bacteriophages), ssRNA (TMV) and dsRNA (wound tumour virus).
Question 7.
Explain the structure of T4 bacteriophage with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
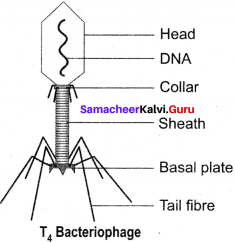
The T4 phage is tadpole shaped and consists of head, collar, tail, base plate and fibres (figure). The head is hexagonal which consists of about 2000 identical protein subunits. The long helical tail consists of an inner tubular core which is connected to the head by a collar. There is a base plate attached to the end of tail The base plate contains six spikes and tail fibres. These fibres are used to attach the phage on the cell wall of bacterial host during replication. A dsDNA molecule of about 50 μm is tightly packed inside the head. The DNA is about 1000 times longer than the phage itself.
Question 8.
Describe in detail about the lytic cycle of phages with diagram.
Answer:
Lytic cycle: During lytic cycle of phage, dis integration of host bacterial cell occurs and the progeny virions are released.
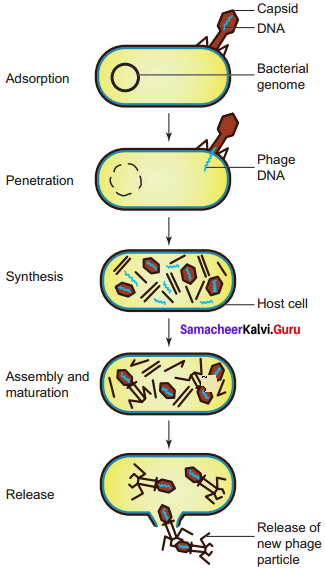
The steps involved in the lytic cycle are as follows:
(i) Adsorption: Phage (T4) particles interact with cell wall of host (E. coli). The phage tail makes contact between the two, and tail fibres recognize the specific receptor sites present on bacterial cell surface. The lipopolysaccharides of tail fibres act as receptor in phages. The process involving the recognition of phage to bacterium is called landing. Once the contact is established between tail fibres of phage and bacterial cell, tail fibres bend to anchor the pins and base plate to the cell surface. This step is called pinning.
(ii) Penetration: The penetration process involves mechanical and enzymatic digestion of the cell wall of the host. At the recognition site phage digests certain cell wall structure by viral enzyme (Jysozyrne). After pinning the tail sheath contracts (using ATP) and appears shorter and thicker. After contraction of the base plate enlarges through which DNA is injected into the cell wall without using metabolic energy. The step involving injection of DNA particle alone into the bacterial cell is called Transfection. The empty protein coat leaving outside the cell is known as ‘ghost’.
(iii) Synthesis: This step involves the degradation of bacterial chromosome, protein synthesis and DNA replication. The phage nucleic acid takes over the host biosynthetic machinery. Host DNA gets inactivated and breaks down. Phage DNA suppresses the synthesis of bacterial protein and directs the metabolism of the cell to synthesis the proteins of the phage particles and simultaneously replication of phage DNA also takes place.
(iv) Assembly and Maturation: The DNA of the phage and protein coat are synthesized separately and are assembled to form phage particles. The process of assembling the phage particles is known as maturation. After 20 minutes of infection about 300 new phages are assembled
(v) Release: The phage particle gets accumulated inside the host cell and are released by the lysis of the host cell wall
 .
.
Question 9.
Explain the lysogenic multiplication of phages.
Answer:
In the lysogenic cycle the phage DNA gets integrated into host DNA and gets multiplied along with nucleic acid of the host. No independent viral particle is formed.
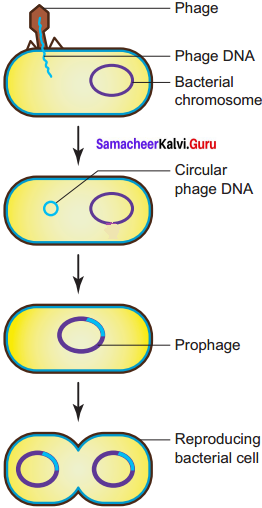
As soon as the phage injects its linear DNA into the host cell, it becomes circular and integrates into the bacterial chromosome by recombination. The integrated phage DNA is now called prophage. The activity of the prophage gene is repressed by two repressor proteins which are synthesized by phage genes. This checks the synthesis of new phages within the host cell. However, each time the bacterial cell divides, the prophage multiplies along with the bacterial chromosome. On exposure to UV radiation and chemicals the excision of phage DNA may occur and results in lytic cycle.
Question 10.
Draw a tabular column and compare the characters of five kingdoms.
Answer:
Question 11.
List out the general characters of bacteria.
Answer:
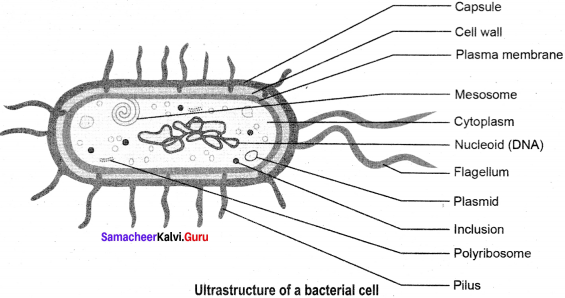
The General Characters of Bacteria:
- They are prokaryotic organisms and lack nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles.
- The genetic material is called nucleoid or genophore or incipient nucleus.
- The cell wall is made up of polysaccharides and proteins.
- Most of them lack chlorophyll, hence they are heterotrophic (Vibrio cholerae) but some are autotrophic and possess Bacteriochlorophyll (Chromatium).
- They reproduce vegetatively by binary fission and endospore formation.
- They exhibit variations which are due to genetic recombination and is achieved through conjugation, transformation and transduction.
Question 12.
Draw and label the ultra structure of a bacterium.
Answer:
The ultra structure of a bacterium:
Question 13.
Write in detail about Plasmids.
Answer:
Plasmids are extrachromosomal double stranded, circular, self – replicating, autonomous elements. They contain genes for fertility, antibiotic resistant and heavy metals. It also help 1 in the production of bacteriocins and toxins which are not found in bacterial chromosome.
The size of a plasmid varies from 1 to 500 kb usually plasmids contribute to about 0.5 to 5% of the total DNA of bacteria. The number of plasmids per cell varies. Plasmids are classified into different types based on the function. Some of them are F (Fertility) factor, R (Resistance) plasmids, Col (Colicin) plasmids, Ri (Root inducing) plasmids and Ti (Tumour inducing) plasmids.

Question 14.
Describe the structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial cell wall using diagram.
Answer:
Most of the gram positive cell wall contain considerable amount of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid. In addition, they may contain polysaccharide molecules. The gram negative cell wall contains three components that lie outside the peptidoglycan layer:
- Lipoprotein
- Outer membrane and
- Lipopolysaccharide.
Thus the different results in the gram stain are due to differences in the structure and composition of the cell wall.
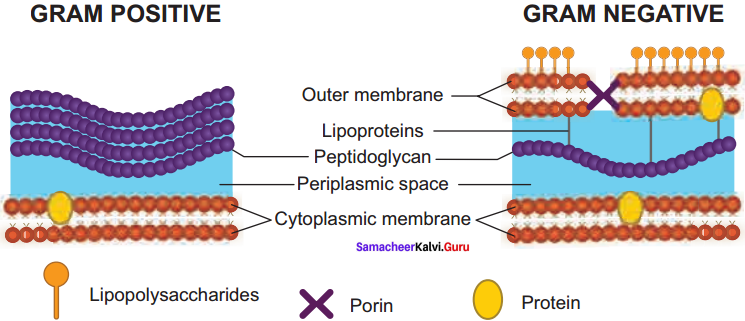
Question 15.
Tabulate the differences between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
Answer:
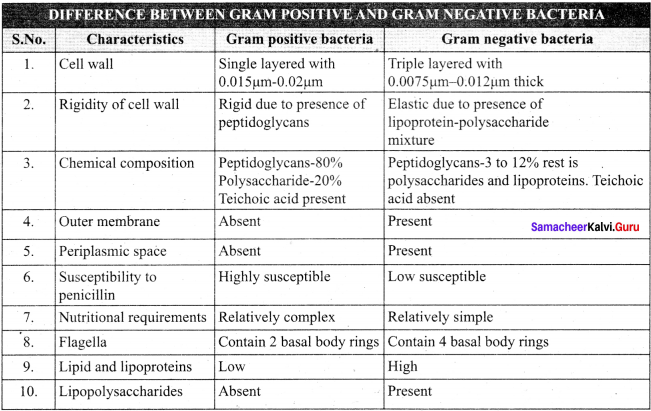
Question 16.
Give an account on respiration types of bacteria.
Answer:
Two types of respiration is found in bacteria.
They are:
- Aerobic respiration
- Anaerobic respiration
1. Aerobic respiration: These bacteria require oxygen as terminal acceptor and will not grow under anaerobic conditions (i.e. in the absence of O2) Example: Streptococcus.
(i) Obligate aerobes: Some Micrococcus species are obligate aerobes (i.e. they must have 1 oxygen to survive).
2. Anaerobic respiration:
These bacteria do not use oxygen for growth and metabolism but obtain their energy from fermentation reactions. Example: Clostridium.
(i) Facultative anaerobes: There are bacteria that can grow either using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor or anaerobically using fermentation reaction to obtain energy. When a facultative anaerobe such as E. coli is present at a site of infection like an abdominal abscess, it can rapidly consume all available O2 and change to anaerobic metabolism producing an anaerobic environment and thus allow the anaerobic bacteria that are present to grow and cause disease.
Example: Escherichia coli and Salmonella.
(ii) Capnophilic bacteria: Bacteria which require CO2 for their growth are called as capnophilic bacteria.
Example: Campylobacter.

Question 17.
Explain the mode of nutrition in bacteria.
Answer:
On the basis of their mode of nutrition bacteria are classified into two types namely autotrophs and heterotrophs.
I. Autotrophic bacteria:
Bacteria which can synthesis their own food are called autotrophic bacteria. They may be further subdivided as
A. Photoautotrophic bacteria – Bacteria use sunlight as their source of energy to synthesize food. They may be:
- Photolithotrophs: In Photolithotrophs the hydrogen donor is an inorganic substance.
- Green sulphur bacteria: In this type of bacteria the hydrogen donor is H2S and possess pigment called Bacterioviridin. Example: Chlorobium.
- Purple sulphur bacteria: For bacteria belong to this group the hydrogen donor is thiosulphate, Bacteriochlorophyll is present. Chlorophyll containing chlorosomes are present. Example: Chromatium.
- Photoorganotrophs: They utilize organic acid or alcohol ‘as hydrogen donor. Example: Purple non-sulphur bacteria – Rhodospirillum.
B. Chemoautotrophic bacteria – They do not have photosynthetic pigment hence they cannot use sunlight energy. These type of bacteria obtain energy from organic or inorganic substance.
1. Chemolithotrophs: This type of bacteria oxidize inorganic compound to release energy.
Examples:
- Sulphur bacteria – Thiobacillus thiooxidans
- Iron bacteria – Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans
- Hydrogen bacteria – Hydrogenomonas and
- Nitrifying bacteria – Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
2. Chemoorganotrophs: This type of bacteria oxidize organic compounds to release energy.
Examples:
- Methane bacteria – Methanococcus
- Acetic acid bacteria – Acetobacter and
- Lactic acid bacteria – Lactobacillus
II. Heterotrophic bacteria:
They are parasites (Clostridium and Mycobacterium), Saprophytes (Bacillus mycoides) or symbiotic (Rhizobium in root nodules of leguminous crops).
Question 18.
Describe the process of transformation.
Answer:
The process of transformation:
Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another is called transformation. In 1928, the bacteriologist Fredrick Griffith demonstrated transformation in mice using Diplococcus pneumoniae. Two strains of this bacterium are present. One strain produces smooth colonies and are virulent in nature (S type), in addition another strain produced rough colonies and are avirulent (R type). When S-type of cells were injected into the mouse, the mouse died. When R-type of cells were injected, the mouse survived. He injected heat killed S-type cells into the mouse the mouse did not die.
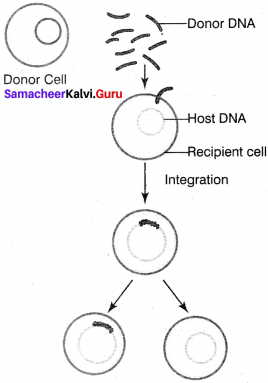
When the mixture of heat killed S-type cells and R-type cells were injected into the mouse. The mouse died. The avirulent rough strain of Diplococcus had been transformed into S-type cells. The hereditary material of heat killed S-type cells had transformed R-type cell into virulent smooth strains. Thus the phenomenon of changing the character of one strain by transferring the DNA of another strain into the former is called transformation.

Question 19.
Define conjugation and its mechanism.
Answer:
J. Lederberg and Edward L Tatum demonstrated conjugation in E. coil in the year 1946. In this method of gene transfer the donor cell gets attached to the recipient cell with the help of pili.
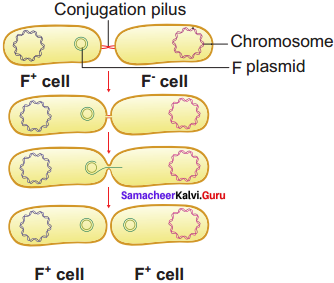
The pilus grows in size and forms the conjugation tube. The plasmid of donor cell which has the F+ (fertility factor) undergoes replication. Only one strand of DNA is transferred to the recipient cell through conjugation tube. The recipient completes the structure of double stranded DNA by synthesizing the strand that complements the strand acquired from the donor.
Question 20.
Write in detail about transduction and its types.
Answer:
Zinder and Lederhcrg (1952) discovered transduction in Salmonella typhimurum. Phage mediated DNA transfer is called transduction.
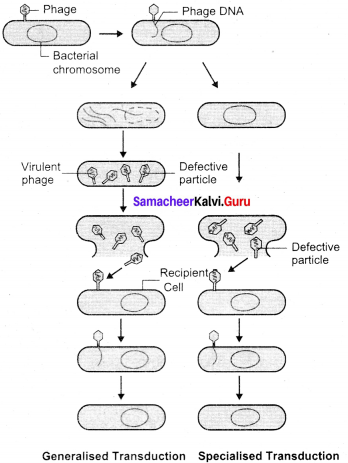
Transduction is of two types:
- Generalized transduction and
- Specialized or restricted transduction.
1. Generalized transduction: The ability of a bacteriophage to carryr genetic material of any region of bacterial DNA is called generalised transduction.
2. Specialized or restricted transduction: The ability of the bacteriophage to carry only a specific region of the bacterial DNA is called specialized or restricted transduction.
Question 21.
List out the uses of bacteria in industries.
Answer:
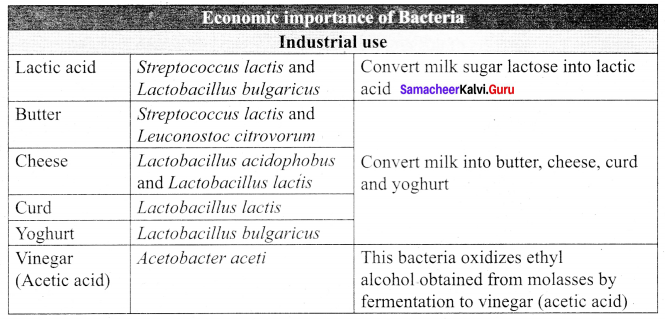
The uses of bacteria in industries:
Question 22.
Explain the role of bacteria in antibiotic production and medicines.
Answer:
The role of bacteria in antibiotic production and medicines:
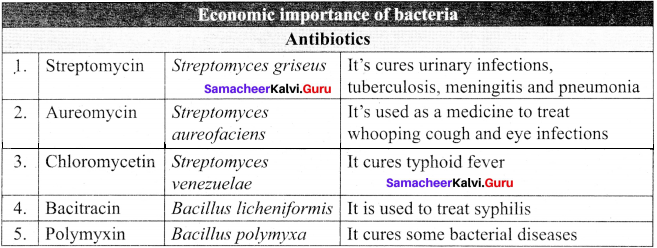
Question 23.
Explain the role of bacteria in soil fertility.
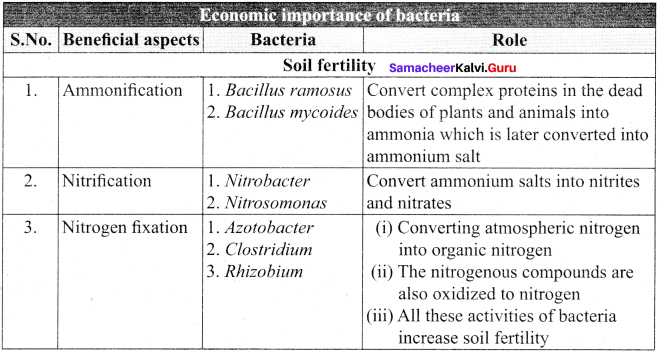
Answer:
The role of bacteria in soil fertility:
Question 24.
List out the salient features of cyanobacteria.
Answer:
The Salient Features Of Cyanobacteria:
- The members of this group are prokaryotes and lack motile reproductive structures.
- The thallus is unicellular in Chroococcus, colonial in Gloeocapsa and filamentous trichome in Nostoc.
- Gliding movement is noticed in some species (Oscillatoria).
- The protoplasm is differentiated into central region called centroplasm and peripheral region bearing chromatophore called chromoplasm.
- The photosynthetic pigments include c-phyocyanin and c-phycoerythrin along with myxoxanthin and myxoxanthophyll.
- The reserve food material is cyanophycean starch.
- In some forms a large colourless cell is found in the terminal or intercalary position called heterocysts. They are involved in nitrogen fixation.
- They reproduce only through vegetative methods and produce akinetes (thick wall dormant cell formed from vegetative cell), hormogonia (a portion of filament get detached and reproduce by cell division), fission and endospores.
- The presence of mucilage around the thallus is characteristic feature of this group. Therefore, this group is also called Myxophyceae.
- Sexual reproduction is absent.
- Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos-aquae cause water blooms and release toxins and affect the aquatic organism. Most of them fix atmospheric nitrogen and are used as biofertilizers (Example: Nostoc and Anabaena). Spirulina is rich in protein hence it is used as single cell protein.

Question 25.
Explain the various types of asexual reproduction in fungi.
Answer:
The Various Types Of Asexual Reproduction In Fungi:
- Zoospores: They are flagellate structures produced in zoosporangia (Example: Chytrids)
- Conidia: The spores produced on condiophores (Example: Aspergillus)
- Oidia / Thallospores / Arthrospores: The hypha divide and develop into spores called oidia (Example: Erysiphe).
- Fission: The vegetative cell divide into 2 daughter cells. (Example: Schizosaccharomyces – yeast).
- Budding: A small outgrowth is developed on parent cell, which gets detached and become independent. (Example: Saccharomyces-yeast).
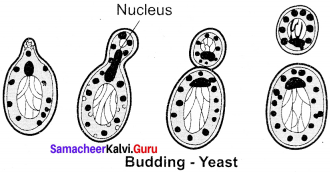
- Chlamydospore: Thick walled resting spores are called chlamydospores. (Example: Fusarium).
Question 26.
Explain the various types of sexual reproduction in fungi.
Answer:
The Various Types Of Sexual Reproduction In Fungi:
- Planogametic copulation: Fusion of motile gamete is called planogametic copulation.
- Isogamy – Fusion of morphologically and physiologically similar gametes. (Example: Synchytrium).
- Anisogamy – Fusion of morphologically or physiologically dissimilar gametes (Example: Allomyces).
- Oogamy – Fusion of both morphologically and physiologically dissimilar gametes. (Example: Monoblepharis).
- Gametangial contact: During sexual reproduction a contact is established between antheridium and oogonium (Example: Albugo).
- Gametangial copulation: Fusion of gametangia to form zygospore. (Example: Mucor and Rhizopus).
- Spermatization: Auninucleate pycniospore/microconidium is transferred to receptive hyphal cell (Example: Puccinia / Neurospora)
- Somatogamy: Fusion of two somatic cells of the hyphae (Example: Agaricus).
Question 27.
List out the salient features of zygomycetes.
Answer:
The salient features of zygomycetes:
- Most of the species are saprophytic and live on decaying plant and animal matter in the soil. Some lead parasitic life (Example: Entomophthora on housefly)
- Bread mold fungi (Example: Mucor and Rhizopus) and Coprophilous fungi (Fungi growing on dung Example: Pilobolus) belong to this group.
- The mycelium is branched and coenocytic.
- Asexual reproduction by means of spores produced in sporangia.
- Sexual reproduction is by the fusion of the gametangia which results in thick walled zygospore. It remains dormant for long periods. The zygospore undergoes meiosis and produce spores.
Question 28.
List out the salient features of ascomycetes.
Answer:
Features of Ascomycetes:
- Ascomycetes include a wide range of fungi such as yeasts, powdery mildews, cup fungi, morels and so on.
- Although majority of the species live in terrestrial environment, some live in aquatic environments both fresh water and marine.
- The mycelium is well developed, branched with simple septum.
- Majority of them are saprophytes but few parasites are also known. (Powdery mildew – Erysiphe).
- Asexual reproduction takes place by fission, budding, oidia, conidia and chlamydospore.
- Sexual reproduction takes place by the fusion of two compatible nuclei.
- Plasmogamy is not immediately followed by karyogamy, instead a dikaryotic condition is prolonged for several generations.
- A special hyphae called ascogenous hyphae is formed.
- A crozier is formed when the tip of the ascogenous hyphae recurves forming a hooked cell. The two nuclei in the penultimate cell of the hypha fuse to form a diploid nucleus. This cell form young ascus.
- The diploid nucleus undergo meiotic division to produce four haploid nuclei, which further divide mitotically to form eight nuclei. The nucleus gets organised into 8 ascospores.
- The ascospores are found inside a bag-like structure called ascus. Due to the presence of ascus, this group is popularly called “Sac fungi”.
- Asci gets surrounded by sterile hyphae forming fruit body called ascocarp.
- There are 4 types of ascocarps namely Cleistothecium (Completely closed), Perithecium (Flask shaped with ostiole), Apothecium (Cup shaped and open type) and Pseudothecium.
Question 29.
List out the salient features of Basidiomycetes.
Answer:
Features of Basidiomycetes:
- Basidiomycetes include puffballs, toad stools, Bird nest’s fungi, Bracket fungi, stink horns, rusts and smuts.
- The members are terrestrial and lead a saprophytic and parasitic mode of life.
- The mycelium is well developed, septate with dolipore septum (bracket like). Three types of mycelium namely primary (Monokaryotic), secondary (Dikaryotic) and tertiary are found.
- Clamp connections are formed to maintain dikaryotic condition.
- Asexual reproduction is by means of conidia, oidia or budding.
- Sexual reproduction is present but sex organs are absent. Somatogamy or spermatisation results in plasmogamy. Karyogamy is delayed and dikaryotic phase is prolonged. Karyogamy takes place in basidium and it is immediately followed by meiotic division.
- The four nuclei thus formed are transformed into basidiospores which are borne on sterigmata outside the basidium (Exogenous). The basidium is club shaped with four basidiospores, thus this group of fungi is popularly called “Club fungi”. The fruit body formed is called Basidiocarp.

Question 30.
Compare the characters of different types of Mycorrhiza.
Answer:
The characters of different types of Mycorrhiza:
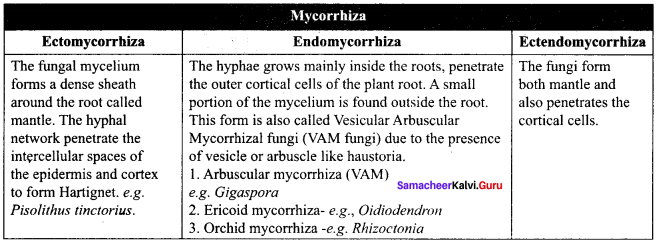
Question 31.
List out the beneficial aspects of lichens.
Answer:
The Beneficial Aspects of Lichens:
- Lichens secrete organic acids like oxalic acids which corrodes the rock surface and helps in weathering of rocks, thus acting as pioneers in Xerosere.
- Usnic acid produced from lichens show antibiotic properties.
- Lichens are sensitive to air pollutants especially to sulphur-di-oxide. Therefore, they are considered as pollution indicators.
- The dye present in litmus paper used as acid base indicator in the laboratories is obtained from Roccella montagnei.
- Cladonia rangiferina (Reindeer moss) is used as food for animals living in Tundra regions.
V. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs)
Question 1.
Viruses and viroids are infectious particles. How do you differentiate one from other?
Answer:
Viruses and viroids are infectious particles:
| S.No. |
Viruses |
Viroids |
| 1. |
Viruses may have DNA or RNA as genetic material. |
Viroids has ssRNA as genetic material |
| 2. |
Capsid is present |
Capsid is absent |
Question 2.
In R.H. Whittaker’s classification, how many kingdoms come under prokaryotes and how many kingdoms come under eukaryotes.
Answer:
Monera is the only prokaryotic kingdom in Whittaker’s classification, whereas protista, fungi, plantae and animalia comes under eukaryotes.
Question 3.
Arrange the following in a proper sequence with respect to fungal sexual cycle. Karyogamy, protoplasmic fusion, meiosis and spores production.
Answer:
Protoplasmic fusion → Karyogamy → Meiosis → Spores production.
Question 4.
List out major attributes and features that a cell must possess to call it as a living one.
Answer:
Growth, reproduction, metabolism, nutrition, movement and irritability, etc.
Question 5.
In five kingdom classification, actinomycetes and mycoplasma belongs to same kingdom.
(a) Name the kingdom.
(b) Which level of body organization does they exhibit.
Answer:
Actinomycetes and Mycoplasma belongs to kingdom Monera. Moneras are unicellular organisms.

Question 6.
Viruses are useful to us – Justify. Majority of viruses are harmful, causing wide range of diseases among organisms. But certain viruses of Baculoviridae group are commercially used as insecticides.
Answer:
E.g. Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis granulo viruses and Entomopox viruses.
Question 7.
Write the appropriate term for each of the following:
(a) Complex sugar that makes fungal cell wall.
(b) Blue green algae
Answer:
(a) Chitin
(b) Cyanobacteria.
Question 8.
Why fungi is not placed under kingdom plantae, though it has cell wall?
Answer:
Though fungi has cell wall, it differs from plants in their mode of nourishment. Fungi shows heterotropic mode of nutrition, whereas plants are autotrophs.
Question 9.
Which organisms is more complex and highly evolved among blue green algae, mushroom and maize? Give reason.
Answer:
Maize plant is more complex and highly evolved as it is a eukaryotic and autotrophic organism, showing tissue grade organisation. The blue green algae is a unicellular prokaryote and mushroom is a fungus, which is heterotrophic with no tissue grade of organisation.

Question 10.
Why viruses are not included in the category of microorganisms?
Answer:
Viruses possess characters of both living and non – living and also they does not have well defined body organisation. Hence they are not included in the category of microorganism.
Question 11.
Generally nucleic acid in viruses is present as single unit. Name any two viruses that possess segmented nucleic acid.
Answer:
- Wound tumour virus
- Influenza virus
Question 12.
Name any two recent viral diseases that threaten human life.
Answer:
- Ebola
- Nipah
Question 13.
When does a prophage enter lytic cycle?
Answer:
On exposure to UV radiation and chemicals, the prophage enters the lytic cycle.
Question 14.
Capsule layer helps the bacterium. How?
Answer:
Capsule in bacteria protects the cell from desiccation and antibiotics.

Question 15.
Imagine yourself as Carl Woese and explain your colleagues about your classification.
Answer:
I (Carl Woese) classified the living organisms into three domains based on the differences in rRNA nucleotide sequence and lipid structure of the cell membrane. The three domains are Bacteria, Archae and Eukarya.
Question 16.
Name the strains used in Gram staining procedure.
Answer:
Crystal violet and safranin.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

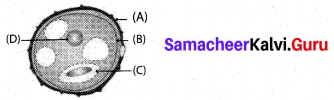
![]()
![]()
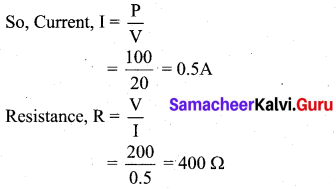
![]()
![]()

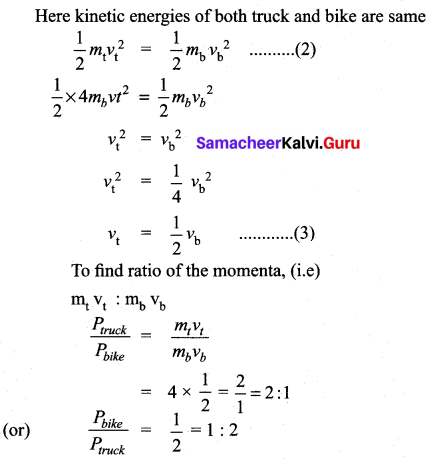
![]()
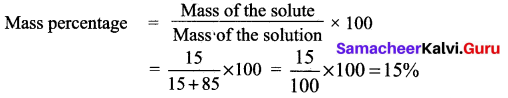
![]()



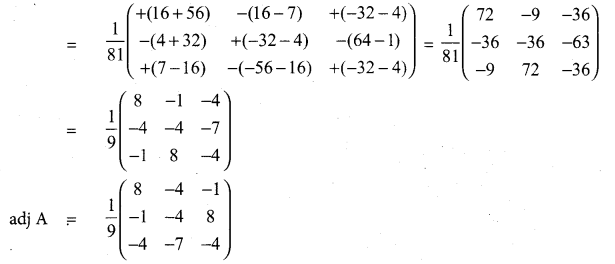
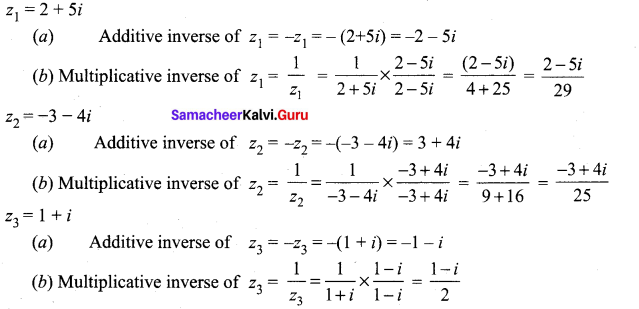
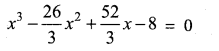
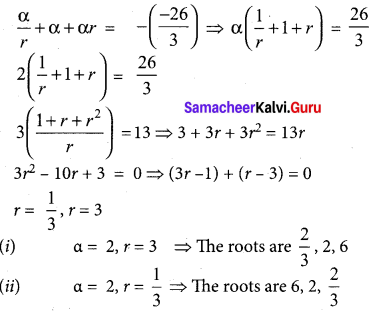
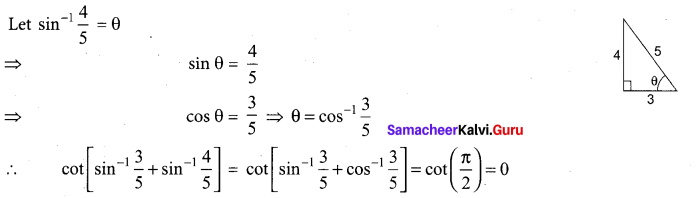
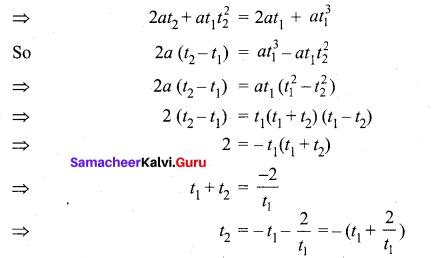
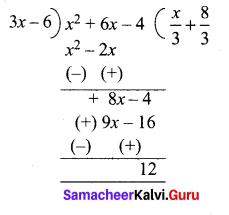
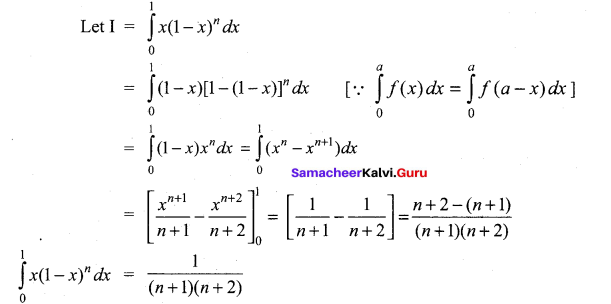
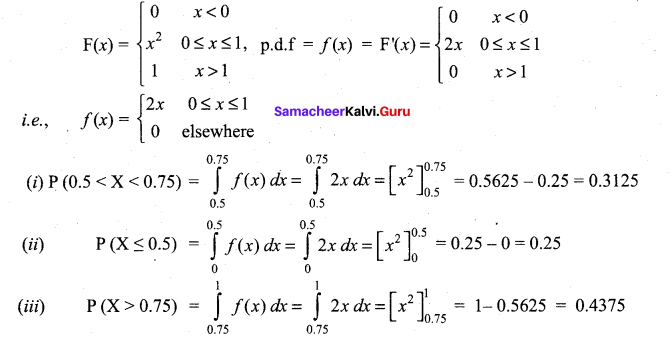
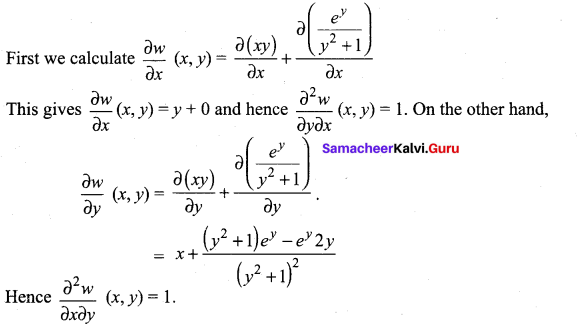
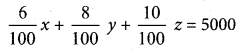
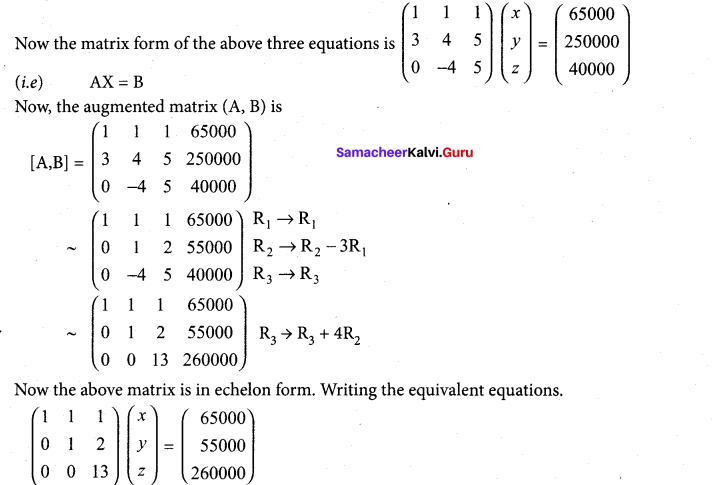

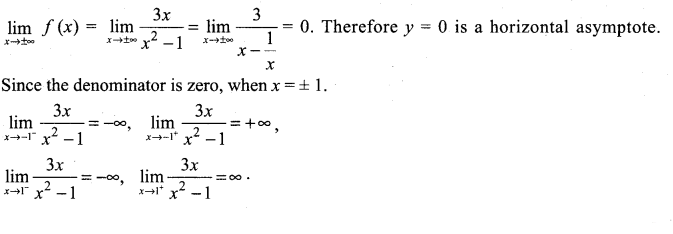
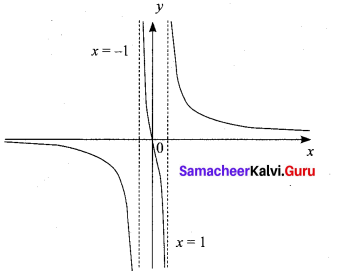
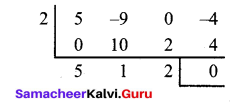
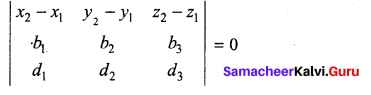


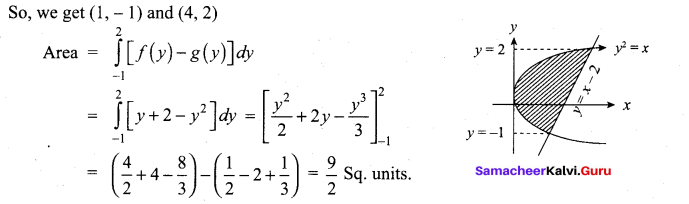
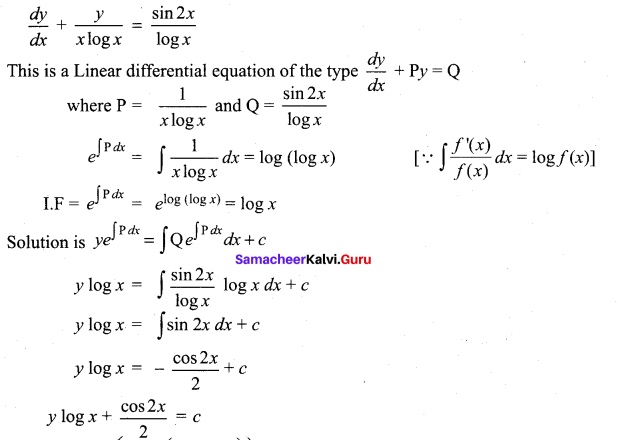
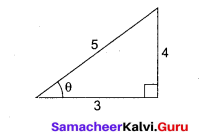





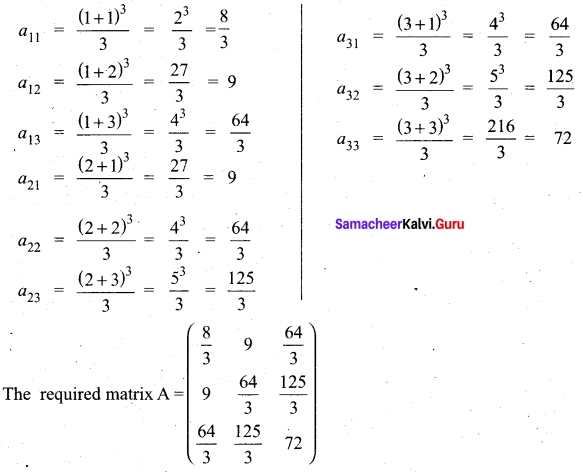
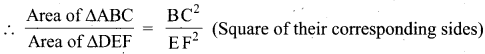
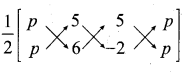
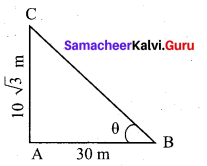
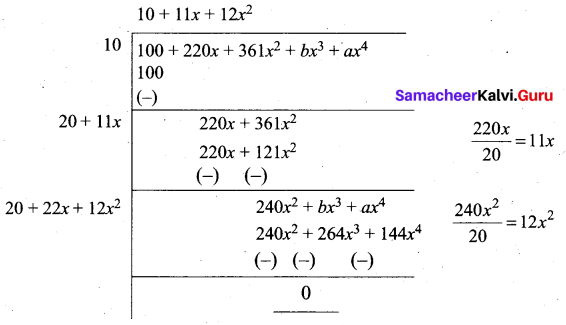
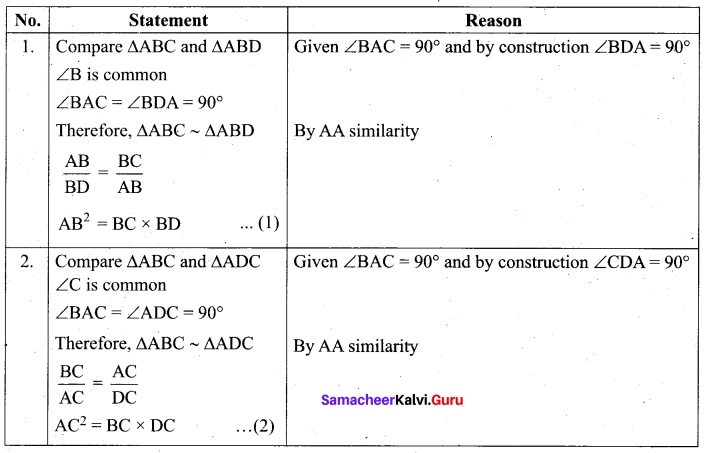

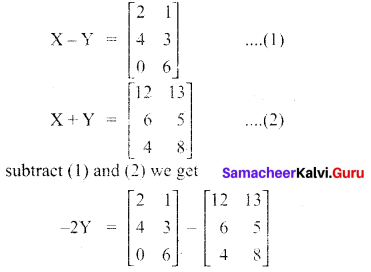
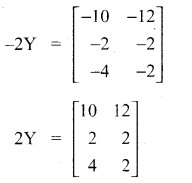
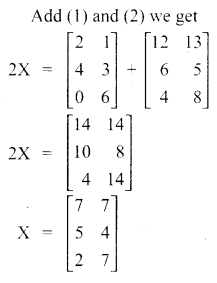
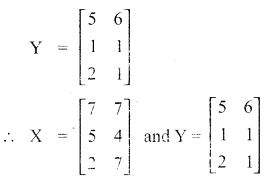
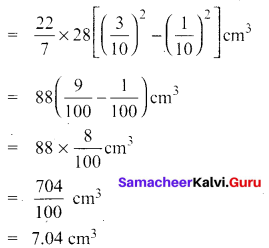

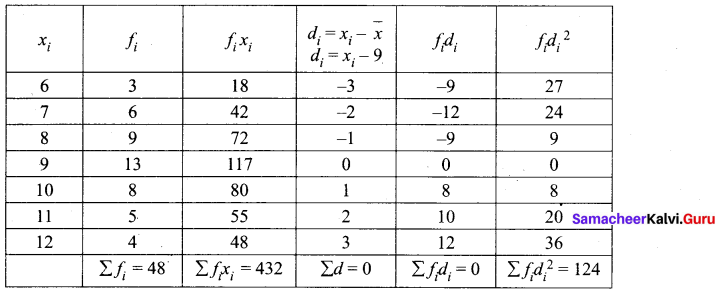
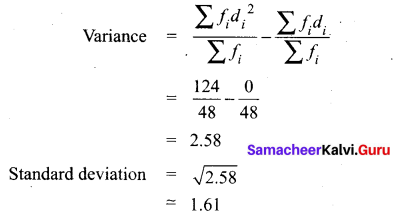
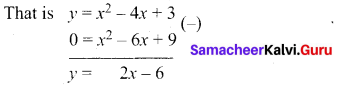
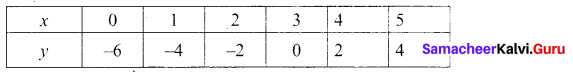
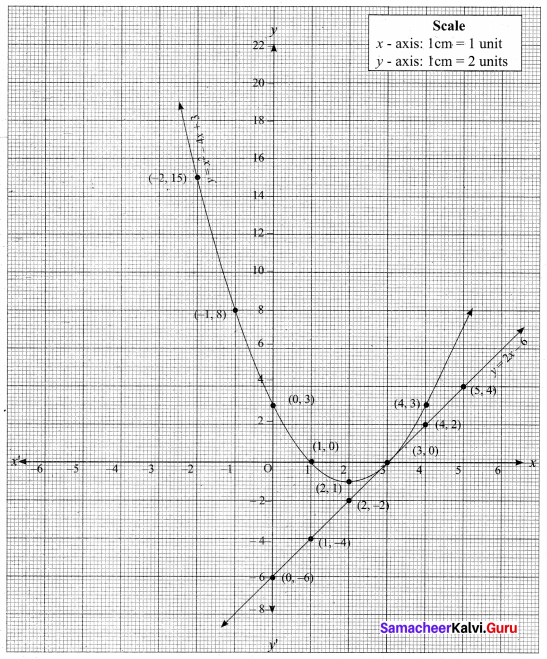
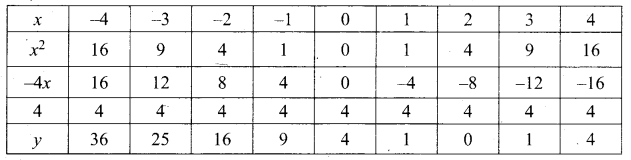




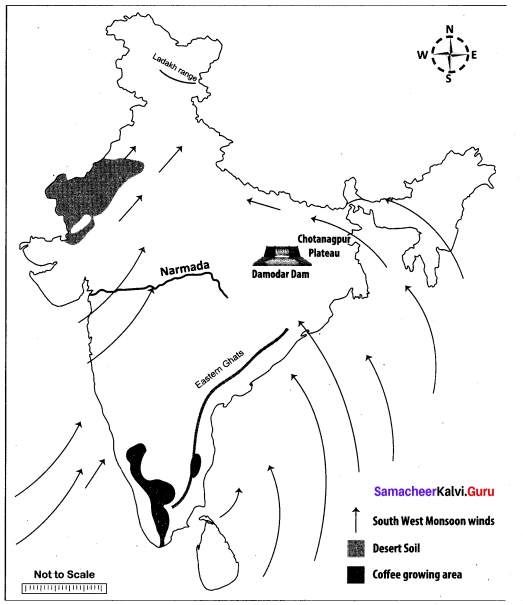
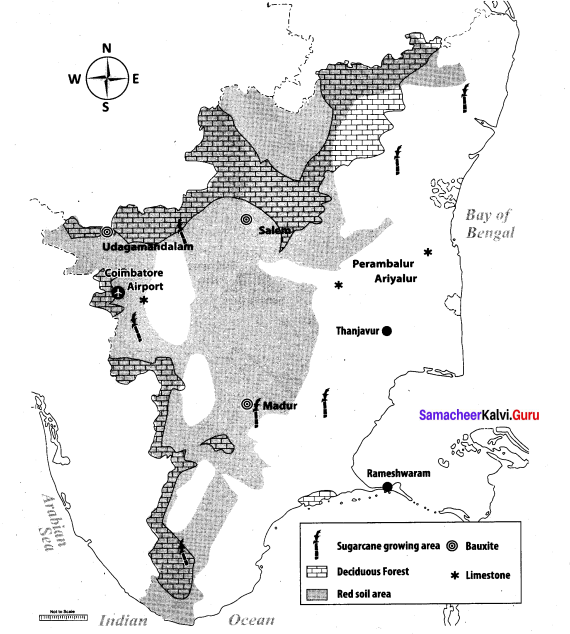
































 Find the name of the tool & write its uses.?
Find the name of the tool & write its uses.?