Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are of five marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are of Eight marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
Who said “imperialism is the highest stage of capitalism”?
(a) Lenin
(b) Marx
(c) Sun-Yat-Sen
(d) MaoTsetung
Answer:
(a) Lenin
Question 2.
Which President of the USA pursued “Good Neighbour” policy towards Latin America?
(a) Roosevelt
(b) Truman
(c) Woodrow Wilson
(d) Eisenhower
Answer:
(a) Roosevelt
![]()
Question 3.
Whose campaign and work led to the enactment of Widow Remarriage Reform Act of 1856?
(a) Iswarchandra Vidyasagar
(b) Raja Rammohan Roy
(c) Annie Besant
(d) Jyotiba Phule
Answer:
(a) Iswarchandra Vidyasagar
Question 4.
Who had established close relationship with the three agents of Chanda Sahib?
(a) Velunachiyar
(b) Kattabomman
(c) Puli Thevar
(d) Oomai thurai
Answer:
(c) Puli Thevar
Question 5.
Periyar wanted religion to be replaced by ……………..
(a) Nationalism
(b) Iconoclasm
(c) Rationalism
(d) Spiritualism
Answer:
(c) Rationalism
Question 6.
The extent of Himalayas in the east-west is about ………………….
(a) 2,500 km
(b) 2,400 km
(c) 800 km
(d) 2,200 km
Answer:
(a) 2,500 km
Question 7.
Black Soil is also called as ………………….
(a) Arid soil
(b) Saline soil
(c) Regur soil
(d) Mountain soil
Answer:
(c) Regur soil
Question 8.
The first Nuclear Power station was commissioned in ………………….
(a) Gujarat
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(c) Maharashtra
Question 9.
Which one of the following river flows into the Arabian sea?
(a) Periyar
(b) Cauvery
(c) Cuddalore
(d) Theni
Answer:
(a) Periyar
![]()
Question 10.
Literacy rate of Tamil Nadu as per 2011 census is ………………….
(a) 80.32%
(b) 62.33%
(c) 73.45%
(d) 80.33%
Answer:
(d) 80.33%
Question 11.
A foreigner can acquire Indian citizenship through ………………….
(a) Descent
(b) Registration
(c) Naturalisation
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Naturalisation
Question 12.
Apartheid is ………………….
(a) An international association
(b) Energy diplomacy
(c) A Policy of racial discrimination
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) A Policy of racial discrimination
Question 13
…………………. approach is the value added by each intermediate good is summed to estimate
the value of the final good.
(a) Expenditure approach
(b) Value added approach
(c) Income approach
(d) National Income
Answer:
(b) Value added approach
Question 14.
Tuticorin is known as ………………….
(a) Gateway of India
(b) Gateway of Tamil Nadu
(c) Pump city
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Gateway of Tamil Nadu
Part – II
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 x 2 = 20]
Question 15.
What was the result of Mussolini’s march on Rome?
Answer:
- In October 1923, in the context of a long ministerial crisis, Mussolini organised the fascist March on Rome.
- Impressed by the show of force, the king invited Mussolini to form a government.
Question 16.
The Suez Canal crisis confirmed that Israel had been created to serve the cause of western interests -Elaborate.
Answer:
(i) In 1956, Nasser, the President of Egypt, nationalised Suez Canal. This measure undermined British interests with the failure of diplomacy, Britain and France decided to use force.
(ii) Israel saw this as an opportunity to open the Gulf of Aqaba to Israeli shipping and put a stop to Egyptian border roads.
(iii) On 29 October Israels forces invaded Egypt, Britain used this opportunity to demand that its troops be allowed to occupy the canal zone to protect the canal. When Egypt refused British demand, it was bombed. Britain and France also attached Suez Canal area.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the territories annexed by the British under the Doctrine of Lapse.
Answer:
Satara, Sambalpur, parts of Punjab, Jhansi and Nagpur.
Question 18.
List out the personalities who contributed to the revival of Tamil literature through their writings.
Answer:
C.W. Damotharanar, U.V. Swaminathar, F.W. Ellis, Robert Caldwell, Subramania Bharati, Thiru Vi. Kalyanasundaram, Singaravelar, Pandithar Iyotheethassar, Sundaram Pillai and Maraimalai Adigal.
Question 19.
Write a short note on Deccan Plateau.
Answer:
- The Deccan Plateau is a triangular landmass that lies to the south of the river Narmada.
- This is the largest physiographic division of our country.
- It covers an area of about 16 lakh sq.km (about half of the total area of the country)
- It is an old rocky plateau region. –
- The topography consists of a series of plateaus and hill ranges interspersed with river valleys.
- It is higher in the west and slopes gently eastwards.
- The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats mark the western and the eastern edges of the Deccan plateau respectively.
- Aravalli hills mark the north-western boundary of the plateau region.
- Its northern and north-eastern boundaries are marked by the Bundelkhand upland, Kaimur and Rajmahal hills.
Western Ghats lie parallel to the Western coast. They are continuous and can be crossed
through passes only like Thai, Bhor and the Pal Ghats. It is higher then the Eastern Ghats. It cause orographic rain by facing the rain-bearing moist winds to rise along the western slopes of the Ghats. The height of the Western Ghats progressively increases from north to south. The highest peak include the Anaimudi (2,695 metres) and the DodaBetta (2,637 metres). …
The Eastern Ghats stretch from the Mahanadi valley to the Nilgiris in the south. The Eastern Ghats are discontinuous and irregular and dissected by rivers draining into the Bay of Bengal. Mahendragiri (1,501 metres) is the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats. Shevroy Hills and the Javadi Hills are located to the southeast of the Eastern Ghats. The famous hill stations of Udagamandalam, popularly Known as Ooty and the Kodaikanal are located here.
One of the distinct features of the peninsular plateau is the black soil area known as Deccan Trap. This is of volcanic region hence the rocks are igneous. These rocks have denuded over time and are responsible for the formation of black soil.
Question 20.
Write any four advantages of railways.
Answer:
- Railways are the price mode of transport for goods and passengers in India.
- They make it possible to conduct varied activities like business, sight seeing and pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
- They are suitable for long distance travel and play an important role in national integration.
- They bind the economic life of the country as well as they accelerate the development of the industry and agriculture.
Question 21.
What is ‘Teri’?
Answer:
The sand dunes formed along the coast of Ramanathapuram and Thoothukudi districts are called Teri.
Question 22.
Name the important multipurpose projects of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Mettur Dam, Amaravathi Dam, Papanasam Dam, Bhavani Sagar Dam.
Question 23.
What is meant by Citizenship?
Answer:
Citizenship is the status of a person recognized under the custom or law as being a legal member of a sovereign state or belonging to a nation.
Question 24.
Highlight the contribution by Nehru to India’s foreign policy.
Answer:
Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister, was opposed to the rivalry’ of the two superpowers (America and Russia). The aim of India’s foreign policy of that time was ‘world co-operation, world peace, end of colonial imperialism, racial equality and non-alignment’.
Question 25.
Write the importance of gross domestic product.
Answer:
The GDP is one of primary indicators used to measure the health of a country’s economy. It represents the total dollar value of all goods and services produced over a specific time period, often referred to as the size of the economy.
![]()
Question 26.
Write short note on Multinational corporation.
Answer:
- Multinational corporation is a corporate organisation which owns or controls production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country. MNCs are also called Transnational corporation (TNC) or Multinational Enterprise (MNE).
- Most of the MNCs at present belong to the four major exporting countries – USA, UK, France and Germany.
Question 27.
Write the canons of tax system?
Answer:
- Every type of tax has some advantages and some disadvantages. So we have a tax system, that is, a collection of variety of taxes. All countries use a variety of taxes.
- There are some characteristics of tax system that economists think should be followed
while designing a tax system. These characteristics are called as canons of taxation.
Question 28.
What are the minerals and its types?
Answer:
Mineral is a natural substance of organic or inorganic origin with definite chemical and Physical properties.
Types of Minerals are:
- Metallic minerals
- Non – metallic minerals.
Part – III
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 x 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) ………………. known as the “Father of modem china.
(ii) Our National Integration is strengthened by the ……………….
(iii) Fundamental duties have been gives to the citizen of India under Article ……………….
(iv) ………………. is an innovator of new ideas and business process.
(v) The difference between the value of exports and imports is called ……………….
Answers:
(i) Dr. Sun-Yat-Sen
(ii) Railways
(iii) 51 A
(iv) Entrepreneur
(v) Balance of trade.
Question 30.
Match the following:

Answers:

Question 31.
Match the following:

Answers:

Question 32.
(a) Distinguish between
(i) Western Coastal Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains,
(ii) Tropical Evergreen forest and Deciduous forest.
Answer:
(a) (i) Western Coastal Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains
Western Coastal Plains :
- It lies between the Western Ghats and Arabian Sea
- It is a narrow plain, which stretches from Gujarat to Kerala with an average width of 50 – 80 Km.
- This plain is drained by less rivers like Nar-mada and Tapi forming estuaries.
- It consists of three sections. The northern part of the coast is called the Konkan (Mumbai – Goa), the Central stretch is called the Kannad plain while the southern stretch is referred to as the Malabar coast.
Eastern Coastal Plains:
- It lies between the Eastern Ghats and Bay of Bengal.
- They are wide and level plains with an aver¬age width of 80-100 Km.
- This plain is drained by more rivers forming deltas like Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri.
- It consists of two sections. In the northern part, it is referred to as the Northern Circar, while the southern
- part is known as the Coromandal coast. Lake Chilka is an important feature along the eastern coast.
(ii) Tropical Evergreen forest and Deciduous forest.
Tropical Evergreen forest:
- These forests are located in regions of heavy rainfall more than 200 cm of rainfall.
- The trees in these forests are evergreen.
- These forest are very dense and composed of tall trees reaching up to the height of above 60 metres.
- The important trees of these forests are Rosewood, Ebony, Mahogany, and Chinchona, Bamboo and Lianas.
Deciduous forest :
- These forests are located in regions of rainfall between 70-200 cm.
- The trees in the deciduous forests shed their leaves due to dryness during the spring and early summer.
- The tropical deciduous forests are commercially important as they yield valuable timber and other forest products.
- The main trees of these forests are Teak, Sal, Sisam, Sandalwood, Wattle and Neem.
(b) Give reason: Chottanagpur Plateau is rich in mineral resources.
Chottanagpur Plateau is a store house of mineral resources such as mica, bauxite, copper, limestone, iron ore and coal.
Question 33.
Discuss the circumstances that led to the Reform movements of 19th century.
Answer:
(i) The nineteenth century India was plagued with a number of social evils such as sati, child marriage, female infanticide, polygamy and so on.
(ii) Women were subjugated by men and were not allowed to get education. They were restricted to home and hearth. They were considered inferior to men.
(iii) The condition of the depressed classes was miserable. They were subj ect to untouchability. Their entry to schools, temples and other public places, meant for upper castes, was banned. Hence, there was no education among the people belonging to lower castes.
(iv) There were other evil practices prevalent in the Indian society such as excessive superstitious religious beliefs, animal sacrifice, which needed attention of the social reformers for the benefit of the common people of the society.
(v) There was total absence of reason in the society. The system of child marriage was prevalent which resulted to child widows. These widows were never accepted in the family and were destined to lead a pathetic life. These were the circumstances that led to the Reform movements in the nineteenth century.
![]()
Question 34.
Attempt an essay on foundation and development of Tamil Renaissance in the 19th century.
Answer:
- In Tamil Nadu, the proliferation of the printing press acted as a catalyst for the publication and spread of secular ancient Tamil literature.
- In the nineteenth century, Tamil scholars like C.W. Damotharanar, and U.V. Swaminathar spent their lifetime in the rediscovery of the Tamil classics.
- C.W. Damotharanar collected and edited different palm leaf manuscripts of the Tamil grammars and literature. U.V. Swaminathar took efforts to publish the classical texts. These triggered an intellectual revolution and it was popularly known as Tamil Renaissance.
- The transformation not only revived Tamil language and literature but also Tamil culture. It challenged the prevailed caste hierarchy and influenced the rise of Dravidian consciousness and established Tamil as a language of the Dravidian people.
- Tamil renaissance questioned the cultural hegemony of Brahminism. These developments were reflected in art, literature, religion, etc.
Question 35.
Give a detailed account on the Great Northern Plains.
Formation:
- • The Northern Plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems namely – The Indus, The Ganga, and The Brahmaputra along with their tributaries.
- • This plain is formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basis lying on the foothills of the Himalayas over millions of years formed this fertile plain.
Extension:
It spread over an area of 7 lakh sq.km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division.
Importance:
With a rich soil caves combined with adequate water supply and favourable climate it is agriculturally a very production past of India.
Important Features:
- In the lower course, due to gentle slope, the velocity of the river decreases which results in the formation of riverine islands. Majuli, in the Brahmaputra River is the largest inhabited riverine island in the world.
- The rivers in their lower course split into numerous channels due to the deposition of silt. These channels are known as tributaries.
- The Northern Plain is broadly divided into three sections. Punjab plains, Ganga plains and Brahmaputra plains.
- According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions – Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar and Khadar.
Punjab Plains:
- The Western part of the Northern plain is referred to as the Punjab plains formed by the Indus and its tributaries.
- The larger part of this plain lies in Pakistan Indus and its tributaries – The Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Sutlej originate in the Himalayas. This section of the plain is dominated by the doabs.
Ganga Plains:
They extend between Ghagger and Teesta rivers. It is spread over the states of North India like
Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, Partly Jharkhand and West Bengal.
Brahmaputra plains:
- In the east of Ganga plains lies the Brahmaputra plains. They cover the areas of Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
- According to the variations in relief features, the Northern plains can be divided into four regions.
Bhabar:
The rivers after descending from the mountains deposit pebbles in a narrow belt of about 8 to 16 km in width lying parallel to the slopes of the Shivaliks. It is known as Bhabar. All the streams disappear in this Bhabar belt.
Terai:
- South of this belt, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet swampy and marshy region known as ‘Terai’. This was a thickly forested region full of wildlife.
- The Terai is wider in the eastern parts of the Great plains, especially in Brahmaputra valley due to heavy rainfall. In many states, the Terai forest have been cleaned for cultivation.
Khadar:
- The newer younger deposits of the flood plains are called Khadar. They are renamed almost every year and so are fertile. Thus ideal for intensive agriculture.
- The Khadar tracts are enriched by fresh deposits of silt every year during rainy seasons. The Khadar land consists of sand, silt, clay and mud. It is highly fertile soil.
Delta Plains:
- The deitaic plains is an extension of the Khadar land. It covers about 1.9 sq.km in the lower reaches of the Ganga River. It is an area of deposition as the river flows in this tract sluggishly.
- The deltaic plain consists mainly of old mud, new mud and marsh. In the delta region, the uplands are called “chars”. While the marshy areas are called ‘Bils’.
Question 36.
Explain the characteristic features of summer and winter seasons of Tamil Nadu.
Summer Seasons:
- The apparent migration of the sun towards north during March, April and May results in the reception of vertical sun’s rays by South India. Thus there is a steady rise in temperature from the equator.
- Hence, Tamil Nadu located to the south of Tropic of Cancer, experiences high temperature. Generally the temperature varies from 30°C to more than 40°C.
- During this season particularly in the month of May, southern part of the state receives some rainfall from pre-monsoon showers (Mango/Blossom showers) and some parts experience convectional rainfall.
Winter Seasons:
- During January and February, the vertical rays of the sun fall between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Equator. Hence, Tamil Nadu and India on the whole receive slanting rays from the sun.
- So, the weather is slightly cooler during these months. The difference between summer and winter temperature is not very high. Winter temperature in Tamil Nadu varies from 15°C to 25°C. However, in the hill stations, the winter temperature drops below 5°C occasionally.
- Some valleys in the Nilgiris record even 0°C. This drop in temperature leads to the formation of thick mist and frost. This season is practically dry.
Question 37.
What are the Duties and functions of Prime Minister of India.
Answer:
Duties and functions of the Prime Minister are given below
- The Prime Minister decides the rank of his ministers and distributes various departments among them.
- He decides the dates and the agenda of the meeting of the Cabinet which he presides.
- He supervises the work of various ministers.
- The Prime Minister acts as a link between the President and the Council of Ministers.
- He is the leader of the nation and the chief spokesperson of the country.
- He is the head of the Cabinet and other Ministers are his colleagues.
- As the leader of the nation, the Prime Minister represents our nation at all international conferences like the commonwealth etc.
Question 38.
Point out the basic concepts of India’s foreign policy.
Answer:
- Preservation of national interest.
- Achievement of world peace.
- Disarmament
- Fostering cordial relationship with other countries.
- Solving conflicts by peaceful means.
- Independence of thought and action as per the principle of NAM.
- Equality in conducting international relations.
- Anti-Colonialism, anti-imperialism anti- racism.
Question 39.
What are the limitations of the Gross Domestic Product?
The GDP is the most widely used measure of the state of the economy. While appreciating its usefulness, we should be aware of some of its limitations –
(i) Several important goods and services are left out of the GDP – The GDP includes only the goods and services sold in the market. Clean air, which is vital for a healthy life, has no market value and is left out of the GDP.
(ii) GDP measures only quantity but not quality – In the 1970’s schools and banks were not allowed to use ball point pens – because of their poor quality. Since then, not only has these been a substantial increase in the quantity of ballpoint pens produced in India but their quality has also improved a lot. The improvement in quality of goods is very important but it is not captured by the GDP.
(iii) GDP does not tell us about the way income is distributed in the country – The GDP of a country may be growing rapidly but income may be distributed unequally that only a small percentage of people may be benefiting from it.
(iv) GDP does not tell us about the kind of life people are living – A high level of per capita real GDP can go hand – in – hand with very low health condition of people, an undemocratic political system, high pollution and high suicide rate.
![]()
Question 40.
Explain the role of Entrepreneur.
Role of an Entrepreneur:
Entrepreneurs play a most important role in the economic growth and development of a country’s economy.
- They promote development of industries and help to remove regional disparities by industrialising rural and backward areas.
- They help the country to increase the GDP and Per Capita Income.
- They contribute towards the development of society by reducing concentration of income and wealth.
- They promote capital formation by mobilising the idle savings of the citizens and country’s export trade.
- Entrepreneurs provide large-scale employment to artisans, technically qualified persons and professionals and work in an environment of changing technology and try to maximise profits by innovations.
- They enable the people to avail better quality goods, at lower prices, which results in the improvement of their standard of living.
Question 41.
Draw a time line for the following:
Write any five important events between 1905-1920
1905 – Partition of Bengal / Swadeshi Movement
1906 – Swadeshi Steam Navigation Company was started
1916 – Home Rule League / Lucknow Pact
1917 – Champaran Satyagraha
1918 – Kheda Satyagraha
1919 – Rowlatt Act, Jalianwala Bagh Massacre
1920 – Khilafat Movement / Non Co-operation Movement
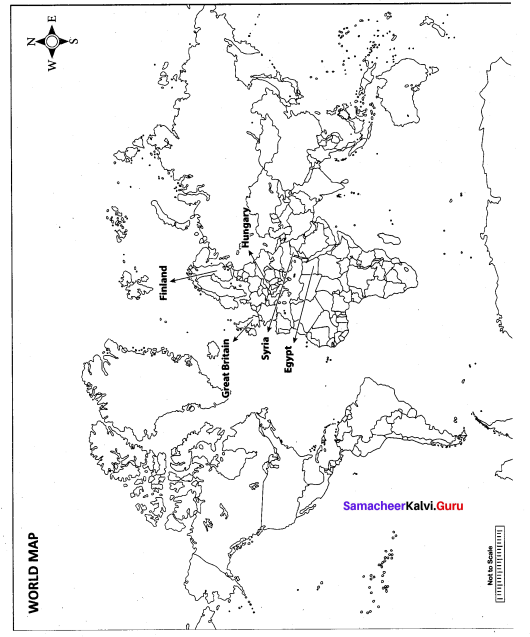
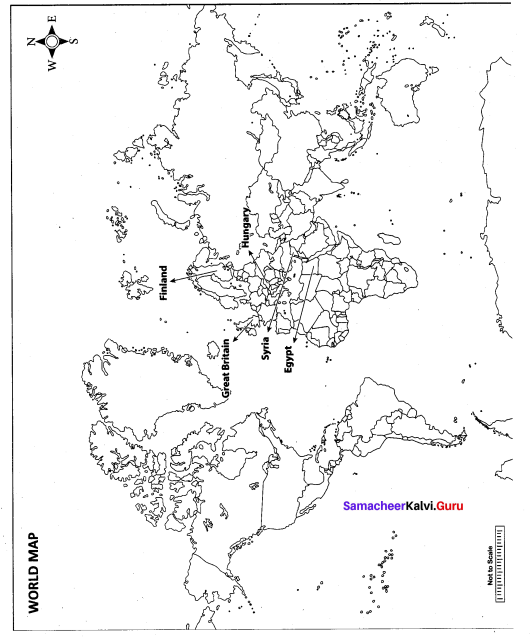
Question 42.
Mark the following places on the world map.
(i) Egypt
(ii) Finland
(iii) Hungary
(iv) Syria
(v) Great Britain
Part – IV
Answer both questions. [2 x 8 = 16]
Question 43.
(a) Ho Chi Minh
(i) Where was Ho Chi Minh born?
(ii) How did Ho Chi Minh become a popular Vietnam Nationalist?
(iii) What do you know of Ho Chi Minh’s Revolutionary Youth Movement?
(iv) How was the League for Independence called in Indo-China?
Answer:
(a) Ho Chi Minh:
(i) Ho Chi Minh was bom in Tongking in 1890.
(ii) Ho Chi Minh went to Europe at the age of twenty one. From London he went to Paris and in the Paris Peace conference, he lobbied for the independence of Vietnam. He wrote several articles in newspapers. His pamphlet, French Colonialism on Trial, made him well known as a Vietnam nationalist.
(iii) In 1925, when Ho Chi Minh was in canton, he founded the Revolutionary Youth Movement. It was an organisation for the training of Vietnamese nationalists.
(iv) The League for Independence in Vietnam was called Viet Minh.
(b) Organs of the EU
(i) Which is the Legislative body of the EU?
(if) Where is the seat of the Court of Justice?
(iii) What is the function of the European commission?
(iv) Who is responsible for the foreign exchange operation?
Answer:
(b) Organs of the EU:
(i) The European Parliament
(ii) Luxemburg
(iii) It is responsible for initiating legislation and the day to day running of the EU.
It drafts proposals for New European laws and presents to the European parliament and the council.
(iv) The European central bank.
[OR]
Question 43.
(c) Subash Chandra Bose and INA.
(i) How did Subhas Chandra Bose reach Japan?
(ii) Who headed the women wing of Indian National Army?
(iii) How did Subash Chandra Bose reorganize the INA?
(iv) Name the slogan provided by Subash Chandra Bose.
Answer:
(c) Subash Chandra Bose and INA:
(i) First he went to Germany, from there he made his way to Japan on a submarine and took control of the Indian National Army.
(ii) Lakshmi Sahgal headed the women wing of the Indian National Army.
(iii) Bose reorganised the INA into three brigade: Gandhi Brigade, Nehru Brigade and a women’s brigade named after Rani Lakshmi Bai.
(iv) He gave the slogan ‘Dilli Chalo’. ‘
(d) Revolutionary Movement in Tamil Nadu.
(i) List a few revolutionaries in Tamil Nadu.
(ii) Why did Subramania Bharathi moved to Pondicherry?
(tii) Name a few of the revolutionary literature?
(iv) What did Vanchinathan do?
Answer:
(d) Revolutionary Movement in Tamil Nadu:
(i) Some revolutionaries in Tamil Nadu were M.P.T. Acharya, V.V.S. Iyer and T.S.S. Rajan.
(ii) Subramania Bharati went to Pondicherry to escape imprisonment after the Tirunelveli uprising in 1908. Pondicherry was under French rule.
(iii) Some revolutionary literature includes India, Vijaya, and Suryodayam, which came out of Pondicherry.
(iv) Vanchinathan shot dead by Robert W.D ’E. Ashe, the collector of Tirunelveli, at Maniyachi junction on 17th June 1911. He shot himself after that.
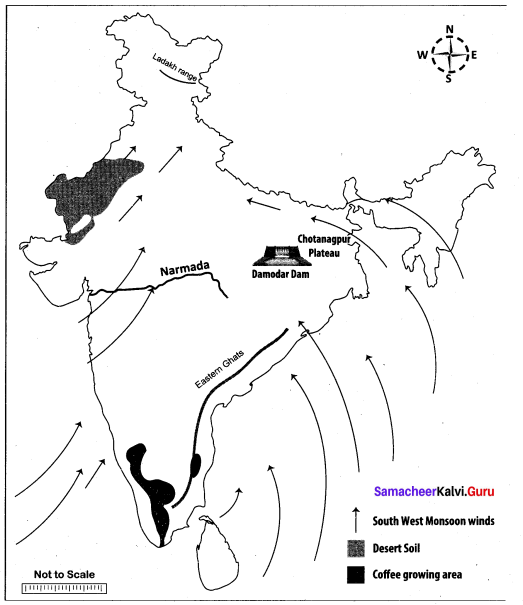
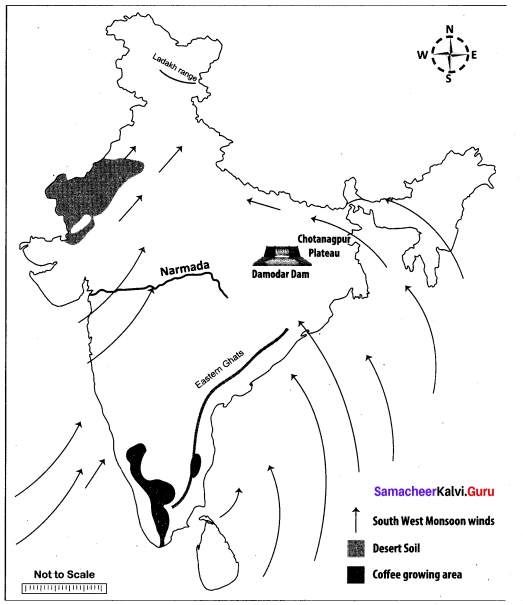
Question 44.
Mark the following places on the given outline map of India.
(i) Ladakh range
(ii) Eastern Ghats
(iii) River Narmada
(iv) Chotanagpur Plateau
(v) South west Monsoon Winds
(vi) Coffee growing area
(vii) Desert Soil
(viii) Damodar dam
Answer:
[OR]
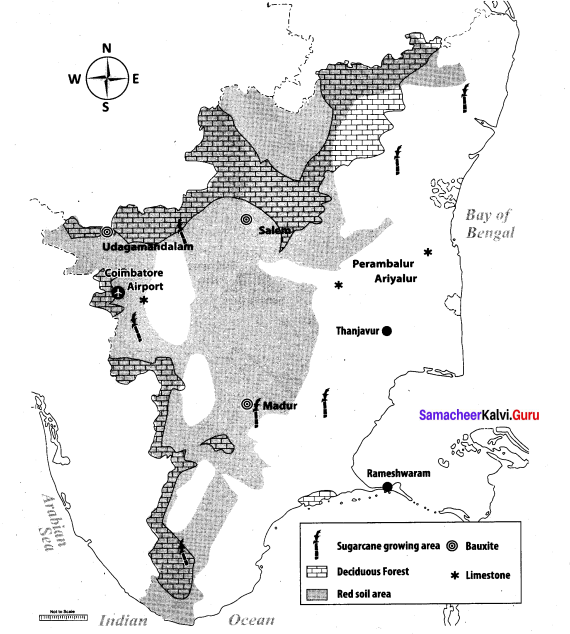
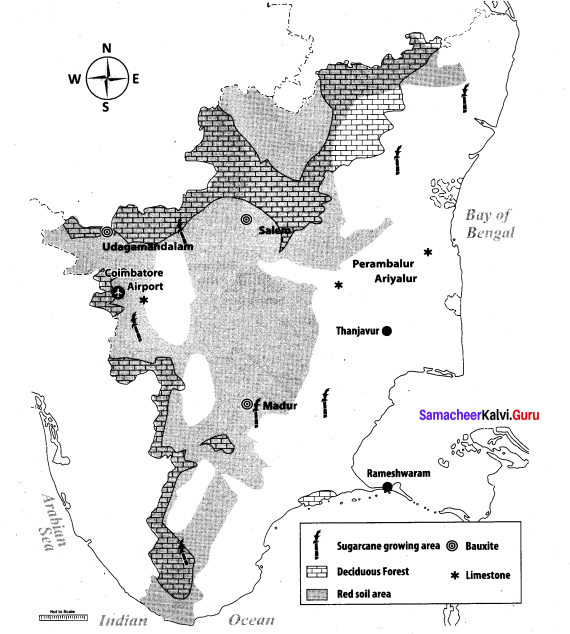
Mark the following places on the given outline map of Tamil Nadu:
(i) Red soil area
(ii) Deciduous forest
(iii) Thanjavur
(iv) Sugarcane growing area
(v) Bauxite area
(vi) Lime stone area
(vii) Rameshwaram
(viii) Coimbatore airport
Answer:
![]()
Map for Q. 42
(i) Egypt
(ii) Finland
(iii) Hungary
(iv) Syria
(v) Great Britain
Answer:
Map for Q.44
(i) Ladakh range
(ii) Eastern Ghats
(iii) River Narmada
(iv) Chotanagpur Plateau
(v) South west Monsoon Winds
(vi) Coffee growing area
(vii) Desert Soil
(viii) Damodar dam
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
(i) Red soil area
(ii) Deciduous forest
(iii) Thanjavur
(iv) Sugarcane growing area
(v) Bauxite area
(vi) Lime stone area
(vii) Rameshwaram
(viii) Coimbatore airport
Answer: