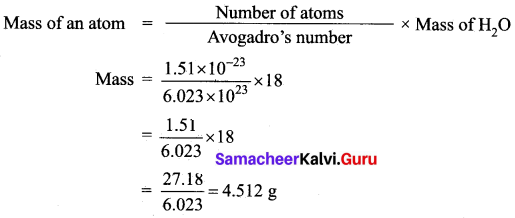
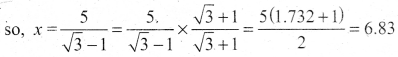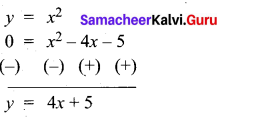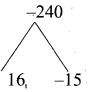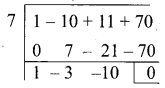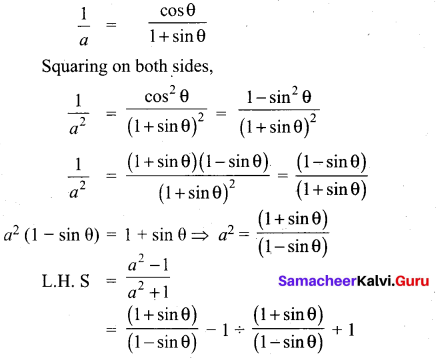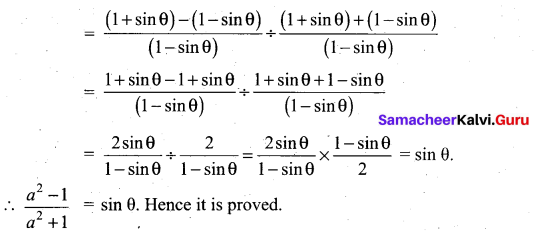Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Instructions
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Quèstions of one-mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and.writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II àre two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are eight-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 100
PART-I
I. Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [Answers are in bold] [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
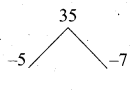
If n(A × B) = 6 and A = {1, 3} then n (B) is ………….. .
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 6
Answer:
(3) 3
![]()
Question 2.
Given F1 = 1, F2 = 3 and Fn = Fn-1+ Fn-2 then F5 is ………….. .
(1) 3
(2) 5
(3) 8
(4) 11
Answer:
(4) 11
Question 3.
In an A.P., the first term is 1 and the common difference is 4. How many terms of the A.P must be taken for their sum to be equal to 120?
(1) 6
(2) 7
(3) 8
(4) 9
Answer:
(3) 8
Question 4.
f = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, b), (5, c)} is a ………….. .
(1) identity function
(2) one-one function
(3) many-one function
(4) constant function
Answer:
(3) many-one function
Question 5.
The number of points of intersection of quadratic polynomial x2 + 4x + 4 with the x axis is ………….. .
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) 0 (or) 1
(4) 2
Answer:
(2) 1
![]()
Question 6.
The non-diagonal elements in any unit matrix are ………….. .
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) m
(4) n
Answer:
(1) 0
Question 7.
If A is a 2′ 3 matrix and B is a 3′ 4 matrix, how many columns does AB have?
(1) 3
(2) 4
(3) 2
(4) 5
Answer:
(2) 4
Question 8.
In figure CP and CQ are tangents to a circle with centre at O. ARB is another tangent touching the circle at R. If CP = 11 cm and BC = 7 cm then the length of BR is ………….. .
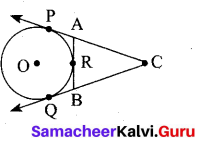
(1) 6 cm
(2) 5 cm
(3) 8 cm
(4) 4 cm
Answer:
(4) 4 cm
Question 9
The slope of the line joining (12, 3), (4, a) is \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\). The value of ‘a’ is ………….. .
(1) 1
(2) 4
(3) -5
(4) 2
Answer:
(4) 2
![]()
Question 10.
If x = a tan θ and y = b sec θ then ………….. .
(1) \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\)
(2) \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\)
(3) \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\)
(4) \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=0\)
Answer:
(1) \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\)
Question 11.
A letter is chosen at random from the letter of the word “PROBABILITY”. Find the probability that it is not a vowel.
(1) \(\frac{1}{5}\)
(2) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(3) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(4) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Answer:
(2) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 12.
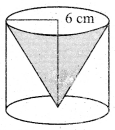
The height of a right circular cone whose radius is 5 cm and slant height is 13 cm will be ………….. .
(1) 12 cm
(2) 10 cm
(3) 13 cm
(4) 5 cm
Answer:
(1) 12 cm
Question 13.
If the mean and co-efficient of variation of a data are 4 and 87.5% then the standard deviation is ………….. .
(1) 3.5
(2) 3
(3) 4.5
(4) 2.5
Answer:
(1) 3.5
![]()
Question 14.
Variance of first 20 natural numbers is ………….. .
(1) 32.25
(2) 44.25
(3) 33.25
(4) 30
Answer:
(3) 33.25
PART-II
II. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 × 2 = 20]
Question 15.
Define a function.
Answer:
A relation “f” between two non-empty sets X and Y is called a function from X to Y if for each x ∈ X there exists only one y ∈ Y such that (x, y) ∈ f
Question 16.
Compute x such that 104 ≡ x (mod 19)
Answer:
102 = 100 ≡ 5 (mod 19)
104 = (102)2 ≡ 52 (mod 19)
104 = 25 (mod 19)
104 = 6 (mod 19)
(since 25 ≡ 6 (mod 19))
Therefore, x = 6
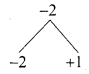
Question 7.
Simlify \(\frac{4 x^{2} y}{2 z^{2}} \times \frac{6 x z^{3}}{20 y^{4}}\)
Answer:
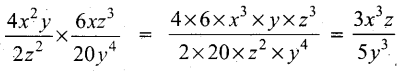
Question 18.
Pari needs 4 hours to complete the work. His friend Yuvan needs 6 hours to complete the work. How long will it take to complete if they work together?
Answer:
Let the work done by Pari and Yuvan together be x
Work done by Pari = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
Work done by Yuvan = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
By the given condition
\(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{6}=\frac{1}{x} \Rightarrow \frac{3+2}{12}=\frac{1}{x}\)
\(\frac{5}{12}=\frac{1}{x}\)
5x = 12 ⇒ x = \(\frac{12}{5}\)
x = \(2 \frac{2}{5}\) hours (or) 2 hours 24 minutes
![]()
Question 19.
Find the values of x, y and z from the following equation \(\left( \begin{matrix} 12 & 3 \\ x & \frac { 3 }{ 2 } \end{matrix} \right) =\left( \begin{matrix} y & z \\ 3 & 5 \end{matrix} \right) \)
Answer:
Since the given matrices are equal then all the corresponding elements are equal. y = 12, z = 3, x = 3
The value of x = 3, y = 12 and z = 3
Question 20.
What length of ladder is needed to reach a height of 7 ft along the wall when the base of the ladder is 4 ft from the wall? A
Answer:
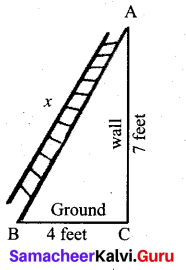
Let x be the length of the ladder. BC = 4 ft, AC = 7 ft.
By Pythagoras theorem we have, AB2 = AC2 + BC2
x2 = 72 + 42 gives x2 = 49 + 16
x2 = 65. Hence, x = √65
The number √65 is between 8 and 8.1.
82 = 64 < 65 < 65.61 = 8.12
Therefore, the length of the ladder is approximately 8.1 ft.
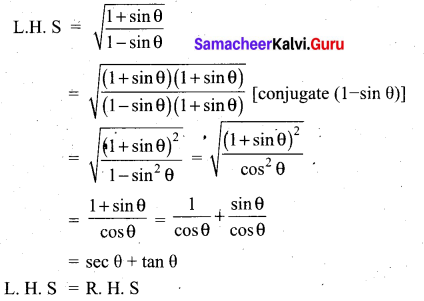
Question 21.
Prove that \(\sqrt{\frac{1+\cos \theta}{1-\cos \theta}}\) = cosec θ + cot θ
Answer:
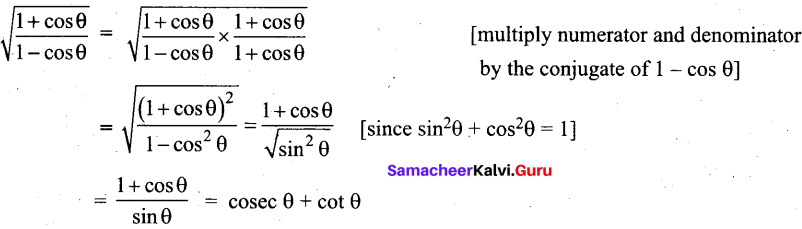
![]()
Question 22.
The radius of a sphere increases by 25%. Find the percentage increase in its surface area.
Answer:
Let the radius of the be “r”
Surface area of the sphere = 4πr2sq.units …… (1)
If the radius is increased by 25%
New radius = \(\frac { 25 }{ 100 }\) × r + r
= \(\frac { r }{ 4 }\) + 4
= \(\frac{r+4 r}{4}=\frac{5 r}{4}\)
Surface area of the sphere
= 4π\(\left(\frac{5 r}{4}\right)^{2}\) sq.units
= 4 × π × \(\frac{25 r^{2}}{16}\)
= \(\frac{25 \pi r^{2}}{4}\) sq.units
Difference in surface area
= \(\frac{25 \pi r^{2}}{4}-4 \pi r^{2}\)
= \(\pi r^{2}\left(\frac{25}{4}-4\right)\)
= \(\pi r^{2}\left(\frac{25-16}{4}\right)\)
= \(\pi r^{2}\left(\frac{9}{4}\right)=\frac{9 \pi r^{2}}{4}\)
Percentage of increase in surface area
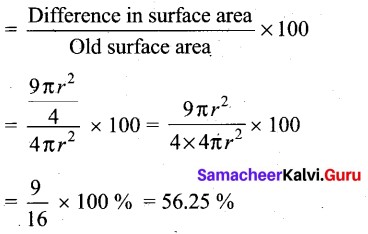
Percentage of increase in surface area = 56.25%
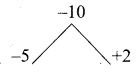
Question 23.
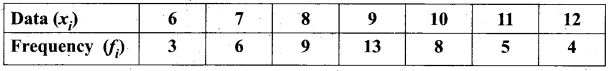
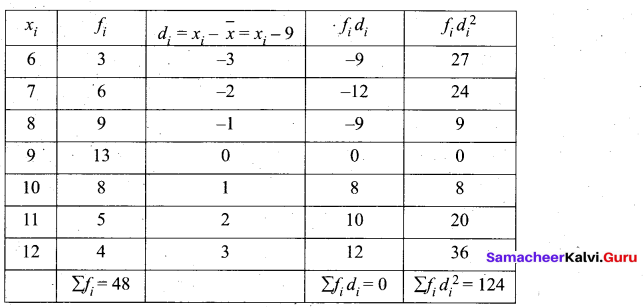
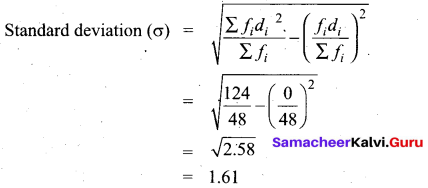
The standard deviation and mean of a data are 6.5 and 12.5 respectively. Find the coefficient of variation.
Answer:
Standard deviation of a data (σ) = 6.5
Mean of the data (x̄) = 12.5
Coefficient of variation = \(\frac{\sigma}{x} \times 100 \%\) ⇒ \(\frac{6.5}{12.5} \times 100 \%\) = 52%
Coefficient of variation = 52%
![]()
Question 24.
If f{x) = 3 + x, g(x) = x – 4, then check whether fog = gof
Answer:
f(x) = 3 + x ; g(x) = x – 4
fog = f[g(x)]
= f(x – 4)
= 3 + x – 4
= x – 1
gof = g [f(x)}
= g(3 + x)
= 3 + x – 4
= x – 1
∴ fog = gof
Question 25.
An organization plans to plant saplings in 25 streets in a town in such a way that one sapling for the first street, three for the second, nine for the third and so on. How many saplings are needed to complete the work?
Answer:
Here n = 25, a = 1, r = 3
Sn = \(a \frac{\left(r^{n}-1\right)}{r-1}\)
S25 = \(\frac{1\left(3^{25}-1\right)}{3-1}\)
= \(\frac{3^{25}-1}{2}\)
Question 26.
Find the 19th term of an A.P. – 11, -15, -19,……..
Answer:
First term (a) = -11
Common difference (d) = -15 – (-11)
= -15 + 11 = -4
n = 19 .
tn = a + (n – 1) d
tn = -11 + 18(-4)
= -11 – 72
t19 = -83
∴ 19th term of an A.P. is – 83
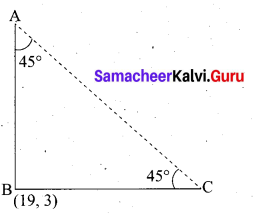
Question 27.
Find the value of ZB AC in the given triangle.
Answer:
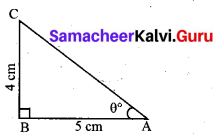
In right triangle ABC

θ = tan-1 \(\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)\) = tan-1 (0.8)
θ = 38.7° (since tan 38.7° = 0.8011)
∠BAC = 38.7°
Question 28.
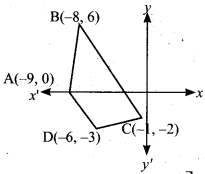
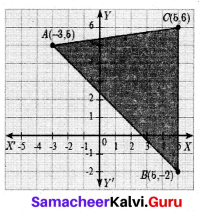
The vertices of a triangle are A(-1,3), B(-1, 1) and C(5, 1). Find the length of the median through the vertex C.
Answer:
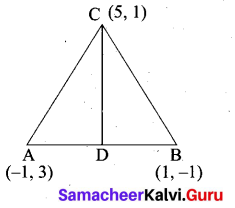
Mid point of AB = \(\left(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}, \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{-1+1}{2}, \frac{3-1}{2}\right)\)
= (0,1)
Length of the median CD = \(\sqrt{\left(x_{2}-x_{1}\right)^{2}+\left(y_{2}-y_{1}\right)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{(5-0)^{2}+(1-1)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{25}\) = 5
![]()
PART – III
III. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 × 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Let f be a function f : N → N be defined by f(x) = 3x + 2, x ∈ N
(i) Find the images of 1, 2,3
(ii) Find the pre – images of 29, 53
(iii) Identify the type of function.
Answer:
The function f: N → N is defined by f(x) = 3x + 2
(i) If x = 1, f(1) = 3(1) + 2 = 5
If x = 2, f(2) = 3(2) + 2 = 8
If x = 3, f(3) = 3(3) + 2=11
The images of 1, 2, 3 are 5, 8, 11 respectively.
(ii) If x is the pre-image of 29, then f(x) = 29 . Hence 3x + 2 = 29
3x = 21 ⇒ x = 9.
Similarly, if x is the pre-image of 53, then f(x) = 53.
Hence 3x + 2 = 53 3x = 51 ⇒ x = 17.
Thus the pre-images of 29 and 53 are 9 and 17 respectively.
(iii) Since different elements of N have different images in the co-domain, the function f is one – one function.
The co-domain of f is N.
But the range of f = {5, 8, 11, 14, 17,…} is a proper subset of N.
Therefore f is not an onto function. That is, f is an into function.
Thus f is one – one and into function.
Question 30.
Let f: A → B be a function defined by f(x) = \(\frac { x }{ 2 }\) – 1, where A = {2,4,6,10,12} and B = {0,1,2, 4,5,9}. Represent f by
(i) set of ordered pairs (ii) a table (iii) an arrow diagram (iv) a graph
Answer:
A= {2, 4, 6, 10, 12} and B = {0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 9}
f(x) = \(\frac { x }{ 2 }\) – 1
f(2) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 2 }\) – 1 = 1 – 1 = 0
f(4) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 2 }\) – 1 = 2 – 1 = 1
f(6) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 }\) – 1 = 3 – 1 = 2
f(10) = \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 }\) – 1 = 5 – 1 = 4
f(12) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 2 }\) – 1 = 6 – 1 = 5
(i) Set of ordered pairs
f = {(2, 0) (4, 1) (6, 2) (10, 4) (12, 5}
(ii) Table
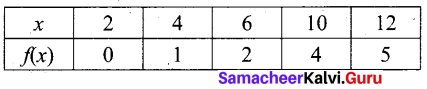
(iii) Arrow diagram
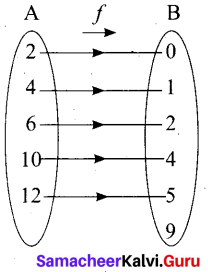
(iv) Graph
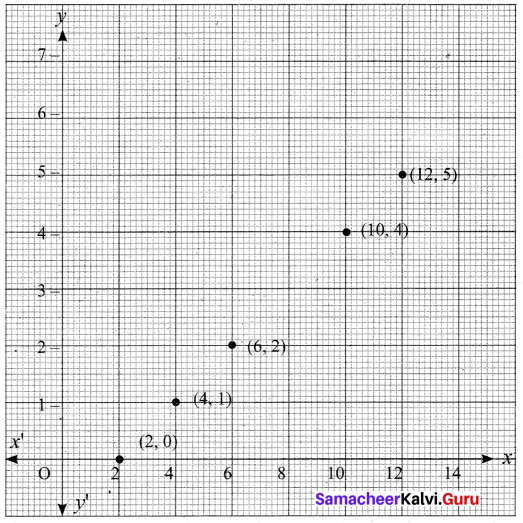
![]()
Question 31.
The ratio of 6th and 8th term of an A.P is 7:9. Find the ratio of 9th term to 13th terms.
Answer:
Given t6 : t8 = 7 : 9 (using tn = a + (n – 1)d
a + 5d : a + 7d =7 : 9
9(a + 5d) = 7(a + 7d)
9a + 45d = 7a + 49d
9a – 7a = 49d – 45d
2a = 4d
a = 2d
To find t9 : t13
t9 : t13 = a + 8d : a + 12d
= 2d + 8d : 2d + 12d
= 10d : 14d
= 5 : 7
∴ t9 : t13 = 5 : 7
Question 32.
The sum of first n, In and 3n terms of an A.P. are S1 S2 and S3 respectively. Prove that S3 = 3 (S2 – S1).
Answer:
If S1 S7 and S3 are sum of first n, 2n and 3n terms of an A.P. respectively then
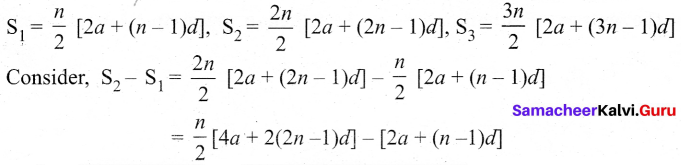
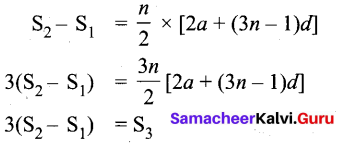
Question 33.
Find the values of m and n if the exprtession \(\frac{1}{x^{4}}-\frac{6}{x^{3}}+\frac{13}{x^{2}}+\frac{m}{x}+n\) is a perfect a square.
Answer:
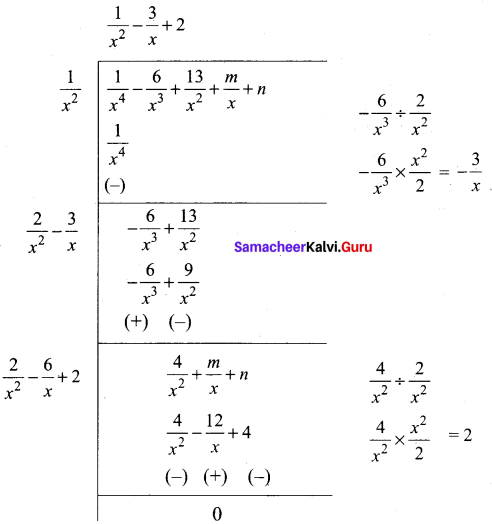
Since it is a perfect square
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)(m + 12) = 0
m + 12 = 0
m = -12
n – 4 = 0
n = 4
∴ The value of m = -12 and n = 4
![]()
Question 34.
If α, β are the roots of the equation 2x2 – x – 1 = 0 then form the equation whose roots are α2β, β2α.
Answer:
2x2 – x – 1 = 0 ⇒ Here a = 2, b = -1,c = -1
α + β = \(\frac{-b}{a}=\frac{-(-1)}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
α + β = \(\frac{c}{a}=\frac{-1}{2}\)
Given roots are α2β, β2α
Summ of the roots α2β + β2α = αβ (α + β) = \(-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=-\frac{1}{4}\)
Product of the roots (α2β) × (β2α) = α3β3 = (αβ)3 =
\(\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{3}=-\frac{1}{8}\)
The required equation is x2 – (Sum of the roots) x + (Product of the roots) = 0
\(x^{2}-\left(-\frac{1}{4}\right) x-\frac{1}{8}=0\) gives 8x2 + 2x – 1 = 0
Question 35.
P and Q are the mid-points of the sides CA and CB respectively of a ∆ABC, right angled at C. Prove that 4(AQ2 + BP2) = 5AB2.
Answer:
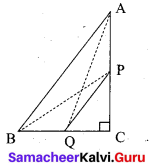
Since, ∆AQC is a right triangle at C, AQ2 = AC2 + QC2 ……. (1)
Also, ∆BPC is a right triangle at C, BP2 = BC2 + CP2 ……… (2)
From (1) and (2), AQ2 + BP2 = AC2 + QC2 + BC2 + CP2
4(AQ2 + BP2) = 4AC2 + 4QC2 + 4BC2 + 4CP2
= 4AC2 + (2QC)2 + 4BC2 + (2CP)2
= 4AC2 + BC2 + 4BC2 + AC2 (Since P and Q are mid points)
= 5(AC2 + BC2)
4(AQ2 + BP2) = 5AB2 (By Pythagoras Theorem)
Question 36.
Find the equation of a straight line passing through (1, -4) and has intercepts which are in the ratio 2:5.
Answer:
Let the x-intercept be 2a and the y intercept 5a
The equation of a line is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{a}=1\) ⇒ \(\frac{x}{2 a}+\frac{y}{5 a}=1\)
The line passes through the point (1, -4)
\(\frac{1}{2 a}+\frac{(-4)}{5 a}=1\) ⇒ \(\frac{1}{2 a}-\frac{4}{5 a}=1\)
Multiply by 10a
(L.C.M of 2a and 5a is 10a)
5 – 8 = 10a ⇒ -3 = 10a ⇒ a = \(\frac{-3}{10}\)
The equation of the line is \(\frac{x}{2(-3 / 10)}+\frac{y}{5(-3 / 10)}=1\)
\(\frac{x}{-3 / 5}+\frac{y}{-3 / 2}=1\) ⇒ \(\frac{5 x}{-3}+\frac{2 y}{-3}=1\)
\(\frac{-5 x}{3}-\frac{2 y}{3}=1\)
Multipy by 3
– 5x – 2y = 3 ⇒ – 5x – 2y – 3 = 0
5x + 2y + 3 = 0
The equation of a line is 5x + 2y + 3 = 0
![]()
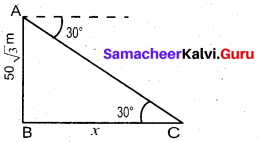
Question 37.
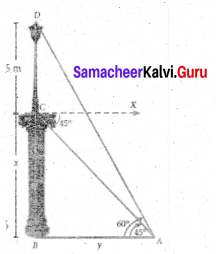
From the top of the tower 60m high the angles of depression of the top and bottom of a vertical lamp post are observed to be 38° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the lamp post (tan 38° = 0.7813, √3 = 1.732)
Answer:
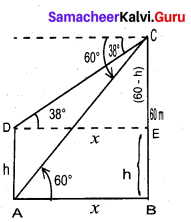
Let the height of the lamp post be “h”
The height of the tower (BC) = 60 m
∴ EC = 60 – h
Let AB be x
In the right ∆ ABC
tan 60° = \(\frac{B C}{A B}\)
√3 = \(\frac{60}{x}\)
x = \(\frac{60}{\sqrt{3}}\) …… (1)
In the right ∆ DEC, tan 38° = \(\frac{E C}{D E}\)
0.7813 = \(\frac{60-h}{x}\)
x = \(\frac{60-h}{0.7813}\) ….. (2)
Froom (1) and (2) we get
\(\frac{60}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{60-h}{0.7813}\)
60 × 0.7813 = 60√3 – √3h
46.88 = 60√3 – √3h
√3h = 60√3 – 46.88
= 60 × 1.732 – 46.88
= 103.92 – 46.88
1.732 h = 57.04 ⇒ h = \(\frac{57.04}{1.732}\)
h = \(\frac{5704}{1732}\) = 32.93m
∴ Height of the lamp post = 32.93 m
Question 38.
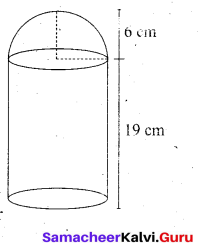
Calculate the weight of a hollow brass sphere if the diameter is 14 cm and thickness is 1 mm, and whose density is 17.3 g/cm3.
Answer:
Let r and R be the inner and outer radii of the hollow sphere.
Given that, inner diameter d = 14 cm; inner radius r = 7 cm; thickness = 1 mm = \(\frac{1}{10}\) cm
Outer radius R = 7 + \(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{71}{10}\) = 7.1 cm
Volume of hollow sphere = \(\frac{4}{3}\) π (R3 – r3) cu. cm
= \(\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7}\)(357.91 -343) = 62.48 cm3
But, weight of brass in 1 cm3 = 17.3 gm
Total weight = 17.3 × 62.48 = 1080.90 gm
Therefore, total weight is 1080.90 grams.
![]()
Question 39.
Find the Co-efficient of variation of 24, 26,33,37,29,31
Answer:
Arrange in ascending order we get 24, 26,29, 31,33,37
Assumed mean = 29
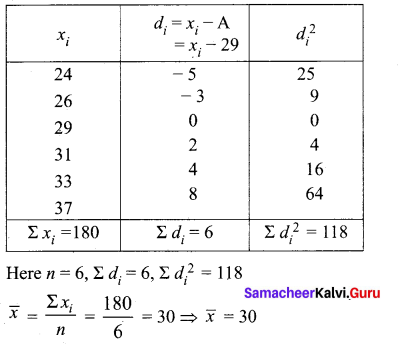
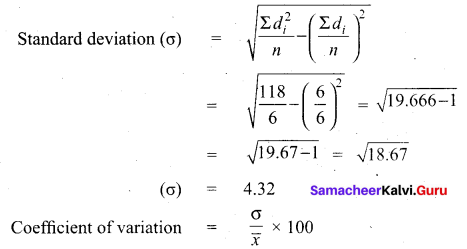
\(\frac{4.32}{30} \times 100\) = \(\frac{432}{30}=14.4\)
Coefficient of variation = 14.4%
Question 40.
Two dice, one blue and one grey, are thrown at the same time. Write down all the possible outcomes. W hat is the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is ………………. .
Answer:
When we roll two dice
Sample space = {(1. 1) (1,2) (1, 3) (1, 4) (1, 5) (1, 6)
(2, 1) (2, 2) (2, 3) (2, 4) (2, 5) (2, 6)
(3, 1) (3, 2) (3, 3) (3, 4) (3, 5) (3, 6)
(4, 1) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 4) (4, 5) (4, 6)
(5, 1) (5, 2) (5, 3) (5, 4) (5, 5) (5, 6)
(6, 1) (6, 2) (6, 3) (6. 4) (6, 5) (6, 6)}
n(S) = 36
(i) Let A be the event of getting the sum of two number is 8
A = {(2, 6) (3, 5) (4, 4) (5, 3) (6, 2)} 5
n(A) = 5
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{5}{36}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting the sum of the two numbers is 13.
B = { }
n(B) = 0
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{0}{36}=0\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting the sum of the two numbers is less than 12 or equal to 12.
n(C) = 36
P(C) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{C})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{36}{36}=1\)
Question 41.
Find two consecutive positive integers, sum of whose squares is 365.
Answer:
Let the two consecutive positive integers be “x” and x + 1
Sum of squares = 365
x2 + (x+1)2 = 365
2x2 + 2x – 364 = 0
x2 + x – 182 = 0
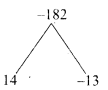
(x + 14) (x – 13) = 0
x + 14 = 0 or x – 13 = 0
x = -14 or x = 13 (rejecting -14. Given positive integer)
The consecutive terms are 13 and 14.
![]()
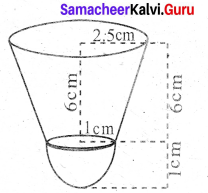
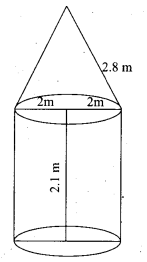
Question 42.
A cylindrical bucket of 32 cm high and with radius of base 18 cm, is filled with sand completely. This bucket is emptied on the ground and a conical heap of sand is formed. If the height of the conical heap is 24 cm, find the radius and slant height of the heap.
Answer:
Cylindrical bucket
Height of the bucket (h) = 32 cm
Radius of the bucket (r) = 18 cm
Conical heap
Height of the cone (H) = 24 cm
Let the radius of the conical heap be “P ”
By the given condition
Volume of the conical heap = Volume of the cylindrical bucket
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)πR2H = πr2
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) × R2 × 24 = r2H
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) × R2 × 24 = 18 × 18 × 32
R2 = \(\frac{18 \times 18 \times 32 \times 3}{24}\)
= \(\frac{18 \times 18 \times 4 \times 3}{3}\)
= 18 × 18 × 4
= 36 cm
Slant height of the cone (l) = \(\sqrt{H^{2}+R^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{24^{2}+36^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{(12 \times 2)^{2}+(12 \times 3)^{2}}\)
= 12\(\sqrt{2^{2}+3^{2}}\)
= 12√13
Slant height of the cone = 12√13 cm
Radius of the cone = 36 cm
PART – IV
IV. Answer all the questions. [2 × 8 = 16]
Question 43.
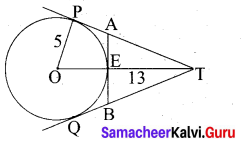
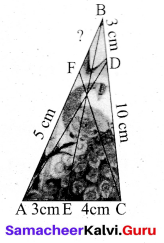
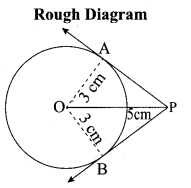
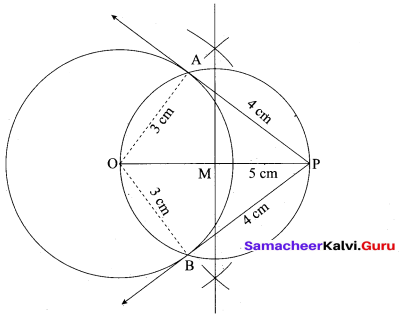
(a) PQ is a chord of length 8 cm to a circle of radius 5 cm. The tangents at P and Q intersect at a point T. Find the length of the tangent TP.
Answer:
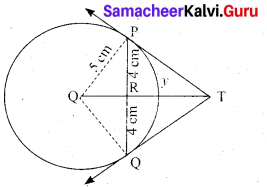
Let TR = y. Since, OT is perpendicular bisector of PQ
PR = QR = 4 cm
In ∆ORP, OP2 = OR2 + PR2
QR2 = OP2 – PR2
OR2 = 52 – 42 = 25 – 16 = 9
OR = 3 cm
OT = OR + RT = 3 + y …. (1)
In ∆PRT , TP2 = TR2 + PR2 …. (2)
and ∆OPT we have, OT2 = TP2 + OP2
OT2 = (TR2 + PR2) + OP2 (substitute for TP2 from (2)
(3 + y)2 = y2 + 42 + 52(substitute for OT from (1))
9 + 6y + y2 = y2 + 16 + 5 There fore y = TR = \(\frac{16}{3}\)
6y = 41 – 9 we get y = \(\frac{16}{3}\)
From (2) TP2 = TR2 + PR2
TP2 = \(\left(\frac{16}{3}\right)^{2}+4^{2}=\frac{256}{9}+16=\frac{400}{9} \mathrm{so}, \mathrm{TP}=\frac{20}{3} \mathrm{cm}\)
![]()
[OR]
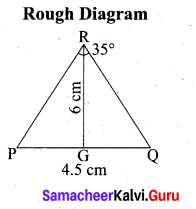
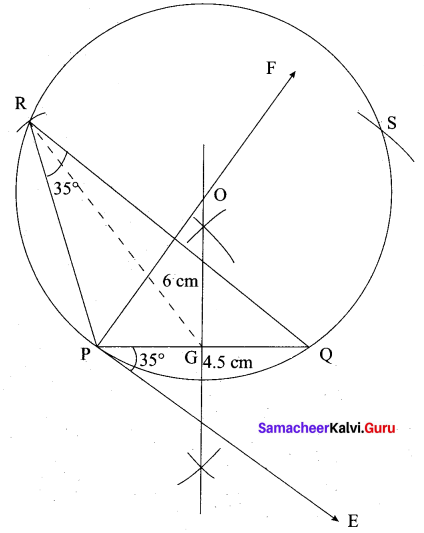
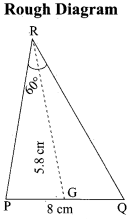
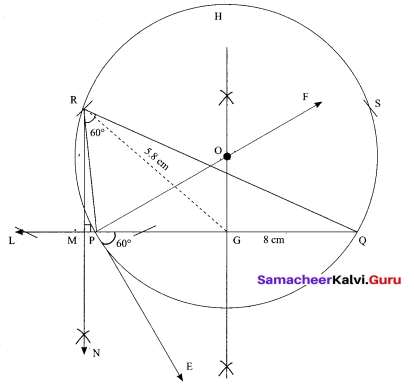
(b) Draw a triangle ABC of base BC = 8 cm, ∠A = 60° and the bisector of ∠A meets BC at D such that BD = 6 cm.
Answer:
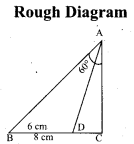
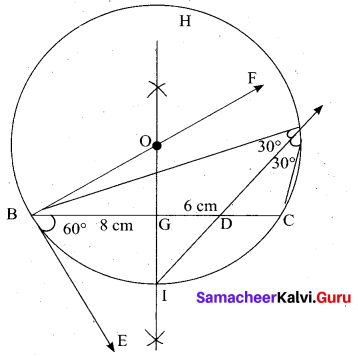
Step 1 : Draw a line segment BC = 8 cm.
Step 2 : At B, draw’ BE such that ∠CBE = 60° .
Step 3 : At B, draw BF such that ∠EBF = 90° .
Step 4 : Draw the perpendicular bisector to BC, w’hich intersects BF at O and BC at G.
Step 5 : With O as centre and OB as radius draw a circle.
Step 6 : From B, mark an arc of 6 cm on BC at D.
Step 7 : The perpendicular bisector intersects the circle at I. Joint ID.
Step 8 : ID produced meets the circle at A. Now join AB and AC.
Then ∆ABC is the required triangle.
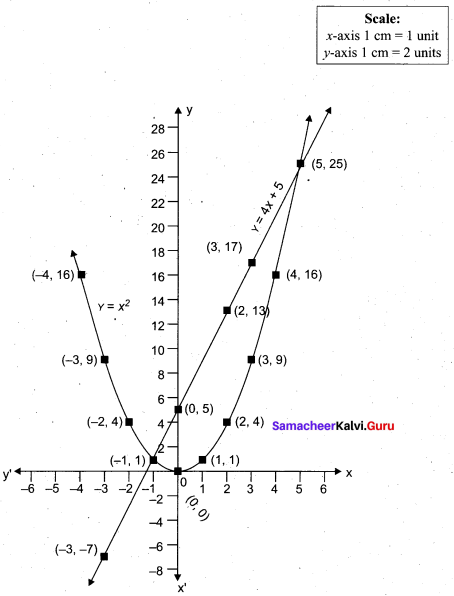
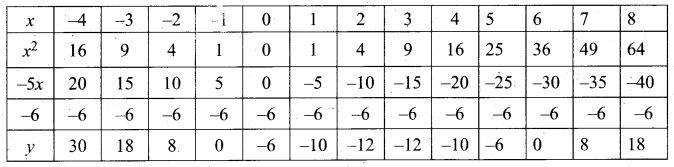
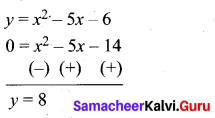
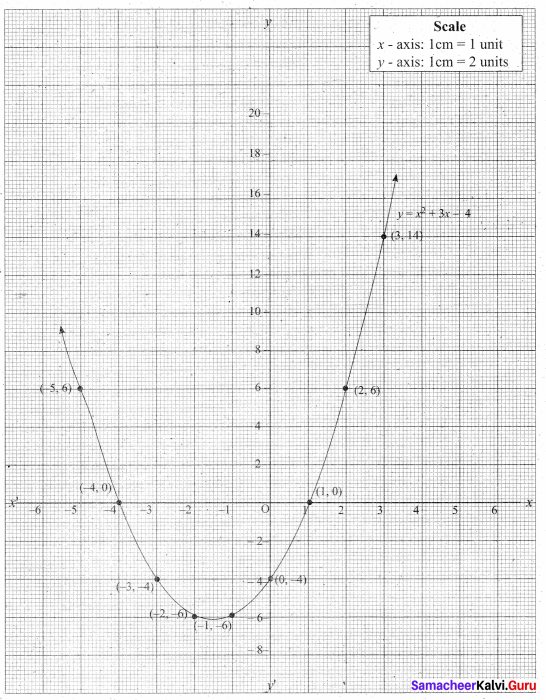
Question 44.
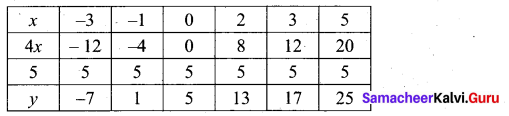
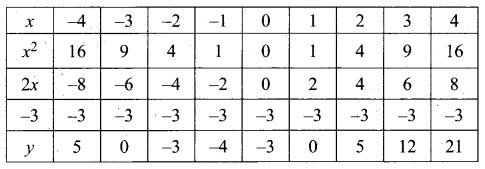
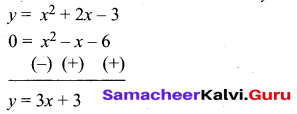
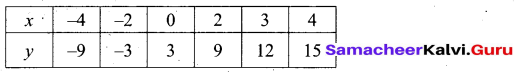
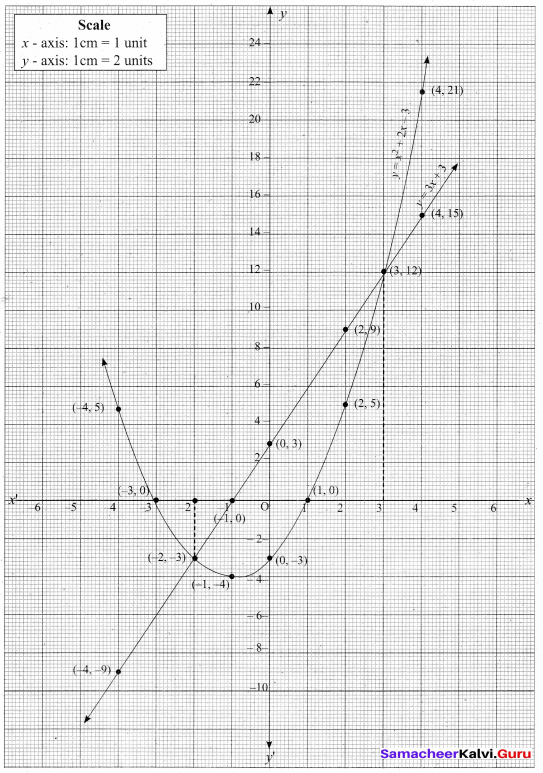
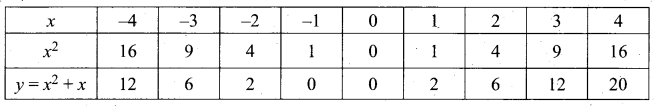
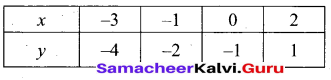
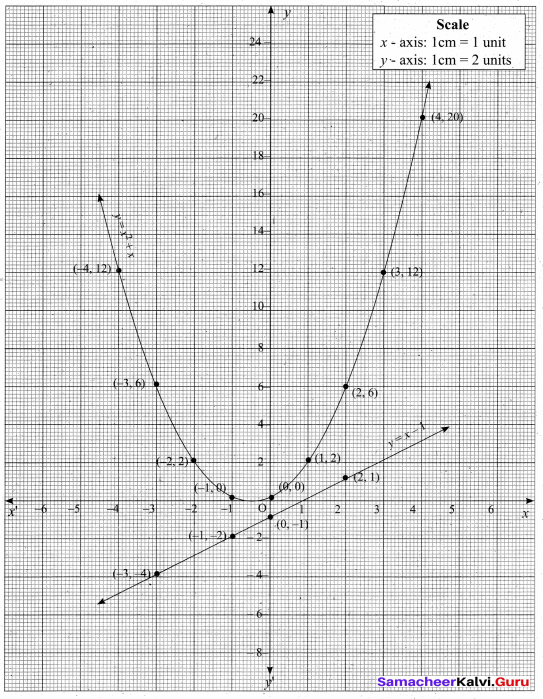
(a) Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x – 4 and hence use it to solve x2 + 3x – 4 = 0.
Answer:
Let y = x2 + 3x – 4
(i) Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x – 4
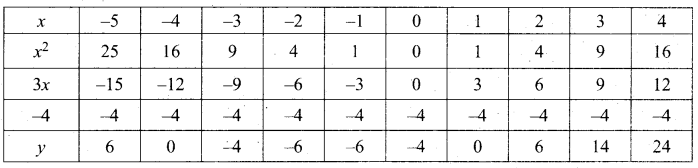
(ii) Plot the points (-5, 6), (-4, 0), (-3, -4), (-2, -6), (-1, -6), (0, -4), (1, 0), (2, 6), (3, 14) on the graph using suitable scale.
(iii) Join the points by a free hand smooth curve.
The smooth curve is the graph of y = x2 + 3x – 4
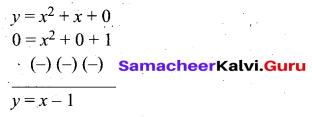
(iv) To solve x2 + 3x – 4 = 0, subtract x2 + 3x – 4 = 0 from y = x2 + 3x – 4.
y = o
∴ The point of intersection with the X – axis is the solution set.
The solution set is -4 and 1.
[OR]
![]()
(b) A motor boat whose speed is 18 km/hr in still water takes 1 hour more to go to 24 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream.
Answer:
Let the speed of the stream be “x” km/hr
Speed of the motor boat to go for upstream = (18 – x) km/hr
Speed of the motor boat to go for down stream = (18 + x) km/hr
Time taken to go for upstream = \(\frac{24}{18-x}\) hour
Time taken to go for down stream = \(\frac{24}{18-x}\)
By the given condition
\(\frac{24}{18-x}-\frac{24}{18+x}=1\)
\(\frac{24(18+x)-24(18-x)}{(18-x)(18+x)}=1\)
432 + 24x + 432 + 24x = (18 – x)(18 – x)
48x = 324 – x2
x2 + 48x – 324 = 0
x2 + 54x – 6x – 324 = 0
x(x + 54) – 6 (x + 54) = 0
(x + 54) (x – 6) = 0
x + 54 = 0 or x – 6 = 0
x = -54 or x = 6 (speed cannot be negative)
∴ Speed of the boat = 6 km/hr