Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions Prose Chapter 7 The Dying Detective
You can Download The Dying Detective Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf Prose Chapter 7 help you to revise complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Attempt all english grammar practice sections covered in the Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Grammar Book and excel in reading, writing, and speaking english with great fluency.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions Prose Chapter 7 The Dying Detective
The Dying Detective Warm up:
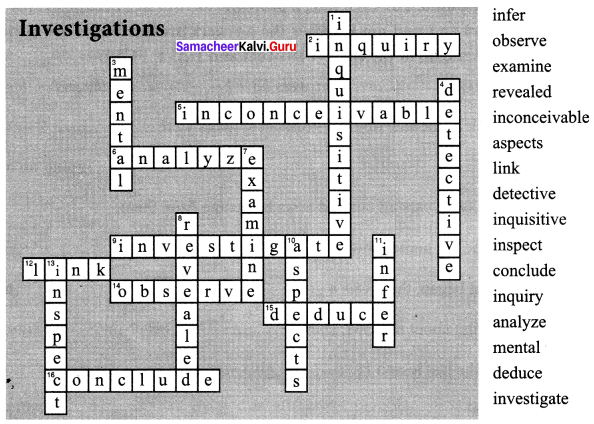
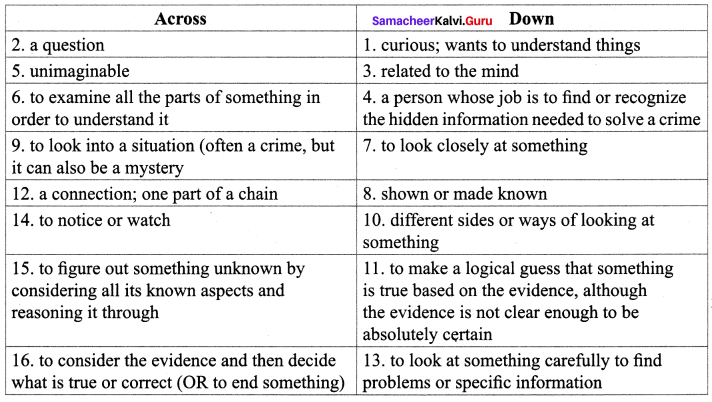
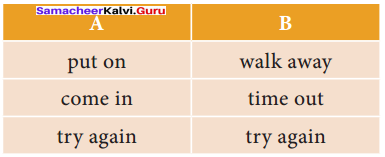
1. Solve the crossword using the list of words and the clues.
Answer:
The Dying Detective Intext Questions
Question a.
How did Watson feel when he heard of Holme’s illness?
Answer:
Watson felt horrified when he heard of Holme’s illness.
Question b.
Why didn’t the landlady call the doctor?
Answer:
The landlady didn’t call the doctor because Holmes would not allow her to bring one.
Question c.
What was the condition of Holmes when Watson saw him?
Answer:
When Watson saw Holmes, his eyes had the brightness of fever, his cheeks were flushed and his hand twitched all the time.
Question d.
According to Holmes what was the disease he was suffering from?
Answer:
Holmes was suffering from Tarpaunli fever or black Formosa plague.
Question e.
Who did Watson see when he entered the room?
Answer:
Watson saw the butler when he entered the room.
Question f.
What were the instructions given by Holmes to Watson?
Answer:
Holmes did not want Watson to go before six. He asked Watson to persuade Smith to come, to tell Smith that Holmes was dying and force Smith to come. Watson should return to Holmes’ house, before Smith’s arrival. He asked Watson to light the gas and keep it half-on.
Question g.
Why did Holmes plead with Smith?
Answer:
Holmes pleaded with Smith to get a cure for his deadly disease.
Question h.
Who was responsible for Victor Savage’s death? What was the evidence for it?
Answer:
Culverton Smith was responsible for Victor Savage’s death. The ivory box was the last piece of evidence of it.
Question i.
What explanation did Holmes give for speaking rudely to Watson?
Answer:
Holmes explained to Watson that he had spoken rudely to Watson because he didn’t want Watson to know that he was not ill.
Question j.
How was Holmes able to look sick?
Answer:
Holmes starved for three days without food and water to look really sick.
The Dying Detective Textual Questions
A. Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
Who was Mrs. Hudson? Why was she worried?
Answer:
Mrs. Hudson was the landlady of Holmes. She was worried of Holmes illness.
Question 2.
Why didn’t Holmes let Watson examine him?
Answer:
Holmes didn’t let Watson examine him by telling him that he was suffering from a deadly and contagious disease. In fact, Holmes was acting as if he was a sick person. If Watson examined him, he would know that Holmes was not ill.
Question 3.
Why did Holmes warn Watson against touching his things? What was Watson’s reaction?
Answer:
Holmes warned Watson because he hated his things to be touched by others. Eventually, Watson sat in silent dejection.
Question 4.
What did Watson find on the table near the mantelpiece?
Answer:
Watson found a small black and white ivory box with a sliding lid, on the mantelpiece.
Question 5.
Who is Mr. Culverton Smith?
Answer:
Mr. Culverton Smith is a planter. He lives in Sumatra. He murdered his nephew Victor savage.
Question 6.
What did Holmes ask Watson to do before leaving his room?
Answer:
Holmes asked Watson to put the money in his pockets, light the gas lamp half on, and place some letters and paper on the table. He also asked him to place the ivory box within his reach.
Question 7.
What instructions did Holmes give Watson to get Mr. Smith?
Answer:
Holmes asked Watson to convince Mr. Smith to bring to Holmes, house to cure him.
Question 8.
Why did Holmes want Smith to treat him?
Answer:
Holmes wanted Smith, to treat him because he was the only man with the knowledge of the disease Holmes was suffering from.
Question 9.
According to Smith how did Holmes get the disease?
Answer:
According to Smith, Holmes got the illness by touching the sharp spring inside the box.
Question 10.
Who arrested Smith? What were the charges against him?
Answer:
Inspector Morton arrested Smith on charges of murder of Victor Savage.
Additional Questions
Question 1.
How did Holmes show his madness to Dr. Watson?
Answer:
When Dr. Watson offered to examine symptoms and treat him Holmes said he would have a doctor in whom he had confidence. This was really very rude of Holmes and showed his madness.
Question 2.
Why was Smith startled?
Answer:
Smith was startled to know that Holmes was seriously ill. He had sent for him pleading to cure him.
Question 3.
How did Dr. Watson manage to avoid accompanying Smith during his visit to Holmes?
Answer:
Dr. Watson pretended to have some other appointment. Thus he avoided accompanying Mr. Smith during his visit to Holmes.
Question 4.
Who came to visit Holmes when Dr. Watson was waiting for his cab?
Answer:
Mr. Morton Inspector of Scotland Yard in plain clothes had come to visit Holmes.
Question 5.
What was shocking to Dr. Watson?
Answer:
The dying Holmes had the boldness to bolt the door and order him to stay indoors till six p.m.
Question 6.
Who is Victor Savage?
Answer:
Victor Savage is Smith’s nephew. He was murdered by Culverton Smith but was believed to be dead on the fourth day in spite of being a strong and healthy man because of an Eastern disease.
Question 7.
Why didn’t Holmes want Dr. Watson to go before six?
Answer:
Holmes did not want Watson to go and meet Smith before six since he would not be able to find Smith in his study.
Question 8.
Who stopped Dr. Watson at Smith’s house?
Answer:
Dr. Watson was stopped by the butler who appeared at the doorway to Smith’s room.
B. Answer the following questions in about 80 – 100 words.
Question 1.
How did Holmes trap Mr. Culverton Smith to confess the murder?
Answer:
Introduction:
Sherlock Holmes was seriously ill. His housekeeper Mrs. Hudson was worried. The lesson “The Dying Detective” brings out the mystery behind Holme’s illness and how Watson helped to solve the mystery.
Sherlock Holmes on Death Bed:
Sherlock Holmes had been seriously ill for 3 days. His housekeeper wanted to bring in a doctor, but Holmes refused and at last, he asked her to call Dr. Watson.
Dr. Watson arrives:
Dr. Watson arrived and he was shocked to see Holmes lying listless. Holmes did not allow Watson to examine him. Holmes asked Watson to bring a specialist to treat his disease.
Holmes Strange Condition:
When Watson attempted to leave to get the doctor. Holmes asked Watson to sit and leave at 6’0 clock. Watson got bored. He picked up an ivory box. At once, Holmes shouted and asked him to keep the box down and warned him.
Mr. Culverton Smith arrives:
Mr. Culverton Smith arrived and entered the darkroom. Before that Watson had to enter the next room before Smith comes and Holmes asked Watson to leave the gaslight half-on.
The Truth is out:
Mr. Culverton Smith accepted that he only murdered his nephew for the property. He thought that Holmes got the contagious disease by touching the sharp spring inside the box. Now, Holmes asked Watson to turn the gaslight fully. It was a signal for Inspector Morton who was waiting outside. Morton came inside and arrested Smith.
Conclusion:
Holmes explained to Watson that he acted to confess Smith’s crime and asked sorry for behaving rudely to Watson. He didn’t eat food or drink for three days. So he was weak. Thus Watson unknowing helped Holmes to catch smith.
Question 2.
How did Watson help his friend to arrest the criminal?
Answer:
Dr. Watson is called to tend Holmes, who is apparently dying of a rare tropical disease, Tarpaunli fever, contracted while he was on a case at Rotherhithe. Mrs. Hudson says that Holmes has neither eaten nor taken any liquids in the last three days. Holmes forbids Watson to go near him because the illness is highly infectious. In fact, he refutes Watson and insults his abilities. Although Watson wishes to examine Holmes himself or send for a specialist, Holmes demands that Watson wait several hours before seeking help.
While Watson waits, he examines several objects in Holmes’s room. Holmes is angered when Watson touches things on his table stating his dislike for people fidgeting his things. At six o’clock, Holmes asks Watson to turn the gaslight on, but only half-full. He then instructs Watson to bring Mr. Culverton Smith from 13 Lower Burke Street to see Holmes but to make sure that Watson returns to Baker Street before Smith arrives. Watson goes to Smith’s address. Although Smith refuses to see anyone, Watson forces his way in.
Once Watson explains his duty on behalf of Sherlock Holmes, Smith’s assertiveness changes significantly. Smith agrees to come to Baker Street within half an hour. Watson excuses himself, saying that he has another appointment, and returns to Baker Street before Smith’s arrival. Believing that they are alone, Smith is frank with Holmes. It soon appears, to the hiding Watson’s horror, that Holmes has been sickened by the same illness that killed Smith’s nephew Victor.
In the end, Holmes calls for Watson to come out from behind the screen, to present himself as another witness to the conversation. Holmes explains his illness was feigned as a trick to induce Smith to confess to his nephew’s murder. Starving himself for three days and claiming to be suffering from a deadly infectious disease was to keep Watson from examining him and discovering the ruse, since, as he clarifies, he has every respect for his friend’s medical skills.
‘A detective’s perspective traps the criminal.’
Additional Questions
Question 1.
What makes Culverton Smith fall prey to Holmes’s trap?
Answer:
Watson goes to Mr. Culverton Smith at 13 Lower Burke Street. He finds it difficult to see his friend dying. Although Smith refuses to see anyone, Watson forces his way in. As soon as Watson explains his errand, Smith’s attitude changes drastically. He persuades him to see Holmes as he is in a dying state. Smith agrees to come to Baker Street within half an hour.
Watson excuses himself, saying that he has another appointment and returns to Baker Street before Smith’s arrival as instructed by Holmes. Believing that they are alone, Smith is frank with Holmes. Holmes tells Smith that he will forget the happenings of Victor Savage and pleads with him to cure him. Smith denies and tells Holmes that he should have never crossed his path. Smith sees the little ivory box, which he had sent to Holmes by post containing a sharp spring infected with the illness.
Smith pockets it thinking to have removed the only evidence of his crime. He then resolves to stay there and watch Holmes die. However, Holmes asks Smith to turn the gas up full, which Smith does. Inspector Morton enters and Holmes tells Morton to arrest Culverton Smith for the murder of his nephew and also for the attempted murder of Sherlock Holmes.
‘You cannot escape from a detective’s eye.’
Vocabulary
C. Complete the following sentences by choosing the correct options given.
- Niteesh bought a ………………. (knew/new) cricket bat.
- The shepherd ………………… (herd/heard) the cry of his sheep.
- Lakshmi completed her baking ……………….. (course/coarse) successfully.
- Priya has broken her …………….. (four/fore) limbs.
- Leaders of the world must work towards the ……………… (peace/piece) of the human race.
Answers
- new
- heard
- course
- fore
- peace
Use the given examples and make sentences of your own.
Commonly confused words
brought – past participle of bring. E.g. Anitha had brought a book from the library.
Kavitha brought sweets on her birthday.
bought – past participle of buy. E.g. Lalitha had bought a new dress last week.
Avinash bought a new Hero cycle.
affect – to have an effect on. E.g. The pet’s death affected his master.
The fever affected Dhanush’s studies.
effect – anything brought about by a cause or agent; result. E.g. Both El Nino and La Nina are opposite effects of the same phenomenon.
The effect of ozone layer depletion is catastrophic.
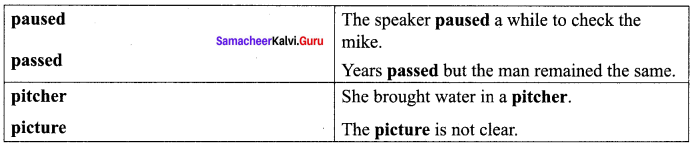
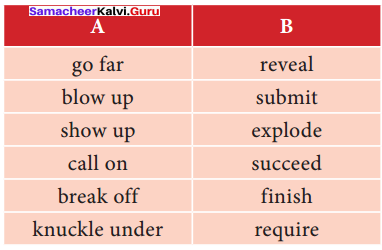
D. Complete the tabular column by finding the meaning of both the words given in the boxes. Use them in sentences of your own.
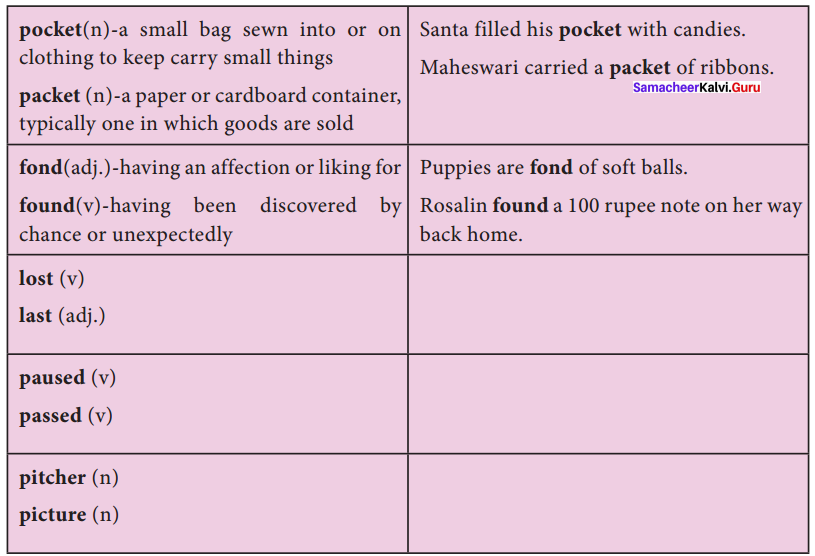
Answer:

Listening Activity:
E. Listen to the story and answer the question given below.
“Something is very wrong,” says the detective.
“I know!” says Ms. Gervis. “It is wrong that someone has stolen from me!”
The detective looks around Ms. Gervis’ apartment. “ at is not what I am talking about, ma’am. What is wrong is that I do not understand how the robber got in and out.”
Ms. Gervis and the detective stand in silence. Ms. Gervis’ eyes are full of tears. Her hands are shaking.
“The robber did not come through the window,” says the detective. “These windows have not been opened or shut in months.”
The detective looks at the fireplace. “The robber did not squeeze down here.”
The detective walks to the front door. He examines the latch. “And since there are no marks or scratches, the robber definitely did not try to break the lock.”
“I have no idea how he did it,” says a bothered Ms. Gervis. “It is a big mystery.”
“And you say the robber stole nothing else?” asks the detective. “No money, no jewelry, no crystal?”
“That’s right, detective. He took only what was important to me,” Ms. Gervis says with a sigh. “There is only one thing I can do now.”
“And what is that?” the detective asks with surprise.
“I will stop baking cakes,” Ms. Gervis says. “They are mine to give away. They are not for someone to steal.”
“You can’t do that!” says the detective with alarm. “Who will bake those delicious cakes?”
“I am sorry. I do not know,” says Ms. Gervis.
“I must solve this case immediately!” says the detective.
1. Where does this story take place?
(a) in a bakery
(b) at the police station
(c) in Ms. Gervis’ house
(d) in Ms. Gervis’ apartment
Answer:
(d) in Ms. Gervis’ apartment
2. Near the beginning of the story, “Ms. Gervis’ eyes are full of tears. Her hands are shaking.” How does Ms. Gervis probably feel?
(a) She is upset
(b) She is tired
(c) She is hungry
(d) She is confused
Answer:
(d) She is confused
3. What makes the detective sure that the robber did not come through the windows?
(a) The windows are locked
(b) The windows face the police station
(c) The windows have not been used in months
(d) The windows are too small for a person to fit through
Answer:
(c) The windows have not been used in months
4. What else was stolen from the apartment?
(a) crystal
(b) jewelry
(c) money
(d) nothing
Answer:
(d) nothing
5. “And the robber definitely did not use the front door.” Which is the best way to rewrite this sentence?
(a) “And the robber may not have used the front door.”
(b) “And the robber probably did not use the front door.”
(c) “And the robber was not able to use the front door.”
(d) “And the robber certainly did not use the front door.”
Answer:
(d) “And the robber certainly did not use the front door.”
6. What does Ms. Gervis do with her cakes?
(a) She eats them
(b) She sells them
(c) She hides them
(d) She gives them away
Answer:
(d) She gives them away
7. What does the detective seem to think will happen if he solves the mystery?
(a) Ms. Gervis will start baking cakes again
(b) Ms. Gervis will bake him extra cakes
(c) Ms. Gervis will give him her secret recipe
(d) Ms. Gervis will give him money and jewels
Answer:
(a) Ms. Gervis will start baking cakes again
8. Do you like mysteries? What is your favorite kind of story? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, I do.
I like detective stories. Lena Tamilvanan and Rajesh Kumar are good detective story writers.
The novels written by them are gripping and sustain the readers interest till the last page.
Speaking Activity
F. Exercise
1. Present the review of a movie that you have watched recently.
Review of Super Deluxe Movie I saw
Thiagarajan Kumararaja’s Super Deluxe opens with a shot of Vaembu (Samantha) lying beside someone on a bed. The camera slowly moves around the room, pulling you in the direction it travels. Soon you realise that it’s not the camera, but the director Thiagarajan Kumararaja who has lured you into his world.
And this world has eccentric characters like Arputham (Mysskin), who believes that he is god’s right hand because he was the only one who survived the Tsunami when millions died. Kumararaja doesn’t stop there. His thoughts are out-of-the-world (literally), outlandish, and outstanding.
There are 4 parallel plots taking place at the same time, involving the lives of Shilpa (Vijay Sethupathi), Leela (Ramya Krishnan), and Arputham (Mysskin), Vaembu (Samantha) and Mugil (Fahadh Faasil), and another one involving four boys. The best part about the writing is that these plotlines don’t merge at one point.
One sub-plot becomes an influencing factor in another, but after that, they part ways. The way the events unfold is interesting and makes the movie more engrossing. The trademark qualities NalanKumarasamy and Mysskin’s writing is seen at a lot of places. A lot of humourous portions belong to Nalan’s ‘crazy’ world. Who else can write a scene where a man dies while having sex? On the other hand, towards the end, there a sequence involving Mysskin, set in a subway, with green lighting.
What more do we need to figure out that this has been written by Mysskin himself?
PS Vinod and Nirav Shah’s visuals have an ever-lasting effect on us. The wise usage of ffame- within-frame shots through doors, windows, and alleys creates a sense of being trapped, and this has been used for all major characters. The wise usage of vintage tracks of Ilayaraja falls on point.
Yuvan Shankar Raja makes sure we feel the heat and soul of the scenes through his brilliant background scores and apt silences. The walls on all the houses and a police station, “the make-shift flower pot on one of the apartments, the borders of sarees, the costumes of the characters, are all blue in colour. While this is supposed to create a stable feel, the characters are all unstable. This irony has been effectively used to elevate our cinematic experience. Vaembu and Mugil’s story becomes melodramatic after a point of time.
And the biggest issue with the film is that they have the maximum screentime. Even the way their conflict gets resolved looks implausible. But, the way the terrific FahadhFaasil and Samantha act, these issues are covered up. Shilpa’s characterization brings out the best in Vijay Sethupathi, but not Vijay Sethupathi. Apart from the main leads, BhagavathiPerumal and Master Aswanth, have done their job well and scored in their plot points. On the flip side, the second half could have been a bit more crisp, due to the three hours runtime.
2. Give the review of a book that has interested you a lot.
’ Review of the most interesting book I read The Noodle Maker by Ma Jian The pace of change in China over the last fifteen years has been extraordinarily fast; the pace at which its literature reaches us in translation shamefully slow. Chinese dissident writer Ma Jian is already known in the English-speaking world for his award-winning travel memoir of rural China in the 1980s, Red Dust. Since the Chinese takeover of Hong Kong in 1997, he has been living with his partner and translator in London.
The Noodle Maker, the first of Jian’s novels to appear in English, is set soon after the events of Tiananmen Square in 1989, already ancient history to today’s young entrepreneurs, artists, and university students. Reading The Noodle Maker now has some of the blurred effects of a time-lapsed photograph- -it is a hard-hitting satire of a cultural moment that has already come and gone. Only a reviewer intimate with today’s China could judge to what extent its critique is still sharp. Perhaps this question of timeliness should be irrelevant.
The Noodle Maker is fiction, after all, constructed with a good deal of artfulness on the frame of a drunken evening shared between a professional writer and his best friend, a professional blood donor. The professional blood donor considers himself a practical man; he boasts of the excellent pay and perks he receives as rewards for being bled for the benefit of the nation.
Each Sunday he brings good food and drinks to the writer, who is, of course, a poverty-stricken idealist. Their discussion is interwoven with the stories the professional writer is crafting based on people he has known: an actress who stages her own suicide; her boyfriend, a painter with a talking three-legged dog
(the novel’s most reliable narrator); a literary editor humiliated by the success of his wife, an acclaimed novelist; a father trying to abandon his retarded daughter; an entrepreneur whose success with a musically-enhanced crematorium gives him the confidence to bum his own mother alive. Each of these characters is manipulated not only by the noodle-making hands of the professional writer, but by a ruthless society, which with its new “Open Door Policy” has imported some superficial commercial elements of Westemness, yet still maintains a stranglehold on personal freedom.
(“Imported” products as symbols of moral weakness, hypocrisy, and corruption are a satiric mantra throughout the book.) Fans of the absurdity and dark humour of Milan Kundera’s portraits of life behind the Iron Curtain will appreciate these same elements in Ma Jian’s work-though Kundera is a good deal lighter on his feet and the clever and humorous aspects of The Noodle Makerstruck this reviewer as heavy-handed.
As fiction that comments on social and political reality, The Noodle Maker is far less emotionally engaging than Yu Hua’s Chronicle of a Blood Merchant, which tells the life of another professional blood donor, and is a character-driven social realist novel in the old nineteenth-century Dickensian mode, though written in a crisp contemporary style.
It tells us about China, but something convincing about people, too. For all its postmodern strands, the heart of The Noodle Maker (like all satire?) is in a kind of journalism, so that ultimately its success depends on whether or not it still tells a timely truth.
3. Review an event which your school has hosted recently.
A school is a place where we get to know about different activities for the first time. Participating in these activities is always memorable and exciting. My favorite school event is the “Mental Maths Competition”. This event is held once a year. One student is selected from each section of a class. Then they are teamed up with other students to form three teams.
This competition is basically to enhance mental skills. Students have to answer these questions in a time span of seconds. Questions are not repeated at all and students have to be very quick in understanding the questions, in calculations, and then answering it. Last year I was also selected as one of the finalists. Our team A and team C reached the final rounds. The winning round lasted for thirty questions as both teams were not ready to give up. In the end, team C couldn’t answer a question and we answered it to win the event.
We were highly appreciated and were given certificates and shields. Winning is always exciting and encouraging. I would always like to participate in this event again because this event helps me in enhancing my mental skills and to speed up my mental calculations.
Reading:
Read the story carefully and answer the questions asked below
A Mystery Case:
For a man of ease, John Mathew kept an arduous schedule. On Wednesdays, for example, he was awakened at 9.00 and served breakfast in bed by Emanuel, his chef. Next came a quick fitness session with Basky, his personal trainer. Then, at 10.30, John Mathew answered his mail, returned phone calls and rearranged his social calendar helped by Louise, his secretary.
At noon, John Mathew drove his Jaguar to the station and took a commuter train into Guindy for his weekly lunch with Lalli and Lolly, his two oldest and dearest friends. Then, on to a little shopping. The 4:05 nonstop would bring him back to Tambaram. As John Mathew drove up to the house at 5:00, Basky would have already set up the massage table and warmed the scented oils for a soothing herbal wrap. It was a grueling life but John seemed to thrive on it. On this Wednesday, however, there was an unexpected change of plans.
Today John’s shopping errand involved taking his diamond bracelet into the jeweller’s for cleaning. He threw the expensive jewel into his purse and proceeded on to lunch. As John waved his friend’s good-bye and exited the restaurant, he sensed he was being followed. The feeling continued until he reached Tenth Avenue. Then, as he joined the throng of shoppers, John felt a hug. Within a split-second, a man riding a pillion on a bike rode past him, grabbing his purse. He couldn’t guess who the culprit was?
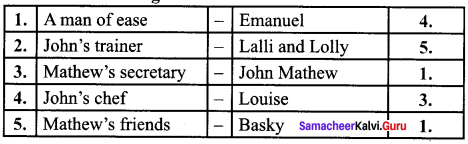
G. Match the following.
1. A man of ease – Emanuel
2. John’s trainer – Lalli and Lolly
3. Mathew’s secretary – John Mathew
4. John’s chef – Louise
5. Mathews friends – Basky
Answer:
H. State whether the given statements are true or false. If false correct the statements.

Answer:
1. Mathew is a very busy man
[true]
2. He woke up very late in the morning
[True]
3. He always had lunch with his family
[False] He always had lunch with Lalli and Lolly, his two oldest and dearest friends.
4. He exercised with Louise every day.
[True]
5. He preferred handling mail by himself
[True]
Writing
Pamphlet
I. Create a pamphlet for the following:
1. Make a pamphlet on ‘Dengue Awareness’ (Focus on its causes, preventions, symptoms, and precautions).

2. Make an attractive pamphlet for your school’s Fair organised for raising funds for (any) relief (Specify the date, time, types of stalls, and the reasons for the fair).

3. Make a pamphlet on the latest gadgets (Mention the variety of models, uses, need and availability).

J. Write a letter of enquiry for the following
1. You’re a librarian in a newly established school. Write a letter to the book dealer inquiring about the list of newly arrived English children’s storybooks and various subject books relevant to 10 – 14 age groups.
From
S. Sangeetha
Librarian
ABC School
XXXX
23.04.2019
To
Sales Manager
Higginbothams Books dealers
Mount Road
Chennai 2
Sir,
Sub: Enquiry about children’s story book-Reg.
I would like to know about the new arrivals in English children’s storybooks and subject books appropriate to the children in the age group of 10-14. Kindly send the list/catalogue with the price and the details of the discount offered to schools.
Thank you
Yours sincerely
S. Sangeetha
Sales Manager
Higginbothams Books dealers
Mount Road
Chennai 2
2. Venkat hails from a remote village of Kancheepuram District, Tamil Nadu who aspires to become an IAS officer. Currently, he is in class X. He notices an advertisement on free classes for the IAS aspirants by a trust in a newspaper. He writes a letter to the coordinator of the trust inquiring for further details.
From
R Venkat
14, Velakkadi Koil St
Kancheepuram 2
[email protected]
13.08.2018
To
The Liasion Officer
Manitha Neyam Trust
CITNagar
Chennai 17
Sir,
Sub: Enquiry about IAS orientation programme – Reg.
I saw your advertisement in The Hindu Tamil newspaper dated 12th August, about a free seminar, in Pallavaram Govt. Hr. Sec. School.
I am doing my Std. X, I cherish the dream of becoming an IAS officer. I heard the entry is free for graduates. Will you please allow me also to attend the seminar? I wish to listen to achievers and subject experts. Kindly communicate your consent through my email venkat2002@gmail. com.
Thank you
Yours sincerely
P. Venkat
To
The Liasion Officer
Manitha Neyam Trust
CIT Nagar
Chennai 17
3. Write a letter to the head of the BSNL office enquiring regarding the internet broadband scheme launched recently.
From
K.Joseph
18, Akilan St
Kalpakkam
jose2000@gmail. com
20.03.2019
To
Manager
BSNL Office
head Office
Chengalpattu
Kancheepuram 10
Sir,
Sub: Enquiry about internet broadband scheme launched recently – Reg.
I heard that you have recently launched an attractive scheme for students to promote the use of high-speed Broadband connectivity. I would like to know the details of the cost involved, bandwidth, usage limit (i.e.) GB per day, details about speed, type of modem, and warranty details. As a representative of my school, I would like to share this with my school also for the upcoming ICT lab in the school. Kindly mention the scheme for Institute and individuals separately.
Thank you
Yours sincerely
K. Joseph
To
Manager
BSNL Office
Head Office
Chengalpattu
Kancheepuram 10
Grammar
A. Transform the following sentences as instructed.
1. On seeing the teacher, the children stood up. (into Complex)
As soon as the children saw the teacher, they stood up.
2. At the age of six, Varsha started learning music, (into Complex)
When Varsha was six, she started learning music.
3. As Vanin is a voracious reader, he buys a lot of books, (into Simple)
Being a voracious reader, Varun buys a lot of books.
4. Walk carefully lest you will fall down, (into Complex)
If you don’t walk carefully, you will fall down.
5. Besides being a dancer, she is a singer, (into Compound)
She is not only a dancer but also a singer.
6. He is sick but he attends the rehearsal, (into Simple)
In spite of being sick, he attends the rehearsal.
7. If Meena reads more, she will become proficient in the language, (into Compound) Meena should read more or she will not become proficient in English.
8. He confessed that he was guilty, (into Simple)
He confessed his guilt.
9. The boy could not attend the special classes due to his mother’s illness, (into Compound)
The boy’s mother was ill and so he did not attend the special classes.
10. He followed my suggestion, (into Complex)
He followed what I suggested.
B. Combine the pairs of sentences below into simple, complex, and compound
1. Radha was ill. She was not hospitalised
In spite of being ill, Radha was not hospitalised, (simple)
Radha was ill but she was not hospitalised, (compound)
Though Radha was ill, she was not hospitalised, (complex)
2. The students were intelligent. They could answer the questions correctly
Being intelligent, the students were able to answer the questions correctly, (simple)
The students were intelligent and so they were able to answer the questions correctly, (compound)
As the students were intelligent, they were able to answer the questions correctly, (complex)
3. I must get a visa. I can travel abroad
I must get a visa to travel abroad, (simple) .
I must get a visa or else I can’t travel abroad, (compound)
If I don’t get a visa, I can’t travel abroad, (complex)
4. I saw a tiger it was wounded
I saw a wounded tiger, (simple)
I saw a tiger and it was wounded, (compound)
I saw a tiger which was wounded, (complex)
5. There was a bandh. The shops remained closed
The shops were closed due to Bandh. (simple)
There was a bandh and so the shops were closed, (compound)
As there was a bandh, the shops were closed, (complex)
The Dying Detective by About the Author:
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (1859-1930) was a British writer popularly known the world over for his detective stories involving Sherlock Holmes stories, which are generally considered milestones in the field of fiction. Doyle wrote forty-six short stories featuring the famous detective. His notable works included “Stories of Sherlock Holmes and the Lost World”.
The Dying Detective summary:

Introduction:
The author has given an interesting accord of how the detective outsmarted the culprit to zero in on him.

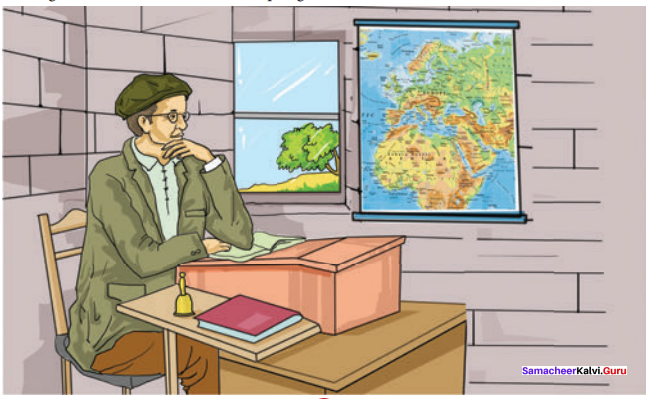
Home’s incurable disease Dr. Watson was informed by Mrs. Hudson, the landlady of Sherlock Holmes that Mr. Holmes was dying. He was bedridden for three days. He had neither taken food nor drinks. He was sinking. The landlady was permitted to inform only Dr. Watson about his ill health. She could not call for a doctor because Sherlock Holmes had prevented her from doing so. When Dr. Watson reached Holmes, he cautioned him to stay away from him as he was suffering from some contagious disease that he had picked up from Rotherhithe. The disease from Sumatra was deadly and could spread even with a touch.

Home’s peculiar behaviour
Watson advanced to examine symptoms but was stopped midway by the stem warning from Holmes. Sherlock Holmes declared that he wanted a doctor in whom he would have confidence. This really upset Dr. Watson. He offered to bring the best doctors of London viz. Sir Jasper Meek or Penrose Fisher.
Holmes reprimanded Dr. Watson’s ignorance and asked him what he knew about Tarpaunli fever or black Formosa plague. When Dr. Watson offered to bring Dr. Ainstree, Holmes bolted the door and ordered him not to move till six in the evening. Dr. Watson did not know what to do for two hours. He just walked around the room slowly. He came across a small black and white ivory box with a sliding lid.
When he was about to examine its contents, he heard a dreadful cry from Holmes. He forbade him from touching his things. In a kind of delirium, Holmes ordered to take out his coins and keep all the half-crowns in his watch pocket. He was instructed to light the gas lamp and keep it half on. He requested him to place some letters on the table within his reach.
He instructed him to slide the lid of the ivory box with Tongs and put the Tongs and the ivory box on the table. He instructed Dr. Watson to bring Mr. Culverton Smith from 13, Lower Burke Street, as Holmes was serious. Dr. Watson was hesitant to go.
Holmes clarified that he was not a doctor but a plantation man with a deep knowledge of the disease. Holmes asked Watson to plead with him to come and save Holmes who was seriously ill. Dr. Watson offered to bring him in a cab. However, Holmes instructed that he should plead with him and reach Holmes before him.



Holmes’ plan
While waiting for the cab, Mr. Morton, in civil dress asked after Holmes. Dr. Watson entered Mr. Culverton Smith’s room by force. On hearing Mr. Holmes’s name, he enquired how Holmes was doing. When he learned that he was very ill and believed that only he could save his life, he enquired how Holmes got the eastern disease. Dr. Watson told him all he knew. Dr. Watson, on the pretext of an appointment, returned to Holmes earlier and stayed in a room there as per Holmes’s order.

Smith’s careless attitude
Smith arrived and called out for Holmes. Holmes responded to his questions in a feeble voice. He asked Holmes to describe the symptoms. When Holmes completed describing the symptoms Smith was strangely happy. He blurted out, “Poor victor Savage was a dead man on the fourth day. A strong and healthy young man. What a coincidence indeed!” Holmes said, “I know that you did it”. Holmes groaned and asked for water. Smith gladly gave him water. He requested Smith to cure him and offered to forget his hand in the murder of Victor.

Smith said that Watson shared the information that Holmes got the fever from Chinese sailors. He wanted to know seriously if there could be any other reason.

Holmes outsmarts Smith
Holmes said, ‘successful acting’. Just then Inspector Morton said to Smith that he was arrested on a charge of murder. There was a scuffle. Inspector Morton overpowered Smith and handcuffed him. Holmes apologized to Dr. Watson for being rude to him and undermining his capability as a doctor. All the acting was done just to bring Smith there. Even the coin trick was to make Watson believe that Holmes was really delirious. Holmes asked Dr.Watson to take him to eating something nutritious at Simpson’s.

Conclusion
The author has made us understand a criminal cannot get away for long. The criminal may also be caught by his own words.

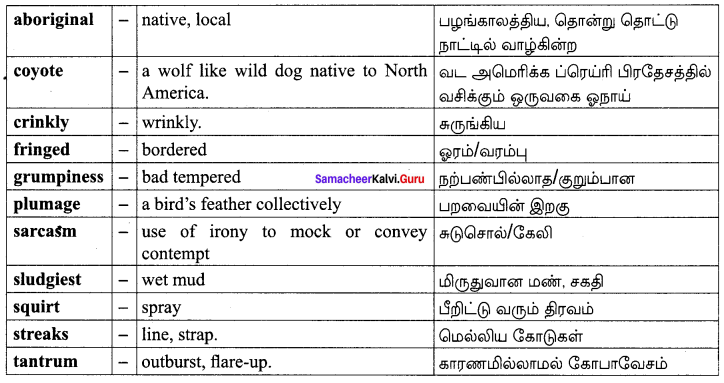
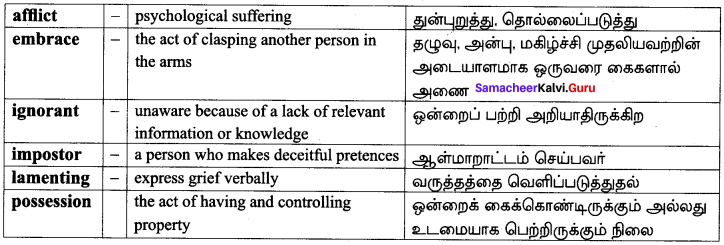
The Dying Detective Glossary:
Textual:

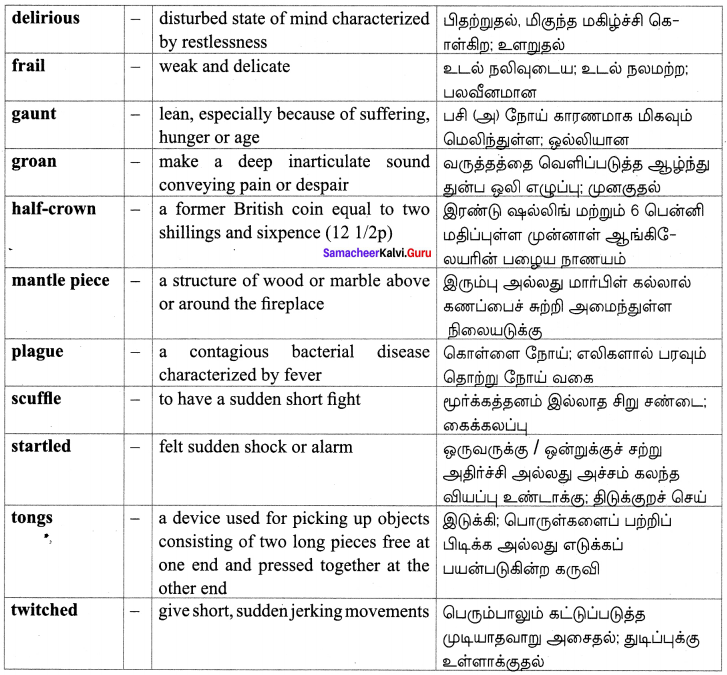
Additional:

Synonyms
Choose the most appropriate synonym of the underlined word.
1. He has been sinking.
(a) rising
(b) deteriorating
(c) improving
(d) dreaming
Answer:
(b) deteriorating
2. The sick room was a gloomy spot.
(a) spotless
(b) illuminated
(c) dim
(d) bright
Answer:
(c) dim
3. The gaunt face was staring at the ceiling
(a) stout
(b) strong
(c) thick
(d) lean
Answer:
(d) lean
4. The dying man bolted the door.
(a) closed
(b) opened
(c) broke
(d) slithered
Answer:
(a) closed
5. It was a contagious disease.
(a) impregnable
(b) crisp
(c) cussed
(d) infectious
Answer:
(d) infectious
6 His hand twitched.
(a) trembled
(b) got crushed
(c) shivered
(d) jerked
Answer:
(d) jerked
7. How ignorant you are!
(a) knowledgeable
(b) uninformed
(c) well informed
(d) wise
Answer:
(b) uninformed
8. I heard a dreadful cry.
(a) loud
(b) mild
(c) frightening
(d) sweet
Answer:
(c) frightening
9. I sat in silent dejection.
(a) optimism
(b) depression
(c) hope
(d) delight
Answer:
(b) depression
10. You will persuade him to come.
(a) deny
(b) urge
(c) order
(d) request
Answer:
(b) urge
11. He was delirious.
(a) relaxed
(b) calm
(c) composed
(d) incoherent
Answer:
(d) incoherent
12. He was frail.
(a) plump
(b) weak
(c) strong and tall
(d) well-built
Answer:
(b) weak
13. The little man was startled.
(a) reassured
(b) alarmed
(c) annoyed
(d) agreed
Answer:
(b) alarmed
14. I left him pretending that I had an appointment.
(a) feigning
(b) imagining
(c) lending
(d) receiving
Answer:
(a) feigning
15. Go and fetch Smith.
(a) see off
(b) summon
(C) bring
(d) send
Answer:
(C) bring
16. “My mind is gone. help me”, pleaded Holmes.
(a) ordered
(b) begged
(c) urged
(d) commanded
Answer:
(b) begged
17. “I arrest you on charge of murder’ he said.
(a) fees
(b) rate
(c) indictment
(d) appreciation
Answer:
(c) indictment
18. What a coincidence indeed.
(a) actually
(b) in pursuit
(c) in charge
(d) in spate
Answer:
(a) actually
19. You can only cure me.
(a) inflict pain
(b) alleviate pain
(c) heal
(d) curse
Answer:
(c) heal
20. Holmes groaned.
(a) whispered
(b) whined
(c) sang in joy
(d) grounded
Answer:
(b) whined
Antonyms
Choose the most appropriate antonym of the underlined word.
1. He has been sinking.
(a) drowning
(b) floating
(c) running
(d) sleeping
Answer:
(b) floating
2. I don’t dare disobey him.
(a) rebel
(b) defy
(c) challenge
(d) obey
Answer:
(d) obey
3. He brought this illness back with him.
(a) sickness
(b) ailment
(c) disease
(d) health
Answer:
(d) health
4. It is deadly and contagious.
(a) safe
(b) unsafe
(c) dangerous
(d) lethal
Answer:
(a) safe
5. I said advancing towards him.
(a) going forward
(b) retreating
(c) regurgitating
(d) belching
Answer:
(b) retreating
6. How ignorant you are!
(a) tacking in know ledge
(b) well- informed
(c) uninformed
(d) unaware
Answer:
(b) well- informed
7. You will persuade him to come.
(a) dissuade
(b) urge
(c) distract
(d) disembark
Answer:
(a) dissuade
8. He was a frail man.
(a) weak
(b) feeble
(c) strong
(d) thin
Answer:
(c) strong
9. The man was startled.
(a) reassured
(b) amused
(c) alarmed
(d) annoyed
Answer:
(a) reassured
10. You will tell him exactly how you have left one.
(a) accurately
(b) carefully
(c) adequately
(d) superficially
Answer:
(d) superficially
11. You disappear to the next room.
(a) vanish
(b) distress
(c) distinct
(d) appear
Answer:
(d) appear
12. He pleaded to cure him.
(a) requested
(b) beseeched
(c) ordered
(d) begged
Answer:
(c) ordered
13. It was successful acting.
(a) victorious
(b) unsuccessful
(c) joyful
(d) triumphant
Answer:
(b) unsuccessful
14. James at last talked in his natural voice.
(a) innate
(b) native
(c) nature
(d) unnatural
Answer:
(d) unnatural
15. There was silence.
(a) solemnity
(b) noise
(c) contempt
(d) concept
Answer:
(b) noise
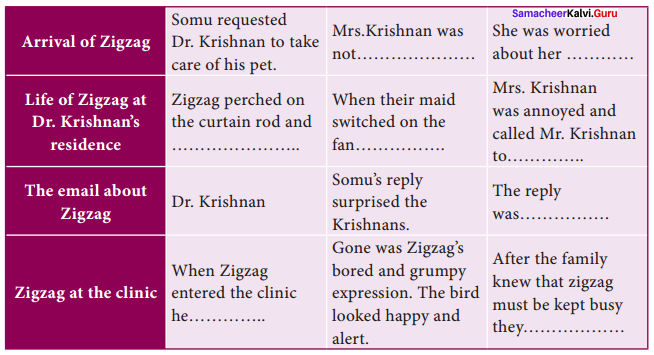

































 Answer:
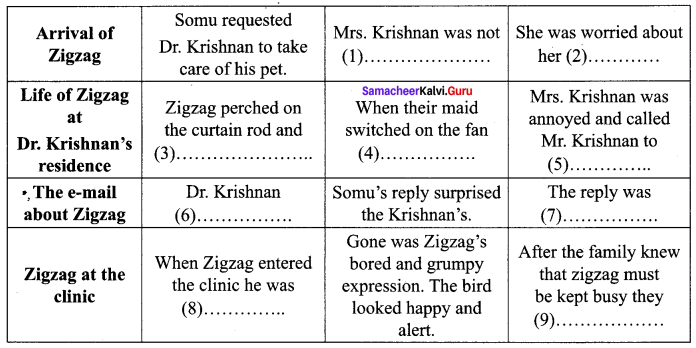
Answer:








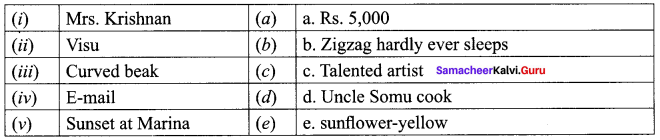
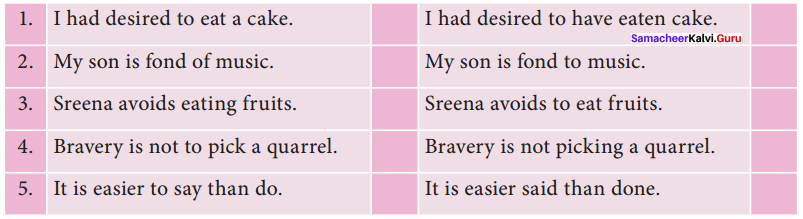 Answer:
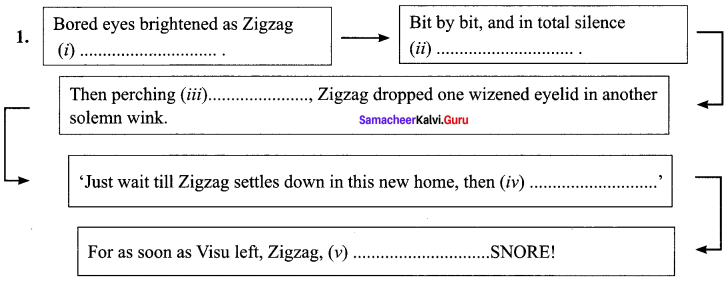
Answer: