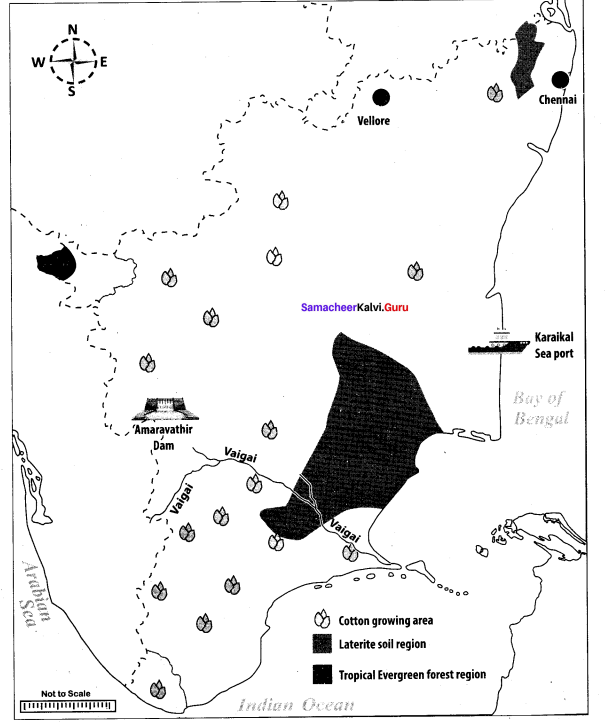
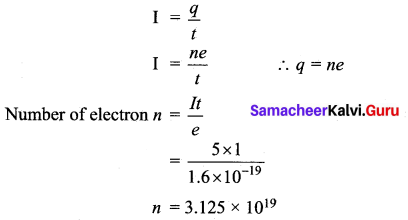
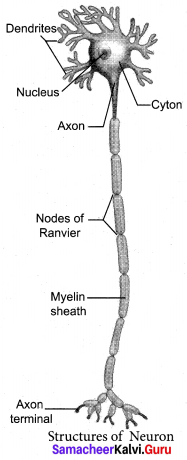
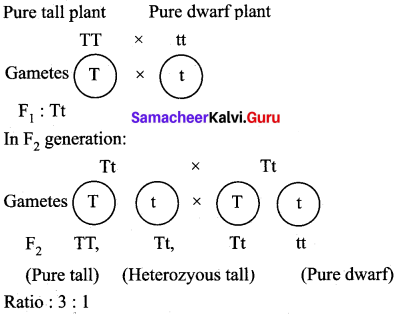
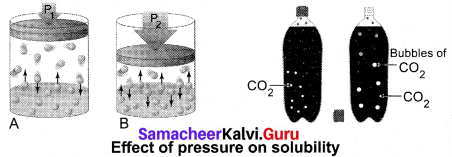
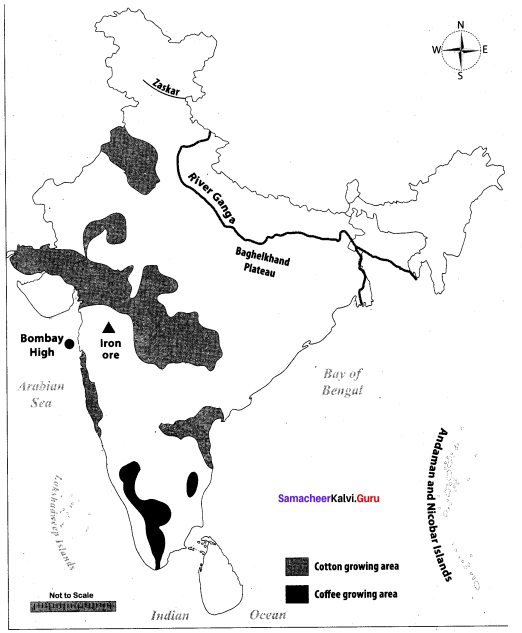
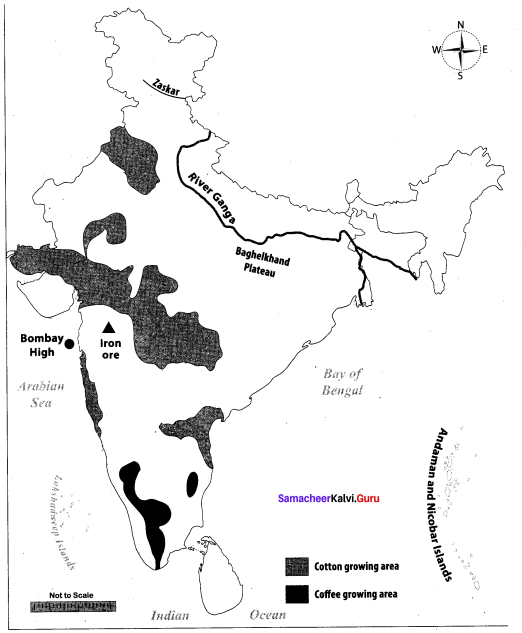
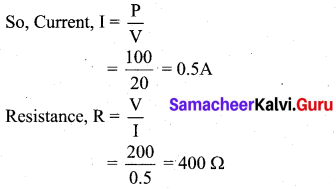
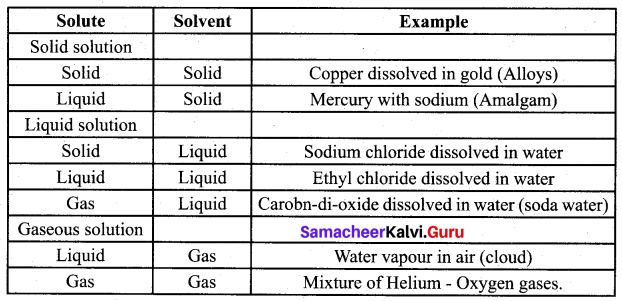
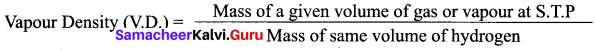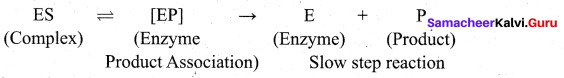Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 10 Surface Chemistry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 10 Surface Chemistry
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Chapter 10 Surface Chemistry Textual Evaluation Solved
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
For freudlich isotherm a graph of log \(\frac{x}{m}\) is plotted against log P. The slope of the line and its y – axis intercept respectively corresponds to
(a) \(1 / n\), k
(b) log \(1 / n\), k
(c) \(1 / n\), log k
(d) log \(1 / n\), log k
Answer:
(c) \(1 / n\), log k
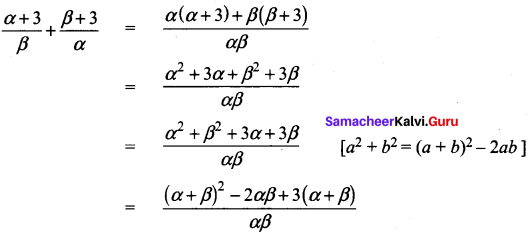
\(\frac{x}{m}\) = \(\mathrm{k} \cdot \mathrm{p}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\)
log\((\frac{x}{m})\) = log k + \(\frac { 1 }{ n }\)log p
y = c + mx
m = \(\frac { 1 }{ n }\) and c = log k
Question 2.
Which of the following is incorrect for physisorption?
(a) reversible
(b) increases with increase in temperature
(c) low heat of adsorption
(d) increases with increase in surface area
Answer:
(b) increases with increase in temperature
Physisorption is an exothermic process. Hence increase in temperature decreases the physisorption.

Question 3.
Which one of the following characteristics are associated with adsorption?
(a) ∆G and ∆H are negative but ∆S is positive
(b) ∆G and ∆S are negative but ∆H is positive
(c) ∆G is negative but ∆H and ∆S are positive
(d) ∆G. AH and ∆S all are negative.
Answer:
(d) ∆G, ∆H and ∆S all are negative.
Adsorption leads to decrease in randomness (entropy).i.e. ∆S < 0 for the adsorption to occur, ∆G should be – ve. We know that ∆G = ∆H – T∆S if ∆S is – ve, T∆S is + ve. It means that ∆G will become negative only when ∆H is – ve and ∆H > T∆S
Question 4.
Fog is colloidal solution of ……………..
(a) solid in gas
(b) gas in gas
(c) liquid in gas
(d) gas in liquid
Answer:
(c) liquid in gas
dispersion medium-gas, dispersed phase-liquid
Question 5.
Assertion: Coagulation power of Al3+ is more than Na.
Reason: greater the valency of the flocculating ion added, greater is its power to cause precipitation
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (Hardy-Sechuize nile)
Question 6.
Statement: To stop bleeding from an injury, ferric chloride can be applied. Which comment about the statement is justified?
(a) It is not true, ferric chloride is a poison.
(b) It is true, Fe3+ ions coagulate blood which is a negatively charged sol
(c) It is not true; ferric chloride is ionic and gets into the blood stream.
(d) It is true, coagulation takes place because of formation of negatively charged sol with Cl–.
Answer:
(b) It is true, Fe3+ ions coagulate blood which is a negatively charged sol
Question 7.
Hair cream is …………..
(a) gel
(b) emulsion
(c) solid sol
(d) sol.
Answer:
(b) emulsion
Emulsion dispersed phase, Dispersion medium -liquid
Question 8.
Which one of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Emulsion – Smoke
(b) Gel – butter
(c) foam – Mist
(d) whipped cream – sol
Answer:
(b) Gel – butter
Question 9.
The most effective electrolyte for the coagulation of As2S3 Soils
(a) NaCI
(b) Ba(NO3)2
(c) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(d) AI3+
Answer:
(d) AI3+
As2S3 is a – vely charged colloid. It will be most effectively coagulated by the cation with greater valency. i.e., Al3+.
Question 10.
Which one of the is not a surfactant?
(a) CH3 – (CH2)15 – N – (CH3)2CH2Br
(b) CH3 – (CH2)15 – NH2
(c) CH3 – (CH2)16 – CH2OSO2 – Na+
(d) OHC – (CH2)14 – CH2 – COO–Na+
Answer:
(b) CH3 – (CH2)15 – NH2

Question 11.
The phenomenon observed when a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution is ………….
(a) Cataphoresis
(b) Electrophoresis
(c) Coagulation
(d) Tyndall effect
Answer:
(d) Tyndall effect-scattering of light
Question 12.
In an electrical field, the particles of a colloidal system move towards cathode. The coagulation of the same sol is studied using K2SO4
(i). Na3PO4
(ii). K4[Fe(CN)6]
(iii). and NaCI
(iv). Their coagulating power should be …………..
(a) II > I >IV > III
(b) III > II > I > IV
(c) I > II > III > IV
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) III > II > I > IV
Question 13.
Collodion is a 4% solution of which one of the following compounds in alcohol – ether mixture?
(a) Nitroglycerine
(b) Cellulose acetate
(c) Glycoldinitrate
(d) Nitrocellulose
Answer:
(a) Nitrocellulose
pyroxylin (nitro cellulose)
Question 14.
Which one of the following is an example for homogeneous catalysis?
(a) manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process
(b) manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process
(c) hydrogenation of oil
(a) Hydrolysis of sucrose in presence of all HCI
Answer:
(a) Hydrolysis of sucrose in presence of all HCl
Both reactant and catalyst are in same phase. i.e. (1)
Question 15.
Match the following.
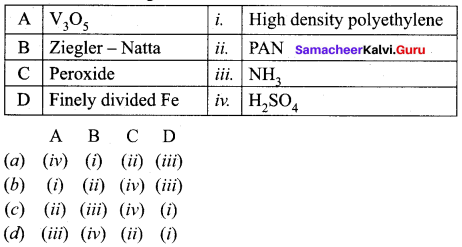
Answer:
(a) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
Question 16.
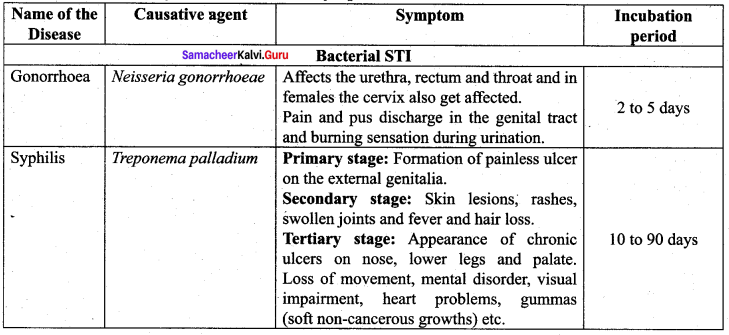
The coagulation values in millimoles per litre of the electrolytes used for the coagulation of AS2S3 are given below
(I) (NaCI) = 52
(II) (BaCl) = 0.69
(III) (MgSO4) = 0.22
The correct order of their coagulating power is ……….
(a) III > II > I
(b) I > II > III
(c) I >III > II
(d) II > III > I
Answer:
(a) III > II > I
coagulating power ± \(\frac{1}{\text { coagulation value }}\)

Question 17.
Adsorption of a gas on solid metal surface is spontaneous and exothermic, then ……………
(a) ∆H increases
(b) ∆S increases
(c) ∆G increases
(d) ∆S decreases
Answer:
(a) ∆S decreases – ∆S is -ve
Question 18.
If x is the amount of adsorbate and m is the amount of adsorbent, which of the following relations is not related to adsorption process?
(a) x/m = f(P) at constant T
(b) x/m = f(T) at constant P
(c) P = f(T) at constant x/m
(d) x/m = PT
Answer:
(d) x/m = mPT
Question 19.
On which of the following properties does the coagulating power of an ion depend?
(a) Both magnitude and sign of the charge on the ion.
(b) Size of the ion alone
(c) the magnitude of the charge on the ion alone
(d) the sign of charge on the ion alone.
Answer:
(a) Both magnitude and sign of the charge on the ion.
Question 20.
Match the following.
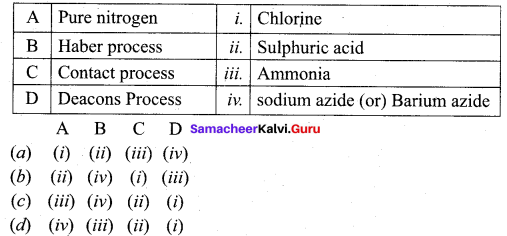
Answer:
(d) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give two important characteristics of physisorption.
Answer:
Important characteristics of physisorption:
- It is reversible
- It has low heat of adsorption
- It has weak van der Waals forces of attraction with adsorbent.
- It increases with increase in pressure.
- It forms multi molecular layer.
Question 2.
Differentiate physisorption and chemisorption.
Answer:
Chemical adsorption or Chemisorption or Activated adsorption
- It is very slow
- It is very specific depends on nature of adsorbent and adsorbate.
- chemical adsorption is fast with increase pressure, it can not alter the amount.
- When temperature is raised chemisorption first increases and then decreases.
- Chemisorption involves transfer of electrons between the adsorbent and adsorbate,
Heat of adsorption is high i.e., from 40 – 400kJ/mole.
- Monolayer of the adsorbate is formed.
- Adsorption occurs at fixed sites called active centres. It depends on surface area.
- Chemisorption involves the formation of activated complex with appreciable activation energy.
- Physical adsorption or van der Waals adsorption or Physisorptlon
- It is irreversible.
Physical adsorption or van der Waals adsorption or physisorption.
- It is instantaneous
- It is non-specific
- In Physisorption. when pressure increases the amount of adsorption increases.
- Physisorption decreases with an increase in temperature.
- No transfer of electrons
- Heat of adsorption is low in the order of 40 kJ/mole.
- Multilayer of the adsorbate is formed on the adsorbent.
- It occurs on all sides.
- Activation energy is insignificant.
- It is reversible.

Question 3.
In the case of chemisorption, why adsorption first increases and then decrease with temperature?
Answer:
1. Chemisorption involves high activation energy so it is also referred to as activated adsorption.
2. It is found in chemisorption that it first increases and then decreases with increase in temperature. When adsorption is plotted, the graph first increases and then decreases with temperature.
3. The initial increase illustrates the requirement of activation of the surface for adsorption is due to fact that the formation of activated complex requires certain energy. But later it decreases at high temperature is due to desorption as the kinetic energy of the adsorbate increases (exothermic nature)
Question 4.
Which will be adsorbed more readily on the surface of charcoal and why; NH3 or CO2?
Answer:
1. The gases having low critical temperature are adsorbed slowly, while gases with high critical temperature are adsorbed readily.
2. Among CO2, and NH3, NH3 will be more readily adsorbed on the surface of the charcoal. This is because the critical temperature of ammonia gas is quite high than the CO2. Hence, it easily combines with the materials than the CO2 whether it is solid, liquid or any gases.
Question 5.
Heat of adsorption is greater for chemisorptions than physisorption. Why?
Answer:
Chemisorption has higher heat of adsorption. because in chemisorption the chemical bonds are much stronger. In adsorbed state the adsorbate is hold on the surface of adsorbent by attractive forces (bond). And chemisorption is irreversible one. Therefore, heat of adsorption is greater for chenil sorptions than physisorption. Chemisorption, heat of adsorption range 40 – 400kJ/mole.
Question 6.
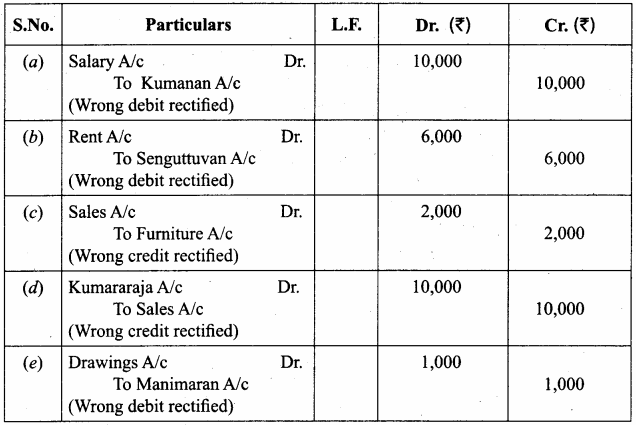
In a coagulation experiment 10 mL of a colloid (X) is mixed with distilled water and 0.1M solution of an electrolyte AB so that the volume is 20 mL. It was found that all solutions containing more than 6.6 mL of AB coagulate with in 5 minutes. What is the flocculation values of AB for sol (X)?
Answer:
A minimum of 6.6mL of AB is required to coagulate the sol. The moles of AB in the sol is
\(\frac{6.6 \times 0.01}{20}\) = 0.033 moles
This means that a minimum of 0.033 moles or 0.0033 x 1000 = 3.3 milli moles are required for coagulating one litre of sol. Flocculation value of AB for X = 3.3
Question 7.
Peptising agent is added to convert precipitate into colloidal solution. Explain with an example.
Answer:
1. Ions either positive or negative of peptizing agent (electrolyte) are adsorbed on the particles of precipitate. They repel and hit each other and break the particles of the precipitate into colloidal size.
2. For example, when we add a small volume of very dilute hydrochloric acid solution peptising agent to a fresh precipitate of a silver chloride, it leads to formation of silver chloride colloidal solution,

Question 8.
What happens when a colloidal sol of Fe(OH)3 and As2S3 are mixed?
Answer:
On mixing Fe(OH)3 positive sol and As2S3 negative sol, mutual coagulation occurs which causes precipitation. When these sol got mixed with each other, due to Fe3+ and S2- ions neutralisation of charges will happen and precipitate will be formed.
Fe(OH)3 + As2S3 → Fe2S3 + As(OH)3
Question 9.
What is the difference between sol and a gel?
Answer:
Sol
- The liquid state of a colloidal solution is called sol.
- The sol does not have a definite structure.
- The dispersion medium of the sol may be water.
- The sol can be converted to gel by cooling The sol can be easily dehydrated.
- The viscosity of the sol is very low.
- Sol is categorized into lyophobic and lyophilic sols.
- Example: Blood
Gel
- The solid or semi-solid state of a colloidal solution is called gel.
- The gel possesses honey comb-like structure.
- The dispersion medium of gel will be hydrated colloid particles.
- The gel can be converted sol by heating.
- The gel cannot be dehydrated.
- The viscosity of the gel is very high.
- There is no such classification of gel.
- Example: Fruit jelly, cooked gelatin jelly.
Question 10.
Why are lyophillic colloidal sols are more stable than lyophobic colloidal sol?
Answer:
1. A lyophilic colloidal sols are stable due to the charge and the hydration of sol particles.
2. Lyophilic sols are more stable than lyophobilc sols because they are highly hydrated in the solution. And since more is the hydration more will be its stability.
3. Lyophilic sols are stabilized by electrostatic charge and hydration where as lyophobile sols are only stabilized by charge, so they easily gets coagulated and requires a stabilising agent. Hence, lyophilic sols are more stable than lyophobilc sols.
Question 11.
Addition of Alum purifies water. Why?
Answer:
Purification of drinking water is activated by coagulation of suspended impurities in water using alums containing Al3+. That is why we are adding to purify water.
Question 12.
What are the factors which influence the adsorption of a gas on a solid?
Answer:
Factors which influence the adsorption of a gas on a solid is as follows:
1. Nature of the gas:
Easily liquefiable gases such as NH3, HCl etc are adsorbed to a great extent in comparison to gases such as H2, O2, etc. This is because van der Waal’s forces are stronger is easily liquifiable gases.
2. Surface area of the solid:
The greater the surface area of the adsorbent, the greater is the adsorption of gas on the solid surface.
3. Effect of pressure:
Adsorption is a reversible process and is accompanied by a decrease in pressure. Therefore, adsorption increases with an increase in pressure.
4. Effect of temperature:
Adsorption is an exothermic process. Thus in accordance with Le – Chatelier’s principle, the magnitude of adsorption decreases with an increase in temperature.

Question 13.
What are enzymes? Write a brief note on the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
Answer:
Enzymes are complex protein molecules with three-dimensional structures. They catalyse the chemical reaction in a living organism. They are often present in colloidal state and extremely specific in catalytic action.
Each enzyme produced in a particular living cell can catalyse a particular reaction in the cell. Mechanism of enzyme catalysis: Mechanism of enzyme catalysed reaction is known as lock and key mechanism.
1. Enzymes arc highly specific in their action.
2. This specificity is due to the pressure of active sites. The shape of active site of any given enzyme is like cavity such that only a specific substrate can fit into it.
In the same way a key fits into lock. The specific binding needs the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex which accounts for high specificity of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
3. Once the proper orientation is attained the substrate molecules react to form the product in two steps.
4. Since the product molecule does not have an affinity for the enzyme they leave the enzyme surface making room for the fresh substrate.
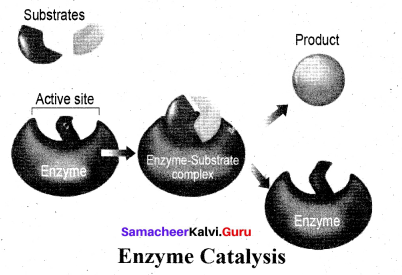
step 1: Formation of the enzyme-substrate complex

Step 2: Dissociation of the enzyme-substrate complex to form product
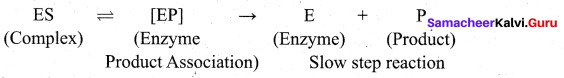
The rate of the formation of the product depends upon the concentration of ES.
Question 14.
What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalyst?
Answer:
1. Activity of Catalyst:
The activity of a catalyst is its ability to increase the rate of a particular reaction, Chemisorption is the main factor in deciding the activity of a catalyst. The adsorption of reactants in the catalyst surface should be neither too strong nor too weak. It should just be strong enough to make the catalyst active.
2. Selectivity of the catalyst:
The ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product is referred to as the selectivity of the catalyst. For example, by using different catalysts, we can get different products for the reaction between H2 and CO.
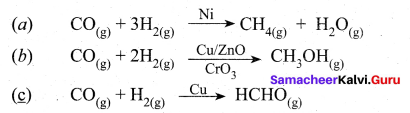
Question 15.
Describe some features of catalysis b Zeolites.
Answer:
- Zeolites are microporous, crystalline, hydrated aluminosilicates, made of silicon and aluminium tetrahedra.
- There are about 50 natural zeolites and 1 50 synthetic zeolites. As silicon is tetravalent and aluminium is trivalent, the zeolite matrix carries an extra negative charge. To balance the negative charge, there are extra framework cations, for example, H+ or Na+ ions.
- Zeolites earring protons are used as solid acids, catalysis and they are extensively used in the petrochemical industry for cracking heavy hydrocarbon fractions into gasoline, diesel, etc.
- Zeolites earring Na ions are used as basic catalysis.
- One of the most important applications of zeolites is their shape selectivity. In zeolites, the active sites namely protons are lying inside their pores. So, reactions occur only inside the pores of zeolites.
Question 16.
Give three uses of emulsions.
Answer:
- The cleansing action of soap is due to emulsions.
- It is used in the preparation of vanishing cream.
- It is used in the preparation of cold liver oil.

Question 17.
Why does the bleeding stop by rubbing moist alum?
Answer:
Blood is a colloidal sol. When we nib the injured part with moist alum then coagulation of blood takes place. Hence main reason is coagulation, which stops the bleeding. Therefore bleeding stop by rubbing moist alum.
Question 18.
Why is desorption important for a substance to act as good catalyst?
Answer:
Desorption is important for a substance to act as a good catalyst, so that after the reaction, the products found on the surface separate out (desorbed) to create free surface again for other reactant molecules to approach the surface and react. If desorption does not occur then other reactants are left with no space on the surface of the catalyst for adsorption and the reaction will stop.
Question 19.
Comment on the statement: Colloid is not a substance but it is a state of substance.
Answer:
The statement is true. Because the same substance may exist as a colloid under certain conditions and as a crystalloid under certain other conditions. For example. NaCl in water behaves as a crystalloid while in benzene, it behaves as a colloid. Similarly, dilute soap solution behaves
like a crystalloid while concentrated solutions behaves as a colloid. It is the size of the particles which matters. That is the state in which the substance exists. If the size of the particles lies in the range 1 nm to 1oo nm, it is in the colloidal state.
Question 20.
Explain any one method for coagulation
Answer:
The flocculation and setting down of the sol particles is called coagulation. Various method of coagulation are given below:
- Addition of electrolytes
- Electrophoresis
- Mining oppositely charged sols
- Boiling.
Addition of electrolytes
A negative ion causes the precipitation of positively charged sol and vice versa. When the valency of ion is high, the precipitation power is increased. For example, the precipitation power of some cations and anions varies in the following order
Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+, Similarly [Fe(CN)6]-3 > SO4-2 > Cl–
The precipitation power of electrolyte is determined by finding the minimum concentration (millimoles/lit) required to cause precipitation of a sol in 2hours. This value is called the flocculation value. The smaller the flocculation value greater will be precipitation.
Question 21.
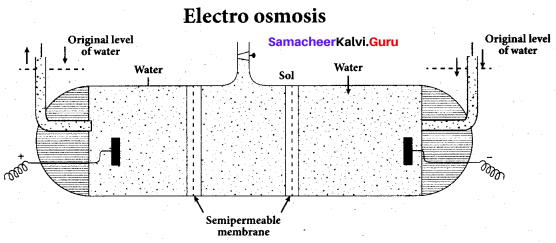
Write a note on electroosmosis.
Answer:
Electro osmosis:
A sol is electrically neutral. Hence the medium carries an equal but opposite charge to that of dispersed particles. When sol particles are prevented from moving, under the influence of electric field the medium moves in a direction opposite to that of the soil particles. This movement of dispersion medium under the influence of electric potential is called electro-osmosis.
Question 22.
Write a note on catalytic poison
Answer:
Catalytic poison:
Certain substances when added to a catalysed reaction, decreases or completely destroys the activity of catalyst and they are often known as catalytic poisons. For example, In the reaction,
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 with a Pt catalyst, the poison is AS2O3.
i.e., AS2O3 destroys the activity of pt. AS2O3 blocks the activity of the catalyst. So, the activity is lost.
Question 23.
Explain the intermediate compound formation theory of catalysis with an example.
Answer:
The intermediate compound formation theory:
A catalyst acts by providing a new path with low energy of activation. in homogeneously catalysed reactions a catalyst may combine with one or more reactant to form an intermediate which reacts with other reactant or decompose to give products and the catalyst is regenerated.
Consider the reactions:
A + B → AB ……………(1)
A + C → AC (intermediate) ………….(2)
C is the catalyst
AC + B → AB + C …………(3)
Activation energies for the reactions (2) and (3) are lowered compared to that of (1). Hence the formation and decomposition of the intermediate accelerate the rate of the reaction.
Example:
The mechanIsm of Fridel crafts reaction is given below
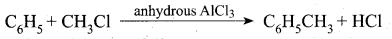
The action of catalyst is explained as follows .

This theory describes,
- The specificity of a catalyst.
- The increase in the rate of the reaction with increase in the concentration of a catalyst.
Limitations
- The intermediate compound theory fails to explain the action of catalytic poison and activators (promoters).
- This theory is unable to explain the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysed reactions.
Question 24.
What is the difference between homogenous and hetrogenous catalysis?
Answer:
Hornogenous Catalysis:
- In a catalysed reaction the reactants, products and catalyst are present in the same phase.
- For example.
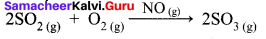
Hence NO act as catalyst.
- Homogeneous catalysis explained by intermediate compound formation theory.
Heterogeneous Catalysis:
- In a reaction, the catalyst is present in a different phase. i.e., catalyst is not present in the same phase as that of reactants and products.
- For example.
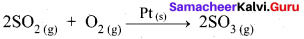
Hence Pt(s) act as catalyst.
- Hetenogeneous catalysis explained by adsorption theory.
Question 25.
Describe adsorption theory of catalysis.
Answer:
Adsorption theory:
Langmuir explained the action of catalyst in heterogeneous catalysed reactions based on adsorption. The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the catalyst surfaces, so this can also he called as contaçt catalysis.
According to this theory, the reactants arc adsorbed on the catalyst surface to form an activated complex which subsequently decomposes and gives the product. The various steps involved in a heterogeneous catalysed rcacton arc given as follows:
- Reactant molecules diffuse from bulk to the catalyst surface.
- The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.
- The adsorbed reactant molecules are activated and form activated complex which is decomposed to form the products.
- The product molecules are desorbed.
- The product diffuse away from the surface of the catalyst.
Advantages of adsorption theory:
The adsorption theory explains the following .
1. Increase in the activity of a catalyst by increasing the surface area. Increase in the surface area of metals and metal oxides by reducing the particle size increases the rate of the reaction.
2. The action of catalytic poison occurs when the poison blocks the active centres of the catalyst.
3. A promoter or activator increases the number of active centres on the surfaces.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry Additional Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry 1 mark Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer and write it. Answers are in bold it.
Question 1.
Which one of the following is used to absorb colourants from sugar?
(a) Silica gel
(b) Magnesia
(c) Charcoal
(d) Alumina
Answer:
(c) Charcoal
Question 2.
Silica gel is usually adsorbed………….
(a) Colourants
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Liquid Helium
(d) Water
Answer:
(d) Water
Question 3.
Which one of the following is called adsorbate?
(a) Charcoal
(b) Silica gel
(c) Ammonia
(d) Magnesia
Answer:
(c) Ammonia
Question 4.
Which of the following can act as adsorbent?
(a) Silica gel
(b) Ammonia
(c) Colourants
(d) Water
Answer:
(a) Silica gel
Question 5.
The surface of separation of two phases where the concentration of adsorbed molecule is high is known as …………..
(a) adsorbate
(b) adsorbent
(c) interface
(d) residual phase
Answer:
(c) interface

Question 6.
Consider the following statement.
(i) High adsorption is the result of high surface area of the adsorbent.
(ii) The process of removing an adsorbed substance is called absorption.
(iii) Adsorbed substance is called an adsorbate.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(c) (ii) only
Question 7.
Which metal cannot act as adsorbent?
(a) Pt
(b) Ag
(c) Pd
(d) Al
Answer:
(d) Al
Question 8.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Adsorption is spontaneous process.
(ii) Adsorption is always accompanied by an increase in free energy.
(iii) Adsorption is an endothermic reaction.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (ii) & (i)
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(b) (ii) & (iii)

Question 9.
Absorption and adsorption if simultaneously occurs, it is called ……………
(a) occlusion
(b) sorption
(c) desorption
(d) dissolution
Answer:
(b) sorption
Questioin 10.
The process of sorption of gases on the metal surface is called ……………
(a) Desorption
(b) Dissolution
(c) Occlusion
(d) Condensation
Answer:
(c) Occlusion
Question 11.
When gas molecules are held to the surface by the formation of the chemical bond the heat energy released is nearly equal to
(a) 40 kJ/mole
(b) 800 kJ/mole
(c) 400 kJ/mole
(d) 4 kJ/mole
Answer:
(c) 400 kJ/mole
Question 12.
Which of the following is physical adsorption?
(a) Adsorption of H2 on nickel
(b) Friedel crafts reaction
(c) Synthesis of SO3 in the presence of NO
(d) Corrosion of iron
Answer:
(a) Adsorption of H2 on nickel
Question 13.
Which one of the following is chemical adsorption?
(a) Adsorption of O2 on tungsten
(b) Adsorption of ethyl alcohol vapours on nickel
(c) Adsorption of N2 on mica
(d) Rusting of iron
Answer:
(d) Rusting of iron
Question 14.
Which of the following occurs at low temperatures?
(a) Adsorption of O2 on tun gsen
(b) Adsorption of N2 on mica
(c) Adsorption of ethyl alcohol vapours on nickel
(d) Adsorption of H2 on nickel
Answer:
(b) Adsorption of N2 on mica

Question 15.
Consider the following statements:
(i) Chemical adsorption is an instantaneous process
(ii) Multilayer of the adsorbate is formed on the adsorbent
(iii) Chemisorption involves the formation of the activated complex.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (i) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) & (ii)
Question 16.
Consider the following statements:
(i) In chemisorption, heat of adsorption is high
(ii) Monolayer of the adsorbate is formed during chemisorption
(iii) Physisorption increases with an increase in temperature.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct’?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) only
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(b) (iii) only
Question 17.
The extent of surface adsorption does not depend on
(a) Nature of the adsorbent
(b) Pressure
(c) Temperature
(d) Density
Answer:
(d) Density
Question 18.
Which of the following gases is not a permanent gas?
(a) NH3
(b) H2
(c) N2
(d) O2
Answer:
(a) NH3
Question 19.
Which of the following is liquefiable gas?
(a) SO2
(b) H2
(c) N2
(d) O2
Answer:
(a) SO2

Question 20.
Which one of the following is a permanent gas?
(a) NH3
(b) SO3
(c) N2
(d) CO2
Answer:
(c) N2
Question 21.
Consider the following statements.
(i) When pressure increases, the amount of physisorplion also increases.
(ii) Permanent gases like H2, N2 and O2 cannot be liquefied easily.
(iii) Lesser is the surface area, higher is the amount adsorbed.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) only
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(a) (i) & (ii)
Question 22.
Which one of the following is used in blast furnace for drying air?
(a) Activated charcoal
(b) Silica gel
(c) Alumina
(d) Permutit
Answer:
(b) Silica gel
Question 23.
Which is employed in the softening of hardwater to absorb Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions?
(a) Alumina
(b) Silica gel
(c) Permutit
(d) Charcoal
Answer:
(c) Permutit
Question 24.
The formula for permit is …………
(a) Ca Al2 Si4 O12
(b) CaAl3SiO2. xH2O
(c) Na2 Al2 Si4 O12
(d) Na2 SiO3
Answer:
(c) Na2 Al2 Si4 O12
Question 25.
Which one of the following is used to regenerate permutit in the softening of hard water?
(a) Common salt
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
(d) Quick lime
Answer:
(a) Common salt
Question 26.
Which of the following is used to demineralise water?
(a) Permutit
(b) Common salt
(c) Ion exchange resin
(d) Charcoal

Question 27.
Which of the following is used during world war as gas masks?
(a) Permutit
(b) Silica gel
(c) Fuller’s earth
(d) Charcoal
Answer:
(d) Charcoal
Question 28.
Which of the following is used in petroleum refining and refining of vegetable oils?
(a) Charcoal
(b) Silica gel
(c) Pcrmutit
(d) Nickel
Answer:
(b) Silica gel
Question 29.
The catalyst used in the hydrogenation of oils to obtain vanaspati is …………
(a) Iron
(b) Molybdenum
(c) Nickel
(d) Copper
Answer:
(c) Nickel
Question 30.
The catalyst and promoter used in Haber’s process are respectively ………..
(a) Mo, Fe
(b) Fe, Mo
(c) Pt, H2S
(d) Pt, V2O5
Answer:
(b) Fe, Mo
Question 31.
Which method is used for identification, detection, and estimation of many substances even if they are in micro quantities?
(a) Lassaigne’s test
(b) Canus method
(c) Kjeldhals method
(d) Chromatography
Answer:
(d) Chromatography
Question 32.
Which one of the following is used in the identification of Al3+ ion in Al(OH)3?
(a) Red litmus
(b) Blue litmus
(c) Phenol red
(d) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
(b) Blue litmus
Question 33.
Which ores are concentrated by the froth floatation process?
(a) Oxide ore
(b) Carbonate ore
(c) Sulphate ores
(d) Suiphide ores
Answer:
(d) Suiphide ores
Question 34.
In froth floatation process, the lighter ore particles are wetted by …………..
(a) Olive oil
(b) Pine oil
(c) Soap oil
(d) Neem oil
Answer:
(b) Pine oil
Question 35.
Which one of the following is an example of homogeneous catalysis?
(a) Decomposition of acetaldehyde by 12 catalysts
(b) Hydrolysis of cane sugar with a mineral acid
(c) Ester hydrolysis with alkali
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above

Question 36.
Which one of the following is an example for homogeneous catalysis?
(a) Manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process
(b) Manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process
(c) Oxidation of ammonia carried out in the presence of platinum gauze
(d) Hydrolysis of cane sugar with mineral acid
Answer:
(d) Hydrolysis of cane sugar with mineral acid
Question 37.
Which one of the following is an example for heterogeneous catalysis?
(a) Decomposition of acetaldehyde by I2 catalyst
(b) Decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of Pt catalyst
(c) Acid hydrolysis of ester
(d) Hydrolysis of cane sugar with mineral acid
Answer:
(b) Decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of Pt catalyst
Question 38.
Which one of the following is not an example for homogeneous catalysis?
(a) Contact process of manufacture of H2SO4
(b) Haber’s process of manufacture of NH3
(c) Acid hydrolysis of ester
(d) Freidel crafts reaction
Answer:
(c) Acid hydrolysis of ester
Question 39.
Consider the following statements:
(i) A catalyst needed in very small quantity
(ii) A catalyst can initiate a reaction
(iii) Catalyst are highly specific in nature
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i) & (iii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(d) (ii) only
Question 40.
Consider the following statements.
(i) A solid catalyst will be more effective if it is taken in a finely divided form
(ii) A catalyst cannot initiate a reaction
(iii) For a chemical reaction4 catalyst is needed in very large quantity
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i) & (ii)
Question 41.
The catalyst poison in the contact process of manufacture of SO3 is …………
(a) As2O3
(b) H2S
(c) CO
(d) As2S3
Answer:
(a) As2O3
Question 42.
In Haber’s process of manufacture of ammonia, the Fe catalyst is poisoned by the pressure of …………….
(a) Mo
(b) Co
(c) H2S
(d) As2O3
Answer:
(c) H2S

Question 43.
In the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O acts as a catalytic poison for Pt catalyst.
(a) Co
(b) Mo
(c) As2O3
(d) H2S
Answer:
(a) Co
Question 44.
The negative catalyst in the decomposition of H2O2 is …………..
(a) Ethanol
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Ethanoic acid
(d) Methanol
Answer:
(a) Ethanol
Question 45.
Which one of the following is an example tar an autocatalysis?
Answer:
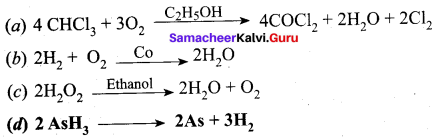
Question 46.
In the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide which acts as a negative catalyst?
(a) Dilute acid
(b) Glycerol
(c) a (or) b
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(c) a (or) b
Question 47.
The energy required for the reactants to reach the activated complex is called …………
(a) threshold energy
(b) activation energy
(c) internal energy
(d) Gibbs free energy
Answer:
(b) activation energy
Question 48.
Which of the following is explained by intermediate compound formation theory?
(a) Mechanism of Friedel crafts reaction
(b) Thermal decomposition of KClO3 in the presence of MnO2
(c) Oxidation of HCl by air in the presence of CuCl2
(d) Manufacture of NH3 by Haber’s process
Answer:
(d) Manufacture of NH3 by Haber’s process

Question 49.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Intermediate compound theory describes the specificity of a catalyst.
(ii) Intermediate compound theory explains the action of catalytic poison and activators.
(iii) Intermediate compound theory is unable to explain the mechanism of heterogeneously catalysed reactions.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (ii) only
(b) (i) & (iii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (i) & (ii)
Answer:
(a) (ii) only
Question 50.
Who explained the action of catalyst in adsorption theory?
(a) Berzellius
(b) Langmuir
(c) Thomas Graham
(d) Dalton
Answer:
(b) Langmuir
Question 51.
Consider the following statements.
(i) The action of catalytic poison occurs when the poison blocks the active centres of the catalyst.
(ii) A promoter decreases the number of active centres on the surfaces.
(iii) Increase in the activity of a catalyst by increasing the surface area.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
(a) (ii) only
(b) (iii) only
(c) (i) & (iii)
(d) (ii) & (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i) & (iii)
Question 52.
Which of the following catalyse the chemical reaction in a living organisms?
(a) enzymes
(b) protein
(c) lipids
(d) serum
Answer:
(c) lipids
Question 53.
Which of the following enzyme catalyse the hydrolysis of starch into maltose?
(a) maltase
(b) irivertase
(c) diastase
(d) zymase
Answer:
(c) diastase
Question 54.
Which enzyme catalyses the conversion of glucose into ethanol?
(a) maltase
(b) invertase
(c) diastase
(d) zymase
Answer:
(c) diastase

Question 55.
Which of the following act as catalyst in the oxidation of alcohol into acetic acid?
(a) pepsin
(b) diastase
(c) micro derma
(d) urease
Answer:
(c) micro derma
Question 56.
Which catalyst is used in the hydrolysis of urea?
(a) micro derma
(b) zymase
(c) pepsin
(d) urease
Answer:
(d) urease
Question 57.
Which of the following enzyme is present in soya beans?
(a) urease
(b) zymase
(c) pepsin
(d) lactase
Answer:
(a) urease
Question 58.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Enzymes are complex protein molecules with three-dimensional structures.
(ii) Enzymes catalyse the chemical reaction in living organism.
(iii) Enzymes arc not specific in catalytic action.
Which of the above statement is J are correct?
(a) (iii) only
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (i) & (ii)
(d) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i) & (ii)
Question 59.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Enzyme catalysed reaction has maximum rate at optimum temperature
(ii) Enzyme catalysis is highly specific in nature
(iii) Catalytic activity of enzyme is decreased by coenzyrnes or activators.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (iii) only
(b) (i) only
(c) (ii) only
(d) (i) & (ii)
Question 60.
The temperature at which enzyme activity is high (or) maximum is called ………….
(a) critical temperature
(b) optimum temperature
(c) low temperature
(d) high temperature
Answer:
(b) optimum temperature

Question 61.
Enzymes can be active in human body at a temperature of ………….
(a) 98°F
(b) 105°F
(c) 37°F
(d) 50°F
Answer:
(a) 98°F
Question 62.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Zeolites are alumino silicates made of silicon and aluminium tetrahedra.
(ii) Zeolites carrying Na ions are used as basic catalyst.
(iii) As silicon is tetravalent and aluminium is trivalent, the zeolite matrix carries extra positive charge.
Which of the above statement is / are correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) & (iii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) & (ii)
Question 63.
Which one of the following is used in the petrochemical industry for cracking heavy hydrocarbon fractions into gasoline, diesel, etc.?
(a) permutit
(b) zeolite
(c) pepsin
(d) protein
Answer:
(b) zeolite
Question 64.
Which one of the following is used as a catalyst in the conversion of Lindane to cyclohexane?
(a) Fe°/Pd°
(b) Ni
(c) Zn + HCl
(d) LiAIH4
Answer:
(a) Fe°/Pd°
Question 65.
Which one of the following is used as catalyst in homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis?
(a) enzymes
(b) zeolite
(c) nanocatalyst
(d) coenzyme
Answer:
(c) nanocatalyst
Question 66.
Who studied and analysed about colloids?
(a) Berzelius
(b) Thomas Graham
(c) Langmuir
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(b) Thomas Graham
Question 67.
Which one of the following is lyophillic colloid?
(a) Protein sol
(b) Gold sol
(c) Silver sol
(d) Platinum sol
Answer:
(a) Protein sol
Question 68.
Which one of the following is lyophobic colloid?
(a) Protein sol
(b) Starch sol
(c) Gel
(d) Gold sol
Answer:
(d) Gold sol
Question 69.
An example of liquid aerosol is ………..
(a) Soda water
(b) Milk
(c) Fog
(d) Inks
Answer:
(c) Fog

Question 70.
Which of the following is an example of Emulsion?
(a) mayonnaise
(b) shaving cream
(c) fumes
(d) paint
Answer:
(a) mayonnaise
Question 71.
The dispersed phase and dispersion medium in smoke, fumes and dust are …………..
(a) gas, solid
(b) solid, gas
(c) gas, liquid
(d) solid, liquid
Answer:
(b) solid, gas
Question 72.
Inks, paints arc considered as …………
(a) liquid in solid
(b) solid in liquid
(c) gas in gas
(d) solid in solid
Answer:
(b) solid in liquid
Question 73.
Which of the following is an example for gel?
(a) Pumice stone
(b) Pearls
(c) Coloured glass
(d) Butter
Answer:
(c) Coloured glass
Question 74.
Which one of the following is an example for solid sol?
(a) Butter
(b) Cheese
(c) Pearls
(d) Pumice stone
Answer:
(c) Pearls
Question 75.
Soda water is an example for ………..
(a) gel
(b) emulsion
(c) foam
(d) sol
Answer:
(c) foam
Question 76.
Colloidal ink and graphite are prepared by …………
(a) colloid mill
(b) Bredig’s arc
(c) ultrasonic homogenizer
(d) peptisation
Answer:
(a) colloid mill
Question 77.
Which method is used to prepare metal sols?
(a) ultrasonic dispersion
(b) mechanical dispersion
(c) Bredigs arc method
(d) peptisation
Answer:
(c) Bredigs arc method
Question 78.
Who prepared non-aqueous inflammable liquids like Benzene and ether by Bredig’s arc method?
(a) George Bredig
(b) Sved berg
(c) Thomas Graham
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(b) Sved berg

Question 79.
Which method is used to prepare mercury colloid?
(a) peptisation
(b) mechanical dispersion
(c) ultrasonic dispersion
(d) Bredig’s arc method
Answer:
(c) ultrasonic dispersion
Question 80.
Mercury sol is obtained by subjecting it to sound waves of frequency more than ………..
(a) 20 Hz
(b) 20 kHz
(c) 200 kHz
(d) 2000 kHz
Answer:
(b) 20 kHz
Question 81.
The conversion of a precipitate into colloid is called …………..
(a) coagulation
(b) hydrolysis
(c) condensation
(d) peptisation
Answer:
(d) peptisation
Question 82.
Gold sol is prepared by reduction of auric chloride using …………..
(a) water
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3COOH
Answer:
(b) HCHO
Question 83.
Which method is suitable to prepare I2 sol and Se sol?
(a) Reduction
(b) Hydrolysis
(c) oxidation
(d) peptisation
Answer:
(c) oxidation
Question 84.
Which condensation method is used to prepare sulphur sol?
(a) Hydrolysis
(b) Decomposition
(c) Reduction
(d) Peptisation
Answer:
(b) Decomposition

Question 85.
Arsenic sulphide colloid is prepared by ………..
(a) hydrolysis
(b) reduction
(c) double decomposition
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(c) double decomposition
Question 86.
By which method phosphorous colloid can be prepared’?
(a) Decomposition
(b) Exchange of solvent
(c) Hydrolysis
(d) Reduction
Answer:
(b) Exchange of solvent
Question 87.
Which one of the following is not used to purify colloids?
(a) Dialysis
(b) Peptisation
(c) Electrodialysis
(d) Uhrafilteration
Answer:
(b) Peptisation
Question 88.
The process of conversion of colloidal solution into precipitate is known as …………..
(a) peptisation
(b) dispersion
(c) coagulation
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(c) coagulation
Question 89.
Which one of the following is named collodion?
(a) 4% solution of nitro cellulose in a mixture of alcohol and water
(b) 40% solution of cellulose acetate in acetic acid.
(c) agar-agar along with gel
(d) semipermeable membrane
Answer:
(a) 4% solution of nitro cellulose in a mixture of alcohol and water
Question 90.
Which of the following is the size of the colloidal particle?
(a) 100 μm diameter – 1000 μm diameter
(b) 1 mμ to 1 μm diameter
(c) 1 mμ to 100 μm diameter
(d) 1 μm to 1 μm diameter
Answer:
(b) 1 mμ to 1 μm diameter

Question 91.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Colloidal solutions are quite stable and are not affected by gravity
(ii) Colloids diffuse more readily through membranes
(iii) Colloidal solutions show colligative properties
Which of the above statement is / are correct?
(a) (i) & (iii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) & (iii)
Question 92.
The shape of tungstic acid W3O5 sol is ………….
(a) spherical
(b) disc
(c) plate-like
(d) rod like
Answer:
(d) rod like
Question 93.
Which one of the following colloids has spherical shape?
(a) AS2S3
(b) Fe(OH)3
(c) W3O5
(d) dust
Answer:
(a) AS2S3
Question 94.
Tyndall effect is possible in colloid due to ……………
(a) absorption of light
(b) adsorption of light
(c) scattering of light
(d) reflection of light
Answer:
(c) scattering of light
Question 95.
Which one of the following does not show Tyndali effect and Brownian movement?
(a) Milk
(b) common salt solution
(c) smoke
(d) tungstic acid sol
Answer:
(b) common salt solution
Question 96.
The migration of sol particles under the influence of electric field is called ……………
(a) electro osmosis
(b) electro dialysis
(c) electrophoresis
(d) dialysis
Answer:
(c) electrophoresis

Question 97.
Which one of the following is used for detection of pressure of charge on sol particles?
(a) Cataphoresis
(b) Electrodialysis
(c) Dialysis
(d) Ultrafiltration
Answer:
(a) Cataphoresis
Question 98.
Which of the following is positively charged colloid?
(a) haemoglobin
(b) starch
(c) clay
(d) AS2S3
Answer:
(a) haemoglobin
Question 99.
Which one of the following is a positively charged colloid?
(a) Ag
(b) AU
(c) Basic dyes
(d) Clay
Answer:
(c) Basic dyes
Question 100.
Which one of the following is a negatively charged colloid?
(a) Pt
(b) Al(OH)3
(c) Fe (OH)3
(d) Basic dyes
Answer:
(a) Pt
Question 101.
Which one of the following is a negatively charged colloid?
(a) Ferric hydroxide
(b) Clay
(c) Basic dyes
(d) Haemoglobin
Answer:
(b) Clay
Question 102.
The movement of dispersion medium under the influence of electric potential is called ………….
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Cataphoresis
(c) Electro osmosis
(d) Electro dialysis
Answer:
(c) Electro osmosis
Question 103.
Which one of the following is added to gold sol to protect it?
(a) Gelatine sol
(b) Gum
(c) Starch
(d) Basic dye
Answer:
(a) Gelatine sol

Question 104.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Smaller the gold number, greater the protective power
(ii) Greater the gold number, greater the protective power
(iii) Colloidal sols with opposite charges are mixed, mutual coagulation takes place.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (i) & (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (ii) & (iii)
Answer:
(c) (ii) only
Question 105.
Which one of the following can act as emulsifier?
(a) glue
(b) dye
(c) water
(d) starch
Answer:
(a) glue
Question 106.
Which one of the following is not used to identify the types of emulsion?
(a) dye test
(b) viscosity test
(c) conductivity test
(d) Tollen’s test
Answer:
(d) Tollen’s test
Question 107.
By adding which one of the following oil in water emulsion containing potassium soap can be converted into water in oil emulsion?
(a) MCl3
(b) NaCI
(c) KCI
(d) C6H5Cl
Answer:
(a) MCl3
Question 108.
Which of the following colloid is used as a medicine for stomach troubles?
(a) colloidal Au
(b) colloidal Ca
(c) milk of magnesia
(d) silver sol
Answer:
(c) milk of magnesia
Question 109.
Which one of the following is used in the purification of drinking water?
(a) silver sol protected by gelatine
(b) milk of magnesia
(c) Alum containing Al3+
(d) Argyrol
Answer:
(c) Alum containing Al3+
Question 110.
Which of the following is used as tonics?
(a) milk of magnesia
(b) Argyrol
(c) colloidal Au & colloidal Ca
(d) Alum
Answer:
(c) colloidal Au & colloidal Ca
Question 111.
Which one of the following is used in tanning of leather?
(a) chromium salt
(b) colloidal Au
(c) Argyrol
(d) Fe (OH)3
Answer:
(a) chromium salt
Question 112.
Carbon dust in air is solidified by ………..
(a) cottrell’s precipitator
(b) colloidal mill
(c) Bredig’s arc
(d) peptisation
Answer:
(a) cottrell’s precipitator

Question 113.
Which of the following voltage is used in cottrell’s precipitator?
(a) 5000 V
(b) 50,000 V
(c) 1,000V
(d) 10,000V
Answer:
(b) 50,000 V
Question 114.
The blue colour of the sky is due to …………
(a) coagulation
(b) peptisation
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) Brownian movement
Answer:
(c) Tyndall effect
Question 115.
Which one of the following is used to distinguish Natural honey and artificial honey?
(a) Ammoniacal AgNO3
(b) Fehling’s solution
(c) Arsenic suiphide sol
(d) gelatin
Answer:
(a) Ammoniacal AgNO3
Question 116.
Which one of the following is the catalyst poison in Haber’s process?
(a) AS2S3
(b) AS2O3
(c) Co
(d) H2S
Answer:
(d) H2S
Question 117.
Which one of the following is an example for water in oil emulsion?
(a) Milk
(b) Vanishing cream
(c) Butter
(d) Soap
Answer:
(c) Butter
Question 118.
Which of the following is contributed towards the extra stability of lyophillic colloid?
(a) Hydration
(b) Charge
(c) Colour
(d) Tyndall effect
Answer:
(a) Hydration
Question 119.
A catalyst is a substance which
(a) increases the equilibrium concentration of the product
(b) changes the equilibrium constant of the reaction
(c) shortens the time to reach equilibrium
(d) supplies energy to the reaction
Answer:
(c) shortens the time to reach equilibrium
Question 120.
The ability of an ion to bring about coagulation of a given colloid depends upon …………
(a) its size
(b) magnitude of its charge
(c) the sign of its charge
(d) both the magnitude and sign of the charge
Answer:
(d) both the magnitude and sign of the charge
Question 121.
Which one of the following is an incorrect statement for physisorption?
(a) It is a reversible process
(b) It requires less heat of adsorption
(c) It requires activation energy
(d) It take place at low temperature
Answer:
(c) It requires activation energy
Question 122.
Which is not a colloid?
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) Egg
(c) Ruby glass
(d) Milk
Answer:
(a) Chlorophyll

Question 123.
Which of the following electrolytes is most effective in the coagulation of gold sol?
(a) NaNO3
(b) K4[Fe(CN)6]
(c) Na3PO4
(d) MgCl2
Answer:
(b) K4[Fe(CN)6]
Question 124.
Gold number gives ………………..
(a) the amount of gold present in the colloid
(b) the amount of gold required to break the colloid
(c) the amount of gold required to protect the colloid
(d) the measure of protective power of a lyophillic colloid
Answer:
(d) the measure of protective power of a lyophillic colloid
Question 125.
Identify the gas which is readily adsorbed by activated charcoal?
(a) N2
(b) SO2
(c) H2
(d) O2
Answer:
(b) SO2
Question 126.
Starch dispersed in hot water is an example of …………..
(a) emulsion
(b) hydrophobic sol
(c) lyophilic sol
(d) associated colloid
Answer:
(c) lyophilic sol
Question 127.
Which one is an example of gel?
(a) soap
(b) cheese
(c) milk
(d) fog
Question 128.
The random, zig-zag motion of colloidal particles in the dispersion medium is referred to as …………..
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Brownian movement
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) Electro osmosis
Answer:
(b) Brownian movement

Question 129.
Which of the following electrolytes is least effective in causing flocculation of ferric hydroxide sol?
(a) K4 [Fe(CN)6]
(b) K2CrO4
(c) KBr
(d) K2SO4
Answer:
(c) KBr
Question 130.
Gelatin is mostly used in making icecream in order to …………..
(a) prevent making of colloid
(b) to stabilize the colloid and to prevent the crystallization
(c) to stabilise the mixture
(d) to enrich the aroma
Answer:
(b) to stabilize the colloid and to prevent the crystallization
Question 131.
Which one of the following is not a colloidal solution?
(a) smoke
(b) ink
(c) air
(d) coffee
Answer:
(c) air
Question 132.
Milk can be preserved by adding a few drops of …………
(a) HCOOH
(b) HCHO
(c) CHCOOH
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(b) HCHO
Question 133.
Bleeding is stopped by the application of ferric chloride. This is because …………
(a) ferric chloride seal the blood cells
(b) blood starts flowing in ohter direction
(c) blood is coagulated and blood vessel is sealed
(d) blood is peptised
Answer:
(c) blood is coagulated and blood vessel is sealed
Question 134.
Delta at the rivers are formed due to …………
(a) peptisation
(b) coagulation
(c) hydrolysis
(d) precipitation
Answer:
(b) coagulation
Question 135.
Alum purifies muddy water by …………..
(a) dialysis
(b) adsorption
(c) coagulation
(d) forming a true solution
Answer:
(c) coagulation
Question 136.
Reactions of zeolite catalysts depend on ………….
(a) pores
(b) apertures
(c) size of cavily
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 137.
chemisorption ……………
(a) increases with increase in temperature
(b) decreases with increase in temperature
(c) remains unaffected by the, change of temperature
(d) first increases and then decreases.
Answer:
(d) first increases and then decreases.

Question 138.
Adsorption is always …………
(a) endothermic
(b) exothermic
(c) iso thermic
(d) either a (or) b
Answer:
(a) endothermic
Question 139.
Which one of the following can be explained by the adsorption theory?
(a) Homogeneous catalysis
(b) Acid-base catalysis
(c) Heterogeneous catalysis
(d) Enzyme catalysis
Answer:
(c) Heterogeneous catalysis
Question 140.
Physical adsorption is inversly proportional to ……………..
(a) volume
(b) concentration
(c) temperature
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) temperature
Question 141.
Noble gases are adsorbed by ……………
(a) anhydrous CaCl2
(b) Fe(OH)3
(c) Conc. H2SO4
(d) activated charcoal
Answer:
(d) activated charcoal
Question 142.
Animal charcoal is used in decolourising agent in the manufacture of sugar because it is a good …………..
(a) adsorbate
(b) adsorbent
(c) oxidising agent
(d) dehydrating agent
Answer:
(a) adsorbate
Question 143.
Gold number is associated only with …………
(a) lyophobic colloids
(b) lyophilic colloids
(c) both lyophobic and lyophilic colloids
(d) Au in water
Answer:
(b) lyophilic colloids
Question 144.
Which of the following forms a colloidal solution with water?
(a) NaCl
(b) Glucose
(c) Starch
(d) Barium sulphate
Answer:
(c) Starch
Question 145.
Which one of the following is an example for homogeneous catalysis?
(a) Hydrogenation of oil
(b) manufacture of NH3 by Haber’s process
(c) manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process
(d) hydrolysis of sucrose in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid
Answer:
(d) hydrolysis of sucrose in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid

Question 146.
Which of the following does not involve coagulation?
(a) peptisation
(b) formation of delta regions
(c) treatment of drinking water by potash alum
(d) clotting of blood by the use of ferric chloride
Answer:
(a) peptisation
Question 147.
Among the electrolytes Na2SO4, CaCI2, Al2(SO4)3 and NH4Cl, the most effective coagulating agent for Sb2S3 Sol is ……………
(a) Na,SO4
(b) CaCl2
(c) Al2(SO4)3
(d) NH4Cl
Answer:
(c) Al2(SO4)3
Question 148.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding physisorption?
(a) It occurs because of Van der Waals forces
(b) more easily liquefiable gases are adsorbed easily
(c) under high pressure, it resuLts into multimolecular layer on adsorbent surface
(d) enthalpy of adsorption is low and positive
Answer:
(d) enthalpy of adsorption is low and positive
Question 149.
Rate of physical adsorption increase with ………..
(a) increase in temperature
(b) decrease in pressure
(c) decrease in temperature
(d) decrease in surface are
Answer:
(c) decrease in temperature

Question 150.
Gold numbers of protective eolloids, A, B, C and D are respectively 0.50, 0.01, 0.10 and 0.005. The correct order of the stability of colloids is ……..
(a) B < D < A < C
(b) D < A < C < B
(c) C < B < D < A
(d) A < C < B < D
Answer:
(d) A < C < B < D
II. Fill in the blanks
- The surface of separation of the two phases where the concentration of adsorbed molecule is high is known as …………..
- In adsorption, if the concentration of a substance in the interface is high, it is called ……………
- The process of removing a adsorbed substance from the surface is called ……………
- Adsorption is always accompanied by decrease in ……………
- A term …………… is used for sorption of gases on metal surfaces
- M.C. Bain introduced a term …………… to represent the simultaneous adsorption and absorption.
- In chemical adsorption, gas molecules are held to the surface by formation of chemical bond and nearly …………… is given out as heat of adsorption
- In physical adsorption …………… exist between adsorbent and adsorbate
- Heat of adsorption is low hence physical adsorption occurs at ……………
- …………… involves the formation of activated complex with appreciable activation energy.
- Adsorption occurs at fixed sites called ……………
- Gases like NH3, SO3 and CO2 are …………… as have greater Van der Waals force of attraction.
- gases like H2, N2, O2 have low critical temperature and ………….. slowly
- A plot between the amount of adsorbate adsorbed and pressure or concentration of adsorbate at constant temperature is called …………..
- Freundlich adsorption isothermal equation is applicable fo adsorption of …………..
- During World War I ………….. gas mask was employed
- ………….. is used to create high vaccum in vessels.
- In blast furnace ………….. is used for drying air
- For dehydration and also purification of gases like CO2, N2, CI2, O2 and He ………….. and are employed.
- …………..is employed in the softening of hard water to adsorb Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions
- In the process of softening of hard water, exhausted permutit is regenerated by adding a solution of …………..
- ………….. are used to demineralise water.
- ………….. and ………….. are used in petroleum refining and refining of vegetable oil.
- ………….. is used to decolourising agent in manufacture of sugar from molasses.
- In forth floation process, the suiphide are particles are wetted by …………..
- ………….. is defined as a substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing chemical change.
- The decomposition of acetaldehyde by I2 catalyst is an example of ………….. catalysis.
- Manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process is an example of ………….. catalysis.
- Friedel crafts reaction is an example of ………….. catalysis.
- The substances increases the activity of a catalyst are called …………..
- ………….. or ………….. used as promoter for iron in Haber’s process
- ………….. destroys the activity of platinum in contact process
- In the reaction CH3COOC2H5 + H2O → CH3COOH + C2H5OH ………….. is act as auto calyst.
- The decomposition of H2O2 rate is decreased by …………..
- As …………..is lowered in the presence of catalyst, more molecules take part in the reaction and hence the rate of the reaction increases.
- The mechanism of friedel crafts reaction is explained by ………….. theory.
- The catalyst used for the oxidation of HCl by air is …………..
- Thermal decomposition of KClO3 in the presence of ………….. follows ………….. theory.
- Intermediate compound formation theory is unable to explain the mechanism of …………..
- Hydrogenation of ethylene in the presence of nickel catalyst follows ………….. theory.
- ………….. are complex protein molecules and catalyse the chemical reaction in living organism.
- The enzyme ………….. hydrolyses starch into maltose.
- The enzyme ………….. oxidises alcohol into acetic acid.
- Enzyme catalysed reaction has ………….. rate at optimum temperature.
- ………….. in hibits the action of bacteria and used for curing pneumonia.
- ………….. are microporous, hydrated alumino silicates.
- Zeolites carrying ………….. are used as basic catalysts
- Like heterogeneous catalyst ………….. can be recovered and recycled.
- Sols of gold, silver, platinum and copper are examples of …………..
- So is of protein and starch are examples of …………..
- A liquid in liquid colloid is called …………..
- Pearls, opals and Ruby red glass are belong the colloid named …………..
- Rubber forns colloidal solution with …………..
- In colloid mill, the two metal plates rotating in opposite directions of nearly ………….. revolution per minute.
- Colloidal solutions of ink and graphite are prepared by ………….. method.
- A brown colloidal solution of platinum was prepared by ………….. in 1898.
- ………….. is added as an stabilising agent for making platinum colloid.
- Metal hydroxide is added as an ………….. for making noble metal sols.
- Claus obtained ………….. by subjecting ………….. to high frequency ultrasonic vibrations,
- In the preparation of AgCI colloid from AgCl precipitate, the peptising or dispersing agent used is …………..
- Gold sol is prepared by reduction of auric chloride using …………..
- Arsenic sulphide colloid can be prepared by ………….. method.
- 12 sol is obtained from HIO3 by ………….. method.
- The process of conversion of colloidal solution into precipitate is called …………..
- In the dialysis of kidney. recycling of patient’s blood is done through semipermeable tube in an ………….. solution
- Collodion is 4% solution of ………….. in a mixture of …………..
- The size of colloidal particles ranges from …………..
- The shape of blue gold sol (or) Fe(OH)3 sol is …………..
- Pollen grains suspended in water showed …………..
- The flocculation and setting down of sol particles is called …………..
- When the valency of ion is high ………….. power is increased in colloids.
- The smaller the ………….. value, greater will be precipitation of colloids.
- ………….. is added to gold sol to protect it.
- ………….. introduced the term gold number as a measure of protecting power of a colloid.
- An oil in watrer emulsion containing potassium soap as emulsifying agent can be converted into water in oild emulsion by adding ………….. or …………..
- Synthetic polymers like polystyrene, silicones and PVC, are …………..
- ………….. colloid is used as eye lotion.
- ………….. protected by gelatin is known as Argyrol.
- ………….. salts arc used in tanning of leather.
- Natural honey is distinguished artificial honey by adding …………..
Answer:
- interface
- positive adsorption
- desorption
- free energy
- occlusion
- sorption
- 400kJ/rnole
- Van der Waals forces of attraction
- low temperature
- Chemisorption
- active centres
- easily liquefiable
- Permanent, adsorbed
- Adsorption isotherm
- gases on solid surface
- charcoal
- Activated charcoal
- silica gel
- alumina, silica
- Permutit
- common salt
- Con exchange resins
- Fuller’s earth, silica gel
- Animal charcoal
- pine oil
- catalyst
- homogeneous
- heterogeneous
- heterogeneous
- promoters
- Mo (or) Al2O3
- AS2O3 catalyst poison
- CH3COOH
- ethanol (or) Glycerol, negative catalyst
- Activation energy
- intermediate compound formation
- CuCI2
- MnO2, intermediate compound formation theory
- heterogeneous catalysis
- adsorption
- enzymes
- diastase
- micoderma aceti
- maximum
- penicillin
- zeolites
- Na ions
- nano catalyst
- lyophobic sols (or) irreversible sols
- lyophilic sols (or) reversible sols
- emulsion
- solid sol
- benzene
- 7000
- mechanical dispersion
- George Bredig
- alkali hydroxide
- stabilising agent
- mercury sol, mercury
- HCl
- formaldehyde
- double decomposition
- oxidation
- coagulation
- isotonic saline
- nitro cellulose, alcohol and water
- 1 mi to llim diameter
- disc or plate like
- Brownian movement
- coagulation
- precipitation
- flocculation
- geLatine sol
- Zsigmondy
- CaCl2, AlCl3
- colloids
- Argyrol
- Silver sol
- chromium
- Tollens reagent (or) Ammoniacal AgNO3
III. Match the column I & II using the code given below the coulum.
Question 1.
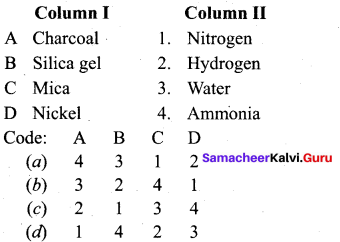
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 2.
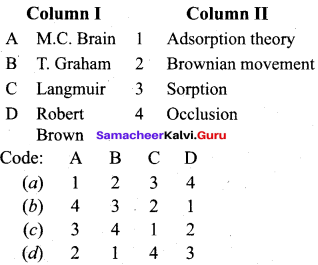
Answer:
(c) 3 4 1 2
Question 3.
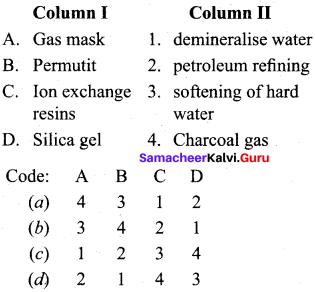
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 4.

Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 5.
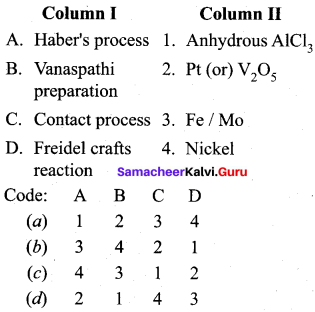
Answer:
(b) 3 4 2 1
Question 6.
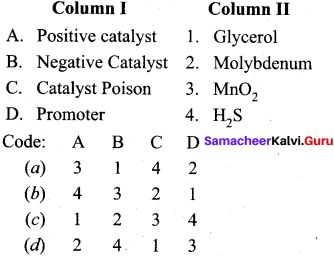
Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 7.
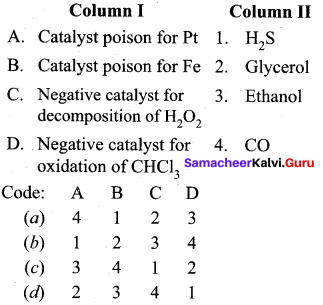
Answer:
(a) 4 1 2 3
Question 8.
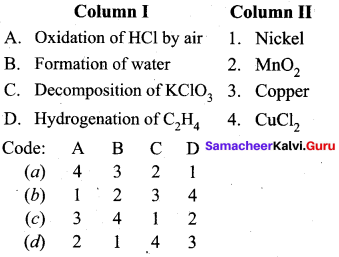
Answer:
(a) 4 3 2 1
Question 9.
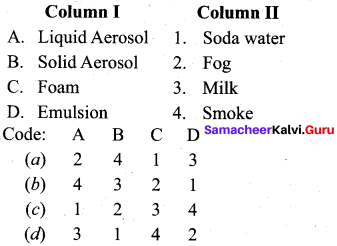
Answer:
(a) 2 4 1 3
Question 10.
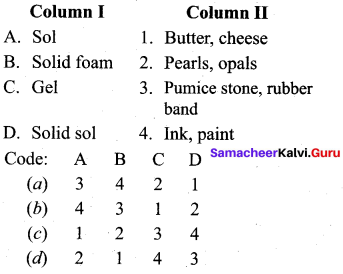
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 11.
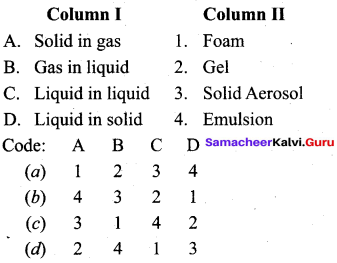
Answer:
(c) 3 1 4 2
Question 12.
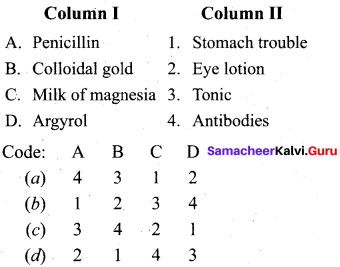
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 13.
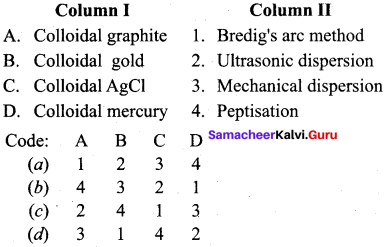
Answer:
(d) 3 1 4 2
Question 14.

Answer:
(b) 4 3 2 1
Question 15.
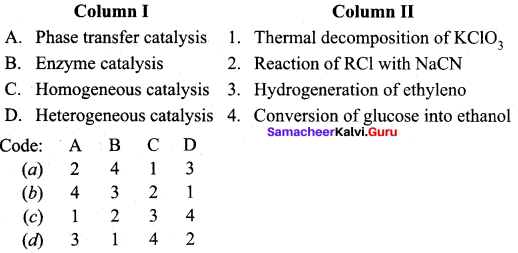
Answer:
(a) 2 4 1 3
Question 16.
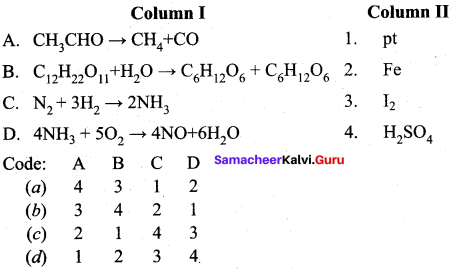
Answer:
(b) 3 4 2 1
Question 17.
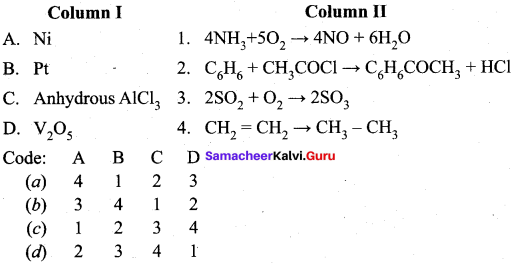
Answer:
(a) 4 1 2 3
Question 18.

Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Absorption is a bulk phenomenon.
Reason (R) : The absorbed molecules are distributed throughout the absorbent.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct but R is wrong.
(c) A is wrong but R is correct.
(d) Both A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Adsorption is a spontaneous process.
Reason (R) : Adsorption is always accompanied by decrease in free energy. When molecules are adsorbed, there is always a decrease in randomness of the molecules.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Chemical adsorption is an exothermic process.
Reason (R) : In chemical adsorption, gas molecules are held to the surface by formation of chemical bonds. Since strong bond is formed, nearly 400kJ/mole is given out as heat adsorption.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : Physical adsorption occurs at low temperature.
Reason (R) : ¡n physical adsorption, weak Van der Waals force of attraction exist. Other weak forces exist in physical adsorption are dipole-dipole interaction and dispersion forces. As these forces are weak, heat of adsorption is low.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 5.
Assertion (A) : Platinised asbestos is a better adsorbent than platinum block.
Reason (R) : Higher the surface area, higher is the amount adsorbed. In platinum coated asbestos the surface area is more and so it act as a better adsorbent.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion (A) : Gases like SO2, NH3 and CO2 are readily adsorbed.
Reason (R) : SO2, NH3 and CO2 are easily liquefiable as have greater van der WaaI’s forces of attraction and adsorbed readily.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and Rare wrong.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
Assertion (A) : Permanent gases like H2, N2 and O2 cannot be adsorbed readily.
Reason (R) : Permanent gases having low critical temperature and adsorbed slowly.
(a) Both A and R are wrong.
(b) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is wrong but R is correct.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(b) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A

Question 8.
Assertion (A) : Chromatography is a very effective method and used for identification, detection and estimation of micro quantities of many substances.
Reason (R) : Chromatography technique is applied for separation and detection of components in a mixture it is mainly based on adsorption of components on the surface of adsorbents.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 9.
Assertion (A) : Ester hydrolysis of acid (or) alkali catalyst is an example of homogeneous catalysis.
Reason (R) : Ester, H2O acid (or) alkali and the products are in liquid form.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct,
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 10.
Assertion (A) : The manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process is an example of heterogeneous catalysis.
Reason (R) : The catalyst Pt (or) VO5, reactants and products are in different phases in contact process.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : Acid hydrolysis of ethylacetate by water to produce acetic acid and ethanol is an example of auto catalysis.
Reason (R) : In acid hydrolysis of ester, the product acetic acid act as catalyst and this process is called autocatalysis.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong.
(c) A is correct hut R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 12.
Assertion (A) : Effective and efficient conversion is the special characteristic of enzyme catalysed reactions.
Reason (R) : An enzyme may transform a million molecules of reactants to products in a minute.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : lyophillic colloids will not get precipitated easily.
Reason (R) : In lyophillic colloids, definite attractive forces exists between dispersion medium and dispersed phase and they are more stable.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : Lyophobic colloids like sols of gold will precipitate readily.
Reason (R) : In lyophobic colloids, no attractive force exists between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium and are less stable.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are correct.
(d) A is correct but R is wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 15.
AssertIon (A) : Iron colloid cannot be prepared by Bredig’s arc method.
Reason (R) : iron cannot react with alkali hydroxide stabilising agent added in water.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct but R is wrong.
(c) A is wrong but R is correct.
(d) Both A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
V. Find the odd one out.
Question 1.
He, Ne, O2, N2, Pt
Answer:
Pt. It is adsorbent and all others are adsorbates.
Question 2.
SO2, NH3, NaCI, Silica gel
Answer:
Silica gel. It is an adsorbent whereas others are adsorbates.
Question 3.
Silica gel, Pt, Ag, Pd, NH3
Answer:
NH3 It is an adsorbate whereas others are adsorbents.

Question 4.
Coconut charcoal, silica gel, mica, SO2, Animal charcoal
Answer:
SO2 It is an adsorbate whereas others are adsorbents.
Question 5.
Mica, Nickel, Charcoal, Tungsten, Ethyl alcohol vapours
Answer:
Ethyl alcohol vapours. It is an adsorbate whereas others are adsorbents.
Question 6.
Pt, Glycerol, MnO2, Ni, I2
Answer:
Glycerol. It is a negative catalyst whereas others are positive catalyst.
Question 7.
Fe, Anhydrous AlCl3, V2O5, Pt, Ethyl alcohol
Answer:
Ethyl alcohol is a negative catalyst whereas others are positive catalyst.
Question 8.
Decomposion of acetaldehyde by I2 Decomposition of H2O2 by Pt, Ester hydrolysis with acid, Hydrolysis of cane sugar.
Answer:
Decomposition of H2O2 by Pt. It is heterogeneous catalysis whereas others are homogeneous catalysis.
Question 9.
Friedel crafts reactopm, Haner’s process, Hydrolysis of cane sugar, contact process.
Answer:
Hydrolysis of cane sugar. It is homogeneous catalysis whereas others are heterogeneous catalysis.
Question 10.
Pepsin, Zymase, Maltase, Diastase, Maltose, Urease.
Answer:
Maltose. It is a carbohydrate whereas others are enzyme catalysts.
Question 11.
Pt, Ni, Fe°/Pd°, Fe/Mo, Sn/HCI
Answer:
Fe°/Pd°. It is a nano catalyst where as others ordinary catalyst.
Question 12.
Milk, coffee, smoke, common salt solution, dust.
Answer:
Common salt solution. It is a true solution whereas others are colloids.
Question 13.
Soda water, Butter, Starch solution, Cheese, Cream.
Answer:
Starch solution. It is a suspension whereas others are colloids.
Question 14.
Ink, Milk, Cream, Mayonnaise.
Answer:
Ink. It is a sol whereas others are Emulsion.
Question 15.
Pearls, Opals, Coloured glass, Alloys, Pumice stone.
Answer:
Pumice stone. It is a solid foam whereas others are solid sol.
Question 16.
Smoke, Froth, Fumes, Dust, Air pollutants.
Answer:
Froth. It is a foam whereas others are solid aerosol.
Question 17.
Pumice stone, Foam, Milk, Rubber band.
Answer:
Milk. It is an emulsion whereas others are solid foam.
Question 18.
Mechanical dispersion, Bredigts arc method, Peptisation, Double decomposition, Ultrasonic dispersion.
Answer:
Double decomposition. It is a condensation method of preparation of colloids whereas others are dispersion methods of preparation of colloids.
Question 19.
Oxidation, Peptisation, Reduction, Decomposition, Hydrolysis.
Answer:
Peptisation. It is a dispersion method of preparation ofcoiloid whereas others are condensation methods of preparation of colloids.
Question 20.
Dialysis, electrophoresis, Ultrafi iteration. Electrodialysis.
Answer:
Electrophoresis is an electrical property of colloids but others are purification methods of colloids.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry 2 Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define
- Adsorbent
- Adsorbate with an example.
Answer:
- Adsorbent is a material on which adsorption takes place. eg., silica gel and metals like Ni, Cu, Pt.
- Adsorbate is a substance which is adsorbed on the adsorbent. e.g., Gaseous molecules like He, Ne, O2, N2 and solutions of NaCI (or) KCI.
Question 2.
Define
- Interface
- Desorption.
Answer:
1. Interface:
The surface of separation of the two phases where the concentration of adsorbed molecule is high is known as interface.
2. Desorption:
The process of removing an adsorbed substance from the substance is called desorption.
Question 3.
What is adsorption? What is meant by positive and negative adsorption?
Answer:
Adsorption is the odhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. In adsorption, if the concentration of a substance in the interface is high, then it is called positive adsorption. 1f it is less, then it is called negative adsorption.
Question 4.
Define chemical adsorption? Give example.
Answer:
Chemical adsorption is a process in which gas molecules are held to the surface by formation of chemical bonds. e.g., Adsorption of O2 on tungsten, Adsorption of H2 on nickel.

Question 5.
Chemical adsorption is an exothermic process. Justify this statement.
Answer:
In chemical adsorption, gas molecules are held to the surface by the formation of strong bond. Due to this 400kJ/mole is given out as heat of adsorption. Since heat is evolved, it is an exothermic process.
Question 6.
Why physical adsorption take place at low temperature?
Answer:
In physical adsorption, the forces between the adsorbent and adsorbate are very weak, heat of adsorption is low and hence physical adsorption occurs at low temperature.
Question 7.
What are the forces exist in physical adsorption?
Answer:
In physical adsorption, physical forces like van der Waals force of attraction exist between adsorbent and adsorbate.
The other forces that can cause physical adsorption are
- dipole-dipole interaction
- dispersion forces.
Question 8.
What is physical adsorption? Give example.
Answer:
Physcial adsorption is a process in which adsorbate are attached to adsorbent by means of weak van der Waals forces of attraction. e.g.,
- Adsorption of N2 on mica
- Adsorption of gases on charcoal.
Question 9.
Finely divided Nickel is a better adsorbent than Nickel crystal.
Answer:
As the adsorption is a surface phenomenon it depends on the surface area of adsorbent. i.e., higher the surface area, higher is the amount adsorbed. Finely divided Nickel has longer surface area and it is a better adsorbent than Nickel crystal.
Question 10.
NH3, CO2 are readily adsorbed where as H2, N2 are slowly adsorbed. Give reason.
Answer:
1. The nature of adsorbate can influence the adsorption. Gases like NH3 CO2 are easily liquefiable as have greater van der Waals forces of attraction and hence readily adsorbed due to high critical temperature.
2. But permanent gases like H2, N2 can not be easily liquefied and having low critical temperature and adsorbed slowly.
Question 11.
What is meant by adsorption isotherm?
Answer:
A plot between the amount of adsorbate adsorbed and pressure or concentration of adsorbate at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm.
Question 12.
Mention Freundlinch adsorption isothermal equation.
Answer:
Freundlinch adsorption isotherm
\(\frac{x}{m}=k p^{1 / n}\)
where x is the amount of adsorbate or adsorbed on ‘m’ gm of adsorbent at a pressure of p. k and n arc constants.
Question 13.
What are the limitations of Freundlich adsorption isotherm?
Answer:
- The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is purely empirical and valid over a limited pressure range.
- The values of constants ‘k’ and ‘n’ also found vary with temperature. No theoritical explanations were given.
Question 14.
How is adsorption applied in the decolourisation of sugar?
Answer:
Sugar prepared from molasses is decolourised to remove coloured impurities. Animcal charcoal is applied to adsorb colouring impurities and sugar is purified.
Question 15.
What is chromatography?
Answer:
1. The chromatographic technique is a process of separation of components in a mixture which is mainly based on adsorption of components on the surface of adsorbents.
2. This method is very effective and used for identification, detection and estimation of many substances even if they are contained in micro quantities.
Question 16.
Explain the application of adsorption ¡n qualitative analysis with an example.
Answer:
1. In the identification of Al3+ ion in Al(OH)3 is obtained as blue lake. Due to adsorption of blue litmus solution added to the aluminium ion solution.
2. A red colouration is seen due to the acidic nature of the solution. Ammonium hydroxide is added to it until the bkie colour develops.
3. During this addition, Al(OH)3 precipitate is formed with blue colour due to the adsorption of litmus compound.

Question 17.
Define catalyst. Give example.
Answer:
A catalyst is defined as a substance which alter the rate of chemical reaction without itself undergoing chemical change. The phenomenon which involves the action of a catalyst is called catalysis.
e.g.,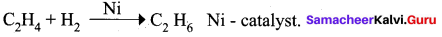
Question 18.
What is homogeneous catalysis? Give example.
Answer:
Homogeneous catalysis is a process in which the reaction, products and catalyst are present in the same phase. NO
e.g. 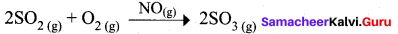
In the above reaction, the catalyst NO, the reactants SO2, O2 and product SO3 are present in the gaseous form
Question 19.
What is heterogeneous catalysis? Give example.
Answer:
Heterogeneous catalysis is a process in which the reactants, products and catalyst are present in different phases.
e.g. 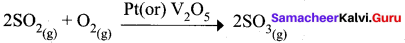
Question 20.
What are promoters? Explain with example.
Answer:
1. In a catalysed reaction, the presence of a certain substance increases the activity of a catalyst. Such substance is called a promoter.
2. For example, in Haber’s process of manufacture of ammonia, the activity of the iron catalyst is increased by the presence of molybdenum. Hence molybdenum is called a promoter.
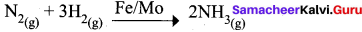
Question 21.
What is meant by catalyst poison?
Answer:
1. The substances when added to a catalysed reaction decreases or completely destroys the activity of a catalyst are often known as catalytic poisons.
2. In the reaction 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 with Pt catalyst, the catalyst poison is AS2O3.
Question 22.
Which is the catalyst and catalyst poison In Haber’s process?
Answer:
In the Haber’s process of the manufacture of ammonia, the Fe is catalyst and it is poisoned by the presence of H2S.
3H2 + N2 → 2NH3 Fe – catalyst, H2S – Catalyst poison
23. In the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O, which ¡s the catalyst and catalyst poison?
Answer:
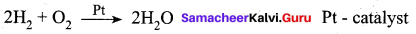 Pt – catalyst
Pt – catalyst- CO act as catalytic poison for Pt catalyst.
Question 24.
Explain the relation between activation energy and the rate of the reaction using catalyst.
Answer:
1. For a chemical reaction to occur, the reactants are to be activated to form a activated complex. The energy required for the reactants to reach the activated complex is called the activation energy. The activation energy can be decreased by increasing the reaction temperature.
2. In the presence of catalyst, the reactants are activated at reduced temperatures. i.e., the activation energy is lowered. The catalyst adsorbs the reactants activates them by weakening the bonds and allow them to react to form products.
3. As activation energy is lowered in the presence of a catalyst, more molecules take part in the reaction and hence the rate of the reaction increases.
Question 25.
What are the merits and limitations of the intermediate compound theory?
Answer:
Merits:
- The specificity of a catalyst
- The mercase in the rate of the reaction with increase in the concentration of catalyst.
Limitations:
- This theory fails to explain the action of catalytic poison and promoters.
- This theory is unable to explain the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysed reactions.
Question 26.
What are active centres?
Answer:
- The surfiice of a catalyst is not smooth. It bears steps, cracks and corners. Hence the atoms on such locations of the surface are coordinatively unsaturated.
- The have residual force of attraction. Such sites are called active centres. So the surface cames high surface free energy.
Question 27.
Enzyme catalysis are more effective and efficient than ordinary catalysis. Prove this statement.
Answer:
1. Effective and efficient conversion ¡s the special chareteristic of enzyme catalysed reactions. An enzyme may transform a million molecules of reactant to product in a minute.
For e.g. 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
2. For this reaction colloidal platinum as a catalyst the activation energy is 11 .7 k.cal/mole. But with the enzyme catalyst the activation energy of this reaction is less than 2k.cal/mole.

Question 28.
Enzyme catalysis is highly specific in nature. Justify this statement.
Answer:
1. Urea can be hydrolysed to urea by the enzyme urease.
The catalyst mease (enzyme) catalyses urea but it does not hydrolyse methyl urea.
Question 29.
Enzyme catalysed reaction has maximum rate at optimum temperature. Prove it.
Answer:
1. At first rate of reaction increases with the increase of temperature, but above a particular temperature, the activity of enzyme is destroyed. The rate may even drop to zero. The temperature at which enzymic activity in high or maximum is called optimum temperature.
2. For e.g., enzymes involved in human body have an optimum temperature 37°C/98°F.
Question 30.
What are the types of colloids based on dispersion medium?
Answer:
1. If the dispersion medium considered as water, then the colloids are referred as hydrosols (or) aquasols.
2. If the dispersion medium is an alcohol, the colloid is termed as alcosol. and if benzene is the dispersion medium, it is called benzosol.
Question 31.
Explain about
- Liquid aerosol
- solid aerosol with example.
Answer:
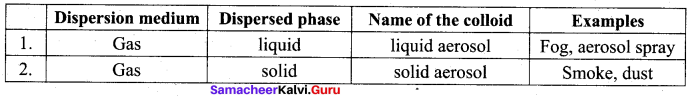
Question 32.
Explain oxidation method of preparation of colloids with two examples.
Answer:
Oxidation:
1. When hydrolodic acid is treated with iodic acid 12 sol is obtained.
HIO3 + 5HI → 3H2O + 3I2 (sol)
2. When O2 is passed through H2Se, a sol of selenium is obtained.
H2Se + O2 → 2H2O + Se (sol)
Question 33.
Explain the method of preparation of gold sol by reduction method.
Answer:
Gold sol is prepared by the reduction of auric chloride using formaldehyde.
2AuCl3 + 3HCHO + 3H2O → 2Au (sol) + 6HCI + 3HCOOH
Question 34.
How would you prepare ferric hydroxide sol by hydrolysis method?
Answer:
Fe(OH)3 sol can be preparcd by the hydrolysis of FeCl3
FeCI3 + 3H2O → Fe(OH)3 (soL) + 3 HCI
Question 35.
How would you prepare colloid by the exchange of solvent method?
Answer:
1. Colloidal solution of few substances like phosphorous or sulphur is obtained by the solutions in alcohol and pouring them into water.
2. As they are insoluble in water, they form colloidal solution.
P in alcohol + water → Psol.
Question 36.
Why colloids are to be purified? If not what will happen?
Answer:
- The colloidal solutions due to their different methods ofpreparation may contain impurities.
- If they are not removed, they may destabilise and precipitate the colloidal solution. This is called coagulation.
- Hence the impurities mainly electrolytes should be removed to increase the stabilisation of colloid.
Question 37.
How is human kidney dialysis take place?
Answer:
- Kidney malfunction results in the building up of electrolyte concentration within the blood to toxic levels.
- In the dialysis. recycling of patient’s blood is done through considerable length of semipermeable tube in an isotomic saline solution.
Question 38.
Write a note about Helmoholtz double laver.
Answer:
The surface of a colloidal particle adsorbs one type of ion due to preferential adsorption. This Stem layer
layer attracts the oppositely charged ions in the. medium and hence the boundary separating the Slpping plane two electrical double layers are set up. This is called Helmholtz electrical double layer. As the particles nearby are having similar charges. they cannot come close and condense. Hence this helps to explain the stability of the colloid.
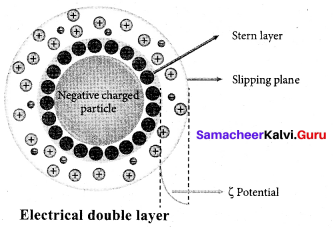
Question 39.
What is meant by gold number?
Answer:
- Zsigmondy introduced the term “Gold number” as a measure of protective power of a colloid.
- Gold number is defined as the number of milligrams of hydrophilic colloid that will just prevent the precipitation of 10 ml of gold sol on the addition of 1 ml of 10% NaCI solution.
Question 40.
Potato starch is less stable than gelatin. Why?
Answer:
- The gold number of gelatin is 0.005 – 1 and the gold number of potato starch is 25.
- Smaller the gold number, greater the protective power.
Question 41.
Write a note about Cortrell’s precipitator.
Answer:
Carbon dust in air is solidified by Cortrell’s precipitator. In it. a high potential difference of about 50.000V is used. The change on carbon is neutralised and solidified. Thus the air is free from carbon particles.
Question 42.
Explain about
- blue colour of the sky
- formation of delta.
Answer:
- The blue colour of the sky in nature is due to Tyndall effect of air particles.
- The electrolytes in sea and river water coagulate the solid particles in river water at their intersection. By this way delta is formed.
Question 43.
Distinguish between the meaning of the terms adsorption and absorption. Give one example each.
Answer:
Adsorption
- Substance is concentrated only at the surface and does notpcnctrate from the surface to the bulkofthe adsorbent.
- It is a surface phenomenon.
Example: Silical gel absorbs water vapour on its surface.
Absorption
- Substnce is uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of the solid.
- It is a bulk phenomenon.
Example: Anhydrous CaCl, absorbs water vapours in it.
Question 44.
Explain the following term giving a suitable example, emulsification.
Answer:
The process of making emulsion using a mixture of two immiscible or partially miscible liquids is called emulsification. For example. Cod liver oil is an emulsion made up of water in oil.
Question 45.
What is the reason for the stability of colloidal sols?
Answer:
Reason for the stability of colloidal sols are:
- Coagulation of the colloidal sol is prevented because of the presence of equal and similar charges on the colloidal particles.
- Colloidal particles are covered by a sheath of liquid in which they are extensively solvated because of which they acquire stability.

Question 46.
Dialysis is a method of purification of sols. But prolonged dialysis of the sol makes it unstable. Why?
Answer:
Traces of electrolytes in the sol, impart charge to the dispersed phase particles making it stable. Prolonged dialysis removes all the electrolytes, thus making the sol unstable.
Question 47.
Why the sun looks red at the time of setting? Explain on the basis of colloidal properties.
Answer:
At the time of setting, the sun is at the horizon. The light emitted by the sun has to travel a longer distance. As a result the blue part of the light is scattered away by the dust particles in the atmosphere. Hence the red part is visible.
Question 48.
What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give one example of each type.
Answer:
An emulsion is a colloidal dispersion in which both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are liquids and the two liquids involved are otherwise immiscible.
1. Oil in water type, in which oil is a dispersed phase and water is the dispersion medium, For example: milk is as emulsion of liquid fat dispersed in water.
2. Water in oil type. in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is thedispersion medium. For example: cod liver oil is an emulsion of water in oil in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the dispersion medium.
Question 49.
How does chemical adsorption of a gas on a solid vary with temperature?
Answer:
Chemical adsorption first increases with increase in temperature and then it decreases, if the pressure remains constant.
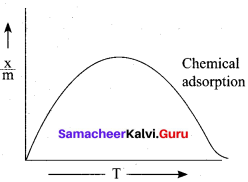
Question 50.
What are lyophilic and lyophobic sols? Give one example of each type. Why are hydrophobic sols easily coagulated?
Answer:
Lyophilic Sols:
Colloidal sols directly formed by rnixing substances like gums, gelatin, starch, rubber. etc. with a suitable liquid (The dispersion medium) are lyophilic sols. An important characteristic of these sols is that if the dispersion medium is separated from the dispersed phase
(say by evaporation) the sol can be reconstituted by simply remixing with the dispersion medium. That is why these sols are also called reversible sols. These sols are quite stable and cannot be easily coagulated.
Lyophobic sols:
These colloidal sols can only be prepared by some special methods. These sols are readily precipitated on the addition of small amount of electrolytes, by heating or by shaking and hence are not stable.
Hydrophobic sols are water hating. They are formed by indirect method. These sols are irreversible sols. These sols are readily precipitated by the addition of small amount of electrolytes, by heating or by shaking and hence are not stable.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry 3 Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the characteristics of adsorption?
Answer:
1. Adsorption can occur in all interfacial faces i.e., the adsorption can occur in between gas – solid, liquid – solid, liquid – liquid, solid – solid and gas – liquid.
2. Adsorption is always accompanied by decrease in free energy. When ∆G reaches zero, the equilibrium is attained.
3. Adsorption is a spontaneous process.
4. When molecules are getting adsorbed, there is always decrease in randomness of the molecules.
∆G = ∆H – T∆S where ∆G = change in free energy
∆H change in enthalpy
∆S change in entropy
∆H = ∆G + T∆S
5. Adsorption is exothermic and it is a quick process.
6. If simultaneous adsorption and absorption take place, it is termed as ‘sorption and sorption of gases on metal surface is called occlusion.
Question 2.
Explain graphical representation of chemical adsorption and physical adsorption.
Answer:
1. Adsorption isotherms represents the variation of adsorption at constant temperature.
2. When amount ?f adsorption is plotted versus temperature at constant pressure is called adsorption iso bar
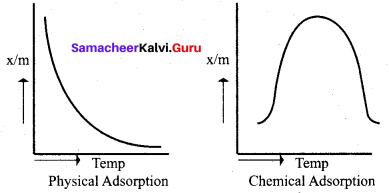
3. In physical adsorption x/m decreases with increase in T. But in chemical adsorption x/m increases with rise in temperature and then decreases. The increase illustrate the requirement of activation of the surface for adsorption is due to the fact that formation of activated complex require certain energy. The decrease at high temperature is due to desorption, as the kinetic energy of the adsorbate increases.
Question 3.
Write any 3 applications of adsorption.
Answer:
- Gas masks: During World War I. charcoal gas mask was employed.
- To create high vaccum in vessels, activated charcoal is used. For dehydration and purification of gases like CO2, N2, O2 and He, alumina and silica gel are employed.
- In blast furnace, silica gel is used for drying air.

Question 4.
Explain the function of permutit in the softening of hard water.
Answer:
1. Permutit is employed for softening 6 hard water. It adsorbs Ca2 and Mg2 ions in its surface, there is an ion exchange as shown below it occurs on the surface.
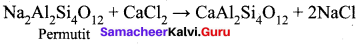
2. Exhausted permutit is generated by adding a solution of commonsalt.
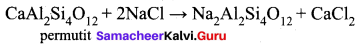
Question 5.
Explain about the application of ion exchange resins In adsorption.
Answer:
- Ion exchange resins are working only based on the process of adsorption.
- Ion exchange resins are used to demmeralise water. This process is carried out by passing water through two columns of cation and anion exchange resins.
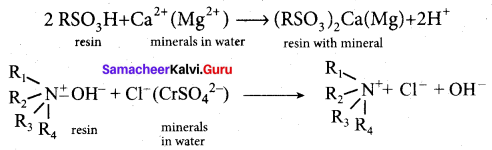
Question 6.
What is catalysis? Explain with two examples.
Answer:
Catalysis is a process in which a chemical reaction takes place in a faster rate with the help of catalyst.
Haber’s process:
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 In this process. Fe is the catalyst and Mo is the promoter.
The surface of Fe catalyses the reaction.
Vanaspathi preparation:
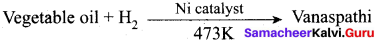
Nickel surface catalyses the reaction.
Question 7.
In the following fields, how adsorption ¡s applied?
- Medicine
- Metallurgy
- Mordant & Dyes
- indicators
Answer:
1. Medicine:
Drugs cure diseases by adsorption on body tissues.
2. Metallurgy:
Sulphide ores are concentrated by a process called froth floation in which lighter ore particles are adsorbed by pine oil. .
3. Mordants and Dyes:
Most of the dyes are adsorbed on the surface of the fabric. Mordants are the substances used for fixing dyes onto the fabric.
4. In the precipitation titrations, the end point is indicated by an external indicator which changes its colour aller getting absorbed on precipitate. It is used to indicate the end point of filtration.
Question 8.
Differentiate homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.
Answer:
Homogeneous catalysis
- The reaction in which, the reactants, products and catalyst are present in the same phase, is called homogeneous catalysis.
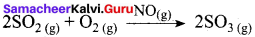
- Homogeneous catalysis mechanism is ex plained by intermediate compound formation theory.
Heterogeneous catalysis
- The reaction in which the reactants, products and catalyst are present in different phases is called heterogeneous calalysis.

- Heterogeneous catalysis mechanism is explained by adsorption theory.
Question 9.
Give three examples for homogeneous catalysis.
Answer:
1. Decomposition of acetaldehyde by I2 catalyst.
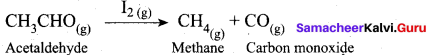
2. Hydrolysis of cane sugar with mineral acid
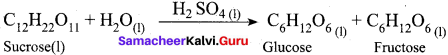
3. Acid hydrolysis of an ester

Question 10.
Give three examples for heterogeneous catalysis
Answer:
1. hydrogenation of ethylene in the presence of Nickel
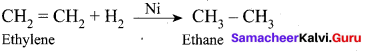
2. Decomposition of H2O2 with Pt catalyst
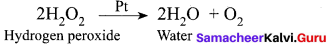
3. Friedel crafts reaction

Question 11.
What is auto ctalysis? Give two examples
Answer:
The process in which one of the product formed act as a catalyst is termed auto catalysis

Acetic acid acts as auto catalyst.
Decomposition of Arsenic hydride
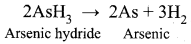
Arsenic act as auto catalyst.
Question 12.
What is negative catalysis? Explain with example.
Answer:
1. In certain reactions, presence of certain substances decreases the rate of the reaction. Such substances are called negative catalyst and the process is called negative catalysis.
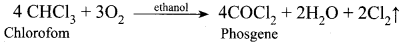
2. In oxidation of chloroform, ethanol decreases the rate of the reaction and ethanol act as negative catalyst.
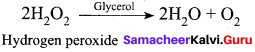
Question 13.
Explain the formation of water with copper catalyst by Intermediate compound formation theory.
Answer:
1. Formation of water due o the reaction of H2 and O2 in the presence of Cu can be given as
2. 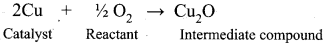
3. 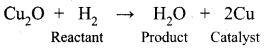
Question 14.
Explain the mechanism of oxidation of HCl by air in the presence of CuCl2
Answer:
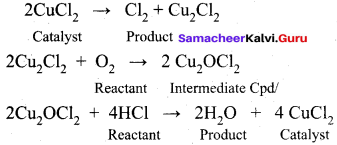
Question 15.
Explain the thermal decomposition of potssium chlorate by intermediate compound formation theory.
Answer:
1. Thermal decomposition of KClO3 in the presence of MnO2 proceeds as follows.
2. 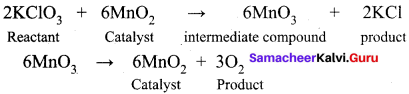
Question 16.
Describe the action of active centres present in the catalyst.
Answer:
1. Active centres increases the rate of the reaction by adsorbing and activating the reactants.
2. Increase in the activity of a catalyst by increasing the surface area. Increase in the surface area of metals and metal oxides by reducing the particle size increases the rate of the reaction.
3. The action of catalytic poison occurs when the poison blocks the active centres of the catalyst.
4. A promoter (or) activator increases the number of active centres on the surface.
Question 17.
Write a note about nano catalyst.
Answer:
- Nano materials such as metallic nano particles, metal oxide are used as catalyst in many chemical transformation.
- Nano catalysts carry the advantages of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.
- Like homogeneous catalyst the nino catalyst give 100% selective transformations and excellent yield and show extremely high reactivity.
- Like the heterogeneous catalyst, nano catalysts can be recovered and recycled.
- Nano catalysts are actually soluble heterogeneous catalyst.
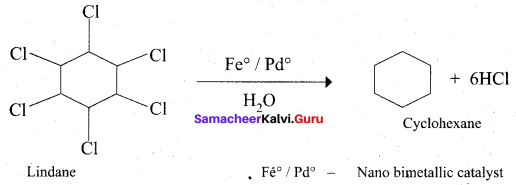
Question 18.
Differentiate lyophillic and lyophobic colloids
Answer:
Lyophiltic colloids
- In lyophillic colloids (or) sols definite attractive force (or) affinity exists between dispersion medium and dispersed phase.
- e.g., Sols of protein, starch
- They are more stable and will not get precipitated readily.
- They can be brought back to colloidal solution even after the precipitation by addition of dispersion medium
- They arc called reversible sols
Lyophobic colloids
- In lyophobic colloid no attractive force exists between dispersed phase and dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
- e.g., sols of gold, silver
- They are less stable and get precipitated readily
- They cannot be produced again by adding the dispersion medium.
- They are called irreversible sols.
Question 19.
Explain about dispersion mediu, dispersed phase and example of
- foam,
- emulsion
- sol
Answer:
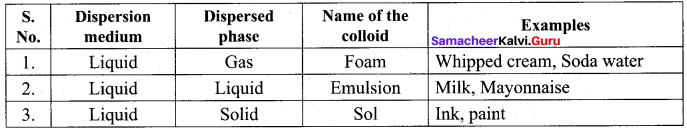
Question 20.
Explain about dispersion medium, dispersed phase and example of
- solid foam
- Gel
- Solid sol.
Answer:
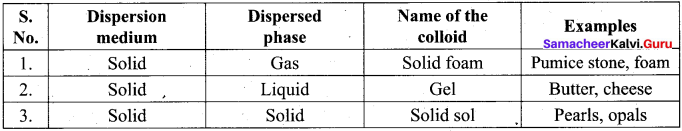
Question 21.
How would you prepare colloids of ink and graphite? (OR)
Answer:
Explain about mechanical ‘dispersion method.
1. Using a colloid mill, the solid is ground to colloidal dimension. Coarse dispersion The colloid mill consists of two metal plates rotating in opposite directions at very high speed of nearly 7000 revolution per minute.
2. The colloidal particles of required colloidal size is obtained by adjusting the distance between the two plates.
3. By this method, colloidal solutions of ink and graphite and prepared.
Question 22.
Explain about Bredic’s arc method (or) Electro dispersion method (or) How would you prepare colloids of noble metals?
Answer:
1. An electrical arc is struck between electrodes dispersed in water surrounded by ice. When a current of I amp! 100V is passed, an arc produced forms vapours of metal which immediately condense to from colloidal solution.
2. By this method, colloidal solution of many metals like copper, silver, gold. platinum can be prepared.
3. Alkali hydroxide is an added an stabilising agent for the colloid solution.
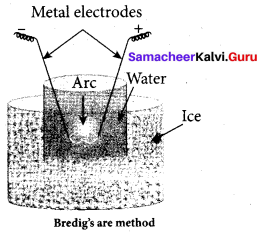
Question 23.
Explain about ultrasonic dispersion. (or) How would you prepare mercury colloid?
Answer:
1. Sound waves of frequency more than 20kHz (audible limit) could cause transformation of coarse suspension to colloidal solution.
2. Claus obtained mercury sol by subjecting mercury to sufficiently high frequency ultrasonic vibrations.
3. The ultrasonic vibrations produced by generator spread the oil and transfer the vibration to the vessel with mercury in water.
Question 24.
Explain the methods of preparation of colloids of
- AS2S3
- S.
Answer:
1. Double decomposition:
When hydrogen suiphide gas is passed through a solution of arsenic oxide, a yellow coloured arsenic sulphide is obtained as a colloidal solution.
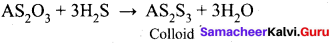
2. Decomposition:
When few drops of an acid is added to a dilute solution of sodium thio sulphate, the insoluble free sulphur produced by the decomposition of sodium thiosuiphate accumulates into clusters which impart various colours blue, yellow and even red to the system depending on their growth within the size of colloidal dimensions.
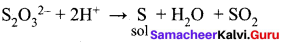
Question 25.
Describe about
- Dialysis
- Electro dialysis.
Answer:
1. Dialysis:
Thomas Graham separated the electrolyte from a colloid using a semipermeable membrane. In this method, the colloidal solution is taken in a bag made up of semipermeable membrane. It is suspended in a trough of flowing water, the electrolytes diffuse out of the membrane and they are carried away by water. membrane and they are carried away by water.
2. Electro dialysis:
The presence of electric field increases the speed of removal of electrolytes from colloidal solution. The colloidal solution containing an electrolyte as impurity is placed between two dialysing membranes enclosed into two compartments filled with water.
When current is passed, the impurities pass into water compartment and get removed periodically. This process is faster than dialysis, as the rate of diffusion of electrolytes is increased by The application of electricity.
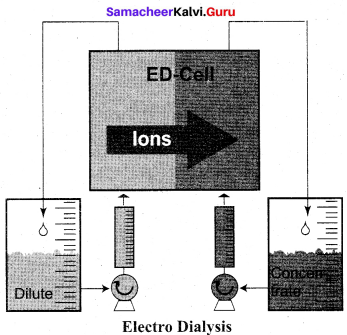
Question 26.
Explain about ultrafiltration.
Answer:
1. The pores of ordinary filter papers permit the passage of colloidal solutions. In ultrafilteration, the membranes are made by using collodion, cellophane or visiking.
2. Vhen a colloidal solution is filtered using such a filter, colloidal particles are separated on the filter and the impurities are removed as washings.
3. This process is quickened by application of pressure. The separation of sol particles from electrolyte by fikration through an ultrafilter is called ultrafiltration.
4. Collodian is 4% solution of nitrocellulose in a mixmre of alcohol and water.
Question 27.
Write a note about shape of colloidal particles.
Answer:
Colloidal particles possess various shapes.
Collidal particle
- AS2S3
- Fe(OH)3 (blue gold sol)
- W3O5 sol(tungstic acid sol)
Shape
- Spherical
- Disc (or) plate like
- Rod like
Question 28.
What is meant by Tyndall effect? (or) Explain about the optical property of colloid.
Answer:
Answer:
- Colloids have optical property. When a homogeneous solution is seen in the direction of light, it appears clear but it appears dark in a perpendicular direction.
- When light passes through colloidal solution, it is scattered in all direction and it is known as Tyndall effect.
- The colloidal particles absorbs a portion of light and remaining portion is scattered from the surface of the colloid. Hence the path of light is made clear.
Question 29.
What is meant by Brownian movement?
Answer:
1. Robert Brown observed that when the pollen grains suspended in water were viewed through an ultra microscope, they showed a random, zigzag, ceaseless motion. This is called Brownian movement of colloidal particles.
2. The colloidal sol particles are continuously bombard with the molecules of dispersion mediuri and hence they follow a zigzag. random, continuous movement.
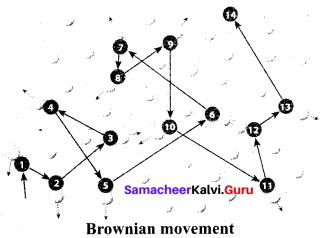
Question 30.
Mention the uses of Brow nian movement.
Answer:
1. Brownian movement enables us to calculate Avogadro Number.
2. It is used to confirm kinetic theory which considers the ceaseles rapid movement of molecules that increases with increase in temperature.
3. It is used to understand the stability of colloids. As the particles are in continuous rapid movement, they do not come close and hence not get condensed. That is Brownian movement does not allow the particles to be acted on by force of gravity.
Question 31.
What is coagulation? Mention the method used to coagulate a colloid.
Answer:
- The flocculation and setting down of the sol particles is called coagulation.
- Various methods of coagulation are
- addition of an electrolyte
- Electrophoresis
- mixing oppositely changed sols
- boiling

Question 32.
The precipitation power of ions are in the order Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+.
Similarly [Fe(CN)6]4-SO42- Cl–. Give the reason behind this.
Answer:
1. A negative ion causes the precipitation of positively changed sol and vice versa.
2. When the valency of ion is high, the precipitation power increased. So in cations the precipitation power order is Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na and in anions the precipitation power order is [Fe(CN)6]4- > SO42- > Cl–.
3. The precipitation power of electrolyte is determined by finding the minimum concentration required to cause precipitation of sol in 2hrs. This value is called flocculation value. The smaller the flocculation value, greater will be precipitation.
Question 33.
Explain how coagulation of colloid is carried out by
- Flectrophoresis
- By mixing two oppositely changed sols
- By boiling.
Answer:
1. Electrophoresis:
In eleetrophoresis, charged particles migrate to the electrodes of opposite sign. It is due to neutralization of the charge of the colloids. The particles are discharged and sothey get precipitated.
2. By mixing two oppositely charged sols: When colloidal sols with opposite charges are mixed, mutual coagulation takes place. It is due to migration of ions from the surface of the particles.
3. By boiling – When colloidal sol is boiled, due to increased collisions, the sol particles combine and settle down.

Question 34.
Explain about protective action of colloid.
Answer:
1. Lyophobic sols are precipitated readily even with small amount of electrolytes. But they are stabilised by the addition of small amount of lyophillic colloid.
2. A small amount of gelatine sol is added to gold sol to protect gold sol.
3. Gold number is a measure of protecting power of a colloid, Gold number is defined as the number of milligrams of hydrophillic colloid that will just prevent the precipitation of 10ml of gold sol on the addition of imi of 10% NaG solution. Smaller the gold number, greater the protective power.
Question 35.
What are emulsions? Give its types. Explain with examples.
Answer:
- Emulsions are colloidal solution in which a liquid is dispersed in another liquid.
- There are two types of emulsions.
- Oil in water (0/W)
- Water in Oil (W/O)
- Oil in Water : Oil dispersed in water. e.g., mayonnaise. icecrearn.
Water in Oil: Water dispersed in Oil. e.g., stiff grease, butter, cold cream.
Question 36.
Write 3 examples for emulsifiers.
Answer:
- Most of the lyophillic colloids act as emulsifiers. Example, glue. gelatin.
- Long chain compounds with polar groups like soap and suiphonic acid.
- Insoluble powders like clay and lamp black also act as emulsifier,

Question 37.
What is meant by inversion of phase? Explain with example.
Answer:
- The change of W/O emulsion into O/W emulsion is called inversion of phase.
- Example: An oil in water emulsion containing potassium soap as emulsifying agent can be converted into water in oil emulsion by adding CaCl2 (or) AlCl3. This is called inversion of phase.
Question 38.
Write a note about medicinal applications of colloids.
Answer:
- Antibodies such as penicillin and streptomycin are produced in colloidal form for suitable injections. They cure pneumonia.
- Colloidal gold and colloidal calcium are used as tonics.
- Milk of magnesia is used for stomach troubles.
- Silver sol protected by gelatine known as Argyrol is used as eye lotion.

Question 39.
How colloids are used in
- Tanning of leather
- Rubber industry
- Sewage disposal.
Answer:
1. Tanning of leather:
Skin and hides are protein containing positively charged particles which are coagulated by adding tannin to give hardened leather for further application. Chromium salts are used for tanning of leather. Chrome tanning can produce soft and polishable leather.
2. Rubber industry:
Latex is the emulsion of natural rubber with negative particles. By heating rubber with sulphur, vulcanized rubbers are produced for tyres, tubes etc.
3. Sewage disposal:
Sewage containing dirt, mud and wastes dispersed in water. Th e passage of electnic current deposits the wastes materials which can be used as a manure.

Question 40.
How would you distinguish natural honey from artificial honey?
Answer:
- Natural honey is a colloidal sol. It is distinguished from artificial one by adding ammonia cal AgNO3.
- In the case of natural honey, a metallic silver is produced assumes a reddish yellow colour due to the traces of albumin or ethereal oil which acts as a protective colloid,
- In case of artificial honey, a dark yellow (or) greenish yellow precipitate is formed.
Question 41.
Give four uses of emulsions.
Answer:
- The cleansing action of soap is due to emulsions.
- It is used in the preparation of vanishing cream.
- It is used in the preparation of cod liver oiL.
- It is used in the preparation of butter, cream etc.
Question 42.
- Adsorption of a gas on the surface of solid is generally accompanied by a decrease in entropy. Still ¡t is a spontaneous process. Explain.
- How does an increase in temperature affect both physical as well as chemical adsorption?
Answer:
1. According to the equation ∆G = ∆H – T∆S For a process to be spontaneous, ∆G should be negative. ∆H of adsorption is always negative. For a gas. ∆S is also negative. Thus, in an adsorption process, which is spontaneous, a. combination of these two factors always makes ∆G negative.
2. On increasing the temperature desorption occurs in case of physical adsorption. Chemical adsorption first increases and then decreases with increase in temperature.

Question 43.
- What is the difference between a colloidal solution and an emulsion? Give one example of each.
- What are emulsifiers?
Answer:
1. In a colloidal solution, the dispersed phase is a solid and the dispersion medium is liquid. In an emulsion, both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are liquid. Example – Colloidal sol — cell fluids, muddy water. Emulsion – milk, cold cream
2. Emulsifiers – The substance which are added to stabilise the emulsions are called emulsifiers. Example – Soaps of various kinds and lyophilic colloids (proteins, gum etc.)
Question 44.
Explain what is observed when.
- KCl, an electrolyte, is added to an hydrated ferric hydroxide sol.
- An electric current is passed through a colloidal solution.
- A beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution.
Answer:
- Feme hydroxide Fe(OH)3 is a positively charged sol, so it gets coagulated by the chloride ions released from KCI solution.
- When an electric current is passed through a colloidal solution due to charge on the colloidal particles they migrate towards the oppositely charged electrode.
- When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution the path of light becomes visible.

Question 45.
Write three distinct differences between physical adsorption and chemisorption.
Answer:
Physical adsorption
- Forces of attraction between the adsorbent and adsorbate molecules are weak Van der Waals’ forces,
- Heat of adsorption is low (20-40 kJ mol1)
- It is temporary and reversible.
Chemical adsorption
- Forces between the adsorbent and the adsorbate are strong chemical bond.
- Heat of adsorption is high (80-24OkJ mol1)
- It is permanent and irreversible.
Question 46.
Explain the following observations.
Answer:
- Lyophilic colloid is more stable than lyophobic colloid.
- Coagulation takes place when sodium chloride solution added to a colloidal solution of ferric hydroxide.
- Sky appears blue in colour.
Answer:
1. A lyophilic sol is stable duc to the charge and the hydration of the sol particles. Such a sol can only be coagulatd by removing the water and adding solvents like alcohol, acetone, etc. and then an electrolyte. On the other hand, a lyophobic soils stable due to charge only and hence it can he easily coagulated by adding small amount of an electrolyte.
2. The colloidal particles get precipitated. i.e., ferric hydroxide is precipitated.
3. The atmospheric particles of colloidal range scatter blue component of the white sunlight preferentially. That is why the sky appears blue.

Question 47.
- Heat of adsorption is greater for chemisorption than physisorption. Why?
- What is colloldion?
- Differentiate between peptization and coagulation.
Answer:
- Due to the formation of chemical bond between adsorbate and adsorbent.
- 4% solution of nitro cellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether.
- Peptisation is the process of converting a precipitate into colloidal sol by adding an electrolyte. Rut coagulation is the settling of colloidal particles.
Question 48.
Give reasons for the following.
- Enzyme catalysts are highly specific in their action.
- The path of light beconies visible wheti it is passed through As2S3 sol ¡n water.
- The enthalpy in case of chemisorption is usually higher than that of physisorption.
Answer:
1. This is because each enzyme has a specific active site on which only a particular substrate can bind. ,
2. This is because of Tyndall effect caused due to the scattering of light by colloidal particles of As2S3 sol.
3. Chemisorption involves the formation ofa chemical bond between adsorbent and adsorbate molecule which involves high energy changes while in physisorption, the molecules of adsorbate and adsorbent arc held by weak van der Waals’ interactions.

Question 49.
What is adsorption? How does adsorption ola gas on a solid surface vary with pressure? Illustrate with the help of an appropriate graph.
Answer:
Adsorption is the phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid, resulting in higher concentration of the molecules on the surface.
Effect of pressure:
At constant temperature, the adsorption of gas increases with increase of pressure of the gas. At low pressure. it increases rapidly. At an equilibrium pressure. the extent of adsorption (x/m) reaches its maximum value after which adsorption is independent of pressure.
\(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{m}}=\mathrm{kP}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\)
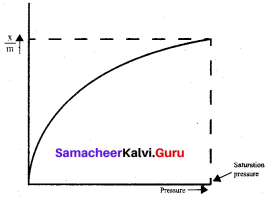
Question 50.
How do size of particles of adsorbent, pressure of a gas and prevailing temperature influence of extent of adsorption of a gas on a solid?
Answer:
1. Effect of size of the particles of adsorbent: Greater the specific area of the solid available for adsorption of adsorbent, greater would be its adsorbing power. That is why porous or finely divided forms of adsorbents more strongly. However, the size of pores should be large enough to allow the diffusion of gas molecules.
2. Effect of pressure:
Increase in pressure initially increases the adsorption which later attains equilibrium at high pressure.
\(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{m}}=\mathrm{kP}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\) (n>1)
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Surface Chemistry 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is adsorption isotherm? Explain about Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Answer:
1. Adsorption isotherms represents the variation of adsorption at constant temperature. Adsorption isoterm can be studied quantitatively.
2. A plot between the amount of adsorbate adsorbed and pressure or concentration of adsorbate at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherms.
3. Freundlich adsorption isotherm. According to Freundlich
\(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{m}}=\mathrm{kP}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\)
Where x is the amount of adsorbate (or) adsorbed on ‘m’ gm of adsorbent at a pressure of P. k and n are constants. Value of’n’ is always less than unity.
4. This equation is applicable for adsorption of gases on solid surfaces. The Same equation becomes \(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{m}}=\mathrm{kc}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\) when used for adsorption in solutions with ‘c’ as concentration.
5. These equation quantitatively predict the effect of pressure (or concentration) on the adsorption of gases (or adsorbates) at constant temperature.
6. Taking log on both sides of equation
\(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{m}}=\mathrm{kP}^{1 / \mathrm{n}}\)
log \(\frac { x }{ m }\) = log k + \(\frac { 1 }{ n }\) log P
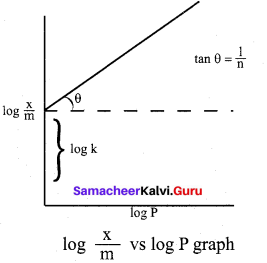
7. Hence the intercept represents the value of log k and the slope \(\frac { b }{ q }\) gives \(\frac { 1 }{ n }\)
8. This equation explains the increase of with increase in pressure. But experimental values shows the deviation at low pressure.
9. Limitations:
- This equation is purely empirical and valid over a limited pressure range.
- The value of k and n also found vary with temperatures. No theoretical explanations were given.

Question 2.
Define catalyst. What are the characteristics of catalysts?
Answer:
A catalyst is defined as a substance which alters the rate of chemical reaction without itself undergoing chemical change.
Characteristics of catalyst:
1. For chemical reaction, catalyst is needed in very small quantity. Generally, a pinch of catalyst is enough for a reaction in bulk.
2. There may be some physical changes, but the catalyst remains unchanged in mass and chemical composition in a chemical reaction.
3. A catalyst itself cannot initiate a reaction. It means it cannot start a reaction which is not taking place. Rut, lithe reaction is taking place in a slow rate it can increase its rate.
4. A solid catalyst will be more effective if it is taken in a finely divided form.
5. A catalyst can catalyse a particular type of reaction, hence they are said to be specific in nature.
6. In an equilibrium reaction, presence of catalyst reduces the time for attainment of equilibrium and hence it does not affect the position
of equilibrium and the value of equilibrium constant.
7. A catalyst is highly effective at a particular temperature called as optimum temperature.
8. Presence of a catalyst generally does not change the nature of products.
9. For example 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
This reaction is slow in the absence of a catalyst, but fast in the presence of Pt catalyst.
Question 3.
What is enzyme catalysis? Give the characteristics of enzyme catalysed reaction?
Answer:
Enzymes are complex protein molecules with three dimensional structures. They catalyse the chemical reaction in living organism. They are often present in colloidal state and extremely specific in catalytic action. This process is called enzyme catalysis.
Special characteristics of enzyme catalysis:
1. Effective and efficient conversion is the special characteristic of enzyme catalysed reactions. An enzyme may transform a million molecules of reactant in a minute.
For e.g., 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
For this reaction, activation energy is 1 8k.cal/mole without a catalyst. With colloidal platinum as a catalyst, the activation energy is 11.7 k.cal/mole. But with the enzyme catalyst. the activation energy of this reaction is less than 2 k.cal / mole.
2. Enzyme catalysis is highly specific in nature.
H2N – CO – NH2 + H2O → 2NH3 + H2O
The enzyme urcase which catalyses the reaction of urea does not catalyse the hydrolysis of methyl urea (NH2 – CO – NHCH3)
3. Enzyme catalysed reaction has maximum rate at optimum temperature. At first rate of the reaction increases with increase of temperature, but above a particular temperature, the activity of enzyme is destroyed. The rate may even drop to zero. The temperature at which enzyrnic activity is high (or) maximum is called as optimum temperature. e.g., enzyme involved in human body have an optimum temperature 37°C / 98°F.
4. The rate of enzyme catalysed reactions varies with the pH of the system. The rate is maximum at a pH called optimum pH.
5. Enzymes can be inhibited i.e., poisoned. Activity of an enzyme is decreased and destroyed by a poison. The physiological action of drugs is related to their inhibiting action. e.g.. sulpha drugs, penicillin inhibits the action of bacteria and used for curing diseases like
pneumonia, dysentery, cholera.
6. Catalytic activity of enzymes is increased by coenzymes or activators. A small non protein (vitamin) called a coenzyme promotes the catalytic activity of enzyme.

Question 4.
Explain about phase transfer catalysis.
Answer:
1. Consider the reactant of a reaction is present in one solvent and the other reactant is present in an another solvent. The reaction between them is very slow, if the solvents are immisible.
2. As the solvents form separate phases, the reactants have to migrate across the boundary to react. But migration of reactants across the boundary is not easy. For such situation, a third solvent is added which is miscible with both. So, the phase boundary is eliminated the reactants freely mix and react fast.
3. But for large scale preparation of any product, use of a third solvent is not convenient as it may be expensive. For such problems, phase transfer catalysis provides a simple solution, which avoids the use of solvents.
4. it directs the use of a phase transfer catalyst (a phase transfer reagent) to facilitate transport of a reactant in one solvent to other solvent where the second reactant is present. As the reactants are now brought together, they rapidly react and form the product.
5. Example – Substitution of C1 and CN in the following reaction.
R Cl = 1 – chloro octane
R CN = 1 – cyano octane
6. By direct heating of two phase mixture of organic 1 – chioro Octane with aqueous sodium cyanide for several days, 1 – cyano octane is not obtained. However, if a small amount of quarternary ammonium salt like tetra alkyl ammonium cation which has hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends, transports CN – from the aqueous phase to the organic phase using its hydrophilic end and facilitates the reactions with 1 – chloro octane as shown below

7. So phase transfer catalyst, speeds up the reaction by transporting one reactant from one phase to another.
Question 5.
Explain about the classification of colloids based on the physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium with example.
Answer:
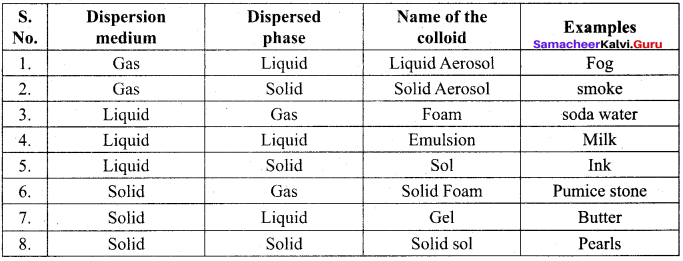
Question 6.
Describe about condensation methods of preparation of colloids. (OR) Describe chemical methods of preparation of colloids. When the substance for colloidal particle is present as smalL sized particle, molecule or ion, they are brought to the colloidal dimension by condensation methods.
Answer:
1. Oxidation method:
When hydroiodic acid is treated with iodle acid J, sol is obtained.
HIO3 + 5HI → 3H2O + 3I2(sol)
2. Reduction method:
Gold sol is prepared by reduction of aune chloride using formaldehyde.
2 AuCl3 + 3HCHO + 3H2O → 2 Au(sol) + 6HCI + 3HCOOH
3. Hydrolysis:
Ferric chloride is hydrolysed to get ferric hydroxide colloid
FeCl3 + 3H2O → Fe(OH)3(sol) + 3HCI
4. Double decomposition:
When hydrogen suiphide gas is passed through a solution of arsenic oxide, a yellow coloured arsenic sulphide is obtained as a colloidal solution.
As2O3 – 3H2S → As2S3 + 3H2O
5. Decomposition:
When few drops of an acid is added to a dilute solution of sodium thiosulphate, sulphur colloid is produced by the decomposition of sodium thio sulphate.
S2O32- + 2H+ → S(sol) + H2O + SO2

7. Describe about the properties of colloids.
Answer:
1. Colour:
The colour of a sol is not always the same as the colour of the substance in the bulk. For example, bluish tinge is given by diluted milk in reflected light and reddish tinge in transmitted light.
2. Size:
The size of colloidal particles ranges from Imp to 1pm diameter.
3. Colloidal solutions are heterogeneous in nature:
They have two distinct phases. Experiments like dialysis. ultrafiltration show the heterogeneous in nature but they are considered as borderline cases.
4. Filterability:
As the size of pores in ordinary filter paper are large, the colloidal particles easily pass through the ordinary filter papers.
5. Non setting nature:
Colloidal solutions are quite stable i.e., they are not affected by gravtiy.
6. Concentration and density:
When the colloidal solution is dilute, it is stable. When the volume of medium is decreased, coagulation occurs. Density of sol decreases with
decrease in the concentration.
7. Diffusability:
Unlike true solution, colloids diffuse less readily through membranes.
8. Colligative properties:
The colloidal solutions show colligative properties such as elevation of boiling point, depression in freezing point and osmotic pressure. These. properties are used to determine molecular weight of colloidal particles.
9. Shape of colloidal particles:
Colloidal particles have various shapes
Collidal particle
- AS2S3
- Fe(OH)3 (blue gold sol)
- W3O5 sol(tungstic acid sol)
Shape
- Spherical
- Disc (or) plate like
- Rod like
10. Optical property:
The path of the light is visible when it is passes through a colloidal solution due to the scattering of light by colloidal particles. This is known as Tyndall effect.
11. Kinetic property:
When colloidal solution is viewed through an ultra microscope, they showed a random, zigzag ceaseless motion which is called Brownian movement.
12. Electrical property:
Helmholtz double layer. electrophoresis and electro osmosis are electrical properties of colloids.
Question 8.
Explain about Electrophoresis (or) Cataphoresis (or) How would you detect the presence of charges on sol particles? (or) Explain about the method used to detect the presence of charge on sol particles. Electrophoresis (or) cataphoresis:
Answer:
1. When electric potential is applied across two platinum electrodes dipped in a hydrophilic sol, the dispersed particles move toward one or other electrode. This migration of sol particles under the influence of electric field is called electrophoresis.
2. If the sol particles migrate to the cathode, then they possess positive charges and if the sol particles migrate to the anode, they have negative charges. Thus from the direction Afiet of migration of sol particles, we can determine the charge of the sol particles. Hence electrophoresis is used for the detection of presence of change on the sol particles.
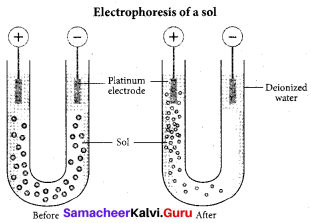
3.
Positively charged coiloids
Fe(OH)3, Al(OH)3
Basic dyes, Haemoglobin
Negatively charged colloids
Ag, Au & Pt, AS2S3,
Clay, Starch
Question 9.
What are emulsion? Mention its type with example. What is emulsification? How the types of emulsions are identified?
Answer:
1. Emulsions arc colloidal solution in which a liquid dispersed in another liquid.
2. Two types of emulsions
- Oil in Water (O/W) e.g., mayonnaise
- Water in Oil (W/O) e.g., Butter
3. The process of preparation of emulsion by the dispersal of one liquid in another liquid is called emulsification.
4. Identification of types of emulsions. The two types of emulsions can be identified by the following tests
- Dye test – A small amount of dye soluble in oil is added to emulsion. The emulsion is shaken well. The aqueous emulsion will not take the colour whereas oily emulsion will take up the colour of the dye.
- Viscosity test – Viscosity of the emulsion is determined by experiments. Oily emulsions will have higher value than aqueous emulsions.
- Conductivity test – Conductivity of aqueous solutions are always higher than oily emulsions.
- Spreading test – Oily emulsions spread readily than aqueous emulsion when spread on an oily surface.

Question 10.
What is deeniulsification? Explain about the various techniques of deemulsification.
Answer:
Emulsion can be separated into two separate layers. This process is called Deemulsification. Various deemulsilication techniques are given below.
- Distilling of one component
- Adding an electrolyte to destroy the charge.
- Destroying the emulsifier using chemical methods.
- Using solvent extraction to remove one component.
- By freezing one of the components.
- By applying centrifugal force.
- Adding dehydrating agents for water in oil type.
- Using ultrasonic waves.
- Heating at high pressures.
Question 11.
(a) How can a colloidal solution and a true solution of the same colour be distinguished from each other?
(b) List four applications of adsorption.
Answer:
- The path of light becomes visible when passed through a colloidal solution while it is not visible in case of a true solution. This is because of Tyndall effect caused by the scattering of light by colloidal particles.
- Applications of adsorption:
- Activated charcoal is used in gas masks to remove poisonous gases such as CH4, CO, etc.
- Animal charcoal is used as decoloriser in the manufacture of sugar.
- Silica is used for removing moisture.
- The ion exchange resins are used for removing hardness of water.

Question 12.
Illustrate with examples.
- Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols
- Homogeneous and Heterogeneous catalysis.
Answer:
1. The substances such as proteins, starch, rubber, etc. directly passes into the colloidal state when brought in contact with the solvent. Such colloids are known as lyophillic sols, The substances like metals, their suiphides. hydroxides, etc. do not form colloidal sol readily when mixed with dispersion medium. The colloidal sols can only be prepared by some special methods. Such sols are called lyophobic sols.
2. Homogeneous catalysis:
Here the reactants and catalyst are present in the same phase. For example, lead chamber process for the manufacture of H2SO4.
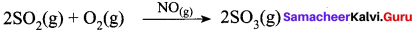
Heterogeneous catalysis:
Here the reactants and catalyst are present in different phases. For example, contact process for manufacture of H2SO4.
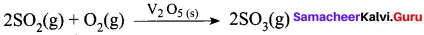
Common Errors
- Students may get confused with the words absorption and adsorption
- There may be a confusion between physical adsorption and chemical adsorption
- Catalyst poison and negative catalyst are different.
- Colloids : There may be a doubt between dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
- Electro dialysis, Electrophoresis, Electro osmosis may get confused.
Rectifications
1. In surface chemistry, we should use only adsorption. Adsorption mainly explains surface phenomenon.
Physical adsorption – Weak Vander walls forces, multilayer formation, Heterogenous catalysis.
2. Chemical adsorption:
Bond formation, mono-layer formation, Homogeneous catalysis.
Catalyst poison: decreases the catalytic activity of catalyst. Negative catalyst: reduces the rate of a chemical reaction.
3. Dispersion medium:
Larger in amount. Dispersed phase – Smaller in amount. Colloid is dispersed phase in dispersion
4. medium. For e.g., smoke is colloid in which carbon solid particles dispersed in air dispersion medium.
Electrodialysis – Purification of colloid by electric current.
5. Electrophoresis:
Movement of colloidal particles (dispersed phase) towards the oppositely charged electrode under the influence of electric current. Electro osmosis: Movement of dispersion medium towards the oppositely charged electrode under the influence of electric current.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()