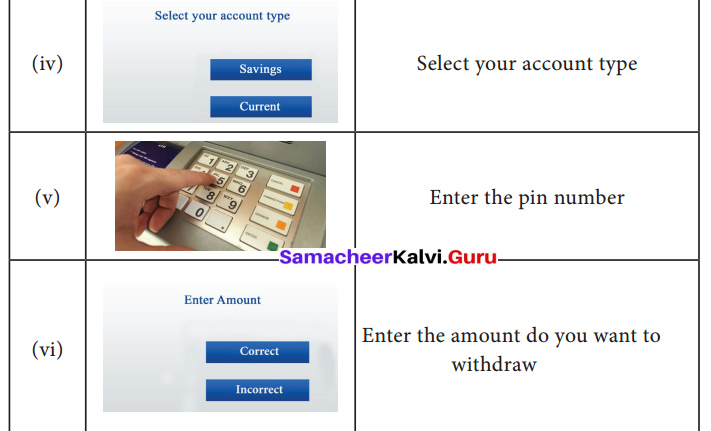
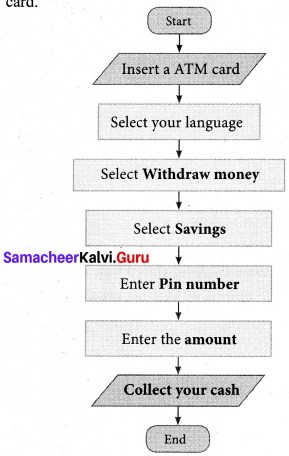
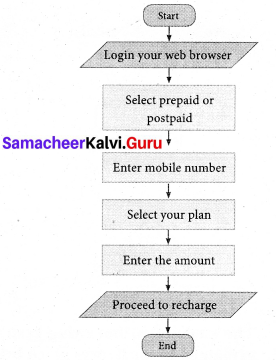
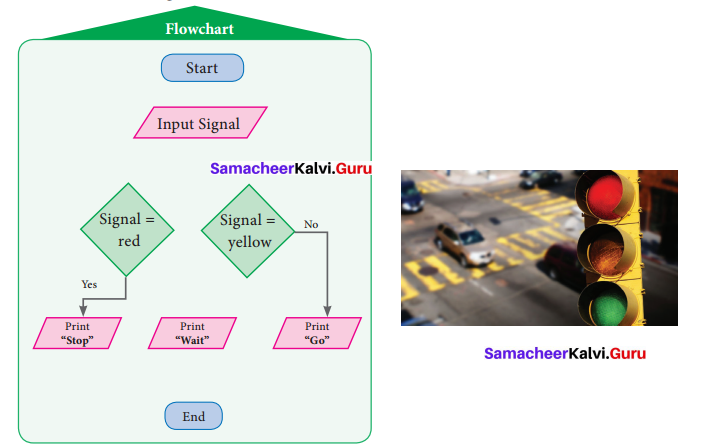
Students can Download English Lesson 1 Journey by Train Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Activity, Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Solutions Term 3 Prose Chapter 1 Journey by Train
Read And Understand
A. Fill in the table
Answer:
| Problems Faced By Mr. Fogg And His Team |
Solution |
| The train stopped in the middle of the forest. |
The passengers must provide themselves a means of transport from Kholby to Allahabad. |
| They couldn’t hire the elephant. |
Mr. Fogg purchased it for 2000 pounds. |
| They were in need Of an elephant driver. |
A young man offered his service as a guide. |
B. Answer the questions briefly
Question 1.
Who inhabited the jungles that the train passed through?
Answer:
The elephants inhabited the jungles that the train passed through.

Question 2.
What was the reaction of the inhabitants?
Answer:
Snakes and tigers fled at the noise Of the train. The elephants stood gazing with sad eyes at the train, as it passed.
Question 3.
What did Mr. Fogg mean by, ‘it was foreseen’?
Answer:
Mr. Fogg knew that some obstacle would arise on his route. So he said that the difficulty was foreseen.
Question 4.
Describe the elephant driver in your own words.
Answer:
The elephant driver was intelligent and a skilled young man. He covered the elephant’s back with saddle-cloth. He attached seats on each of its sides. He sat on the neck of the elephant and set out from the village with the three passengers.
C. Think and Answer.
Question 1.
What qualities of Mr. Phileas Fogg are highlighted in this extract? Support your answer with suitable examples.
Answer:
Mr. Phileas Fogg was a man of adventure. He was ready to take a risk. Otherwise, he would not have accepted a wager. 20,000 dollars set by his friends at the Reform Club. Mr. Phileas Fogg always maintained his calm and cool temperament. He did not get angry even when the train stopped suddenly.
Mr. Fogg was a man of farsightedness. He had foreseen some obstacles on his route sooner or later to arise. Mr. Fogg was a man of good planning. He had planned to catch the steamer that would leave Calcutta for Hongkong on 25th. Mr. Fogg was a man of generosity. He promised a generous reward for the guide.
When the elephant owner refused to hire, at the excessive sum of two thousand pounds, for the role of the animal, Mr. Fogg was not in the least flurried. These incidents show the determination of Mr. Fogg in executing his decisions.
Vocabulary
D. Fill in the blanks with correct travel words.
(schedule,reach,book,railway,pack,board)
Answer:
To make travel convenient, we must book tickets well in advance. Then we have to Pack our things and schedule our trip. We have to reach the railway station in time and board the train in order to reach our destination.
E. Match the phrasal verbs with their meanings

Answer:
- b
- f
- a
- e
- c
- d
F. Dictionary Task
Refer to a dictionary. Find the meaning of the following words and write them down.
Answer:
- journey – The act of travelling from one place to another.
- picnic – a trip or excursion to the country, seaside, etc, on which people bring food to be eaten in the open air
- pilgrimage – a religious journey.
- tour – a journey for pleasure in which several places are visited
- vacation – holiday.
- excursion – a short journey or trip.
Listening
G. Listen to the teacher reading the Weather forecast and complete the report.
Answer:
The name of the Cyclone is Gaja it may affect the places North Tamil Nadu and Puducherry Heavy rains are expected on November 14th and 15th It is 880 km away from Nagapattinam.

Speaking
H. Your family has decided to go on a tour during the vacation. You are calling a travel agency and seeking information regarding package, places of visit, cost, etc. Work in pairs and role play as a receptionist and a customer.
Answer:
Receptionist: Good morning. This is Sai Dwaraka Mai Travel Agency. How can I help you?
Customer: We would like to go on a tour of the Shirdi temple. Can you give us the information regarding the package, places of visit, and the cost for it?
Receptionist: Yes, Madam. We offer flight packages from Chennai to Shirdi at affordable prices.
Customer: Okay Sir, what are the places of visit over there?
Receptionist: We take you to places like Dwarkamai, Chavadi, Gurusthan, Sai Museum, Maruthi temple, and Nandadeep.
Customer: Okay fine. We would like to book tickets for the tour, as we would like to go any day between 23rd November and 27th November. What is the cost for four people?
Receptionist: It costs Rs. 9,9991- per person. So the total amount for four people would be Rs. 39,996/-
Customer: Thank you, Sir, I will get back to you immediately, after discussing with my family members.
Receptionist: Thank you for calling, Madam. Have a nice day.
Grammar
I. Rewrite the story in the past tense.
Answer:

The boy chased a cat. The cat climbed up the tree and purred from the branch of the tree. The cat jumped to another tree. The boy who was chasing the cat noticed a snake under the tree. He left his attempt to catch the cat and he ran home screaming for help

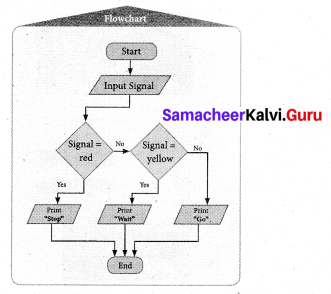
J. Look at the picture and complete the following

Answer:
Nila told Miruthula that that hotel was famous for masala idli Miruthula said that the idly was soft and spongy Nila said that it was delicious too. She also said that they had added Kashmiri chili. Miruthula said very much.
Writing
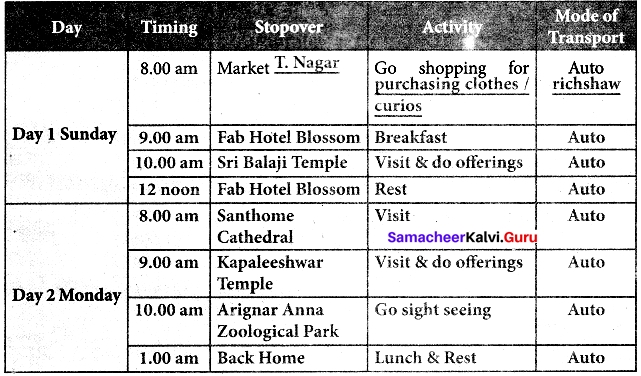
K. Your friend is coming to your city/town to spend a week with you. He /she wants to visit some tourist places and enjoy the special food items in the place. Prepare a two-day itinerary for the visit.
Answer:
Creative Writing
L. You are waiting to board a train at a railway station. The train is delayed by an hour. Write a paragraph about the crowded scene in the railway station based on your observation.
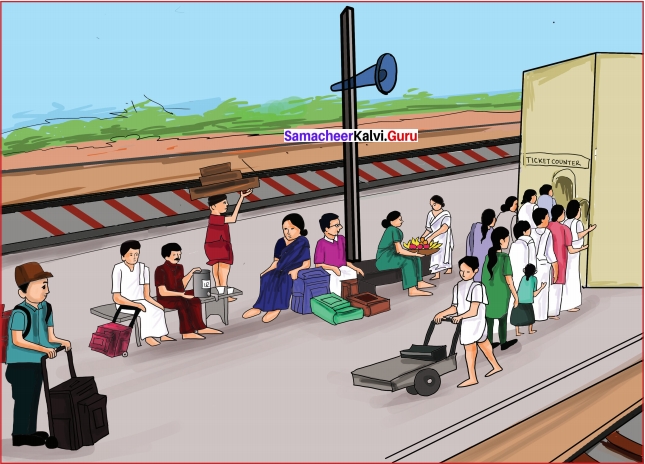
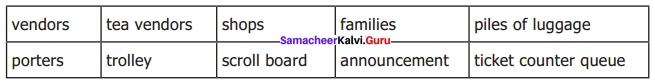

Answer:
I was waiting to board a train at a railway station. The train was delayed by an hour. A lot of families were waiting eagerly for the announcement of the arrival of the train. Some of the porters were carrying the luggage of the passengers. Piles of luggage were seen all over. There were fruit vendors, tea vendors, and other shops selling water, milk, and snacks. By the ticket counter, there was a queue, waiting to buy tickets. The scroll board was displaying the necessary information for the passengers. The porters were also using trolleys to carry the luggage.
Journey by Train Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct Synonyms from the options below.
Question 1.
proceeded
(a) stopped
(b) halted
(c) moved
(d) passed
Answer:
(c) moved

Question 2.
fertile
(a) vast
(b) productive
(c) barren
(d) incapable
Answer:
(b) productive
Question 3.
territory
(a) barrier
(b) border
(c) Limit
(d) region
Answer:
(d) region
Question 4.
gazing
(a) look steadily
(b) looking away
(c) scanning
(d) blinking
Answer:
(a) look steadily
Question 5.
hasty
(a) slow
(b) wise
(c) quickly
(d) lazy
Answer:
(c) quick
Question 6.
curled
(a) straightened
(b) erected
(c) evened
(d) twined
Answer:
(d) twined
Question 7.
obstacle
(a) assist
(b) aid
(c) support
(d) difficulty
Answer:
(d) difficulty

Question 8.
halt
(a) start
(b) stop
(c) go
(d) continue
Answer:
(b) stop
Question 9.
foreseen
(a) predicted
(b) neglected
(c) disregarded
(d) failed
Answer:
(a) predicted
Question 10.
rapidly
(a) slowly
(b) suddenly
(c) quickly
(d) easily
Answer:
(c) quickly
II. Choose the correct Antonyms from the options below.
Question 1.
different
(a) same
(b) unlike
(c) dissimilar
(d) contrast
Answer:
(a) same
Question 2.
punctually
(a) promptly
(b) timely
(c) regularly
(d) early
Answer:
(d) early

Question 3.
straggling
(a) few
(b) rare
(c) abundant
(d) irregular
Answer:
(c) abundant
Question 4.
waking
(a) sleeping
(b) arousing
(c) raising
(d) getting up
Answer:
(a) sleeping
Question 5.
abandoned
(a) deserted
(b) forsakened
(c) casted
(d) inhabited
Answer:
(d) inhabited
Question 6.
skilled
(a) trained
(b) qualified
(c) inexperienced
(d) practised
Answer:
(c) inexperienced
Question 7.
announced
(a) reported
(b) declared
(c) notified
(d) suppressed
Answer:
(d) suppressed

Question 8.
snapped
(a) became happy
(b) broke
(c) crackled
(d) fractured
Answer:
(a) became happy
Question 9.
disadvantage
(a) effectiveness
(b) unfavourable
(c) drawback
(d) advantage
Answer:
(d) advantage
Question 10.
hesitation
(a) fluctuation
(b) unwillingness
(c) willingness
(d) stutter
Answer:
(c) willingness
III. Choose the Correct Answer (MCQ).
Question 1.
The train had started _________
(a) delayed
(b) punctually
(c) late
(d) after an hour
Answer:
(b) punctually
Question 2.
An hour after leaving _________ the train had passed the bridges and the island of salcette.
(a) Allahabad
(b) Calcutta
(c) Lucknow
(d) Bombay
Answer:
(d) Bombay

Question 3.
At half-past _________ the train stopped at Burhampoor.
(a) ten
(b) twelve
(c) six (d) eight
Answer:
(b) twelve
Question 4.
The _________ at once stepped out.
(a) General
(b) attendant
(c) club member
(d) driver
Answer:
(a) General
Question 5.
Sir Francis was _________
(a) happy
(b) furious
(c) cool
(d) cheerful
Answer:
(b) furious
Question 6.
A steamer leaves Calcutta for _________ at noon on the 25th.
(a) Hongkong
(b) Persia
(c) Norway
(d) Burhampoor
Answer:
(a) Hongkong
Question 7.
‘Good Heavens’, what a price for an _________
(a) eagle
(b) ox
(c) elephant
(d) ostrich
Answer:
(c) elephant

Question 8.
The driver _________ himself on the elephant’s neck.
(a) lost
(b) perched
(c) unsettled
(d) lowered
Answer:
(b) perched
Question 9.
A young man, with an _________ face, offered his services as a guide.
(a) averse
(b) ugly
(c) intelligent
(d) inapt
Answer:
(c) intelligent
Question 10.
The travellers made a hasty _________
(a) lunch
(b) dinner
(c) moment
(d) breakfast
Answer:
(d) breakfast
7th Standard Journey By Train Short Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Who is the author of this novel ‘Around the world in Eighty Days’?
Answer:
The author of this novel is Jules Verna.
Question 2.
Who was there among the passengers?
Answer:
There were a number of officers, Government officials, and merchants.
Question 3.
Who occupied a seat opposite Mr. Fogg?
Answer:
Sir Francis Cromarty occupied a seat opposite to him.
Question 4.
Who was Sir Francis?
Answer:
Sir Francis was one of the friends of Mr. Fogg.
Question 5.
Where did he meet him?
Answer:
He met him on the ship Mongolia that brought him to Bombay.

Question 6.
When will the steamer leave Calcutta for Hong Kong?
Answer:
The steamer would leave Calcutta for Hong Kong at noon on the 25th.
Question 7.
What was Mr. Fogg resolved to hire?
Answer:
He was resolved to hire an Indian elephant for his journey to Allahabad.
Question 8.
How much did Mr. Fogg offer to hire the Elephant at first?
Answer:
He offered ten pounds per hour to hire the elephant.
Question 9.
Where did the train stop at half-past twelve?
Answer:
It stopped at Burhampoor at half-past twelve.
Question 10.
Which mountains separated the Khandesh from Bundelcund?
Answer:
The Sutpour mountains separated the Khandesh from Bundelcund.
V. Paragraph Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
What did Passepartout see, when he was crossing India in a railway train?
Answer:
Passepartout on waking looked out. He could not believe that he was actually crossing India. The locomotive, guided by an English engineer and fed with coal, threw out its smoke upon cotton, coffee, nutmeg, clove, and pepper plantations. The steam curled in spirals around groups of palm-trees. In the midst of these trees were attractive bungalows, viharas, and marvellous temples, decorated by the rich work of Indian architecture. There were vast areas extending to the horizon with jungles and forests. There he saw snakes, tigers, and elephants.
Question 2.
Who served as a guide to Mr. Fogg and others? How did he manage to take all three to Allahabad?
Answer:
A young intelligent man offered his services as a guide. The elephant was led out and equipped. The skilled driver covered the elephant’s back with a sort of saddle-cloth and attached to each of its side some uncomfortable howdahs. While Sir Francis and Mr. Fogg took the howdahs on either side, Passepartout got on to the saddle-cloth between them. The driver positioned himself on the elephant’s neck and they set out from the village at nine o’clock by short cuts through the dense forests of palms.
Journey by Train Grammar Additional
Reported Speech
The actual words spoken by a person are Direct speech. They are enclosed within quotation marks.
When we later report this, making changes to the words the speaker originally said, it is Reported Speech. (Indirect Speech)
| Sentence |
Direct Speech |
Indirect Speech |
| I want an ice cream |
Ram said to Rakesh, “I want an ice cream” |
Ram told Rakesh that he wanted ice cream. |
| I am coming to
Chennai tomorrow. |
My uncle said to me, “I am coming to Chennai tomorrow.” |
My uncle told me that he was coming to Chennai the next day |
| I want to become a doctor. |
Monica said, “I want to become a doctor.” |
Monica said that she wanted to become a doctor. |
| The comic books are kept on the second shelf. |
The librarian said, “The comic books are kept on the second shelf” |
The librarian said that the comic books were kept on the second shelf. |
| The monument is beautiful. |
Sidharthan said, “The monument is beautiful.” |
Sidharthan said that the monument was beautiful. |
I. Change into Indirect Speech.
Question 1.
He said, “I live in the city centre”.
Answer:
He said that he lived in the city centre.

Question 2.
Radha said, “I am going out”.
Answer:
Radha said that she was going out.
Question 3.
Ravi said, “I can swim”
Answer:
Ravi said that he could swim.
Question 4.
He said, “I arrived before you”.
Answer:
He said that he had arrived before him.
Question 5.
My father said, “I will be in Pairs on Monday”.
Answer:
My father said that he would be in Paris on Monday.
Warm-Up
Work in pairs. Choose six items which are essential for a camp. Rank their priority and justify your answer.

Answer:
- Torch Light
- Tent
- Cell Phone
- Rope
- Hammer
- Stove
These things are essential for a camp because, without these things, we cannot enjoy our camp. Camping is an amazing experience. So we should prepare ourselves properly with the essential items taken along with us. This will avoid frustration and stress.
Journey by Train Summary
Section – I
This story tells us of an amazing journey by an Englishman Mr. Phileas Fogg. He is a ruthless perfectionist who cares more about the bet than the native places, he sees on his travels. He will do anything, even lie and cheat, to get what he wants.
Mr. Phileas Fogg along with his French attendant, Passepartout, attempts to go round the world in eighty days by taking a bet for $ 20,000. They travel through some parts of India. That was the time when the railways were being built in the country. The train started at the scheduled time from Bombay. There were a number of passengers like officers, government officials, and merchants on the train. Sir Francis Cromarty, one of Mr. Fogg’s friends, occupied a seat opposite to them.
The train passed the bridges, the Island of Salcette, mountains, jungles, forests, and the fertile territory of Khandesh.
Passepartout couldn’t believe that he was actually crossing India on a railway train. Tigers and snakes fled at the noise of the train. Elephants stood gazing at the train with sad eyes. At half-past twelve, the train stopped at Burhampoor. The travellers had a hasty breakfast. The train entered the valleys of Sutpour Mountains at three in the morning.

Question 1.
Give a picturesque view through which the train travels.
Answer:

Section – II
The train stopped at 8 o’clock some fifteen miles beyond Rothal. Phileas Fogg and others were annoyed. They were wondering why there was a halt of the train in the midst of the forest. When they enquired, the conductor informed them that the railroad lines ends at Kholby, 50 miles short of Allahabad. The line begins again from there in Allahabad. Sir Francis got angry because they sold the tickets from Bombay to Calcutta, without confirming about the railroad lines.
The passengers had to provide means of transportation for themselves from Kholby to Allahabad. So, Mr. Fogg, his attendant, and Sir. Francis planned to reach Allahabad in time by some means of transport, as a steamer was ready to leave Calcutta for Hongkong on the 25th. They had two days left to reach Calcutta.
Discuss and answer – Intext Questions.
Question 1.
Why did the train stop in the middle of the forest?
Answer:
The train stopped in the middle of the forest as there were no railroad lines beyond that place.
Question 2.
Why was Sir Francis angry?
Answer:
There were no railroad lines from Kholby to Allahabad. But the tickets were sold from Bombay to Calcutta. So Sir Francis was angry.
Section – III
After searching the village from end to end, Mr. Fogg and Sir. Francis came back without finding any means of transport. But Passepartout suggested that they can travel on an Indian elephant. As it could travel rapidly for a long time, Mr. Fogg determined to hire it. Even though Mr. Fogg offered an excessive amount to hire the elephant, the elephant’s owner refused to hire it. So Mr. Fogg finally purchased the elephant for two thousand pounds. A young man offered his services as a guide to them.
While Mr. Fogg and Sir Francis took the howdahs on either side, Passepartout got on to the saddle-cloth between them. The driver sat on the elephant’s neck and at 9 o’clock set out from the village to Allahabad.
Discuss and answer.
Question 1.
Which mode of transport did Fogg choose?
Answer:
At first, Fogg chose to go on foot to Allahabad. Then he purchased an elephant to take them to Allahabad.
Question 2.
Did he hire Kiouni? Why?
Answer:
No, he did not hire Kiouni, but purchased it for 2000 pounds, because the owner of the elephant intended to make a big bargain and so refused to hire him.

Question 3.
Why was the elephant owner happy with the deal?
Answer:
The elephant owner was happy with the deal because Mr. Fogg offered him 2000 pounds to purchase the elephant.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()