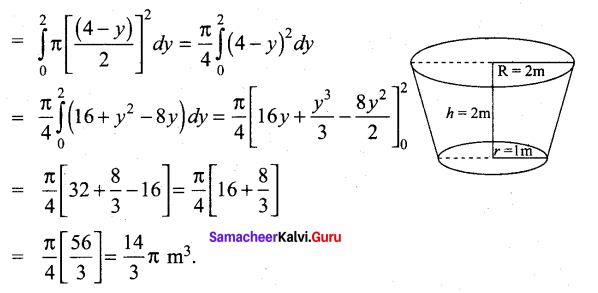
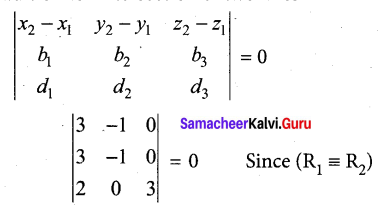
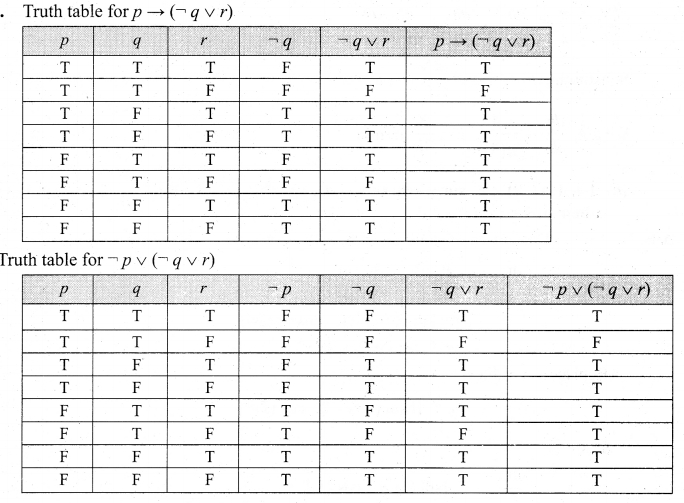
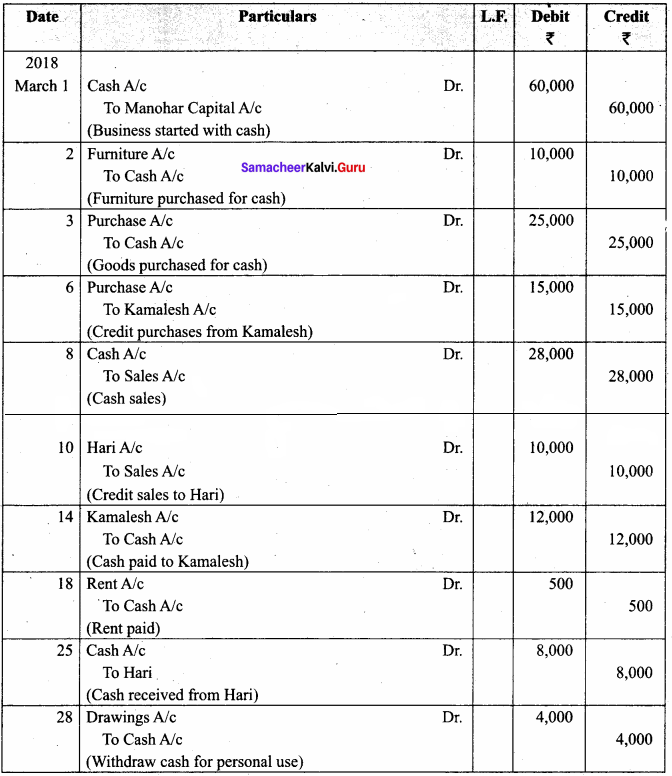
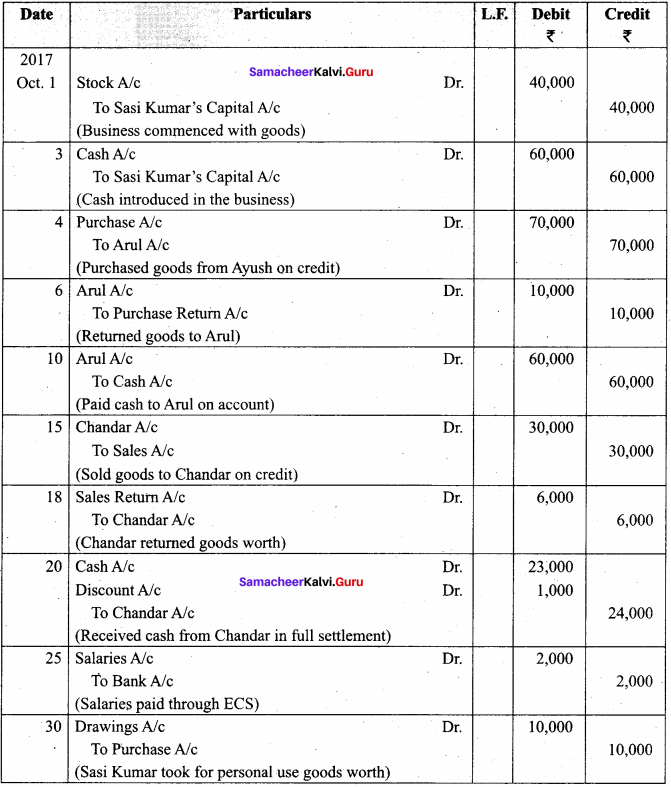
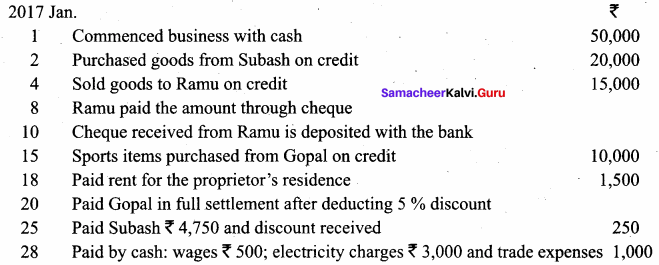
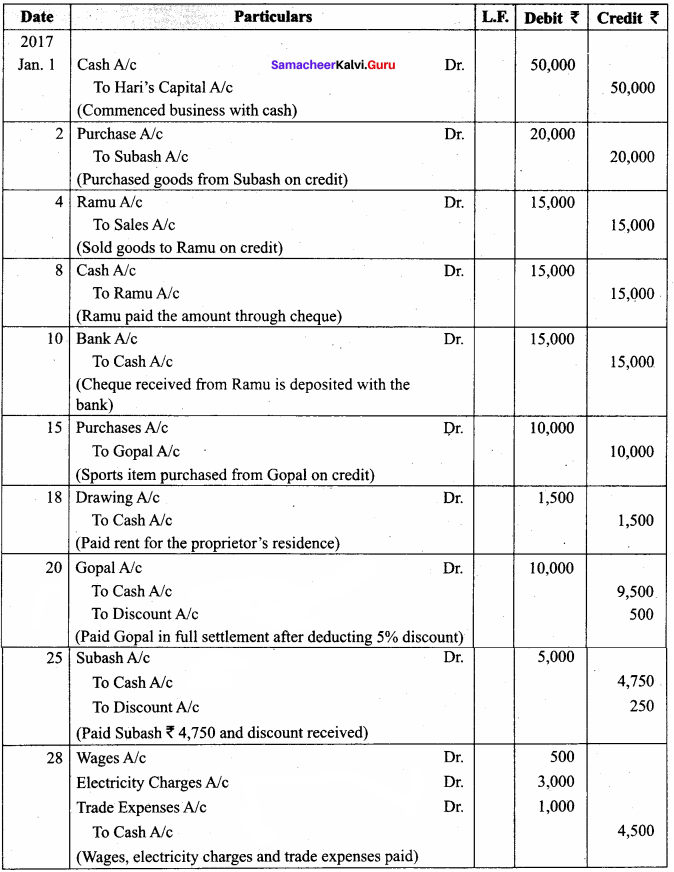
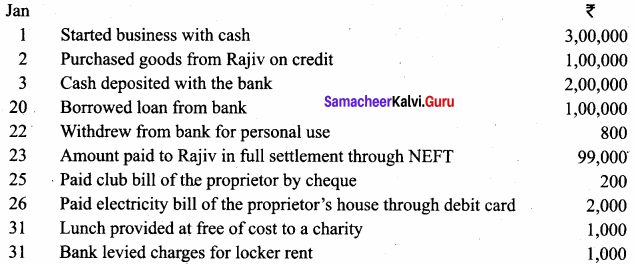
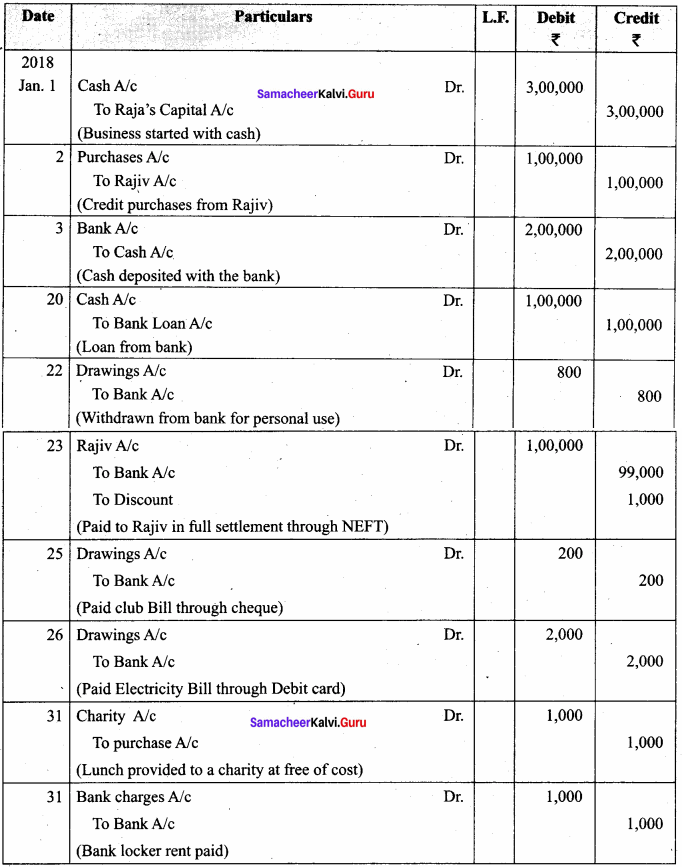
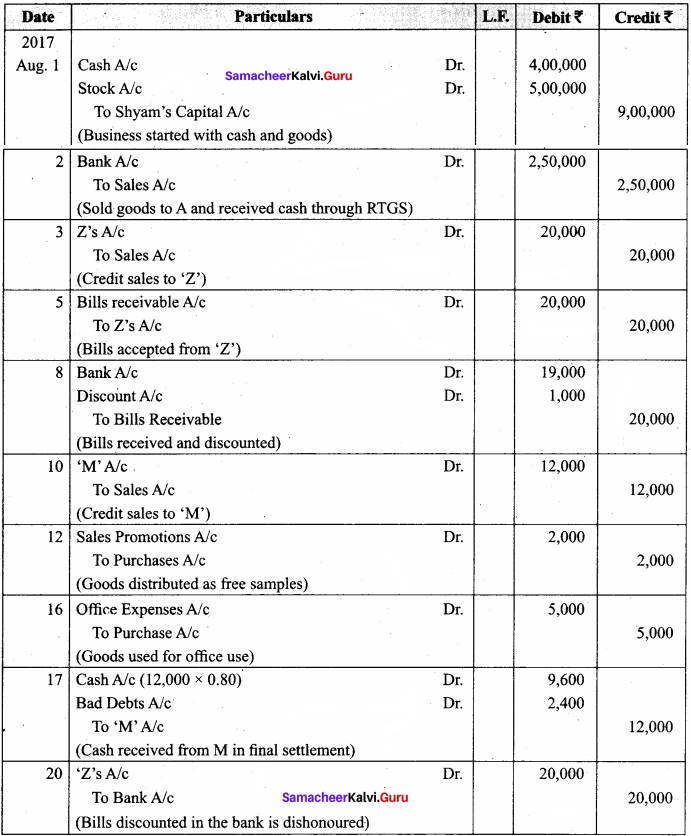
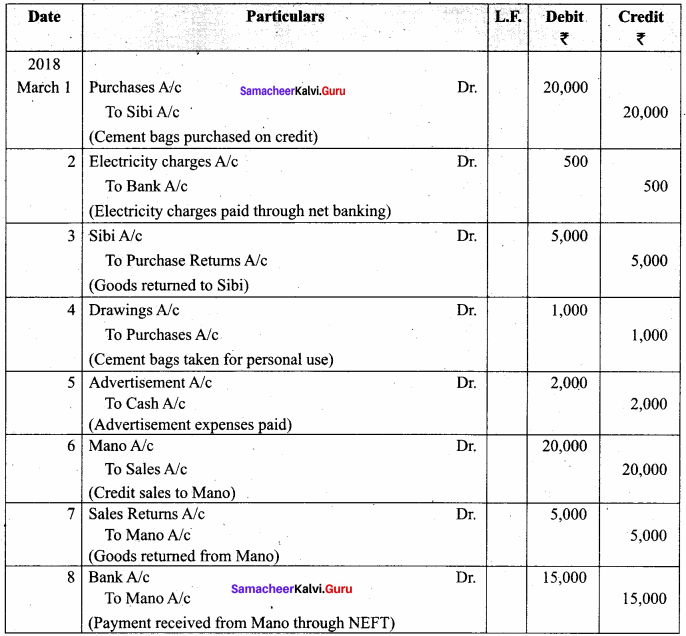
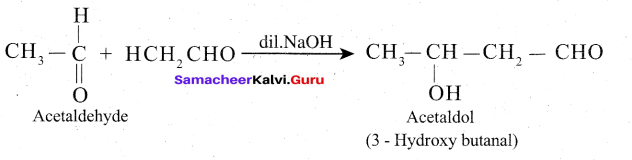
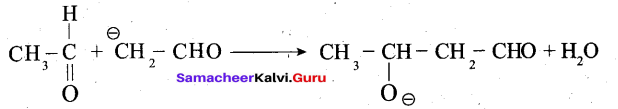
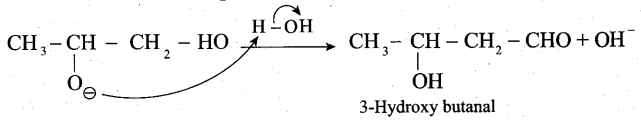
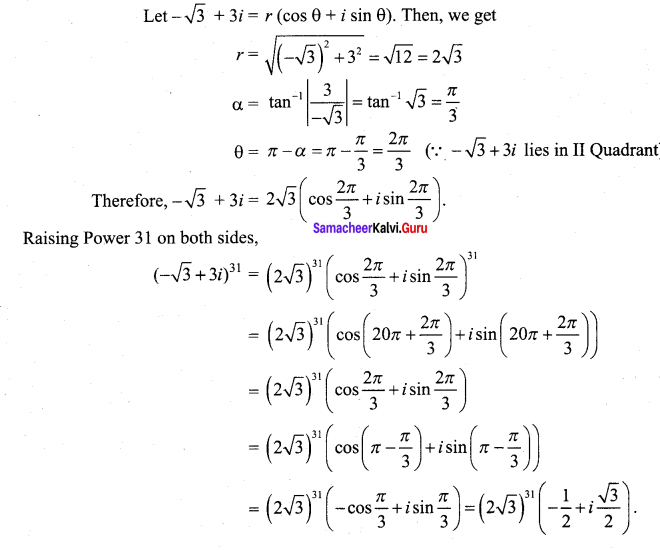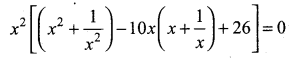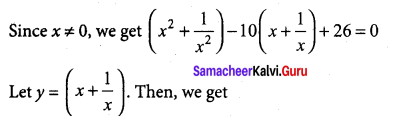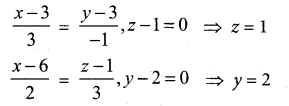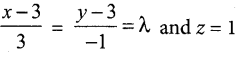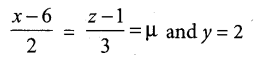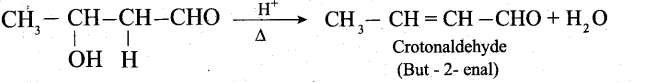Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 14 Importing C++ Programs in Python
Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 14 Importing C++ Programs in Python Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 14 Importing C++ Programs in Python
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Importing C++ Programs in Python Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Best Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a scripting language?
(a) JavaScript
(b) PHP
(c) Perl
(d) HTML
Answer:
(d) HTML
Question 2.
Importing C++ program in a Python program is called …………………………
(a) wrapping
(b) Downloading
(c) Interconnecting
(d) Parsing
Answer:
(a) wrapping
![]()
Question 3.
The expansion of API is ……………………….
(a) Application Programming Interpreter
(b) Application Programming Interface
(c) Application Performing Interface
(d) Application Programming Interlink
Answer:
(b) Application Programming Interface
Question 4.
A framework for interfacing Python and C++ is ………………………….
(a) Ctypes
(b) SWIG
(c) Cython
(d) Boost
Answer:
(d) Boost
Question 5.
Which of the following is a software design technique to split your code into separate parts?
(a) Object oriented Programming
(b) Modular programming
(c) Low Level Programming
(d) Procedure oriented Programming
Answer:
(b) Modular programming
![]()
Question 6.
The module which allows you to interface with the Windows operating system is ………………………….
(a) OS module
(b) sys module
(c) csv module
(d) getopt module
Answer:
(a) OS module
Question 7.
getopt( ) will return an empty array if there is no error in splitting strings to …………………………..
(a) argv variable
(b) opt variable
(c) args variable
(d) ifile variable
Answer:
(c) args variable
![]()
Question 8.
Identify the function call statement in the following snippet.
if_name ==’_main_’:
main(sys.argv[l:])
(a) main(sys.argvfl:])
(b) _name_
(c) _main_
(d) argv
Answer:
(b) _name_
Question 9.
Which of the following can be used for processing text, numbers, images, and scientific data?
(a) HTML
(b) C
(c) C++
(d) PYTHON
Answer:
(d) PYTHON
![]()
Question 10.
What does name contains?
(a) C++ filename
(b) main( ) name
(c) python filename
(d) os module name
Answer:
(c) python filename
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What is the theoretical difference between Scripting language and other programming language?
Answer:
The theoretical difference between the two is that scripting languages do not require the 228 compilation step and are rather interpreted. For example, normally, a C++ program needs to be compiled before running whereas, a scripting language like JavaScript or Python need not be compiled. A scripting language requires an interpreter while a programming language requires a compiler.
Question 2.
Differentiate compiler and interpreter?
Answer:
Compiler:
- It converts the whole program at a time
- It is faster
- Error detection is difficult. Eg. C++
Interpreter:
- line by line execution of the source code.
- It is slow
- It is easy Eg. Python
![]()
Question 3.
Write the expansion of
- SWIG
- MinGW
Answer:
SWIG (Simplified Wrapper Interface Generator. Both C and C++)
MinGW (Minimalist GNU for Windows)
Question 4.
What is the use of modules?
Answer:
We use modules to break down large programs into small manageable and organized files. Furthermore, modules provide reusability of code. We can define our most used functions in a module and import it, instead of copying their definitions into different programs.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the use of cd command. Give an example?
Answer:
The syntax to change from c:\> to the folder where Python is located is
cd <absolute path>
where “cd” command refers to change directory and absolute path refers to the complete path where Python is installed.
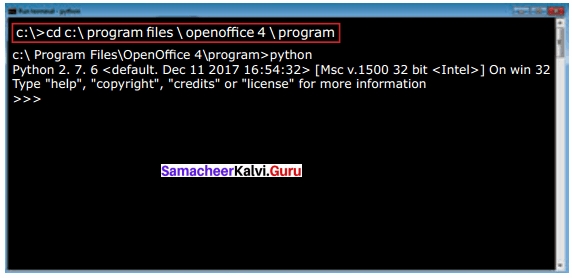
In this Example to go to the folder where Python is located we should type the following command “cd C:\Program Files\OpenOffiice 4\Program”:
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate PYTHON and C++?
Answer:
PYTHON:
- Python is typically an “interpreted” language
- Python is a dynamic-typed language
- Data type is not required while declaring variable
- It can act both as scripting and general purpose language
C++:
- C++ is typically a “compiled” language
- C++ is compiled statically typed language
- Data type is required while declaring variable
- It is a general purpose language
![]()
Question 2.
What are the applications of scripting language?
Answer:
Applications of Scripting Languages
- To automate certain tasks in a program
- Extracting information from a data set
- Less code intensive as compared to traditional programming language
- can bring new functions to applications and glue complex systems together
![]()
Question 3.
What is MinGW? What is its use?
Answer:
MinGW refers to a set of runtime header files, used in compiling and linking the code of C, C++ and FORTRAN to be run on Windows Operating System.
MinGw-W64 (versionofMinGW) is the best compiler for C++ on Windows. To compile and execute the C++ program, you need ‘g++’ for Windows. MinGW allows to compile and execute C++ program dynamically through Python program using g++.
Python program that contains the C++ coding can be executed only through minGW-w64 project run terminal. The run terminal open the command-line window through which Python program should be executed.
![]()
Question 4.
Identify the module, operator, definition name for the following
welcome.display( )
Answer:
welcome – module name
– dot operator
display( ) – function name
![]()
Question 5.
What is sys.argv? What does it contain?
Answer:
sys.argv is the list of command-line arguments passed to the Python program, argv contains all the items that come along via the command-line input, it’s basically an array holding the command-line arguments of the program.
To use sys.argv, you will first have to import sys. The first argument, sys.argv[0], is always the name of the program as it was invoked, and sys.argv[l] is the first argument you pass to the program (here it is the C++ file).
For example:
main(sys.args[1]) Accepts the program file (Python program) and the input file (C++ file) as a list(array). argv[0] contains the Python program which is need not to be passed because by default _main_ contains source code reference and argv[l] contains the name of the C++ file which is to be processed.
PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Write any 5 features of Python?
Answer:
- Python uses Automatic Garbage Collection
- Python is a dynamically typed language.
- Python runs through an interpreter.
- Python code tends to be 5 to 10 times shorter than that written in C++.
- In Python, there is no need to declare types explicitly
- In Python, a function may accept an argument of any type, and return multiple values without any kind of declaration beforehand.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain each word of the following command?
Answer:
The syntax to execute the Python program is
Python <filename.py> -i <C++filename without cpp extension>
Where,
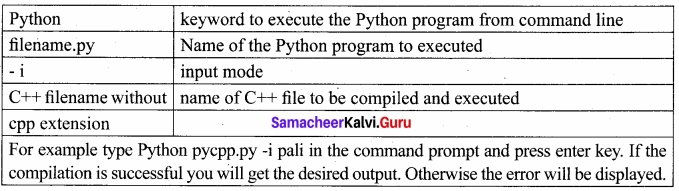
![]()
Question 3.
What is the purpose of sys,os,getopt module in Python. Explain?
Answer:
1. Python’s sys module
This module provides access to some variables used by the interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter.
sys.argv:
sys.argv is the list of command-line arguments passed to the Python program, argv contains all the items that come along via the command-line input, it’s basically an array holding the command-line arguments of the program.
To use sys.argv, you will first have to import sys. The first argument, sys.argv[0], is always the name of the program as it was invoked, and sys.argv) 1] is the first argument you pass to the program (here it is the C++ file). For example
main(sys.argv[ 1 ]) Accepts the program file (Python program) and the input file (C++ file) as a list(array). argv[0] contains the Python program which is need not to be passed because by default main contains source code reference and argv[l] contains the name of the C++ file which is to be processed.
2. Python’s OS Module
The OS module in Python provides a way of using operating system dependent functionality. The functions that the OS module allows you to interface with the Windows operating system where Python is running on.
os.system( ): Execute the C++ compiling command (a string contains Unix, C command which also supports C++ command) in the shell (Here it is Command Window). For Example to compile C++ program g++ compiler should be invoked. To do so the following command is used.
os.system (g++’ + <varciiable_namel> ‘-<mode>’+ <variable_name2>
where,
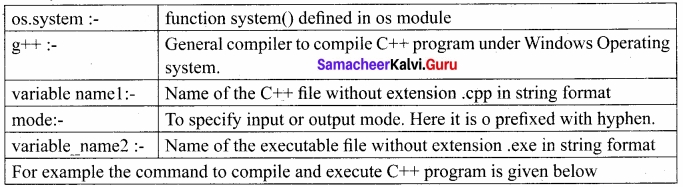
os.system(‘g++ ‘+ cpp_file + ‘-o ‘+ exe_file) g++ compiler compiles the file_cpp_file and -o (output) send to exe file
Note
‘+’ in os.system( ) indicates that all strings are concatenated as a single string and send that as a List.
3. Python getopt module
The getopt module of Python helps you to parse (split) command-line options and arguments. This module provides two functions to enable command-line argument parsing, getopt.getopt method
This method parses command-line options and parameter list. Following is the syntax for this method
<opts>,<args>=getopt.getopt(argv, options, {long_options])
Here is the detail of the parameters –
argv – This is the argument list of values to be parsed (splited). In our program the complete command will be passed as a list.
options – This is string of option letters that the Python program recognize as, for input or for output, with options (like ‘i’ or ‘o’) that followed by a colon (:). Here colon is used to denote the mode.
long options – This parameter is passed with a list of strings. Argument of Long options should be followed by an equal sign (‘=’). In our program the C++ fde name will be passed as string and ‘i’ also will be passed along with to indicate it as the input file.
getopt( ) method returns value consisting of two elements. Each of these values are stored separately in two different list (arrays) opts and args. Opts contains list of splitted strings like mode, path and args contains any string if at all not splitted because of wrong path or mode, args will be an empty array if there is no error in splitting strings by getopt( ).
For example The Python code which is going to execute the C++ file p4 in command line will have the getopt( ) method like the following one. opts, args = getopt.getopt (argv, “i:”,[‘ifile=]) where opto contains [(‘-i’, ‘c:\ \pyprg\\p4’)]
-i: – option nothing but mode should be followed by:
‘c: \ \pyprg\\p4’ value nothing but the absolute path of C++ file.
In our examples since the entire command line commands are parsed and no leftover argument, the second argument args will be empty [ ]. If args is displayed using print( ) command it displays the output as [ ].
>>>print(args)
[ ]
![]()
Question 4.
Write the syntax for getopt( ) and explain its arguments and return values?
Answer:
Python getopt module
The getopt module of Python helps you to parse (split) command-line options and arguments. This module provides two functions to enable command-line argument parsing, getopt.getopt method
This method parses command-line options and parameter list. Following is the syntax for this method –
<opts>,<args>=getopt.getopt(argx>, options, {.long_options])
Here is the detail of the parameters –
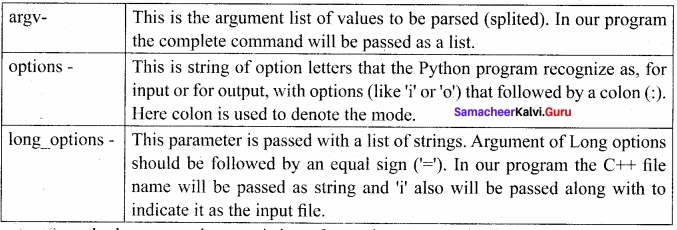
getopt( ) method returns value consisting of two elements. Each of these values are storec separately in two different list (arrays) opts and args .Opts contains list of splitted strings like mode, path and args contains any string if at all not splitted because of wrong path or mode, args will be an empty array if there is no error in splitting strings by getopt( ).
For example The Python code which is going to execute the C++ file p4 in command line will have the getopt( ) method like the following one. opts, args = getopt.getopt (argv, “i:”,[‘ifile=’])

In our examples since the entire command line commands are parsed and no leftover argument, the second argument args will be empty [ ]. If args is displayed using print( ) command it display the output as [ ].
>>>print(args)
[ ]
Some more command for wrapping C++ code
if_name_==’_main_’
main(sys.argv[1:])
_name_(A Special variable) in Python
Since there is no main() function in Python, when the command to run a Python program is given to the interpreter, the code that is at level 0 indentation is to be executed. However, before doing that, interpreter will define a few special variables. _name_ is one such special variable which by default stores the name of the file. If the source file is executed as the main program, the interpreter sets the _name_ variable to have a value as “_main_” name is a built-in variable which evaluates to the name of the current module. Thus it can be used to check whether the current script is being run on its own.
For example consider the following
if_name_ ==’_ main_’
main(sys.argv[1:])
if the command line Python program itself is going to execute first, then _main_ contains the name of that Python program and the Python special variable _name_ also contain the Python program name. If the condition is true it calls the main which is passed with C++ file as argument.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a Python program to execute the following C++ coding?
Answer:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ cout«“WELCOME”;
return (0);
}
The above C++ program is saved in a file welcome.cpp
Python program
Type in notepad and save as welcome.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
cout<<“WELCOME”;
retum(0);
}
Open Notepad and type python program and save as welcome.py
import sys,os,getopt
def main(argv):
cppfile =”
exefile = ”
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”, [ifile = ‘])
for o,a in opts:
if o in (“_i”,” ifile “):
cpp_file = a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print(“compiling” +cpp_file)
os.system(‘g++’ +cpp_file + ‘_o’ + exe_file)
print(“Running” + exe_file)
print(“………………………….”)
print
os.system(exe_file)
print
if — name — == ‘–main –‘;
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output:
——————-
WELCOME
——————-
Practice Programs
Question 1.
Write a C++ program to create a class called Student with the following details?
Answer:
Protected member
Rno integer
Public members
void Readno(int); to accept roll number and assign to Rno
void Writeno( ); To display Rno.
The class Test is derived Publically from the Student class contains the following details
Protected member
Mark1 float
Mark2 float
Public members
void Readmark(float, float); To accept mark1 and mark2
void Writemark( ); To display the marks
Create a class called Sports with the following detail
Protected members
score integer
Public members
void Readscore(int); To accept the score
void Writescore( ); To display the score
The class Result is derived Publically from Test and Sports class contains the following – details
Private member
Total float
Public member
void display( ) assign the sum of mark1, mark2, score in total
invokeWriteno( ), Writemark( ) and Writescore( ). Display the total also.
Save the C++ program in a file called hybrid. Write a python program to execute the hybrid.cpp
Answer:
In Notepad, type the C++ program
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class student
{
protected:
int mo;
public:
void readno(int rollno)
{
mo = rollno;
}
void writeno( )
{
cout<< “\n Roll no:” <<rno;
}};
class test: public student
{
protected:
float mark1,mark2;
public:
void readmark(float m1, float m2)
{
mark1 = m1;
mark2 = m2;
}
void writemark( )
{
cout<< “\n mark1 ” << mark1;
cout<< “\n mark2 ” <<mark2;
}};
class sports
{
protected:
int score;
public:
void readscore(int s)
{
score = s;
}
void writescore( )
{
cout<< “SCORE : ” <<score;
}};
class result: public test, public sports
{
private: float total; public:
void display( )
{
total = mark1 + mark2;
cout<< “TOTAL MARKS: ” <<total;
}};
int main( )
{
result r;
r.readno(5);
r.readmark(100,100);
r.readscore(200);
r.writeno( );
r.writemark( );
r.display( );
r.writescore( );
}
save this file as hybrid.cpp
Now type the python program in New Notepad file.
# python hybrid.py -i hybrid.cpp
import sys,os,getopt def main(argv): cpp Jile =” exe_file =”
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”,[‘ifile-])
for o, a in opts:
if o in(“-i”, “–file”):
cpp_file =”a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exefile)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print(“Compiling” + cpp_file)
os.system(‘g++ ‘+ cpp_file + ‘-o ‘+ exe_file)
print(“Running” + exefile)
print(“———————“)
print
os.system(excfile)
print
if name ==’ main
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output:
Rollno : 5
Mark1 : 100
Mark2 : 100
TOTAL MARKS : 200
SCORE : 200
![]()
Question 2.
Write a C++ program to print boundary elements of a matrix and name the file as Border.cpp. Write a python program to execute the Border.cpp?
Answer:
Select File → New in Notepad and type the C++ program.
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX =100;
void printBoundary(int a[][max], int m, int n)
{
for (int i=0; i < m; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j < n; j++)
{
if(i= =0 || j= =0 || i= =n-l ||j==n-l)
cout <<a[i][j]
<< ” else
cout <<“”
cout<<”
}
cout <<” \n”;
}}
int main( )
{
int a[4][MAX] = { {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8}, {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8}};
print Boundary(a,4,4);
return 0;
}
save it as Border.cpp
open a New notepad file and type the python program to execute border.cpp
#python border.py -i border.cpp
import sys,os,getopt
def main(argv):
cpp_file =”
exe_file =”
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”,[‘ifile=’])
for o, a in opts;
if o in(“-i”, “-ifile”):
cpp_file =a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print(“Compiling” + cpp_file)
os.system(‘g++ ‘+ cpp_file + ‘-o ‘+ exe_file)
print(“Running” + exe_file)
print(“———————“)
print
os.system(exe_file)
print
if_name_==’_main_’:
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output:

Samacheer kalvi 12th Computer Science Importing C++ Programs in Python Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which one of the following language act as both scripting and general purpose language?
(a) python
(b) c
(c) C++
(d) html
Answer:
(a) python
Question 2.
Find the correct statement.
(a) C++ is a dynamic typed language
(b) python is a dynamic typed language
Answer:
(b) python is a dynamic typed language
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the script language from the following.
(a) Html
(b) Java
(c) Ruby
(d) C++
Answer:
(c) Ruby
Question 4.
Pick the odd one out Perl, Ruby, ASP, Tel, Java
Answer:
Java
![]()
Question 5.
Read the statement given below and choose the correct option.
(I) All scripting languages are progamming languages.
(II) A scripting language requires an interpreter
(III) Programming language requires a compiler
(a) (I) – False, (II), (III) – True
(b) (I), (II) – False
(c) All are true
(d) All are false
Answer:
(c) All are true
Question 6.
How many values can be returned by a function in python?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) many
Answer:
(d) many
Question 7.
The process by which python periodically frees and reclaims block of memory that no longer are in use is called ……………………………..
Answer:
Garbage Collection
Question 8.
………………………. is a python like language for writing c extensions.
Answer:
cython
![]()
Question 9.
Which of the following language codes are linked by minGW on windows OS?
(a) C
(b) C++
(c) FORTRAN
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 10.
……………………. is the best compiler for C++ on windows.
(a) MinGW-w64
(b) MinGW-w63
(c) MinGW-w62
(d) MinGW-w60
Answer:
(a) MinGW-w64
Question 11.
MinGW allows to compile and execute C++ program dynamically through python program using ……………………….
(a) C++
(b) g++
(c) a++
(d) x++
Answer:
(b) g++
Question 12.
g++ is a program that calls GNU C compiler called …………………………….
(a) GCC
(b) CCC
(c) GGC
(d) GGG
Answer:
(a) GCC
![]()
Question 13.
The command to change directory is …………………………….
(a) cc
(b) cd
(c) dc
(d) changed
Answer:
(b) cd
Question 14.
………………………. keyword is used to execute the python program from command line
Answer:
Python
Question 15.
The input mode in python command is given by ………………………….
(a) -i
(b) o
(c) -p
Answer:
(a) -i
![]()
Question 16.
Which command is used to clear the screen?
(a) clear
(b) clean
(c) cls
(d) clrscr
Answer:
(c) cls
Question 17.
……………………… refer to a file containing python statements and definitions.
Answer:
Modules
Question 18.
pythons’ …………………………… provides access to same variables and functions that interact with the interpreter.
Answer:
sys module
![]()
Question 19.
Which is the list of command-line arguments passed to the python program.
(a) sys.ar
(b) sys.argv
(c) sys.sys
(d) sys.opt
Answer:
(b) sys.argv
Question 20.
Match the following related to OS module.
1. g++ – (i) Name of C++file
2. variable namel – (ii) General compiler
3. mode – (iii) input output mode
4. variable_name2 – (iv) Name of exe file
(a) 1-i, 2-ii, 3-iii, 4-iv
(b) 1-ii, 2-i, 3-iii, 4-iv
(c) 1-iv, 2-iii, 3-ii, 4-i
(d) 1-iv, 2-i, 3-iii, 4-ii
Answer:
(b) 1-ii, 2-i, 3-iii, 4-iv
Question 21.
Which in os.system( ) indicates that all strings are concatenated?
(a) +
(b) –
(c) #
(d) *
Answer:
(a) +
![]()
Question 22.
Which module helps to parse(split) command line options and arguments?
(a) getopt
(b) argopt
(c) get
(d) putopt
Answer:
(a) getopt
Question 23.
How many functions are there in getopt module to enable command line argument parsing?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 24.
getopt mode is given by ………………………….
(a) ;
(b) =
(c) #
(d) :
Answer:
(d) :
![]()
Question 25.
Argument of long options in the getopt method is followed by ………………………….
(a) ‘
(b) =
(c) #
(d) :
Answer:
(b) =
Question 26.
When the command to run a python program is given to interpreter, code at …………………………. indentation is executed.
(a) level 0
(b) level 1
(c) level 2
(d) level 3
Answer:
(a) level 0
Question 27.
Which one is a special variable which by default stores the name of the file.
(a) main
(b) none
(c) _name_
(d) get
Answer:
(c) _name_
![]()
Question 28.
The line number starts from …………………………… script.
Answer:
python
Question 29.
The …………………………… definition invoke the g++ compiler and creates the exe file?
Answer:
Question 30.
Which command of os module executes the exe file?
(a) run
(b) system( )
(c) main
(d) name
Answer:
(a) run
Question 31.
Which opeator is used to access the functions of a imported value?
(a) +
(b) *
(c) .
(d) /
Answer:
(c) .
![]()
Question 32.
………………………….. refers to a set of runtime header files used in compiling and linking the code of c, C++, Fortran to run on window os
(a) MaxGW
(b) CountGW
(c) MinGW
(d) AvgGW
Answer:
(c) MinGW
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Write note on scripting language?
Answer:
A scripting language is a programming language designed for integrating and communicating with other programming languages. Some of the most widely used scripting languages are JavaScript, VBScript, PHP, Perl, Python, Ruby, ASP and Tel.
![]()
Question 2.
Write note on Modular programming?
Answer:
Modular programming is a software design technique to split your code into separate parts. These parts are called modules.The focus for this separation should have modules with no or just few dependencies upon other modules.
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Name some commonly used Interfaces for importing C++ files on python?
Answer:
Importing C++ Files in Pythona:
Importing C++ program in a Python program is called wrapping up of C++ in Python. Wrapping or creating Python interfaces for C++ programs are done in many ways. The commonly used interfaces are
- Python-C-API (API-Application Programming Interface for interfacing with C programs)
- Ctypes (for interfacing with c programs)
- SWIG (Simplified Wrapper Interface Generator.Both C and C++)
- Cython (Cython is both a Python-like language for writing C-extensions)
- Boost. Python (a framework for interfacing Python and C++)
- MinGW (Minimalist GNU for Windows)
![]()
Question 2.
How will you import modules in python?
Answer:
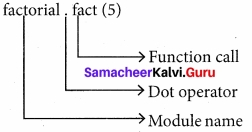
We can import the definitions inside a module to another module. We use the import keyword to do this. To import the module factorial we type the following in the Python prompt.
>>> import factorial
Using the module name we can access the functions defined inside the module. The dot(.)
operator is used to access the functions. The syntax for accessing the functions from the module is
<module name>.<function name>
For example:
>>> factorial.fact(5)
120
![]()
Question 3.
Give the syntax for getopt module?
Answer:
The syntax for this method
<opts> ,<args>=getopt.getopt(argv, options, [long_options])
Here is the detail of the parameters –

Question 4.
Write the steps for executing the C++ program to check whether a given number is palindrome or not?
Answer:

PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Explain Pythons OS Module?
Answer:
Python’s OS Module:
The OS module in Python provides a way of using operating system dependent functionality. The functions that the OS module allows you to interface with the Windows operating system where Python is running on.
os.system( ): Execute the C++ compiling command (a string contains Unix, C command which also supports C++ command) in the shell (Here it is Command Window). For Example to – compile C++ program g++ compiler should be invoked. To do so the following command is used.
os.system (g++’ + <varaiable_namel> ‘-<mode>’+ <variable_name2>
where,
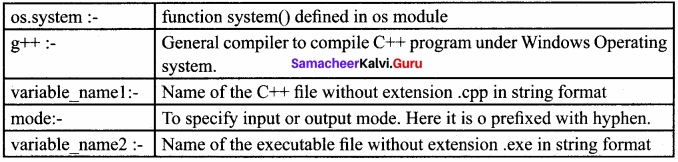
For example the command to compile and execute C++ program is given below
os.system(’g++ ’+ cpp_file + ‘-o ‘+ exe_file) g++ compiler compiles the file cpp_file and -0(output) send to exe_file
![]()
Question 2.
Write a C++ program to check whether the given number is palindrome or not. Write a program to execute it?
Answer:
Example:- Write a C++ program to enter any number and check whether the number is palindrome or not using while loop.
/*. To check whether the number is palindrome or not using while loop.*/
//Now select File-> New in Notepad and type the C++ program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; intmain( )
{
int n, num, digit, rev = 0;
cout << “Enter a positive number:”;
cin>>num;
n = num;
while(num)
{ digit=num% 10;
rev= (rev* 10) +digit;
num = num/10;
cout << “The reverse of the number is:”<<rev <<end1;
if (n ==rev)
cout<< “The number is a palindrome”;
else
cout<< “The number is a palindrome”;
return 0;
}
//save this file as pali_cpp.cpp
#Now select File → New in Notepad and type the Python program
#Save the File as pali.py.Program that complies and executes a .cpp file
import sys, os, getopt
def main(argv);
cpp_file=”
exe_file=”
opts.args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”,[‘ifile-])
for o, a in opts:
if o in (“-i”, “—file”):
cpp_file =a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file =a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print(“Compiling” + eppfile)
os.system(‘g++’ + cpp_file +’ -o’ + exe file)
print(“Running” + exe_file)
print(“——————“)
print
os.system(exefile)
print
if_name_==’_main_’: #program starts executing from here
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output of the above program
C:\Program Files\OpenOffice 4\program>Python c:\pyprg\pali.py -i c:\pyprg\pali_cpp
Compiling c:\pyprg\pali_cpp.cpp
Running c:\pyprg\pali_cpp.exe
———————————–
Enter a positive number: 56765
The reverse of the number is: 56765
The number is a palindrome
C:\Program Files\OpenOffice 4\program>Python c:\pyprg\pali.py -i c:\pyprg\pali_cpp Compiling c:\pyprg\pali_cpp.cpp Running c:\pyprg\pali_cpp.exe
Enter a positive number: 56756
The reverse of the number is: 65765
The number is not a palindrome
————————
![]()
Question 3.
Write a C++ program to check whether the given number is palindrome or not. Write a program to execute it?
Write a C++ program to enter any number and check whether the number is palindrome or not using while loop?
Answer:
//Now select File-> New in Notepad and type the C++ program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
intmain( )
{
int a[3][3], i, j;
for(i=o; j<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{count<<“enter the value for array [”<<i+1<<“]<<”<<“[“<<j+1<<“]”;
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
system(“cls”); .
cout<<“\n \nOriginal Array\n”;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<3; j++)
cout<<a[i] [j]
cout<<end1;
}
cout<<end1;
}
return 0;
}
// Save this file as trans_cpp.cpp
// Now select File → New in Notepad and type the Python program
#Save the File as transpose.py.Program that compiles and executes a .cpp file
#Python tanspose.py -i trans_cpp
import sys, os, getopt
def main(argv):
cpp_file =”
exefile =”
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”,[‘ifile=’])
for o, a in opts:
if o in (“-i”,–ifile”):
cpp_file =a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe file):
print(“Compiling” + cppfile)
os.system(‘g++’ + cpp_file + ‘-o ‘+ exe_file)
print(“Running” + exefile)
print(“———————-“)
print
os.system(exe_file)
print
if_name_==’_main_’:
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output of the above program
Original Array
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
The Transpose of Matrix
1 4 7
2 5 8
3 6 9
![]()
Question 4.
Write a C++ program to find cube of a number. Write a python program to execute it?
Answer:
/* Write a C++program using a user definedfunction to function cube of a number. */
//Now select File → New in Notepad and type the C++program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Function declaration
int cube(int num); int main( )
{
int num; int c;
cout<<“Enter any number: “<<end1;
cin>>num;
c = cube(num);
cout<<“Cube of’ <<num<<” is “<<c;
return 0;
}
//Function to find cube of any number
int cube(int num)
{
return (num * num * num);
}
//Save this file as cube_file.cpp
#Now select File → New in Notepad and type the Python program
#Save the File as fun.py
#Program that compiles and executes a .cpp file
#Python fun.py -i c:\pyprg\cuheJile.cpp
import sys, os, getopt
def main(argv):
cpp_Jile =”
exe_file =”
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, “i:”,[‘ifile-])
for o, a in opts:
if o in(“-i”, —ifile”):
cpp_file =a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe file):
print(“Compiling” + cppfile)
os.system(‘g++’+ cpp file + ‘-o ‘+ exe file)
print(“Running” + exe_file)
print(“——————–“)
print
os. sy stem(exe_file)
print
if_name_==’_main_’:
main(sys.argv[1:])
Output of the above program
Compiling c:\pyprg\cube_file.cpp
Running c:\pyprg\cube_file.exe
———————-
Enter any number:
5
Cube of 5 is 125
![]()
Question 5.
Write a C++ program to implement multilevel inheritance. Write a python program to execute it?
Answer:
// C++program to implement Multilevel Inheritance
//Now select File → New in Notepad and type the C++program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// base class
class Vehicle
{
public:
Vehicle( )
{
cout<< “This is a Vehicle” <<end1;
}
};
class threeWheeler: public Vehicle
{public:
threeWheeler( )
{
cout<<“Objects with 3 wheels are vehicles”<<end1;
}
};
// sub class derivedfrom two base classes
class Auto: public threeWheeler
{
public:
Auto( )
{
cout<<“Auto has 3 Wheels”<<end1;
}
// main function
int main( )
{
//creating object of sub class will invoke the constructor of base classes
Auto obj;
return 0;
}
// Save this file as inheri_cpp.cpp
//Now select File —* New in Notepad and type the Python program
#Save the File as classpy.py
#Python classpy.py -i inheri_cpp command to execute C++ program
import sys, os, getopt
def main (argv):
cpp_file =”
exe file= 11
opts, args = getopt.getopt (argv, 11i: 11 ,[‘ifile=’])
for o, a in opts:
if o in (“-i”, —ifile”):
cpp_file =a+ ‘.cpp’
exe_file = a+ ‘.exe’
run (cpp file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print (”Compiling 11 + cpp file)
os.system (‘g++’ + cpp_file +’ -o ‘+ exe_file)
print (“Running”+ exe file)
print(“———————“)
print
os.system (exefile) print
if_name_==’_main_’:
main (sys.argv[1:])
Output of the above program
Compiling c:\pyprg\class_file.cpp
Running c:\pyprg\class_file.exe
This is a Vehicle
Objects with 3 wheels are vehicles
Auto has 3 Wheels