Students can Download Bio Botany Chapter 7 Ecosystem Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 7 Ecosystem
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Ecosystem Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a abiotic component of the ecosystem?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Humus
(c) Organic compounds
(d) Inorganic compounds
Answer:
(b) Humus
Question 2.
Which of the following is / are not a natural ecosystem?
(a) Forest ecosystem
(b) Rice field
(c) Grassland ecosystem
(d) Desert ecosystem Pond is a type
Answer:
(b) Rice field
![]()
Question 3.
Pond is a type of __________
(a) Forest ecosystem
(b) grassland ecosystem
(c) marine ecosystem
(d) fresh water ecosystem Pond ecosystem
Answer:
(d) fresh water ecosystem Pond ecosystem
Question 4.
Pond ecosystem is __________
(a) not self sufficient and self regulating
(b) partially self sufficient and self regulating
(c) self sufficient and not self regulating
(d) self sufficient and self regulating
Answer:
(d) self sufficient and self regulating
Question 5.
Profundal zone is predominated by heterotrophs in a pond ecosystem, because of __________
(a) with effective light penetration
(b) no effective light penetration
(c) complete absence of light
(d) a and b
Answer:
(d) a and b
Question 6.
Solar energy used by green plants for photosynthesis is only __________
(a) 2 -8%
(b) 2-10%
(c) 3-10%
(d) 2-9%
Answer:
(b) 2-10%
Question 7.
Which of the following ecosystem has the highest primary productivity?
(a) Pond ecosystem
(b) Lake ecosystem
(c) Grassland ecosystem
(d) Forest ecosystem
Answer:
(c) Grassland ecosystem
Question 8.
Ecosystem consists of __________
(a) decomposers
(b) producers
(c) consumers
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 9.
Which one is in descending order of a food chain?
(a) Producers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Tertiary consumers
(b) Tertiary consumers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Producers
(c) Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Producers
(d) Tertiary consumers → Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers Significance of food web is / are
Answer:
(c) Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Producers
Question 10.
Significance of food web is / are __________
(a) it does not maintain stability in nature
(b) it shows patterns of energy transfer
(c) it explains species interaction
(d) b and c
Answer:
(d) b and c
Question 11.
The following diagram represents __________
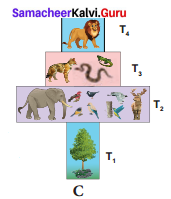
(a) pyramid of number in a grassland ecosystem
(b) pyramid of number in a pond ecosystem
(c) pyramid of number in a forest ecosystem
(d) pyramid of biomass in a pond ecosystem
Answer:
(c) pyramid of number in a forest ecosystem
Question 12.
Which of the following is / are not the mechanism of decomposition?
(a) Eluviation
(b) Catabolism
(c) Anabolism
(d) Fragmentation
Answer:
(c) Anabolism
Question 13.
Which of the following is not a sedimentary cycle?
(a) Nitrogen cycle
(b) Phosphorous cycle
(c) Sulphur cycle
(d) Calcium cycle
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen cycle
![]()
Question 14.
Which of the following are not regulating services of ecosystem services?
(i) Genetic resources
(ii) Recreation and aesthetic values
(iii) Invasion resistance
(iv) Climatic regulation
(a) i and iii
(b) ii and iv
(c) i and ii
(d) i and iv
Answer:
(c) i and ii
Question 15.
Productivity of profundal zone will be low. Why?
Answer:
- The deeper region of a pond below the limnetic zone is called profundal zone with no effective light penetration.
- This layer is predominance with heterotrophs and low biodiversity. So the productivity of profundal zone will be low.
Question 16.
Discuss the gross primary productivity is more efficient than net primary productivity.
Answer:
Gross primary productivity:
- It refers to the total amount of food energy or organic matter produced in an ecosystem by autotrophs.
- GPP = NPP + Respiration
Net primary productivity:
- It refers to the amount of energy that remain in autotrophs after respiration loss.
- NPP = GPP – Respiration
Question 17.
Pyramid of energy is always upright. Give reasons.
Answer:
- Pyramid of energy is always upright because the bottom of the pyramid of energy is occupied by the producers.
- There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to the upper levels.
[1000] 2 100J 2 10J 21J20.1J] - Thus the pyramid of energy is always upright.
Question 18.
What will happen if all producers are removed from ecosystem?
Answer:
Producers are the autotrophs which occupy the first tropic level in an ecosystem. The energy produced by them is utilized by the herbivores and then by carnivores, thereby maintaining the stability of ecosystem. If producers are removed from an ecosystem, it would lead to starvation and death of herbivores and subsequently the carnivores, thus terminating the entire food web.
Question 19.
Construct the food chain with the following data.
Hawk, plants, frog, snake, grasshopper.
Answer:
Plants → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- The movement of energy from producers upto top carnivores is known as food chain.
- In this food chain energy flows from producers (plants) to primary consumers (grasshopper) to secondary consumer (frog) to tertiary consumer (snake) to predator (hawk)
- It shows linear network link.
Question 20.
Name of the food chain which is generally present in all type of ecosystem. Explain and write their significance.
Answer:
Detritus food chain is common in all type of ecosystem. In detritus food chain, the dead remains of plant and animals or their excreta are broken down by detrivores and the organic and inorganic substances are returned back to environment. Thus maintaining die company of various biogeochemical cycles. Also Microbes growing on detritus makes the soil nutritious for consumers.
Question 21.
Shape of pyramid in a particular ecosystem is always different in shape. Explain with example.
Answer:
- In forest ecosystem the pyramid of number is somewhat different in shape because
- The base of the pyramid occupies large-sized trees (producer Tl) which are lesser in number.
- (Herbivores T2) fruit-eating birds, elephant deer occupying the second trophic level are more in number than producers.
- In final trophic level (Tertiary consumer T4) lion are lesser in number than the secondary consumer (T3) fox and snake.
- Therefore the pyramid of number in forest ecosystem looks spindle-shaped.
![]()
Question 22.
Generally human activities are against to the ecosystem, where as you a student how will you help to protect ecosystem?
Answer:
- Buying and using only ecoffiendly products and recycle them.
- Growing more trees.
- Choosing sustained farm products (vegetables, fruits and greens, etc.)
- Reducing the use of natural resources.
- Recycling the waste and reduce the amount of waste you produce.
- Reducing consumption of water and electricity.
- Reducing or eliminating the use of house-hold chemicals and pesticides.
- Maintaining your cars and vehicles properly to reduce carbon emission.
- Creating awareness and educate about ecosystem protection among your friends and family members and ask them to find out solution to minimise this problem.
Question 23.
Generally in summer the forest are affected by natural fire. Over a period of time it recovers itself by the process of successions. Find out the types of succession and explain. Secondary succession.
Answer:
The development of a plant community in an area where an already developed community has been destroyed by natural causes is known as secondary succession. This type of succession takes less time to occur.
Question 24.
Draw a pyramid from following details and explain in brief.
Answer:
Quantities of organisms are given-Hawks-50, plants-1000, rabbit and mouse-250 +250, pythons and lizard – 100 + 50 respectively
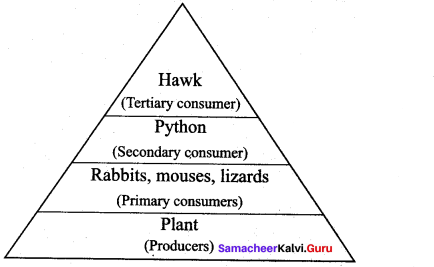
T4 (50) T3 (100) T2 (550) T1 (1000)
The pyramid produced is an upright pyramid of numbers where there is a gradual decrease in number of organisms at each trophic level from T1 to T4. This is an example for grassland ecosystem.
Question 25.
Various stages of succession are given bellow. From that rearrange them accordingly. Find out the type of succession and explain in detail.
Answer:
The type of succession is hydrosere. It includes the following stages.
- Phytoplankton stage
- Submerged plant stage
- Submerged free-floating stage
- Reed-swamp stage
- Marsh meadow stage
- Shrub stage
- Forest stage
1. Phytoplankton stage:
It is the first stage of succession consisting of the pioneer community like blue green algae, green algae, diatoms, bacteria, etc., The colonization of these organisms enrich the amount of organic matter and nutrients of pond due to their life activities and death. This favours the development of the next serai stages.
2. Submerged plant stage:
As the result of death and decomposition of planktons, silt brought from land by rain water, lead to a loose mud formation at the bottom of the pond. Hence, the rooted submerged hydrophytes begin to appear on the new substratum. Example: Chara, Utricularia. The death and decay of these plants will build up the substratum of pond to become shallow. Therefore, this habitat now replaces another group of plants which are of floating type.
3. Submerged free floating stage:
During this stage, the depth of the pond will become almost 2-5 feet. Hence, the rooted hydrophytic plants and with floating large leaves start colonising the pond. Example: Rooted floating plants like Nelumbo, Nymphaea and Trapa. By death and decomposition of these plants, further the pond becomes more shallow. Due to this reason, floating plant species is gradually replaced by another species which makes new serai stage.
4. Reed-swamp stage:
It is also called an amphibious stage. During this stage, rooted floating plants are replaced by plants which can live successfully in aquatic as well as aerial environment. Example: Typha
5. Marsh meadow stage:
When the pond becomes swallowed due to decreasing water level, species of Cyperaceae and Poaceae. They form a mat-like vegetation with the help of their much branched root system. This leads to an absorption and loss of large quantity of water. At the end of this stage, the soil becomes dry and the marshy vegetation disappears gradually and leads to shrub stage.
6. Shrub stage:
As the disappearance of marshy vegetation continues, soil becomes dry. Hence, these areas are now invaded by terrestrial plants like shrubs (Salix and Cornus) and trees (Populus and Alnus). These plants absorb large quantity of water and make the habitat dry. Further, the accumulation of humus with a rich flora of microorganisms produce minerals in the soil, ultimately favouring the arrival of new tree species in the area.
7. Forest stage:
It is the climax community of hydrosere. A variety of trees invade the area and develop any one of the diverse type of vegetation. Example: Temperate mixed forest
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Ecosystem Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Question
Question 1.
Ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of ecology. This statement was given by ___________
(a) Tansley
(b) Odum
(c) Charles Elton
(d) Edwin
Answer:
(b) Odum
![]()
Question 2.
Identify the incorrect option among the following component sequence.
(a) air, water, sunlight and temperature
(b) latitude, altitude, direction of mountain and aptitude
(c) soil air, pH of soil, saltwater and soil moisture
(d) carbohydrate, protein, lipids and humic substances
Answer:
(b) latitude, altitude, direction of mountain and aptitude
Question 3.
Pick out the edaphic factor among the following.
(a) Rainfall
(b) Temperature
(c) Soil pH
(d) Latitude
Answer:
(c) Soil pH
Question 4.
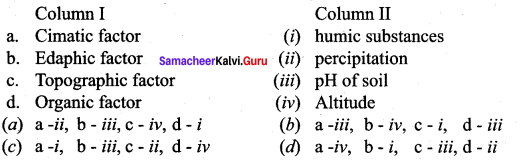
Answer:
a -ii, b – iii, c – iv, d-i
Question 5.
Which is not a macro consumer?
(a) Herbivore
(b) Carnivore
(c) Ominivore
(d) Decomposer
Answer:
(d) Decomposer
Question 6.
Photosynthetically Active Radiation ranges between the wavelength of.
(a) 400 – 600 nm
(b) 600 – 700 nm
(c) 400 – 500 nm
(d) 400 – 700 nm
Answer:
(d) 400 – 700 nm
Question 7.
Who coined the term Ecosystem?
Answer:
A.G. Tansley
Question 8.
Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) Carbon stored in oil is referred to as Grey carbon
(b) Carbon stored in atmosphere is referred as Blue carbon
(c) Carbon stored in industrialized forests is referred to as Green carbon
(d) Carbon emitted from gas, died engine is referred as Black carbon
Answer:
(c) Carbon stored in industrialized forests is referred to as Green carbon
![]()
Question 9.
Which group of organism occupies the third trophic level in an ecosystem?
(a) Primary consumers
(b) Secondary consumers
(c) Secondary carnivores
(d) Omnivores
Answer:
(b) Secondary consumers
Question 10.
Which is irrelevant to the first law of thermodynamics?
(a) Energy can be transmitted from one system to other in many forms.
(b) Energy transformation results in reduction of free energy.
(c) Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
(d) Energy in the universe is constant.
Answer:
(b) Energy transformation results in reduction of free energy.
Question 11.
If 1200 Joules of solar energy is trapped by producers, how much of Joules of energy does the organism in the third trophic level will receive?
(a) 120 Joules
(b) 12 Joules
(c) 1.2 Joules
(d) 0.12 Joules
Answer:
(c) 1.2 Joules
Question 12.
Which of the following food chain is in improper sequence?
(a) Plants → snake → rabbit → lizard → eagle
(b) Plants → grasshopper → lizard → snake → hawk
(c) Plants → lizard → rabbit → snake → eagle
(d) Plants → rabbit → lizard → hawk → eagle
Answer:
(b) Plants → grasshopper → lizard → snake → hawk
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not a functional unit of an ecosystem?
(a) Productivity
(b) Conductivity
(c) Energy flow
(d) Decomposition
Answer:
(b) Conductivity
Question 14.
The upright pyramid is not a feature of. __________
(a) Pond ecosystem
(b) Grassland ecosystem
(c) Forest ecosystem
(d) Terminal ecosystem
Answer:
(a) Pond ecosystem
Question 15.
The type of ecosystem with maximum net primary productivity is __________
(a) Desert ecosystem
(b) Deciduous forest ecosystem
(c) Tropical rain forest ecosystem
(d) Grassland ecosystem
Answer:
(c) Tropical rain forest ecosystem
Question 16.
Pyramid of numbers with broad base indicates __________
(a) High population of old individuals
(b) Low population of young individuals
(c) High population of young individuals
(d) Low population of old individuals
Answer:
(b) Low population of young individuals
Question 17.
Spindle shaped pyramid is a character of __________
(a) Pond ecosystem
(b) Grassland ecosystem
(c) Parasite ecosystem
(d) Forest ecosystem
Answer:
(d) Forest ecosystem
Question 18.
Read the statement and select the correct terminology for the same:
“Carrying away of inorganic compounds of soil by water”.
(a) Eluviation
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Humification
(d) Mineralisation
Answer:
(a) Eluviation
Question 19.
Complete the food chain by filling the link X:
Paddy → Grassopper → Frog → X → Hawk
(a) King cobra
(b) Gorilla
(c) Rabbit
(d) Tasmanial wolf
Answer:
(a) King cobra
Question 20.
Which of the following is abundant in rock deposits and guano?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Phosphorous
(c) Oxygen
(d) Calcium
Answer:
(b) Phosphorous
![]()
Question 21.
The bottom most zone of a pond is termed as
(a) Limnetic zone
(b) Littoral zone
(c) Benthic zone
(d) Profundal zone
Answer:
(c) Benthic zone
Question 22.
Observe the figures and select the correct type of pyramid of numbers
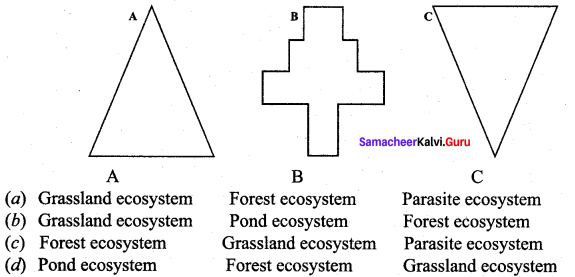
Answer:
(a) (A) Grassland ecosystem (B) Forest Echosystem (c) Parasite ecosystem
Question 23.
Lotic ecosystem refers to ___________
(a) Open water ecosystem
(b)Running water ecosystem
(c) Standing water
(d) Ocean water ecosystem
Answer:
(b)Running water ecosystem
Question 24.
Identify the correct sequence of various zones from surface to depth in a pond ecosystem.
(a) Profundal, limnetic, littoral and benthic
(b) Benthic, littoral, profundal and limnetic
(c) Limnetic, profundal, littoral and benthic
(d) Littoral, limnetic, profundal and benthic
Answer:
(d) Littoral, limnetic, profundal and benthic
Question 25.
Which type of ecosystem service does the genetic resources comes under?
(a) Provisioning services
(b) Supporting services
(c) Regulating services
(d) Cultural services
Answer:
(a) Provisioning services
Question 26.
Assertion (A): Pyramid of energy is upright.
Reason (R): During the energy transfer at successive trophic levels from producers there will be a gradual decrease
(a) Both A and R are wrong
(b) A is right R is wrong
(c) R explains A
(d) A is right R is not the correct explanation for A
Answer:
(c) R explains A
Question 27.
Assertion (A): In forest ecosystem, the pyramid of number is spindle shaped.
Reason (R): Tropical level (T1) of the pyramid occupies large trees which are maxium in number
(a) Both A and R are wrong
(b) A is right R is wrong
(c) R explains A
(d) A is right R is not the correct explanation for A
Answer:
(b) A is right R is wrong
Question 28.
Species that indicate the health of the ecosystem are called as __________
Answer:
Flagship species
Question 29.
Succession initiating on a sand referred as
(a) Hydrosere
(b) Psammosere
(c) Halosere
(d) Lithosere
Answer:
(b) Psammosere
Question 30.
Match the column I with column II

Answer:
(a) a – iii, b – iv, c – i, d – ii
Question 31.
Statement (I): Allogenic succession occurs as a result of abiotic factors.
Statement (II): Autogenic succession occurs as result of biotic factors.
(a) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statements I and II are correct.
(d) Both Statements I and II are incorrect.
Answer:
(c) Both Statements I and II are correct.
![]()
Question 32.
Statement (I): The first invaded plants in a barren area are called as pioneers.
Statement (II): Marsh meadow stage of hydrosere succession is also called as amphibious stage.
(a) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statements I and II are correct.
(d) Both Statements I and II are incorrect.
Answer:
(a) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
Question 33.
_______ is the climax community of hydrosere.
(a) Reed swamp stage
(b) Marsh medow stage
(c) Shrub stage
(d) Forest stage
Answer:
(d) Forest stage
2-Mark Questions
Question 1.
According to A.G. Tansley, what is an ecosystem?
Answer:
A.G. Tansley (1935), who defined ecosystem as ‘the system resulting from the integration of all the living and non-living factors of the environment.
Question 2.
Mention any two climatic factors and edaphic factors of an ecosystem.
Answer:
- Climatic factors: Light and Air.
- Edaphic factors: Soilwaer and pH of soil.
Question 3.
Define ‘Standing state’ with regard to ecosystem.
Answer:
The total inorganic substances present in any ecosystem at a given time is called standing quality (or) standing state.
Question 4.
What are biotic components?
Answer:
Biotic (living) components includes all living organisms like plants, animals, fungi and bacteria. They form the trophic structures of any ecosystem.
Question 5.
Name the macro consumers and micro consumers.
Answer:
- Macro consumers are herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
- Micro consumers are decomposers.
Question 6.
How will you define decomposers?
Answer:
Decomposers are organisms that decompose the dead plants and animals to release organic and inorganic nutrients into the environment which are again reused by plants.
Example: Bacteria, Actinomycetes and Fungi.
Question 7.
What is standing crop?
Answer:
The amount of living materials present in a population at any given time is known as standing crop, which may be expressed in terms of number or biomass per unit area.
Question 8.
What do you mean by PAR? Mention its significance.
Answer:
The amount of light available for photosynthesis of plants is called Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) which is between the range of 400-700 mm wave length.
![]()
Question 9.
Pointout the factors that affects the photosynthetically active radiation.
Answer:
PAR is not always constant because of clouds, tree shades, air, dust particles, seasons, latitudes and length of the daylight availability.
Question 10.
Define Grey carbon and Black carbon.
Answer:
Grey carbon – carbon stored in fossil fuel (coal, oil and biogas deposits in the lithosphere). Black carbon – carbon emitted from gas, diesel engine and coal fired power plants.
Question 11.
What is meant by productivity of an ecosystem?
Answer:
The rate of biomass production per unit area in a unit time is called productivity. It can be expressed in terms of gm /m2/year or Kcal/m2/ year.
Question 12.
How Net Primary Productivity can be derived?
Answer:
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) is derived by the difference between Gross primary productivity (GPP) and respiration.
NPP = GPP – Respiration
Question 13.
Expand GPP and define it.
Answer:
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) is the total amount of food energy or organic matter or biomass produced in an ecosystem by autotrophs through the process of photosynthesis is called gross primary productivity.
Question 14.
Write the name of four important aspects of ecosystem.
Answer:
- Productivity
- Energy flow
- Decomposition
- Nutrient cycling
Question 15.
State the role of herbivores and microconsumers in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Answer:
- Herbivores acts as primary consumers of producers (Plants).
- Microconsumers decomposes the dead remains and excreta of plants and animals.
Question 16.
Name the category of organisms that occupy the first tropic level (T1) and fourth tropic level (T4) in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Producers (autotrophs) occupy the first tropic level (T4) whereas the fourth tropic level (T4) is occupied by Tertiary Consumers (Secondary carnivore).
Question 17.
What is energy flow?
Answer:
The transfer of energy in an ecosystem between trophic levels can be termed as energy flow. It is the key function in an ecosystem. Energy flow is always unidirectional in an ecosystem.
Question 18.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
Answer:
First law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transmitted from one system to another in various forms. Energy cannot be destroyed or created. But it can be transformed from one form to another. As a result, the quantity of energy present in the universe is constant.
Question 19.
State the ten percent law.
Answer:
Ten percent law states that during transfer of food energy from one trophic level to other, only about 10% stored at every level and rest of them (90%) is lost in respiration, decomposition and in the form of heat.
Question 20.
Define food chain.
Answer:
The movement of energy from producers upto top carnivores is known as food chain, i.e., in any food chain, energy flows from producers to primary consumers, then from primary consumers to secondary consumers, and finally secondary consumers to tertiary consumers. Hence, it shows linear network links.
Question 21.
Name the two types of the food chain.
Answer:
- Grazing food chain
- Detritus food chain
Question 22.
Which is the first link in a grazing food chain and a detritus food chain?
Answer:
- The first link of grazing food chain is plants (Producers).
- The first link of detritus food chain is dead remains and excreta of plants and animals.
![]()
Question 23.
Rearrange the components of the ecosystem and frame a food chain. Also mention the type of food chain.
Hawk, Earthworm, Animal excreta and Blackbird.
Answer:
Animal excreta → Earthworm → Blackbird → Hawk. It is a detritus food chain.
Question 24.
Define food web.
Answer:
The interlocking pattern of a number of food chain form a web-like arrangement called food web. It is the basic unit of an ecosystem, to maintain its stability in nature.
Question 25.
What is Eltoian pyramid?
Answer:
Eltonian pyramid or Ecological pyramid is a graphic representation of the trophic structure and function at successive trophic levels of an ecosystem.
Question 26.
Why do we obtain an inverted pyramid in a parasite ecosystem?
Answer:
The pyramid of number in a parasite ecosystem is always inverted, because it starts with a single tree. Therefore there is gradual increase in the number of organisms in successive trophic levels from producer to tertiary consumers.
Question 27.
What is pyramid of biomass?
Answer:
A graphical representation of the amount of organic material (biomass) present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of biomass.
Question 28.
Biogeochemical cycle comprises both gaseous cycle and sedimentary cycle. How they differ from one another?
Answer:
- The components of gaseous cycle are placed in an atmosphere
E.g: Oxygen in air - whereas in sedimentary cycle, the components are present in/on Earth.
E.g: Phosphorous in rocks.
Question 29.
Name the type of ecosystem that exhibits the following types of the pyramid.
- Inverted pyramid of biomass
- Spindle-shaped pyramid of number
Answer:
- Pond ecosystem
- Forest ecosystem.
Question 30.
Cite few examples of biomolecules that contain phosphorus.
Answer:
DNA, RNA, ATP and NADP.
Question 31.
What are Blue carbon ecosystems?
Answer:
Seagrasses and mangroves of Estuarine and coastal ecosystems are the most efficient in carbon sequestration. Hence, these ecosystems are called “Blue carbon ecosystems”.
Question 32.
Mention the four categories of ecosystem services.
Answer:
- Provisioning services
- Cultural services
- Supporting services
- Regulating services
Question 33.
What is meant by Ecosystem resilience?
Answer:
Ecosystem is damaged by disturbances from fire, flood, predation, infection and drought, etc. removing a great amount of biomass. However, the ecosystem is endowed with the ability to resist the damage and recover quickly. This ability of an ecosystem is called ecosystem resilience or ecosystem robustness.
Question 34.
Ecosystem management – comment on the statement.
Answer:
Ecosystem management is a process that integrates ecological, socio-economic and institutional factors into a comprehensive strategy in order to sustain and enhance the quality of the ecosystem to meet current and future needs
Question 35.
Which kind of organisms constitutes the pioneer community and climax community of a Hydrosere succession?
Answer:
Phytoplanktons from the pioneer community and a variety of trees makes the climax community of a Hydrosere
Question 36.
Define plant succession.
Answer:
Successive replacement of one type of plant community by the other of the same area/place is known as plant succession.
Question 37.
Define
- Hydrosere
- Xerosere
Answer:
- Hydrosere: Succession of plants in a freshwater ecosystem.
- Xerosere: Succession of plants in areas with minimal amount of water.
3 – Mark Questions
Question 38.
What is secondary productivity? Explain its types.
Answer:
The amount of energy stored in the tissues of heterotrophs or consumers is called secondary productivity.
- Gross secondary productivity: It is equivalent to the total amount of plant material ingested by the herbivores minus the materials lost as faces.
- Net secondary productivity : Storage of energy or biomass by consumers per unit area per unit time, after respiratory loss is called net secondary productivity.
![]()
Question 39.
List the factors affecting primary productivity.
Answer:
Primary productivity depends upon the plant species of an area, their photosynthetic capacity, availability of nutrients, solar radiation, precipitation, soil type, topographic factors (altitude, latitude and direction), and other environmental factors.
Question 40.
Give an account on the concept of trophic level in an ecosystem.
Answer:
A trophic level refers to the position of an organism in the food chain. The number of trophic levels is equal to the number of steps in the food chain. The green plants (producers) occupying the first trophic level (T1) are called producers. The energy produced by the producers is utilized by the plant eaters (herbivores) they are called primary consumers and occupy the second trophic level (T2).
Herbivores are eaten by carnivores, which occupy the third trophic level (T3). They are also called secondary consumers or primary carnivores. Carnivores are eaten by the other carnivores, which occupy the fourth trophic level (T4). They are called tertiary consumers or secondary carnivores. Some organisms which eat both plants and animals are called as omnivores (Crow). Such organisms may occupy more than one trophic level in the food chain.
Question 41.
State the second law of thermodynamics.
Answer:
Second law of thermodynamics states that energy transformation results in the reduction of the free energy of the system. Usually, energy transformation cannot be 100% efficient. As energy is transferred from one organism to another in the form of food, a portion of it is stored as energy in living tissue, whereas a large part of the energy is dissipated as heat through respiration. The transfer of energy is irreversible natural process.
Question 42.
Explain the Grazing food chain with an example.
Answer:
Main source of energy for the grazing food chain is the Sun. It begins with the first link, producers (plants). The second link in the food chain is primary consumers (mouse) which get their food from producers. The third link in the food chain is secondary consumers (snake) which get their food from primary consumers. Fourth link in the food chain is tertiary consumers (eagle) which get their food from secondary consumers.
Grass → Mouse → Snake → Eagle
Producers Primary consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary consumers
Question 43.
Write a brief note on Detritus food chain.
Answer:
Detritus food chain is a type of food chain which begins with dead organic matter which is an important source of energy. A large amount of organic matter is derived from the dead plants, animals and their excreta. This type of food chain is present in all ecosystems. The transfer of energy from the dead organic matter, is transferred through a series of organisms called detritus consumers (detritivores)- small carnivores – large (top) carnivores with repeated eating and being eaten respectively. This is called the detritus food chain.
Fallen leaves → Earthworm → Blackbird → Hawk
Detritus Detritivores Small carnivores Top carnivores
Question 44.
Enumerate the significance of food webs.
Answer:
Significance of food web
- Food web is constructed to describe species interaction called direct interaction.
- It can be used to illustrate indirect interactions among different species.
- It can be used to study bottom-up or top-down control of community structure.
- It can be used to reveal different patterns of energy transfer in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Question 45.
Name the three types of ecological pyramids.
Answer:
- pyramid of number
- pyramid of biomass
- pyramid of energy.
Question 46.
Spindle shaped pyramid of number is noticed in forest ecosystem. Give reasons.
Answer:
In a forest ecosystem the pyramid of number is spindle in shape, it is because the base (T1) of the pyramid occupies large sized trees (Producer) which are lesser in number. Herbivores (T2) (Fruit eating birds, elephant and deer) occupying second trophic level, are more in number than the producers. In final trophic level (T4), tertiary consumers (lion) are lesser in number than the secondary consumer (T3) (fox and snake).
![]()
Question 47.
Pyramid of energy is always upright – Justify.
Answer:
A graphical representation of energy flow at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramids of energy. The bottom of the pyramid of energy is occupied by the producers. There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to the upper levels. Therefore, the pyramid of energy is always upright.
Question 48.
What does the term ‘Eluviation’ stands for?
Answer:
The movement of decomposed, water soluble organic and inorganic compounds from the surface to the lower layer of soil or the carrying away of the same by water is called leaching or eluviation.
Question 49.
What is biogeochemical cycle? Explain its types.
Answer:
Circulation of nutrients within the ecosystem or biosphere is known as biogeochemical cycles and also called as cycling of materials.
There are two basic types:
- Gaseous cycle – It includes atmospheric Oxygen, Carbon and Nitrogen cycles.
- Sedimentary cycle – It includes the cycles of Phosphorus, Sulphur and Calcium – Which are present as sediments of Earth.
Question 50.
Explain the cycling of phosphorus in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Phosphorus cycle is a type of sedimentary cycle in which phosphorus is found in the biomolecules like DNA, RNA, ATP, NADP and phospholipid molecules of living organisms. Phosphorus is not abundant in the biosphere, whereas a bulk quantity of phosphorus is present in rock deposits, marine sediments and guano. It is released from these deposits by weathering process.
After that, it circulates in lithosphere as well as hydrosphere. The producers absorb phosphorus in the form of phosphate ions, and then it is transferred to each trophic level of food chain through food. Again death of the organisms and degradation by the action of decomposers, the phosphorus is released back into the lithosphere and hydrosphere to maintain phosphorus cycle.
Question 51.
Discuss the three zones of a lentic ecosystem.
Answer:
There are three zones, littoral, limnetic and profundal. The littoral zone, which is closest to the shore with shallow water region, allows easy penetration of light. It is warm and occupied by rooted plant species. The limnetic zone refers the open water of the pond with an effective penetration of light and domination of planktons.
The deeper region of a pond below the limnetic zone is called profundal zone with no effective light penetration and predominance of heterotrophs. The bottom zone of a pond is termed benthic and is occupied by a community of organisms called benthos (usually decomposers).
Question 52.
What is ecosystem services? Why it is of much importance?
Answer:
Ecosystem services are defined as the benefits that people derive from nature. Study on ecosystem services acts as an effective tool for gaining knowledge on ecosystem benefits and their sustained use. Without such knowledge gain, the fate of any ecosystem will be at stake and the benefits they provide to us in future will become bleak.
Question 53.
Point out any three mangrove ecosystem services.
Answer:
- Act as a bridge between sea and rivers by balancing sedimentation and soil erosion.
- Help to reduce water force during cyclones, tsunamis, and high tide periods.
- Help in the windbreak, O2 production, carbon sequestration and prevents salt spray from waves.
Question 54.
What are the human activities that disturb an ecosystem?
Answer:
- Habitat destruction.
- Deforestation and overgrazing.
- Erosion of soils.
- Introduction of non-native species.
- Overharvesting of plant material.
- Pollution of land, water and air.
- Rim off pesticides, fertilizers and animal wastes.
Question 55.
What is primary succession?
Answer:
The development of plant community in a barren area where no community existed before is called primary succession. The plants which colonize first in a barren area are called pioneer species or primary community or primary colonies. Generally, Primary succession takes a very long time for the occurrence in any region.
Example: Microbes, Lichen and Mosses.
![]()
5 – Mark Questions
Question 56.
Describe the various stages of decomposition process.
Answer:
- Fragmentation – The breaking down of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores like bacteria, fungi and earth worm is known as fragmentation. These detritivores secrete certain substances to enhance the fragmentation process and increase the surface area of detritus particles.
- Catabolism – The decomposers produce some extracellular enzymes in their surroundings to break down complex organic and inorganic compounds in to simpler ones. This is called catabolism
- Leaching or Eluviation – The movement of decomposed, water-soluble organic and inorganic compounds from the surface to the lower layer of soil or the carrying away of the same by water is called leaching or eluviation.
- Humification – It is a process by which simplified detritus is changed into dark coloured amorphous substance called humus. It is highly resistant to microbial action, therefore
decomposition is very slow. It is the reservoir of nutrients. - Mineralisation – Some microbes are involved in the release of inorganic nutrients from the humus of the soil, such process is called mineralisation.
Question 57.
Give a detailed account of Biotic and abiotic components of a pond ecosystem. Abiotic components
Answer:
A pond ecosystem consists of dissolved inorganic (CO2, O2, Ca, N and Phosphate) and organic substances (amino acids and humic acid) formed from the dead organic matter. The function of pond ecosystem is regulated by few factors like the amount of light, temperature, pH value of water and other climatic conditions.
Biotic components:
They constitute the producers, variety of consumers and decomposers (microorganisms).
(a) Producers: A variety of phytoplanktons like Oscillatoria, Anabaena, Eudorina, Volvox and Diatoms. Filamentous algae such as Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Cladophora and Oedogonium; floating plants Azolla, Salvia, Pistia, Wolffia and Eichhornia; sub-merged plants Potamogeton and Phragmitis; rooted floating plants Nymphaea and Nelumbo; macrophytes like Typha and Ipomoea, constitute the major producers of a pond ecosystem.
(b) Consumers: The animals represent the consumers of a pond ecosystem include zooplanktons like Paramoecium and Daphnia (primary consumers); benthos (bottom living animals) like molluscs and annelids; secondary consumers like water beetles and frogs; and tertiary consumers (carnivores) like duck, crane and some top carnivores which include large fish, hawk and man, etc.
(c) Decomposers: They are also called as microconsumers. They help to recycle the nutrients in the ecosystem. These are present in mud water and bottom of the ponds. Example: Bacteria and Fungi. Decomposers perform the process of decomposition in order to enrich the nutrients in the pond ecosystem.
Question 58.
What are the strategies of eco system management?
Answer:
Strategy of ecosystem management
- It is used to maintain biodiversity of ecosystems.
- It helps in indicating the damaged ecosystem (Some species indicate the health of the ecosystem: such species are called a flagship species).
- It is used to recognize the inevitability of ecosystem change and plan accordingly.
- It is one of the tools used for achieving sustainability of ecosystem through sustainable development programme (or projects).
- It is also helpful in identifying ecosystems which are in need of rehabilitation.
- It involves collaborative management with government agencies, local population, communities and NGO’s.
- It is used to build the capacity of local institutions and community groups to assume responsibility for long term implementation of ecosystem management activities even after, the completion of the project.
Question 59.
List the characteristics of ecological succession.
Answer:
- It is a systematic process which causes changes in specific structure of plant community.
- It is resultant of changes of abiotic and biotic factors.
- It transforms unstable community into a stable community.
- Gradual progression in species diversity, total biomass, niche specialisation, and humus content of soil takes place.
- It progresses from simple food chain to complex food web.
- It modifies the lower and simple life form to the higher life forms.
- It creates inter-dependence of plants and animals.
![]()
Question 60.
Differentiate Primary succession and Secondary succession
Answer:
Primary succession:
- Developing in an barren area.
- Initiated due to a biological or any other external factors.
- No soil, while primary succession starts
- Pioneer species come from outside environment.
- It takes more time to complete.
Secondary succession:
- Developing in disturbed area.
- Starts due to external factors only.
- It starts where soil covers is already present.
- Pioneer species develop from existing environment.
- It takes comparatively less time to complete.
Question 61.
Write in detail about Autogenic succession and Allogenic succession.
Answer:
Autogenic succession
Autogenic succession occurs as a result of biotic factors. The vegetation reacts with its environment and modifies its own environment causing its own replacement by new communities. This is known as autogenic succession.
Example: In forest ecosystem, the larger trees produce broader leaves providing shade to the forest floor area. It affects the shrubs and herbs which require more light (heliophytes) but supports the shade tolerant species (sciophytes) to grow well.
Allogenic succession:
Allogenic succession occurs as a result of abiotic factors. The replacement of existing community is caused by other external factors (soil erosion and leaching, etc) and not by existing organisms.
Example: In a forest ecosystem soil erosion and leaching alter the nutrient value of the soil leading to the change of vegetation in that area.
Question 62.
What are the significance of plant succession?
Significance of Plant Succession
Answer:
- Succession is a dynamic process. Hence an ecologist can access and study the serai stages of a plant community found in a particular area.
- The knowledge of ecological, succession helps to understand the controlled growth of one or more species in a forest.
- Utilizing the knowledge of succession, even dams can be protected by preventing siltation.
- It gives information about the techniques to be used during reforestation and afforestation.
- It helps in the maintenance of pastures.
- Plant succession helps to maintain species diversity in an ecosystem.
- Patterns of diversity during succession are influenced by resource availability and disturbance by various factors.
- Primary succession involves the colonization of habitat of an area devoid of life.
- Secondary succession involves the re-establishment of a plant community in disturbed area or habitat.
- Forests and vegetation that we come across all over the world are the result of plant succession.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Nutrients are retained in the ecosystem. Discuss how and name the process through which it is achieved?
Answer:
Nutrients will retain in the ecosystem through biogeo chemical cycles. Various nutrients present in soil and atmosphere enter the organism at various trophic levels through food and other process and are cycled back to their origin. Thus the nutrients are not lost but retained in the ecosystem.
Question 2.
According to ten percent law, how many Joules of energy does the individuals at the fourth tropic level will receive; if the individuals at first trophic level receives 1000 Joules of energy?
Answer:
Organism at T4 level will receive 0.1 Joule of energy as per ten percent law.
![]()
Question 3.
Frame any two food chain patterns from the given organisms. Each chain must contain a minimum of four organisms.
Diatoms, Hawk, Rabbit, Vallisneria Stoke, guppies, grass, snake, large fishes, grasshopper, crane.
Answer:
- Diatom → Guppies → Large fishes → Crane
- Grass → Rabbit → Snake → Hawk
Question 4.
Mention any two vital biomolecules that requires phosphorous for their biosynthesis.
Answer:
DNA and ATP
Question 5.
The below diagramatic sketch shows the stratisfication of pond ecosystem. Considering it, name X and Y.
Answer:
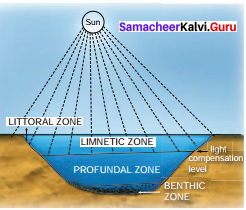
Diagrammatic sketch shows strarification of Pond ecosystem
X – Limnetic Zone
Y – Benthic Zone