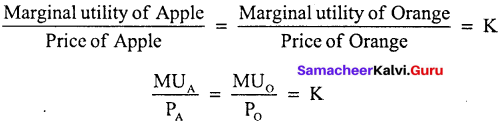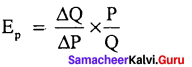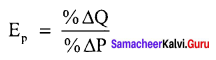Students can Download Economics Chapter 2 Consumption Analysis Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 2 Consumption Analysis
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Consumption Analysis Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Pick the odd one out
(a) Luxuries
(b) Comforts
(c) Necessaries
(d) Agricultural
Answer:
(d) Agricultural
Question 2.
Choice is always constrained or limited by the …………………… of our resources.
(a) Scarcity
(b) Supply
(c) Demand
(d) Abundance
Answer:
(a) Scarcity

Question 3.
The chief exponent of the Cardinal utility approach was
(a) J.R.Hicks
(b) R.G.D.Allen
(c) Marshall
(d) Stigler
Answer:
(c) Marshall
Question 4.
Marginal Utility is measured by using the formula of ……………………..
(a) TUn – TUn-1
(b) TUn – TUn+1
(c) TUn + TUn+1
(d) TUn – TUn+1
Answer:
(a) TUn – TUn-1
Question 5.
When marginal utility reaches zero, the total utility will be
(a) Minimum
(b) Maximum
(c) Zero
(d) Negative
Answer:
(b) Maximum
Question 6.
Gossen’s first law is known as ……………………..
(a) Law of equi-marginal utility
(b) Law of diminishing marginal utility
(c) Law of demand
(d) Law of Diminishing returns.
Answer:
(b) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Question 7.
The basis for the law of demand is related to
(a) Law of diminishing marginal utility
(b) Law of supply
(c) Law of Equi-marginal utility.
(d) Gossen’s Law.
Answer:
(a) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Question 8.
The concept of consumer’s surplus is associated with ……………………….
(a) Adam smith
(b) Marshall
(c) Robbins
(d) Ricardo
Answer:
(b) Marshall
Question 9.
Given the potential price is Rs.250 and the actual price is Rs.200. Find the consumer surplus,
(a) 375
(b) 175
(c) 200
(d) 50
Answer:
(d) 50
Question 10.
Indifference curve approach is based on ………………………..
(a) Ordinal approach
(b) Cardinal approach
(c) Subjective approach
(d) Psychological approach
Answer:
(a) Ordinal approach
Question 11.
The concept of elasticity of demand was introduced by
(a) Ferguson
(b) Keynes
(c) Adam Smith
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(d) Marshall
Question 12.
Increase in demand is caused by ……………………..
(a) Increase in tax
(b) Higher subsidy
(c) Increase in interest rate
(d) decline in population
Answer:
(b) Higher subsidy
Question 13.
The movement on or along the given demand curve is known as _______.
(a) Extension and contraction of demand.
(b) Shifts in the demand,
(c) Increase and decrease in demand.
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Extension and contraction of demand.

Question 14.
In case of relatively more elastic demand, the shape of the curve is ……………………..
(a) Horizontal
(b) Vertical
(c) Steeper
(d) Flatter
Answer:
(d) Flatter
Question 15.
A consumer is in equilibrium when marginal utilities from two goods are
(a) Minimum
(b) Inverse
(c) Equal
(d) Increasing
Answer:
(c) Equal
Question 16.
Indifference curve was first introduced by ………………………..
(a) Hicks
(b) Allen
(c) Keynes
(d) Edgeworth
Answer:
(d) Edgeworth
Question 17.
The elasticity of demand is equal to one indicates
(a) Unitary Elastic Demand
(b) Perfectly Elastic Demand
(c) Perfectly Inelastic Demand
(d) Relatively Elastic Demand
Answer:
(a) Unitary Elastic Demand
Question 18.
The locus of the points which gives the same level of satisfaction is associated with ……………………….
(a) Indifference Curves
(b) Cardinal Analysis
(c) Law of Demand
(d) Law of Supply
Answer:
(a) Indifference Curves
Question 19.
Ordinal Utility can be measured by
(a) Ranking
(b) Numbering
(c) Wording
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Ranking
Question 20.
The indifference curve are ………………………..
(a) Vertical
(b) Horizontal
(c) Positive sloped
(d) Negatively sloped
Answer:
(d) Negatively sloped
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
Define Utility.
Answer:
- The utility is the capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants.
- The utility cannot be cardinally measured but can be ranked or compared or ordered by an ordinal number such as I, II, III, and so on.
Question 22.
Mention the classifications of wants.
Answer:
(a) Necessaries
(b) Comforts
(c) Luxuries.
Question 23.
Name the basic approaches to consumer behavior.
Answer:
The Basic Approaches to Consumer Behaviour:
- Cardinal Utility Analysis
- Ordinal Utility Analysis
Question 24.
What are the degrees of price elasticity of Demand?
Answer:
The Degrees of Price Elasticity of Demand:
- Perfectly Elastic Demand (Ep = α)
- Perfectly Inelastic Demand (Ep = 0)
- Relatively Elastic Demand (Ep >1)
- Relatively Inelastic Demand (Ep < 1)
- Unitary Elastic Demand (Ep =1).
Question 25.
State the meaning of indifference curves?
Answer:
Indifference curves mean all those combinations of any two goods which give equal satisfaction to the consumer.
Question 26.
Write the formula of consumer surplus.
Answer:
Consumer’s surplus = Potential price – Actual price.
Consumer’s surplus = TU-(P × Q)
TU – Total Utility,
P – Price,
Q – Quantity.

Question 27.
What are Giffen goods? Why it is called that?
Answer:
The Giffen goods are inferior goods which are an exception to the law of demand. When the price of an inferior good falls, the poor will buy less and vice versa.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 28.
Describe the feature of human wants.
Answer:
The Feature of Human:
- Wants are unlimited
- Wants become habits
- Wants are satiable
- Wants are alternative
- Wants are competitive
- Wants are complementary
- Wants are recurring.
Question 29.
Mention the relationship between marginal utility and total utility.
Answer:
Total Utility:
- If Total utility increases
- If Total utility reaches maximum.
- If Total utility diminishes
Marginal Utility:
- Marginal utility declines
- Marginal utility reaches zero
- Marginal utility becomes negative
MUn = TUn – TUn-1.
Question 30.
Explain the concept of consumer’s equilibrium with a diagram.
Answer:
Consumer surplus is the difference between the potential price and the actual price. Consumer’s surplus = Potential price – Actual price.
(or)
Consumer’s surplus = TU – (P × Q)
TU – Total Utility, P – Price, Q – Quantity
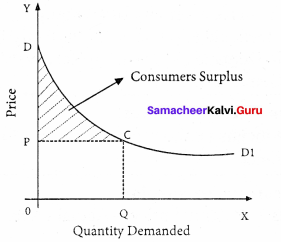
In the diagram, X-axis shows the amount demanded and Y-axis represents the price. DD shows the consumer’s utility from the purchase of different amounts of a commodity.
Hence Actual price of OPCQ
Potential price ODCQ
Consumer’ surplus = ODCQ – OPCQ = PCD.
Question 31.
Explain the theory of “ Consumer’s Surplus ”?
Answer:
The concept of consumer’s surplus is based on the law of diminishing marginal utility. Alfred Marshall defines consumer’s surplus as “The excess of price which a person would be willing to pay rather than go without the thing, over that which he actually does pay is the economic measure of this surplus satisfaction. This may be called a consumer’s surplus.
Question 32.
Distinguish between extension and contraction of demand.
Answer:
If the changes in the quantity demanded is due to the change in price alone then it is called extension and contraction of demand. Buying more at a lower price is an extension of demand and less at a higher price is the contraction of demand.
Question 33.
What are the properties of indifference curves?
Answer:
- The indifference curve must have a negative slope.
- Indifference curves are convex to the origin.
- The indifference curve cannot intersect.
- Indifference curves do not touch the horizontal or vertical axis.
Question 34.
Briefly explain the concept of consumer’s equilibrium.
Answer:
The consumer reaches equilibrium at the point where the budget line is tangent on the indifference curve.
T is the point of equilibrium as budget line AB is tangent on indifference curve IC3 the upper IC which implies a maximum possible level of satisfaction.
At equilibrium point, the slope of IC refers to MRSxy and the slope of BL (Budget Line) refers to the ratio of the price of X to the price of Y i.e. Px / Py. Therefore MRSx,y = Px / Py.

Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 35.
Explain the law of demand and its exceptions.
Answer:
The law of demand was first stated by Augustin Cournot in 1838. Later it was refined and elaborated by Alfred Marshall.
Definition:
The law of demand says as “The quantity demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price” -Marshall.
Assumptions of the law:
- The income, taste, habit, and preference of the consumer remain the same.
- No change in the prices of related goods.
- No substitutes for the commodity.
- The demand for the commodity must be continuous.
- No change in the quality of the commodity.
If there is change even in one of these assumptions, the law will not operate.
Demand schedule:
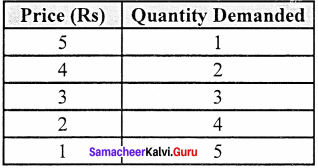
From the above schedule if the price of the good is 5 then the quantity demanded is 1 unit and if the price decrease to 1 quantity demanded raises to 5 which shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Diagram:
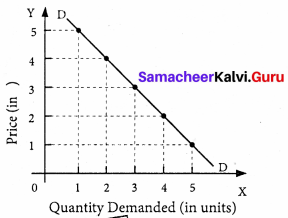
In the above diagram, X-axis represents the quantity demanded and Y-axis represents the price. DD is the demand curve which has a negative slope. It indicates that when the price falls, the demand expands and when price rises, the demand contracts.
Market demand for a commodity:
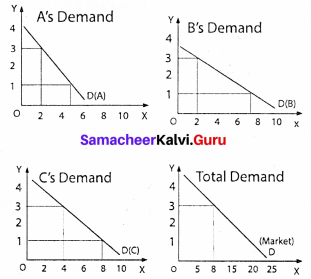
The market demand curve for a commodity is derived by adding the quantum demanded of the commodity by all the individuals in the market.
Exceptions to the law of demand:
- There are some unusual demand curves which slope upwards from left to right. It is known as the exceptional demand curve.
- In the case of an exceptional demand curve, a fall in price brings about contraction and a rise in price brings about an extension of demand.
Reasons for exceptional demand curve:
- Giffen paradox
- Veblen or demonstration
- Ignorance
- Speculative effect
- Fear of shortage

Question 36.
Elucidate the law of diminishing marginal utility with a diagram.
Answer:
H.H. Gosen, an Austrian Economist first formulated this law in 1854. Hence Jevons called this law “Gossen’s first law of consumption”. Marshall perfected this law on the basis of cardinal analysis and it is based on the characteristics of human wants, its wants are satiable.
Definition:
Marshall states that “The additional benefit which a person derives from a given increase of his stock of a thing diminishes with every increase in the stock that he already has”
Assumptions:
- The utility can be measured cardinally.
- The marginal utility of money remains constant.
- The consumer is a rational economic man.
- The units of the commodity consumed must be reasonable in size.
- The commodity consumed should be homogenous in all aspects.
- Consumption takes place continuously at a given period of time.
- No change in the taste, habits, preferences, fashions, income, and character of the consumer during the process of consumption.
Explanation:
The law states that if a consumer continues to consume more or more units of the same commodity, its marginal utility diminishes.
Illustration:
This law can be explained with a simple illustration. Suppose a consumer wants to consume apples one after another the utility from the first apple is 20. But the utility from the second apple will be less than the first (say 15), the third less than the second (say 10), and so on. Finally, the utility from the fifth apple becomes zero.
The utilities from the sixth and seventh apples are negative. This tendency is called “The . law of diminishing marginal utility’”.
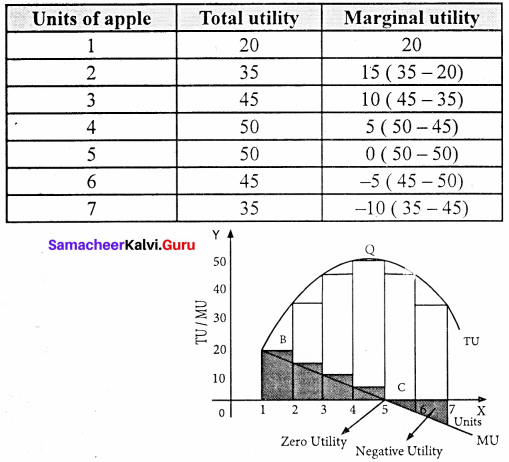
From the above table and diagram. We find that the total utility goes on increasing but at a diminishing rate. Whereas marginal utility goes on diminishing. When marginal utility becomes zero, the total utility is maximum, when marginal utility becomes negative, the total utility diminishes.
Criticisms:
- As utility is subjective, it cannot be measured numerically.
- This law is based on unrealistic assumptions.
- This law is not applicable to indivisible commodities.
Question 37.
Explain the law of Equi-marginal utility.
Answer:
To satisfy unlimited wants a consumer needs more than one commodity. So, the law of diminishing marginal utility is extended and is called the “Law of Equi-marginal utility”. It is also called the “Law of substitution” “The law of consumer’s equilibrium”, “Gossen second law” and “The law of maximum satisfaction”.
Definition:
Marshall states the law as, “If a person has a thing which he can put to several uses, he will distribute it among these uses in such a way that it has the same marginal utility in all. For if it had a greater marginal utility in one use than another he would gain by taking away some of it from the second use and applying it to first”.
Assumptions:
- The rational consumer wants to maximize his satisfaction.
- The utility is measurable cardinally.
- The marginal utility of money remains constant.
- The income of the consumer is given.
- There is perfect competition in the market.
- The prices of the commodities are given.
- The law of diminishing marginal utility operates.
Explanation:
The law can be explained with the help of an example. Suppose a consumer wants to spend his limited income on Apple and Orange. He is said to be in equilibrium, only when he gets maximum satisfaction with his limited income. Therefore, he will be in equilibrium, when
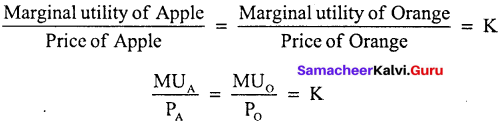
K – Constant marginal unity of money
Table:
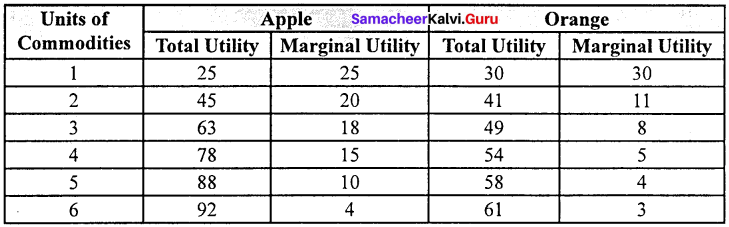
Let us assume that the consumer wants to spend his entire income (Rs.11) on Apple add Orange. The price of an Apple and Orange is Rs. 1 each.
If the consumer wants to attain maximum utility he should buy 6 units of Apples and 5 units of Oranges so that he can get 150 units.
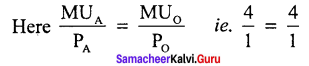
Diagram:
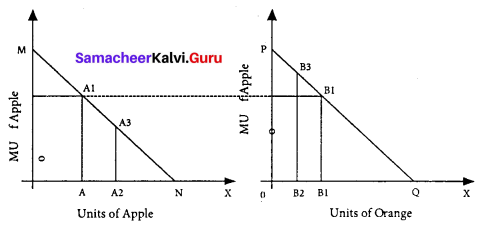
In the diagram, X-axis represents the amount of money spent and the Y-axis marginal utilities of Apple and Orange. If the consumer spends Rs. 6 on Apple and Rs. 5 on Orange, the marginal utilities of both are equal (ie) AA, = BB, Hence he gets maximum utility.

Question 38.
What are the methods of measuring the Elasticity of demand?
Answer:
There are three methods of measuring the elasticity of demand.
1. The percentage method:
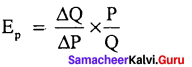
It is also known as the ratio method when we measure the ratio as
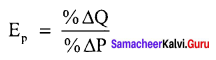
% ∆Q = perCentage change in demand, %∆P = Percentage change in price.
2. Total outlay method:
Marshall suggested that the simplest way to decide whether demand is elastic or inelastic is to examine the change in the total outlay of the consumer or total revenue of the firm.
Total revenue = Price × Quantity sold
TR = P × Q
Total outlay method:
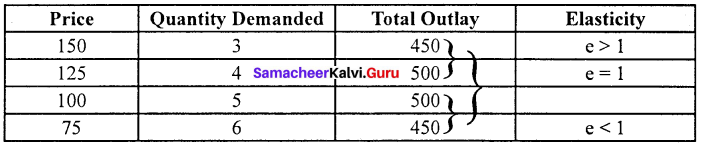
Demand is elastic, if there is an inverse relation between price and total outlay and direct relation means inelastic. Elasticity is unity when the total outlay is constant.
Question 3.
Point or geometrical elasticity:
Answer:
The point elasticity of a linear demand curve is shown by the ratio of the segments of the line to the right and to the left of the particular point.
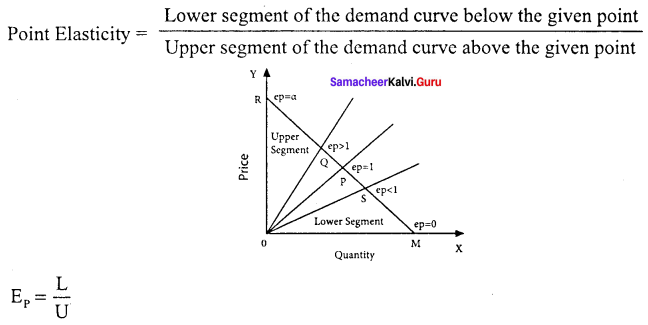
EP – Point Elasticity, L – Lower Segment, U – Upper Segment.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Consumption Analysis Additional Questions and Answers
Part – A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
The utility cannot be measured, because the utility is ………………………. concept.
(a) Social
(b) Subjective
(c) Political
(d) Scientific
Answer:
(b) Subjective

Question 2.
_________ law is helpful in attaining social justice.
(a) Law of Equi-marginal utility
(b) Law of demand
(c) Law of diminishing marginal utility
(d) Law of marginal utility
Answer:
(c) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Question 3.
Consumer surplus is …………………….
(a) Potential price – Actual price
(b) MV = TV – TV
(c) Demand = Supply
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Potential price – Actual price
Question 4.
Income elasticity of demand is the degree of responsiveness of change in demand to
(a) Change is price
(b) Elasticity of demand
(c) Change in substitutes
(d) Change in income
Answer:
(d) Change in income
Question 5.
Marshallian utility approach is …………………….. analysis.
(a) Subjective
(b) Psychological
(c) Ordinal
(d) Cardinal
Answer:
(d) Cardinal
Question 6.
_________ is the major determinant of demand.
(a) Consumption
(b) Price
(c) Supply
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Price
Question 7.
Principle of Economics” was defined by ………………….
(a) Marshall
(b) Hicks
(c) Allen
(d) Keynes
Answer:
(a) Marshall
Question 8.
The formula for point method
(a) Upper segment / Lower segment
(b) Middle segment / Upper segment
(c) Lower segment / Upper segment
(d) Upper segment / Left segment
Answer:
(c) Lower segment / Upper segment

Question 9.
What is the other name of the budget line?
(a) Price ratio line
(b) Quantity ratio line
(c) Equilibrium ratio line
(d) Compulsory ratio line
Answer:
(a) Price ratio line
Question 10.
_________ is the basis of all the laws of consumption.
(a) Law of demand
(b) Law of consumerism
(c) Law of elasticity
(d) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Answer:
(d) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Question 11.
Give the consumer’s surplus is 75 and the actual price 372, Find the potential price
(a) 447
(b) 50
(c) 375
(d) 474
Answer:
(a) 447
Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(a) Consumption is the beginning of economic science
(b) Production is the beginning of economic science
(c) Distribution is the beginning of economic science
(d) Exchange is the beginning of economic science
Answer:
(a) Consumption is the beginning of economic science
Question 2.
(a) The law of diminishing marginal utility is called Gresham’s law.
(b) The law Equi marginal utility is called Marshall’s law.
(c) The law of diminishing marginal utility is called Gossen’s first law of consumption.
(d) The law of demand is called Gossen’s second law of consumption.
Answer:
(c) The law of diminishing marginal utility is called Gossen’s first law of consumption.
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
Question 3.
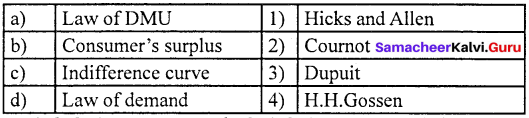
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 3 4 2 1
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 4 3 2 1
Answer:
(b) 3 4 2 1
Question 4.
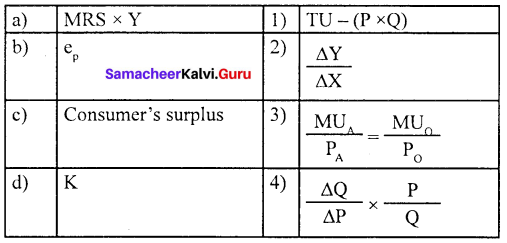
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 3 1 4 2
Answer:
(d) 3 1 4 2
Choose the odd one out
Question 5.
(a) Giffen paradox
(b) Demonstration effect
(c) Speculative effect
(d) Edge worth approach
Answer:
(d) Edge worth approach
Question 6.
(a) F.W. Edge worth
(b) Alfred Marshall
(c) Vilfredo Pareto
(d) J.R. Hicks and R.G.D. Allen
Answer:
(b) Alfred Marshall

Question 7.
(a) Percentage method
(b) Point method
(c) Total outlay method
(d) Income elasticity method
Answer:
(d) Income elasticity method
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 8.
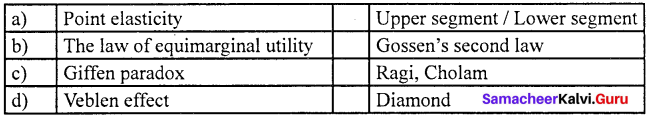
Answer:
(a) Point (i) Upper segment/Lower segment.
Question 9.

Answer:
(b) Unptary elastic demand (i) ep= 0.
Question 10.
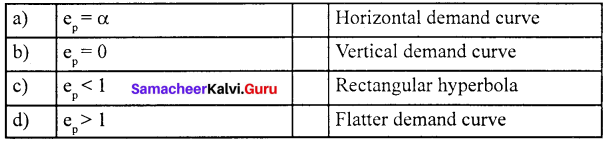
Answer:
(c) ep < 1 (iii) Rectangular hyperbola
Analyze the reason for the following.
Question 11.
Assertion (A): Savings and demand are inversely related.
Reason (R): Increased savings leads to a decrease in consumption.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is true but, (R) is false.
(d) Both (A) and (R) are false.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 12.
Assertion (A): When the price of inferior goods falls, the poor will buy less.
Reason (R): Poor consume less amount of inferior goods.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true
(b) Both (A) and (R) are false
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 13.
(a) The exceptional demand curve slopes upwards,
(b) The good salt is price inelastic
(c) Elasticity is unity when total outlay is constant
(d) Demand is more elastic in the short run than is long run
Answer:
(a) The exceptional demand curve slopes upwards

Question 14.
(a) The law of DMU is based on the characteristics of human wants.
(b) The law of consumer surplus is based on the law of DMU
(c) The indifference curve approach is based on the scale of preference.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 15.
Diamond – water paradox was given by
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Marshall
(c) Robbins
(d) Samuelson
Answer:
(a) Adam Smith
Question 16.
_________ law is helpful in attaining social justice.
(a) Law of demand
(b) Law of diminishing marginal utility
(c) Law of Equi-marginal utility
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Question 17.
_________ is the basis of all the laws of consumption.
(a) Law of demand
(b) Law of consumerism
(c) Law of elasticity
(d) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Answer:
(d) Law of diminishing marginal utility
Choose the best option
Question 18.
_________ is the major determinant of demand.
(a) Consumption
(b) Price
(c) Supply
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Price
Question 19.
If the total utility is maximum then marginal utility is _________
(a) Zero
(b) Negative
(c) Positive
(d) Maximum
Answer:
(a) Zero
Question 20.
Mathematically consumer’s surplus is
(a) TU – TUn-1
(b) TR – (P×Q)
(c) TU – (P×Q)
(d) TC – (Q×P)
Answer:
(c) TU-(P×Q)
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Define “Consumption”?
Answer:
Consumption plays an important role in Economics. “ Consumption is the sole end and object of economic activity” – J.M. Keynes. Consumption is the beginning of economic science. In the absence of consumption, there can be no production; exchange, or distribution. Consumption is also an end of production. Producers produce goods to satisfy the wants of the people.

Question 2.
What is the law of demand?
Answer:
“The quantity demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price” – Marshall.
Question 3.
Write the characteristics of demand?
Answer:
Characteristics of demand:
- Price: Demand is always related to price.
- Time: Demand always means demand per unit of time, per day, per week, per month on per year.
- Market: Demand is always related to the market, buyer, and sellers.
- Amount: Demand is always a specific quantity that a consumer is willing to purchase.
Question 4.
What is marginal utility?
Answer:
Marginal utility is the utility derived from the last or marginal unit of consumption.
Question 5.
What is demand?
Answer:
Demand is the desire backed by the ability to pay and the willingness to buy it.
Question 6.
What is the elasticity of demand?
Answer:
The elasticity of demand is the degree of responsiveness of the quantity demand for a commodity to a change in its price.
Question 7.
What are the determinants of elasticity of demand?
Answer:
- Availability of substitutes
- The proportion of consumer’s income
- Number of uses of the commodity
- Complementarity between goods.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
What is an indifference map?
Answer:
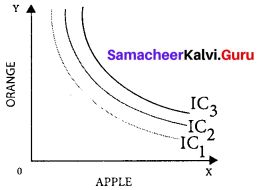
An indifference map is a family or collection or set of indifference curves corresponding to different levels of satisfaction. In the diagram, the indifference curves IC1, IC2, and IC3 represent the indifference map, upper IC representing a higher level of satisfaction compared to lower IC.
Question 2.
Write the importance of the law of diminishing marginal utility?
Answer:
- This law of DMU is one of the fundamental laws of consumption. It has applications in several fields of study.
- The law of DMU is the basis for other consumption laws such as the law of Demand, Elasticity of Demand, Consumer Surplus, and the Law of Substitution, etc.
- The law emphasizes the equitable distribution of wealth. The MU of money to the more -moneyed is low. Hence redistribution of income from rich to poor is justified.

Question 3.
What are the determinants of demand?
Answer:
- Changes in tastes and fashions
- Change in weather
- Taxation and subsidy
- Change in expectations
- Changes in savings
- State of trade activity
- Advertisement
- Change in income
- Change in population.
Question 4.
What is a scale of preference?
Answer:
- A rational consumer usually prefers the combination of goods which gives him a maximum level of satisfaction.
- Thus the consumer can arrange goods and their combination in order of their satisfaction.
- Such an arrangement of a combination of goods in the order of level of satisfaction is called the “Scale of preference”.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()