You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Man and Environment
Man and Environment Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
All external influences and factors that affect the growth and development of living organisms is ………
(a) Environment
(b) Ecosystem
(c) Biotic factors
(d) Abiotic factors.
Answer:
(a) Environment
![]()
Question 2.
The ‘World Population Day’ is observed on every year.
(a) August 11th
(b) September 11th
(c) July 11th
(d) January 11th
Answer:
(c) July 11th
Question 3.
The statistical study of human population is
(a) Demography
(b) Morphology
(c) Etymology
(d) Seismography
Answer:
(a) Demography
Question 4.
The extraction of valuable minerals and other geological minerals from the mines, is …..
(a) Fishing
(b) Lumbering
(c) Mining
(d) Agriculture
Answer:
(c) Mining
Question 5.
The Secondary sector of the economy produces …… from raw materials.
(a) Semi finished goods
(b) Finished goods
(c) Economic goods
(d) raw materials
Answer:
(b) Finished goods
![]()
Question 6.
Gradual increase of the earth’s temperature by the Green house gases in the atmosphere is called …….
(a) Acid rain
(b) thermal pollution
(c) Global warming
(d) Deforestation
Answer:
(c) Global warming
II. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below.
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Ozone layer in the stratosphere is considered as a protective shield.
Reason (R): It prevents the UV radiation from reaching the earth’s surface.
(a) A and R are correct and A explains R
(b) A and R are correct, but A does not explain R
(c) A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) A and R are correct and A explains R
Question 8.
Assertion (A): In tertiary activities, instead of producing goods by themselves, they are in the process of production.
Reason (R): People in Tertiary activities are purely eco friendly.
(a) Both A and R are incorrect
(b) A and R are correct, but A does not explain R
(c) A is correct and R is incorrect.
(d) A and R are correct and A explains R.
Answer:
(c) A is correct and R is incorrect.
III. Match the following:

Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (d)
4. (a)
5. (b)
IV. Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
What do you mean by the term ‘density of population’?
Answer:
- Density of population refers to the number of people living per sq.km.
- Population density = \(\frac { Total population }{ Total land area }\)
![]()
Question 2.
What is ‘black death’?
Answer:
The black death is estimated to have killed 30 – 60 percent of Europe’s total population during the 14th century. The dominant explanation for black death is attributed to the outbreak of plague.
Question 3.
Where do we have high and low densities of population?
Answer:
- Areas of high density (above 50 people per sq.km) – East Asia, South Asia, northwest Europe and Eastern North America.
- Areas of low density (less than 10 people per sq.km) – Central Africa, Western Australia, Northern Russia, Canada, etc.
Question 4.
What is Green House effect?
Answer:
Global warming is caused by the increase of green house gases such as carbondioxide, methane, water vapour and Chloro Fluoro Carbons(CFC), carbon monoxide, photo chemical oxidants and hydrocarbons, which are responsible for the heat retention ability of the atmosphere. Global warming causes climatic change, ozone layer depletion, rise in sea level and drowning of coastal inhabited land, melting of ice, etc., They are posing an even greater threat to human existence and so, man must start thinking of protecting the environment from pollution.
![]()
Question 5.
Write any two ways of how the locals and the government restored Palk Bay. Restoration of Palk Bay
Answer:
Local communities, government and civic organisations all came together not just to conserve the remaining mangroves, but also to restore it.
- Saplings of native species of plants and trees are being grown, planted and cared for.
- Live colonies of coral from the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve are being transplanted to Palk Bay. The existing mangroves and the region are being mapped and the way land is used around the mangrove is being studied.
- The local communities are actively involved in the conservation and restoration of the mangroves. Education and awareness programmes about mangrove ecosystem are being undertaken.
Question 6.
Define
- Population growth
- Census
- Sustainable Development.
Answer:
- Population growth: Population growth refers to an increase in the number of people who reside in a particular area during a particular period.
- Census: It is an official enumeration of population carried out periodically, It records information about the characteristics of population such as age, sex, literacy and occupation.
- Sustainable Development : Sustainable development is a development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their own needs.
V. Distinguish the following:
Question 1.
Birth rate and Death Rate
Answer:
| Birth Rate | Death Rate |
| Number of live births per 1000 people in a year | Number of deaths under one year of age for every 1000 live births in a year |
Question 2.
Emigration and Immigration
Answer:
| Emigration Immigration | Emigration Immigration |
| Emigration means moving out or to leave a place. | Immigration means to enter or come into a new country for the purpose of settling there. |
Question 3.
Rural settlement and urban settlement
Answer:
|
Rural Settlement |
Urban Settlement |
| Any settlement where most of the people are engaged in primary activities like agriculture, forestry, mining and fishery is known as a rural settlement. | Urban is the term related to cities and towns where people are primarily engaged in non-agricultural activities, such as secondary, tertiary and quartemary activities. |
| The most important and unique feature of rural settlements is the vast, open spaces with green, pollution-free environment. | The common characteristic feature of an urban unit is that they are compact, congested and liable to a large number of population. |
Question 4.
Metropolitan and Mega cities
Answer:
| Metropolitan |
Mega cities |
| Cities accommodating population between 10 lakhs and 50 lakhs are metropolitan cities. E.g.: Madurai | Cities with more than 50 lakh population are called Megacities. E.g.: Greater Chennai |
Question 5.
Primary Activities Secondary Activities
Answer:
| Primary Activities | Secondary Activities |
| Primary Activities pertaining to the extraction of raw materials from the earth’s surface. For example food gathering, hunting, lumbering, fishing, cattle rearing, mining and agriculture. | Secondary Activities transform raw materials into finished goods. For example Iron and Steel industries, automobile manufacturing, etc. |
VI. Give reasons for the following:
Question 1.
Reforestation is encouraged throughout the world.
Answer:
- Planting new trees can help to reduce the amount of CO2 in the air.
- Gases like Carbon dioxide and methane are major contributors to the changing climate.
- Reforestation is an effective mitigation strategy to fight global warming.
- Reforestation can help to restore what the erosion has damaged.
![]()
Question 2.
Acid rain destroys the ecosystem.
Answer:
When pollutants combine with water vapour in the presence of sunlight and oxygen, they form dilute sulphuric and nitric acids in the atmosphere. When this mixture precipitates from the atmosphere, it is called acid rain. This would cause lot of damages to life and property. It would affect the health of humans and animals, alter the constituents of water bodies, plants and trees may die as it deteriorates the soil quality and many more damages to nature.
Question 3.
The economy of the quaternary sector is called the knowledge economy.
Answer:
- The quaternary sector of the economy is a way to describe a knowledge-based part of the economy.
- It typically includes knowledge-oriented economic sectors such as information technology, media, research, and development.
- It is based on knowledge and skill.
- It consists of intellectual industries providing information services such as computing and ICT.
Question 4.
Population growth has to be brought under control.
Answer:
Population growth leads to high competition for all available resources. It leads to poor quality of life, education, food supply, low income and so on. The resources of Earth may exhaust one day and would lead to the end of mankind.
![]()
Question 5.
Sustainable development growth has been set to protect the planet.
Answer:
- Sustainable development is the organising principle for meeting human development goals.
- At the same time sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services upon which the economy and society depend.
- In September 2015, the limited Nations General Assembly firmly adopted the “Universal, integrated and transformative” 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, a set of 17 sustainable Development goals (SDGs)
- The goals are to be implemented and achieved in every country from the year 2016 to 2030.
VII. Answer in a paragraph:
Question 1.
Explain the factors affecting the distribution of the population.
Answer:
Population distribution refers to the way in which people are spread out across the earth surface. The world population is not uniformly distributed, owing to the following factors.
(a) Physical factors:
It includes temperature, rainfall, Soil, relief, water, natural vegetation, distribution of minerals and availability of energy resources.
(b) Historical factors:
Regions with historical importance (river valley civilizations, war and constant invasions fall under historical factors responsible for population distribution.
(c) Economic factors:
Educational Institutions, employment opportunities, manufacturing industries, luxurious amenities, trade and commerce and other facilities encourage dense population in an area.
Question 2.
Describe the patterns of rural settlement with neat diagrams.
Answer:
Rectangular pattern:
Rectangular pattern of settlements are found in plain areas or valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angles.
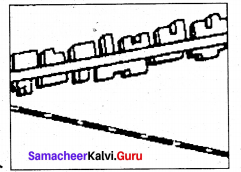
Linear pattern:
In a linear pattern, the houses are located along a road, railway line and along the edge of the river valley or along a levee.
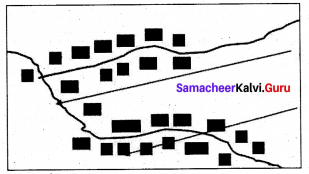
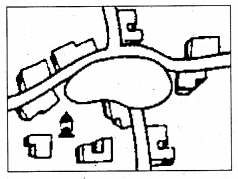
Circular or semicircular pattern:
The pattern of settlement that is found around the lakes, ponds and sea coasts are called circular or semi circular pattern.
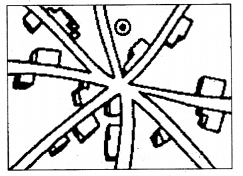
Star-like pattern:
Where several metalled or unmetalled roads converge, star-shaped settlements develop. In the star-shaped settlements, houses are spread out along the sides of roads in all directions.
Triangular pattern:
Triangular patterns of rural settlement generally develop at the confluence of rivers.
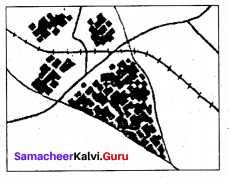
T-Shaped, Y-Shaped, Cross-Shaped or
Cruciform settlements:
T-shaped settlements develop at trijunctions of the roads (T), while Y-shaped settlements emerge as the places where two roads converge with the third one. Cruciform settlements develop on the cross-roads which extend in all four directions.
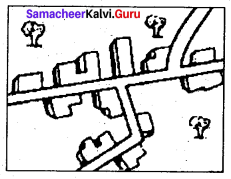
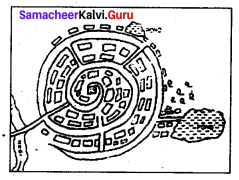
Nebular pattern:
The arrangement of roads is almost circular which ends at the central location or nucleus of the settlement around the house of the main landlord of the village or around a mosque, temple or church.
VIII. HOTS:
Question 1.
Study your area and write down its settlement pattern.
Answer:
- My area is Velachery, Chennai – 42.
- It was developed after late 1990, in the Southern axis radiating out of the city.
- It was built over a complex of low-lying wetlands.
- In an already sunken Velachery, repeated road repairs had led to the roads increasing in height.
- Lifting houses to escape floods.
- Though Velachery is still a low lying area and the rainy season will be bad, it wouldn’t be as bad as before.
- It is a place where we can get all facilities like transport, shopping, restaurants, hair parlours etc., within 1 km
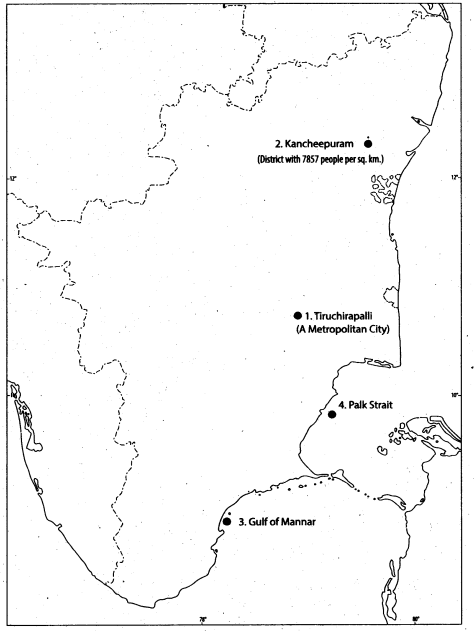
IX. Map skill:
A. On the outline map of the world mark the following.
1. An area of the high density of population in Europe
2. An area of the low density of population in Australia
3. PalkBay
4. A fracking banned country
5. England – A country affected by ‘black death’
6. Denmark – First country where the modem census was conducted «
7. River Hwang Ho
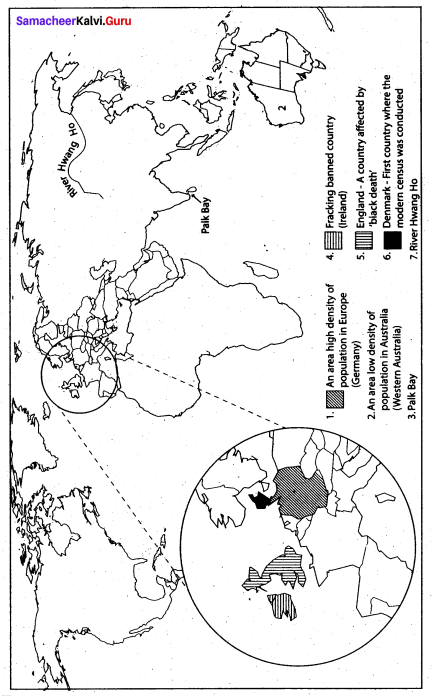
B. On the outline map of Tamil Nadu mark the following.
1. A metropolitan city
2. A district with 7857 people per sq. km.
3. Gulf of Mannar
4. Palk Strait
Man and Environment ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The interaction between man as an individual with his family, occupation and society is ……..
(a) Natural Environment
(b) Human Environment
(c) Man-made Environment
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Human Environment
![]()
Question 2.
The physical factor is ………..
(a) temperature
(b) war
(c) trade
(d) commerce
Answer:
(a) temperature
Question 3.
The economical factor is ……..
(a) rainfall
(b) water
(c) soil
(d) luxurious amenities
Answer:
(d) luxurious amenities
Question 4.
To enter (or) come into a new country for the purpose of settling there is known as ………..
(a) internal migration
(b) emigration
(c) immigration
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) immigration
Question 5.
The rural settlement that is found at the confluence of rivers is ……….
(a) linear pattern
(b) circular pattern
(c) starlike pattern
(d) triangular pattern
Answer:
(d) triangular pattern
![]()
Question 6.
Transforming raw materials into finished goods is an activity.
(a) primary
(b) secondary
(c) tertiary
(d) quinary
Answer:
(b) secondary
![]()
Question 7.
…….. is man-made pollution.
(a) Vehicular emission
(b) Wind erosion
(c) Pollen disposal
(d) Evaporation of organic compounds
Answer:
(a) Vehicular emission
Question 8.
Dry recyclable wastes are ……..
(a) food products
(b) packing plastics
(c) diapers
(d) mobiles
Answer:
(b) packing plastics
Question 9.
Van Mahotsav is a weeklong festival celebrated between ………
(a) 1st and 7th July
(b) 1st and 7th June
(c) 1st and 7th August
(d) 1st and 7th September
Answer:
(a) 1st and 7th July
Question 10.
…… disease is caused by water pollution.
(a) Hypertension
(b) Mental illness
(c) Stress
(d) Diarrhoea
Answer:
(d) Diarrhoea
II. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below:
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Noise pollution is basically a problem in urban areas, industrial areas, transport areas due to bombardment, traffic, etc.
Reason (R): It has an impact on the habitat of animals migration and health of inhabitants.
(a) A and R are correct and A explains R
(b) A and R are correct and A does not explain R
(c) A is incorrect and R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) A and R are correct and A explains R
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Things used for domestic purposes can be reused and recycled.
Reason (R): Organic waste matter should be disposed of far away from settlements.
(a) Both A and R are incorrect
(b) Both A and R are correct
(c) A is correct and R is wrong
(d) A and R are correct and A explains R
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct
III. Match the following:

Answers:
1. (e)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (c)
5. (d)
IV. Fill in the blanks.
1. …….. is the statistical study of the human population.
2. ……. is an official enumeration of the population carried out periodically.
3. …… is a condition when a country has more people than its resources to sustain.
4. Cities with more than 50 lakh population are called ……..
5. ……… Activities pertaining to the extraction of raw materials from the earth’s surface.
6. …….. is a poisonous gas made up of molecules consisting three oxygen atoms.
7. ……. refers to the process of increase in urban population and urban areas in a country.
8. Economic sustainability is successfully implemented through strong ………
Answers:
1. Demography
2. Census
3. Overpopulation
4. megacities
5. Primary
6. Ozone
7. Urbanisation
8. Public Distribution System
V. Answer the following in brief.
Question 1.
Define Environment.
Answer:
The environment is a set of relationships between man and nature. Man has survived through the ages, dwelling within his surrounding called the environment.
Question 2.
Write a short note on “Human Environment”.
Answer:
Human environment is defined as the interaction between man as an individual, with his family, occupation, and society. It is also related to various cultural aspects such as education, religion, economics and politics.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Demography?
Answer:
In ancient Greek, ‘demos’ means people and ‘graphis’ means study Of measurement: So, ‘Demography’is the statistical study of human population.
Question 4.
What does population distribution refer to?
Answer:
Population distribution refers to the way in which people are spread out across the earth’s surface.
Question 5.
What do you mean by Nebular pattern of road arrangement?
Answer:
The arrangement of roads is almost circular which ends at the central location or nucleus of the settlement around the house of the main landlord of the village or around a mosque, temple or church.
Question 6.
Mention the patterns of Rural Settlement.
Answer:
- Rectangular pattern
- Linear pattern
- Circular or semicircular pattern
- Star-like pattern
- Triangular pattern
- T-Shaped, Y-Shaped, Cross-Shaped or Cruciform settlements
- Nebular pattern
Question 7.
What are the control measures for Noise pollution?
Answer:
The control measures of noise pollution are:
- Development of green belt vegetation.
- Installation of decibel meters along highways and in places of public gatherings.
- Planting trees along the compound wall to protect houses.
Question 8.
State the problems of urbanisation.
Answer:
As the town expands, it mounts more pressure on the transport system, water supplies, sewage, and profuse disposal. The overall development creates problems like air pollution, water pollution, traffic congestion and noise pollution, etc., This disturbed environment affects human beings as mental illness, heart troubles, breathing problems, etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Classify wastes.
Answer:
Wastes can be classified into five types, which are commonly found around the house. These include liquid waste, solid rubbish, organic waste, recyclable rubbish and hazardous waste like e-waste.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Environmental Sustainability?
Answer:
Environmental sustainability is the ability of the environment to support a defined level of environmental quality and natural resource extraction rates forever to mankind. Unnecessary disturbances to the environment should be avoided whenever possible.
VI. Distinguish the following
Question 1.
Natural Environment and Human Environment.
Answer:
| Natural Environment | Human Environment |
| The components of natural components of the environment are lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. | The human environment is defined as the interaction between man as an individual, with his family, occupation, and society. |
| This includes the biotic and abiotic components like ponds, lakes, grasslands, forests, mountains, etc. | It is related to various cultural aspects such as education, religion, economics and politics. |
Question 2.
Rectangular Pattern and Linear Pattern.
Answer:
|
Rectangular Pattern |
Linear Pattern |
| Rectangular patterns of settlements is found in plain areas or valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angles. | In a linear pattern, the houses are located along a road, railway line, and along the edge of the river valley or along a levee. |
Question 3.
Tertiary Activities and Quarternary Activities.
Answer:
| Tertiary Activities | Quarternary Activities |
| Activities which by themselves do not produce goods, but support the process of production are called tertiary activities. | The activities related to Research and Development, as well as knowledge are called Quaternary activities. |
| For example Transport, communication, banking, storage, and trade. | For e.g. Services like a consultation, education, and banking. |
Question 4.
Town and City
Answer:
| Town | City |
| A town is generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. It has a population of less than 1 lakh. | Cities are much larger than towns and have a greater number of economic functions. The population in cities is estimated to be more than 1 lakh. |
| E.g.: Arakkonam near Chennai | E.g.: Coimbatore |
VII. Give Reasons
Question 1.
“It is easy to add but difficult to maintain.”
Answer:
- The population is a dynamic phenomenon where distribution and composition are constantly changing.
- Human population increases as babies are born and decreases as people die. So it is easy to increase the number but difficult to maintain.
Question 2.
“Human settlement can be described as any temporary (or) permanent unit area”.
Answer:
- During the early days man preferred tree branches, caves, pits (or) even rock cuts as his shelter.
- Slowly settlements came into existence.
- Later small settlements developed into villages, towns, cities. So he started living in settled areas.
Question 3.
“We must use forest products properly”.
Answer:
Besides providing habitats for animals and livelihoods for humans, forest products are one of the most essential things in our day to day life. Therefore we must use forest products properly.
![]()
Question 4.
“Pollution is an unfavourable modification of the natural world”.
Answer:
Pollute means to degrade or to make dirty. It is caused entirely (or) partly due to direct (or) indirect actions of human beings. So pollution is an unfavourable modification of the natural world.
Question 5.
Why do we get impervious diseases like skin cancer, blindness, loss of plankton?
Answer:
Due to the depletion of the ozone layer, UV rays fall on the earth’s surface and leads to impervious diseases like skin cancer, blindness, loss of plankton etc.
VIII. Answer in a paragraph.
Question 1.
Define Sustainable Development. Explain Social Sustainability and Economic Sustainability.
Answer:
“Sustainable development is a development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their own needs”. For sustainable development to be achieved, it is crucial to harmonize three core elements: economic growth, social aspects and environmental protection. These elements are interconnected and are crucial for the wellbeing of individuals and societies. To achieve true sustainability, we need to balance the economic, social, and environmental factors of sustainability in equal harmony.
Social Sustainability
The ability of a social system such as a country, family, or organization to function at a defined level of social well-being and harmony is called social sustainability. Problems like war, endemic poverty, widespread injustice, and low education rates are symptoms of a system in socially unsustainable. The balancing capacity of a government in maintaining peaceful existence towards other countries and at the same time providing the requirements of its citizens without affecting the environment creates social sustainability.
Economic Sustainability
The people on earth consume far more than what is their fair share.
- Economic sustainability is successfully implemented through a strong Public Distribution System.
- Economic sustainability ensures that our economic growth maintains a healthy balance with our ecosystem.