You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Geography Solutions Chapter 7 Human Geography of Tamil Nadu
Human Geography of Tamil Nadu Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The delta which is known as Granary of South India is ……………….
(a) Cauvery delta
(b) Mahanadi delta
(c) Godavari delta
(d) Krishna delta
Answer:
(a) Cauvery delta
Question 2.
Second staple food of the people of Tamil Nadu is:
(a) Pulses
(b) Millets
(c) Oilseeds
(d) Rice
Answer:
(b) Millets
Question 3.
Literacy rate of Tamil Nadu as per 2011 census is ……………
(a) 80.32%
(b) 62.33%
(c) 73.45%
(d) 80.33%
Answer:
(d) 80.33%
Question 4.
A major hydro-electric power project of Tamil Nadu is:
(a) Mettur
(b) Papanasam
(c) Sathanur
(d) Tungabhadra
Answer:
(a) Mettur
![]()
Question 5.
Number of major and minor ports in Tamil Nadu are
(a) 3 and 15
(b) 4 and 15
(c) 3 and 16
(d) 4 and 16
Answer:
(a) 3 and 15
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Agriculture of Tamil Nadu constitutes …………….. % of its economy.
2. Sathanur dam is constructed across the river …………..
3. Tamil Nadu ranks …………….. in India with a share of over 20% in total road projects under operation in the Public – Private Partnership (PPP).
4. ………….. is the third largest airport in India after Mumbai and Delhi.
5. The difference between the value of exports and imports is called ………….
Answers:
1. 21
2. Thenpennai
3. Second
4. Chennai International Airport
5. Balance of trade
III. Match the following.

Answer:
1. (b)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (c)
IV. Questions 1-2 are assertion and reasoning type
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Coimbatore, Tiruppur and Erode region is called as The Textile Valley of Tamil Nadu.
Reasoning (R): They contribute a major share to the state’s economy through textiles.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but, (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 2.
Assertion (A): The Nilgiris is the least populated district of Tamil Nadu
Reasoning (R): It is located in the western most part of Tamil Nadu.
(а) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but, (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false
(d) (A) is false but (R) is false
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but, (R) does not explain (A)
![]()
V. Answer the following in briefly.
Question 1.
Explain the cropping seasons of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
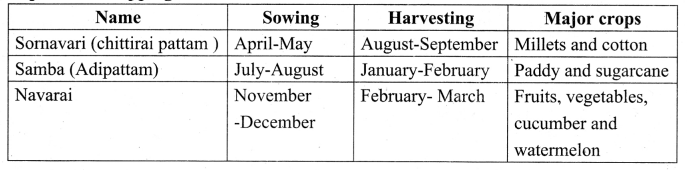
Question 2.
Why is Coimbatore called the Manchester of Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Coimbatore has the ideal conditions for cotton cultivation – Humid weather in the early stages and hot weather during the harvest period. Cotton cultivation and the textile industries are the reasons to call Coimbatore as the “Manchester of Tamil Nadu”.
Question 3.
Name the important multipurpose projects of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Mettur Dam, Amaravathi Dam, Papanasam Dam, Bhavani Sagar Dam.
Question 4.
What is MRTS?
Answer:
- Mass Rapid Transport System (MRTS) a well established suburban railway network. Currently developing a Metro system, with its first underground operation since May 2017.
- It is mainly started to manage the crowd during peak hours. The elevated metro system. Connects the heart of the city from North to South.
![]()
Question 5.
List out the air ports and sea ports of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Airports:
- Chennai International Airport
- Coimbatore International Airport
- Madurai International Airport
- Tiruchirapalli International Airport
Domestic Airports:
- Tuticorin and Salem
Sea Port: Major Sea Ports are:
- Chennai
- Ennore and
- Tuticorin
Intermediate port at Nagapattinam and 15 minor ports.
Question 6.
Have you heard about any stampede in your district? write about that incident briefly.
Answer:
During Athivaradhar festival minor stampede that brokeout on Thursday (18th July 2019) the crowd flocked to Kancheepuram as it was an auspicious day after the lunar eclipse. Four people died.
On 21st April 2019 atleast seven people died in stampede in Tamil Nadu during a temple festival at Muthuaiyampalayam Karuppusamy temple in Thuraiyur a village near Trichy (Sunday).
![]()
VI. Distinguish between the following.
Question 1.
Marine Fishing and Inland fishing
Answer:
| Marine Fishing | Inland Fishing |
| It is carried out in oceans and seas. | Inland fishing is carried out in lakes, rivers, ponds, estuaries, backwaters and swamps. |
| Large mechanised boats are used for fishing. | Catamaran, diesel boats and floating nets are used in fishing. |
| The fish varieties caught are sharks, flying fish, counch, catfish, silver bellies and crabs. | Oysters and prawns are cultured in original nurseries. |
| Chennai, KanyaKumari, Tirunelveli, Nagapattinam, Thanjavur and Ramanathapuram. | Vellore, Cuddalore, Sivagangai and Virudhunagar districts are inland fish production of the state. |
Question 2.
Food Crops and Non- Food Crops
Answer:
| Food Crops | Non- Food Crops |
| Food crops are mainly grown for consumption | They are mainly grown for sale purpose |
| Paddy is the main food crop and cereals, pulses and millets are also the second staple food of the people of Tamil Nadu | Sugarcane, cotton, tree and coffee |
| Cauvery delta is known as the Granary of South India leading in rice cultivation | Tiruvallur, Kancheepuram, Vellore, coimbatore, Cuddalore, Erode, Madurai, Ramanatha Puram, Salem, Thoothukudi, Nilgiris and yercaud. |
Question 3.
Surface Water and Ground Water
Answer:
|
Surface Water |
Ground Water |
| The total surface water potential of the state is about 24,864 mem. | The utilizable groundwater resource of the state is 22,423 mem. |
| There are 17 major river basins in the state with 81 reservoirs and about 41,262 tanks | The current level of utilization of water is about 13,558 mem. |
| Most of the surface water has already been tapped, primarily for irrigation, where water use in the largest. | 60% of the available recharge, while about (8875 mcm) 40% is the balance available for use. |
VII. Give reasons for the following
Question 1.
Farmers switch over from inorganic to organic farming.
Answer:
By continuous usage of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides the soil became unfit for cultivation after some years. It causes a threat to agriculture. So to bring back the soil to fertility and to make it fit for cultivation farmers switch over from inorganic to organic farming. Organic wastes, biological pest control crop residues and animal manure only used under organic farming.
Question 2.
Cities are densely populated than the villages.
Answer:
Agriculture, job opportunities and industrial development are the main causes of population density in the cities then the villages.
Question 3.
Karur is Called the Textile Capital of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Karur is an industry town and is very famous for cottage and hand-loom textile industries. Moreover state’s most of the textile goods exports is from Karur district. That is why Karur is called the textile capital of Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Question 4.
Mostly stampede occurs in Temples.
Answer:
Most of the religious festivals are located in areas like banks of rivers hilly terrains or mountain tops. These areas lack proper pathways, posing a geographical risk to the pilgrims. It often disrupts the orderly movement of crowds resulting in irrational and dangerous movement for self-protection, leading to injuries and fatalities. Because of the lack of physical infrastructure, the mob behaviour increases the sense of threat, which results in a stampede.
VIII. Answer the following in a paragraph.
Question 1.
Write about the plantation farming of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Plantation Crops: Tea, coffee, cashew, rubber, pepper and cinchona.
The hill slopes with laterite soil and acidic-nature is ideal for the plantation crops.
Tea: Tea plantations are found in the hills of the Nilgins and Coimbatore. Notable region for tea estates Nilgiris.
Coffee: Coffee plants are grown in the hills of Western Ghats as well as Eastern Ghats. It is also found in the hilly slopes of Dindigui, Madurai, Theni and Salem districts.
Notable places: Yercaud, Kolli hills and Kodaikanal,
Rubber: Rubber plantations are significant in Kanyakumari.
Cashew: It is extensively cultivated in Cuddalore district.
Pepper: Confined to the warm and wet slopes of Eastern and Western Ghats of Tamil Nadu.
Cinchona: It is planted at heights varying from 1060 to 1280 metres in Anaimalai hills.
Cardamom: Cardamom estates are located at few places in the hills of Madurai region at an elevation of 915 to 1525 metres.
Position: Tamil Nadu stands second in area and production of tea and coffee next to Assam and Karnataka respectively.
Question 2.
Give an account on water resources of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu constitutes 4% of India’s land area and is inhabited by 6% of India’s population, but has-only 2.5% of India’s water resources.
- More than 95% of the surface water and 80% of the ground water have already been put into use.
- Major uses of water include human/animal consumption irrigation and industrial use.
- The state is heavily dependent on monsoon rains.
- The annual average rainfall is around 930 mm (47% during the northeast monsoon, 35% during the south west monsoon, 14% in summer and 4% in winter.

Question 3.
Bring out the mineral distribution in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
(i) Tamil Nadu is the leading holder of country’s resources of vermiculite, magnetite, dunite, rutile, garnet, molybdenum and ilmenite.
(ii) The state accounts for the country’s 55.3% of lignite, 75% of vermiculite, 69% of dunite, 59% of garnet, 52% of molybdenum and 30% of titanium mineral resources.
Important minerals are found in the state are as follows:
- Neyveli has large lignite resources.
- Coal is available in Ramanathapuram
- Oil gas are found in the Cauvery basin
- Iron deposits are found in Kanjamalai region in Salem district and Kalrayan Malai region of Tiruvannamalai district.
- Magnesite ores are available near Salem.
- Bauxite is found in Servarayan Hills, Kotagiri, Udagamandalam, Palani and Kollimalai areas.
- Gypsum is obtained in Tiruchirappalli, Tirunelveli, Thoothukudi and Virudhunagar districts.
- Ilmenite and rutile are found in the sands of Kanyakumari beach.
- Limestone is available in Coimbatore, Cuddalore, Dindigul, Kancheepuram, Karur, Madurai, Nagapattinam, Namakkal, Perambalur, Ramanathapuram, Salem and Tiruvallur districts.
- Magnesite is obtained in Coimbatore, Dharmapuri, Karur, Namakkal, the Nilgiris, Salem.
- Feldspar, quartz, copper and lead are found in some parts of the state.
![]()
Question 4.
State the densely populated regions of Tamil Nadu and account for its high density.
Answer:
- The number of persons living per square km is referred as population density.
- A place is said to have high density of population if number of persons living per sq km is above 800.
- As per 2011 census the density of population in Tamil Nadu is 555 per sq.km
Densely populated regions of Tamil Nadu:
Chennai is the densest district – 26,903 persons per sq.km followed by Kanyakumari (1106), Tiruvallur (1049), Kancheepuram (927), Madurai (823), Coimbatore (748), Cuddalore (1702), Thanjavur (691), Nagapattinam (668-), Salem (663), Vellore (646), Tiruchirappalli (602).
Question 5.
Explain the different modes of transport available in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Roadways:
The State has a total road length of 167,000 km, In which 60,628km are maintained by state Highways Department. It ranks second in India with a share of over 20% in total road projects under operation in the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
Railways:
- Tamil Nadu has a well-developed rail network as part of Southern Railway, headquartered at Chennai.
The present Southern Railway network extends over a large area of India’s southern peninsula, covering Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, minor portions of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. - Tamil Nadu has a total railway track length of 6,693 km with 690 railway stations in the state.
- The system connects it with most of the major cities in India.
- Main rail junctions in the state include Chennai, Coimbatore, Erode, Madurai, Salem, Tiruchirappalli and Tirunelveli.
- Chennai has a well-established suburban railway network, a Mass Rapid Transport System (MRTS) and is currently developing a Metro system, with its first underground stretch in operation since May 2017.
Airways:
- Tamil Nadu has four major international airports. Chennai International Airport is currently the third largest airport in India after Mumbai and Delhi.
Water ways:
- Tamil Nadu has 3 major ports. They are Chennai, Ennore and Tuticorin. It has an intermediate port at Nagapattinam and 15 minor ports. Ennore intermediate port was recently converted as a major port and handles the major coal and ore traffics in Tamil Nadu.
Question 6.
Write about Road safety rules.
Answer:
In recent years the number of road accidents in Tamil Nadu has been increasing. It is reported that 15% of the road accidents of the country takes place in Tamil Nadu.
Basic road safety rules:
- Aware of the road signals
- Stop, look and cross
- Listen and ensure whether a vehicle is approaching
- Don’t rush on roads
- Crossroads in pedestrian crossings
- Don’t stretch hands while driving vehicles.
- Never crossroad at bends and stay safe in a moving vehicle.
- Avoid speeding, Drunk and driving, use helmets and seat belts and follow traffic rules.
“Know – Risk! No – risk!”
IX. Map Study
Question 1.
Mark the areas of major crops, minerals, dams, airport and seaports.
Answer:
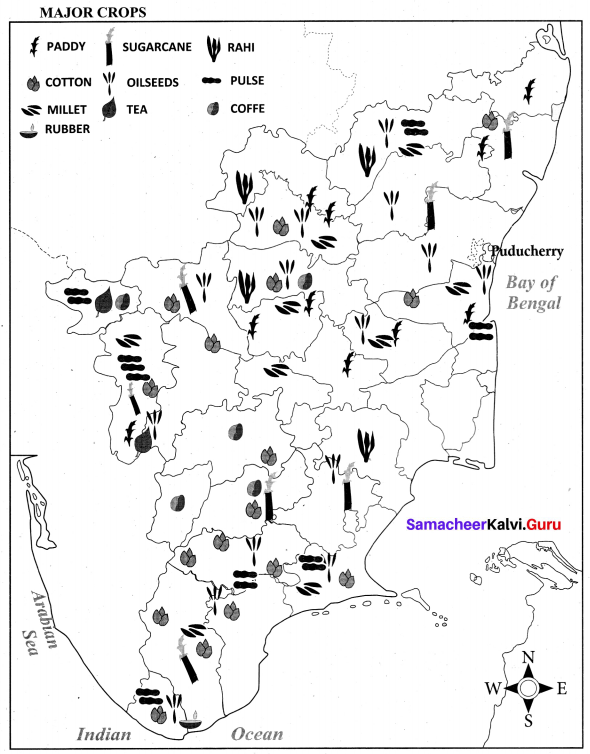
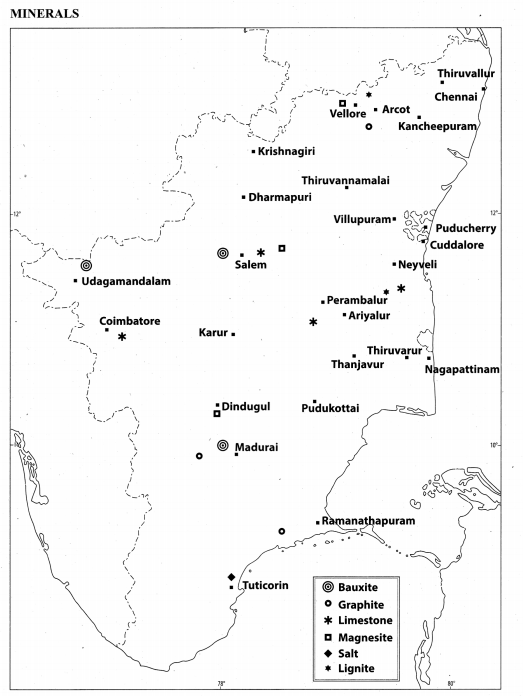
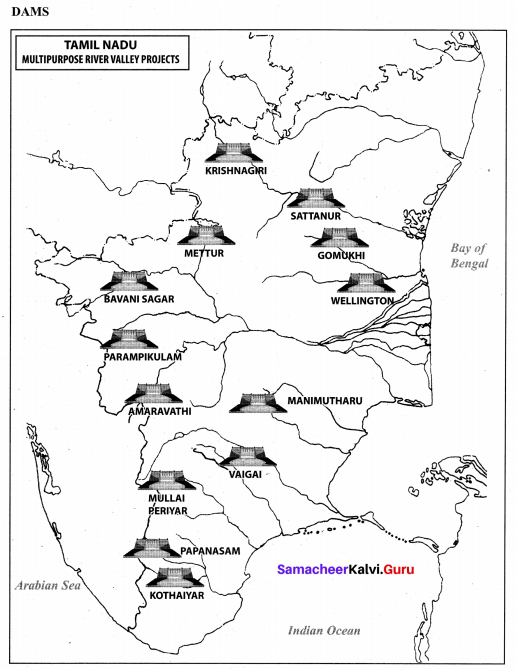
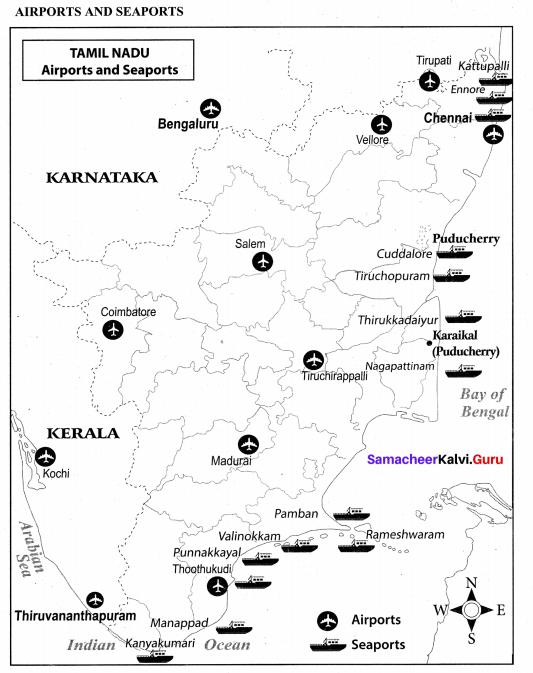
Human Geography of Tamil Nadu Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Tea, Coffee, rubber, pepper and cashew are …………. crops.
(a) Food
(b) Fiber
(c) Plantation
Answer:
(c) Plantation
Question 2.
The word Agriculture is derived from the ……………….. words “ager and Cultura”.
(a) Latin
(b) Greek
(c) Tamil
(d) Spanish
Answer:
(a) Latin
![]()
Question 3.
Rice, Cotton, Sugercane are grown with …………….
(a) Drying farming
(b) Irrigation farming
(c) Cattle reasing
Answer:
(b) Irrigation farming
Question 4.
In Tamil Nadu Rice Research Institute is situated at:
(a) Aduthurai
(b) Madurai
(c) Thiruvallur
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(a) Aduthurai
![]()
Question 5.
Millets are ……………… crops.
(a) Wet crops
(b) Dry crops
(c) Plantation
Answer:
(b) Dry crops
Question 6.
To promote ……………….. a central scheme named ‘National Project on Organic Farming’was launched.
(a) mixed farming
(b) organic farming
(c) aquaculture
(d) plantation farming
Answer:
(b) organic farming
Question 7.
Which is known as the Textile capital of Tamil Nadu?
(a) Salem
(b) Karur
(c) Tirunelveli
Answer:
(b) Karur
Question 8.
……………….. is also known as ‘poor man’s cow’.
(a) Goat
(b) Sheep
(c) Buffalo
(d) Horse
Answer:
(a) Goat
![]()
Question 9.
The most populated district in Tamil Nadu is …………….
(a) Madurai
(b) Tiruvallur
(c) Chennai
Answer:
(c) Chennai
Question 10.
districts lead in the Inland fish production.
(a) Chennai
(b) Cuddalore
(c) Sivagangai
(d) Vellore
Answer:
(d) Vellore
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. …………. irrigation is most predominant irrigation system in TamilNadu.
2. ……….. Dam is one of the biggest earthen dams in the country.
3. Amaravathi reservoir is notable for the …………….
4. Papanasam dam is also known as ………….. dam.
5. Parappalar project is located near …………….
6. Tamil Nadu occupies ……………… position in the country in silk production.
7. The Vellore district is the top exporter of finished …………. in the country.
8. Tamil Nadu accounts for about ………….. of India’s …………. exports.
9. Tamil Nadu ranks among the Indian states in population density.
10. ………… in considered the ‘fire works capital’ of India.
Answers:
1. Well
2. Bhavani
3. Mugger crocodiles
4. Karaiyar
5. Ottanchatram
6. Fourth
7. leather goods
8. 17%, Software
9. 12th
10. Sivakasi
III. Match the following.
a.
| 1. | Rearing of birds | (a) | Apiculture |
| 2. | Rearing of honeybees | (b) | Horticulture |
| 3. | Rearing of silkworms | (c) | Poultry farming |
| 4. | Growing fruits | (d) | Sericulture |
Answer:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3.(d)
4.(b)
b.
| 1. | Wet fanning | (a) | Millets |
| 2. | Dry farming | (b) | Rice |
| 3. | Plantation farming | (c) | Sugarcane |
| 4. | Market gardening | (d) | Tea, Coffee |
| 5. | Irrigation farming | (e) | Kancheepuram |
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (a)
3. (d)
4. (e)
5. (c)
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
What is Agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture is a practice of farming that includes cultivation of crops, rearing of animals, birds, forestry, fisheries and other related activities.
Question 2.
What is the Multipurpose River Valley Projects?
Answer:
Multipurpose river valley projects are basically designed for the development of irrigation for agriculture and hydropower generation they are used for many other purposes as well.
Question 3.
List out the major food crops and commercial crops of the state.
Answer:
- The principal food crops – paddy, millets and pulses.
- The commercial crops – sugarcane, cotton, oilseeds, spices, tea, and coffee and cashew.
Question 4.
Define Trade.
Answer:
Trade-in an exchange of goods and commodities either within the country or between countries.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on Tamil Nadu Rice Research Institute.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu Rice Research Institute was established in April 1985 under Tamil Nadu Agricultural University.
- It is situated at AduthUrai (Thanjavur).
- It’s function is to perform lead function for rice and rice based cropping system research with the help of existing agriculture colleges and research centers.
Question 6.
Name any four districts with low density of population.
Answer:
Nilgiris, Perambalur, Dharmapuri and Sivagangai.
Question 7.
What are minor ports?
Answer:
Minor ports are anchorage ports where cargo is transhipped from the vessel to the store.
Ex. Cuddalore, Nagapattinam, Kolachal and Rameshwaram.
Question 8.
What are the uses of Chinchona?
Answer:
- Chinchona is a forest product.
- From chinchona quinine a drug is extracted.
- Malaria is treated with this medicine.
![]()
Question 9.
Write the expansion of these abbreviated terms.
- TNAU
- TANTEA
- TNPL
- TANCEM
- Gl
- CLRI
- SEZ
- TTDC
Answer:
- TNAU: Tamil Nadu Agriculture University
- TANTEA: Tamil Nadu Tea Plantation Corporation Limited
- TNPL: Tamil Nadu Newsprint and Papers Limited
- TANCEM: Tamil Nadu Cements Corporation Limited
- GI: Geographical Indication
- CLRI: Central Leather Research Institute –
- SEZ: Special Economic Zone
- TTDC: Tamil Nadu Tourism-Development Corporation
Question 10.
Name the factors influencing agriculture.
Answer:
The factors influencing agriculture can be classified as Physical, Social and economic factors.
- Physical factors includes soil, temperature, rainfall, humidity, climate and slope of land.
- The social factors includes traditional knowledge belief and myths of farmers, farm size and holdings and fanners acceptance towards innovation.
- Economic factors are market loan assistance, government subsidy and incentives.
V. Distinguish:
Question 1.
Wet farming and Dry farming
Answer:
|
Wet farming |
Dry farming |
| Water supply is available through out the year from rain fall and irrigation for farming. | Farming is carried out only during rainy season. |
| Rice and sugarcane are grown. | Ragi and millets are grown. |
Question 2.
Commercial crops and Plantation crops
Answer:
| Commercial crops | Plantation crops |
| Sugarcane, tobacco, oil seeds, spices, turmeric etc are commercial crops. | Tea, coffee, rubber, pepper and cashewnut are the main plantation crops. |
| Tobacco is yet another commercial crop grown an Dindigul, Teni and Madurai districts. | Coffee in grown in the W.Ghats and E. Ghats. |
Question 3.
Imports and Exports
Answer:
| Imports | Exports |
| Goods and services bought from overseas producers. | Goods and services sold to overseas consumers. |
| A country that imports goods and services loses foreign exchage currency. | A country that exports goods and services gains foreign exchange currency. |
| Tamil Nadu imports machineries, electrical equipments, mineral, fuel and pharmaceutical products. | Tamil Nadu exports agricultural products, Leather products, Gems, and jewellery, chemical and related products. |
VI. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Tourism is considered as an industry – justify. Give an account on Tourism in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Tourism is considered as an industry because of its enormous potential in creating employment for a large number of people.
- Approximately 28 lakh foreign and 11 crore domestic tourists visit our state (Tamil Nadu) annually.
- Reasons: The presence of ancient temples and monuments, hill stations pilgrim centres, a variety of natural land scapes, long coast line along with rich culture and heritage make Tamil Nadu the best destination for tourists.
- Promoter: Tourism in Tamil Nadu is promoted by Tamil Nadu Tourism Development Corporation (TTDC).
- The state currently ranks the highest among Indian states with about 25 crore arrivals (in 2013).
Question 2.
Give an account for the distribution of Textile industry in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Textile industry is one of the traditionally well-developed industries in Tamil Nadu. Tamil Nadu has a major share in the Indian Textile industry in terms of production and export of yams, fabrics, knitwear and garments. Tamil Nadu contributes 30% of India’s share in export of cotton, yam and fabrics.
Tropical climate availability of raw materials, demand for cotton in market, power supply from numerous power projects and abundant cheap labour are favourable factors for widespread distribution of textile industries in Tamil Nadu. The textile mills are concentrated in Coimbatore, Tirupur, Salem, Palladam, Kamr, Dindigul, Vimdhunagar, Tirunelveli, Thoothukudi, Madurai and Erode. Tamil Nadu has about 3,50,000 power looms manufacturing cotton fabrics.
Maximum units are concentrated in and around Coimbatore region for this region it is known as the “Manchester of South India”. Timpur and Erode contributes much for the state economy, therefore they are referred to as ‘Textile Valley of Tamil Nadu’.
Timpur alone contributes 70% of export of knitwear of Tamil Nadu. Erode specializes in garments and bedspreads. The city of Kamr is known as ‘Textile capital of Tamil Nadu Silk Textiles’. Tamil Nadu occupies fourth place in silk textile production in our country Kancheepuram silk is unique in its quality and is known for its traditional value all over the world. Arani, Rasipuram and Thimbuvanam are other silk centres of Tamil Nadu.
Sericulture Training Institute in Hosur training farmers to adopt agriculture along with farm work to accelerate rural industrialization Mettur, Madurai and Ramanathapuram are specialized areas for manufacturing synthetic clothes.