Students can Download Economics Chapter 8 International Economic Organisations Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 8 International Economic Organisations
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics International Economic Organisations Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
International Monetary Fund was an outcome of …………………….
(a) Pandung Conference
(b) Dunkel Draft
(c) Bretton Woods Conference
(d) Doha Conference
Answer:
(c) Bretton Woods Conference
Question 2.
International Monetary Fund is having its headquarters at …………………….
(a) Washington D.C.
(b) New York
(c) Vienna
(d) Geneva
Answer:
(a) Washington D.C.
![]()
Question 3.
IBRD is otherwise called …………………….
(a) IMF
(b) World Bank
(c) ASEAN
(d) International Finance Corporation
Answer:
(b) World Bank
Question 4.
The other name for Special Drawing Rights is …………………….
(a) Paper gold
(b) Quotas
(c) Voluntary Export Restrictions
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Paper gold
Question 5.
The organization which provides long term loan is …………………….
(a) World Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) World Trade Organisation
(d) BRICS
Answer:
(a) World Bank
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following countries is not a member of SAARC?
(a) Sri Lanka
(b) Japan
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Afghanistan
Answer:
(b) Japan
Question 7.
International Development Association is an affiliate of …………………….
(a) IMF
(b) World Bank
(c) SAARC
(d) ASEAN
Answer:
(b) World Bank
![]()
Question 8.
……………………. relates to patents, copyrights, trade secrets, etc.,
(a) TRIPS
(b) TRIMS
(c) GATS
(d) NAMA
Answer:
(a) TRIPS
Question 9.
The first ministerial meeting of WTO was held at …………………….
(a) Singapore
(b) Geneva
(c) Seattle
(d) Doha
Answer:
(a) Singapore
Question 10.
ASEAN meetings are held once in every ……………………. years.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following is not the member of SAARC?
(a) Pakistan
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Bhutan
(d) China
Answer:
(d) China
Question 12.
SAARC meets once in ……………………. years.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 13.
The headquarters of ASEAN is …………………….
(a) Jaharta
(b) New Delhi
(c) Colombo
(d) Tokyo
Answer:
(a) Jaharta
Question 14.
The term BRIC was coined in …………………….
(a) 2001
(b) 2005
(c) 2008
(d) 2010
Answer:
(a) 2001
![]()
Question 15.
ASEAN was created in …………………….
(a) 1965
(b) 1967
(c) 1972
(d) 1997
Answer:
(b) 1967
Question 16.
The Tenth BRICS Summit was held in July 2018 at …………………….
(a) Beijing
(b) Moscow
(c) Johannesburg
(d) Brasilia
Answer:
(c) Johannesburg
![]()
Question 17.
New Development Bank is associated with …………………….
(a) BRICS
(b) WTO
(c) SAARC
(d) ASEAN
Answer:
(a) BRICS
Question 18.
Which of the following does not come under ‘Six dialogue partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) India
(d) North Korea
Answer:
(d) North Korea
Question 19.
SAARC Agricultural Information Centre (SAIC) works as a central information institution for agriculture related resources was founded on …………………….
(a) 1985
(b) 1988
(c) 1992
(d) 1998
Answer:
(b) 1988
![]()
Question 20.
BENELUX is a form of …………………….
(a) Free trade area
(b) Economic Union
(c) Common market
(d) Customs union
Answer:
(d) Customs union
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions.
Question 21.
Write the meaning of Special Drawing rights?
Answer:
Special Drawing Rights (SDRs):
- The Fund has succeeded in establishing a scheme of Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) which is otherwise called ‘Paper Gold’.
- They are a form of international reserves created by the IMF in 1969 to solve the problem of international liquidity.
- They are allocated to the IMF members in proportion to their Fund quotas.
- SDRs are used as a means of payment by Fund members to meet balance of payments deficits and their total reserve position with the Fund.
- Thus SDRs act both as an international unit of account and a means of payment.
- All transactions by the Fund in the form of loans and their repayments, its liquid reserves, its capital, etc., are expressed in the SDR.
![]()
Question 22.
Mention any two objectives of ASEAN?
Answer:
- To accelerate the economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region;
- To promote regional peace and stability and adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter.
Question 23.
Point out any two ways in which IBRD lends to member countries?
Answer:
The Bank advances loans to members in two ways
- Loans out of its own fund,
- Loans out of borrowed capital.
![]()
Question 24.
Define Common Market?
Answer:
Common market is established through trade pacts. A group formed by countries within a geographical area to promote duty free trade and free movement of labour and capital amongits members, e.g. European Common Market (ECM).
Question 25.
What is Free trade area?
Answer:
- A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free-trade agreement (FTA).
- Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, e.g. SAFTA, EFTA.
Question 26.
When and where was SAARC Secretariat established?
Answer:
South Asian Association For Regional Co – Operation (SAARC):
1. The South Asian Association for Regional Co – operation (SAARC) is an organisation of South Asian nations, which was established on 8 December 1985 for the promotion of economic and social progress, cultural development within the South Asia region and also for friendship and co – operation with other developing countries.
2. The SAARC Group (SAARC) comprises of Bangaladesh, Bhutan, India, The Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
3. In April 2007, Afghanistan became its eighth member.
![]()
Question 27.
Specify any two affiliates of World Bank Group?
Answer:

Part – C
Answer The Following Questions.
Question 28.
Mention the various forms of economic integration?
Answer:
An economic union is composed of a common market with a customs union. The participant countries have both common policies on product regulation, freedom of movement of goods, services and the factors of production and a common external trade policy, (e.g. European Economic Union)
EU > CM > CU > FTA
EU – Economic Union >
CM – Common – Market >
CU – Customs Union >
FTA – Free Trade Area
The regional economic integration among the trade blocks such as SAARC (South Asian nations), ASEAN (South East Asia) and BRICS and their achievements.
![]()
Question 29.
What are trade blocks?
Answer:
1. Trade blocks cover different kinds of arrangements between or among countries for mutual benefit. Economic integration takes the form of Free Trade Area, Customs Union, Common Market and Economic Union.
2. A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free-trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, e.g. SAFTA, EFTA.
3. A customs union is defined as a type of trade block which is composed of a free trade area with no tariff among members and (zero tariffs among members) with a common external tariff, e.g. BENELUX (Belgium, Netherland and Luxumbuarg).
4. Common market is established through trade pacts. A group formed by countries within a geographical area to promote duty free trade and free movement of labour and capital among its members, e.g. European Common Market (ECM).
5. An economic union is composed of a common market with a customs union. The participant countries have both common policies on product regulation, freedom of movement of goods, services and the factors of production and a common external trade policy. (e.g. European Economic Union).
![]()
Question 30.
Mention any three lending programmes of IMF?
Answer:
(I) Establishment of monetary reserve fund:
- The Fund has played a major role in achieving the sizeable stock of the national currencies of different countries.
- To meet the foreign exchange requirements of the member nations, IMF uses its stock to help the member nations to meet foreign exchange requirements.
(II) Monetary discipline and cooperation:
- The IMF has shown keen interest in maintaining monetary discipline and cooperation among the member countries.
- To achieve this objective, it has provided assistance only to those countries which make sincere efforts to solve their problems.
(III) Special interest in the problems of UDCs:
- The notable success of the Fund is the maintenance of special interest in the acute problems of developing countries.
- The Fund has provided financial assistance to solve the balance of payment problem of UDCs.
- However, many UDCs continue to be UDCs, while the developed countries have achieved substantial growth.
![]()
Question 31.
What is Multilateral Agreement?
Answer:
1. Multilateral trade agreement:
It is a multi national legal or trade agreements between countries. It is an agreement between more than two countries but not many.
2. The various agreements implemented by the WTO such as TRIPS, TRIMS, GATS, AoA, MFA have been discussed.
Question 32.
Write the agenda of BRICS Summit, 2018?
Answer:
- South Africa hosted the 10th BRICS summit in July 2018.
- The agenda for BRICS summit 2018 includes Inclusive growth, Trade issues, Global governance, Shared Prosperity, International peace and security.
Question 33.
State briefly the functions of SAARC?
Answer:
Functions of SAARC:
The main functions of SAARC are as follows.
- Maintenance of the co operation in the region
- Prevention of common problems associated with the member nations.
- Ensuring strong relationship among the member nations.
- Removal of the poverty through various packages of programmes.
- Prevention of terrorism in the region.
![]()
Question 34.
List out the achievements of ASEAN?
Answer:
The ASEAN Declaration states the aims and purposes of the Association as:
- To accelerate the economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region;
- To promote regional peace and stability and adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter;
- To promote cooperation among the members of ASEAN through the exchange of knowledge and experience in the field of public sector auditing.
- To provide a conducive environment and facilities for research, training, and education among the members
- To serve as a centre of information and as an ASEAN link with other international organizations.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions.
Question 35.
Explain the objectives of IMF?
Answer:
Objectives Of IMF:
- To promote international monetary cooperation among the member nations.
- To facilitate faster and balanced growth of international trade.
- To ensure exchange rate stability by curbing competitive exchange depreciations.
- To eliminate or reduce exchange controls imposed by member nations.
- To establish multilateral trade and payment system in respect of current transactions instead of bilateral trade agreements.
- To promote the flow of capital from developed to developing nations.
- To solve the problem of international liquidity.
![]()
Question 36.
Bring out the functions of World Bank?
Answer:
Functions of IBRD (or) World Bank:
The World Bank performs the major role of providing loans for development works to member countries, especially to underdeveloped countries. The World Bank provides long¬term loans for various development projects. Article 1 of the Agreement states the functions performed by the world bank as follows.
(I) Investment for productive purposes:
The World Bank performs the function of assisting in the reconstruction and development of territories of member nations through facility of investment for productive purposes. It also encourages the development of productive facilities and resources in less developed countries.
(II) Balanced growth of international trade:
Promoting the long range balanced growth of trade at international level and the maintaining equilibrium in BOPs of member nations by encouraging international investment.
(III) Provision of loans and guarantees:
Arranging the loans or providing guarantees on loans by various other channels so as to execute important projects.
(IV) Promotion of foreign private investment:
The promotion of private foreign investment by means of guarantees on loans and other investment made by private investors. The Bank supplements private investment by providing finance for productive purpose out of its own resources or from borrowed funds.
(V) Technical services:
The World Bank facilitates different kinds of technical services to the member countries through Staff College and experts.
![]()
Question 37.
Discuss the role of WTO in India’s socio economic development?
Answer:
WTO and India:
India is the founding member of the WTO. India favours multilateral trade approach. It enjoys MFN status and allows the same status to all other trading partners. India benefited
from WTO on following grounds:
- By reducing tariff rates on raw materials, components and capital goods, it was able to import more for meeting her developmental requirements. India’s imports go on increasing.
- India gets market access in several countries without any bilateral trade agreements.
- Advanced technology has been obtained at cheaper cost.
- India is in a better position to get quick redressal from the trade disputes.
- The Indian exporters benefited from wider market information.
![]()
Question 38.
Write a note on?
(a) SAARC
(b) BRICS.
Answer:
(a) South Asian Association For Regional Co – Operation (SAARC):
- The South Asian Association for Regional Co – operation (SAARC) is an organisation of South Asian nations, which was established on 8 December 1985 for the promotion of economic and social progress, cultural development within the South Asia region and also for friendship and co-operation with other developing countries.
- The SAARC Group (SAARC) comprises of Bangaladesh, Bhutan, India, The Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- In April 2007, Afghanistan became its eighth member.
- The basic aim of the organisation is to accelerate the process of economic and social development of member states through joint action in the agreed areas of cooperation.
- The SAARC Secretariat was established in Kathmandu (Nepal) on 16th January 1987.
- The first SAARC summit was held at Dhaka in the year 1985.
- SAARC meets once in two years. Recently, the 20th SAARC summit was hosted by Srilanka in 2018.
(b) BRICS:
- BRICS is the acronym for an association of five major emerging national economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Since 2009, the BRICS nations have met annually at formal summits.
- South Africa hosted the 10th BRICS summit in July 2018.
- The agenda for BRICS summit 2018 includes Inclusive growth, Trade issues, Global governance, Shared Prosperity, International peace and security.
- It’s headquarters is at Shanghai, China.
- The New Development Bank (NDB) formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank was established by BRICS States.
- The first BRICS summit was held at Moscow and South Africa hosted the Tenth Conference at Johanesberg in July 2018.
- India had an opportunity of hosting fourth and Eighth summits in 2009 and 2016 respectively.
- The BRICS countries make up 21 percent of global GDP. They have increased their share of global GDP threefold in the past 15 years.
- The BRICS are home to 43 percent of the world’s population.
- The BRICS countries have combined foreign reserves of an estimated $ 4.4 trillion
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics International Economic Organisations Addtional Questions and Answers
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
1.
The IMF has ……………………. member countries with Republic.
(a) 169
(b) 179
(c) 189
(d) 199
Answer:
(c) 189
Question 2.
The Brettonwoods conference proposed IMF, World Bank and International Trade Organisation in …………………….
(a)1914
(b) 1924
(c) 1934
(d) 1944
Answer:
(d) 1944
![]()
Question 3.
The GATT was transformed into …………………….
(a) IMF
(b) World Bank
(c) WTO
(d) IDBI
Answer:
(c) WTO
Question 4.
International Monetary Fund headquarters are present in …………………….
(a) Geneva
(b) Washington DC
(c) England
(d) China
Answer:
(b) Washington DC
![]()
Question 5.
The IMF is maintaining exchange rate stability and emphasising …………………….
(a) valuvation
(b) Devaluevation
(c) Equilibrium
(d) Disequillibrium
Answer:
(b) Devaluevation
Question 6.
The buffer stock financing facility was started in …………………….
(a)1949
(b)1959
(c) 1969
(d) 1979
Answer:
(c) 1969
![]()
Question 7.
……………………. was setup to augment the availability to concessional resources to low Income countries.
(a) SAF
(b) IMF
(c) ESAF
(d) BSF
Answer:
(c) ESAF
Question 8.
Special Drawing called …………………….
(a) Gold
(b) Metal
(c) Paper Gold
(d) Gold Paper
Answer:
(c) Paper Gold
![]()
Question 9.
India has been beneficiaries of the major beneferciaries of the ……………………. fund.
(a) SDR
(b) ESAF
(c) IMF
(d) World Bank
Answer:
(c) IMF
Question 10.
IMF fund has provided finance assistance to solve the balance payment problems of …………………….
(a) SDR
(b) ESAF
(c) IMF
(d) World Bank
Answer:
(c) IMF
![]()
Question 11.
IBRD otherwise called the …………………….
(a) IMF
(b) SDR
(c) SAF
(d) World Bank
Answer:
(d) World Bank
Question 12.
IMF is a prerequisite to become a member of …………………….
(a) SDR
(b) SAF
(c) World Bank
(d) SAF
Answer:
(c) World Bank
Question 13.
……………………. was established to provide long term financial assistance to member countries.
(a) IMF
(b IBRD
(c) SAF
(d) ESAF
Answer:
(b IBRD
![]()
Question 14.
World Bank advances loans out of its own …………………….
(a) Fund
(b) Money
(c) Finance
(d) Credit
Answer:
(a) Fund
Question 15.
The IBRD has ……………………. member countries.
(a) 159
(b) 169
(c) 179
(d) 189
Answer:
(d) 189
Question 16.
World Bank’s membership has 151 countries in …………………….
(a) 1968
(b) 1978
(c) 1988
(d) 1998
Answer:
(c) 1988
![]()
Question 17.
……………………. grants loans to member countries only for productive purposes.
(a) IMF
(b) World bank
(c) SAF
(d) ESAF
Answer:
(b) World bank
Question 18.
……………………. the soft loan window of the bank provides loans to UDC at very low rate of interest.
(a) World Bank
(b) IDA
(c) IMF
(d) IBRD
Answer:
(b) IDA
![]()
Question 19.
……………………. was first suggested by India to the drafting committee.
(a) IBRD
(b) IDA
(c) IMF
(d) SAF
Answer:
(a) IBRD
Question 20.
India was the largest beneficiary of the ……………………. assistance.
(a) IBRD
(b) IDA
(c) IMF
(d) World bank
Answer:
(d) World bank
Question 21.
The WTO was established in 1995 as a 28 successor to the …………………….
(a) World Bank
(b) IDA
(c) GATT
(d) IFC
Answer:
(c) GATT
![]()
Question 22.
The first WTO conference was held at in ……………………. 1996.
(a) Argentia
(b) Kazakhstan
(c) Singapore
(d) America
Answer:
(c) Singapore
Question 23.
A result of ……………………. the dependence of LDCs on advanced countries for seeds, drugs, fertilizers and pesticides.
(a) TRIPS
(b) TRIMS
(c) GATS
(d) GATT
Answer:
(a) TRIPS
![]()
Question 24.
……………………. are related to conditions or restrictions in respect of foreign investment in the country.
(a) TRIPS
(b) TRIMs
(c) GATT
(d) GATS
Answer:
(b) TRIMs
Question 25.
……………………. is the first Multilateral set of rules covering trade in services like banking, insurance, transportation, communication, etc.
(a) TRIPS
(b) TRIMs
(c) GATT
(d) GATS
Answer:
(d) GATS
Question 26.
……………………. governed the world trade in textiles and garments since 1974.
(a) GATS
(b) GATT
(c) MFA
(d) TRIPS
Answer:
(c) MFA
![]()
Question 27.
Agriculture was included for the first time under …………………….
(a) GATS
(b) GATT
(c) MFA
(d) TRIMs
Answer:
(b) GATT
Question 28.
……………………. is the founding member of the WTO.
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Africa
(d) Russia
Answer:
(a) India
II. Match the following and choose the correct answer by using codes given below.
Question 1.
A. ITO – (i) 1945
B. IMF – (ii) 1944
C. WTO – (iii) 1945
D. World Bank – (iv) 1995
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
![]()
Question 2.
A. International Monetary Fund – (i) Washington DC
B. World Trade Organisation – (ii) Washington DC
C. IBRD – (iii) 189 members
D. World Bank – (iv) Geneva
Codes:
(a) A(i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (iv) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (iv) D (ii)
Question 3.
A. SDR – (i) 1963
B. CFF – (ii) Paper Gold
C. BSF – (iii) 1986
D. SAF – (iv) 1969
Codes:
(a) A (iii) B (ii) C(i) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(c) A (i) B (iv) C (iii) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
Answer:
(b) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
![]()
Question 4.
A. SAF – (i) Structural Adjustment Facility
B. BSF – (ii) Special Drawing Rights
C. CFF – (iii) Buffer Stock Facility
D. SDR – (iv) Compensatory Financing Facility
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (iii) C (iv) D (ii)
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C (iii) D (i)
(c) A (iii) B (ii) C(i) D (iv)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(a) A (i) B (iii) C (iv) D (ii)
Question 5.
A. IDA – (i) Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
B. IFC – (ii) International Development Association
C. MIGA – (iii) International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes
D. ICSID – (iv) International Finance Corporation
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
(c) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
Answer:
(c) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
III. State whether the statements are true or false.
Question 1.
(i) Functions of IBRD is called
(a) Investment for productive purposes
(b) Provision of loans and guarantees.
(ii) Functions of IBRD is called
(a) Balanced growth of International trade
(b) Promotion of foreign private investment.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
![]()
Question 2.
Objectives of WTO are
(i) To ensure reduction of tariff and other barriers.
(ii) Low level of standard of living.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 3.
(i) GATS is the first multilateral set of rules covering trade in services like Banking, Insurance, Transportation, Communication, etc.
(ii) GATS are related to conditions or restrictions in respect of Foreign Investment.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
![]()
Question 4.
Major objectives of SAARC
(i) To accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region.
(ii) To promote and strengthen collective self – reliance among the countries of South Asia.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 5.
Major Functions of the ASEAN
(i) It fosters co – operations in many areas including agriculture.
(ii) It paves way for market and investment opportunities for the all nations.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
IV. Which is the following is correctly matched.
Question 1.
(a) ITO – 1944
(b) World bank – 1946
(c) WTO – 1947
(d) IMF – 1995
Answer:
(a) ITO – 1944
Question 2.
(a) World Trade Organisation – Africa
(b) World Bank – Geneva
(c) International Monetary Fund – Washington DC
(d) GATT – Australia
Answer:
(c) International Monetary Fund – Washington DC
![]()
Question 3.
(a) Objectives of IMF – To promote textiles
(b) Functions of IMF – Exchange stability
(c) Facilities offered by IMF – Basic Debit Facility
(d) Achievements of IMF – Country discipline and co-operation
Answer:
(b) Functions of IMF – Exchange stability
Question 4.
(a) World Bank’s procedure – Loans out of its own fund
(b) Functions of IBRD – Promotion of government investment
(c) World Bank – Grants loans for Industry
(d) IDA – High interest of the loan
Answer:
(c) World Bank – Grants loans for Industry
![]()
Question 5.
(a) WTC headquarter – Newyork – USA
(b) WTO conference held at – Australia
(c) WTO Secretary General – Kazakhstan
(d) GATS service like – Industries
Answer:
(a) WTC headquarter – Newyork – USA
V. Which is the following is not correctly matched.
Question 1.
(a) MFA agreement – Textiles and garments
(b) WTO achievements – BOP problems has declined
(c) TRIPS – The dependence of LDCs on advanced countries for seeds, fertilizers, drugs has increased
(d) AOA – Trade development
Answer:
(d) AOA – Trade development
Question 2.
(a) Head quarters of SAARC – Kathmandu
(b) Member countries of IMF – 189
(c) World Trade Organisation – Geneva
(d) Long term loan – SAARC
Answer:
(d) Long term loan – SAARC
![]()
Question 3.
(a) GATT – WTO
(.b) SDR – 1969
(c) ITO – 1944
(d) SAARC – Investment
Answer:
(d) SAARC – Investment
Question 4.
(a) ASEAN – Bangkok
(b) IFC – 1996
(c) BRICS – 2001
(d) WTO conference – Singapore in 1996
Answer:
(b) IFC – 1996
![]()
Question 5.
(a) World Bank – 1945
(b) IFC – World Bank Group
(c) IBRD – World Bank
(d) SDRs – Monetary
Answer:
(d) SDRs – Monetary
VI. Pick the odd one out.
Question 1.
Objectives of WTO
(a) To ensure reduction of tariff and other barriers
(b) To eliminate discrimination in trade
(c) To facilitate low standard of living
(d) To facilitate optimal use of world’s resources
Answer:
(c) To facilitate low standard of living
Question 2.
WTO Agreements
(a) TRIPs
(b) TRIMs
(c) GAS
(d) GATS
Answer:
(c) GAS
![]()
Question 3.
Trade Blocks
(a) A free trade area
(b) A custom union
(c) Big market
(d) An economic union
Answer:
(c) Big market
Question 4.
ASEAN member countries
(a) Indonesia
(b) Malaysia
(c) Philippines
(d) America
Answer:
(d) America
![]()
Question 5.
Objectives of BRICs
(a) To increase trade co-operation by making an exclusive trade block
(b) To increase regional co-operation
(c) This group of nations is expecially meant for North-North frame work for co-operation
(d) To create a seperate trade block made for developing countries for trade co-operation
Answer:
(c) This group of nations is expecially meant for North-North frame work for co-operation
VII. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): BRICS is the acronym for an association of five major emerging national economies Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
Reason (R): Originally the first four were grouped as “BRIC” before the Induction of South Africa in 2010.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 2.
Assertion (A): SAARC is promote the welfare of the people of South Asia and improve their quality of life.
Reason (R): To strengthen co-operation with other under developing countries.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): TRIMs are related to conditions or restrictions in respect of foreign investment in the country.
Reason (R): TRIMs calls for introducing equal treatment for Indian companies.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 4.
Assertion (A): WTO are to ensure reduction of tariff and other barriers.
Reason (R): WTO are standard of living is very low.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The Dunkel Draft, formulated by Arthur Dunkel, its Secretary General became the base for WTO.
Reason (R): The first WTO conference was held at Singapore in 1996.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 6.
Assertion (A): IMF objectives are facilitate faster and balanced growth of Internal trade.
Reason (R): IMF objectives are to promote international monetary co-operation among the member nations.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 1.
Write IMF Functions group?
Answer:
The functions of the IMF are grouped under three heads.
- Financial – Assistance to correct short and medium tenn deficit in BOP;
- Regulatory – Code of conduct and
- Consultative – Counseling and technical consultancy.
![]()
Question 2.
Define IBRD?
Answer:
- The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), otherwise called the World Bank (WB) was established in 1945 under the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944.
- The purpose is to bring about a smooth transition from a war-time to peace-time economy.
- It is known as a sister institution along with the International Monetary Fund.
- The membership in International Monetary Fund is a prerequisite to become a member of IBRD.
- The IBRD was established to provide long term financial assistance to member countries.
Question 3.
Write the World bank activities of Rural areas?
Answer:
The bank now also takes interest in the activities of the development of rural areas such as:
- Spread of education among the rural people
- Development of roads in rural areas and
- Electrification of the villages.
![]()
Question 4.
Define World Trade Centre?
Answer:
- The WTO was established in 1995 as a successor to the GATT.
- It is a new international organization set up as a permanent body and is designed to play the role of watch dog in the spheres of trade in goods and services, foreign investment and intellectual property rights.
- The Dunkel Draft, formulated by Arthur Dunkel, its Secretary General became the base for WTO.
Question 5.
Define World Trade Organisation?
Answer:
- WTC headquarters located at New York, USA.
- It featured the landmark Twin Towers which was established on 4th April 1973.
- Later it was destroyed on 11th September 2001 by the craft attack.
- It brings together businesses involved in international trade from around the globe.
![]()
Question 6.
What is meaning of SAPTA, SAIC, SADF?
Answer:
- SAARC Preferential Trading Agreement (SAPTA)
- SAARC Agricultural Information Centre (SAIC)
- South Asian Development Fund (SADF)
Question 7.
Write the ‘ASEAN’ member of countries?
Answer:
ASEAN was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok by the five original member countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
Question 8.
Who are “dialogue partners”?
Answer:
The ASEAN, there are six “dialogue partners” which have been participating in its deliberations. They are China, Japan, India, South Korea, New Zealand and Australia.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Brief notes on India and IMF?
Answer:
India and IMF:
1. Till 1970, India stood fifth in the Fund and it had the power to appoint a permanent Executive Director.
2. India has been one of the major beneficiaries of the Fund assistance.
3. It has been getting aid from the various Fund Agencies from time to time and has been regularly repaying its debt.
4. India’s current quota in the IMF is SDRs (Special Drawing Rights) 5,821.5 million, making it the 13th largest quota holding country at IMF with shareholdings of 2.44%.
5. Besides receiving loans to meet deficit in its balance of payments, India has benefited in certain other respects from the membership of the Fund.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the objectives of World Bank?
Answer:
The following are the objectives of the World Bank:
- To help member countries for economic reconstruction and development.
- To stimulate long-run capital investment for restoring Balance of Payments (BoP) equilibrium and thereby ensure balanced development of international trade among the member nations.
- To provide guarantees for loans meant for infrastructural and industrial projects of member nations.
- To help war ravaged economies transform into peace economies.
- To supplement foreign private investment by direct loans out of its own funds for productive purposes.
Question 3.
Explain the objectives of WTO?
Answer:
- To ensure reduction of tariff and other barriers.
- To eliminate discrimination in trade.
- To facilitate higher standard of living.
- To facilitate optimal use of world’s resources.
- To enable the LDCs to secure fair share in the growth of international trade.
- To ensure linkages between trade policies, environmental policies and sustainable development.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the TRIPs agreement?
Answer:
Agreement on Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPs):
1. Intellectual Property Rights include copy right, trade marks, patents, geographical indications, trade secrets, industrial designs, etc.
2. TRIPS Agreement provides for granting product patents instead of process patents.
3. The period of protection will be 20 years for patents, 50 years for copy rights, 7 years for trade marks and 10 years for layout designs.
4. As a result of TRIPS, the dependence of LDCs on advanced countries for seeds, drugs, fertilizers and pesticides has increased.
5. Farmers are depending on the industrial firm for their seeds.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the functions of WTO?
Answer:
The following are the functions of the WTO
1. It facilitates the implementation, administration and operation of the objectives of the Agreement and of the Multilateral Trade Agreements.
2. It provides the forum for negotiations among its members, concerning their multilateral trade relations in matters relating to the agreements.
3. It administers the Understanding on Rules and Procedures governing the Settlement of Disputes.
4. It cooperates with the IMF and the World Bank and its affiliated agencies with a view to achieving greater coherence in global economic policy making.
Question 6.
Explain the functions of ASEAN?
Answer:
Functions of the ASEAN:
1. It facilitates free movement of goods, services and investments within ASEAN by creating a single regional market like the European Union.
2. It provides free access to the marketers of one member country to the markets of all other member countries, thus fostering growth in the region.
3. It improves business competitiveness between businesses from different countries and also narrow developmental gaps between member countries.
4. It paves way for market and investment opportunities for the member nations.
5. It fosters co – operations in many areas including industry and trade.
All the ASEAN economies experienced a great economic crisis in the year 1997.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the major achievements of WTO?
Answer:
The major achievements of WTO are as follows
1. Use of restrictive measures for BoP problems has declined markedly;
2. Services trade has been brought into the multilateral system and many countries, as in goods, are opening their markets for trade and investment;
3. The trade policy review mechanism has created a process of continuous monitoring of trade policy developments.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 1.
Explain the IMF functions?
Answer:
Functions of IMF:
(I) Bringing stability in exchange rate:
The IMF is maintaining exchange rate stability and emphasising devaluation criteria, restricting members to go in for multiple exchange rates and also to buy or sell gold at prices other than declared par value. .
(II) Correcting BOP Disequilibrium:
The IMF is helping the member countries in eliminating or minimizing the short-period disequilibrium in their balance of payments either by selling or lending foreign currencies to the member nation.
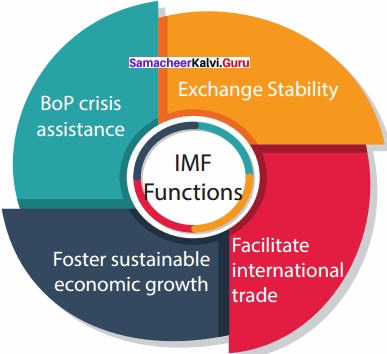
(III) Determining par values:
1. IMF enforces the system of determination of par values of the currencies of the member countries.
2. According to the Articles of Agreement of the IMF, every member nation should declare the par value of its currency in terms of gold or US dollars.
3. Under this article, IMF ensures smooth working of the international monetary system, in favour of some developed countries.
(IV) Balancing demand and supply of currencies:
1. IMF is entrusted with the important function of maintaining balance between demand and supply of various currencies.
2. The Fund (IMF) can declare a currency as scarce currency which is in great demand and can increase its supply by borrowing it from the country concerned or by purchasing the same currency in exchange of gold.
(V) Reducing trade restrictions:
The Fund also aims at reducing tariffs and other trade barriers imposed by the member countries with the purpose of removing restrictions on remittance of funds or to avoid discriminating practices.
(VI) Providing credit facilities:
1. IMF is providing different borrowing and credit facilities with the objective of helping the member countries.
2. These credit facilities offered by it include basic credit facility, extended fund facility for a period of three years, compensatory financing facility and structural adjustment facility.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly explain facilities offered by IMF?
Answer:
Facilities offered by IMF:
The Fund has created several new credit facilities for its members. Chief among them are:
(I) Basic Credit Facility:
- The IMF provides financial assistance to its member nations to overcome their temporary difficulties relating to balance of payments.
- A member nation can purchase from the Fund other currencies or SDRs, in exchange for its own currency, to finance payment deficits.
- The loan is repaid when the member repurchases its own currency with other currencies or SDRs.
- A member can unconditionally borrow from the Fund in a year equal to 25% of its quota.
- This unconditional borrowing right is called the reserve tranche.
(II) Extended Fund Facility:
- Under this arrangement, the IMF provides additional borrowing facility up to 140% of the member’s quota, over and above the basic credit facility.
- The extended facility is limited for a period up to 3 years and the rate of interest is low.
(III) Compensatory Financing Facility:
- In 1963, IMF established compensatory financing facility to provide additional financial assistance to the member countries, particularly primary producing countries facing shortfall in export earnings.
- In 1981, the coverage of the compensatory financing facility was extended to payment problem caused by the fluctuations in the cost of cereal inputs.
(IV) Buffer Stock Facility:
- The buffer stock financing facility was started in 1969.
- The purpose of this scheme was to help the primary goods (food grains) producing countries to finance contributions to buffer stock arrangements for the stabilisation of primary product prices.
(V) Supplementary Financing Facility:
Under the supplementary financing facility, the IMF makes temporary arrangements to provide supplementary financial assistance to member countries facing payments problems relating to their present quota sizes.
(VI) Structural Adjustment Facility:
1. The IMF established Structural Adjustment Facility (SAF) in March 1986 to provide additional balance of payments assistance on concessional terms to the poorer member countries.
2. In December 1987, the Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility (ESAF) was set up to augment the availability of concessional resources to low income countries.
3. The purpose of SAF and ESAF is to force the poor countries to undertake strong macroeconomic and structural programmes to improve their balance of payments positions and promote economic growth.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the achievements of World Bank?
Answer:
Achievements of World Bank:
The World Bank is said to be successful in achieving its primary objective of reconstruction and development of war ravaged nations. It helped greatly in the reconstruction of Europe after the World War II. It has been providing the developed and developing countries the same treatment in the process of growth.
(I) It is noted that the Bank’s membership has increased from the initial number of 30 countries to 68 countries in 1960 and to 151 countries in 1988. The IBRD has 189 member countries,
(II) The Bank grants medium and long-term loans (i.e., payable over a period of 15-20 years) for reconstruction and development purposes to the member countries. The actual term of a loan depends upon the estimated useful life of the equipment or plant financed.
(III) Initially the World Bank’s loans were mainly directed at the European countries for financing their programmes of reconstruction. Later it changed its development loan strategy and lays more emphasis of financing schemes for the poor masses of the developing countries.
(IV) The World Bank grants loans to member countries only for productive purposes particularly for agriculture, irrigation, power and transport. In other words, the Bank strengthens infrastructure needed for further development.
(V) The International Development Association (IDA), the Soft Loan Window of the Bank provides loans to UDCs at very low rate of interest. However, the economic inequality among the member-countries goes on increasing. Many African countries are yet to improve their economic status.
![]()
Question 4.
Bringout the objectives of SAARC?
Answer:
Objectives of SAARC:
According to Article I of the Charter of the SAARC, the objectives of the Association are as follows:
- To promote the welfare of the people of South Asia and improve their quality of life
- To accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region
- To promote and strengthen collective self – reliance among the countries of South Asia
- To contribute to mutual trust, understanding and appreciation of one another’s problems
- To promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in the economic, social, cultural, technical and scientific fields
- To strengthen co – operation with other developing countries
- To strengthen cooperation among themselves in international forums on matters of common interest
- To cooperate with international and regional organisations with similar aims and purposes.
![]()
Question 5.
Briefly explain achievements of SAARC?
Answer:
Achievements of SAARC:
1. The establishment of SAARC Preferential Trading Agreement (SAPTA) and reduction in tariff and non-tariff barriers on imports.
2. The setting up of Technical Committees for economic cooperation among SAARC countries relating to agriculture, communications, education, health and population, rural development, science and technology, tourism, etc.
3. SAARC has established a three-tier mechanism for exchanging information on poverty reduction programmes which is passed on to member countries.
4. SAARC Agricultural Information Centre (SAIC) in 1988 works as a central information institution for agriculture related resources like fisheries, forestry, etc.
5. South Asian Development Fund (SADF) for development projects, human resource development and infrastructural development projects. With all these tall claims, the inter- SAARC Trade has not gone beyond three percent in the last 30 years.