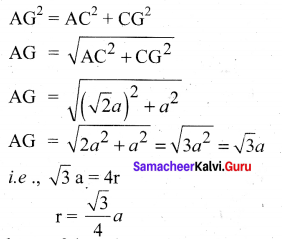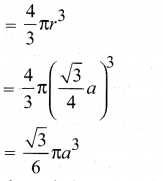Tamil Nadu 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Chemistry Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever: applicable
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are lo be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are lo be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are lo be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [15 × 1 = 15]
Question 1.
Which one of the following ore is best concentrated by froath – floatation method?
(a) Magnetite
(b) Haematite
(c) Galena
(d) Cassiterite
Answer:
(c) Galena
![]()
Question 2.
Which compound is used as flux in metallurgy?
(a) Boric acid
(b) Borax
(c) Diborane
(d) BF3
Answer:
(b) Borax
Question 3.
The shape of XeOF4 is
(a) T Shaped
(b) Pyramidal
(c) Square planar
(d) Square pyramidal
Answer:
(d) Square pyramidal
Question 4.
How many moles of acidified KMnO4 required to oxidise one mole of oxalic acid?
(a) 5
(b) 0.6
(c) 1.5
(s) 0.4
Answer:
(b) 0.6
Question 5.
The type of isomerism exhibited by [Pt(NH3)2 Cl2] ?
(a) coordination isomerism
(b) linkage isomerism
(c) optical isomerism
(d) geometrical isomerism
Answer:
(d) geometrical isomerism
![]()
Question 6.
The fraction of the total volume occupied by the atoms in a fcc is
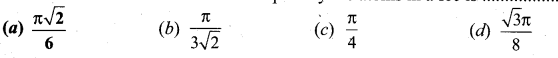
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{\pi \sqrt{2}}{6}\)
Question 7.
The half life period of a radioactive element is 140 days. After 280 days 1g of element will be
reduced to which amount of the following?
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/16
(c) 1/8
(d) 1/2
Answer:
(a) 1/4
Solution:
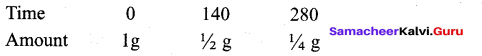
Question 8.
Which is not a Lewis base?
(a) BF3
(b) PF3
(c) CO
(d) F
Answer:
(a) BF3
Question 9.
During electrolysis of molten copper chloride, the time required to produce 0.2 mole of chlorine gas using a current of 2A is ………..
(a) 32.66 min
(b) 321.66 min
(c) 378 min
(d) 260 min
Solution:
m = ZIt (mass of 1 mole of Cl2 gas = 71) m
t = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{Zl}}\) (mass of 0.2 mole of Cl2 gas = 14.2 g)

Question 10.
Smoke is a colloidal solution of …………
(a) Solid in gas
(b) Gas in gas
(c) Liquid in gas
(d) Gas in liquid
Answer:
(c) Liquid in gas
Question 11.
Iso propyl benzene on oxidation in presence of air and dilute acid gives
(a) C6H5COOH
(b) C6H5COCH3
(c) C6H5COC6H5
(d) C6H5OH
Answer:
(d) C6H5OH
![]()
Question 12.
But-2 ene on ozonolyis followed by subsequent cleavage with Zn and water gives …………….
(a) ethanal
(b) Propanal
(c) Propanone
(d) Methanal
Answer:
(a) ethanal
Question 13.
3(i)
This reaction is known as
(a) Friedal- craft’s reaction
(b) HVZ reaction
(c) Schotten – Baumann reaction
(d) Cannizaro reaction
Answer:
(c) Schotten – Baumann reaction
Question 14.
The pyrimidine bases present in DNA are
(a) Cytosine and Adenine
(b) Cytosine and Guanine
(c) Cytosine and Thiamine
(d) Cytosine and Uracil
Answer:
(c) Cytosine and Thiamine
Question 15.
Nylon is an example of
(a) Polyamide
(b) Polythene
(c) Polyester
(d) Polysaccharide
Answer:
(a) Polyamide
Part – II
Answer any six questions. Question No. 24 is compulsory. [6 × 2 = 12]
Question 16.
Write a test to identify borate radical?
Answer:
When boric acid or borate salt is heated with ethyl alcohol in presence of concentrated H2SO4, an ester triethyl borate is formed. The Vapour of this ester bums with a green edged flame and this reaction is used to identify the presence of borate.
![]()
Question 17.
How is pure phosphine prepared from phosphorous acid ?
Answer:
Phosphine is prepared in pure form by heating phosphorous acid.
![]()
Question 18.
What are ionisation isomers? Explain with an example.
Answer:
1. Ionisation isomerism arises when an ionisable counter ion (simple ion) itself can act as a ligand.
2. The exchange of such counter ions with one or more ligands in the coordination entity will result in ionisation isomers. These isomers will give different ions in solution.
3. For example, consider the coordination compound [Pt (en)2 Cl2]Br2. In this compound, both Br– and Cl– have the ability to act as a ligand and the exchange of these two ions result in a different isomer [Pt(en)2Br2]Cl2. In solution, the first compound gives Br– ions while the later gives Cl ions and hence these compounds are called ionization isomers.
Question 19.
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one example.
Answer:
A second order reaction can be altered to a first order reaction by taking one of the reactant in large excess, such reaction is called pseudo first order reaction.
Let us consider the acid hydrolysis of an ester,
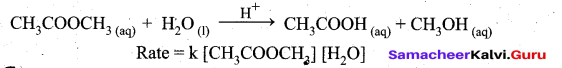
If the reaction is carried out with the large excess of water, there is no significant change in the concentration of water during hydrolysis, i.e., concentration of water remains almost a constant.
Now we can define k [H2O] = k’
.’. The above rate equation becomes, Rate = k’ [CH3COOCH3]
Thus it follows first order kinetics.
![]()
Question 20.
State Faraday’s second law of electrolysis.
Answer:
When the same quantity of charge is passed through the solutions of different electrolytes, the , amount of substances liberated at the respective electrodes are directly proportional to their electrochemical equivalents.
Question 21.
How will you convert glycerol into acrolein?
Answer:
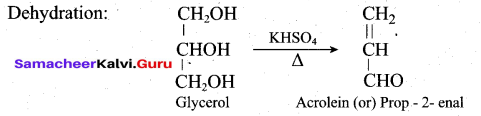
Question 22.
Give any four differences between DNA and RNA.
DNA
- It is mainly present in nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast
- It contains deoxyribose sugar
- It’s life time is high
- It is stable and not hydrolysed easily by alkalis
- It can replicate itself
RNA
- It is mainly present in cytoplasm, nucleolus and ribosomes
- It contains ribose sugar
- It is Short lived
- It is unstable and hydrolyzed easily by alkalis
- It cannot replicate itself. It is formed from DNA.
Question 23.
Write short notes on Antioxidants.
Answer:
- Antioxidants are substances which retard the oxidative deteriotations of food. Food containing fats and oils is easily oxidised and turn rancid.
- To prevent the oxidation of fats and oils, chemical BHT (butyl hydroxy toluene), BHA (butylated hydroxy anisole) are added as antioxidants.
- These materials readily undergo oxidation by reacting with free radicals generated by the oxidation of oils there by stop the chain reaction of oxidation of food.
- Sulphur dioxide, sulphites are also used as antioxidant and also act as antimicrobial agents and
enzyme inhibitors.
Question 24.
50ml of 0.05M HNO3 is added to 50ml of 0.025M KOH. Calculate the pH of the resultant solution.
Answer:
Number of moles of HNO3 = 0.05 × 50 × 10-3 = 2.5 × 10-3
Number of moles of KOH = 0.025 × 50 × 10-3 = 1.25 × 10-3
Number of moles of HNC3 after mixing = 2.5 × 10-3 – 1.5 × 10 -3 = 1.25 × 10-3
![]()
After mixing, total volume = 100 ml = 100 × 10-3 L
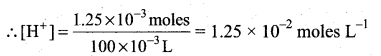
pH = – log [H+]
pH = -log(l.25 × 10-2) = 2 – 0.0969
= 1.9031
Part – III
Answer any six questions. Question No. 33 is compulsory. [6 × 3 = 18]
Question 25.
Explain the electro metallurgy of aluminium.
Answer:
Electrochemical extraction of aluminium -Hall-Herold process: In this method, electrolysis is carried out in an iron tank lined with carbon, which acts as a cathode. The carbon blocks immersed in the electrolyte acts as a anode. A 20% solution of alumina, obtained from the bauxite ore is mixed with molten cyrolite and is taken in the electrolysis chamber. About 10% calcium chloride is also added to the solution. Here calcium chloride helps to lower the melting point of the mixture. The fused mixture is maintained at a temperature of above 1270 K. The chemical reactions involved in this process are as follows:
Ionisation of alumina : Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
Reaction at cathode : 2Al3+ (melt) + 6e– → 2Al (l)
Reaction at anode : 6O2- (melt) → 3O2 + 12e–
Since carbon acts as anode the following reaction also takes place on it.
C (s) + O2- (melt) → CO + 2e– ; C(s) + 2O2- (melt) → CO2 + 4e–
Due to the above two reactions, anodes are slowly consumed during the electrolysis. The pure aluminium is formed at the cathode and settles at the bottom. The net electrolysis reaction can be written as follows:
4Al3+ (melt) + 6O2- (melt) + 3C(s) → 4Al(l) + 3CO2(g)
![]()
Question 26.
Give the uses of helium.
Answer:
- Helium and oxygen mixture is used by divers in place of air oxygen mixture. This prevents the painful dangerous condition called bends.
- Helium is used to provide inert atmosphere in electric arc welding of metals
- Helium has lowest boiling point hence used in cryogenics (low temperature science).
- It is much less denser than air and hence used for filling air balloons.
Question 27.
Explain chromyl chloride Test.
Answer:
(i) When potassium dichromate is heated with any chloride salt in the presence of Conc.H2SO4, orange red vapours of chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) is evolved. This reaction is used to confirm the presence of chloride ion in inorganic qualitative analysis.

(ii) The chromyl chloride vapours are dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution and then acidified with acetic acid and treated with lead acetate. A yellow precipitate of lead chromate is obtained. Cr02Cl2 + 4NaOH -► Na2Cr04 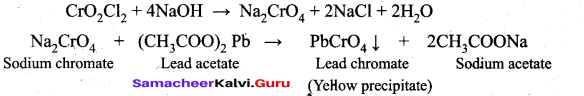
Question 28.
A face centred cubic solid of an element (atomic mass 60 g mol ) has a cube edge of 4A. Calculate its density.
Answer:
For FCC unit cell n 4
Edge length(a) = 4A = 4 × 10-8cm
Mass (M) = 60 g mol-1
Dcnsity(ρ) = ?

Question 29.
Describe the construction of Daniel cell and write its cell reaction.
Answer:
The separation of half reaction is the basis for the construction of Daniel cell. It consists of two half cells.
Oxidation half cell: The metallic zinc strip that dips into an aqueous solution of zinc sulphate taken in a beaker.
Reduction half cell: A copper strip that dips into an aqueous solution of copper sulphate taken in a beaker.
Joining the half cell : The zinc and copper strips are externally connected using a wire through a switch (k) and a load (example: volt meter). The electrolytic solution present in the cathodic and anodic compartment are connected using an inverted U tube containing a agar-agar gel mixed with an inert electrolyte such as KCl, Na2SO4 etc., The ions of inert electrolyte do not react with other ions present in the half cells and they are not either oxidised (or) reduced at the electrodes. The solution in the salt bridge cannot get poured out, but through which the ions can move into (or) out of the half cells.
When the switch (k) closes the circuit, the electrons flows from zinc strip to copper strip. This is due to the following redox reactions which are taking place at the respective electrodes.
Anodic oxidation:- The electrode at which the oxidation occur is called the anode. In Daniel cell, the oxidation take place at zinc electrode, i.e., zinc is oxidised to Zr2+ ions and the electrons. The Zn2+ ions enters the solution and the electrons enter the zinc metal, then flow through the external wire and then enter the copper strip. Electrons are liberated at zinc electrode and hence it is negative (- ve).
Zn(s) → Zn2++(aq) + 2e–
(loss of electron-oxidation)
Cathodic reduction:
As discussed earlier, the electrons flow through the circuit from zinc to copper, where the Cu ions in the solution accept the electrons, get reduced to copper and the same get deposited on the electrode. Here, the electrons are consumed and hence it is positive (+ve).
cu2+ 2e– cu(s)( gain of electron – reduction)
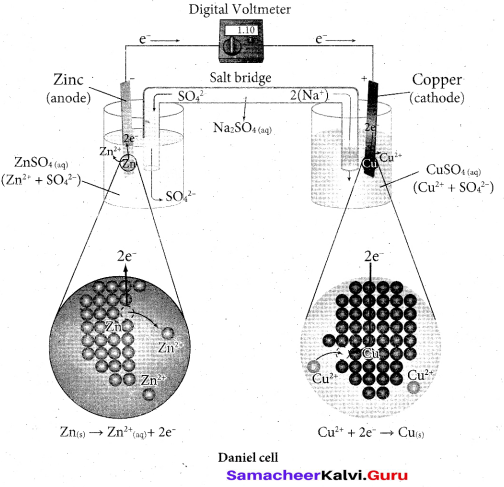
Salt bridge: -The electrolytes present in two half cells are connected using a salt bridge. We have learnt that the anodic oxidation of zinc electrodes results in the increase in concentration of Zn2+ in solution, i.e., the solution contains more number of Zn2+ ions as compared to SO2-4 and hence the solution in the anodic compartment would become positively charged. Similarly, the solution in the cathodic compartment would become negatively charged as the Cu2+ ions are reduced to copper i.e., the cathodic solution contain more number of SO2-4 ions compared to Cu2+ .
Completion of circuit:- Electrons flow from the negatively charged zinc anode into the positively charged copper electrode through the external wire, at the same time, anions move towards anode and cations move towards the cathode compartment. This completes the circuit.
Consumption of Electrodes :- As the Daniel cell operates, the mass of zinc electrode gradually decreases while the mass of the copper electrode increases and hence the cell will function until the entire metallic zinc electrode is converted into Zn2+ or the entire Cu2+ ions are converted into mettalic copper.
Daniel cell is represents as
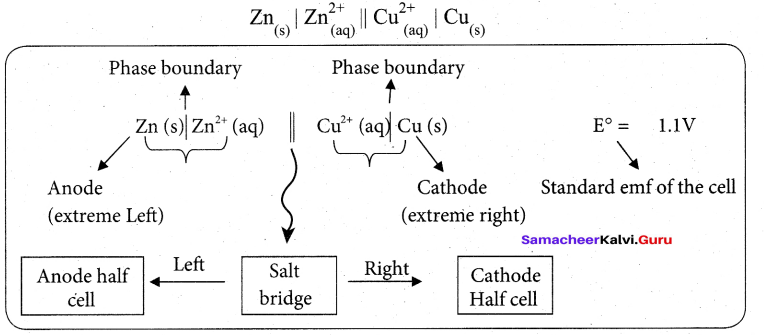
Question 30.
Write short notes on (i) Negative catalyst (ii) Phase transfer catalyst
Answer:
(i) Negative catalyst:
(i) In certain reactions, presence of certain substances decreases the rate of the reaction. Such
substances are called negative catalyst and the process is called negative catalysis.
(ii) In oxidation of chloroform, ethanol decreases the rate of the reaction and ethanol act as negative catalyst.
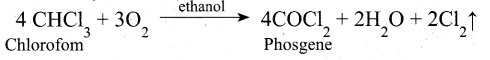
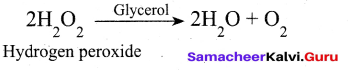
(iii) Decomposition of H202 rate is decreased by glycerol and it act as negative catalyst
(ii) Phase transfer catalyst:
(i) Consider the reactant of a reaction is present in one solvent and the other reactant is present in an another solvent. The reaction between them is very slow, if the solvents are immisible.
(ii) As the solvents form separate phases, the reactants have to migrate across the boundary to react. But migration of reactants across the boundary is not easy. For such situation, a third solvent is added which is miscible with both. So, the phase boundary is eliminated the reactants freely mix and react fast.
(iii) But for large scale preparation of any product, use of a third solvent is not convenient as it . may be expensive. For such problems, phase transfer catalysis provides a simple solution, which avoids the use of solvents.
(iv) It directs the use of a phase transfer catalyst (a phase transfer reagent) to facilitate transport of a reactant in one solvent to other solvent where the second reactant is present. As the reactants are now brought together, they rapidly react and form the product.
(v) Example : Substitution of Cl– and CN– in the following reaction.
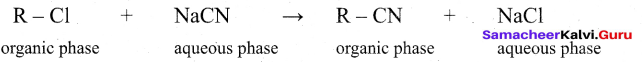
R Cl = 1- chloro octane
R CN = 1- cyano octane
(vi) By direct heating of two phase mixture of organic 1- chloro octane with aqueous sodium cyanide for several days, 1- cyano octane is not obtained. However, if a small amount of quartemary ammonium salt like tetra alkyl ammonium cation which has hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends, transports CN- from the aqueous phase to the organic phase using its hydrophilic end and facilitates the reactions with 1- chloro octane as shown below

(vii) So phase transfer catalyst, speeds up the reaction by transporting one reactant from one phase to another.
![]()
Question 31.
Explain the mechanism of Aldol condensation of acetaldehyde.
Answer:
In presence of dilute base NaOH, or KOH, two molecules of an aldehyde or ketone having α – hydrogen add together to give β- hydroxyl aldehyde (aldol) or β – hydroxyl ketone (ketol). The reaction is called aldol condensation reaction.
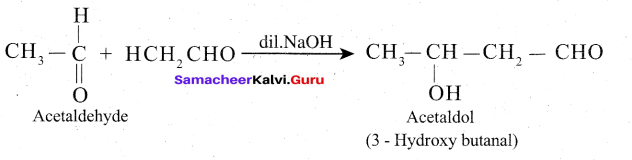
Mechanism
The mechanism of aldol condensation Of acetaldehyde takes place in three steps.
Step 1: The carbanion is formed as the a – hydrogen atom is removed as a proton by the base.

Step 2: The carbanion attacks the carbonyl carbon of another unionized aldehyde to form an alkoxide ion.
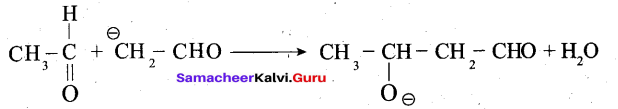
Step 3: The alkoxide ion formed is protonated by water to form aldol.
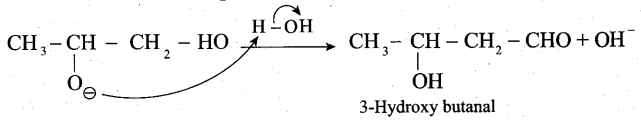
The aldol rapidly undergoes dehydration on heating with acid to form a, p unsaturated aldehyde.
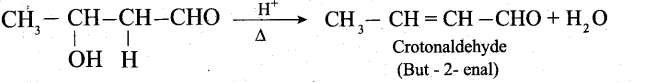
Question 32.
Explain the preparation of Nylon – 6,6 and Buna- S.
Answer:
Nylon 6,6 can be prepared by mixing equimolar adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine. With the elimination of water to form amide bonds.
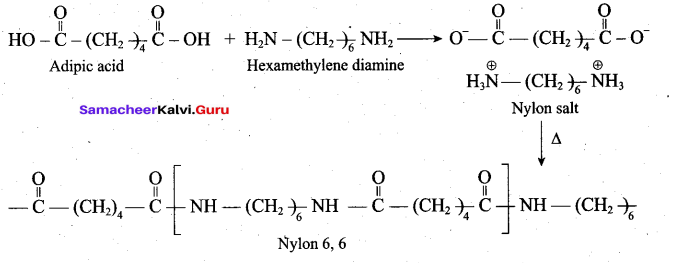
Buna – S is prepared by the polymerisation of buta -1,3 – diene and styrene in the ratio of 3:1 in the presence of sodium.
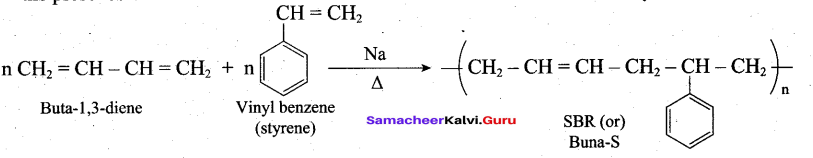
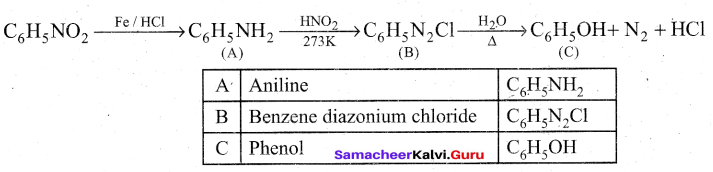
Question 33.
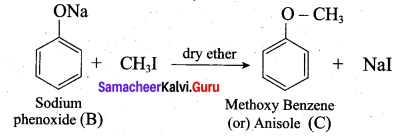
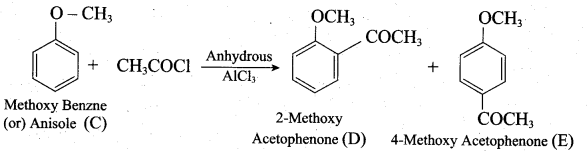
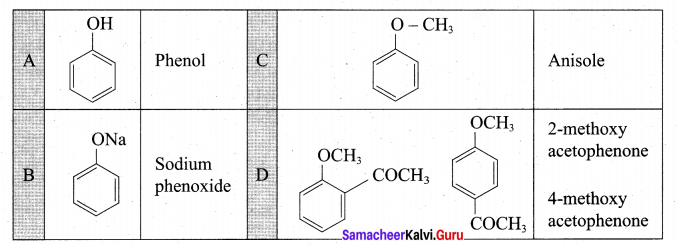
Identify A to C in the following sequence.
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 × 5 = 25]
Question 34.
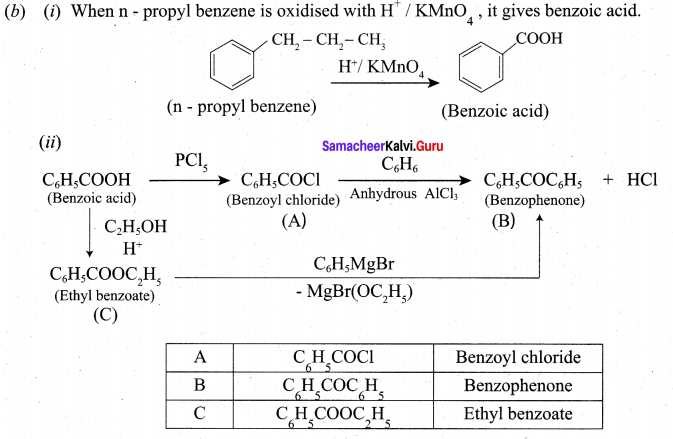
(a) (i) Explain how gold ore is leached by cyanide process
(ii) Explain the classification of lnosilicates
[OR]
(b) (i) What are interhalogen compounds? Give examples
(ii) Explain the preparation of KMn04.
Answer:
(a) (i) 4Au (s) + 8CN– (aq) + 2H2O(aq) + O2(g)→ 4Au(CN)2]–(aq) + 4OH–
2[Au(CN)2]–(aq) + Zn (s) → 2Au (s) + [Zn(CN)4]-2(aq)
In the first reaction Au changes into Au+, i.e. its oxidation takes place. In the second reaction: Au+ → Au° (i.e. ) reduction takes place.
(ii) Ino silicones: Silicates which contain V number of silicate units liked by sharing two or more oxygen atoms are called inosilicates. They are further classified as chain silicates and double chain silicates.
Chain silicates (or pyroxenes): These silicates contain [(SiO3)n]2n- ions formed by linking ‘ri number of tetrahedral [SiO4]4- units linearly. Each silicate unit shares two of its oxygen atoms with other units.
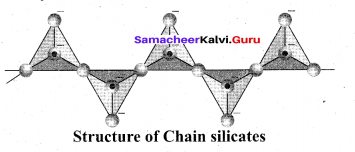
Example: Spodumene – LiAl(SiO3)2 Double chain silicates (or amphiboles): These silicates contains [Si4O11] n6n-. ions. In these silicates there are two different types of tetrahedra : (i) Those sharing 3 vertices (ii) those sharing only 2 vertices.
Examples:
Asbestos: These are fibrous and noncombustible silicates. Therefore they are used for thermal insulation material, brake linings, construction material and filters. Asbestos being carcinogenic silicates, their applications are restricted.
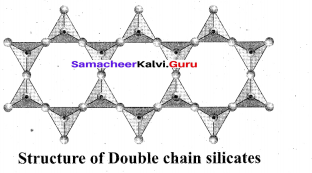
[OR]
(b) (i) Each halogen combines with other halogens to form a series of compounds called interhalogen compounds, e.g., ClF3, IF5, IF7
(ii) Potassium permanganate is prepared from pyrolusite (MnO2) ore. The preparation involves the following steps.
Conversion of MnO2 to potassium manganate:
Powdered ore is fused with KOH in the presence of air or oxidising agents like KNO3 A green coloured potassium manganate is formed.
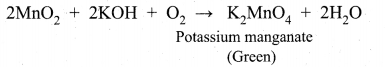
Oxidation of potassium manganate to potassium permanganate:
Potassium manganate can be oxidised in two ways, either by chemical oxidation or electrolytic oxidation.
Chemical oxidation: In this method potassium manganate is treated with ozone (O3) or chlorine to get potassium permanganate.
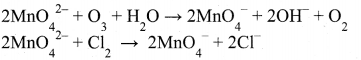
Electrolytic oxidation: In this method aqueous solution of potassium manganate is electrolyzed in the presence of little alkali.
K2MnO4 ⇌ 2K+ + MnO42-
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
Manganate ions are converted into permanganate ions at anode.
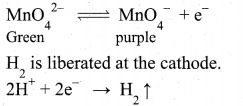
The purple coloured solution is concentrated by evaporation and forms crystals of potassium permanganate on cooling.
![]()
Question 35.
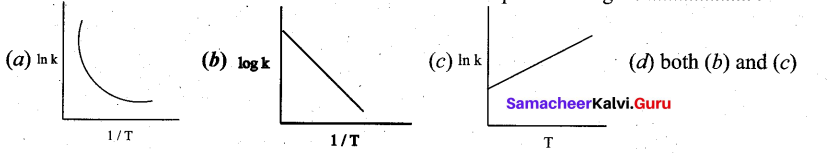
(a) (i) Explain [Fe(CN)6]3- is paramagnetic, using Crystal Field theory
(ii) What is schottky detect?
[OR]
(A) (0 Derive Henderson – Hassel balch equation
(ii) What is kohlraush’s law?
Answer:
(a) (i)
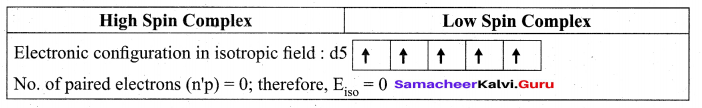
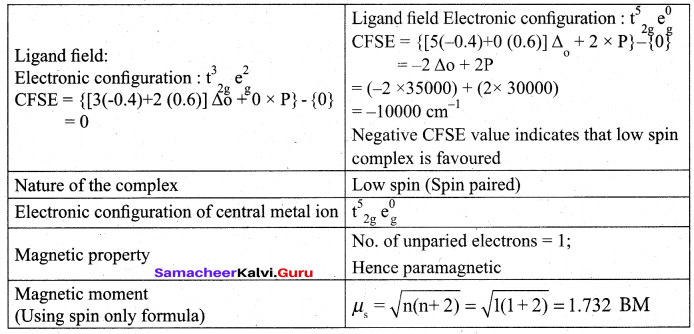
(ii) Schottky defect arises due to the missing of equal number of cations and anions from the crystal lattice. This effect does not change the stoichiometry of the crystal.Ionic solids in which the cation and anion are of almost of similar size show schottky defect. Example: NaCl.
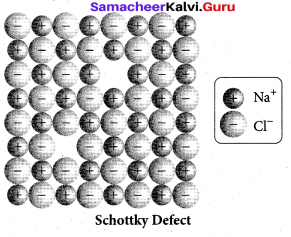
Presence of large number of schottky defects in a crystal, lowers its density.
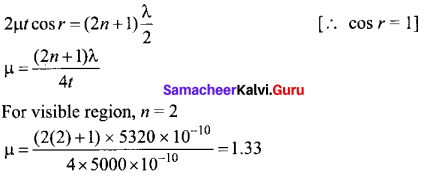
For example, the theoretical density of vanadium monoxide (VO) calculated using the edge length of the unit cell is 6.5 g cm-3 , but the actual experimental density is 5.6 g cm-3 .It indicates that there is approximately 14% Schottky defect in VO crystal. Presence of Schottky defect in the crystal provides a simple way by which atoms or ions can move within the crystal lattice.
[OR]
(b) (i) Henderson – Hasselbalch equation:
1. The concentration of hydronium ion in acidic buffer solution depends on the ratio of concentration of the weak acid to the concentration of its conjugate base present in the solution, i.e.,

2. The weak acid is dissociated only to a small extent. Moreover due to common ion effect, the dissociation is further suppressed and hence the equilibrium concentration of the acid is nearly equal to the initial concentration of the unionised acid. Similarly the concentration of the conjugate base is nearly equal to the initial concentration of the added salt.
![]()
3. [Acid] and [Salt] represent the initial concentration of the acid and salt, respectively used to prepare the buffer solution.
4. Taking logarithm on both sides of the equation
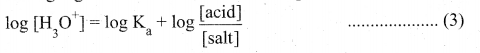
5. Reverse the sign on both sides
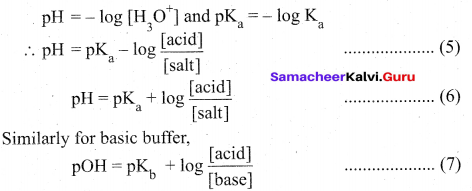
Equation (6) & (7) are called Henderson – Hasselbalch equations.
(ii) Kohlrauselrs law: It is defined as, at infinite dilution the limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivities of its constituent ions.
Question 36.
(a) (i) Explain Intermediate compound formation theory.
(ii) Write short notes on ultra filtration.
[OR]
(b) How the following conversions are effected?
(i) Phenol → Salicylaldehvde
(ii) Phenol → Phenolphthalein
(iii) Glycol → 1.4dioxane
Answer:
(a) (i) The intermediate compound formation theory:
A catalyst acts by providing a new path with low energy of activation.. In homogeneous catalysed reactions a catalyst may combine with one or more reactant to form an intermediate which reacts with other reactant or decompose to give products and the
catalyst is regenerated.
Consider the reactions:
A+B → AB (1)
A+C →AC (intermediate) (2)
C is the catalyst
AC+B → AB+C (3)
Activation energies for the reactions (2) and (3) are lowered compared to that of (1). Hence the formation and decomposition of the intermediate accelerate the rate of the reaction.
(ii) Ultrafiltration:
- The pores of ordinary filter papers permit the passage of colloidal solutions. In ultrafilteration, the membranes are made by using collodion, cellophane or visiking.
- When a colloidal solution is filtered using such a filter, colloidal particles are separated on the filter and the impurities are removed as washings.
- This process is quickened by application of pressure. The separation of sol particles from electrolyte by filtration through an ultrafilter is called ultrafiltration.
- Collodian is 4% solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and water.
[OR]
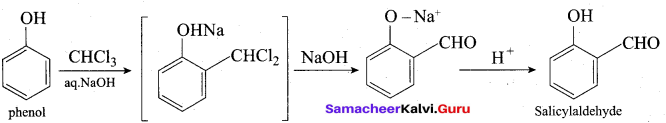
(b) (i) Phenol → Salicylaldehyde:
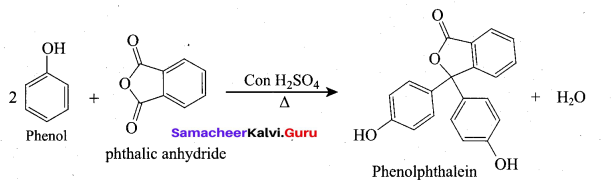
(ii) Phenol → Phenolphthalcin:
On heating phenol with phthalic anhydride in presence of con.H2S04, phenolphthalein
is obtained.
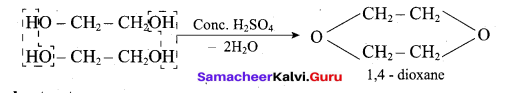
(iii) Glycol →1,4 dioxane:
When distilled with Conc.112S04, glycol forms 1, 4-dioxane
![]()
Question 37.
(a) Write short notes on
(i) Mustard oil reactions
(ii) Carbylamine reaction
(iii) Gabriel pathalimide synthesis
[OR]
(b) Explain the structure of Fructose.
Answer:
(a) (i) Mustard oil reactions:
When primary amines are treated with carbon disulphide (CS2), N – alkyldithio carbonic acid is formed which on subsequent treatment with HgCl2, give an alkyl isothiocyanate.
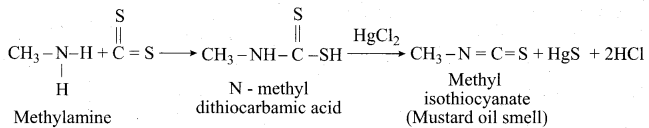
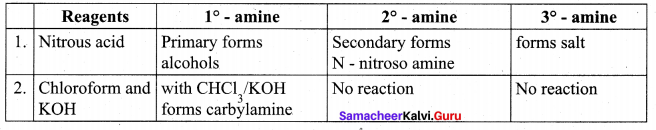
(ii) Carbylamine reaction:
Aliphatic (or) aromatic primary amines react with chloroform and alcoholic KOH to give isocyanides (carbylamines), which has an unpleasant smell. This reaction is known as carbylamines test. This test is used to identify the primary amines.
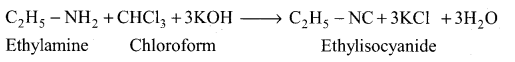
(iii) Gabriel pathalimide synthesis:
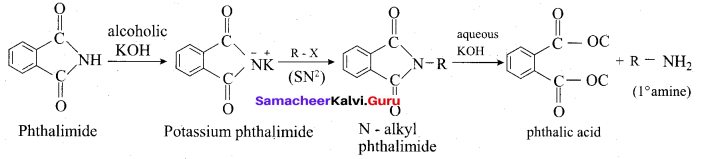
Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of Aliphatic primary amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic KOH forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis gives primary amine.
[OR]
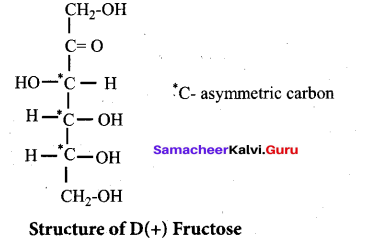
Structure of Fructose:
- Elemental analysis and molecular weight determination of fructose show that it has the molecular formula C6H12O6.
- Fructose on reduction with HI and red phosphorus gives a mixture of n – hexane (major product) and 2 – iodohexane (minor product). This reaction indicates that the six carbon atoms in fructose are in a straight chain.

- Fructose reacts with NH2OH and HCN. It shows the presence of carbonyl groups in the molecules of fructose.
- Fructose reacts with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine to form penta acetate. This reaction indicates the presence of five hydroxyl groups in a fructose molecule.
- Fructose is not oxidized by bromine water. This rules out the possibility of presence of an aldehyde (-CHO) group.
- Partial reduction of fructose with sodium amalgam and water produces mixtures of sorbitol and mannitol which are epimers at second carbon. New asymmetric carbon is formed at C-2. This confirms the presence of keto group.
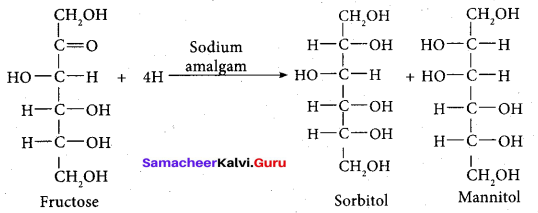
On oxidation with nitric acid, it gives glycolic acid and tartaric acids which contain smaller number of carbon atoms than in fructose.
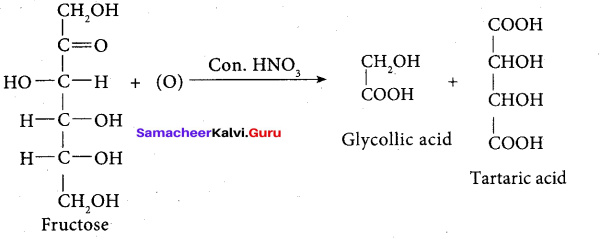
This shows that a keto group is present in C-2. It also shows the presence of 10 alcoholic groups at C- 1 and C- 6. From the above reaction the structure of fructose is
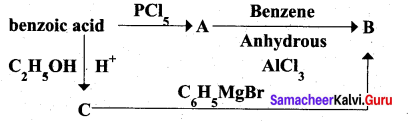
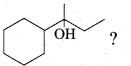
Question 38.
(a) (i) A first order reaction is 40% complete in 50 minutes. Calculate the value of the rate constant. In what time will the reaction be 80% complete?
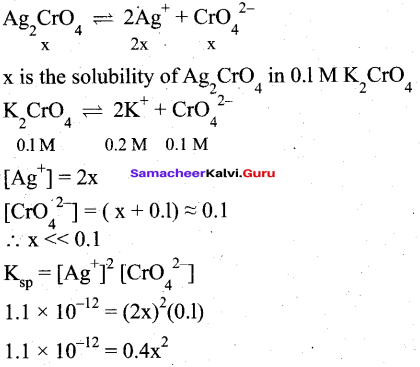
(ii) Ksp of Ag2CrO4 is 1.1 x 10-12. What is the solubility of Ag2CrO4 in 0.1M K2CrO4?
[OR]
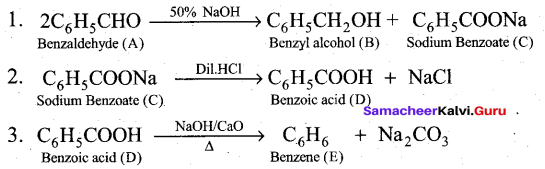
(b) Compound A of molecular formula C7H6O reduces Tollen’s reagent when A reacts with 50% NaOH gives compound B of molecular formula C7H8O and C of molecular formula C7H5O7Na. Compound C on treatment with dil.HCl gives compound D of molecular formula C7H6O2. When D is heated with sodalime gives compound E.
Identify A,B,C,D & E. Write the corresponding equations.
Answer:
(a) (i) 1. For the first order reaction k =\(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{a}{(a-x)}\)
Assume, a = 100 %, x = 40%, t = 50 minutes
Therefore, a – x = 100 – 40 = 60.
k = (2.303/ 50) log (100/ 60)
k = 0.010216 min-1
Hence the value of the rate constant is 0.010216 min-1
2. t = ?, when x = 80%
Therefore, a – x = 100 – 80 = 20
From above, k = 0.010216 min-1
t = (2.303/0.010216) log (100/20)
t = 157.58 min
The time at which the reaction will be 80% complete is 157.58 min.
(ii)
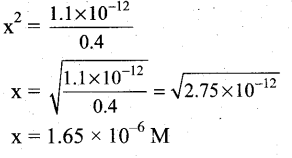
[OR]
(b)

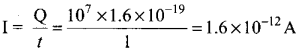
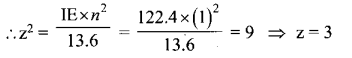
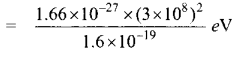
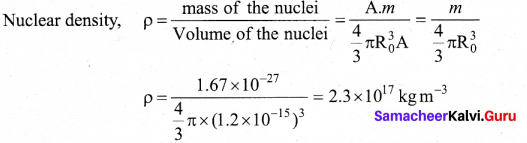
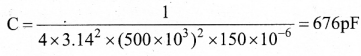
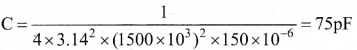


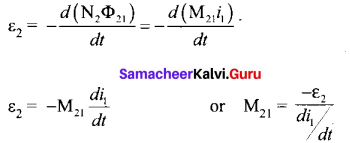
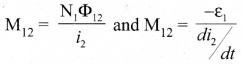























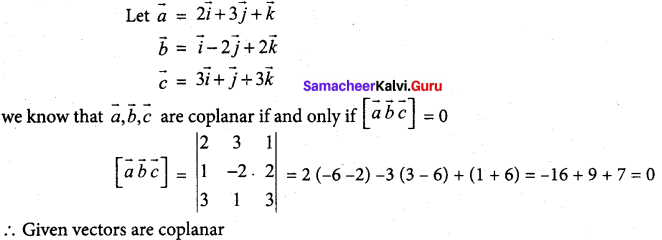
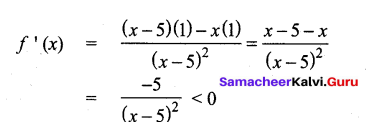


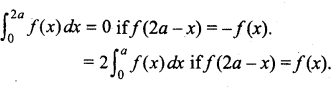
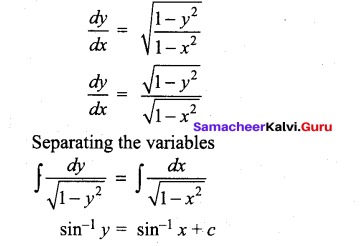
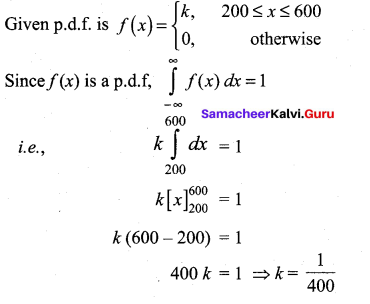
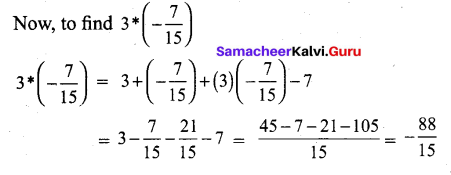

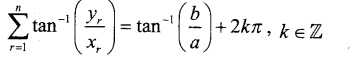
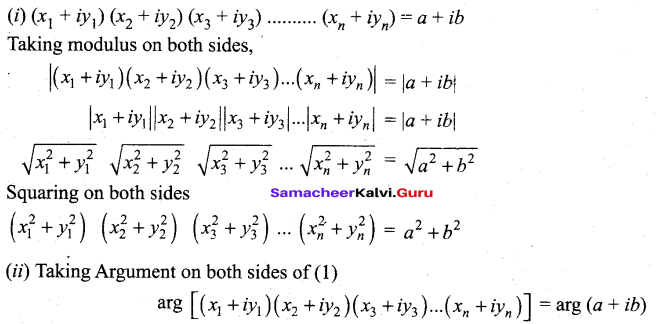
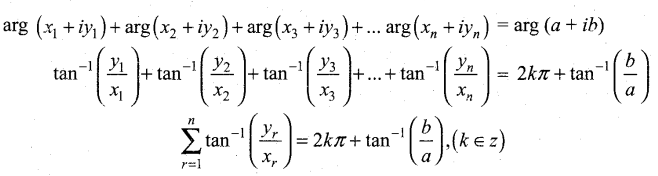
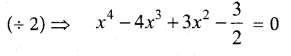
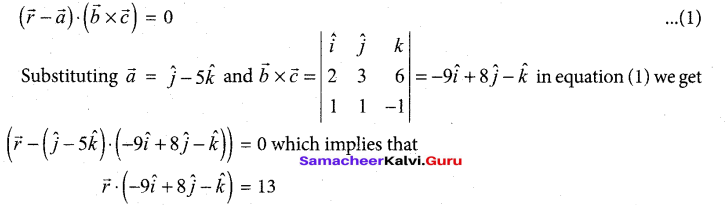
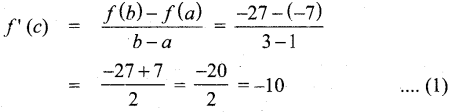
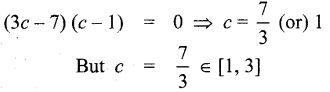
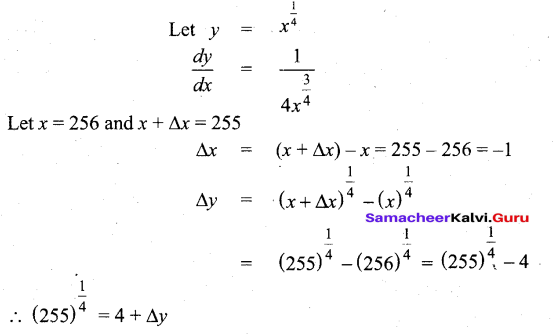
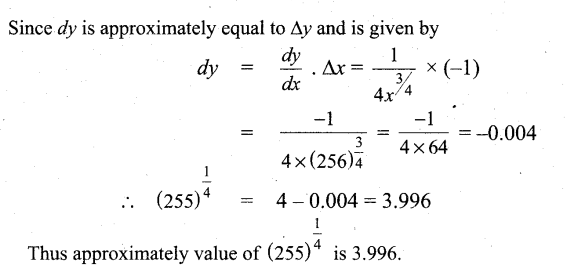
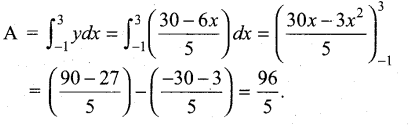
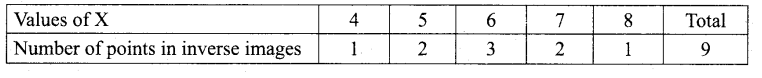
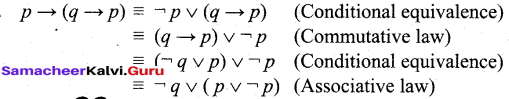
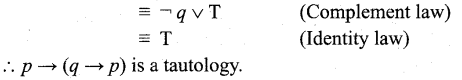
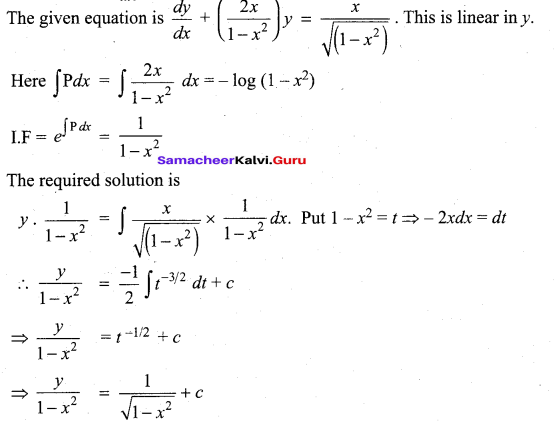
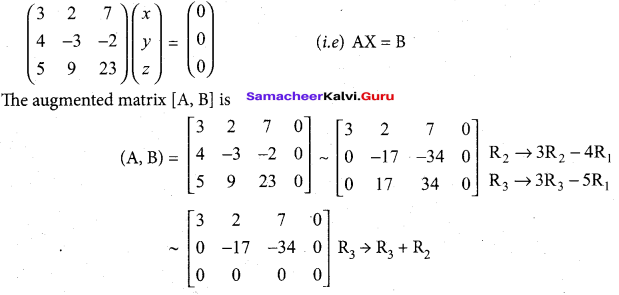
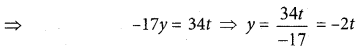

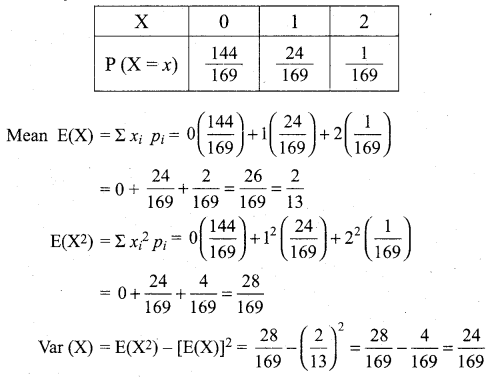
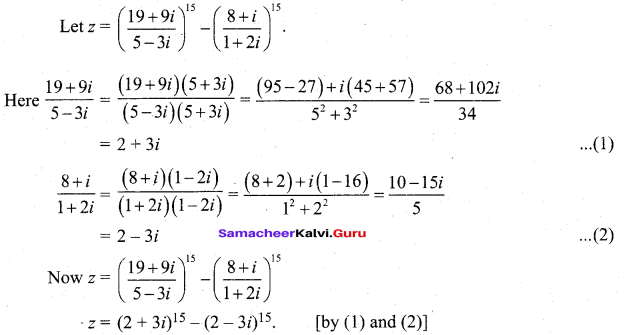
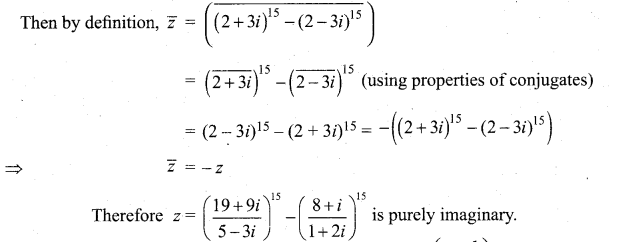
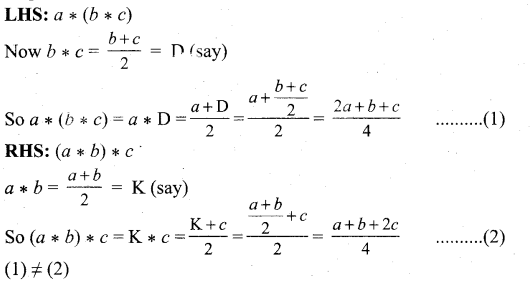
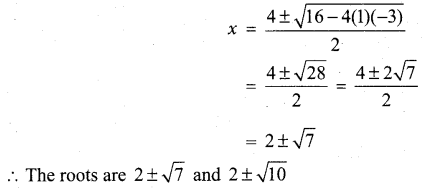
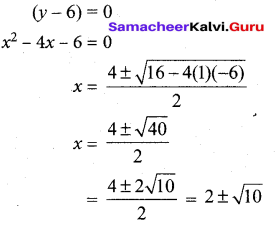
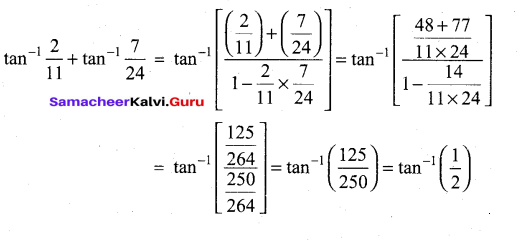
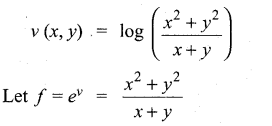
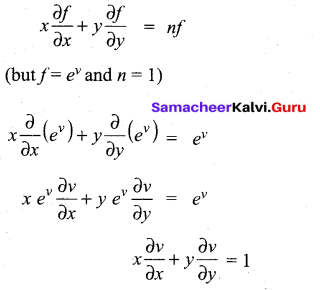
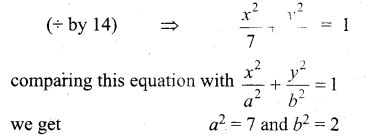
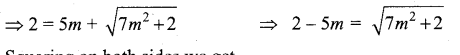
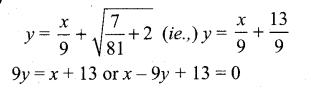
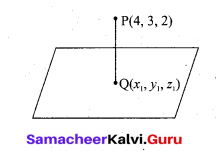
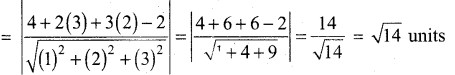

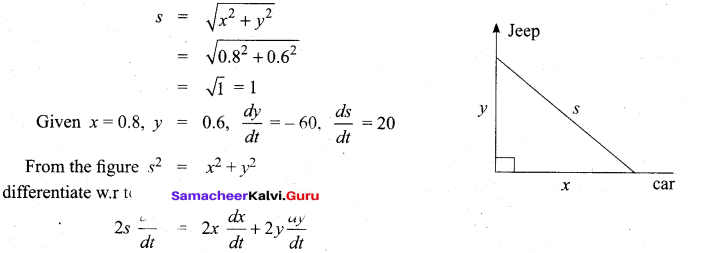
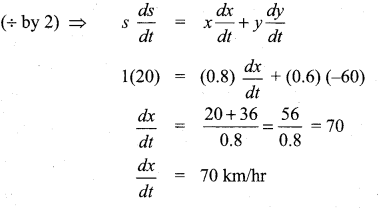
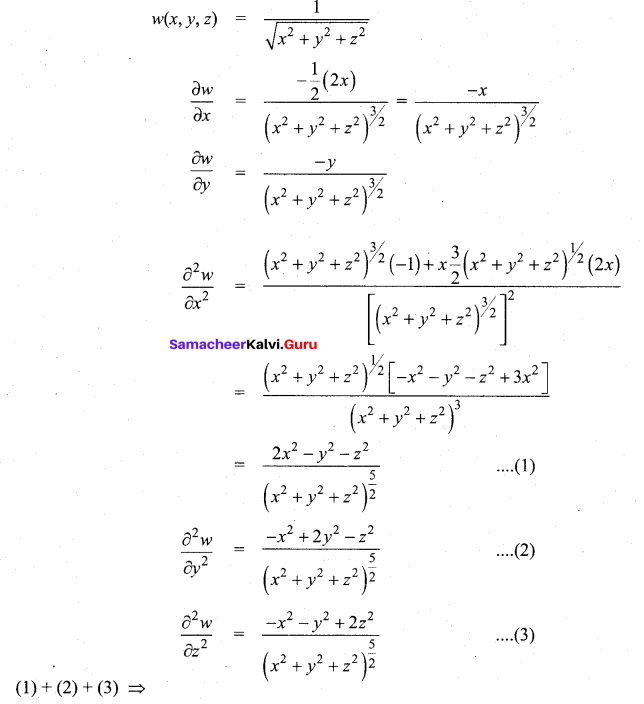
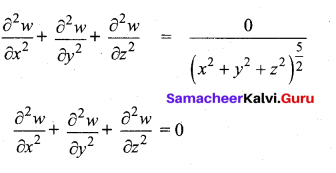
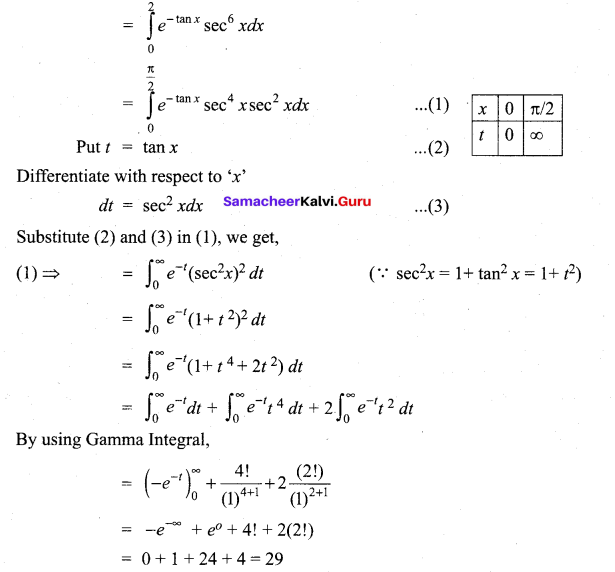










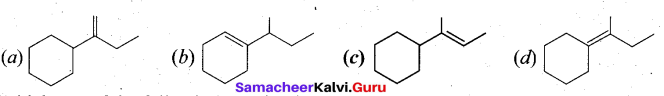
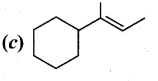

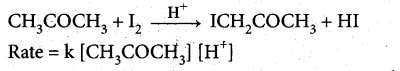
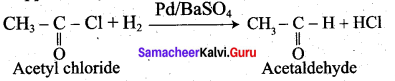
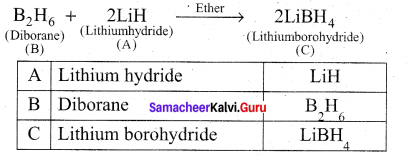
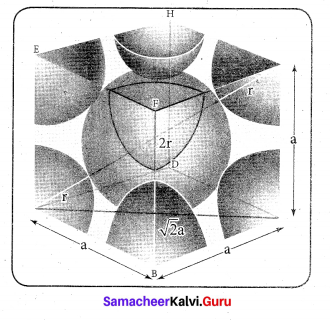
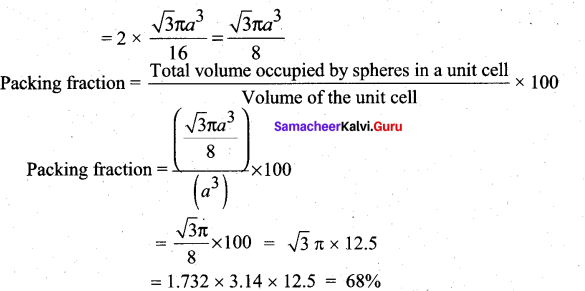
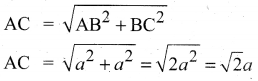 In∆ACG,
In∆ACG,