Students can Download Bio Botany Chapter 4 Principles and Processes of Biotechnology Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 4 Principles and Processes of Biotechnology
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Principles and Processes of Biotechnology Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Restriction enzymes are ___________
(a) Not always required in genetic engineering
(b) Essential tools in genetic engineering
(c) Nucleases that cleave DNA at specific sites
(d) both b and c
Answer:
(d) both b and c
Question 2.
Plasmids are ___________
(a) circular protein molecules
(b) required by bacteria
(c) tiny bacteria
(d) confer resistance to antibiotics
Answer:
(d) confer resistance to antibiotics
Question 3.
EcoRI cleaves DNA at
(a) AGGGTT
(b) GTATATC
(c) GAATTC
(d) TATAGC
Answer:
(c) GAATTC
Question 4.
Genetic engineering is ___________
(a) making artificial genes
(b) hybridization of DNA of one organism to that of the others.
(c) production of alcohol by using micro organisms.
(d) making artificial limbs, diagnostic instruments such as ECG and EEG, etc.
Answer:
(b) hybridization of DNA of one organism to that of the others.
![]()
Question 5.
Consider the following statements:
i. Recombinant DNA technology is popularly known as genetic engineering is a stream of biotechnology which deals with the manipulation of genetic materials by man invitro
ii. pBR322 is the first artificial cloning vector developed in 1977 by Boliver and Rodriguez from E.coli plasmid.
iii. Restriction enzymes belong to a class of enzymes called nucleases. Choose the correct option regarding the above statements
(a) i and ii
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iii
(d) i,ii, and iii
Answer:
(d) i,ii and iii
Question 6.
The process of recombinant DNA technology has the following steps
i. Amplification of the gene.
ii. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cells.
iii. Cutting of DNA at a specific location using a restriction enzyme.
iv. Isolation of genetic material (DNA).
Pick out the correct sequence of steps for recombinant DNA technology.
(a) ii, iii, iv, and i
(b) iv, ii, iii, and i
(c) i, ii, iii and iv
(d) iv, iii, i, and ii
Answer:
(d) iv, iii, i, and ii
Question 7.
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzymes?
(a) 5′ CGTTCG 3′ ATCGTA5′
(b) 5′ GATATG 3′ CTACTA5′
(c) 5′ GAATTC 3′ CTTAAG 5′
(d) 5′ CACGTA 3′ CTCAGT 5′
Answer:
(c) 5′ GAATTC 3′ CTTAAG 5′
Question 8.
pBR 322, BR stands for
(a) Plasmid Bacterial Recombination
(b) Plasmid Bacterial Replications
(c) Plasmid Boliver and Rodriguez
(d) Plasmid Baltimore and Rodriguez
Answer:
(c) Plasmid Boliver and Rodriguez
Question 9.
Which of the following one is used as a Biosensors?
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Bioreactors
(c) Vectors
(d) Electroporation
Answer:
(b) Bioreactors
Question 10.
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Exonuclease | a. add or remove phosphate |
| 2. Endonuclease | b. binding the DNA fragments |
| 3. Alkaline Phosphatase | c. cut the DNA at the terminus |
| 4. Ligase | d. cut the DNA at middle |
(A) a b c d
(B) c d b a
(C) a c b d
(D) c d a b
Answer:
(D) c d a b
Question 11.
In which techniques Ethidium Bromide is used?
(a) Southern Blotting techniques
(b) Western Blotting techniques
(c) Polymerase Chain Reaction
(d) Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Answer:
(d) Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Question 12.
Assertion: Agrobacterium tumifaciens is popular in genetic engineering because of this bacterium is associated with the root nodules of all cereals and pulse crops.
Reason: A gene incorporated in the bacterial chromosomal genome gets automatically transferred to the cross with which bacterium is associated.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true. But reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true. But reason is not a correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
(e) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true. But reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not correct statement?
(a) Ti plasmid causes the bunchy top disease
(b) Multiple cloning site is known as Polylinker
(c) Non-viral method of transfection of Nucleic acid in cell
(d) Polylactic acid is a kind of biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic.
Answer:
(a) Ti plasmid causes the bunchy top disease
Question 14.
An analysis of chromosomal DNA using the southern hybridisation technique does not use
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Blotting
(c) Autoradiography
(d) Polymerase Chain Reaction
Answer:
(a) Electrophoresis
![]()
Question 15.
An antibiotic gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of
(a) Competent cells
(b) Transformed cells
(c) Recombinant cells
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Competent cells
Question 16.
Some of the characteristics of Bt cotton are
(a) Long fibre and resistant to aphids
(b) Medium yield, long fibre and resistant to beetle pests
(c) high yield and production of toxic protein crystals which kill dipteran pests.
(d) High yield and resistant to ball worms
Answer:
(b) Medium yield, long fibre and resistant to beetle pests
Question 17.
How do you use the biotechnology in modern practice?
Answer:
In modem practice, biotechnology is used in the development of herbicide resistance plants, improved crop varieties, producing pharma products like insulin, developing vaccines, diagnosing genetic diseases and designing drgus etc.
Question 18.
What are the materials used to grow microorganism like Spirulinal
Answer:
- Wastewater from Potato processing plants.
- Straw.
- animal Manure
- Molasses
- Sewage.
- Can be used to produce large quantities of SCP.
- To produce large quantities and can serve as food rich in proteins, minerals, fats, carbohydrate and vitamins.
- Such utilization also reduce environmental pollution
- 250 g of methylophilus methylotrophus, as its high rate of biomass production and growth can be expected to produce 25 tonnes of protein.
Question 19.
You are working in a biotechnology lab with a bacterium namely E.coli. How will you cut the nucleotide sequence? explain it.
Answer:
The DNA nucleotide sequence can be cut using Restriction endonucleases (RE). Restriction endonucleases – EcoRI cuts the DNA at GAATTC seqUence, producing sticky ends.CTTAAG
Question 20.
What are the enzymes you can use to cut terminal end and internal phospho diester bond of nucleotide sequence?
Answer:
a) Exonucleases: These enzymes – remove nucleotides one at a time from the end of a DNA molecule. Eg. Bal 31, Exonuclease 111
b) Endonucleases: These are enzymes which break the internal phosphor diester bonds within a DNA molecule Eg. Hind II, EcoR1, Pvul, Bam HI, Taq I.
Question 21.
Name the chemicals used in gene transfer.
Answer:
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and Dextran Sulphate.
Question 22.
What do you know about the word pBR332?
Answer:
pBR 322 plasmid is a reconstructed plasmid and most widely used as cloning vector; it contains 4361 base pairs. In pBR, p denotes plasmid, B and R respectively the names of scientist Roliver and/fodriguez who developed this plasmid. The number is the number of plasmid developed from their laboratory.
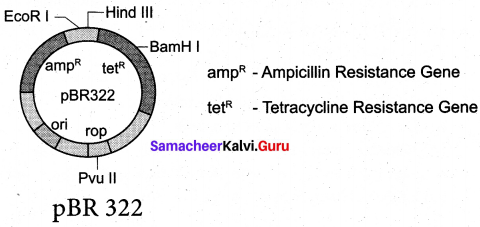
It contains ampR and tetR two different antibiotic resistance genes and recognition sites for several restriction enzymes. (Hind III, EcoRI, BamH I, Sal I, Pvu II, Pst I and Cla I), ori and antibiotic resistance genes. Rop codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Question 23.
Mention the application of biotechnology.
Answer:
- Biotechnology is one of the most important applied interdisciplinary sciences of the 21st century. It is the trusted area that enables us to find the beneficial way of life.
- Biotechnology has wide applications in various sectors like agriculture, medicine,environment and commercial industries.
- This science has an invaluable outcome like transgenic varieties of plants e.g. transgenic cotton (Bt-cotton), rice, tomato, tobacco, cauliflower, potato and banana.
- The development of transgenics as pesticide resistant, stress resistant and disease resistant varieties of agricultural crops is the immense outcome of biotechnology.
- The synthesis of human insulin and blood protein in E.coli and utilized for insulin deficiency disorder in human is a breakthrough in biotech industries in medicine.
- The synthesis of vaccines, enzymes, antibiotics, dairy products and beverages are the products of biotech industries.
- Biochip based biological computer is one of the successes of biotechnology.
- Genetic engineering involves genetic manipulation, tissue culture involves aseptic cultivation of totipotent plant cell into plant clones under controlled atmospheric conditions.
- Single cell protein from Spirulina is utilized in food industries.
- Production of secondary metabolites, biofertilizers, biopesticides and enzymes.
- Biomass energy, biofuel, bioremediation and phytoremediation for environmental biotechnology.
Question 24.
What are restriction enzyme. Mention their type with role in biotechnology.
Answer:
- It was isolated in 1963 from E.coli.
- It cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites.
On the base of mode of action there are 2 types
a) Exonucleases – remove nucleotides one at a time from the end of DNA.
Eg: Bal 31, Exonuclease III
b) Endonucleases – break the internal phosphodiester bonds with in a DNA.
Eg: Hind II, EcoRI, Pvul, Bam HI, Taql.
Question 25.
Is there any possibilities to transfer a suitable desirable gene to host plant without vector? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes – In this method, the foreign gene of interest is delivered into the host plant without the help of vector directly.
Question 26.
How will you identify a vector?
Answer:
- Vectors are able to replicate autonomously to produce multiple copies of them along with their DNA insert in the host cell.
- It should be small in size and of low molecular weight, less than 10 Kb (kilo base pair) in size so that entry/transfer into host cell is easy.
- Vector must contain an origin of replication so that it can independently replicate within the host.
- It should contain a suitable marker such as antibiotic resistance, to permit its detection in transformed host cell.
- Vector should have unique target sites for integration with DNA insert and should have the ability to integrate with DNA insert it carries into the genome of the host cell.
- Most of the commonly used cloning vectors have more than one restriction site. These are Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) or polylinker. Presence of MCS facilitates the use of restriction enzyme of choice.
![]()
Question 27.
Compare the various types of Blotting techniques.
Answer:
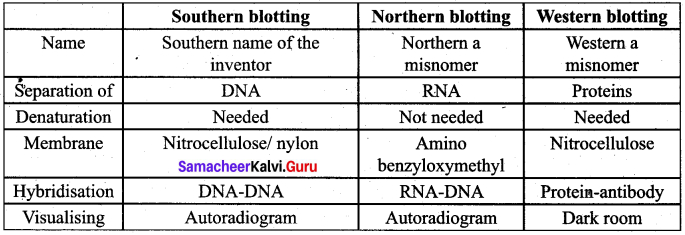
Question 28.
Write the advantages of herbicide tolerant crops.
Answer:
Advantages of Herbicide Tolerant Crops:
- Weed control improves higher crop yields;
- Reduces spray of herbicide;
- Reduces competition between crop plant and weed;
- Use of low toxicity compounds which do not remain active in the soil; and
- The ability to conserve soil structure and microbes.
Question 29.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of Bt cotton.
Answer:
The advantages of Bt cotton are:
- Yield of cotton is increased due to effective control of bollworms.
- Reduction in insecticide use in the cultivation of Bt cotton
- Potential reduction in the cost of cultivation.
- Cost of Bt cotton seed is high.
- Effectiveness up to 120 days after that efficiency is reduced.
- Ineffective against sucking pests like jassids, aphids and whitefly.
- Affects pollinating insects and thus yield.
Question 30.
What is bioremediation? Give some examples of bioremediation.
Answer:
Definition: It is the use of microorganisms or plants to clean up environmental pollution.
Uses:
Approach to treat
- wastewater
- industrial waste
- solid waste, etc
To remove
- remove of oil spills
- petro chemicals residues
- pesticides or heavy metals from soil or groundwater.
Advantages:
- Less expensive.
- More sustainable than other physical or chemical methods.
- Cheaper & eco-friendly approach.
- More effective in dealing with lower concentrations of contaminants.
Examples:
- Genetically modified Bacteria -pseudomonas Putida used as superbug to clean oil spills in the sea.
- Fungi – Used as Bioremediation agent.
Some examples of bioremediation technologies are:
- phytoremediation: use of plants to bring about remediation of environmental pollutants Mycoremediation: use of fungi to bring about remediation of environmental pollutants.
- Bioventing: is the process that degradation of environmental pollutants.
- Bioleaching: is the use of microorganisms in solution to recover metal pollutants from contaminated sites
- Bioaugmentation: is the addition of selected microbes to speed up degradation process.
- Composting: is the process by which the solid waste is composted by the use of microbes into manure which acts as a nutrient for plant growth.
- Rhizofiltration : is the uptake of metals or degradation of organic compounds by rhizosphere microorganisms
- Rhizostimulations: is the stimulation of plant growth by the rhizosphere by providing better growth
- condition or reduction in toxic materials.
Question 31.
Write the benefits and risk of Genetically Modified Foods.
Answer:
GM Food – Benefits:
- High yield without pest.
- 70% reduction of pesticide usage.
- Reduce soil pollution problem.
- Conserve microbial population in soil.
Risks – believed to:
- Affect liver, kidney function and cancer.
- Hormonal imbalance and physical disorder.
- Anaphylactic shock (sudden hypersensitive reaction) and allergies.
- Adverse effect in immune system because of bacterial protein.
- Loss of viability of seeds show in terminator seed technology of GM crops.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Principles and Processes of Biotechnology Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following person coined the term biotechnology?
(a) Ernst Hoppe
(b) Stanley Cohen
(c) Ian Wilmet
(d) Karl Ereky
Answer:
(d) Karl Ereky
Question 2.
Zymology deals with
(a) Study of yeast fungus and its practical applications.
(b) Study of fermentation and its uses.
(c) Study of Bioreactors and their construction methodology.
(d) Study of zymase producing microbes and its benefits.
Answer:
(b) Study of fermentation and its uses.
Question 3.
Match column I with column II
| Column I | Column II |
| A. One gene one enzyme hypothesis | i. Kohler and Milstein |
| B. Monoclonal antibodies | ii. Kary Mullis |
| C. First transgenic animal | iii. Beadle and Tatum |
| D. Development of PCR technology | iv. Ian Wilmet |
(a) A – iii, B – i, C – iv, D – ii
(b) A – i, B – iv, C – ii, D – iii
(c) A – iv, B – iii, C – ii D – i
(d) A – ii, B – iv C – i, D – iii
Answer:
(a) A – iii, B -1, C – iv, D – ii
Question 4.
Identify the incorrect statement:
(a) French chemist Louis Pasteur demonstrated the fermentation.
(b) Fermentor is a vessel providing optimal condition for microbial action.
(c) Solvent extraction is an upstream process of fermentation.
(d) Distillation and filtration comes under down stream process.
Answer:
(c) Solvent extraction is an upstream process of fermentation.
Question 5.
Pick out the mismatched pair(s):
(i) Amphotericin-B – Streptomyces notatum
(ii) Penicillin – Penicillum nodosus
(iii) Streptomycin – Streptomyces grises
(iv) Tetracycline – Streptomyces aureofacins
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) iii and iv
(d) i only
Answer:
(a) i and ii
![]()
Question 6.
Identify the non-fungal species used in SCP production.
(i) Candida
(ii) Chlorella
(iii) Chlamydomonas
(iv) Cellulomonas
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) ii, iii and iv
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) ii, iii and iv
Question 7.
Select the correct restriction enzyme which breaks the phosphodiester bond within a DNA
molecule.
(i) Bal 31
(ii) Hind II
(iii) Bam HI
(iv) Pvul
(a) i and iii
(b) i, ii and iii
(c) ii, iii and iv
(d) i only
Answer:
(c) ii, iii and iv
Question 8.
Cohesive ends are _______
(a) Blunt ends
(b) Flush ends
(c) Sticky ends
(d) Symmetric cuts
Answer:
(c) Sticky ends
Question 9.
Self-ligation is prevented by __________
(a) DNA Polymerase
(b) Helicase
(c) Alkaline phosphate
(d) DNA lipase
Answer:
(c) Alkaline phosphate
Question 10.
Observe the diagram and name A and B.
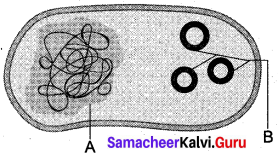
(a) A – Plasmid – B – Vector
(b) A – Nucleoid – B – Plasmid
(c) A – Bacterial chromosome B – Vector
(d) A – Nucleoid – B – x phage DNA
Answer:
(b) A – Nucleoid – B – Plasmid
Question 11.
A vector should __________
(i) contain suitable marker
(ii) contain ori site
(iii) have poly linkess
(iv) be small in size
(a) i, ii and iii
(b) ii, iii and iv
(c) i, ii and iv
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
![]()
Question 12.
Number of base pairs does pBR 322 plasmid contains __________
(a) 322
(b) 4322
(c) 4361
(d) 3264
Answer:
(c) 4361
Question 13.
__________ is the plasmid present in Agrobacterium.
Answer:
Ti plasmid
Question 14.
ptlC 19 is an example for.
(a) Shuttle vector
(b) Expression vector
(c) Cosmid
(d) Phagemid vector
Answer:
(b) Expression vector
Question 15.
Statement 1: YAC plasmid behaves like a yeast chromosome.
Statement 2: Circular YAC multiplies in bacteria.
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is also correct.
(b) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect.
(c) Both the statements are incorrect.
(d) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is also correct.
Question 16.
Statement 1: Liposomes are the artificial lipoprotein vesicles. Statement 2: Liposomes are highly used in gene transfer.
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is also correct.
(b) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect.
(c) Both the statements are incorrect.
(d) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
(d) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct.
Question 17.
Statement 1: DNA is a hydrophobic molecule.
Statement 2: T-DNA is a part of E-coli plasmid.
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is also correct.
(b) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect.
(c) Both the statements are incorrect.
(d) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are incorrect.
Question 18.
Statement 1: Bioventing procedure increases 02 flow to accelerate degradation of pollutants.
Statement 2: Bioaugmentation uses microbes to recover metal pollutants from contaminated sites.
(a) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is also correct.
(b) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect.
(c) Both the statements are incorrect.
(d) Statement 1 is incorrect and Statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
(b) Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is incorrect.
Question 19.
Assertion (A) : Golden rice helps to overcome childhood blindness.
Reason (R) : It is rich in P carotene.
(a) Both A and R are wrong.
(b) A is right R is wrong.
(c) R explains A.
(d) A and R are right, R does not explain A.
Answer:
(c) R explains A.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): Expression vectors are suitable for expressing foreign proteins.
Reason (R): pBR 322 is an expression vectors.
(а) Both A and R are wrong.
(b) A is right R is wrong.
(c) R explains A.
(d) A and R are right, R does not explain A.
Answer:
(b) A is right R is wrong.
Question 21.
Assertion (A) : Pseudomonas putida is utilized in the production of Biological hydrogen.
Reason (R): During photosynthesis, it releases oxygen.
(a) Both A and R are wrong.
(b) A is right R is wrong.
(c) R explains A.
(d) A and R are right, R does not explain A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are wrong.
Question 22.
Assertion (A): DMH -11 is a transgenic mustard.
Reason (R): It is developed by using bamase/ barstar technology.
(a) Both A and R are wrong.
(b) A is right R is wrong.
(c) R explains A.
(d) A and R are right, R does not explain A.
Answer:
(c) R explains A.
Question 23.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was isolated from
(a) Aequorea victoria
(b) Arabidopsis thaliana
(c) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
(d) Escherichia coli
Answer:
(a) Aequorea victoria
Question 24.
Tetracycline is obtained from
(a) S.nodosus
(b) S.aureofacins
(c) S.grises
(d) P. chryosogenum
Answer:
(a) S.aureofacins
Question 25.
Today more than restriction enzymes have been isolated.
(a) 800
(b) 900
(c) 1000
(d) 870
Answer:
(6) 900
2. Mark Questions
Question 1.
How modern biotechnology differs from conventional biotechnology?
Answer:
There are two main features of modem biotechnology, that differentiated it from the conventional technology are its:
(i) ability to change the genetic material for getting new products with specific requirement through recombinant DNA technology
(ii) ownership of the newly developed technology and its social impact.
![]()
Question 2.
What is a fermentor?
Answer:
Bioreactor (Fermentor) is a vessel or a container that is designed in such a way that it can provide an optimum environment in which microorganisms or their enzymes interact with a substrate to produce the required product. In the bioreactor, aeration, agitation, temperature and pH are controlled.
Question 3.
Define fermentation.
Answer:
Fermentation refers to the metabolic process in which organic molecules (normally glucose) are converted into acids, gases, or alcohol in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chain.
Question 4.
What are primary metabolites? Give example.
Answer:
Metabolites produced for the maintenance of life process of microbes are known as primary metabolites.
E.g. Ethanol, citric acid, lactic acid and acetic acid.
Question 5.
How microbial enzymes are produced? Mention its significance.
Answer:
When microbes are cultured, they secrete some enzymes into the growth media. These enzymes are industrially used in detergents, food processing, brewing and pharmaceuticals.
E.g. Protease, amylase, isomerase, and lipase.
Question 6.
Mention any two bacterial species used as SCP.
Answer:
- Cellulomonas
- Alcaligenes
Question 7.
Name any two fungal species used as SCP.
Answer:
- Agaricus campestris
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Question 8.
Expand PCR and mention its use.
Answer:
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction.
PCR is a common lab technique used to make copies of particular region of DNA.
Question 9.
What is Restriction Endonuclease?
Answer:
A restriction enzyme or restriction endonuclease is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within the molecule known as restriction sites.
Question 10.
What is a palindrome sequence?
Answer:
Palindrome is a sequence of nucleotide in DNA strands at the site which reads the same in 5′-3′ direction and in the 3′-5′ direction.
Question 11.
Write an palindrome sequence of DNA.
Answer:
5′ … CATTATATAATG … 3′
3′ … GTAATATATTAC … 5′
Question 12.
Differentiate between flush end and cohesive end of DNA.
Answer:
Flush End:
Some restriction enzymes cut the strands of DNA through the centre resulting in blunt end or flush end or symmetric cuts.
Cohesive End:
Some restriction enzymes cut the strands in a way producing protruding and recessed ends known as cohesive end or sticky end or asymmetric cuts.
Question 13.
What is the role of DNA ligase in genetic engineering?
Answer:
DNA ligase enzyme joins the sugar and phosphate molecules of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) with 5’-P04 and a 3’-OH in an Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) dependent reaction. This is isolated from T4 phage.
Question 14.
Define plasmids.
Plasmids are extrachromosomal, self replicating ds circular DNA molecules, found in the bacterial cells in addition to the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids contain Genetic information for their own replication.
![]()
Question 15.
Classify vectors and explain them.
Answer:
Vectors are of two types:
- Cloning Vector
- Expression Vector.
Cloning vector is used for the cloning of DNA insert inside the suitable host cell. Expression vector is used to express the DNA insert for producing specific protein inside the host.
Question 16.
What are expression vectors?
Answer:
Vectors which are suitable for expressing foreign proteins are called expression vectors. This vector consists of signals necessary for transcription and translation of proteins in the host. This helps the host to produce foreign protein in large amounts.
Example: pUC 19.
Question 17.
Name any four vectors that you know?
Answer:
Cosmid, plasmid, Bacteriophage and Phagemids.
Question 18.
Write a brief note on BAC vector.
Answer:
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) Vector is a shuttle plasmid vector, created for cloning large-sized foreign DNA. BAC vector is one of the most useful cloning vector in r-DNA technology they can clone DNA inserts of upto 300 Kb and they are stable and more user-friendly.
Question 19.
What does Blotting refers to?
Answer:
Blotting refers to the process of immobilization of sample nucleic acids on solid support (nitrocellulose or nylon membranes). The blotted nucleic acids are then used as target in the hybridization experiments for their specific detection.
Question 20.
Point out any two disadvantages of Bt cotton?
Answer:
Bt cotton has some limitations:
- Cost of Bt cotton seed is high.
- Effectiveness up to 120 days after that efficiency is reduced.
Question 21.
What are the benefits of Genetically Modified plants?
Answer:
GM Food – Benefits:
- High yield without pest.
- 70% reduction of pesticide usage.
- Reduce soil pollution problem.
- Conserve microbial population in soil.
Question 22.
Expand:
- PEG
- PHB
Answer:
- PEG – Poly Ethylene Glycol
- PHB – Poly Hydroxy Butyrate
Question 23.
What is Biopharming?
Answer:
Biopharming also known as molecular pharming is the production and use of transgenic plants genetically engineered to produce pharmaceutical substances for use of human beings. This is also called “molecular farming or pharming”. These plants are different from medicinal plants which are naturally available.
Question 24.
Define the terms
- Bioventing
- Bioaugmentation
Answer:
- Bioventing is the process that increases the oxygen or air flow to accelerate the degradation of environmental pollutants.
- Bioaugmentation is the addition of selected microbes to speed up degradation process.
Question 25.
How hydrogen is biologically synthsized?
Answer:
The biological hydrogen production with algae is a method of photo biological water splitting. In normal photosynthesis the alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii releases oxygen. When it is deprived of sulfur, it switches to the production of hydrogen during photosynthesis and the electrons are transported to ferredoxins. [Fe]-hydrogenase enzymes combine them into the production of hydrogen gas.
Question 26.
Define Biopiracy.
Answer:
Biopiracy can be defined as the manipulation of intellectual property rights laws by corporations to gain exclusive control over national genetic resources, without giving adequate recognition or remuneration to the original possessors of those resources.
Question 27.
What are polylinkers?
Answer:
Mostly cloning vectors have more than one restriction sites. These are called as Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) or polylinkers. Presence of MCS facilitates the use of restriction enzyme of choice.
3-Mark Questions
Question 28.
Mention any three historical events which took place in the 21st century for the development of biotechnology.
Answer:
2002 – First crop plant genome sequenced in Oryza sativa.
2003 – Human genome project is completed, providing information on the locations and 1 sequence of human genes on all 46 chromosomes.
2016 – Stem cells injected into stroke patients re-enable patient to walk – Stem cell therapy.
Question 29.
In the fermentation process, what does upstream and downstream refers to? Explain.
Answer:
Upstream process:
All the process before starting of the fermenter such as sterilization of the fermenter, preparation and sterilization of culture medium and growth of the suitable inoculum are called upstream process.
Downstream process:
All the process after the fermentation process is known as the downstream process. This process includes distillation, centrifuging, filtration and solvent extraction. Mostly this process involves the purification of the desired product.
Question 30.
Provide a stepwise procedure of fermentation process.
Procedure of Fermentation
Answer:
- Depending upon the type of product, bioreactor is selected.
- A suitable substrate in liquid media is added at a specific temperature, pH and then diluted.
- The organism (microbe, animal/plant cell, sub-cellular organelle or enzyme) is added to it.
- Then it is incubated at a specific temperature for the specified time.
- The incubation may either be aerobic or anaerobic.
- Withdrawal of product using downstream processing methods.
Question 31.
What are secondary metabolites? Give two examples.
Answer:
Secondary metabolites are those which are not required for the vital life process of microbes, but have value added nature, this includes antibiotics
e.g. -Amphotericin-B (Streptomyces nodosus) and Penicillin (Penicillium chryosogenum).
![]()
Question 32.
What is SCP? Mention its nutritional value.
Answer:
Single Cell Protein (SCP) are dried cells of microorganisms that are used as protein supplement in human foods or animal feeds. SCP are rich in proteins, aminoacids, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. It is used as food source by Astronauts and Antarctica expedition scientists.
Question 33.
Mention any three algal species used for SCP production.
Answer:
Spirulina, Chlorella and Chlamydomonas.
Question 34.
Though SCP is a rich protein source, it has not been widely used as food supplement. Point a reason to support this statement.
Answer:
Yes, although SCP is a rich protein source it is not widely used by most of the people in countries due to its higher nucleic acid content and slow digestibility.
Question 35.
Point out few advantages of single cell protein.
Answer:
Applications of Single-Cell Protein:
- It is used as protein supplement.
- It is used in cosmetics, products for healthy hair and skin.
- It is used in poultry as the excellent source of proteins and other nutrients, it is widely used for feeding cattle, birds and fishes, etc.
- It is used in food industry as aroma carriers, vitamin carrier, emulsifying agents to improve the nutritive value of baked products, in soups, in ready-to-serve-meals, in diet recipes.
- It is used in industries like paper processing and leather processing as foam stabilizers.
Question 36.
Classify restriction enzymes based on their mode of action.
Answer:
Based on their mode of action restriction enzymes are classified into Exonucleases and Endonucleases.
a. Exonucleases are enzymes which remove nucleotides one at a time from the end of a DNA molecule,
e.g. Bal 31 and Exomiclease III.
b. Endonucleases are enzymes which break the internal phosphodiester bonds within a DNA molecule,
e.g. Hind II, EcoRI, Pvul, BamHI and TaqI.
Question 37.
Which type of restriction enzyme is widely used in rDNA technology? Why?
Answer:
Type II enzyme is preferred for use in recombinant DNA technology as they recognise and cut DNA within a specific sequence typically consisting of 4-8 bp.
Question 38.
Explain the procedure behind the naming of Restriction Enzymes by citing an example.
Answer:
Restriction endonucleases are named by a standard procedure. The first letter of the enzymes indicates the genus name, followed by the first two letters of the species, then comes the strain of the organism and finally a roman numeral indicating the order of discovery. For example, EcoRI is from Escherichia (E) coli (co), strain RY 13 (R) and first endonuclease (I) to be discovered.
Question 39.
Give a short note on Alkaline phosphate.
Answer:
Alkaline phosphate is a DNA modifying enzymes and adds or removes specific phosphate group at 5’ terminus of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) or single stranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA. Thus it prevents self ligation. This enzyme is purified from bacteria and calf intestine.
Question 40.
What are the features that a vector must possess to facilitate cloning?
Answer:
The following are the features that are required to facilitate cloning into a vector.
- Origin of replication (ori): This is a sequence from where replication starts and piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells.
- Selectable marker: In addition to ori the vector requires a selectable marker, which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants,
- Cloning sites: In order to link the alien DNA, the vector needs to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
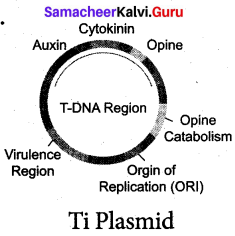
Question 41.
Draw and label Ti plasmid
Answer:
Question 42.
What do you mean by the term “walking genes”? Could you explain?
Answer:
Transposons (Transposable elements or mobile elements) are DNA sequence able to insert itself at a new location in the genome without having any sequence relationship with the target locus and hence transposons are called walking genes or jumping genes. They are used as genetic tools for analysis of gene and protein functions, that produce new phenotype on host cell. The use of transposons is well studied in Arabidopsis thaliana and bacteria such as Escherichia coli.
Question 43.
How does shuttle vectors differ from other types of vectors?
Answer:
The shuttle vectors are plasmids designed to replicate in cells of two different species. These vectors are created by recombinant techniques. The shuttle vectors can propagate in one host and then move into another host without any extra manipulation. Most of the Eukaryotic
vectors are Shuttle Vectors.
Question 44.
Given below are the three different DNA palindrome sequences. Name the respective restriction enzymes which cleaves those sequences and also mention the microbial sources of the enzymes.
Answer:
(a) 5 AGCT3′
(b) 5 GGCC3′
(c) 5 GAATTC3′
Answer:
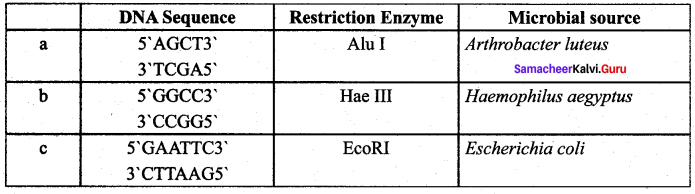
Question 45.
Why is it difficult for DNA to pass through cell membrane? How the bacterial cells can be made competent to take up DNA?
Answer:
Since the DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, it cannot pass through cell membranes, In order to force bacteria to take up the plasmid, the bacterial cells must first be made competent to take up DNA. This is done by treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent cation such as calcium.
![]()
Question 46.
Write a brief note on Biolistics.
Answer:
The foreign DNA is coated onto the surface of minute gold or tungsten particles (1-3 pm) and bombarded onto the target tissue Or cells using a particle gun (also called as gene gun/micro projectile gun/shotgun). Then the bombarded cells or tissues are cultured on selected medium to regenerate plants from the transformed cells.
Question 47.
Agrobacterium – a natural genetic engineer of plants. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Among the various vectors used for plant transformation, the Ti-plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been used extensively. This bacterium has a large size plasmid, known as Ti plasmid (Tumor inducing) and a portion of it referred as T-DNA (transfer DNA) is transferred to plant genome in the infected cells and cause plant tumors (crown gall). Since this bacterium has the natural ability to transfer T-DNA region of its plasmid into plant genome, upon infection of cells at the wound site, it is also known as the natural genetic engineer of plants.
Question 48.
Give a brief account on antibiotic resistant marker.
Answer:
An antibiotic resistance marker is a gene that produces a protein that provides cells with resistance to an antibiotic. Bacteria with transformed DNA can be identified by growing on a medium containing an antibiotic. Recombinants will grow on these medium as they contain genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as amphicillin, chloroamphenicol, tetracycline or kanamycin, etc., while others may not be able to grow in these media, hence it is considered useful selectable marker.
Question 49.
Mention the types of Blotting techniques.
Answer:
Types of Blotting Techniques:
- Southern Blotting: The transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nitrocellulose membrane.
- Northern Blotting: The transfer of RNA to nitrocellulose membrane.
- Western Blotting: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins to nitrocellulose membrane:
Question 50.
Expand CRISPR – Cas9.
Answer:
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9.
Question 51.
What is RNA interference (RNAi)? How it is carried out?
Answer:
RNA interference is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression or translation. This is done by neutralising targeted mRNA molecules.
A simplified model for the RNAi pathway is based on two steps, each involving ribonuclease enzyme. In the first step, the trigger RNA (either dsRNA or miRNA primary transcript) is processed into a short interfering RNA (siRNA) by the RNase II enzymes called Dicer and Drosha. In the second step, siRNAs are loaded into the effector complex RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The siRNA is unwound during RISC assembly and the single- stranded RNA hybridizes with mRNA target. This RNAi is seen in plant feeding nematodes.
Question 52.
Prepare a protocol for Glyphosphate resistant potato plant development.
Answer:
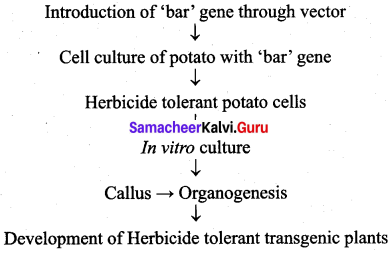
Question 53.
How Bt cotton crops are developed?
Answer:
Bt cotton is a genetically modified organism (GMO) or genetically modified pest resistant plant cotton variety, which produces an insecticide activity to bollworm. Strains of the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produce over 200 different Bt toxins, each harmful to different insects. Most Bt toxins are insecticidal to the larvae of moths and butterflies, beetles, cotton bollworms and gatflies but are harmless to other forms of life.The genes are encoded for toxic crystals in the Cry group of endotoxin.
When insects attack and eat the cotton plant the Cry toxins are dissolved in the insect’s stomach.The epithelial membranes of the gut block certain vital nutrients thereby sufficient regulation of potassium ions are lost in the insects and results in the death of epithelial cells in the intestine .membrane which leads to the death of the larvae.
Question 54.
Comment on Golden rice.
Answer:
Golden rice is a variety of Oryza sativa (rice) produced through genetic engineering of biosynthesized beta-carotene, a precursor ofVitamin-A in the edible parts of rice developed by – Ingo Potrykus and his group. The aim is to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary Vitamin-A, which kills so many children under five year age.
Golden rice differs from its parental strain by the addition of three beta-carotene biosynthesis , genes namely ‘psy’ (phytoene synthase) from daffodil plant Narcissus pseudonarcissus and ‘crt-1’ gene from the soil bacterium Erwinia auredorora and ‘lyc’ (lycopene cyclase) gene from wild-type rice endosperm. The endosperm of normal rice, does not contain beta-carotene. Golden-rice has been genetically altered so that the endosperm now accumulates Beta-carotene. This has been done using Recombinant DNA technology. Golden rice can control childhood blindness – Xerophthalmia.
![]()
Question 55.
Name any 3 bacterial species used to generate polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB).
Answer:
Bacillus megaterium.
Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Alcaligenes eutrophus.
Question 56.
Write short note on Green fluorescent protein.
Answer:
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein containing 238 amino acid residues of 26.9 kDa that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to blue to ultraviolet range (395 nm). GFP refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria. GFP is an excellent tool in biology due to its ability to form internal chromophore without requiring any accessory cofactors, gene products, enzymes or substrates other than molecular oxygen. In cell and molecular biology, the GFP gene is frequently used as a reporter of expression. It has been used in modified forms to make biosensors.
Question 57.
How turmeric biopiracy is prevented by Indian Government?
Answer:
The United States Patent and Trademark Office, in the year 1995 granted patent to the method of use of turmeric as an antiseptic agent. Turmeric has been used by the Indians as a home remedy for the quick healing of the wounds and also for purpose of healing rashes. The journal article published by the Indian Medical Association, in the year 1953 wherein this remedy was mentioned.
Therefore, in this way it was proved that the use of turmeric as an antiseptic is not new to the world and is not a new invention, but formed a part of the traditional knowledge of the Indians. The objection in this case US patent and trademark office was upheld and traditional knowledge of the Indians was protected.
5 – Mark Questions
Question 58.
Describe the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
The steps involved in recombinant DNA technology are:
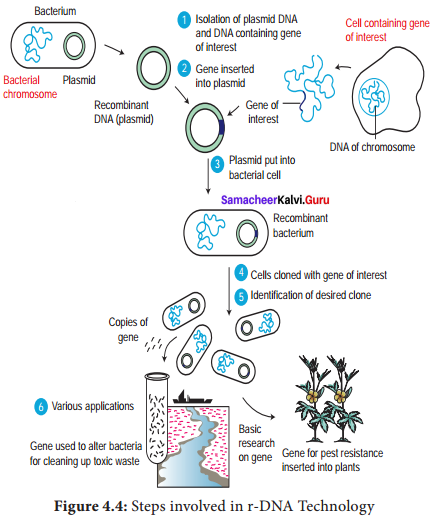
- Isolation of a DNA fragment containing a gene of interest that needs to be cloned. This is called an insert.
- Generation of recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecule by insertion of the DNA fragment into a carrier molecule called a vector that can self-replicate within the host cell.
- Selection of the transformed host cells that is carrying the rDNA and allowing them to multiply thereby multiplying the rDNA molecule. The
- entire process thus generates either a large amount of rDNA or a large amount of protein expressed by the insert.
- Wherever vectors are not involved the desired gene is multiplied by PCR technique. The multiple copies are. injected into the host cell protoplast or it is shot into the host cell protoplast by shot gun method.
Question 59.
Explain in detail about various ty pes of direct gene transfer method,
Answer:
a. Chemical mediated gene transfer: Certain chemicals like polyethylene glycol (PEG) and dextran sulphate induce DNA uptake into plant protoplasts.
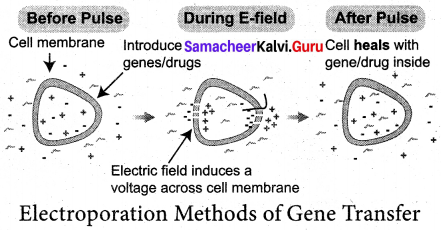
b. Microinjection: The DNA is directly injected into the Electric field induces a voltage across cell membrane nucleus using fine tipped glass needle or micro pipette Electroporation Methods of Gene Transfer to transform plant cells. The protoplasts are immobilised on a solid support (agarose on a microscopic slide) or held with a holding pipette under suction.
c. Electroporation Methods of Gene Transfer: Apulse of high voltage is applied to protoplasts, cells or tissues which makes transient pores in the plasma membrane through which uptake of foreign DNA occurs.
d. Liposome mediated method of Gene Transfer: Liposomes the artificial phospholipid vesicles are useful in gene transfer. The gene or DNA is transferred from liposome into vacuole of plant cells. It is carried out by encapsulated DNA into the vacuole. This technique is advantageous because the liposome protects the introduced DNA from being damaged by the acidic pH and protease enzymes present in the vacuole. Liposome and tonoplast of vacuole fusion resulted in gene transfer. This process is called lipofection.
e. Biolistics: The foreign DNA is coated onto the surface of minute gold or tungsten particles (1-3 pm) and bombarded onto the target tissue or cells using a particle gun (also called as gene gun/micro projectile gun/shotgun). Then the bombarded cells or tissues are cultured on selected medium to regenerate plants from the transformed cells.
Question 60.
Describe the procedure of Blue-White colony selection methods.
Answer:
Blue- White Colony Selection Method is a powerful method used for screening of recombinant plasmid. In this method, a reporter gene lacZ is inserted in the vector. The lacZ encodes the enzyme P-galactosidase and contains several recognition sites for restriction enzyme.P-galactosidase breaks a synthetic substrates called X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloroindolyl- P-D- galacto-pyranoside) into an insoluble blue coloured product. If a foreign gene is inserted into lacZ, this gene will be inactivated.
Therefore, no-blue colour will develop (white) because P-galactosidase is not synthesized due to inactivation of lacZ. Therefore, the host cell containing r-DNA form white coloured colonies on the medium contain X-gal, whereas the other cells containing non-recombinant DNA will develop the blue coloured colonies. On the basis of colony colour, the recombinants can be selected.
![]()
Question 61.
Write a note on Replica plating technique.
Answer:
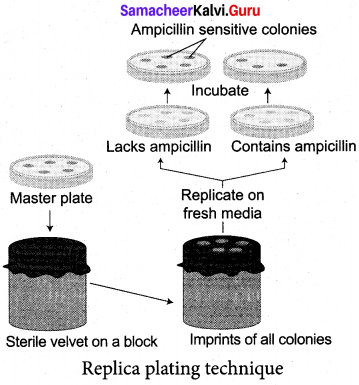
A technique in which the pattern of colonies growing on a culture plate is copied. A sterile filter plate is pressed against the culture plate and then lifted. Then the filter is pressed against a second sterile culture plate. This results in the new plate being infected with cell in the same
– relative positions as the colonies in the original plate. Usually, the medium used in the second plate will differ from that used in the first. It may include an antibiotic or without a growth factor. In this way, transformed cells can be selected. Replica plating technique
Question 62.
How Agarose Gel Electrophoresis is performed?
Answer:
1. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis is used mainly for the purification of specific DNA fragments. Agarose is convenient for separating DNA fragments ranging in size from a few hundred to about 20000 base pairs. Polyacrylamide is preferred for the purification of smaller DNA fragments.
2. The gel is complex network of polymeric molecules. DNA molecule is negatively charged molecule – under an electric field DNA molecule migrates through the gel. The electrophoresis is frequently performed with marker DNA fragments of known size which allow accurate size
3. determination of an unknown DNA molecule by interpolation. The advantages of agarose gel electrophoresis are that the DNA bands can be readily detected at high sensitivity. The bands of DNA in the gel are stained with the dye Ethidium Bromide and DNA can be detected
4. as visible fluorescence illuminated in UV light will give orange fluorescence, which can be photographed.
Question 63.
Explain the procedure of Southern Blotting Technique. Southern Blotting Techniques – DNA
Answer:
The transfer of denatured DNA from Agarose gel to Nitrocellulose Blotting or Filter Paper technique was introduced by Southern in 1975 and this technique is called Southern Blotting Technique.
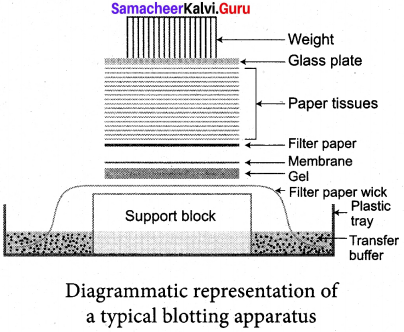
Steps:
The transfer of DNA from agarose gel to nitrocellulose filter paper is achieved by Capillary Action.
A buffer Sodium Saline Citrate (SSC) is used, in which DNA is highly soluble, it can be drawn up through the gel into the Nitrocellulose membrane. By this process ss-DNA becomes ‘Trapped’ in the membrane matrix.
This DNA is hybridized with a nucleic acid and can be detected by autoradiography. Autoradiography – A technique that captures the image formed in a photographic emulsion due to emission of light or radioactivity from a labelled component placed together with unexposed
film.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Give the technical terminologies for the following statements.
(а) Autonomous, self-replicating, circular DNA
(b) Molecular scissors
(c) Symmetrical repreated sequence in DNA strands
(d) Mobile genetic elements
Answer:
(a) Plasmid
(b) Restriction Enzymes
(c) Palindrome sequence
(d) Transposons
Question 2.
Observe the given flow chart and complete it.
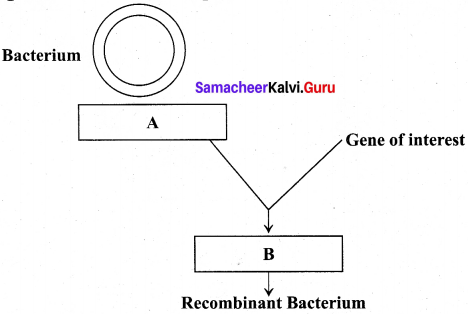
Answer:
A. Plasmid
B. rDNA/chimeric DNA
Question 3.
Name the products of the following combinations.
(a) Bacterial plasmid + cos – site = ______
(b) Bacterial plasmid + phage DNA = ______
Answer:
(a) Cosmid
(b) Phagemid
![]()
Question 4.
Golden rice is a bio-fortified rice developed by rDNA technology. It differes from its parental strain by possessing ‘psy’ gene, ‘crt-1’ gene and ‘lye’ gene which are responsible for beta – carotene synthesis.
(a) Name the sources of the above mentioned genes.
(b) Which disease can be controlled / prevented if a person’s diet has golden rice?
Answer:
(a) ‘psy’ gene is obtained from Daffodil plant (Narcissus pseudonarcissus).
(b) ‘crt-1’ gene is from Erwinia auredorora bacterium.
(c) Tyc gene is from wild-type rice endosperm.
(b) Golden rice can control Xerophthalmia.