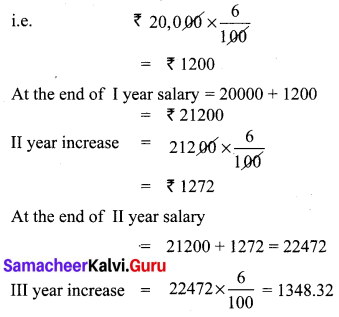
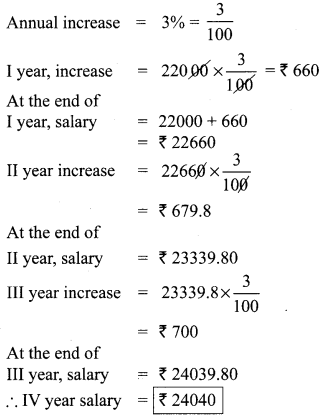
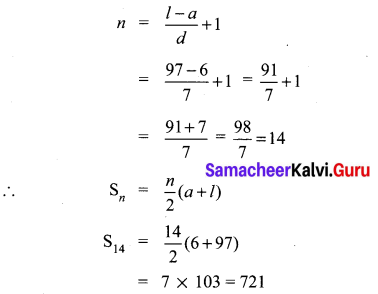
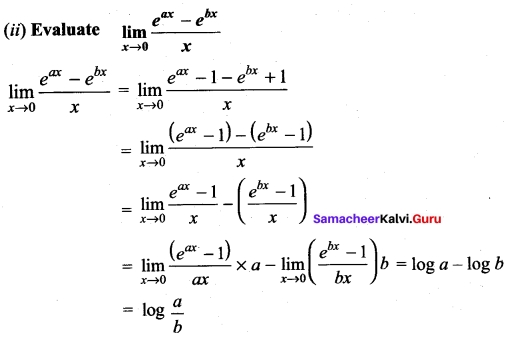
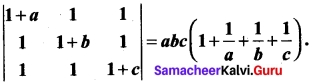
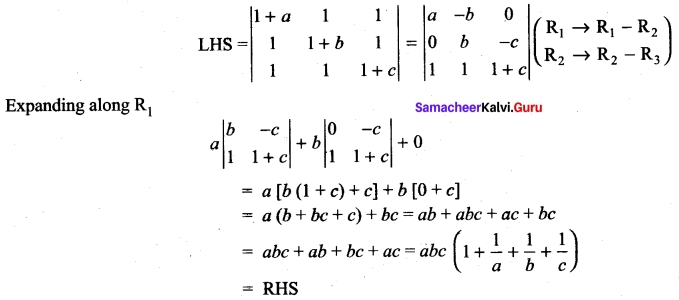
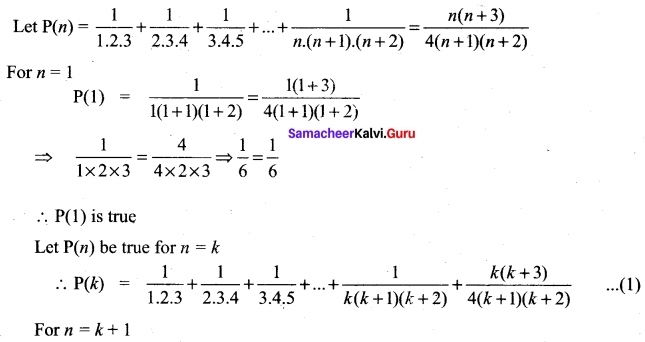
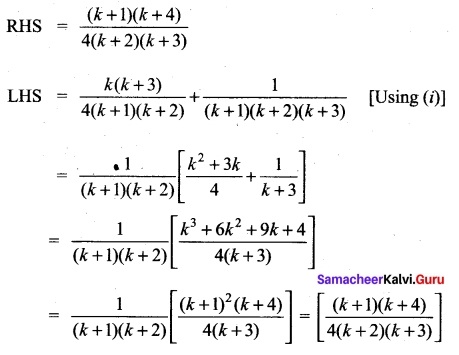
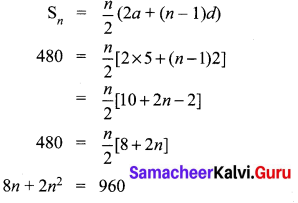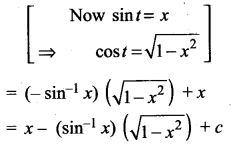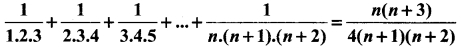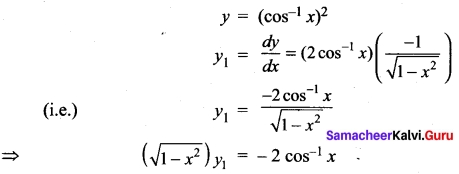Students can Download Bio Zoology Chapter 8 Excretion Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 8 Excretion
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Excretion Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Textbook Evulation Solved
Question 1.
Arrange the following structures in the order that a drop of water entering the nephron would encounter them?
- (a) Afferent arteriole
- (b) Bowman’s capsule
- (c) Collecting duct
- (d) Distal tubule
- (e) Glomerulus
- (f) Loop of Henle
- (g) Proximal tubule
- (h) Renal pelvis
Answer:
- (a) Afferent arteriole
- (b) Bowman’s capsule
- (e) Glomerulus
- (g) Proximal tubule
- (j) Loop of Henle
- (d) Distal tubule
- (c) Collecting duct
- (h) Renal pelvis

Question 2.
Name the three filtration barriers that solutes must come across as they move from plasma to the lumen of Bowman’s capsule. What components of the blood are usually excluded by these layers?
Answer:
1. Glomerulus net filtration pressure – 55 mm Hg
2. Colloidal osmotic pressure – 30 mm Hg
3. Capsular Hydrostatic pressure -15 mm Hg
Protein aminoacid glucose urea, uric acid creatinine, etc are excluded by these layers.
Question 3.
What forces promote glomerular filtration? What forces oppose them? What is meant by net filtration pressure?
Answer:
Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (55 mm Hg) is the force that promotes filtration. The colloidal osmotic pressure (30 mm Hg) and the capsular hydrostatic pressure (15 mm Hg) are the two opposing forces.
The difference between the force promoting and opposing filtration is the net filtration pressure. It is responsible for filtration. Net filtration pressure = Glomerular hydrostatic pressure – (Colloidal osmotic pressure + Capsular hydrostatic pressure).

Question 4.
Identify the following structures and explain their significance in renal physiology?
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- Podocytes
- Sphincters in the bladder
- Renal cortex
Answer:
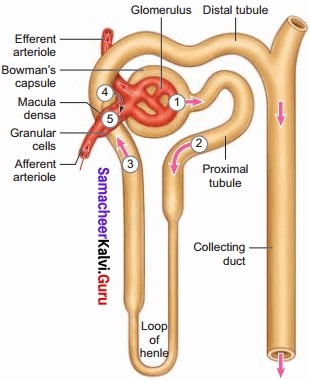
1. Juxtaglomerular apparatus:
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a specialized tissue in the afferent arteriole of the nephron that consists of macula densa and granular cells. The macula densa cells sense distal tubular flow and affect afferent arteriole diameter. The granular cells secrete an enzyme called renin. It plays an important role in reabsorption of water, Na+ and excretion of K+.
2. Podocytes:
The visceral layer of the Bowman’s capsule is made up of epithelial cells called podocytes. The podocytes end in foot processes which cling to the basement membrane of the glomerulus. The openings between the foot processes are called filtration slits. It is important for glomerular filtration.
3. Sphincters in the bladders:
Sphincter muscles in the bladder controls the flow of urine from the bladder. When urinary bladder is filled with urine, it stretches and stimulates the central nervous system through the sensory neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system and brings about contraction of the bladder.
Simultaneously, somatic motor neurons induce the sphincters to close. Smooth muscles contracts resulting in the opening of the internal sphincters passively and relaxing the external sphincter. When the stimulatory and inhibitory controls exceed the threshold, the sphincter opens and the urine is expelled out.
4. Renal cortex:
The outer portion of the kidney is the renal cortex. It contains renal corpuscles and the proximal and distal tubules. It is thin and fibrous.

Question 5.
In which segment of the nephron most of the re-absorption of substances takes place?
Answer:
In proximal convoluted tubule cells, Glucose, lactate, amino acids, Na+ and water, are reabsorbed. In the descending limb of Henle’s loop, water is reabsorbed. In the ascending limb, Na+, Cl and K+ are reabsorbed. In the distal convoluted tubule, water is reabsorbed.
Question 6.
When a molecule or ion is reabsorbed from the lumen of the nephron, where does it go? If a solute is filtered and not reabsorbed from the tubule, where does it go?
Answer:
If a solute is filtered and not reabsorbed from the tubule, where does it go?
- The reabsorbed molecule of the lumen of the nephron goes to interstitial fluid and then goes to the blood.
- The filtered molecule when it is not reabsorbed by the tubules it will be excreted out through urine.

Question 7.
Match each of the following substances with its mode of transportation in proximal tubular reabsorption?
(a) Na+ – 1. indirect active transport
(b) Glucose – 2. endocytosis
(c) Urea – 3. paracellular movement
(d) Plasma – 4. facilitated diffusion
(e) Water – 5. primary active transport
Answer:
(a) 5
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 2
(e) 3
Question 8.
Which segment is the site of secretion and regulated reabsorption of ions and pH homeostasis?
Answer:
Distal convoluted tubule.
Question 9.
What solute is normally present in the body to estimate GFR in humans?
Answer:
Creatinine.

Question 10.
Which part of the autonomic nervous system is involved in the micturition process?
Answer:
Para sympathetic nervous system.
Question 11.
Match the following terms.
(a) a- adrenoceptor – 1. afferent arteriole
(b) Autoregulation – 2. basal lamina
(c) Bowman’s capsule – 3. capillary blood pressure
(d) Capsule fluid – 4. colloid osmotic pressure
(e) Glomerulus – 5. GFR
(f) Podocyte – 6. JG cells
(g) Vasoconstriction – 7. plasma proteins Norepinepherine
Answer:
(a) 7
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 3
(e) 1
(f) 2
(g) 4

Question 12.
If the afferent arteriole of the nephron constricts, what happens to the GFR in that nephron? If the efferent arteriole constricts what happens to the GFR in that nephron? Assume that no autoregulation takes place?
Answer:
If the afferent arteriole of the nephron constricts, GFR is reduced. If the efferent arteriole constricts, GFR is increased.
Question 13.
How is the process of micturition altered by toilet training?
Answer:
The process of release of urine from the bladder is called micturition or urination. It is controlled by central nervous system and smooth muscles of sphincter. In young children, micturition cannot be controlled. By toilet training, one can temporarily postpone the signal reaching from the central nervous system to the motor neurons carrying stimuli to the urinary bladder.
Question 14.
Concentration of urine depends upon which part of the nephron?
a. Bowman’s capsule
b. Length of Henle’s loop
c. P.C.T.
d. Network of capillaries arising from glomerulus
Answer:
b. length of Henle’s loop

Question 15.
If Henle’s loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which one of the following is to be expected?
a. There will be no urine formation.
b. There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed.
c. The urine will be more concentrated.
d. The urine will be more dilute.
Answer:
d. The urine will be more dilute.
Question 16.
A person who is on a long hunger strike and is surviving only on water, will have
a. Less amino acids in his urine
b. Macula densa cells
c. Less urea in his urine
d. More sodium in his urine
Answer:
d. More sodium in his urine
Question 17.
What will happen if the stretch receptors of the urinary bladder wall are totally removed?
a. Micturition will continue
b. Urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder
c. There will be no micturition
d. Orine will not collect in the bladder
Answer:
c. There will be no micturition

Question 18.
The end product of Ornithine cycle is
a. Carbon dioxide
b. Uric acid
c. Urea
d. Ammonia
Answer:
c. Urea
Question 19.
Identify the wrong match
a. Bowman’s capsule – Glomerular Alteration
b. DCT – Absorption of glucose
c. Henle’s loop – Concentration of urine
d. PCT – Absorption of Na+ and K+ ions
Answer:
b. DCT – Absorption of glucose
Question 20.
Podocytes are the cells present on the
a. Outer wall of Bowman’s capsule
b. Inner wall of Bowman’s capsule
c. Neck of nephron
d. Wall glomerular capillaries
Answer:
b. Inner wall of Bowman’s capsule

Question 21.
Glomerular filtrate contains
a. Blood without blood cells and proteins
b. Plasma without sugar
c. Blood with proteins but without cells
d. Blood without urea
Answer:
a. Blood without blood cells and proteins
Question 22.
Kidney stones are produced due to deposition of uric acid and
a. Silicates
b. Minerals
c. Calcium carbonate
d. Calcium oxalate
Answer:
d. calcium oxalate
Question 23.
Animal requiring minimum amount of water to produce urine are
a. Ureotelic
b. Ammonotelic
c. Uricotelic
d. Chemotelic
Answer:
c. Uricotelic

Question 24.
Aldosterone acts at the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct resulting in the absorption of water through
a. Aquaporins
b. Spectrins
c. GLUT
d. Chloride channels
Answer:
a. Aquaporins
Question 25.
The hormone which helps in the reabsorption of water in kidney tubules is ………..
a. Cholecystokinin
b. Angiotensin II
c. Antidiuretic hormone
d. Pancreozymin
Answer:
b. Angiotensin II
Question 26.
Malphigian tubules remove excretory products from ………….
a. Mouth
b. Oesophagus
c. Haemolymph
d. Alimentary canal
Answer:
d. Alimentary canal

Question 27.
Identify the biological term Homeostasis, excretion, glomerulus, urea, glomerular filtration, ureters, urine, Bowman’s capsule, urinary system, reabsorption, micturition, osmosis, glomerular capillaries via efferent arteriole, proteins?
- A liquid which gathers in the bladder?
- Produced when blood is filtered in a Bowman’s capsule?
- The temporary storage of urine?
- A ball of inter-twined capillaries?
- A process that changes glomerular filtrate into urine?
- Removal of unwanted substances from the body?
- Does each contain a glomerulus?
- Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
- Contains urea and many useful substances?
- Blood is filtered through its walls into the Bowman’s capsule?
- Scientific term for urination?
- Regulation of water and dissolved substances in blood and tissue fluid?
- Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
- Consists of the kidneys, ureters and bladder?
- Removal of useful substances from glomerular filtrate?
- The process by which water is transported in the proximal convoluted tubule?
- Where has the blood in the capillaries surrounding the proximal convoluted tubule come from?
- What solute does blood contain that is not present in the glomerular filtrate?
Answer:
- Urine
- Glomerular filtrate
- Urinary bladder
- Glomerulus
- Reabsorption
- Excretion
- Bowman’s capsule
- Ureters
- Glomerular filtrate
- Glomerulus
- Micturition
- Homeostatic
- Ureters
- Urinary system
- Reabsorption
- Osmosis
- Glomerular capillaries via the efferent arteriole
- Proteins

Question 28.
With regards to toxicity and the need for dilution in water, how’ different are ureotelic and uricotelic excretions? Give examples of animals that use these types of excretion?
Answer:
Ureotelic animals excrete urea with minimum loss of water, e.g., Mammals and terrestrial amphibians. Uricotelic animals excrete uric acid with the least loss of water, e.g., Birds and reptiles.
Question 29.
Differentiate protonephridia from metanephridia?
Answer:
| Protonephridia |
Metanephridia |
| 1. Primitive kidneys are protonephridia |
1. Tubular excretory structures are |
| 2. These are found in flatworms. |
2. These are found in annelids and mollusks |
Question 30.
What is the nitrogenous waste produced by amphibian larvae and by adult animals?
Answer:
Amphibian larvae produce ammonia and the adult produces urea.

Question 31.
How is urea formed in the human body?
Answer:
More toxic ammonia produced as a result of breakdown of amino acids is converted into less toxic urea in the liver by a cyclic process called Ornithine cycle.
Question 32.
Differentiate cortical from medullary nephrons?
Answer:
| Cortical nephrons |
Medullary nephrons |
| 1. These are found in the cortex. |
1. These are found in the medulla. |
| 2. These have short Henle’s loop. |
2. These have long Henle’s loop. |
Question 33.
What vessels carry blood to the kidneys? Is this blood arterial or venous?
Answer:
The renal artery carries oxygenated (arterial) blood to the kidney.

Question 34.
Which vessels drain filtered blood from the kidneys?
Answer:
Renal veins carry deoxygenated blood from the kidney.
Question 35.
What is tubular secretion? Name the substances secreted through the renal tubules?
Answer:
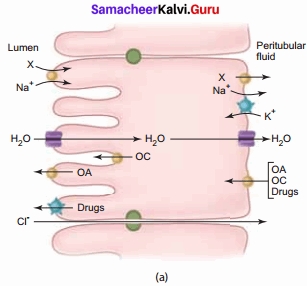
The movement of substances such as H+, K+, NH4+, creatinine, and organic acids from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular fluid, the filtrate is called Tubular secretion.

Question 36.
How are the kidneys involved in controlling blood volume? How is the volume of blood in the body related to arterial pressure?
Answer:
Renin-Angiotensin stimulates Na+ reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate. This stimulates Adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone that causes reabsorption of Na+, K+ excretion and absorption of water.
This reduces the loss of water into the urine. This maintains the volume of blood. An increase in blood volume increases central venous pressure. This increases right atrial pressure, right ventricular end-diastolic pressure, and volume. This increases ventricular stroke volume and cardiac output and arterial blood pressure.
Question 37.
Name the three main hormones that are involved in the regulation of renal function?
Answer:
Antidiuretic hormone, aldosterone and atrial natriuretic peptide factor.
Question 38.
What is the function of the antidiuretic hormone? Where is it produced and what stimuli increase or decreases its secretion?
Answer:
Antidiuretic hormone increases reabsorption of water in the kidney tubules. It is produced in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. When there is excess loss of fluid from the body or increase in the blood pressure, ADH is secreted more. When there is no loss of fluid from the body, it is secreted less.

Question 39.
What is the effect of aldosterone on kidneys and where is it produced?
Answer:
Aldosterone is produced by the Adrenal cortex. It increases reabsorption of sodium and water by distal convoluted tubule and increased secretion of potassium. Hence, it maintains blood volume, blood pressure and urine output.
Question 40.
What evolutionary hypothesis could explain the heart’s role in secreting a hormone that regulates renal function? What hormone is this?
Answer:
The cardiac atrial cells secrete atrial natriuretic peptide or factor. It travels to the kidney and increases blood flow to the glomerulus. It acts as a vasodilator on the afferent arteriole and vasoconstrictor on the efferent arteriole. It decreases aldosterone release for the adrenal cortex and decreases the release of renin Angiotensin-II. Health of the heart depends on the normal blood pressure and hence evolution might have preserved atrial natriuretic factor which acts upon the renal function.
In-Text Questions Solved
Question 1.
What is the importance of having a long loop of Henle and short loop of Henle in a nephron?
Answer:
The major function of Henle’s loop is to concentrate Na+ and Cl–. The longer the Henle’s loop, the more concentrated is the urine that is above the osmotic concentration of plasma.

Question 2.
A person with cirrhosis of the liver has lower than normal levels of plasma proteins and higher than normal GFR. Explain why a decrease in plasma protein would increase GFR?
Answer:
The net filtration pressure of 10 mmHg is responsible for the renal filtration. Net filtration Pressure = Glomerular hydrostatic pressure – (Colloidal osmotic pressure + Capsular hydrostatic pressure). Therefore, when there is decrease in plasma proteins, the value of Colloidal osmotic pressure + Capsular hydrostatic pressure decreases. This contributes to the increased net filtration pressure resulting in increase of GFR.
Question 3.
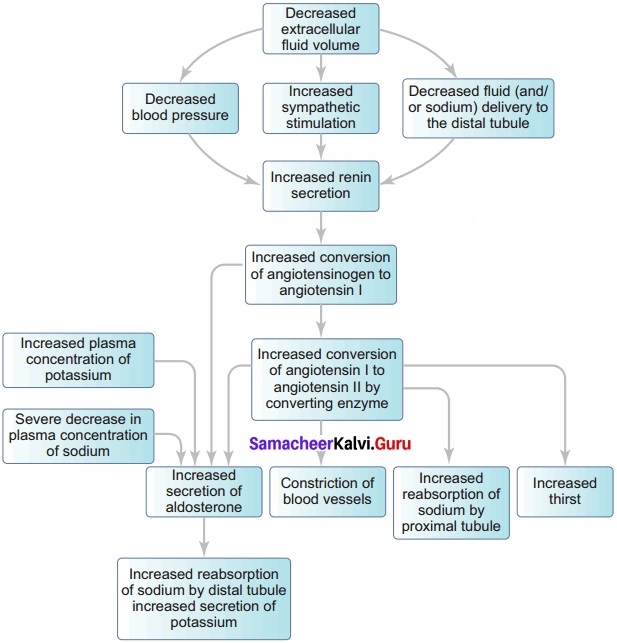
List various pathways involved in the homeostatic compensation in the case of severe dehydration?
Answer:
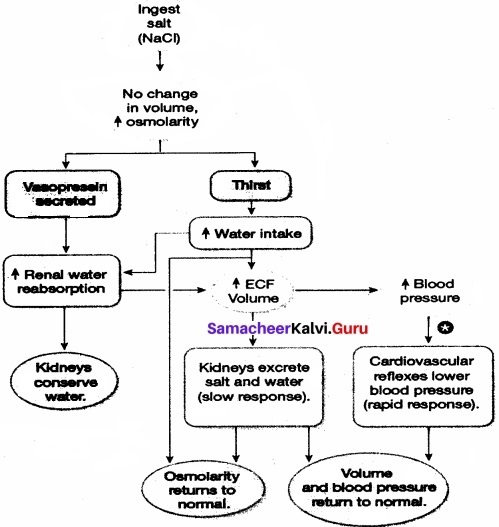
The below flowchart shows the pathways involved in the homeostatic compensation in case of severe dehydration.
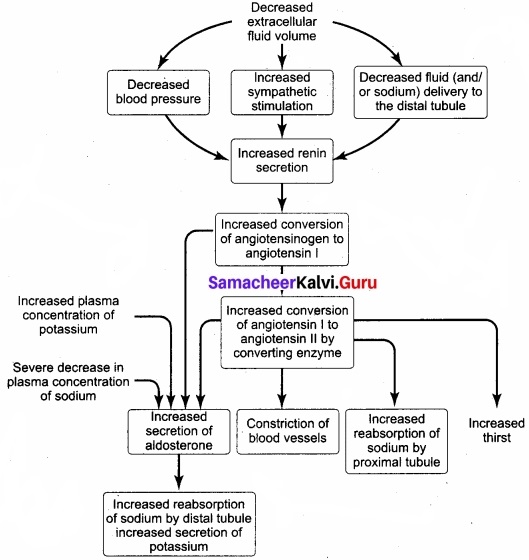
- If there is decreased extracellular fluid volume, it increases sympathetic stimulation and decreases blood pressure and decreases fluid and sodium delivery to the distal tubule.
- This enhances the secretion of renin.
- It converts angiotensinogen to angiotensen 1 and angiotensen 1 to angiotehsen 2.
- This increase in angiotensin 1 increases the secretion of aldosterone which increases the reabsorption of sodium by distal tubule and increased secretion of potassium.
- The increase in angiotensin 2 increases thirst and reabsorption of sodium in the PCT.

Question 4.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are used to treat high blood pressure. Using a flow chart, explain why these drugs are helpful in treating hypertension?
Answer:
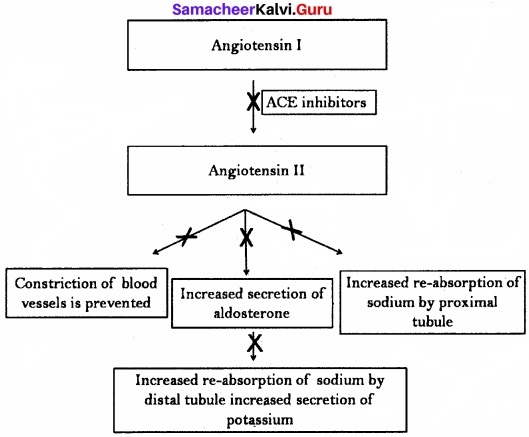
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) prevent the conversion of angiotensinogen into angiotensin I and angiotensin I into angiotensin II. This decreases the reabsorption of sodium by proximal convoluted tubule and secretion of aldosterones. This prevents the increased secretion of potassium. All these reactions help in treating hypertension.

Question 5.
Consider how different foods affect water and salt balance, and how the excretory system must respond to maintain homeostasis?
Answer:
The excessive intake of sodium chloride„i.e. common salt increases osmolarity. This increases thirst and secretion of vasopressin. The vasopressin increases the reabsorption of water in the renal tubule. Kidneys prevent the loss of water. Due to the intake of water due to thirst, extracellular fluid volume increases.
This stimulates kidneys to excrete salt and water to bring osmolarity to normal. When there is an increase in the blood pressure due to increase in the extracellular fluid volume, cardiovascular reflexes occur to reduce the blood pressure. This brings the volume and blood pressure to normal. Thus, the excessive intake of sodium affects the water and salt balance. The excretory system responds to those changes and maintains homeostasis.
Text Book Activities Solved
Question 1.
Visit a nearby health center to observe the analysis of urine. Dip strips can be used to test urine for a range of different factors such as pH, glucose, ketones, and proteins. Dipsticks for detecting glucose contain two enzymes namely, glucose oxidase and peroxidase? These two enzymes are immobilized on a small pad at one end of the stick. The pad is immersed in urine. If the urine contains glucose, a brown colored compound is produced. The resulting colour pad is matched against a color chart. The colour does not indicate the current blood glucose concentrations?
Answer:
Students can visit nearby health centre under the guidance of the teacher.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Excretion Additional Questions & Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
The elimination of ……………………….. requires a large amount of water.
(a) Urea
(b) Uric acid
(c) Ammonia
(d) creatinine
Answer:
(c) ammonia
Question 2.
Reptiles, birds, land snails, and insects excrete ……………..
(a) Ammonia
(b) Urea
(c) Uric
(d) purines
Answer:
(c) uric acid

Question 3.
Solenocytes are the specialized cells for excretion in
(a) Flatworms
(b) Molluscs
(c) Insects
(d) Amphioxus
Answer:
(d) amphioxus
Question 4.
Insects have for excretion.
(a) Flame cells
(b) Malpighian tubules
(c) Solenocytes
(d) Green glands
Answer:
(b) Malpighian tubules
Question 5.
…………………… have antennal glands or green glands which perform an excretory function.
(a) Insects
(b) Annelids
(c) Crustaceans
(d) Flatworms
Answer:
(c) Crustaceans

Question 6.
Reptiles produce very little ……………….. urine
(a) Hypotonic
(b) Hypertonic
(c) Isotonic
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Hypotonic
Question 7.
Mammals have long Henle’s loop, hence they produce ……………………… urine.
(a) Hypotonic
(b) Hyperosmotic
(c) Isotonic
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Hyperosmotic
Question 8.
Aglomerlar kidneys of marine fishes produce little urine that is ………………………. to the body fluid.
(a) Hypotonic
(b) Hyperosmotic
(c) Isoosmotic
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Isoosmotic

Question 9.
The external parietal layer of the Bowman’s capsule is made up of simple ……………………. epithelium.
(a) Columnar
(b) Ciliated
(c) Squamous
(d) Glandular
Answer:
(c) Squamous
Question 10.
The nitrogenous wastes are formed as a result of catabolism of …………..
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Proteins
(c) Fats
(d) Minerals
Answer:
(b) proteins
Question 11.
The net filtration pressure ………………………. of is responsible for renal filtration.
(a) 15mmHg
(b) 30 mmHg
(c) 55 mmHg
(d) 10 mmHg
Answer:
(d) 10 mmHg
Question 12.
Glucose, amino acids, Na+, and water in the filtrate are reabsorbed in the
(a) descending limb of Henle’s loop
(b) ascending limb of Henle’s loop
(c) proximal convoluted tubule
(d) distal convoluted tubule
Answer:
(c) Proximal convoluted tubule

Question 13.
Defects in ADH receptors or inability to secrete ADH leads to a condition called ……………….
(a) diabetes mellitus
(b) diabetes insipidus
(c) Cushing’s syndrome
(d) renal failure
Answer:
(b) diabetes insipidus
Question 14.
The process of release of urine from the bladder is called …………….
(a) Ultra filtration
(b) Reabsorption
(c) Micturition
(d) Secretion
Answer:
(c) Micturition
Question 15.
The pH value of human urine is ……………
(a) 7.5
(b) 6.0
(c) 4.3
(d) 9.5
Answer:
(a) 6.0
Question 16.
On average, …………………… gm of urea is excreted per day.
(a) 10 – 15
(b) 15-20
(c) 40 – 50
Answer:
(d) 25 – 30

Question 17.
…………………….. is characterized by an increase in urea and other non-protein nitrogenous substances like uric acid and creatinine.
(a) Renal calculi
(b) Uremia
(c) Glomerulonephritis
(d) Renal failure
Answer:
(b) Uremia
Question 18.
The formation of hard stone-like masses in the renal tubules of the renal pelvis is called ……………
(a) Uremia
(b) Micturition
(c) Renal calculi
(d) Renal failure
Answer:
(c) Renal calculi
Question 19.
The inflammation of the glomeruli of kidneys due to Streptococcus bacteria is called …………..
(a) Renal failure
(b) Uremia
(c) Glomerulonephritis
(d) Renal calculi
Answer:
(c) Glomerulonephritis

Question 20.
Through hemodialysis, ……………………….. can be removed from the blood.
(a) Ketone bodies
(b) Glucose
(c) Amino acids
(d) Urea
Answer:
(d) Urea
Question 21.
The transfer of a healthy kidney from one person to another person with kidney failure is called ……………
(a) Kidney failure
(b) Haemodialysis
(c) Kidney transplantation
(d) Uremia
Answer:
(c) Kidney transplantation
II. Fill in the Blanks.
Question 1.
……………………………. regulation is the control of tissues osmotic pressure which acts as a driving force for the movement of water across biological membranes.
Answer:
Osmotic

Question 2.
……………………. regulation is the control of the ionic composition of body fluids.
Answer:
Ionic
Question 3.
……………………. is the toxic nitrogenous end product of protein catabolism.
Answer:
Ammonia
Question 4.
…………………….. are able to change their internal osmotic concentration with a change in the external environment.
Answer:
Osmoconformers
Question 5.
…………………….. maintain their internal osmotic concentration irrespective of their external osmotic environment.
Answer:
Osmoregulation
Question 6.
The …………………. animals can tolerate only narrow fluctuations in the salt concentration.
Answer:
stenohaline

Question 7.
The ……………………. animals are able to tolerate wide fluctuations in the salt concentrations.
Answer:
euryhaline
Question 8.
…………………….. is the waste product of protein metabolism in spiders.
Answer:
Guanine
Question 9.
…………………….. requires a large amount of water for its elimination.
Answer:
Ammonia
Question 10.
…………………. is the least toxic waste product of protein metabolism.
Answer:
Uric acid
Question 11.
Animals that excrete ammonia are called …………
Answer:
Ammonites

Question 12.
The animals that excrete uric acid crystals are called ……………………..
Answer:
Uricoteles
Question 13.
The animals that excrete urea are called ……………………..
Answer:
Ureoteles
Question 14.
…………………….. are the excretory structures in flatworms.
Answer:
Flame cells
Question 15.
Solenocytes are the excretory cells present in ……………………..
Answer:
Amphioxus

Question 16.
…………………….. are the excretory structures in insects.
Answer:
Malphigian tubules
Question 17.
…………………….. function excretory function in prawns.
Answer:
Antennal glands/ Green glands
Question 18.
…………………….. are the structural and functional unit of kidneys.
Answer:
Nephrons
Question 19.
The right kidney is placed slightly lower than the left kidney due to the presence of ……………………..
Answer:
liver

Question 20.
The medulla of kidney is divided into a few conical tissue masses called ……………………..
Answer:
Renal pyramids
Question 21.
The urinary bladder opens into ……………………..
Answer:
Urethra
Question 22.
The Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus together constitute the ……………………..
Answer:
Renal corpuscle
Question 23.
Some nephron has a very long loop of Henle that run deep into the medulla and are called ……………………..
Answer:
Juxta medullary nephrons
Question 24.
The nitrogenous waste formed as a result of the breakdown of amino acids is converted to urea in the …………………….. Ornithine cycle.
Answer:
Liver

Question 25.
The filtration of blood that takes place in the ……………………..
Answer:
Glomerulus.
Question 26.
The fluid that leaves the glomerular capillaries and enters the Bowman’s capsule is called the ……………………..
Answer:
Glomerular filtrate
Question 27.
Sodium is reabsorbed by …………………….. in the proximal convoluted Tubule.
Answer:
Active transport
Question 28.
Descending limb of Henle’s loop is permeable to water due to the presence of ……………………..
Answer:
Aquaporins

Question 29.
Reabsorption of …………………….. ions regulates the pH of the blood.
Answer:
Bicarbonate
Question 30.
…………………….. Is the hormone that facilitates the reabsorption of water by increasing the number of aquaporins on the DCT and collecting duct.
Answer:
Antidiuretic hormone/ vasopressin
Question 31.
The under secretion of ADH leads to ……………………..
Answer:
Diabetes insipidus
Question 32.
The granular cells of afferent arteriole secrete an enzyme called ……………………..
Answer:
Renin
Question 33.
Renin converts …………………….. into angiotensin.
Answer:
Angiotensinogen
Question 34.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide or factor decreases the release of …………………….., thereby decreasing angiotensin II.
Answer:
Renin

Question 35.
The process of release of urine from the bladder is called ……………………..
Answer:
Micturition
Question 36.
The yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of a pigment, ……………………..
Answer:
Urochrome
Question 37.
The presence of ketone bodies in the urine is called ……………………..
Answer:
Ketonuria
Question 38.
…………………….. is characterized by an increase in urea and other non-protein nitrogenous substances like uric acid and creatinine in the blood.
Answer:
Uremia
Question 39.
The formation of hard stone-like masses in the renal tubules of the renal pelvis is called ……………………..
Answer:
Renal calculi
Question 40.
Renal calculi are due to the accumulation of soluble crystals of …………………….. and certain phosphates.
Answer:
Sodium oxalates

Question 41.
Renal stones can be removed by techniques like …………………….. or lithotripsy.
Answer:
Pyleothotomy
Question 42.
Inflammation of the glomeruli of both kidneys is known as ……………………..
Answer:
Glomerulonephritis/ Bright’s disease
Question 43.
haematuria, proteinuria, salt and water retention, oligouria, hypertension, and pulmonary oedema are symptoms of ……………………..
Answer:
Glomerulonephritis/ Bright’s disease

Question 44.
The process of removing toxic urea from the person with kidney failure is called ……………………..
Answer:
Haemodialysis
Question 45.
…………………….. drugs are administered to the patient after kidney transplantation to avoid tissue rejection.
Answer:
Immunosuppressive
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What is osmotic regulation?
Answer:
Osmotic regulation is the control of tissue osmotic pressure which acts as a driving force for the movement of water across biological membranes.
Question 2.
What is ionic regulation?
Answer:
Ionic regulation is the control of the ionic composition of body fluids.

Question 3.
Define excretion?
Answer:
The process by which the body gets rid of the nitrogenous waste products of protein metabolism is called excretion.

Question 4.
Distinguish between Osmoconformers and Osmoregulators?
Answer:
| Osmoconformers |
Osmoregulation |
| 1. These animals are able to change their internal osmotic concentration with changes in the external environment. |
1. These animals maintain their internal osmotic concentration irrespective of their external osmotic environment. |
| 2. e.g. Marine mollusks and Sharks |
2. e.g. Otters |
Question 5.
Distinguish between Stenohaline and Euryhaline animals?
Answer:
| Stenohaline |
Euryhaline |
| 1. These animals can tolerate only narrow fluctuations in salt concentration. |
1. These animals are able to tolerate wide fluctuations in salt concentrations. |
| 2. e.g. Goldfish |
2. e.g. Artemia, Tilapia and Salmon. |

Question 6.
Name some nitrogenous waste product produced by various animals?
Answer:
Some of the nitrogenous wastes produced by various animals other than ammonia, urea and uric acid are:
Jrimethyl amine oxide (TMO) in marine teleosts, guanine in spiders, hippuric acid in mammals, reptiles and other nitrogenous wastes include allantonin, allantoic acid, omithuric acid, creatinine, creatine, purines, pyramidines and pterines.
Question 7.
What are ammonotelic animals?
Answer:
Animals that excrete ammonia with excess water are called ammonoteles. e.g., fishes, aquatic amphibians, and aquatic insects.
Question 8.
What are the excretory organs of crustaceans?
Answer:
Antennal glands or green glands.
Question 9.
What is the difference between nephrons present in reptiles and mammals?
Answer:
Reptiles have reduced glomerulus or lack glomerulus and Henle’s loop. Mammals have a long Henle’s loop. Reptiles produce hypotonic urine whereas mammals produce hypertonic urine.

Question 10.
Explain the structure of the human excretory system?
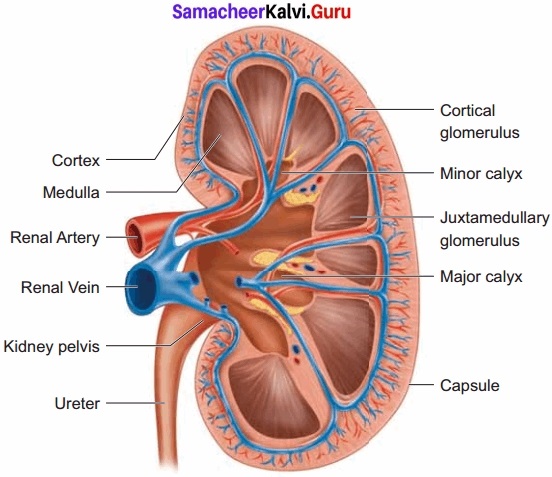
Answer:
1. Excretory system in humans consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Kidneys are reddish-brown, bean-shaped structures that lie in the lumbar region between the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebra.
2. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney. Each kidney weighs about 120-170 grams. The outer layer of the kidney is covered by three layers of supportive tissues namely, renal fascia, perirenal fat capsule and fibrous capsule.
3. The longitudinal section of kidney shows an outer cortex, inner medulla and pelvis. The medulla is divided into a few conical tissue masses called medullary pyramids or renal pyramids.
4. The part of cortex that extends in between the medullary pyramids is the renal columns of Bertini. The centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney has a notch called the renal hilum.
5. Through this ureter, blood vessels and nerves innervate. There is a broad funnel-shaped space called the renal pelvis with projection called calyces.
6. The walls of the calyces, pelvis and ureter have smooth muscles. The calyces collect the urine and empties into the ureter. It is stored in the urinary bladder temporarily. The urinary bladder opens into the urethra through which urine is expelled out.
Question 11.
Explain the structure of Nephron?
Answer:
Each kidney has nearly one million tubular structures called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a filtering corpuscle called renal corpuscle or malphigian body and a renal tubule. The renal tubule opens into a longer tubule called the collecting duct. The renal corpuscle has a double-walled cup-shaped structure called the Bowman’s capsule. It encloses a ball of capillaries called the glomerulus.
The Bowman’s capsule and the Glomerulus together constitute the renal corpuscle. The endothelium of the glomerulus has many pores called fenestrae.
The external parietal layer of the Bowman’s capsule is made up of simple squamous epithelium. The visceral layer is made of epithelial cells called podocytes. The podocytes end in foot processes which cling to the basement membrane of the glomerulus. The openings between the foot processes are called filtration slits.
The renal tubule continues further to form the proximal convoluted tubule, Henle’s loop, and the distal convoluted tubule. The Henle loop has a thin descending limb and a thick ascending limb.
The distal convoluted tubule of many nephrons opens into a collecting duct. The proximal and the distal convoluted tubule are situated in the cortical region whereas Henle’s loop is situated in the medullary region of the kidney.

Question 12.
Explain the mechanism of urine formation in humans?
Answer:
The nitrogenous waste formed as a result of the breakdown of amino acids is converted to urea in the liver by the Ornithine cycle or urea cycle. Urine formation involves three main processes:
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular reabsorption
- Tubular secretion
1. Glomerular Filtration:
Blood enters the kidney from the renal artery, into the glomerulus. The glomerular membrane has a large surface area and is more permeable to water and small molecules present in the blood plasma.
Blood enters the glomerulus faster with greater force through the afferent arteriole and leaves the glomerulus through the efferent arterioles, much slower. This is because of the wider afferent arteriole and glomerular hydrostatic pressure which is around 55 mm Hg.
This is the chief force that pushes water and solutes out of the blood and across the filtration membrane. The pressure is much higher than in other capillary beds. The colloidal osmotic pressure (30 mm Hg) and the capsular hydrostatic pressure (15 mm Hg) are the opposing forces.
The net filtration pressure of 10 mm Hg is responsible for the renal filtration.
Net filtration pressure = Glomerular hydrostatic pressure – (Colloidal osmotic pressure + Capsular hydrostatic pressure) = 55 mm Hg – (30 mm Hg + 15 mm Hg) = 10 mm Hg.
The effective glomerular pressure of 10 mm Hg results in ultrafiltration. The fluid that leaves the glomerular capillaries and enters the Bowman’s capsule is called the glomerular filtrate.
It is similar to blood plasma except that there are no plasma proteins. Kidneys produce about 180L of glomerular filtrate in 24 hours. It has water, glucose, amino acids and minerals along with urea and other nitrogenous waste.
2. Tubular Reabsorption:
The substances of glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed by the renal tubules as they are needed by the body. This process is called selective reabsorption.
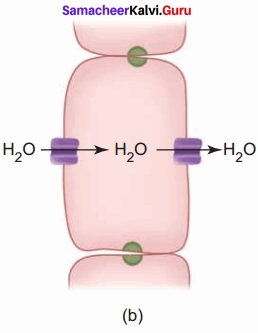
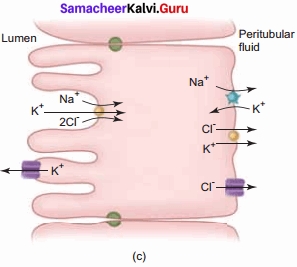
In the Proximal Convoluted Tubule, glucose, lactate, amino acids, Na+, and water are reabsorbed. Sodium is reabsorbed by active transport through the sodium-potassium pump. The descending limb of Henle’s loop is permeable to water due to the presence of aquaporins, but impermeable to salts.
Water is lost in this region and hence Na+ and Cl– get concentrated in the filtrate. In the ascending limb of Henle’s loop, Na+, Cl-, and K+ are reabsorbed. This region is impermeable to water. The distal convoluted tubule reabsorbs water and secretes potassium into the tubule. Na+, Cl-, and water remain in the filtrate. In the collecting duct, water and Na+ are reabsorbed and K+ is secreted.
3. Tubular secretion:
In this process, substances such as H+, K+, NH4+, creatinine and organic acids move into the filtrate from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular fluid. Human produces 1.5 L of urine per day.
Question 13.
What is Diabetes insipidus?
Answer:
The defect in the production of ADH results in the excretion of large quantities of dilute urine, this is called Diabetes insipidus. This results in dehydration and a fall in blood pressure.
Question 14.
What is Micturition?
Answer:
The process of release of urine from the bladder is called micturition or urination.
Question 15.
What is the nature of urine of human beings?
Answer:
The urine formed is a yellow coloured watery fluid which is slightly acidic in nature (pH 6.0).

Question 16.
What is glucosuria and ketonuria?
Answer:
The presence of glucose in the urine is called glucosuria. The presence of ketone bodies in the urine is called ketonuria. These are the indications of Diabetes Mellitus.
Question 17.
Name the pigment present in the urine?
Answer:
The yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of pigment urochrome.
Question 18.
Explain the excretory role of other organs?
Answer:
- Lungs: Lungs remove large quantities of carbon dioxide (18 L /day) and significant quantities of water.
- Liver: The liver secretes bile which contains bilirubin, biliverdin, cholesterol, steroid hormones, vitamins and drugs. These are excreted out along with the digestive wastes.
- Skin: Sweat glands eliminate certain wastes like urea and lactate. Sebaceous glands eliminate sterols, hydrocarbons, and waxes through the serum.
- Saliva: Small quantities of nitrogenous wastes are excreted through saliva.

Question 19.
Explain the hormones regulating kidney function?
Answer:
Antidiuretic hormone or Vasopressin, juxtaglomerular apparatus, and atrial natriuretic factor regulate kidney function. Antidiuretic hormone or Vasopressin When there is excessive loss of fluid from the body or when there is an increase in the blood pressure, the osmoreceptors of the hypothalamus stimulates the neurohypophysis to secrete the antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin.
It facilitates the reabsorption of water by increasing the number of aquaporins on the cell surface membrane of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct.
When the water loss from the body is less or when you drink excess amount of juice, osmoreceptors stop secreting ADH and the aquaporins of the collecting ducts move into the cytoplasm. Hence dilute urine is produced to maintain the blood volume.
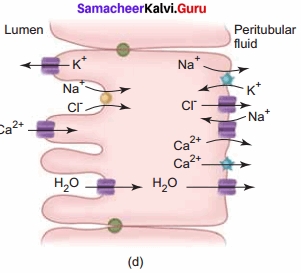
Renin-angiotensin:
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) is a specialized tissue in the afferent arteriole of the nephron. It consists of macula densa and granular cells. The macula densa cells sense distal tubular flow and affect afferent arteriole diameter.
The granular cells secrete an enzyme called renin. A fall in glomerular blood flow, glomerular blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate, can activate JG cells to release renin.
This converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin-I. Angiotensin converting enzyme converts angiotensin-I to angiotensin- II. Angiotensin-II stimulates Na+ reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule by vasoconstriction of the blood vessels and increases the glomerular blood pressure.
Angiotensin- II stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone that causes reabsorption of Na+, K+ excretion, and absorption of water from the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct. This increases the glomerular blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate. This complex mechanism is generally known as Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS).
Atrial natriuretic factor:
The excessive stretch of cardiac atrial cells causes an increase in blood flow to the atria of the heart and release Atrial Natriuretic Peptide or Factor (ANF). It travels to the kidney where it increases Na+ excretion and increases the blood flow to the glomerulus, acting as a vasodilator on the afferent glomerular arterioles and as a vasoconstrictor on efferent arterioles.
It decreases aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex and decreases the release of renin, thereby decreasing angiotensin-II. ANF acts antagonistically to the renin-angiotensin system, aldosterone and vasopressin.

Question 20.
Write a short note on urinary tract infection?
Answer:
The Female’s urethra is very short and its external opening is close to the anal opening, hence improper toilet habits can easily carry faecal bacteria into the urethra. The urethral mucosa is continuous with the urinary tract and the inflammation of the urethra (urethritis) can ascend the tract to cause bladder inflammation (cystitis) or even renal inflammation (pyelitis or pyelonephritis).
Symptoms include dysuria (painful urination), urinary urgency, fever, and sometimes cloudy or blood-tinged urine. When the kidneys are inflammed, back pain and severe headache often occur. Most urinary tract infections can be treated by antibiotics.
Question 21.
Write a short note on Renal Failure or Kidney Failure?
Answer:
Failure of the kidneys to excrete wastes may lead to accumulation of urea with a marked reduction in the urine output. Renal failure is of two types, acute and chronic renal failure.
In acute renal failure, the kidney stops its function abruptly, but there are chances for recovery of kidney functions. In chronic renal failure, there is a progressive loss of function of the nephrons which gradually decreases the function of kidneys.
Question 22.
Write a short note on Uremia?
Answer:
Uremia is characterized by an increase in urea and other non-protein nitrogenous substances like uric acid and creatinine in the blood. Normal urea level in human blood is about 17-30 mg/100 mL of blood. The urea concentration rises to 10 times normal levels during chronic renal failure.

Question 23.
Write a short note on Renal calculi?
Answer:
Renal calculi, also called renal stone or nephrolithiasis, is the formation of hard stone-like masses in the renal tubules of the renal pelvis. It is mainly due to the accumulation of soluble crystals of salts of sodium oxalates and certain phosphates. This results in severe pain called “renal colic pain” and can cause scars in the kidneys. Renal stones can be removed by techniques like pyelolithotomy or lithotripsy.
Question 24.
Write a short note on Glomerulonephritis?
Answer:
Glomerulonephritis is also called Bright’s disease and is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli of both kidneys and is usually due to post-streptococcal infection that occurs in children. Symptoms are haematuria, proteinuria, salt and water retention, oligouria, hypertension, and pulmonary oedema.
Question 25.
Write a short note on Haemodialysis?
Answer:
Malfunction of the kidneys can lead to accumulation of urea and other toxic substances, leading to kidney failure. In such patients, toxic urea can be removed from the blood by a process called haemodialysis. A dialyzing machine or an artificial kidney is connected to the patient’s body. A dialyzing machine consists of a long cellulose tube surrounded by the dialyzing fluid in a water bath.
The patient’s blood is drawn from a convenient artery and pumped into the dialyzing unit after adding an anticoagulant like heparin. The tiny pores in the dialysis tube allow small molecules such as glucose, salts, and urea to enter the water bath, whereas blood cells and protein molecules do not enter these pores.
This stage is similar to the filtration process in the glomerulus. The dialysing liquid in the water bath consists of a solution of salt and sugar in the correct proportion in order to prevent loss of glucose and essential salts from the blood. The cleared blood is then pumped back to the body through a vein.

Question 26.
Write a short note on Kidney Transplantation?
Answer:
Kidney Transplantation is the ultimate method for correction of acute renal failures. This involves the transfer of a healthy kidney from one person (donor) to another person with kidney failure.
The donated kidney may be taken from a healthy person who is declared brain dead or from sibling or close relatives to minimize the chances of rejection by the immune system of the host. Immunosuppressive drugs are usually administered to the patient to avoid tissue rejection.


![]()
![]()
![]()