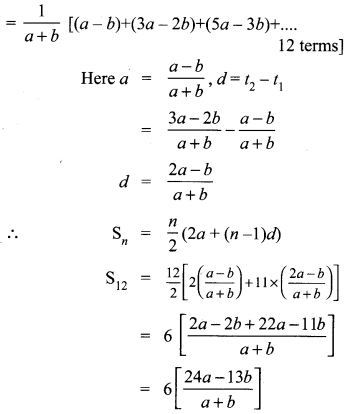You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.6
Question 1.
Find the sum of the following
(i) 3, 7, 11, …….. up to 40 terms.
(ii) 102, 97, 92, ……… up to 27 terms.
(iii) 6 + 13 + 20 + ……… + 97
Solution:
(i) 3, 7, 11,. . . upto 40 terms.
a = 3, d = t2 – t1 = 7 – 3 = 4
n = 40
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) (2a + (n – 1)d)
S40 = \(\frac{20}{2}\) (2× 3 + 39d)
= 20(6 + 39 × 4)
= 20(6 + 156)
= 20 × 162
= 3240
(ii) 102, 97, 952,… up to 27 terms
a = 102,
d = t2 – t1
= 97 – 102 = -5
n = 27

(iii) 6 + 13 + 20 + … + 97
a = 6,d = 7, l = 97
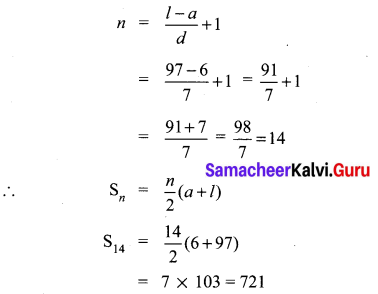
Question 2.
How many consecutive odd integers beginning with 5 will sum to 480?
Answer:
5,7,9, 11, 13,…
Sn = 480
a = 5, d = 2, Sn = 480
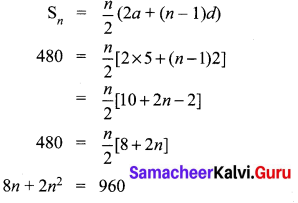
2n2 + 8n – 960 = 0
⇒ n2 + 4n – 480 = 0
⇒ n2 + 24n – 20n – 480 = 0
⇒ n(n + 24) – 20(n + 24) = 0
⇒ (n – 20)(n + 24) = 0
⇒ n = 20,-24
No. of terms cannot be -ve.
∴ No. of consecutive odd integers beginning with 5 will sum to 480 is 20.
![]()
Question 3.
Find the sum of first 28 terms of an A.P. whose nth term is 4n – 3.
Answer:
Number of terns (n) = 28
tn = 4n – 3
t1 = 4(1) – 3 = 4 – 3 = 1
t2 = 4(2) – 3 = 8 – 3 = 5
t3 = 4(3) – 3 = 12 – 3 = 9
Here a = 1, d = 5 – 1 = 4
S28 = \(\frac { n }{ 2 } \) [2a + (n – 1)d]
= \(\frac { 28 }{ 2 } \) [2 + (27) (4)]
= 14 [2 + 108]
= 14 × 110
= 1540
Sum of 28 terms = 1540
Question 4.
The sum of first n terms of a certain series is given as 2n2 – 3n. Show that the series is an A.P.
Solution:
Given Sn = 2n2 – 3n
S1 = 2(1)2 – 3(1) = 2 – 3 = – 1
⇒ t1 = a = – 1
S2 = 2(22) – 3(2) = 8 – 6 = 2
t2 = S2 – S1 = 2 – (-1) = 3
∴ d = t2 – t1 = 3 – (-1) = 4
Consider a, a + d, a + 2d, ….….
-1, -1 + 4, -1 + 2(4), …..…
-1, 3, 7,….
Clearly this is an A.P with a = – 1, and d = 4.
Question 5.
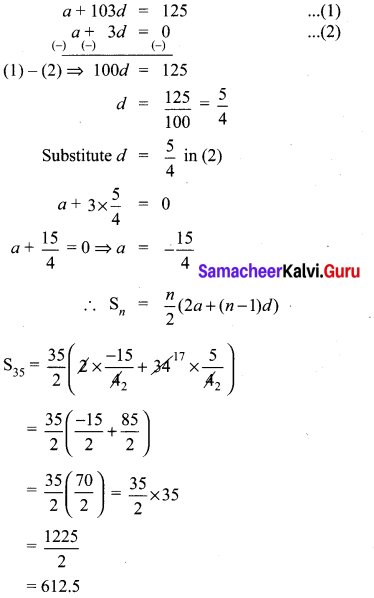
The 104th term and 4th term of an A.P are 125 and 0. Find the sum of first 35 terms.
Solution:
t104 = 125
t4 = 0
a + (n – 1)d = tn
Question 6.
Find the sum of all odd positive integers less than 450.
Solution:
Sum of all odd positive integers less than 450 is given by
1 + 3 + 5 + … + 449
a = 1
d = 2
l = 449
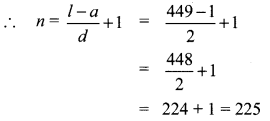
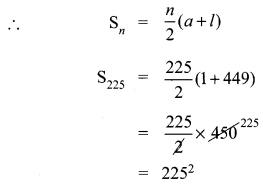
= 50625
Another method:
Sum of all +ve odd integers = n2.
We can use the formula n2 = 2252
= 50625
![]()
Question 7.
Find the sum of all natural numbers between 602 and 902 which are not divisible by 4.
Answer:
Natural numbers between 602 and 902
603,604, …, 901
a = 603, l = 901, d = 1,
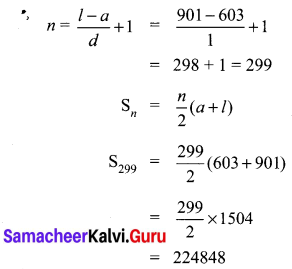
Sum of all natural numbers between 602 and 902 which are not divisible by 4.
= Sum of all natural numbers between 602 and 902
= Sum of all natural numbers between 602 and 902 which are divisible by 4.
l = 902 – 2 = 900
To make 602 divisible by 4 we have to add 2 to 602.
∴ 602 + 2 = 604 which is divisible by 4.
To make 902 divisible by 4, subtract 2 from 902.
∴ 900 is the last number divisible by 4.
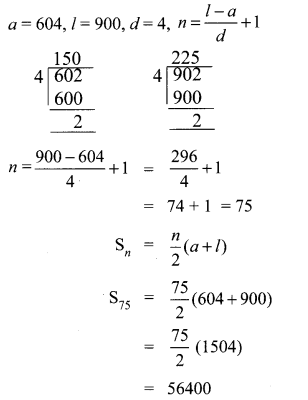
Sum of all natural numbers between 602 and 902 which are not divisible 4.
= 224848 – 56400
= 168448
Question 8.
Raghu wish to buy a Laptop. He can buy it by paying ₹40,000 cash or by making 10 installments as ₹4800 in the first month, ₹4750 in the second month, ₹4700 in the third month and so on. If he pays the money in this fashion, Find
(i) Total amount paid in 10 installments.
(ii) How much extra amount that he pay in installments.
Answer:
(i) Amount paid in 10 installments
4800 + 4750 + 4700 + ……………. 10
Here a = 4800; d = – 50 ; n = 10
Sn = \(\frac { n }{ 2 } \) [2a +(n – 1)d]
S10 = \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 } \) [2 × 4800 +9(-50)]
= \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 } \) [9600 – 450]
= 5 [9150]
= 45750
Amount paid in 10 installments
= ₹45750
(ii) Extra amount paid = amount paid in 10
installment – cost of the laptop
= ₹45750 – 40,000
= ₹ 5750
(i) Amount paid in 10 installments = ₹ 45750
(ii) Difference in payment = ₹ 5750
Question 9.
A man repays a loan of ₹65,000 by paying ₹400 in the first month and then increasing the payment by ₹300 every month. How long will it take for him to clear the loan?
Solution:
Loan Amount = ₹ 65,000
Repayment through installments
400 + 700 + 1000 + 1300 + …
a = 400
d = 300
Sn = 65000
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) (2a + (n – 1)d)
= 65000
\(\frac{n}{2}\)(2 × 400 + (n – 1)300) = 65000
n(800 + 300n – 300) = 130000
n(500 + 300n) = 130000
500n + 300n2 = 130000
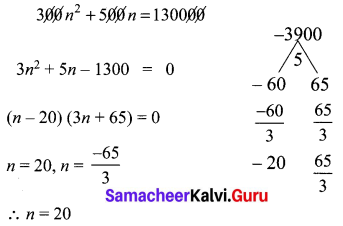
Number of terms should be (+ve) and cannot be (-ve) or fractional number.
∴ He will take 20 months to clear the loans.
Question 10.
A brick staircase has a total of 30 steps. The bottom step requires 100 bricks. Each successive step requires two bricks less than the previous step.
(i) How many bricks are required for the top most step?
(ii) How many bricks are required to build the stair case?
Answer:
Total number of steps = 30
∴ n = 30
Number of bricks for the bottom = 100
a = 100
2 bricks is less for each step
(i) Number of bricks required for the top most step
tn = a + (n – 1)d
t30 = 100 + 29 (-2)
= 100 – 58
= 42
(ii) Number of bricks required
Sn = \(\frac { n }{ 2 } \) [2a + (n-1) d]
S30 = \(\frac { 30 }{ 2 } \) [200 + 29 (-2)]
= 15[200 – 58]
= 2130
(i) Number of bricks required for the top most step = 42 bricks
(ii) Number of bricks required = 2130
![]()
Question 11.
If S1,S2,S3 , …. , Sm are the sums of n terms of m A.P.’s whose first terms are 1,2,3,…,m and whose common differences are 1, 3, 5,…, (2m – 1) respectively, then show that
S1 + S2 + S3 + …. + Sm = \(\frac{1}{2}\) mn(mn + 1).
Solution:
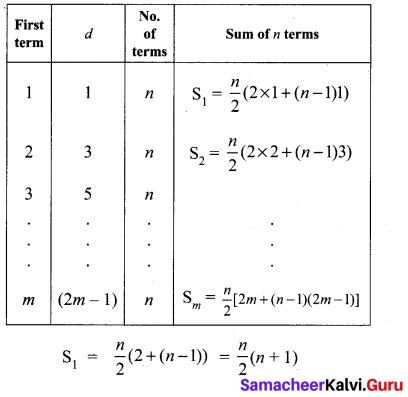
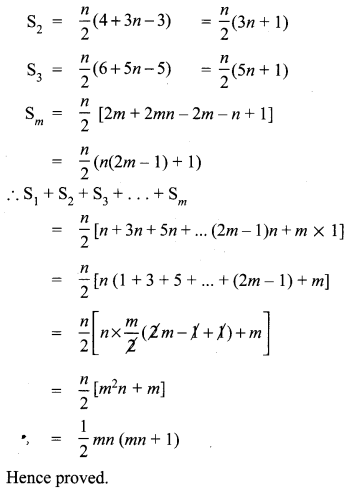
Question 12.
Find the sum
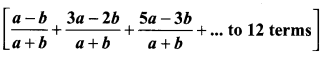
Solution: