Tamil Nadu 12th Tamil Model Question Paper 5
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Tamil Model Question Paper 5 Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Tamil Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Tamil Model Question Paper 5
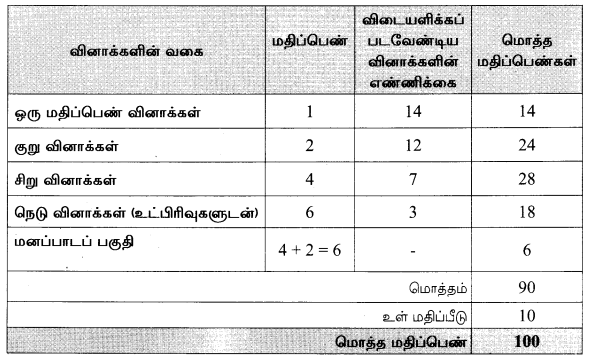
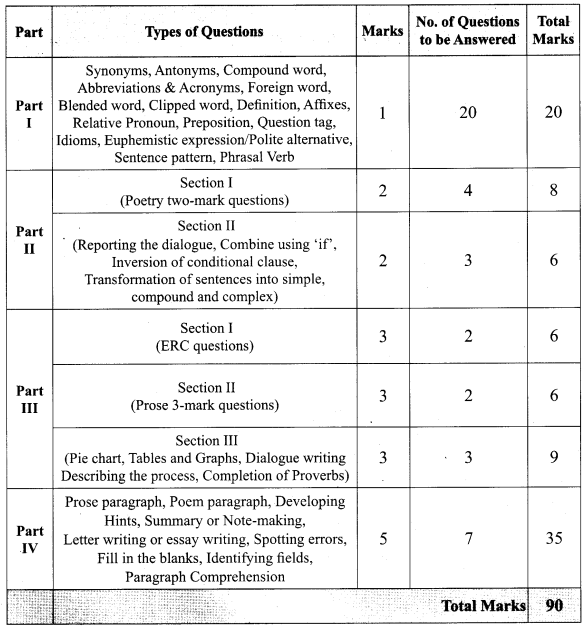
நேரம்: 2.30 மணி
மதிப்பெண்கள் : 90
குறிப்புகள்:
- இவ்வினாத்தாள் ஐந்து பகுதிகளைக் கொண்டது. அனைத்து பகுதிகளுக்கும் விடையளிக்க வேண்டும். தேவையான இடங்களில் உள் தேர்வு வினாக்கள் கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
- பகுதி I, II, III, IV மற்றும் Vல் உள்ள அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் தனித்தனியே விடையளிக்க வேண்டும்.
- வினா எண் 1 முதல் 14 வரை பகுதி-1ல் தேர்வு செய்யும் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன.
ஒவ்வொரு வினாவிற்கும் ஒரு மதிப்பெண். சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்துக் குறியீட்டுடன் விடையினையும் சேர்த்து எழுதவும். - வினா எண் 15 முதல் 30 வரை பகுதி-பால் இரண்டு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. –
- வினா எண் 31 முதல் 43 வரை பகுதி-IIIல் நான்கு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன.
- வினா எண் 44 முதல் 46 வரை பகுதி-IVல் ஆறு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன.அனைத்து வினாவிற்கும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
- வினா எண் 47-ல் பகுதி-Vல் மனப்பாடப்பகுதி தரப்பட்டுள்ளன.
பகுதி – 1
அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விடை தருக. [14:1 = 14]
(விடைகள் தடித்த எழுத்தில் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன)
Question 1.
நரம்புகளுக்குள் வீணை மீட்டிக் கொண்டிருக்கிறது என அய்யப்ப மாதவன் குறிப்பிடுவது …………………….. .
(அ) சூரிய ஒளிக்கதிர்
(ஆ) மழை மேகங்கள்
(இ) மழைத்துளிகள்
(ஈ) நீர்நிலைகள்
Answer:
(இ) மழைத்துளிகள்
![]()
Question 2.
கடலில் பெரியது………….
(அ) உற்ற காலத்தில் செய்த உதவி
(ஆ) பயன் ஆராயாமல் ஒருவர் செய்த உதவி
(இ) தினையளவு செய்த உதவி
(ஈ) மறந்துவிட்ட உதவி
Answer:
(ஆ) பயன் ஆராயாமல் ஒருவர் செய்த உதவி
Question 3.
தேயிலைத் தோட்டப்பாட்டு என்னும் நூலின் ஆசிரியர்………
(அ) முகம்மது இபுராகிம்
(ஆ) முகமது அப்துல் காதர்
(இ) முகமது இராவுத்தர்
(ஈ) அப்துல் ரகுமான்
Answer:
(இ) முகமது இராவுத்தர்
![]()
Question 4.
உலக நாடுகள் மாற்று ஆற்றலை நோக்கிச் சென்றால் மட்டுமே புவி வெப்பமயமாதலைக் கட்டுப்படுத்த முடியும் – இத்தொடர் உணர்த்துவது…………..
(அ) கார்பன் அற்ற ஆற்றல் பயன்பாடே தேவையாகிறது
(ஆ) பசுமைக் குடில் வாயுக்கள் அதிகமாகிறது.
(இ) காலநிலை மாறுபடுகிறது.
(ஈ) புவியின் இயக்கம் வேறுபடுகிறது
Answer:
(அ) கார்பன் அற்ற ஆற்றல் பயன்பாடே தேவையாகிறது
Question 5.
கூற்று: இந்தியாவின் பல பகுதிகளில் இருந்தும் நெசவாளர்கள் சென்னை நோக்கி வந்தனர். காரணம். கிழக்கிந்திய நிறுவனத்தின் வணிகம், துணி சார்ந்ததாகவே இருந்தது.
(அ) கூற்று சரி, காரணம் தவறு
(ஆ) கூற்று தவறு, காரணம் சரி
(இ) கூற்று தவறு, காரணம் தவறு
(ஈ) கூற்று சரி, காரணம் சரி
Answer:
(ஈ) கூற்று சரி, காரணம் சரி\
![]()
Question 6.
ச.த சற்குணரின் உரையைக் கேட்டுத் தூண்டப் பெற்று மயிலை சீனி. வேங்கடசாமி எழுதிய நூல்
(அ) பௌத்தமும், தமிழும்
(ஆ) இசுலாமும், தமிழும்
(இ) சமணமும், தமிழும்
(ஈ) கிறிஸ்தவமும், தமிழும்
Answer:
(ஈ) கிறிஸ்தவமும், தமிழும்
Question 7.
இயற்சீர் வெண்டளை என்பது
(அ) மா முன் நிரை
(ஆ) காய் முன் நேர்
(இ) மா முன் நேர்
(ஈ) விள முன் நிரை
Answer:
(அ) மா முன் நிரை
Question 8.
Metro Train- என்பதன் தமிழ்ச் சொல் …
(அ) நகரத் தொடர் வண்டி
(ஆ) மின் தொடர் வண்டி
(இ) மாநகரத் தொடர் வண்டி
(ஈ) நவீனத் தொடர் வண்டி
Answer:
(இ) மாநகரத் தொடர் வண்டி
![]()
Question 9.
பிழையான தொடரைக் கண்டறிக.
(ஆ) காளைகளைப் பூட்டி வயலை உழுதனர்
(ஆ) மலை மீது ஏறிக் கல்வெட்டுக்களைக் கண்டறிந்தனர்
(இ) காளையில் பூத்த மல்லிகை மனம் வீசியது
(ஈ) நெற்பயிர்கள் மழை நீரில் மூழ்கின
Answer:
(இ) காளையில் பூத்த மல்லிகை மனம் வீசியது
Question 10.
வளர்தலம் – என்பதன் இலக்கணக் குறிப்பு……..
(அ) வேற்றுமைத்தொகை
(ஆ) வினைத்தொகை
(இ) பண்புத்தொகை
(ஈ) உவமைத்தொகை
Answer:
(ஆ) வினைத்தொகை
Question 11.
சரியான நிறுத்தற்குறியுடைய தொடரைக் கண்டறிக.
(அ) “தமிழ் இமயம்” என்று தமிழ் அறிஞர்களால் போற்றப்பட்டவர் வ. சு. ப. மாணிக்கம்
(ஆ) இவர் தமிழ்க் காதல் வள்ளுவம், உள்ளிட்ட பல நூல்களை இயற்றியவர்
(இ) ஆராய்ச்சி, கட்டுரை, நாடகம், கவிதை, உரை, கடித இலக்கியம், பதிப்பு எனப் பல்துறை ஆளுமை கொண்டவர்
(ஈ) “தமிழ் வழிக் கல்வி இயக்கம்” என்ற அமைப்பை நிறுவித் தமிழ்ச் சுற்றுலா மேற்கொண்டவர்
Answer:
(இ) ஆராய்ச்சி, கட்டுரை, நாடகம், கவிதை, உரை, கடித இலக்கியம், பதிப்பு எனப் பல்துறை ஆளுமை கொண்டவர்
![]()
Question 12.
‘உயிர்வரின் உக்குறள் மெய்விட்டோடும்’ என்னும் விதிக்கான சான்று ………….
(அ) ஆங்கவற்றுள்
(ஆ) எத்திசை
(இ) வெங்கதிர்
(ஈ) பூம்பாவாய்
Answer:
(அ) ஆங்கவற்றுள்
Question 13.
‘முதல் கல்’ என்னும் சிறுகதையின் மையக் கருத்து………..
(அ) இயற்கையைப் போற்றுதல்
(ஆ) தன்னலம் காத்தல்
(இ) பொதுநலன் பேணல்
(ஈ) இயற்கையை அழித்தல்
Answer:
Question 14.
பின்வருவனவற்றுள் தொன்மத்திற்குப் பொருந்தா ஒன்றைத் தேர்க.
(அ) கர்ணன் தோற்றான் போ
(ஆ) வயதில் சிறியவன், ஆனாலும் தலைவி
(இ) இந்த நாரதரிடம் எச்சரிக்கையாக இரு
(ஈ) இந்தா போறான் தருமன்
Answer:
(ஆ) வயதில் சிறியவன், ஆனாலும் தலைவி
பகுதி – II
இரண்டு அல்லது மூன்று வரிகளில் விடை தருக. [12X2=24]
பிரிவு – 1
எவையேனும் மூன்றனுக்கு விடை தருக.
Question 15.
கவிஞர் சிற்பி எவற்றை வியந்து பாட, தமிழின் துணை வேண்டும் என்கிறார்?
Answer:
- மாலைப் பொழுதில் சிவப்பு சூரியன் மலைமேட்டில் மறைவான்.
- அப்பொழுது வானமெல்லாம் சிவப்பு நிற பூக்களாய் மாறும். அதுபோல, சிவக்கும் கைகளை உடையவர் உழைக்கும் தொழிலாளர்கள் அவர்களின் உடலில் இருந்து சிந்தும் வியர்வைத்துளிகள் எல்லாம் தோள்களின் மீது முத்துக்களாக ஒட்டிக் கொண்டிருக்கும்.
- இவற்றையெல்லாம் வியந்து பாட செந்தமிழின் துணை வேண்டும் என கவிஞர் சிற்பி கூறுகிறார்.
Question 16.
மறக்கக் கூடாதது மற்றும் மறக்கக் கூடியது எவையெவை?
Answer:
ஒருவர் நமக்குச் செய்த நன்மையை மறப்பது கூடாது. அவர் செய்த தீமையினை அப்பொழுதே மறந்துவிடுவது நல்லது.
![]()
Question 17.
திருமயிலைப் பதிகத்தில் காணப்பெறும் விழாக்களுள் நான்கினை எழுதுக.
Answer:
ஐப்பசி மாதம் – திருவோண விழா
மார்கழி மாதம் – திருவாதிரை விழா
தை மாதம் – தைப்பூச விழா
கார்த்திகை – விளக்குத் திருவிழா
Question 18.
அறிவுடை வேந்தனின் நெறிகுறித்து பிசிராந்தையார் கூறுவன யாவை?
Answer:
அரசன் அறிவில் குறைந்தவனாகி, முறை அறியாத சுற்றத்தாரோடு ஆரவாரமாக, குடிமக்களின் அன்பு கெடுமாறு, நாள்தோறும் வரியைத் திரட்ட விரும்புவது, யானை தான் புகுந்த நிலத்தில் தானும் உண்ணாமல் பிறருக்கும் பயன்படாமல் வீணாக்குவது போன்றது. அரசன் தானும் பயனடைய மாட்டான்; நாட்டு மக்களும் துன்புறுவர்.
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் இரண்டனுக்கு விடை தருக
Question 19.
மையாடல் விழா- குறிப்பு எழுதுக.
Answer:
- சுவடிகளிலுள்ள எழுத்துக்கள் செவ்வனே தெரிவதற்காகச் சுவடியில் வசம்பு, மஞ்சள், மணத்தக்காளி இலைச்சாறு அல்லது ஊமத்தையிலைச்சாறு, மாவிலைக்கரி, தர்ப்பைக்கரி முதலியவற்றைக் கூட்டிச் செய்த மையை அதில் தடவுவார்கள்.
- அந்த மை எழுத்துக்களை விளக்கமாகக் காட்டுவதோடு கண்ணுக்கும் குளிர்ச்சியைத் தரும்.
- இங்ஙனம் மை தடவிப் புத்தகத்தை வாசிக்கத் தொடங்குவதனால் அக்ஷராப்பியாசத்தை மையாடல் விழா ‘ என்று சொல்வார்கள்.
Question 20.
திரைப்பட உத்திகள் சிலவற்றைக் கூறுக.
Answer:
திரைப்படத் துறையில் காட்சி மாற்றங்களுக்காகப் பல உத்திகள் மேற்கொள்ளப்படுகின்றன. அதாவது காட்சி மறைவு, உதயம், கூட்டு, அழிப்பு எனப் பல வகை உத்திகள் திரைப்பட இயக்குநர் மற்றும் படத் தொகுப்பாளர்களால் கையாளப்படுகின்றன.
![]()
Question 21.
‘தமிழர் வளர்த்த அழகுக் கலைகள் – நூல் பற்றிக் குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
- ‘தமிழர் வளர்த்த அழகுக் கலைகள்’ என்ற நூலை எழுதியவர் மயிலை சீனி, வேங்கடசாமி. இந்நூல் கவின் கலைகள் குறித்துத் தமிழில் வெளிவந்த முதல் நூலாகும்.
- தற்காலச் சமூகம் பழைய அழகுக் கலைகளை மறந்து விட்டது. தன் பெருமை தான் அறியாச் சமூகமாக இருந்து வருகிறது.
- இக்காலச் சமூகம் சினிமாக் கலையையும், இசைக்கலையை மட்டுமே பேசுகிறது. அழகுக் கலையை மறந்ததால் தான் இந்நூல் எழுதப்பட்டது என்கிறார் மயிலை வேங்கடசாமி
பிரிவு – 3
எவையேனும் ஏழனுக்கு விடை தருக
Question 22.
உவமைத் தொடரைச் சொற்றொடரில் அமைத்து எழுதுக. எலியும் பூனையும் போல
Answer:
உடன் பிறப்புகள் எந்தச் சூழலிலும் எலியும் பூனையும் போல பகைமை கொள்ளக் கூடாது.
Question 23.
உயர்திணைப் பன்மைப் பெயர்கள், பன்மை விடுதி பெற்று வருமாறு இரண்டு தொடர்களை எழுதுக.
Answer:
- (அ) தமிழகத்தின் இரண்டு ஆசிரியர்கள் இந்தியக் குடியரசுத் தலைவரிடம் தேசிய நல்லாசிரியர் விருது பெற்றனர்.
- (ஆ) இரண்டு பெண்கள் ஒரே சீராகச் சிவபுராணம் பாடினார்கள்.
![]()
Question 24.
வல்லின மெய்யை இட்டும், நீக்கியும் எழுதுக.
Answer:
நம் வாழ்க்கையின் தரம் நமது கவனத்தின் தரத்தை பொறுத்திருக்கிறது. புத்தகம் படிக்கும் பொழுது கூர்ந்தக் கவனம் அறிவை பெறுவதற்கும் வளர்ப்பதற்குமான அடிப்படை தேவையாகும். விடை. நம் வாழ்க்கையின் தரம் நமது கவனத்தின் தரத்தைப் பொறுத்திருக்கிறது. புத்தகம் படிக்கும் பொழுது கூர்ந்த கவனம் அறிவைப் பெறுவதற்கும் வளர்ப்பதற்குமான அடிப்படைத் தேவையாகும்.
Question 25.
தொடரிலுள்ள பிழைகளை நீக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
(அ) ஐப்பசி அட மழையில் ஊருணி நிறைந்தது
(ஆ) மானம் பார்த்த பூமியில் பயிறு வகைகள் பயிரிடப்படுகின்றன.
(அ) ஐப்பசி அடை மழையில் ஊருணி நிறைந்தது
(ஆ) வானம் பார்த்த பூமியில் பயிறு வகைகள் பயிரிடப்படுகின்றன.
Question 26.
ஏதேனும் ஒன்றனுக்கு மட்டும் பகுபத உறுப்பிலக்கணம் தருக.
Answer:
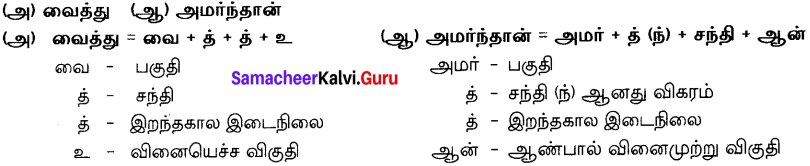
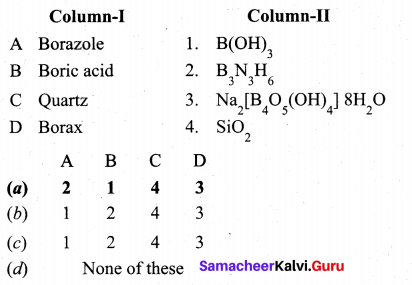
Question 27.
கலைச் சொற்களுக்கேற்ற தமிழ்ச் சொல் எழுதுக.
Answer:
(அ) ANIMATION
(ஆ) TIPS
(அ) இயங்குபடம்
(ஆ) சிற்றீகை
![]()
Question 28.
மரபுப் பிழைகளை நீக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
(அ) கற்பகம் சோறு சாப்பிட்டுப் பால் குடித்தான் கற்பகம் சோறு தின்று பால் அருந்தினாள்.
(ஆ) பனை மட்டையால் கூரை வைத்திருந்தனர். பனையோலையால் கூரை வேய்ந்திருந்தனர்.
Question 29.
ஏதேனும் ஒன்றனுக்குப் புணர்ச்சி விதி தருக.
Answer:
(அ) ஏழையென (ஆ) அருங்கானம்
(அ) ஏழையென – ஏழை + என = ஏழை +ய் + என = ஏழையன
விதி : ” இ ஈ ஐ வழி யவ்வும்”, “உடல்மேல் உயிர் வந்து ஒன்றுவது இயல்பே ”
(ஆ) அருங்கானம் – அருமை + கானம் = அரு + கானம் = அருங்கானம்
விதி: ஈறுபோதல். இனமிகல்
Question 30.
குறியீட்டு உத்தியின் அடிப்படை இலக்கணங்களுள் இரண்டனை எழுதுக.
Answer:
- சுட்டிய பொருளுக்கும் குறியீட்டுப் பொருளுக்கும் ஏதேனும் ஒரு தொடர்பு இருத்தல் வேண்டும்.
- சுட்டும் பொருள் என்பது எல்லோரும் அறிந்த ஒன்றாக இருத்தல் வேண்டும்.
- இத்தொடர்பின் வாயிலாக குறியீட்டுப் பொருள் நுண்ணிய முறையில் வெளிப்படுத்தப் பட வேண்டும்.
பகுதி – III
ஐந்து அல்லது ஆறு வரிகளில் விடை தருக. [ 7 × 4 = 28]
பிரிவு -1
எவையேனும் இரண்டனுக்கு மட்டும் விடை தருக
Question 31.
நெடுநல்வாடை – குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
- பாண்டியன் நெடுஞ்செழியனைப் பாட்டுடைத்தலைவனாகக் கொண்டு, மதுரைக் கணக்காயனார் மகனார் நக்கீரர் இயற்றிய நூல் நெடுநல்வாடை
- இது பத்துப்பாட்டு நூல்களுள் ஒன்று, 188 அடிகளைக் கொண்டது. ஆசிரியப்பாவால் இயற்றப்பட்டது.
- இப்பாடலின் பெயர் இருவகையில் பொருள் சிறந்து விளங்குகிறது. தலைவனைப் பிரிந்த தலைவிக்குத் துன்பமிகுதியால் நெடுவாடை நீண்ட வாபை யாகவும் போர்ப் பாசறையிலிருக்கும் தலைவனுக்கு வெற்றி பெற ஏதுவான நல்வாடையாகவும் இருப்பதால் நெடுநல்வாடை எனும் பெயர் பெற்றது.
![]()
Question 32.
‘மூன்றான காலம் போல் ஒன்று ‘ எவை? ஏன்? விளக்குக.
Answer:
- எண்ணம், வெளியீடு , கேட்டல் இவை மூன்றுமே மூன்றான காலம் போல் ஒன்றாகும்.
- ஏனெனில் காலம் என்பதை ஒன்றாகவும் அதாவது ஒரே கருத்தியலாகவும் உணர முடியும்.
- இறந்த காலம், நிகழ்காலம், எதிர்காலம் என்ற பகுப்புக்களுடன் மூன்றாகவும் உணரமுடியும். முந்தைய காலத்தவர் ஒன்றாகவும், பிந்தைய காலத்தவர் ஒன்றாகவும் உண்டு.
Question 33.
ஏதேனும் இரண்டு மெய்ப்பாடுகள் தோன்றுவதற்கான சூழ்நிலையைக் கற்பனையாகப்
படைக்க.
Answer:
நகை – சிரிப்பு:
நகை என்பது சிரிப்பு. தன் மனம் எந்தவித கவலையும் இல்லாத நிலையிலும், எந்தவித மனபாரமும், எந்தவித அழுத்தமும், இல்லாத சூழ்நிலையில் உருவாவதே சிரிப்பு சிரிப்புக்கு முக்கிய காரணம் எந்தவித எதிர்பார்ப்புமின்றி தான் செய்யும் அனைத்து செயல்களையும், வேலைகளையும் தானே விரும்பி, பிடித்தமானதாக நன்றாக மாற்றிக்கொண்டு செய்யும் வேலைகள் சிறப்பாக அமையும் மனதிற்கு மகிழ்ச்சியை கொடுக்கும், மனதிற்கு சிரிப்பை கொடுக்கும்.
வெகுளி – சினம் :
சினம் தன்னையும், தன்னை சார்ந்தவர் அனைவரையும் அழித்துவிடும் பெரும் ஆயுதம். சினத்தால் அழிந்தவர்கள் இந்த உலகத்தில் பலர் உண்டு. சினம் மனதிற்கு பயத்தை கொடுக்கும், பதட்டத்தை கொடுக்கும், அழுத்தத்தைக் கொடுக்கும், மனதின் மகிழ்ச்சியை அழித்துவிடும். முகத்தில் உள்ள சிரிப்பை அழித்துவிடும். எனவே சினத்தை முடிந்தவரை குறைத்து கொள்ள முயற்சிக்க வேண்டும்.
Question 34.
“ஈசன் மகன் நின்றனர்
ஓர் ஏழையான ஓர்மின்” – இடஞ்சுட்டிப் பொருள் விளக்குக.
இடம்: எச். ஏ. கிருட்டிணனார் பாடி இரட்சணிய யாத்திரிகம் பாடலில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ளது.
பொருள் :
இயேசு பெருமான் அன்பு என்னும் உறுதியான கட்டிலிருந்து விடுபட முடியாமல் தான், எந்த உதவியும் பெற இயலாத ஓர் ஏழையைப் போல அமைதியுடன் நின்றார்.
விளக்கம் :
இறைமகன் தன்னைப் பிறர் கயிற்றால் கட்டும் போது அதற்கு உடன்பட்டு நின்றார். அச்செயலானது. இயல்பாக மனிதர்களிடம் காணப்படுகிற சாதாரண அன்புச்செயல் என்று கருத வேண்டியதில்லை. தம்மீது பகை கொண்டு தனக்கு இழிவான செயல்களைச் செய்த இம்மனிதர்கள் தாங்கள் வாழும் காலம் முழுவதும் துன்பத்தில் இருப்பார்களோ என்று எண்ணி அவர்களுக்காக இரக்கப்படுகிற தன்மையே காரணம். அந்த அன்பு என்னும் உறுதியான கட்டிலிருந்து விடுபட முடியாமல் தான், எந்த உதவியும் பெற இயலாத ஓர் ஏழையைப் போல அமைதியுடன் நின்றார்.
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் இரண்டனுக்கு மட்டும் விடை தருக
Question 35.
‘சங்கப் பாடல்களில் ஒலிக்கோலம் குறிப்பிடத்தக்க ஒரு பண்பாகும்’ – விளக்குக.
Answer:
உயிர் நெடில் ஒலிகளின் வருகையும், சில சொற்களும் மேலும் சில ஒலிகளும் மீண்டும் வரும் தன்மை பெற்றிருப்பதைக் காண முடியும்.
இவற்றுடன் சொல் விளையாட்டுக்களும் வருவது குறிப்பிடத்தக்கதாகும். இத்தகைய ஒலிக் கோலம் சங்கப் பாடல்களில் முக்கியமான ஒரு பண்பாகத் திகழ்கிறது.
உதாரணம்:
”நுந்தை தந்தைக்கு இவன் தந்தை”
”பாட அம் ஈத்த கெடாஅ நல்லிசை” – புறப்பாட்டு
இப்பாடலடிகளை ஒப்பிட்டுப் பார்த்தால் ஒலிக்கோலத்தின் வலிமையை நம்மால் உணர்ந்து கொள்ள முடியும்.
![]()
Question 36.
வாழிடம் பற்றிச் சங்க இலக்கியம் கூறுவது யாது?
Answer:
- பண்டைத் தமிழர்கள் குடும்பம் என்னும் அமைப்புடன் வாழ்ந்த இடங்கள் பற்றி சங்க இலக்கியங்கள் பலவாறு கூறுகின்றன.
- தொல்காப்பியம் இல், மனை என்ற இரண்டினைச் சுட்டுகிறது. மேலும் குரம்பை, புலப்பில், முன்றில், குடில், கூரை வரைப்பு முற்றம். நகர். மாடம் போன்றவை குடும்ப வாழ்விடங்களில் வேறுபாட்டைக் குறிக்கின்றன.
- தற்காலிகத் தங்குமிடம் புக்கில் ‘ என்றும், கணவன், மனைவி தன் பெற்றோரை விட்டுப் பிரிந்து வாழுமிடம் தன்மனை எனவும் வழங்கப்படுகிறது.
Question 37.
சென்னையின் பண்பாட்டு அடையாளங்களில், இன்று நிலைத்து இருப்பனவற்றைக் குறிப்பிடுக.
Answer:
சென்னையின் பண்பாட்டு அடையாளங்களில், இன்றும் நிலைத்து இருப்பன :
- இன்று சென்னையின் புகழுக்குச் சான்றாக நிற்கும் பல்வேறு கல்வி நிறுவனங்கள் ஆங்கிலேயரால் ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்டவை.
- 8 ஆம் நூற்றாண்டிலேயே சென்னையில் ஐரோப்பிய முறைக் கல்வி கற்பிக்கும் நிறுவனங்கள் தோன்றின.
- 1715 இல் உருவான புனித மேரி தேவாலய தர்மப் பள்ளி ‘ ஆசியாவில் உருவான முதல் ஐரோப்பியக் கல்வி முறையிலான பள்ளியாகும்.
- 19 ஆம் நூற்றாண்டில் பள்ளிகள் பெருகின.
- 1812 இல் உருவான சென்னைக் கோட்டைக் கல்லூரி.
- 1837 இல் தொடங்கப்பட்ட கிறித்துவக் கல்லூரி.
- 1840 இல் உருவான பிரசிடென்சி பள்ளி (பின்னாளில் மாநிலக் கல்லூரி) போன்ற பல்வேறு கல்வி நிறுவனங்கள் சென்னையில் கல்வி வளர்ச்சிக்குப் பெரும் பங்காற்றின.
![]()
Question 38.
வேளாண் மேலாண்மை குறித்து நீவிர் பரிந்துரைப்பனவற்றை எழுதுக.
Answer:
- வேளாண்மைக்குள்ளும் மேலாண்மைக் கூறுகள் உண்டு.
- சரியான பயிரைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்தல், உரிய நேரத்தில் விதைத்தல், நீர் மேலாண்மையை நெறிப்படுத்துதல், அறுவடைக்குப்பின் பாதுகாத்தல், உரிய விலை வரும் வரை இருப்பு வைத்தல் என்று ஒவ்வொரு கட்டத்திலும் விழிப்புணர்வும் பொறுப்புணர்வும் நிருவாக நெறியும் இணைந்தால் தான் வேளாண்மை செழிக்கும்.
- கம்பராமாயணத்தில், தசரதன் தன் நாட்டை மிகவும் செப்பமாகவும், நுணுக்கமாகவும் ஆட்சி செய்தான் என்பதைக் கம்பர்,
“வையகம் முழுவதும் வறிஞன் ஓம்பும் ஓர்
செய் எனக் காத்து இனிது அரசு செய்கின்றான்” - என்றார். வறியவன் ஒருவன் தன் சிறு வயலைப் பாதுகாப்பது போல, இவ்வுலகம் முழுவதையும் பாதுகாத்து மிகச்சிறந்த முறையில் ஆட்சி செய்தான் என்று அவர் குறிப்பிடுகிறார்.
பிரிவு – 3
(எவையேனும் மூன்றனுக்கு விடை தருக
Question 39.
‘குற்றம் பார்க்கில் சுற்றம் இல்லை’ – என்னும் பழமொழியினை வாழ்க்கை நிகழ்வில் அமைத்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
பழமொழி விளக்கம்:
நம்மோடு பழகுபவரிடம் குற்றம் கண்டு உரைத்தால், அவருக்கும் நமக்கும் உள்ள உறவில் விரிசல் வரும்.
வாழ்க்கை நிகழ்வு:
தாமுவும், சோமுவும் நல்ல நண்பர்கள் தாமு படிப்பில் கெட்டிக்காரன் சோமுவோ விளையாட்டில் கெட்டிக்காரன். ஒரு முறை கபடி விளையாட்டுப் போட்டியில் கலந்து கொண்ட சோமு 2 சந்தர்ப்பங்களில் தவறு செய்து தனது அணிக்குத் தோல்வி வரக் காரணமாகிவிட்டான். இது பற்றி தாமு சோமுவிடம் சுட்டிக் காட்டியதால் அது முதல் சோமு தாமுவுடன் பேசுவதைத் தவிர்த்தான். அப்போது தாமு ‘குற்றம் பார்க்கில் சுற்றம் இல்லை’ என்பதைத் தாம் உணர்ந்து கொண்டதாகப் பிற நண்பர்களிடம் கூறினான்.
Question 40.
தமிழாக்கம் தருக.
Answer:
Periyar was not only a great social revolutionary; he was something more than that. He is known as a great champion of the underprivileged; even in this sphere, he was much more than that. His sphere of activity was very wide and when he took up any issue he went deep into it, understood all the aspects of it and did not rest until he had found a permanent solution to it. Communal differences in our society were deep-tooted and appeared to be permanent features of our society until Periyar came on the scene.
பெரியார் மிகப் சிறந்த சமூக சீர்த்திருத்தவாதி மட்டுமல்ல அதற்கும் மேலானவர் ஆவார். அவர் ஏழை எளிய மக்களுக்கு பரிந்துரையாடும் மகத்தான வீரனாக திகழ்ந்தார். இங்கு அவர் எதிர்பார்ப்பை தாண்டிய சேவை செய்தார். அவரின் செயற்திறனின் யுக்தி விசாலமானதாக இருக்கும் மற்றும் எந்த ஒரு பிரச்சனையையும் ஆழச் சென்று அதன் தன்மையை புரிந்து கொண்டு அதற்கு தீர்வு காணும் வரை அயராது உழைத்தார். பெரியார் தலையிடும் வரையில் மக்களிடையே ஜாதி-மத வேறுபாடுகள் வேரூன்றி இருந்தது. அவர்களது எதிர்காலம் சரியாகும் வரை பெரியார் வேறு எந்தச்
செயலிலும் ஈடுபடமாட்டார்.
![]()
Question 41.
சொற்பொருள் பின்வருநிலை அணியை விவரி
Answer:
அணிவிளக்கம் :
ஒரு செய்யுளில் வந்த சொல்லே மீண்டும் மீண்டும் வந்து, தந்த அதே பொருளையே தருமாறு அமைவது சொற்பொருள் பின்வருநிலை அணியாகும்.
எடுத்துக்காட்டு :
‘நோயெல்லாம் நோய் செய்தார் மேலவாம் நோய்செய்யார் நோயின்மை வேண்டு பவர்’.
பொருத்தம் :
இக்குறளில் நோய் என்ற சொல் மீண்டும் மீண்டும் வந்து ‘துன்பம்’ என்ற ஒரே பொருளைத் தருவதால் இதில் சொற்பொருள் பின்வருநிலை அணி பயின்று வந்துள்ளது.
(அல்லது)
உவமை அணியைச் சான்றுடன் விவரி.
அணிவிளக்கம் :
உவமானம், உவமேயம், உவமை உருபு மூன்றும் செய்யுளில் வெளிப்படையாக வருவது உவமை அணியாகும்.
எடுத்துக்காட்டு :
அகழ்வாரைத் தாங்கும் நிலம் போலத் தம்மை இகழ்வார்ப் பொறுத்தல் தலை’.
பொருத்தம் :
அகழ்வாரைத் தாங்கும் நிலம் என்ற உவமானம், இகழ்வார்ப் பொறுத்தல் தலை என்ற உவமேயம் இவற்றின் இடையே போல என்ற உவமை உருபும் வெளிப்படையாக வந்துள்ளது. எனவே இக்குறளில் உவமை அணி பயின்று வந்துள்ளது.
![]()
Question 42.
பாடலைப் படித்துணர்ந்து மையக் கருத்தினை எழுதி, ஏற்புடைய நயங்கள் மூன்றினை மட்டும் எழுதுக.
Answer:
பிறப்பினால் எவர்க்கும் – உலகில்
பெருமை வாரா தப்பா!
சிறப்பு வேண்டுமெனில் – நல்ல
செய்கை வேண்டு மப்பா!
நன்மை செய்பவரே – உலகம்
நாடும் மேற்குலத்தார்!
தின்மை செய்பவரே – அண்டித்
தீண்ட ஒண்ணாதார் !
– கவிமணி தேசிக விநாயகம் பிள்ளை
முன்னுரை:
கவிமணி தேசிக விநாயகம் சமதர்ம சமுதாய மேம்பாட்டுக்காகக் குரல் கொடுத்த சிறந்த கவிஞர் ஆவார்.
மையக் கருத்து :
பிறப்பினால் பெருமை வராது. நற்செயல்களால் தான் பெருமை வரும். உலகம் விரும்புவது நன்மை செய்பவர்களைத் தான். தீமை செய்பவரை உலகம் தீண்டாது.
மோனைத் தொடை நயம்:
இப்பாடலில்
பிறப்பினால் – பெருமை ; சிறப்பு – செய்கை; நன்மை – நாடும்; தின்மை – தீண்ட ஆகிய சொற்களில் முதல் எழுத்துக்கள் ஒன்றி வரத் தொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. மோனைத் தொடை நயம் வந்துள்ளது.
எதுகைத் தொடை நயம்:
செய்யுளில் இரண்டாம் எழுத்து ஒன்றி வருமாறு அமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ள சொற்களாவன:
பிறப்பினால் – சிறப்பு
நன்மை – தின்மை
இதில் எதுகைத் தொடை நயம் அமைந்துள்ளது.
இயைபுத் தொடை நயம்:
பாடலின் ஈற்றுச் சீரின் ஈற்றொலிகள்.
வாராதப்பா – வேண்டுமப்பா என ‘ஆ’ ஒலியிலும்.
மேற்குலத்தார் – ஒண்ணாதார் என ஈற்றுச் சீரின் ஈற்றொலி ஆர்’ எனவும் ஒன்றி வருவது உள்ளதால் இயைபுத் தொடை நயம் அமைந்துள்ளது.
முடிவுரை:
பாடல் சமதர்ம சிந்தனையை வளர்ப்பதாகவும், இசை அமைரிப் பாடுவதற்கேற்ற இனிய சந்த நயமும், மோனை, எதுகை, இயைபு ஆகிய நயங்களும் நிறைந்ததாகச் சிறப்பாகத் திகழ்கிறது.
![]()
Question 43.
பின்வரும் தலைப்புகளில் ஒன்றின் கவிதை புனைக.
Answer:
பொன் மாலைப் பொழுது அல்லது) விடா முயற்சி

பகுதி – IV
பின்வரும் வினாக்களுக்கு இரு பக்கங்களுக்கு மிகாமல் விடை தருக. [3:6 = 18]
Question 44.
(அ) பண்பின் படிமமாகப் படைக்கப்பட்ட இராமன், பிற உயிர்களுடன் கொண்டிருந்த உறவுநிலையை நும் பாடப்பகுதி வழி விளக்குக.
Answer:
குகனிடம் இராமன் கூறியது:
வேடுவ தலைவர் குகனிடம் இராமன் நீ என் தம்பி; இலக்குவன் உன் தம்பி, அழகிய வெற்றியைக் கொண்ட சீதை, உன் அண்ணி ; குளிர் கடலும் இந்நிலமும் எல்லாம் உனதேயாகும். நான் உன்னுடைய ஏவலுக்கேற்பப் பணிபுரிபவன்.
துன்பு உளது எனின் அன்றோ
சுகம் உளது? அது அன்றிப்
குகனின் வருத்தம் :
(இராமன் காட்டிற்குச் சென்று துன்புறுவானே என்று குகன் வருந்தினான். அதை உணர்ந்த இராமன் கூறுகிறான்) குகனே! துன்பம் என்று ஒன்று இருந்தால்தானே இன்பம் என்பது புலப்படும்.
துன்பத்திற்குப் பின் இன்பம் உறுதியாக உண்டு. நமக்கிடையே இப்போது இப்பிரிவு நேர்கிறது என்று எண்ணாதே. இதுவரை நாங்கள் நால்வரே உடன் பிறந்தவர் என்றிருந்தோம். உறவு என்பது எங்கள் நால்வரோடு நின்றுவிடவில்லை. இப்போது உன்னையும் சேர்த்து நாம் ஐவர் ஆகின்றோம்.
இராமன் செய்த இறுதிச்சடங்கு :
கழுகு வேந்தன் சடாயு, இராவணன் சீதையைச் சிறையெடுத்தபோது தடுத்துச் சண்டையிட்டுக் காயப்படுகிறான். இராமனிடம் நடந்ததைக் கூறுகிறான்; பின் இறந்துவிடுகிறான். இராமன், தன் தந்தையின் நண்பனான அக்கழுகு வேந்தனையும் தன் தந்தையாகவே கருதி, மகன் நிலையில் அவனுக்குரிய இறுதிச் சடங்குகளைச் செய்கிறான் எப்படிப்பட்ட சிறப்பான விறகுகள் இவை” என்று கண்டவர் வியக்கும்படியான கரிய அகில் கட்டைகளையும், சந்தனக் கட்டைகளையும் இராமன் கொண்டுவந்து வைத்தான். தேவையான அளவு தருப்பைப் புற்களையும் ஒழுங்குபட அடுக்கினான். பூக்களையும் கொண்டுவந்து தூவினான். மணலினால், மேடையைத் திருத்தமாக அமைத்தான். நன்னீரையும் எடுத்து வந்தான். இறுதிச்சடங்கு செய்யப்படக் கூடிய மேடைக்குத் தன் தந்தையாகிய சடாயுவைப் பெரிய கைகளில் தூக்கிக் கொண்டு வந்தான்.
குகனும் விடணும் இராமனின் தம்பியாதல் :
இராமனின் தம்பிகள் நால்வர் உடன்பிறந்தவர்களாக இருந்தோம் குகனுடன் சேர்த்து நாங்கள் ஐவர் ஆனோம். பின்னர் மேருமலையைச் சுற்றி வரும் கதிரவனின் மகனான சுக்ரீவனுடன் அறுவர் ஆனோம். உள்ளத்தில் அன்பு கொண்டு எங்களிடம் வந்த அன்பனே, உன்னுடன் சேர்த்து எழுவர் ஆனோம். புகுதற்கரிய கானக வாழ்வை மேற்கொள்ளும்படி என்னை அனுப்பிய உன் தந்தையாகிய தசரதன், இதனால் புதல்வர்களைக் கூடுதலாக அடைந்து பெருமை பெறுகிறான்.
சவரியின் விருந்து:
சவரி, இராமனைப் புகழ்ந்து அன்பின் கனிவினால் அருவி இழிவது போலக் கண்ணீர் வடித்தாள். (இராமனைக் கண்டதால் என் பொய்யான உலகப்பற்று அழிந்தது, அளவற்ற காலம் நான் மேற்கொண்டிருந்த தவம் பலித்தது. என் பிறவி ஒழிந்தது’ என்று கூறினாள், வேண்டிய எல்லாம் கொண்டுவந்து அவள் இராம இலக்குவருக்கு விருந்து செய்விக்க, அவர்களும் விருந்தை ஏற்றனர்.
![]()
Question 44.
(ஆ) எச். ஏ. கிருட்டிணனார் ‘கிறித்துவக் கம்பரே – நிறுவுக.
Answer:
- கிருத்துவக் கம்பர் என்ற ஆல்பிரட் கிருஷ்ணபிள்ளை (H.A. கிருஷ்ணபிள்ளை ) ஏப்ரல் 23, 1827 ஆண்டு திருநெல்வேலி மாவட்டம் கரையிருப்பில் ரெட்டியார் பட்டி என்னும் சிற்றூரில் பிறந்தவர்.
- இவரது பெற்றோர் சங்கர நாராயண பிள்ளை, தெய்வ நாயகியம்மை. ஹென்றி ஆல்பிரடு என்ற பெயர்களின் சுருக்கமே H.A . ஆகும்.
- தமிழ் ஆசிரியராகப் பணியாற்றிய இவரது படைப்புகள் போற்றித் திருவருகல், இரட்சணிய யாத்திரிகம், இரட்சணிய மனோகரம் ஆகியவை இவர் எழுதியதாக சொல்லப்படும் இரட்சணிய குரல், இரட்சணிய பாலா போதனை என்ற நூல்கள் தற்பொழுது கிடைக்கவில்லை.
- இரட்சணிய மனோகரத்தின் பெரும் பகுதி இரட்சணிய யாத்திரிகத்திலிருந்து எடுத்துத் தொகுக்கப்பட்டது ஆகும்.
- H.A . கிருஷ்ணபிள்ளை தென்தமிழ் நாடாகிய நெல்லை நாடு. (தற்போதைய திருநெல்வேலி மாவட்டம்) பல மேலை நாட்டு அறிஞர்களை தமிழ் தொண்டராக்கிய பெருமை இவருக்கும் சேரும்.
- இத்தாலிய தேசத்து வித்தகராகிய வீரமாமுனிவரது தமிழ்ப் புலமைக்கு அடிகோலியது நெல்லை நாடும், இவரும் தான். பெருந்தமிழ் தொண்டராகிய போப்பையருக்கத் தமிழ் அறிவு ஊட்டியது நெல்லை நாடு தான்.
- மொழி நூற்புலமையில் சிறந்து விளங்கிய கால்டுவெல் ஐயர் வாழ்ந்ததும் நெல்லை நாடு தான். இவ்வாறு பிற நாட்டு அறிஞரை தமிழ்ப் பணியில் ஈடுபடுத்திய தென்தமிழ் நாட்டில் ரெட்டியார்பட்டி என்ற சிற்றூர் உள்ளது.
- அந்த ஊரில் வேளாளர் குலத்தில் வைணவ மதத்தில் பிறந்தவர் தான் H.A. கிருஷ்ணபிள்ளை . இளமையிலே தமிழில் உள்ள நீதி நூல்களையும், சமய நூல்களையும் அக்கால முறைப்படி நன்கு கற்றார்.
- அப்போது நெல்லை நாட்டிலே கிருஸ்துவ சங்கங்கள் கிளர்ந்து எழுந்தது. சிறந்த சமயத் தொண்டும் செய்யப்பட்டது. சர்ச்சு முறை சங்கத்தில் சிறப்பாக சார்சந்தர் என்னும் சிலர் சிறந்த பணி செய்தனர்.
- அதன் காரணமாக கிருத்துவ மதத்தின் மீது H.A. கிருஷ்ணபிள்ளைக்கு அதிக ஈடுபாடு வந்தது. அந்த மதம் தொடர்பான பல நூல்கள் இவரால் எழுதப்பட்டது. போற்றித் திருவருகல்
- இரட்சணிய யாத்திரிகம்
- இரட்சணிய மனோகரம்
- இரட்சணிய குறள்
- இரட்சணிய பாலா
போன்ற கிருஸ்துவ தொடர்பான பல படைப்புகள் இவரால் எழுதப்பட்டது. இதன் காரணமாகவே கிறித்துவ கம்பர் என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறார்.
![]()
Question 45.
(அ ) பண்டைக் காலக் கல்வி முறையில், ஆசிரியர் மற்றும் மாணவர்களுக்கிடையே நிகழ்ந்த கற்றல், கற்பித்தல் முறைகளைத் தொகுத்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
நம்முடைய நாட்டில் மிகப் பழைய காலத்தில் ஆசிரியருடைய வீடே பள்ளிக்கூடமாக இருந்தது. அதைக் குருகுலம் என்பார்கள். கணக்காயரென்பது உபாத்தியாயருக்குப் பெயர். கணக்கு என்பது நூலின் பெயர்.
மன்றங்கள் :
ஊர்தோறும் பொதுவான இடத்தில் ஒரு பெரிய மரத்தினடியே மேடையொன்று அமைக்கப்பட்டிருக்கும். அதனை மன்றமென்றும் அம்பலமென்றும் கூறுவர். மன்றமென்பது மரத்தடியில் உள்ள திண்ணையே அதுவே பிறகு திண்ணைப் பள்ளிக்கூடமாக மாறியதென்று தோன்றுகிறது.
பள்ளிகள் :
மரத்தடியில் இருந்த பள்ளிக்கூடங்கள் நாளடைவில் சிறு குடிசைகளாக மாறின. பல இடங்களிலே மடங்களிற் பாடசாலைகள் உண்டாயின. பள்ளியெனும் சொல் ஜைன மடங்களுக்கும் பாடசாலைகளுக்கும் பொதுவான பெயர். பாடசாலைகள் வேறு, மடங்கள் வேறு என்ற வேறுபாடின்றி இரண்டும் ஒன்றாகவே கருதப்பட்டமையின், பள்ளியென்னும் பெயர் இரண்டிற்கும் பொதுவாக வழங்கியதென்று தோன்றுகின்றது.
வித்தியாரம்பம் :
முதன் முதலில் ஐந்தாம் பிராயத்தில் வித்தியாப்பியாசம் செய்யும் பொழுது தாய் தந்தையர் பிள்ளைகளை ஆசிரியர்களிடம் அடைக்கலமாகக் கொடுத்து வந்தார்கள்.
பிள்ளைகளைப் பள்ளிக்கூடத்தில் வைக்கும் காலம் ஒரு பெரிய விசேஷ நாளாகக் கொண்டாடப் பெறும். ஏட்டின் மீது மஞ்சள் பூசிப் பூசித்துப் பையனிடம் கொடுத்து வாசிக்கச் செய்வார்கள். உபாத்தியாயர் நெடுங்கணக்கைச் சொல்லிக்கொடுக்க, மாணாக்கன் அதனை பின்பற்றிச் சொல்லுவான். இப்படி உபாத்தியாயர் ஒன்றைச் சொல்ல அதை மாணாக்கர்கள் பலரும் சேர்ந்து சொல்வதை முறை வைப்பதென்று கூறுவார்கள். உபாத்தியாயருக்குப் பிரதியாகச் சில சமயங்களில் சட்டாம்பிள்ளை முறை வைப்பதுண்டு.
மனனப் பயிற்சி :
அக்காலத்துப் பாடமுறைக்கும் இக்காலத்துப் பாட முறைக்கும் பெரிய வேறுபாடு உண்டு. அடிப்படையான நூல்களெல்லாம் பிள்ளைகளுக்கு மனனமாக இருக்கும். தமிழில் நிகண்டு, நன்னூல், காரிகை, தண்டியலங்காரம், நீதி நூல்கள் முதலியன பாடமாக இருக்கும். கணிதத்தில் கீழ்வாயிலக்கம், மேல்வாயிலக்கம், குழிமாற்று முதலிய பலவகை வாய்பாடுகள் பாடமாக வேண்டும். தலைகீழ்ப் பாடம்’ என்று சொல்வதை அம்முறைகளில் காணலாம். சிறுவர்கள் படிக்கும் ஆத்திசூடி, கொன்றை வேந்தன் என்பவை அகராதி வரிசையில் அமைந்தமை அவர்களுடைய ஞாபகத்தில் அவை பதிவதன் பொருட்டேயாகும். இப்படியே அந்தாதி முறையைக் கொண்டும் எதுகை மோனைகளைக் கொண்டும் செய்யுட்களை ஞாபகப்படுத்திக் கொள்வார்கள்.
அன்பினால் அடக்குதல் :
முற்காலத்தில் கொடிய தண்டனைகள் இல்லை. ஆசிரியர்கள் மாணாக்கர்களை அன்பினால் வழிப்படுத்தி வந்தார்கள். அவர்கள் பால் இருந்த மரியாதை மாணாக்கர்களுக்குப் பயத்தை உண்டாக்கியது. பிழைகளை மறந்தும் புரியாத நிலையில் அவர்கள் இருந்தனர்.
பின்னுரை :
காலத்தின் வேகம் அந்தப் பழைய காலத்துப் பள்ளிக்கூடங்களை மாற்றியமைத்து விட்டாலும், அவற்றால் உண்டான நற்பயன்களையும் அவற்றிற் படித்த பேரறிஞர்கள் நமக்கு ஈட்டி வைத்துள்ள நூற்செல்வத்தையும் நினைக்கும் போது, நம்மையறியாமல் நமக்கு ஒரு பெருமிதம் உண்டாகின்றது. அக்காலத்து முறைகளை மீளாவிடினும், அப்பள்ளிக்கூடங்களின் அடிப்படையான உண்மைகளையேனும் நாம் அறிந்து கொண்டு வாழ முயல வேண்டும்.
![]()
Question 45.
ஆ) திரைப்படத்துறை என்பது ஆயிரம் பேரைக் காப்பாற்றும் தொழிலா? அல்லது கலைகளின் சங்கமமா? உங்கள் பார்வையைக் கட்டுரையாக்குக.
Answer:
கலை நம் வாழ்வின் உயிர்நாடி. கலையில்லையேல் வாழ்வில் சுவையிருக்காது. திரைப்படம் ஓர் அற்புதமான கலை உலகில் பல்வேறு மொழிகள் இருப்பினும் மக்கள் அனைவரும் எளிதில் புரிந்து கொள்ளும் உலக மொழி திரைப்படம். மக்களைத் தன் வயப்படுத்தும் ஆற்றல் திரைப்படத்திற்கு உண்டு. இத்துறையின் வளர்ச்சி திரை பின்னால் எத்தனைத் துறைகளின் வாழ்வு அடங்கியுள்ளது.
ஊமைப் படங்களைப் பேசும் படங்களாக மாற்றுவதற்குப் பல்வேறு அறிவியல் அறிஞர்கள் அயராது உழைத்தார்கள். அதனால் திரைப்படத்துறை மாபெரும் வளர்ச்சியை எட்டியது. திரைப்படத்திற்கு கதை. கதைமாந்தர் தேர்வு, உரையாடல், பாடல், ஆடை, அணிகலன், உடைவடிவமைப்பாளர், நடிகர், நடிகையர், தோழர், தோழியர், பணியாளர் என பலர் தேர்வு செய்யப்படுகின்றனர்.
கலைஞர்கள் அனைவரையும் ஒன்றிணைத்து இத்துறை மாபெரும் வெற்றிப் பெற்றதாக மாறியுள்ளது. ஒரு திரைப்படம் எடுக்க பல கோடிகள் செலவீனங்கள் ஆகின்றன. இப்படங்கள் பலவிதங்களில் எடுக்கப்படுகின்றன. அரசியல். குடும்பப்படங்கள், பக்திப்படம், திகில் படங்கள் என்பல பிரிவுகள் உள்ளன.
திரைப்படத்துறையில் முழு ஈடுபாடு உள்ளவர்களால் மட்டுமே இதில் வெற்றிப்பெற இயலும் திரைப்படத்துறையை ஒரு பல்கலைக்கழகம் பலகலைகளின் சங்கமம் என்றே கூறலாம். திரைத்துறைச் சார்ந்த பல பட்டப்படிப்புகள் தற்போது உருவாகி உள்ளன.
இதில் பல கலைகள் வளர்ந்து வருகின்றன என்பதும் மறுக்க முடியாத உண்மை . நடிப்புக்கலை, நாடகக்கலை, ஓவியக்கலை, அழகியல் கலை, கட்டடக்கலை போன்ற பல கலைகளை வளர்த்து வருகின்றன. ஒரு திரைப்படம் என்பது கேளிக்கை மட்டுமே அல்ல. பல குடும்பங்களின் வாழ்வியல் ஆதாரம் எனலாம். ஆயிரக்கணக்கான குடும்பங்கள் இதை நம்பியே உள்ளன எனலாம்.
மக்களைத் தம்பால் ஈர்த்துக்கட்டிப் போடும் ஆற்றல் கொண்டது திரை உலகம் . “கல்லார்க்கும் கற்றோர்க்கும் களிப்பருளும் களிப்பே” என்னும் வரிகள் திரைப்படத்திற்கும் பொருந்தும். இத்திரைப்படம் கலைகளின் சங்கமமாகவும் பல குடும்பங்களை வாழ வைக்கும் இடமாகவும்
விளங்குகிறது எனலாம்.
Question 46.
(அ) சாலை விபத்தில்லாத் தமிழ்நாடு ‘ – இக்கூற்று நனவாக நாம் செய்ய வேண்டியன யாவை?
Answer:
குறிப்புச் சட்டகம்
- முன்னுரை
- சாலை விதிகள்
- கணக்கீடு
- சாலைக்குறியீடு
- மோட்டார் வாகனச் சட்டம்
- முடிவுரை
முன்னுரை: வாழ்வை முழுமையாக்கும் கூறுகளுள் முதன்மையானது பயணம். அதிலும் சாலை வழிப் பயணம் மனதிற்கு இன்பத்தை அளிக்கக் கூடியது. அத்தகைய பயணத்தை அனைவரும் பாதுகாப்பாக மேற்கொள்ள வேண்டும். சாலை விதிகளைத் தெரிந்து கொள்வதும் கல்விதான். போக்குவரத்து குறித்த விதிகளையும், பாதுகாப்பு வழிகளையும் இக்கட்டுரை வழி காண்போம்.
- விபத்தில் 5,000 பேர் உயிரிழக்கின்றனர். சுமார் 2 இலட்சம் பேர் உடலுறுப்பை இழக்கின்றனர்.
- நாளொன்றுக்கு 1317 விபத்துக்களும் அதில் 413 பேர் உயிரிழக்கின்றார்கள்.
- இந்தியாவில் நடக்கும் விபத்துகளில் 15 சதவீதம் தமிழ்நாட்டில் நடப்பது வேதனைக்குரியது.
சாலை விதிகள்:
- சாலையின் வகைகள், மைல் கற்களின் விவரங்கள் பற்றித் தெரிந்து வைத்திருக்க வேண்டும்.
- போக்குவரத்தினை முறைப்படுத்தும் குறியீடுகள் மற்றும் போக்குவரத்துக் காவலர்களின் சாலை உத்தரவுகளுக்கு ஏற்பச் சாலையைப் பயன்படுத்த வேண்டும்.
- நடைமேடை, நடைபாதையைப் பயன்படுத்துபவர்களையும், சாலையைக் கடப்பவர்களையும் அச்சுறுத்தக் கூடாது.
- சாலைச் சந்திப்புகளில் எச்சரிக்கையான அணுகுமுறை தேவை. தேவையான இடங்களில் சரியான சைகையைச் செய்ய வேண்டும்.
- எதிரில் வரும், கடந்து செல்ல முற்படும் ஊர்திகளுக்கு வழிவிட வேண்டும். தேவையெனில் வேகம் குறைத்து இதர வாகனங்களுக்குப் பாதுகாப்புடன் வழிவிட வேண்டும்.
- பிற ஊர்தி ஓட்டிகளுக்கு விட்டுக்கொடுப்பது சிறந்தது.
- இதர சாலைப் பயனாளிகளை நண்பராக எண்ண வேண்டும்.
சாலைக் குறியீடு : சாலைகளில் இடம் பெற்றிருக்கும் குறியீடுகள் போக்குவரத்தினைச் சீர் செய்யவும் பாதுகாப்பாகப் பயணிக்கவும் உதவுகின்றன. அவை
- உத்தரவுக் குறியீடுகள்
- எச்சரிக்கைக் குறியீடுகள்
- தகவல் குறியீடுகள்
இக்குறியீடுகளை கவனத்தில் கொண்டு பயணித்தல் சிறந்தது. சாலை போக்குவரத்து உதவிக்கு 103 என்ற எண்ணைத் தொடர்பு கொள்ளலாம்.
மோட்டார் வாகனச் சட்டம் :
- 18 வயதிற்குட்பட்ட குழந்தைகள் வாகனம் இயக்கக் கூடாது. அதை மீறி இயக்கினால் பெற்றோர்களுக்கு 3 ஆண்டு சிறைத் தண்டனை கிடைக்கும்.
- ஓட்டுநர் உரிமம் இல்லாமல் இயக்கினால் ரூ.5,000 தண்டனைத் தொகையோ அல்லது மூன்று மாதச் சிறைத் தண்டனையோ அல்லது இரண்டுமோ கிடைக்கும்.
- அபாயகரமான முறையில் ஊர்தியை இயக்கினால் ரூ.5,000 தண்டத்தொகைப் பெறப்படும்.
- மது அருந்திவிட்டு இயக்கினால் ரூ.10,000 தண்டத்தொகைக் கட்ட நேரும்.
- மிக வேகத்தில் ஊர்தியை இயக்கினால் ரூ.5,000 தண்டத்தொகை கட்ட நேரும்.
- இருவருக்கு மேல் இரண்டு சக்கர ஊர்தியில் பயணித்தால் ரூ.2,000 தண்டத்தொகை அல்லது 3 மாதத்திற்கு ஓட்டுநர் உரிமம் நீக்கம்.
- தலைக்கவசம் அணியாமல் இருந்தால் ரூ.1,000 தண்டத்தொகையுடன் மூன்று மாதம் ஓட்டுநர் உரிமம் நீக்கம்.
முடிவுரை:
சாலைப் பாதுகாப்பு உயிர் பாதுகாப்பு என்பதை உணர்ந்து போக்குவரத்து விதிகளைக் கடைப்பிடித்தல் அவசியமாகும். போக்குவரத்து விதிகளை பின்பற்றுவதன் மூலம் நம் உயிரையும் உடல் உறுப்புகளையும், உடைமைகளையும், மற்றவரின் உயிரையும் காக்க முடியும், மாணவர்களாகிய நீங்களும் பாதுகாப்புடன் பயணம் செய்யவும், மற்றவர்களுக்கும் அதனை எடுத்துரைக்கவும்.
(அல்லது)
![]()
Question 46.
(ஆ) சங்க கால வரலாற்றை அறிந்து கொள்ள, புகளூர் கல்வெட்டு எவ்வகையில் துணை புரிகிறது? விளக்குக.
Answer:
புகளூர் கரூர் மாவட்டத்தில் அமைந்துள்ளது. இந்த ஊரில் ஆறுநாட்டான் என்று ஒரு மலை உள்ளது மலையடி வாரத்து ஊரை வேலாயுதம் பாளையம் என்பர். இம்மலைப்பகுதியில் இக்கல்வெட்டுகள் காணப்படுகின்றன. மொத்தம் 12 கல்வெட்டுகள் காணப்படுகின்றன. இவை அனைத்தும் சங்ககாலத் தமிழ் எழுத்தில் எழுதப் பெற்றுள்ள மொழி தமிழாகும். இவற்றுள் இரு கல்வெட்டுகள் சேர மன்னர்கள் வழங்கிய கொடை பற்றிக் கூறுகின்றன. எனவே, இக்கல்வெட்டுகள் சங்க வரலாற்றைத் தெரிந்து கொள்ள பெரிதும் துணைப்புரிகின்றன.
கல்வெட்டு -1
மூதா அமண்ணன் யாற்றூர்
செங்காயபன் உறைய்
ஆதன் செல்லிரும் பொறை மகன்
பெருங்கடுங்கோன் மகன் (இளங்
கடுங்கோ (இளங்கோ ஆக அறுத்த கல்
யாற்றூரைச் சேர்ந்த செங்காயபன் என்னும் துறவிக்கு சேர மன்னர் செல்லிரும்பொறை மகனான பெருங்கடுங்கோவின் மகன் இளங்கடுங்கோ இளவரசர் ஆவதை முன்னிட்டு வழங்கப்பட்ட கொடை சேர அரசின் மூன்று தலைமுறை இதன் மூலம் தெரிய வந்துள்ளது. இதிலுள்ள அரசர்கள் பதிற்றுப்பத்தில் 7, 8, 9 ஆம் பத்திற்குரிய தலைவர்களாக அடையாளப்படுத்தப் பெற்றுள்ளனர்.
கல்வெட்டு – 2,3
யாற்றூர் செங்காயப்பன்
(தா) வன் பின்னம் கொற்றன்
அறுபித்த அதிட்டானம்
யாற்றூரில் செங்காயபனுக்குத் தாவன் பின்னன் கொற்றன் என்பவர் அதிட்டானம் கொடுத்தது பற்றிக் கூறுகிறது. அதிட்டானம் என்றால் தரைப்பகுதி என்று பொருள்.
கல்வெட்டு -4)
நலிய) ஊர் பிடன் குறும் மகள் கீரள்
கொற்றி செய்பிதபளி
நலி ஊரை சேர்ந்த பிடனுடைய இள மகளான கீரன் கொற்றி செய்பித்த பாளியைப் பற்றி கூறுகிறது.
கல்வெட்டு – 5
நலிய ஊர் பிடந்தை மகள் கீரன்
கொறி அதிட்டான்
நலி ஊரை சேர்ந்த பிடந்தையின் மகளான கீரன் கொற்றி கொடுத்த படுக்கை. மேற்கண்டவாறு மொத்தம் 10 கல்வெட்டுகள் கிடைத்துள்ளன. அவை அனைத்தும் தமிழின் தமிழரின் பெருமையையும் அரசனின் பெருமையையும் எடுத்தியம்புகின்றன.
சிறப்புக்கள்:
- சங்ககால சேர அரசர்களின் கல்வெட்டு
கோ ஆதன் செல்லிரும் பொறை பெருங்கடுங்கோ. இளங்கடுங்கோ ஆகிய அரசர்களின் பெயர்கள் குறிப்பிடப் பெற்றுள்ளன. - சேர அரசின் மூன்று தலைமுறை இதன் மூலம் தெரியவந்துள்ளது.
- பதிற்றுப்பத்தில் 7. 8, 9 ஆம் பத்திற்குரிய தலைவர்களாக அடையாளப்படுத்த பெற்றுள்ளனர்.
பகுதி – V
அடிமாறாமல் செய்யுள் வடிவில் எழுதுக.
Question 47.
(அ) வையகம் பனிப்ப – எனத் தொடங்கும் நெடுநல்வாடைப் பாடல். [134 = 4]
Answer:
வையகம் பனிப்ப வலனேர்பு வளைஇப்
பொய்யா வானம் புதுப்பெயல் பொழிந்தென்
ஆர்கலி முனைஇய கொடுங்கோல் கோவலர்
ஏறுடை இனநிரை வேறுபுலம் பரப்பிப்
புலம்பெயர் புலம்பொடு கலங்கி கோடல்
நீடு இதழ்க் கண்ணி நீர் அலைக் கலாவ
மெய்க்கொள் பெரும்பனி நலிய பலருடன்
கைக்கொள் கொள்ளியர் கவுள் புடையூஉ நடுங்க
– நக்கீரர்
(ஆ) சினம்’ என முடியும் குறள். [1×2 = 2]
Answer:
தன்னைத் தான் காக்கின் சினங்காக்க காவாக்கால் தன்னையே கொல்லும் சினம்.
![]()