You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Geography Solutions Chapter 2 Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes
Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Weathering the Storm in Ersama MCQ Questions Class 9 English with Answers.
Question 1.
The disintegration or decomposition of rocks is generally called as …………………
(a) weathering
(b) erosion
(c) transportation
(d) deposition
Answer:
(a) weathering
Question 2.
The process of the levelling up of land by means of natural agents.
(a) aggradation
(b) degradation
(c) gradation
(d) none
Answer:
(c) gradation
Question 3.
……………. is seen in the lower course of the river.
(a) Rapids
(b) Alluvial fan
(c) Delta
(d) Gorges
Answer:
(c) Delta
![]()
Question 4.
Karst topography is formed due to the action of ………………
(a) Glacier
(b) Wind
(c) Sea waves
(d) Ground water
Answer:
(d) Ground water
Question 5.
Which one of the following is not a depositional feature of a glacier?
(a) cirque
(b) Moraines
(c) Drurrtlins
(d) Eskers
Answer:
(a) cirque
Question 6.
Deposits of fine silt blown by wind is called as …………….
(a) Loess
(b) Barchans
(c) Hamada
(d) Ripples
Answer:
(a) Loess
Question 7.
Stacks are formed by …………….
(a) Wave erosion
(b) River erosion
(c) Glacial erosion
(d) Wind deposion
Answer:
(a) Wave erosion
Question 8.
……………… erosion is responsible for the formation of cirque.
(a) wind
(b) glacial
(c) river
(d) underground water
Answer:
(b) glacial
Question 9.
Which one of the following is a second order land form?
(a) Asia
(b) Deccan Plateau
(c) Kulu valley
(d) Marina Beach
Answer:
(b) Deccan Plateau
II. Match the following.

Answer:
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (e)
5. (b)
III. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
Define weathering.
Answer:
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of the material of the earth’s crust by its exposure to the atmosphere.
Question 2.
What do you mean by biological weathering?
Answer:
Biological weathering occurs due to the penetration and expansion of plant roofs, earthworms, burrowing animals (rabbits, rats), and same human activities.
Question 3.
Mention the three courses of a river with any two landforms associated with each course.
Answer:
- The course of a river is divided into
- The Upper course
- The Middle course
- The Lower course.
- The land features carved by a river in its upper course are V-shaped valleys, gorges, canyons, rapids, potholes, spurs, and waterfalls.
- In the middle course of a river some typical landforms like alluvial fans, flood plains, meanders, oxbow lakes, etc., are formed.
- The lower course of a river develops typical landforms like delta and estuary.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the Ox-bow lakes?
Answer:
- Meanders in due course of time become almost a complete circle with narrow necks.
- This in turn gets abandoned and forms a lake. This is called an Ox-bow lake.
Question 5.
How does a cave differ from a sea arch?
Answer:
|
Sea cave |
Sea Arch |
| A prolonged wave attack on the base of a cliff erodes rock materials which results in the formation of caves. | When two caves approach one another from either side of a headland and Unite, they form an arch, e.g., Neil Island, Andaman & Nicobar. |
Question 6.
List out any four karst topographical areas found in India.
Answer:
Karts areas in Indian are given below:
- Guptadham caves – Western Bihar
- Robert cave and Tapkeshwar Temple – Uttarakhand.
- Pandav caves – Pachmarhi, Madhya Pradesh.
- Kutumsar – Bastar District in Chattisgarh
- Borra caves of Visakhapatnam – Andhra Pradesh.
Question 7.
What do you mean by a hanging valley?
Answer:
These are valleys eroded by the tributary glacier and that hangs over the main valley.
Question 8.
Define:
(a) Moraine
(b) Drumlin
(c) Esker.
Answer:
(a) Moraine:
Landforms formed by the glacial deposits of the valley or continental glaciers are termed as Moraines. They are of various shapes and sizes, like the ground, terminal, and lateral moraine, etc.
(b) Drumlins:
Drumlins are deposits of glacial moraines that resemble giant inverted teaspoons or half cut eggs.
(c) Eskers:
Long Narrow ridges composed of boulders gravel and sand deposited by streams of melting water which run parallel to a glacier are called Eskers.
Question 9.
Mention the various features formed by wind erosion.
Answer:
- The erosional landforms of wind: Mushroom rocks, Inselbergs, and Yardangs
- The Depositional Landforms of wind: Sand dunes, Barchans, and loess.
![]()
Question 10.
What are the wave-cut platforms?
Answer:
- Flat surface found at the foot of sea cliffs are called wave platform
- Wave cut platform is also referred to as beach, shelf, terrace, and plain.
IV. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Physical and chemical weathering
Answer:
| S.No. | Physical weathering | Chemical weathering |
| (i) | It is the breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition through the action of physical forces. | Disintegration and. decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions is called Chemical weathering. |
| (ii) | Cracks are formed and disintegration occurs eventually. | Chemical weathering takes place through the processes of oxidation, carbonation solution and hydration. |
| (iii) | Exfoliation, block disintegration, granular disintegration, etc., are the different types of weathering. | The agents of Chemical weathering are oxygen, CO2 and Hydrogen. |
Question 2.
Delta and Estuary
Answer:
| S.No. | Delta | Estuary |
| (i) | A triangular-shaped low lying area formed by the river at its mouth is called Delta. | Deltas have fine deposits of sediments enriched with minerals. |
| (ii) | Estuary is formed where the rivers meet the sea. | Deposition of silt by the river is not possible in the estuaries like Delta as if the waves keep on eroding the deposits e.g. River Narmada, River Tapti. |
Question 3.
Stalactite and stalagmite
Answer:
| Stalactite | Stalagmite |
| When the water containing dissolved calcite gradually drips from the ceiling of the caves, water evaporates and the remaining calcite hangs from the ceiling and thus Stalactites are formed. | When the calcite deposits rises upward like a pillar Stalagmites are formed. |
![]()
Question 4.
Longitudinal and Transverse sand dunes
Answer:
| Longitudinal | Transverse sand dunes. |
| Longitudinal dunes are long narrow ridges of sand, which extend in a direction parallel to the prevailing winds. These dunes are called Seifs in Sahara. | Transverse dunes are asymmetrical in shape. They are formed by alternate slow and fast winds that blow from the same direction. |
Question 5.
Inselbergs and yardangs
Answer:
| S.No. | Inselbergs | Yardangs |
| (i) | Certain hard rocks like igneous rocks are more resistant to wind action. | In arid regions, certain rocks .have hard and soft layers arranged vertically. |
| (ii) | Isolated residual hills rising abruptly from their surroundings are termed as inselbergs. e.g., Uluru (or) Ayers Rock – Australia. | When winds blow over these rocks, the soft layers get eroded leaving irregular crests. These are called Yardangs. |
Question 6.
Spit and bar
Answer:
|
Spit |
Bar |
| A spit is a ridge (or) embankment of sediment, attached to the land on one end and terminating in open water on the other end. Spits are common at the mouth of estuaries, e.g., Kakinada Spit. | A bar is an elongated deposit of sand, shingle (or) mud found in the sea almost parallel to the shoreline. |
V. Give Reasons.
Question 1.
Chemical weathering is predominant in hot and humid zones.
Answer:
- Chemical is predominant in hot and humid zones because the warm temperature and rainfall increases the chemical weathering.
- It encourages the decomposition of plant matter to produce chemicals such as humic acids and CO2
These chemicals increase the rate of weathering.
Question 2.
Slit deposits are less at estuaries than deltas.
Answer:
- Deltas form at the mouths of large rivers when sediments and silt accumulate.
- As sediments continue to accumulate, the course of the river may even be changed.
- Estuary is formed where the rivers meet the sea.
- Deposition of silt by the river is not possible here in the estuaries like delta as if the waves keep on eroding the deposits.
![]()
Question 3.
The snow line is at the sea level in Polar regions.
Answer:
The snow line is at the sea level in Polar regions because the higher the latitude lowers the snow line from sea level. –
Question 4.
Wind can possibly erode the rocks from aO sides.
Answer:
- Wind erosion can occur in any area where the Soil (or) Sand is not compacted (or) if it is finely granulated in nature.
- Wind can loosen the materials and send them in all directions.
Question 5.
In limestone regions, surface drainage is rarely found.
Answer:
- Groundwater percolating through cracks removes the soluble rock while leaving an enlarged channel for the further flow of water.
- If there is a thick cover of soil above the soluble rock, surface streams may flow above the subterranean karst drainage system.
- But most commonly, dissolution features occur at the surface.
- Therefore there are a few continuous surface streams.
VI. Answer in Paragraph.
Question 1.
Write a note on weathering classify and explain.
Answer:
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of materials of the earth’s crust by their exposure to the atmosphere. There are three types of weathering,
(a) Physical weathering
(b) Chemical weathering
(c) Biological weathering
Physical weathering: It is the breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition, through the action of physical forces. The constant freezing and thawing of rocks during the night and day leads to the expansion and contraction of rocks. Cracks are formed and disintegration occurs eventually. Exfoliation, block disintegration, granular disintegration, etc., are the different types of weathering.
Chemical weathering: Disintegration and decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions are called Chemical Weathering. This is predominantly high in the hot and humid regions such as the equatorial, tropical, and subtropical zones. Chemical weathering takes place through the processes of oxidation, carbonation, solution, and hydration. The agents of Chemical weathering are Oxygen, Carbon-dioxide, and Hydrogen.
Biological weathering: Biological weathering occurs due to the penetration and expansion of plant roots, earthworms, burrowing animals (rabbits, rats), and some human activities.
Question 2.
Explain the erosional landforms formed by underground water.
Answer:
(a) Erosional landforms formed by underground water.
- Most of the erosions take place due to the process of solution.
- When rainwater mixes with carbon-di-oxide and enters a limestone region, it dissolves and destroys much of the limestone.
- As a result, landforms such as Terra Rossa, Lappies, sinkholes, swallow holes, dolines, uvulas, poljes, caves, and caverns are formed.
(b) Terra Rossa: The deposition of red clay soil on the surface of the Earth is due to the dissolution of limestone content in rocks.
(c) When the joints of limestone rocks are corrugated by groundwater, long furrows are formed. These are called Lappies.
(d) A funnel-shaped depressions formed due to the dissolution of limestone rock is called sinkholes.
(e) Caves are hollows that are formed by the dissolution of limestone rocks when carbon-di-oxide in the air turns into carbonic acid. Caverns are caves with irregular floors.
Question 3.
What is a glacier? Explain its types.
Answer:
A Glacier is a large mass of ice that moves slowly over the land, from its place of accumulation. It is also known as the ‘River of ice’. The place of accumulation is called a snowfield. The height above which there is a permanent snow cover in the higher altitude or latitude is called snowline. The higher the latitude, the lower the snowline from sea level.
The gradual transformation of snow into granular ice is called ‘firn’ or ‘ neve’ and finally, it becomes solid glacial ice.
Movement of Glacier: The large mass of ice creates pressure at its bottom and generates heat. Due to this, the glacier melts a little and starts to move The rate of movement of a glacier varies from a few centimeters to several hundred meters a day. The movement of glaciers depends on slope, the volume of the glacier, thickness, roughness at the bottom (friction), etc., and Temperature. Like the rivers, glaciers also carry out erosion, transportation, and deposition.
Types of Glacier: Glaciers are broadly divided into two types based on the place of occurrences, such as Continental glacier and valley glacier.
Question 4.
Describe the depositional work of winds.
Answer:
(a) Depositional landforms of wind:
- Deposition occurs when the speed of wind is reduced by the presence of obstacles like bushes, forests and rock structures.
- The sediments carried by wind get deposited on both the windward and leeward sides of these obstacles.
(b) Sand dunes: In deserts, during sandstorms, wind carries loads of sand. When the speed of wind decreases, huge amount of sand gets deposited. These mounds or hills of sand are called sand dunes.
(c) Barchans: Barchans are isolated, crescent-shaped sand dunes. They have gentle slopes on the windward side and steep slopes on the leeward side.
(d) Transverse dunes: They are asymmetrical in shape. They are formed by alternate slow and fast winds that blow from the same direction.
(e) Longitudinal dunes: Longitudinal dunes are long narrow ridges of sand, which extend in a direction parallel to prevailing winds.
(f) Loess:
- The term loess refers to the deposits of fine silt and porous sand over a vast region.
- Extensive loess deposits are found in Northern and Western China, the Pampas of Argentina, in Ukraine, and in the Mississippi valley of the United States.
![]()
Question 5.
Give a detailed account of the three orders of landforms.
Answer:
Major land forms:
(i) First order landforms : Continents & Oceans
(ii) Second-order landforms: Mountains, Plateaus, and plains minor land forests
(iii) Third-order landforms: Deltas, Fjords coasts, Sand dimes, Beaches, Valleys, Cirques, Mushroom rocks, Limestone rocks.
First-order land forms:
- Continents: (i) It is a very large area of land.
(ii) One of the seven large landmasses on the earth’s surface, surrounded by sea.
Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. - Oceans: A very large expanse of sea, Atlantic ocean, Arctic ocean, Pacific ocean, Indian ocean, and Antarctic ocean.
Second-order landforms: Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains.
- Mountains: A large natural elevation of the earth’s surface, rising abruptly from the surrounding level, e.g., the Himalayas.
- Plateaus: An area of fairly level high ground, e.g., Tibetan plateau.
- Plains: A large area of flat land, e.g., Coastal plains.
Third-order landforms: Deltas, Fjords, Sand dunes, Beaches, Valleys, Cirques, Mushroom rocks, Limestone rocks.
- Deltas: A triangular-shaped low lying area formed by the river at its mouth is called Delta. Fjords: These are glacial valleys that are partly submerged in the sea.
- Sand Dunes: In deserts, a huge amount of sand gets deposited. These mounds (or) hills of sand are called sand dunes.
- Beaches: Sand and gravel are moved and deposited by waves along the shore to form Beaches. Valleys: A low area of land between hills (or) mountains typically with a river (or) stream flowing through it.
- Cirques: The glacier erodes the steep sidewalls of the mountain and farms bowl shaped armchair. It is termed as a cirque.
- Mushroom rocks: By the constant wearing down action of wind the bottom of the rock gets eroded away to form a mushroom-like structure. This is called Mushroom rock (or) Pedestal rock.
- Limestone rocks: The underground water creates distinct landforms in limestone regions called Karst Topography. It consists of calcite, aragonite.
VII. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below.
Question (i).
1. ‘I’ shaped valley is an erosional feature of the river.
2. ‘U’ shaped valley is an erosional feature of the glacier.
3. ‘V’ shaped valley is an erosional feature of the glacier.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii) are right
(b) (i) and (ii) are right
(c) (i) and (iii) are right
(d) only (i) is right
Answer:
(d) only (ii) is right
Question (ii).
Statement I: Running water is an important agent of gradation.
Statement II: The work of the river depends on the slope of land on which-it flows.
(a) Statement I is false II is true
(b) Statement I and II are false
(c) Statement I is true II is false
(d) Statement I and II are true
Answer:
(a) Statement I is false II is true
Question (iii).
Statement: Limestone regions have less underground water.
Reason : Water does not percolate through limestone.
(a) The statement is right reason is wrong.
(b) The statement is wrong Reason is right.
(c) The statement and reason are wrong.
(d) The statement and reason are right.
Answer:
(d) The statement and reason are right.
VIII. HOTS
Question 1.
Is wind the only gradational agent in the desert?
Answer:
Yes, the wind is the only gradational agent in the desert.
e.g., Erosional activity: Yardung
Depositional activity: Sand Dimes.
![]()
Question 2.
Underground water is more common in limestone areas than surface runoff. Why?
Answer:
The chief constituent of limestone is calcium carbonate which is soluble in pure water and easily soluble in carbonated water.
Question 3.
The river channels in the lower course are wider than the upper course.
Answer:
The reasons are,
- The river splits into a number of channels called distributaries.
- The river brings downloads of debris from its upper and middle.
- The river deposits and develop typical landforms like Delta and Estuary.
In-text HOTs Questions
Question 1.
Is weathering a pre-requisite in the formation of soil?
Answer:
- Yes, weathering a pre-requisite in the formation of soil.
- The rock materials in due course of time are weathered further to form soil.
- Soil is a mixture of disintegrated rock material.
Question 2.
The snowline of the Alps’is 2700 metre whereas the snowline of Greenland is just 600 mts. Find out the reason.
Answer:
On tropical mountains, the snowline may be as high as 500 mts, but when traced poleward it descends to 2700 mts in the European Alps to 600 meters in Greenland and just to se-a level near the poles. –
IX. Map Skill.
Question 1.
On the given outline map of the world, mark the following.
1. Any two deltas
2. A Karst region
3. Any two hot and cold deserts
Answer:
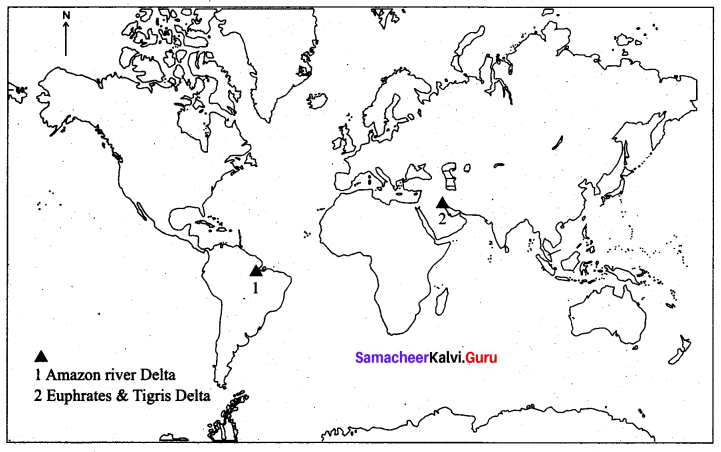
1. Any two deltas – Euphrates & Tigris Delta and Amazon river Delta
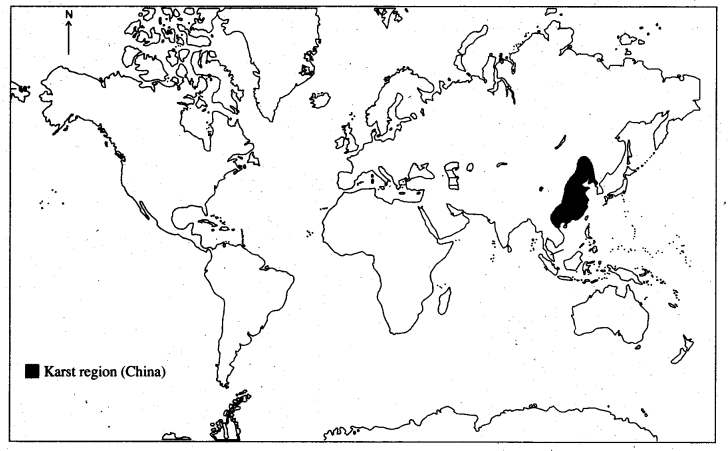
2. A Karst region – China
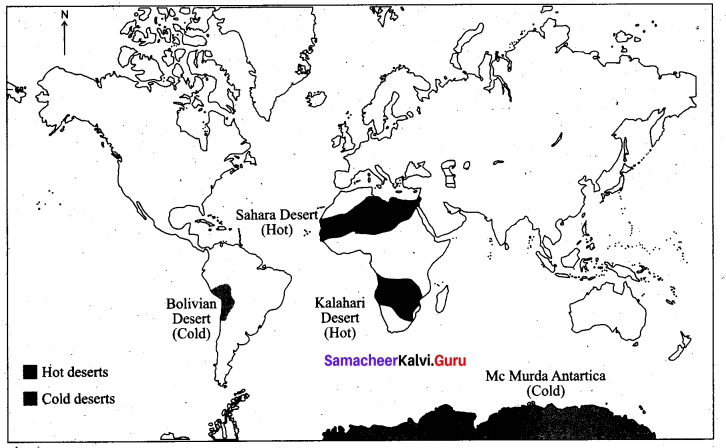
3. Any two hot and cold desets
X. Give geographical terms for the following:
Question 1.
(a) Chemical alteration of carbonate rocks on limestone region.
(b) Flat surfaces near cliffs.
(c) Erosion + Transportation + Deposition =
(d) The bottom line of a snowfield.
Answers:
(a) Carbonation
(b) Plateau
(c) Gradation
(d) The snowline
Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The process of dissolution of rock substances in water is …………….
(a) oxidation
(b) solution
(c) gradation
(d) hydration
Answer:
(b) solution
Question 2.
This generally originate from mountains.
(a) lake
(b) sea
(c) river
(d) ocean
Answer:
(c) river
Question 3.
The cylindrical holes drilled vertically in the river bed are …………….
(a) Potholes
(b) canyons
(c) rapid
(d) Gorge
Answer:
(a) Potholes
Question 4.
The largest Delta in the world is …………….
(a) The Nile River Delta
(b) The Ganga – Brahmaputra Delta
(c) The Yellow river Delta
(d) The Indus Delta
Answer:
(b) The Ganga – Brahmaputra Delta
![]()
Question 5.
The redness of the red clay soil is due to. the presence of ……………
(a) iron oxide
(b) carbon
(c) copper
(d) magnesium
Answer:
(a) iron oxide
Question 6.
The most powerful agents of gradation are ……………
(a) Rivers
(b) Glaciers
(c) Sea waves
(d) Streams
Answer:
(c) Sea waves
II. Match the following.

Answer:
1. (e)
2. (a)
3. (d)
4. (b)
5. (a)
III. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
Define Granular Disintegration.
Answer:
Granular disintegration takes place in crystalline rocks where the grains of the rocks become loose and fall out. This is due to the action of temperature & frost.
Question 2.
Mention the land features carved by a river in its upper course.
Answer:
‘V’ shaped valleys, Gorges, Canyons, rapids, potholes, spurs and waterfalls.
Question 3.
What are “Pot Holes”?
Answer:
Due to the river action, cylindrical holes are drilled vertically in the river bed with varying depth and diametre.
Question 4.
State the other erosional features of Karst regions in other parts of the world.
Answer:
Swallow Holes, Uvalas, Dolines, Poljis are the other erosional features.
Question 5.
What are Transverse Dunes?
Answer:
- Transverse Dunes are asymmetrical in shape.
- They are formed by alternate slow and fast winds that blow from the same direction.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the wave-cut Platforms?
Answer:
Flat surface found at the foot of the sea cliffs are called a wave Cut platform. It is also referred to as Beach, shelf, terrace, and plain.
IV. Distinguish between.
Question 1.
Oxidation and Carbonation.
Answer:
| S.No. | Oxidation | Carbonation |
| (i) | Oxygen in the atmosphere reacts with the Iron found in rocks thus leading to the formation of Iron oxide. This process is known as oxidation. | Carbonation is the mixing of water with atmospheric CO2 forming carbonic acid. |
| (ii) | Oxidation weakens the rocks. | It is important in the formation of caves, in the limestone region. |
Question 2.
Alluvial Plain and Flood Plain.
Answer:
| S.No. | Alluvial Plain | Flood Plain |
| (i) | A fan-shaped deposition made by the river at the foothills is called an alluvial plain. | Fine sediments are deposited on river banks when a river floods and is called flood plain. |
| (ii) | These deposits are rich and fertile useful for cultivation. | These sediments make the region rich and fertile. |
Question 3.
Arete and Matterhorn.
Answer:
| Arete | Matterhorn |
| Aretes are narrow ridges formed when two cirque walls joined together back to back and forms narrow knife-like ridges. | The pyramidal peaks formed when three (or) more cirques meet together are referred as matterhoms. |
Question 4.
Sea Cave and Sea Arch.
Answer:
|
Sea Cave |
Arch |
| Prolonged wave attack on the base of a cliff erodes rock materials which result in the formation of caves. | When two caves approach one another from either side of a headland and Unite, they form an arch, e.g., Neil Island, Andaman Nicobar. |
V. Give reasons.
Question 1.
Why do Biological weathering occur?
Answer:
Biological weathering occurs due to the penetration and expansion of plant roots, earthworms, burrowing animals (rabbits and rats), and some human activities.
Question 2.
Why is Karst Topography formed?
Answer:
Karst Topography is formed due to the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and Gypsum.
Question 3.
Why do the Pedestal rock look like mushroom?
Answer:
By the constant wearing down action of wind, the bottom gets eroded away to form a mushroom-like structure. So the Pedestal rock looks like a mushroom.
VI. Answer in a Paragraph.
Question 1.
Explain the origin of the river and its course.
Answer:
Rivers generally originate from mountains and end in a sea or lake. The whole path that a river flows through is called its course. The course of a river is divided into:
(i) The upper course
(ii) The middle course and
(iii) The lower course
(i) The Upper Course: Erosion is the most dominant faction of the river in the upper course. In this course, a river usually tumbles down the steep mountain slopes. The steep gradient increases the velocity and the river channel performs erosion with great force to widen and deepen its valley. The land features carved by a river in its upper course are V-shaped valleys, gorges, canyons, rapids, potholes, spurs, and waterfalls.
(ii) The Middle Course: The river enters the plain in its middle course. The volume of water increases with the confluence of many tributaries and thus increases the load of the river. Thus, the predominant action of a river is transportation. The deposition also occurs due to the sudden decrease in velocity. The river in the middle course develops some typical landforms like alluvial fans, flood plains, meanders, ox-bow lakes, etc.,
(iii) The Lower course: The river, moving downstream across a broad, level plain is loaded with debris, brought down from its upper and middle courses. Large deposits of sediments are found at the level bed and the river splits into a number of channels called distributaries. The main work of the river here is a deposition and it develops typical landforms like delta and estuary.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the Erosional landforms of Sea.
Answer:
Some of the erosional landforms of sea waves are sea cliff, sea cave, arch, stack, beach, bar and spit and wave-cut platform.
- Sea Cave: Prolonged wave attack on the base of a cliff erodes rock materials, which results in the formation of caves.
- Sea Arch: When two caves approach one another from either side of a headland and unite, they form an arch, e.g., Neil Island, Andaman, and Nicobar.
- Sea Stack: Further erosion by waves ultimately leads to the total collapse of the arch. The seaward portion of the headland will remain as a pillar of rock known as a stack. Eg the Old man of Hoy in Scotland.
- Sea Cliffs: Sea cliffs are steep rock faces formed when sea waves dash against them. The rocks get eroded to form steep vertical walls.
- WaveCut Platforms: Flat surface found at the foot of sea cliffs are called wave-cut platforms. Wave cut platform is also referred to as beach, shelf, terrace, and plain.
VII. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below.
Question 1.
(i) The nature and magnitude of weathering differ from place to place and region to region.
(ii) Granular disintegration takes place due to the action of volcanoes.
(iii) Weathering is a pre-requisite in the formation of soil.
Which of the above statement is/are the right statement.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii) are right
(b) (i) & (ii) are right
(c) (i) & (iii) are right
(d) only (i) is right.
Answer:
(c) is right
Question 2.
(i) Small streams that join the main river is tributary.
(ii) River Gangas is a tributary.
Which of the above statement is/are the right statement.
(a) The statement is the right reason is wrong
(b) The statement is the wrong reason is right
(c) The statement & reason are wrong
(d) The statement & reason are right
Answer:
(a) is right.
VIII. Map Skill.
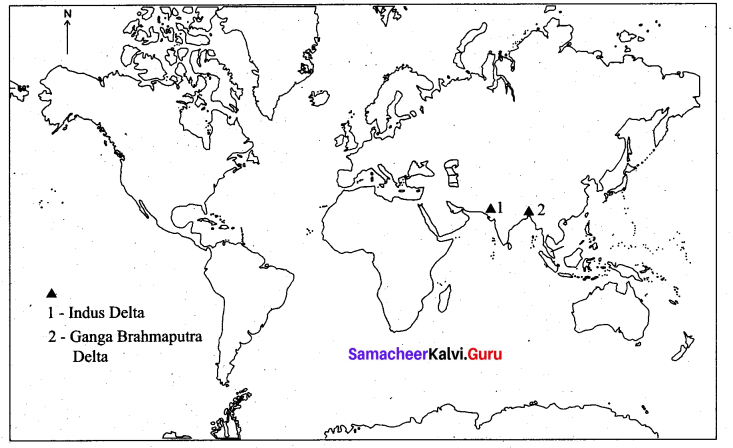
Question 1.
Indus and Ganga Brahmaputra Delta
Answer:
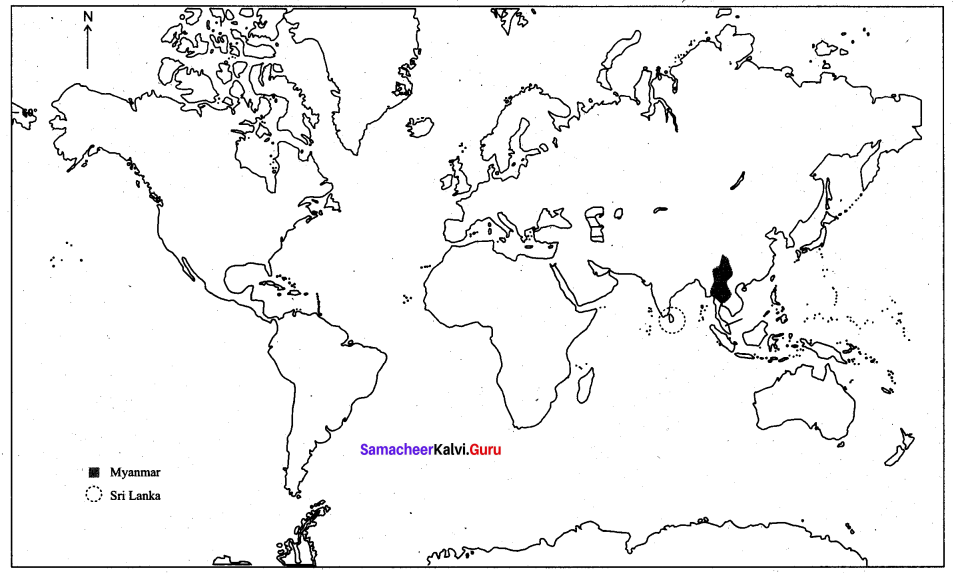
2. Sri Lanka & Myanmar