You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 5 The Cell
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Cell Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
The unit of measurement used for expressing dimension (size) of cell is
(a) centimeter
(b) millimeter
(c) micrometer
(d) meter
Answer:
(c) micrometer
Question 2.
Under the microscope Priya observes a cell that has a cell wall and distinct nucleus. The cell that she observed is
(a) a plant cell
(b) an animal cell
(c) a nerve cell
(d) a bacteria cell
Answer:
(a) a plant cell
Question 3.
A control centre’ of the eukaryotic cell is
(a) Cell wall
(b) Nucleus
(c) Vacuoles
(d) Chloroplast
Answer:
(b) Nucleus
Question 4.
Which one of the following is not an unicellular organism?
(a) Yeast
(b) Amoeba
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Bacteria
Answer:
(c) Spirogyra
Question 5.
Most organelles in a eukaryotic cell are found in the
(a) Cell wall
(b) cytoplasm
(c) nucleus
(d) Vacuole
Answer:
(b) cytoplasm
![]()
II. Fill in the Blanks:
- The instrument used to observe the cell is _______
- I control the food production of a cell. Who am I? _______
- I am like a policeman. Who am I _______ ?
- The Term “ cell” was coined by _______
- The egg of an Ostrich is the _______ single cell.
Answers:
- microscope
- chloroplast
- cell wall
- Robert hooke
- largest
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct answer:
Question 1.
A cell is the smallest unit of life.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Nerve cell is the longest cell.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Prokaryotes were the first form of life on earth.
Ans:
True
Question 4.
The organelles of both plants and animals are made up of cells.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
New cells are produced from existing cells.
Answer:
True
![]()
IV. Match the following:
| 1. Control center | Cell membrane |
| 2. Food producer (Plant cell) | Mitochondria |
| 3. Gate of the nucleus | Nucleus |
| 4. Gate of the cell | Chloroplasts |
| 5. Energy producer | Nuclear membrane |
Answer:
| 1. Control center | Nucleus |
| 2. Food producer (Plant cell) | Chloroplasts |
| 3. Gate of the nucleus | Nuclear membrane |
| 4. Gate of the cell | Cell membrane |
| 5. Energy producer | Mitochondria |
![]()
V. Arrange in a correct sequence:
Question 1.
Elephant, Cow, Bacteria, Mango, Rose plant.
Answer:
Bacteria, Rose plant, Mango, Cow, Elephant.
Question 2.
Hen egg, Ostrich egg, Insect egg.
Answer:
Insect egg, Hen egg, Ostrich egg.
VI. Analogy:
Question 1.
Prokaryote : Bacteria :: Eukaryote : _______
Answer:
Plant or animal cell.
Question 2.
Spirogyra : Plant cell:: Amoeba :
Answer:
animal cell.
Question 3.
Food producer : Chloroplasts :: Power house _______
Answer:
mitochondria.
VII. Give very short answer:
Question 1.
Who discovered the cell in 1665?
Answer:
The English scientist Robert Hooke discovered the cell in 1665 from cork slices kept under a microscope.
Question 2.
What type of cells do we have?
Answer:
We have Eukaryotic cells.
Question 3.
What are the essential components of a cell?
Answer:
Cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Vacuoles, Nucleus, Nucleus membrane are essential components of a cell
Question 4.
What are the organelles found only in plant cell?
Answer:
Chloroplasts and cell walls are the organelles found only in plant cell.
Question 5.
Give any three examples of the eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
Plant cell, animal cell, fungi, and algae cell.
Question 6.
Which one is called as “Area of movement”?
Answer:
The cytoplasm is called as “Area of movement”.
Question 7.
Shiva said, “ Bigger onion has larger cells when compared to the cells of the smaller onion”! Do you agree with his statement or not? Explain Why?
Answer:
No, I don’t agree with the statement. Cell size has no relation to the size of an organism.
![]()
VIII. Give a short answer:
Question 1.
Why cells are called building blocks of life?
Answer:
A cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. All the living things are made up of billions – of cells. They are the basic units of life and come from other cells. They can reproduce, build, and change. That is why they are called ‘building blocks of life’.
Question 2.
Identify any four parts of the Plant cell.
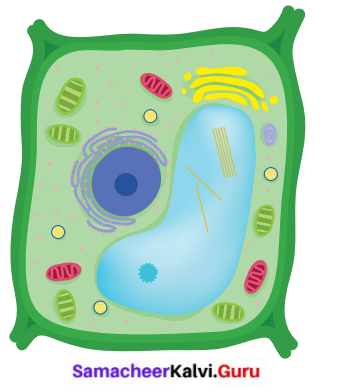
Answer:
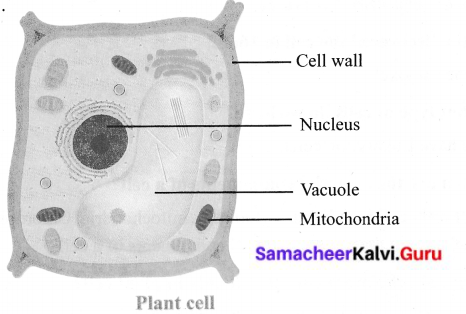
Question 3.
Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell:
- It’s diameter ranges from 1 to 2 micron
- Absence of membrane-bound organelles
- Nucleus consisting of no nuclear membrane
- Absence of nucleoli
Eukaryotic cell:
- It’s diameter ranges from 10 to 100 micron
- Presence of membrane-bound organelles
- True nucleus consisting of the nuclear membrane
- Presence of nucleoli
Question 4.
Make sketches of animal and plant cells that you observe under the microscope.
Answer:
Plant cell:
- It is usually larger in size. It is hard in nature.
- Plant cell have a cell wall in addition to their cell membrane.
- Plant cell have chloroplast which contain chlorophyll
- Plant cells have large vacuoles. Centrioles are absent.
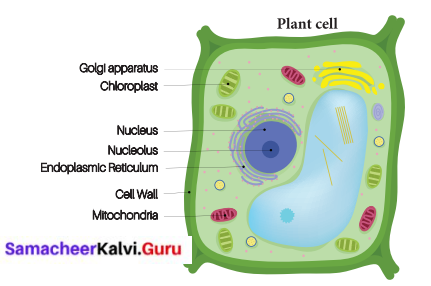
Animal cell:
- Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells. It is not so hard as plant cell.
- A cell wall is absent.
- The chloroplast is usually absent.
- An animal cell may have many small vacuoles.
- Centrioles are found in animal cells.
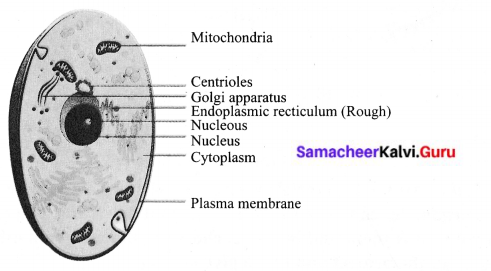
Question 5.
Write about the contribution of Robert Hooke in cell biology.
Answer:
- Robert Hooke was an English Scientist.
- He improved the microscope and built – a compound microscope.
- He used a water lens to illuminate the specimen.
- He observed a thin section of cork surprised to see hexagonal cells.
- He published a book name Micrographia in 1665. he also first used the term cell.
- The study of cells is called cell Biology.
![]()
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Tabulate any five cell organelles and their function.
Answer:
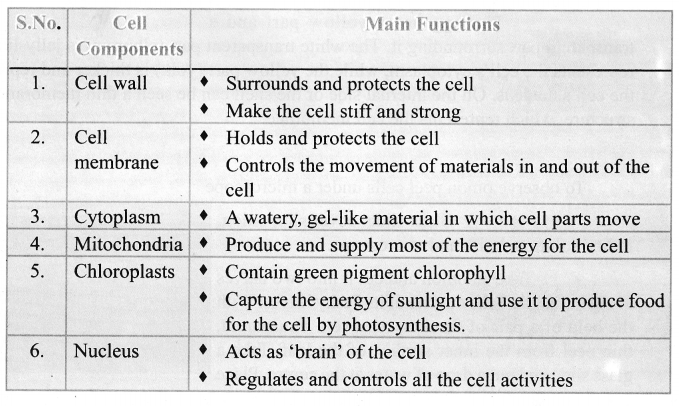
Question 2.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
Answer:
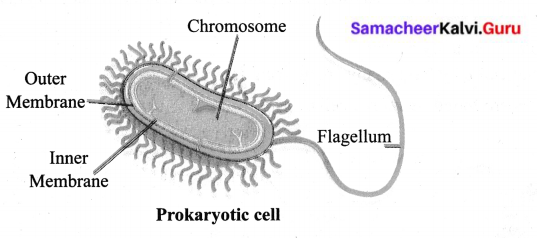
X. Project:
1. Use your imagination and create a 3-D model of a plant cell?
2. You can use numerous food materials such as jelly and some cake to make a cell body. Cell organelles can be made using nuts and dry fruits. You can display the model in your classroom and invite teachers or students from other classes to rise questions on the project and try to give answers.
Answer:
Activities to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Cell Intext Activities
Activity 1
Aim:
To observe the structure of a single cell (Hen’s egg).
Materials Needed: A hen’s egg and a plate.

Method: Crack the shell and break open the egg in a plate.
Observation: The egg has a yellow part and a transparent part surrounding it. The white transparent part (albumin) is jelly-like and represents the cell’s cytoplasm, while the yellow part (yolk) is thicker and represents the cell’s nucleus. On the internal side of the shell can be seen as a thin membrane-like structure, which represents the cell membrane.
![]()
Activity 2
Aim: To observe onion peel cells under a microscope
Materials Required: Glass slide, coverslip, onion, iodine solution, knife, and microscope.
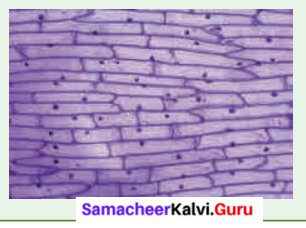
Procedure: Take an onion and cut it into two halves along its length. Take out one of its fleshy leaves. With the help of a pair of forceps, remove a transparent, thin peel from the inner surface of the leaf. Take a glass slide and put a drop of water at the centre. Place the peel on the drop of water. Pour a drop of iodine solution on the peel. Now place a coverslip over the material. Observe under the microscope.
Observation: You will be able to see rectangular cells of the onion peel, with a nucleus in each of them.
Activity 3
Aim: To rectify the variation between 2-D shape and 3-D shape.
Material required: Polythene bag, water, marble ball (golli gundu)
Procedure: Take a polythene bag with water. Put a marble ball into the polythene bag. Then draw a picture in your notebook about this task. If you draw a picture in a round shape. It will be called a 2-Dimenstional picture. If you draw a picture in spherical shape it is called 3-dimensional.
Result: Now you understand your misconceptions. So the animal cells are spherical in shape and structure, not in a round shape.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Cell Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which one is the prokaryotic cell among the following?
(a) Plant cell
(b) Animal cell
(c) Nerve cell
(d) Cyanobacteria cell
Answer:
(d) Cyanobacteria cell
Question 2.
The habitat of Escherichia coli bacteria is
(a) It is a soil-inhabiting bacteria
(b)It lives in the human intestine
(c) It is an aquatic bacteria
(d) It lives in the air
Answer:
(b) It lives in the human intestine
Question 3.
A typical cell consists of ______ major parts
(a) Two
(b) Four
(c) Three
(d) Five
Answer:
(c) Three
Question 4.
The central yellow coloured yolk of the egg is
(a) cytoplasm
(b) cell membrane
(c) Reserve material
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(d) Nucleus
Question 5.
Approximate number of cells in the human body is ______
(a) 3.7 × 1013
(c) 3.7 × 1014
(b) 3.7 × 1012
(d) 3.7 × 1015
Answer:
(a) 3.7 × 1013
Question 6.
Prokaryotic cell type of nucleus is called as _______
(a) nucleolus
(b) nuclear membrane
(c) organelles
(d) nucleoid
Answer:
(d) nucleoid
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
- _______ is the basic structural and functional unit of every living organism.
- Nowadays an _______ microscope is used to magnify the cells
- In Latin, the word ‘cellula’ means a _______
- The branch of science that deals with the study of cells are called __________
- The outer covering part of the cell is called _______
- _______ cells were the first form of life on earth.
- _______ is present in plant cell only.
- Plants prepared food with the help of _______
Answers:
- Cell
- electron
- small chamber
- cell biology
- cell membrane
- Prokaryotic
- Chloro plant
- chlorophyll
![]()
III. Find whether the following sentences are true or false. If false Correct the statement:
Question 1.
The cell is self-sufficient and carries out all the fundamental and essential functions of an organism.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Robert Hooke saw many objects like Butterfly’s compound eyes, Bee’s wings, etc.
Answer:
False. Robert Hooke saw many objects like Butterfly’s wings, Bees company eyes, etc.
Question 3.
All the cells can be seen with our naked eye.
Answer:
False. All the cells cannot be seen with our naked eye.
Question 4.
The size of the bacterial cell ranges from 0.01 micrometer to 0.5 micrometers.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Spirogyra and Human beings are unicellular.
Answer:
False. Spirogyra and Human beings are multicellular.
![]()
IV. Matching:
| 1. Discovery of cell | (a) | Nerve cell |
| 2. Unicellular organism | (b) | spirogyra |
| 3. Multicellular organism | (c) | Robert Hooke |
| 4. Longest cell | (d) | Cyanobacteria |
| 5. Prokaryotic cell | (e) | Amoeba |
Answer:
- – c
- – e
- – b
- – a
- – d
![]()
V. Analogy
Question 1.
Smallest cell: virus.
Biggest cell: _______
Answer:
Ostrich egg
Question 2.
Unicellular organism: Chlamydomonas.
Multicellular organism : _______
Answer:
Human beings
Question 3.
No true nucleus : Prokaryotic cell.
True nucleus : _______
Answer:
Eukaryotic cell
Question 4.
Plant cell: Chloroplast.
Animal cell: _______
Answer:
Centrioles
VI. Give a short answer
Question 1.
Give two examples of prokaryotic cells?
Answer:
Cyanobacteria and Escherichia coli bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells.
Question 2.
What are the two types of cells?
Answer:
Cells are classified into two types. The first one is the Prokaryotic cell. It has no true nucleus. Another one is the Eukaryotic cell. It has a true nucleus.
Question 3.
Define Prokaryotic cells.
Answer:
- It has no true nucleus.
- This type of nucleus is called a nucleoid.
- No nuclear membrane is around the nucleoid.
- It is ranging from 0.003 to 2.0 micrometer in diameter.
Question 4.
Write about chloroplasts.
Answer:
- It is found in plant cells only.
- It contains green pigment chlorophyll.
- It captures the energy of sunlight and uses it to produce food for photosynthesis.
- it is called as producers for the cell.
Question 5.
What are the functions of the nucleus?
Answer:
- It acts as the brain of the cell.
- It regulates and controls all cell activities.
Question 6.
The cell wall is called a supporter or protector. Why?
Answer:
- It surrounds and protects the cell.
- It makes the cell stiff and strong.
- It is called a supporter or protector.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Write the characteristics of plant cells with a diagram.
Answer:
Plant cell:
- It is usually larger in size. It is hard in nature.
- the plane cell has a cell wall in addition to their cell membrane.
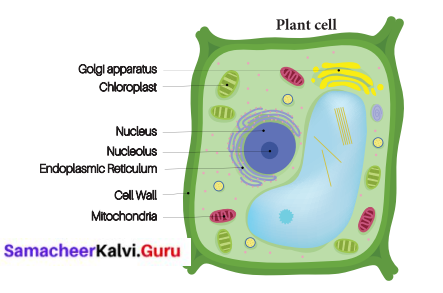
- Plant cell have chloroplast which contains chlorophyll
- Plant cells have large vacuoles. Centrioles are absent.
Question 2.
Write the characteristics of animal cells with a diagram.
Answer:
Animal cell:
- Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells. It is not so hard as plant cells.
- A cell wall is absent.
- The chloroplast is usually absent.
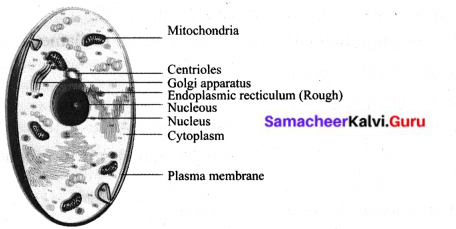
- An animal cell may have many small vacuoles.
- Centrioles are found in animal cells.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw the 3-dimensional cell structure and label the parts.
Answer:
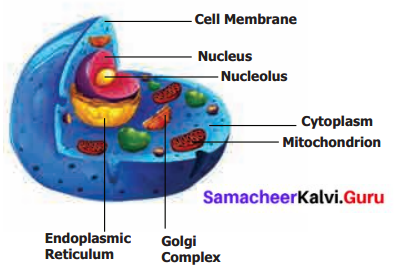
Question 4.
Give the difference between an animal cell and plant cell.
Answer:
Animal cell:
- Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells. It is not so hard as plant cells.
- A cell wall is absent.
- The chloroplast is usually absent.
- An animal cell may have many small vacuoles.
Plant cell:
- It is usually larger in size. It is hard in nature.
- A plant cell has a cell wall in addition to their cell membrane.
- Plant cell haves chloroplast which contains chlorophyll
- Plant cells have large vacuoles. Centrioles are absent.