You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Bill, Profit and Loss Ex 3.1
Question 1.
A School purchases some furniture and gets the following bill.
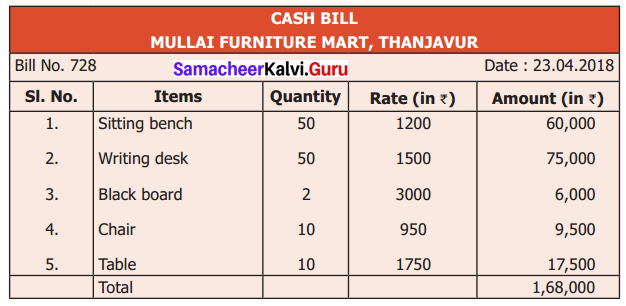
(i) What is the name of the store?
(ii) What is the serial number of the bill?
(iii) What is the cost of a blackboard?
(iv) How many sets of benches and desks does the school buy?
(v) Verify whether the total bill amount is correct.
Solution:
(i) Mullai Furniture Mart, Thanjavur
(ii) Serial No. 728
(iii) Cost of a blackboard is ₹ 3000
(iv) 50 sets
(v) Yes, the total bill amount is correct.
Question 2.
Prepare a bill for the following books of biographies purchased from Maruthu Book Store, Chidambaram on 12.04.2018 bearing the bill number 507.
10 copies of Subramanya Bharathiar @ ₹ 55 each, 15 copies of Thiruvalluvar @ ₹ 75 every 12 copies of Veeramamunivar @ ₹ 60 each and 12 copies of Thiru. Vi.Ka @ ₹ 70 each.
Solution:
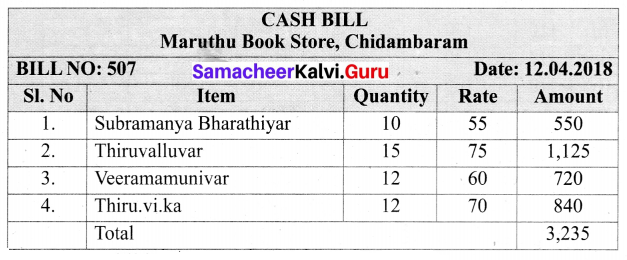
Question 3.
Fillup the appropriate boxes in the following table.
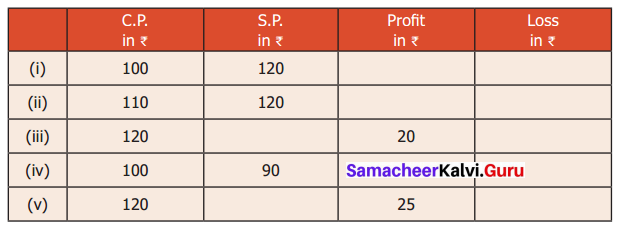
Solution:
(i) Here Cost price < Selling price
Profit = S.P – C.P = 120 – 100 = ₹ 20
Here S.P > C.P
Profit = S.P – C.P = 120 – 110 = ₹ 10
(iii) Profit = ₹ 20
Profit = S.P. – C.P
⇒ 20 = S.P. – 120
⇒ 20 + 120 = S.P
⇒ S.P = ₹ 140
(iv) C.P = ₹ 100
S.P = ₹ 90
Here S.P < C.P
Loss = 100 – 90 = ₹ 10
(v) Profit = S.P – C.P
⇒ 25 = S.P – 120
⇒ 25 + 120 = S.P
⇒ S.P = ₹ 145
![]()
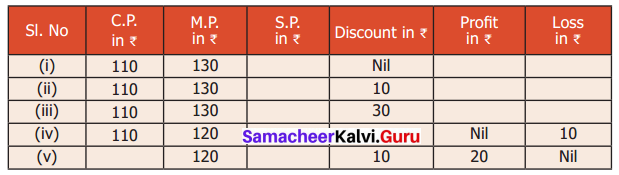
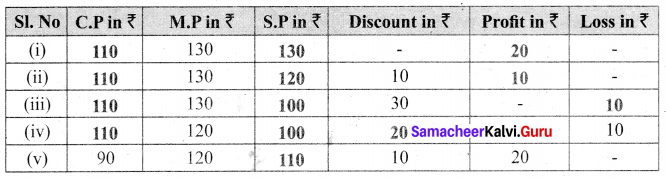
Question 4.
Fill up the appropriate boxes in the following table.
Solution:
(i) S.P. = M.P – Discount
S.P = ₹ 130
Here S.P > C.P
Profit = S.P – C.P = 130 – 110 = ₹ 20
(ii) S.P = M.P – Discount = 130 – 10 = ₹ 120
Here S.P > C.P
Profit = S.P – C.P = ₹ 120 – ₹ 110 = ₹ 10
(iii) S.P = M.P – Discount = 130 – 30 = ₹ 100
Here S.P < C.P
Loss = 110 – 100 = ₹ 10
(iv) C.P = ₹ 110
M.P = ₹ 120
Loss = ₹ 10
Loss = C.P – S.P
⇒ 10 = 110 – SP
⇒ SP = 110 – 10 = ₹ 100
Discount = M.P – S.P = 120 – 100 = ₹ 20
(v) M.P = ₹ 120
Discount = ₹ 10
Discount = M.P – S.P
⇒ 10 = 120 – S.P
⇒ S.P = 120 – 10 = ₹ 110
Profit = ₹ 20
Profit = S.P – C.P
⇒ 20 = 110 – C.P
⇒ C.P = 110 – 20 = 90
Question 5.
Rani bought a set of bangles for Rs 310. Her neighbour liked it the most. So, Rani sold it to her for Rs 325. Find the profit or loss to Rani.
Solution:
The cost price of the bangles = ₹ 310
The selling price of the bangles = ₹ 325
Here S.P > C.P
Profit = S.P – C.P = 325 – 310 = ₹ 15
Profit = ₹ 15
Question 6.
Sugan bought a pair of Jeans pant for ₹ 750. It did not fit him. He sold it to his friend for ₹ 710. Find the profit or loss to sugan.
Solution:
C.P of the Jeans pant = ₹ 750
S.P of the Jeans pant = ₹ 710
Here S.P < C.P
Loss = C.P – S.P = 750 – 710 = ₹ 40
Loss = ₹ 40
Question 7.
Somu bought a second-hand bike for Rs 28,000 and spent Rs 2,000 on its repair. He sold it for Rs 30,000. Find his profit or loss.
Solution:
Cost of bike = ₹ 28,000
Spent on Repairs = ₹ 2,000
Cost Price of bike = ₹ 30,000
Selling Price = ₹ 30,000
Selling Price = Cost Price
∴ There is neither profit nor loss.
Question 8.
Muthu has a car worth ₹ 8,50,000 and he wants to sell it at a profit of ₹ 25,000. What should be the selling price of the car? Solution:
Cost price of the car = ₹ 8,50,000
Expected profit = ₹ 25,000
We know that profit = S.P – C.P
25000 = S.P – 8,50,000
⇒ 25,000 + 8,50,000 = S.P
⇒ S.P = 8,75,000
Selling Price of the car should be ₹ 8,75,000
Question 9.
Valarmathi sold her pearl set for Rs 30,000 at a profit of Rs 5,000. Find the cost price of the pearl set.
Solution:
Selling price of the pearl set = ₹ 30,000
Profit = ₹ 5000
Profit = S.P – C.P
⇒ 5000 = 30,000 – C.P
⇒ C.P = 30,000 – 5,000 = ₹ 25,000
Cost price of the Pearl set = ₹ 25,000
Question 10.
If Guna marks his product to be sold for ₹ 325 and gives a discount of ₹ 30, then find the S.P.
Solution:
Marked Price of the Product = ₹ 325
Discount = ₹ 30
Selling Price = M.P – Discount = 325 – 30 = ₹ 295
S.P. = ₹ 295
![]()
Question 11.
A man buys a chair for 1,500. He wants to sell it at a profit of Rs 250 after making a discount of Rs 100. What is the M.P. of the chair?
Solution:
Cost of the chair = ₹ 1500
Profit needed = ₹ 250
Discount = ₹ 100
Profit = Selling price – Cost price
⇒ 250 = S.P – 1500
⇒ S.P = 250 + 1500
⇒ S.P = ₹ 1750
Also, S.P = M.P – Discount
⇒ 1750 = M.P – 100
⇒ 1750 + 100 = M.P
⇒ M.P. = ₹ 1850
Marked Price = ₹ 1850
Question 12.
Amutha marked her home product of pickle as ₹ 300 per pack. But she sold it for only ₹ 275 per pack. What was the discount offered by her per pack?
Solution:
M.P of the pickle = ₹ 300
S.P = ₹ 275
S.P = M.P – Discount
⇒ 275 = 300 – Discount
⇒ Discount = 300 – 275 = ₹ 25
Discount per pack = ₹ 25
Question 13.
Valavan bought 24 eggs for Rs 96. Four of them were broken and also he had a loss of Rs 36 on selling them. What is the selling price of one egg?
Solution:
Number of eggs bought = 24
Number of eggs broken = 4
Number of good eggs = 24 – 4 = 20
Cost price of 20 eggs = 96
Loss = ₹ 36
Loss = C.P – S.P
⇒ 36 = 96 – S.P
⇒ S.P = 96 – 36 = ₹ 60
S.P of 20 eggs = ₹ 60
S.P of 1 egg = \(\frac{60}{20}\) = ₹ 3
Selling price of 1 egg = ₹ 3
Question 14.
Mangai bought a cell phone for ₹ 12,585. It fell down. She spent ₹ 500 on it repair. She sold it for ₹ 7,500. Find her profit or loss.
Solution:
Cost of the cell phone = ₹ 12,585
Spent on repairs = ₹ 500
Cost price = Cost of cell phone + repair charge = 12,585 + 500 = ₹ 13,085
S.P. = 7,500
Here C.P > S.P
∴ It is a loss
Loss = C.P – S.P = 13,085 – 7500 = ₹ 5,585
Loss = ₹ 5,585
![]()
Objective Type Questions
Question 15.
Discount is subtracted from ……… to get S.P.
(a) M.P
(b) C.P
(c) Loss
(d) Profit
Solution:
(a) M.P
Question 16.
‘Overhead expenses’ is always included in _____.
(a) S.P
(b) C.P.
(c) Profit
(d) Loss
Solution:
(b) C.P.
Question 17.
There is no profit or loss when
(a) C.P = S.P
(b) C.P > S.P
(c) C.P < S.P
(d) M.P = Discount
Solution:
(a) C.P = S.P
Question 18.
Discount = M.P _____
(a) Profit
(b) S.P
(c) Loss
(d) C.P
Solution:
(b) S.P