Students can Download Commerce Chapter 23 Elements of Entrepreneurship Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 23 Elements of Entrepreneurship
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Elements of Entrepreneurship Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the below is a factor of production?
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Entrepreneurship
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 2.
Entrepreneur is not classified as ________
(a) Risk Bearer
(b) Innovator
(c) Employee
(d) Organizer
Answer:
(b) Innovator
![]()
Question 3.
What are the characteristics of an entrepreneur?
(a) Spirit of enterprise
(b) Flexibility
(c) Self Confidence
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 4.
Which of the below is not classified into managerial functions?
(a) Planning
(b) Marketing
(c) Organizing
(d) Controlling
Answer:
(c) Organizing
Question 5.
Which of the below is a commercial function?
(a) Accounting
(b) Coordination
(c) Discovery of idea
(d) Planning
Answer:
(a) Accounting
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention any two features of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Features of Entrepreneurs:
- Spirit of Enterprise: Entrepreneur should be bold enough to encounter risk arising from the venture undertaken.
- Self Confidence: Entrepreneur should have a self confidence in order to achieve high goals in the business.
Question 2.
List down the managerial functions of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
- Planning
- Organising
- Directing
- Controlling
- Coordination
![]()
Question 3.
List down the promotional functions of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
- Discovery of Idea
- Determining the business objectives
- Detailed Investigation
- Choice of form of enterprise
- Fullfillment of the formalities
- Preparation of Business Plan
- Mobilisation of funds
- Procurement of Machines and Materials
Question 4.
Define Intrapreneur.
Answer:
Intrapreneur is one who thinks and acts like an entrepreneur for the firm’s development during the course of employment in an organisation.
Question 5.
List the problems faced by the women entrepreneurs.
Answer:
There is a tremendous growth in the women entrepreneurship in India. But there are certain problems met by women entrepreneurs. They are as follows:-
- Problem of Finance: The external sources of funds for the women is limited because they do not generally own properties in their own name. They are depending on their own savings and small loans from friends and relatives.
- Lack of Education: Illiterate and semi-literate women entrepreneurs face difficulties in respect of accounts, money matters, marketing and day-to-day operations.
- Lack of Network Support: The success of business depends on the support of family members, friends and relatives. But it is reported that the women entrepreneurs get very limited support in times of crisis.
- Stiff Competition: They have to face acute competition for their goods from organised sector and from their male counterparts.
- Lack of Information: The lack of knowledge or limited knowledge about subsidies, concessions and incentives given by Government will affect the business.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Entrepreneur.
Answer:
The person who establishes business is termed as entrepreneur. The output of an entrepreneurial process ends up in establishing an enterprise.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Entrepreneur and Manager.
Answer:
| Basis of difference | Entrepreneur | Manager |
| Motive | The very motive of an entrepreneur is to start a venture by setting of an entity. | The very motive of manager is to render service in an entity setup for execution of venture. |
| Status | Entrepreneur is owner of the entity. | Manager is a salaried employee in the entity set up for carrying on the venture. |
| Risk Bearing | Entrepreneur bears the eventual risk and uncertainty in operating the enterprise. | Manager doesn’t bear any risk in the venture, where the venture is unsuccessful he/she simply quits the enterprise. |
Question 3.
List down the commercial functions of Entrepreneur and explain them shortly.
Answer:
Commercial Functions of Entrepreneur:
(i) Production or Manufacturing: Under production function, entrepreneur has to take decision relating to selection of factory site, design and layout, type of products to be manufactured, research and development, product design, etc.
(ii) Marketing: Entrepreneur has to carry out following functions pertaining to marketing aspect namely consumer research, product planning and development, standardisation, packaging, pricing, warehousing, distribution, promotion etc.
(iii) Accounting: Entrepreneur has to arrange to prepare trading and profit and loss account in order to know the profit or loss incurred out of operation of the business and prepare balance sheet to know the financial status of business at a particular day.
(iv) Finance: In the sphere of financial function, an entrepreneur has to take decisions like choosing the right type of financing, framing the best dividend policy, acquiring of funds, efficiently managing fixed and current assets, maximising shareholders wealth and investing of funds efficiently and effectively.
(v) Human Resource Management: Entrepreneur has to estimate the manpower needs of the enterprise and accordingly decide the size of manpower required for various slots of organisational structure.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the promotional functions of entrepreneur.
Promotional Functions of Entrepreneur
Answer:
(i) Discovery of Idea: The first and foremost function of entrepreneur is idea generation. A person may conceive his own ideas or develop the ideas contributed by others. Ideas can be generated through several ways like own experience and exposure of entrepreneur, keen observation of environment, education, training, market survey, environmental scanning and so on.
(ii) Determining the business objectives: Entrepreneur has to develop business objectives in the backdrop of nature of business and type of business activity i.e. nature of business, manufacturing or trading, type of business organisation chosen so that he/she can organise the venture in accordance with the objectives determined by him/her.
(iii) Detailed Investigation: Entrepreneur should investigate commercial feasibility of the product proposed to be produced and conduct market study to ascertain the potential demand for the product.
(iv) Choice of form of enterprise: Entrepreneur has to choose the appropriate form of organisation suited to implement the venture. There are various forms of organisation namely sole proprietor, partnership, company and co-operatives etc. which are in existence.
(v) Fulfilment of the formalities: Having chosen the appropriate type of organisation, entrepreneur has to take necessary steps to establish the form of organisation chosen. As regards sole trader, the formalities are barest minimum. In the case of partnership firm, entrepreneur has to arrange for partnership deed and he has to get the deed registered.
(vi) Preparation of Business Plan: Entrepreneur has to prepare a business plan or project report of the venture that he is proposing to take up.
(vii) Mobilisation of funds: Entrepreneur has to take steps to mobilise capital needed to implement the venture. Entrepreneur has to estimate the fixed capital and working capital required for running the project.
(viii) Procurement of Machines and Materials: Entrepreneur has to locate the various sources of supply of machineries, equipments and materials.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the commercial functions of entrepreneur.
Answer:
(i) Production or Manufacturing: Under production function, entrepreneur has to take decision relating to selection of factory site, design and layout, type of products to be manufactured, research and development, product design, etc. The efficient and effective performance of production function depends on the proper production planning and control to a major extent.
(ii) Marketing: Entrepreneur has to carry out following functions pertaining to marketing aspect namely consumer research, product planning and development, standardisation, packaging, pricing, warehousing, distribution, promotion etc. The term marketing mix denotes the combination of four components namely product, price, promotion and physical distribution in the case of physical products and three more components are included in the case of service products namely people, process and physical evidence.
(iii) Accounting: Entrepreneur has to arrange to prepare trading and profit and loss account in order to know the profit or loss incurred out of operation of the business and prepare balance sheet to know the financial status of business at a particular day. Besides, cash flow and fund flow statements are prepared to ensure the adequacy of funds and cash for meeting various working capital needs of the business.
(iv) Finance: In the sphere of financial function, an entrepreneur has to take decisions like choosing the right type of financing, framing the best dividend policy, acquiring of funds, efficiently managing fixed and current assets, maximising shareholders wealth and investing of funds efficiently and effectively.
(v) Human Resource Management: Entrepreneur has to estimate the manpower needs of the enterprise and accordingly decide the size of manpower required for various slots of organisational structure. After determining the required manpower, the entrepreneur has to organise for recruitment procedure
selecting manpower, induction and training, determining compensation structure and incentives, designing motivation programmes, structuring wellbeing measures for employees, putting in place safety mechanism at workplace, performance evaluation and career advancement and structuring social security programmes.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
How do you classify entrepreneurs?
Answer:
Entrepreneurs are now broadly classified into three groups namely risk bearer, organiser and
innovator.
1. Entrepreneur as a risk bearer : Entrepreneurs acts as an agent combining all factors of production to produce a product or service in order to sell at uncertain price in future.
2. Entrepreneur as an organiser : Entrepreneur is one who brings together various factors of production and creates an entity to produce product or service and supervise and coordinates several functions in the process.
3. Entrepreneur as an innovator : According to Joseph A. Schumpeter in the year 1934 used innovation as a criterion to define an individual as entrepreneur. According to him, entrepreneur is one who
-
- Introduces a brand new product in the market.
- Institutes new technology to produce a new product.
- Discovers new course of supply of raw materials.
Question 2.
What are the characteristics of an entrepreneur?
Answer:
Characteristics of an Entrepreneur:
1. Spirit of Enterprise: Entrepreneur should be bold enough to encounter risk arising from Elements of Entrepreneurship 145 the venture undertaken.
2. Self-confidence: Entrepreneur should have self-confidence in order to achieve high goals in the business.
3. Flexibility: Entrepreneur should not doggedly stick to decisions in a rigid fashion.
4. Innovation: Entrepreneur should contribute something new or something unique to meet the changing requirements of customers namely new product, new method of production or distribution, adding new features to the existing product, uncovering a new territory for business, innovating new raw material, etc.
5. Resource Mobilisation: Entrepreneur should have the capability to mobilise both tangible inputs like manpower, money materials, technology, market, method etc., which are scattered over a wide area and certain intangible inputs like motivation, morale and innovativeness.
Question 3.
Distinguish between an Entrepreneur and an Intrapreneur.
Answer:
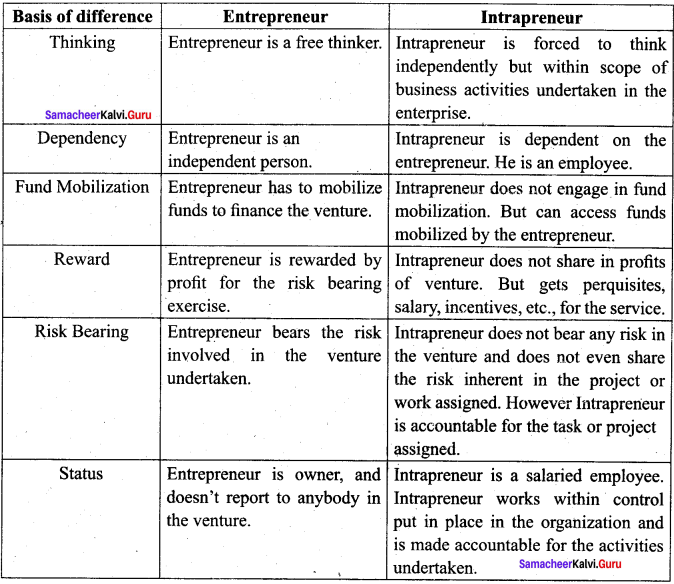
Question 4.
Discuss the problems faced by Women Entrepreneurs.
Answer:
There is a tremendous growth in the women entrepreneurship in India. But there are certain problems met by women entrepreneurs.
They are as follows:-
- Problem of Finance: The external sources of funds for the women is limited because they do not generally own properties in their own name. They are depending on their own savings and loan from friends and relatives.
- Lack of Education: Illiterate and semi-literate women entrepreneurs face difficulties in respect of accounts, money matters, marketing and day-to-day operations.
- Lack of Network Support: The success of business depends on the support of family members, friends and relatives. But it is reported that the women entrepreneurs get very limited support in times of crisis.
- Stiff Competition: They have to face acute competition for their goods from organised sector and from their male counterparts.
- Lack of Information: The lack of knowledge or limited knowledge about subsidies, concessions and incentives given by Government will affect the business.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain in detail the various functions of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
The functions of an entrepreneur is divided into
(a) Promotional functions,
(b) Managerial functions
(c) Commercial functions.
(a) Promotional functions:
(i) Discovery of Idea: The first and foremost function of entrepreneur is idea generation. A person may conceive his own ideas or develop the ideas contributed by others. Ideas can be generated through several ways like own experience and exposure of entrepreneur, keen observation of environment, education, training, market survey, environmental scanning and so on.
(ii) Detailed Investigation: Entrepreneur should investigate commercial feasibility of the product proposed to be produced and conduct market study to ascertain the potential demand for the product.
(iii) Mobilisation of funds: Entrepreneur has to take steps to mobilise capital needed to implement the venture. Entrepreneur has to estimate the fixed capital and working capital required for running the project.
(b) Managerial functions:
(i) Planning: In this function, the entrepreneur has to lay down the objectives, goals, vision, mission, policies, procedures, programmes, budget, schedules etc., for enabling the venture to proceed towards established destinations.
(ii) Directing: In this function, the entrepreneur has to motivate, lead, guide and communicate with subordinates on an ongoing basis in order to accomplish pre-set goals.
(c) Commercial functions:
(i) Production or Manufacturing: Under production function, entrepreneur has to take decision relating to selection of factory site, design and layout, type of products to be manufactured, research and development.
(ii) Accounting: Entrepreneur has to arrange to prepare trading and profit and loss account in order to know the profit or loss incurred out of operation of the business and prepare balance sheet to know the financial status of business.