Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 9 Lists, Tuples, Sets and Dictionary Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 9 Lists, Tuples, Sets and Dictionary
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Lists, Tuples, Sets and Dictionary Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
1. Choose The Best Answer
Question 1.
Pick odd one in connection with collection data type?
(a) List
(b) Tuple
(c) Dictionary
(d) Loop
Answer:
(d) Loop
Question 2.
Let list1=[2 ,4, 6, 8, 10], then print (List1[-2]) will result in ……………………….
(a) 10
(b) 8
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer:
(b) 8

Question 3.
Which of the following function is used to count the number of elements in a list?
(a) Count( )
(b) Find( )
(c) Len( )
(d) Index( )
Answer:
(c) Len( )
Question 4.
If List=[10, 20, 30, 40, 50] then List[2]=35 will result –
(a) [35, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
(b) [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 35]
(c) [10, 20, 35, 40, 50]
(d) [10, 35, 30, 40, 50]
Answer:
(c) [10, 20, 35, 40, 50]

Question 5.
If List=[17, 23, 41, 10] then List.append (32) will result –
(a) [32, 17, 23, 41, 10]
(b) [17, 23, 41, 10, 32]
(c) [10, 17, 23, 32, 41]
(d) [41, 32, 23, 17, 10]
Answer:
(b) [17, 23, 41, 10, 32]
Question 6.
Which of the following Python function can be used to add more than one element within an existing list?
(a) append( )
(b) append_more( )
(c) extend( )
(d) more( )
Answer:
(c) extend( )

Question 7.
What will be the result of the following Python code?
S = [x**2 for x in range(5)]
print(S)
(a) [0, 1, 2, 4, 5]
(b) [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
(c) [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
(d) [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Answer:
(b) [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
Question 8.
What is the use of type( ) function in python?
(a) To create a Tuple
(b) To know the type of an element in tuple.
(c) To know the data type of python object.
(d) To create a list.
Answer:
(c) To know the data type of python object.

Question 9.
Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) A list is mutable
(b) A tuple is immutable.
(c) The append( ) function is used to add an element.
(d) The extend( ) function is used in tuple to add elements in a list.
Answer:
(d) The extend( ) function is used in tuple to add elements in a list.
Question 10.
Let set A={3, 6, 9}, set B={1, 3, 9} What will be the result of the following snippet?
print (setA|setB)
(a) {3, 6, 9, 1, 3, 9}
(b) {3, 9}
(c) {1}
(d) {1, 3, 6, 9}
Answer:
(d) {1, 3, 6, 9}

Question 11.
Which of the following set operation includes all the elements that are in two sets but not the one that are common to two sets?
(a) Symmetric difference
(b) Difference
(c) Intersection
(d) Union
Answer:
(a) Symmetric difference
Question 12.
The keys in Python, dictionary is specified by …………………………
(a) =
(b) ;
(c) +
(d) :
Answer:
(d) :
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What is List in Python?
Answer:
A list in Python is known as a “sequence data type” like strings. It is an ordered collection of values enclosed within square brackets [ ]. Each value of a list is called as element.

Question 2.
How will you access the list elements in reverse order?
Answer:
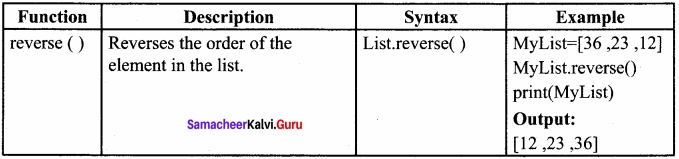
Question 3.
What will be the value of x in following python code?
Answer:
List1=[2, 4, 6, [1, 3, 5]]
x=len(List1)
Ans: 4
Question 4.
Differentiate del with remove( ) function of List?
Answer:
There are two ways to delete an element from a list viz. del statement and remove( ) function, del statement is used to delete known elements whereas remove( ) function is used to delete elements of a list if its index is unknown. The del statement can also be used to delete entire list.

Question 5.
Write the syntax of creating a Tuple with n number of elements?
Answer:
# Tuple with n number elements
Tuple _ Name = (E1, E2, E2 ……………… En)
# Elements of a tuple without parenthesis
Tuple_Name = E1, E2, E3 …………………. En
Question 6.
What is set in Python?
Answer:
In python, a set is another type of collection data type. A Set is a mutable and an unordered collection of elements without duplicates. That means the elements within a set cannot be repeated. This feature used to include membership testing and eliminating duplicate elements.
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What are the advantages of Tuples over a list?
Answer:
- The elements of a list are changeable (mutable) whereas the elements of a tuple are unchangeable (immutable), this is the key difference between tuples and list.
- The elements of a list are enclosed within square brackets. But, the elements of a tuple are enclosed by paranthesis.
- Iterating tuples is faster than list.

Question 2.
Write a short note about sort( )?
Answer:
sort( ) function sorts the element in list.
Syntax:
List.sort (reverse = True/False, Key = myFunc)
Both arguments are optional
- If reverse is set as True, list sorting is in descending order.
- Ascending is default.
- Key=myFunc; “myFunc” – the name of the user defined function that specifies the sorting criteria.
Example
My List=[‘Thilothamma’, ’Tharani’, ‘Anitha’, ‘SaiSree’, ‘Lavanya’]
MyList.sort( )
print(MyList)
Output:
[‘Anitha’, ‘Lavanya’, ‘SaiSree’, ‘Tharani’, ‘Thilothamma’]

Question 3.
What will be the output of the following code?
list=[2**x for x in range(5)
print(list)
[1, 2, 4, 8, 16]
Question 4.
Explain the difference between del and clear( ) in dictionary with an example?
Answer:
In Python dictionary, del keyword is used to delete a particular element. The clear( ) function is used to delete all the elements in a dictionary. To remove the dictionary, we can use del keyword with dictionary name.
Dict={‘Roll No’: 12001, ‘SName’: ‘Meena’, ‘Mark1’: 98, ‘Mar12’: 86}
print(“Dictionary elements before deletion: \n”, Dict)
del Dict[‘Mark1’] # Deleting a particular element
Dict.clear( ) # Deleting all elements

Question 5.
List out the set operations supported by python?
Answer:
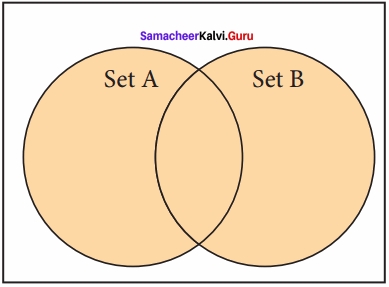
(i) Union:
It includes all elements from two or more sets
In python, the operator | is used to union of two sets. The function union( ) is also used to join two sets in python.
(ii) Intersection:
It includes the common elements in two sets
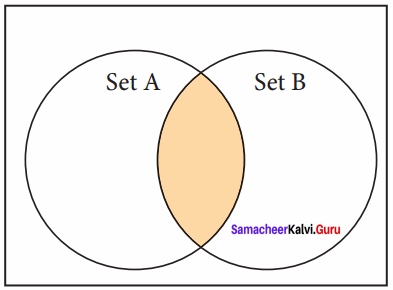
The operator & is used to intersect two sets in python. The function intersection( ) is also used to intersect two sets in python.
(iii) Difference:
It includes all elements that are in first set (say set A) but not in the second set (say set B)
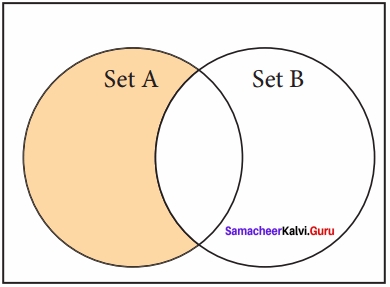
The minus(-) operator is used to difference set operation in python. The function difference( ) is also used to difference operation.
(iv) Symmetric difference:
It includes all the elements that are in two sets (say sets A and B) but not the one that are common to two sets.
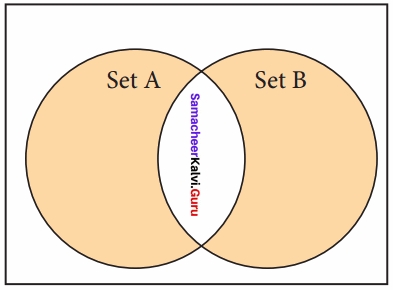
The caret (^) operator is used to symmetric difference set operation in python. The function symmetric_difference( ) is also used to do the same operation.

Question 6.
What are the difference between List and Dictionary?
Answer:
Difference between List and Dictionary
- List is an ordered set of elements. But, a dictionary is a data structure that is used for matching one element (Key) with another (Value).
- The index values can be used to access a particular element. But, in dictionary key represents index. Remember that, key may be a number of a string.
- Lists are used to look up a value whereas a dictionary is used to take one value and look up another value.
PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What the different ways to insert an element in a list. Explain with suitable example. Inserting elements in a list?
Answer:
append( ) function in Python is used to add more elements in a list. But, it includes elements at the end of a list. If you want to include an element at your desired position, you can use insert () function is used to insert an element at any position of a list.
Syntax:
List, insert (position index, element)
Example:
>>> MyList=[34,98,47, ‘Kannan’, ‘Gowrisankar’, ‘Lenin’, ‘Sreenivasan’ ]
>>> print(MyList)
[34, 98, 47, ‘Kannan’, ‘Gowrisankar’, ‘Lenin’, ‘Sreenivasan’]
>>> MyList.insert(3, ‘Ramakrishnan’)
>>> print(MyList)
[34, 98, 47, ‘Ramakrishnan’, ‘Kannan’, ‘Gowrisankar’, ‘Lenin’, ‘Sreenivasan’]
In the above example, insertf) function inserts a new element ‘Ramakrishnan’ at the index value 3, ie. at the 4th position. While inserting a new element in between the existing elements, at a particular location, the existing elements shifts one position to the right.

Question 2.
What is the purpose of range( )? Explain with an example?
Answer:
(i) The range( ) is a function used to generate a series of values in Python. Using range( ) function, you can create list with series of values. The range( ) function has three arguments.
Syntax of range( ) function:
range (start value, end value, step value)
where,
- start value – beginning value of series. Zero is the default beginning value.
- end value – upper limit of series. Python takes the ending value as upper limit – 1.
- step value – It is an optional argument, which is used to generate different interval of values.
Example: Generating whole numbers upto 10
for x in range (1, 11):
print(x)
Output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
(ii) Creating a list with series of values
Using the range( ) function, you can create a list with series of values. To convert the result of range( ) function into list, we need one more function called list( ). The list( ) function makes the result of range( ) as a list.
Syntax:
List_Varibale = list ( range ( ) )
Note
The list( ) function is all so used to create list in python.
Example
>>> Even_List = list(range(2,11,2))
>>> print(Even_List)
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
In the above code, list( ) function takes the result of range( ) as Even List elements. Thus, Even _List list has the elements of first five even numbers.
(iii) We can create any series of values using range( ) function. The following example explains how to create a list with squares of first 10 natural numbers.
Example: Generating squares of first 10 natural numbers
squares = [ ]
for x in range(1,11):
s = x ** 2
squares.append(s)
print (squares)
Output
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]

Question 3.
What is nested tuple? Explain with an example.?
Answer:
In Python, a tuple can be defined inside another tuple; called Nested tuple. In a nested tuple, each tuple is considered as an element. The for loop will be useful to access all the elements in a nested tuple.
Example:
Toppers = ((“Vinodini”, “XII-F”, 98.7), (“Soundarya”, “XII-H”, 97.5),
(“Tharani”, “XII-F”, 95.3), (“Saisri”, “XII-G”, 93.8))
for i in Toppers:
print(i)
Output:
(‘Vinodini’, ‘XII-F’, 98.7)
(‘Soundarya’, ‘XII-H’, 97.5)
(‘Tharani’, ‘XII-F’, 95.3)
(‘Saisri’, ‘XII-G’, 93.8)
Question 4.
Explain the different set operations supported by python with suitable example?
Answer:
Set Operations:
As you leamt in mathematics, the python is also supports the set operations such as Union, Intersection, difference and Symmetric difference.
(i) Union:
It includes all elements from two or more sets
In python, the operator | is used to union of two sets. The function union( ) is also used to join two sets in python.
Example: Program to Join (Union) two sets using union operator
set_A={2,4,6,8}
set_B={‘A’, ’B’, ‘C, ‘D’}
U_set=set_A|set_B
print(U_set)
Output:
{’D’, 2, 4, 6, 8, ‘B’, ’C, A’}
(ii) Intersection:
It includes the common elements in two sets
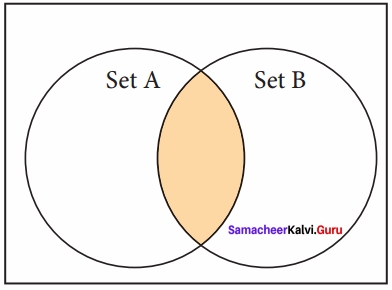
The operator & is used to intersect two sets in python. The function intersection ) is also used to intersect two sets in python.
Example: Program to insect two sets using intersection operator
set_A={A’, 2, 4, ‘D’}
set_B={A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’}
print(set_A & set_B)
Output:
{’A, ‘D’}
Example: Program to insect two sets using intersection operator
set_A={‘A’, 2, 4, ’D’}
set_B={A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’}
print(set_A.intersection(set_B))
{‘A’, ‘D’}
(iii) Difference:
It includes all elements that are in first set (say set A) but not in the second set (say set B)
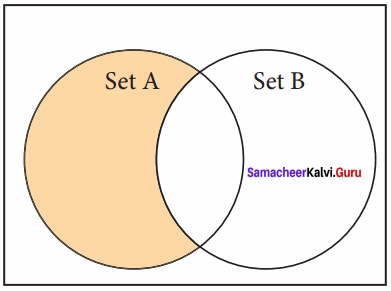
The minus (-) operator is used to difference set operation in python. The function difference() is also used to difference operation.
Example: Program to difference of two sets using minus operator
set_A={‘A’, 2, 4, ‘D’} set_B={‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C, ‘D’} print(set_A – set_B)
Output:
{2,4}
Example: Program to difference of two sets using difference function
set_A={‘A’, 2, 4, TV} set_B={‘A’, ’B’, ’C, ’D’} print(set_A.difference(set_B))
Output:
{2,4}
(iv) Symmetric difference:
It includes all the elements that are in two sets (say sets A and B) but not the one that are common to two sets.

The caret (^) operator is used to symmetric difference set operation in python. The function symmetric_difference( ) is also used to do the same operation.
Example: Program to symmetric difference of two sets using caret operator
set_A={‘A’, 2, 4, ‘D’}
set_B={‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C, ‘D’}
print(set_A^A set_B)
Output:
{2, 4, ‘B’, ‘C’}
Example: Program to difference of two sets using symmetric difference function
set_A={‘A’, 2, 4, ‘D’}
set_B={‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’}
print(set_A. symmetric_difference(set_B))
Output:
{2, 4, ‘B’, ‘C’}
Practice Programs
Question 1.
Write a program to remove duplicates from a list.
Method I:
mylist = [2,4,6,8,8,4,10]
myset = set(mylist)
print(myset)
Output:
{2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
Method II:
def remove(duplicate):
final_list=[ ]
for num in duplicate:
if num not in final_list:
final_list.append(num)
return final_list
duplicate = [2, 4, 10, 20, 5, 2, 20, 4]
print(remove(duplicate))
Output:
[2, 4, 10, 20, 5]

Question 2.
Write a program that prints the maximum value in a Tuple?
Answer:
tuple = (456, 700, 200)
print(“max value : “, max(tuple))
Output:
max value : 700
Question 3.
Write a program that finds the sum of all the numbers in a Tuples using while loop?
Answer:
tuple = (1, 5, 12)
s = 0
i = 0
while(i < len (tuple)):
s = s + tuple[i]
i+ = 1
print(“Sum of elements in tuple is “, s)
Output:
Sum of elements in tuple is 18

Question 4.
Write a program that finds sum of all even numbers in a list?
Answer:
numlist = [ ]
evensum = 0
number = int(input(“Please enter the total no of list elements”))
for i in range(1, number +1):
value = int(input(“Please enter the value “))
numlist.append(value)
for j in range(number):
if(numlist[j]% 2 == 0):
even_sum = even_sum + numlist[j]
print(“Sum of even no. in this list = “, even_sum)
Output:
Please enter the total no of list elements : 5
Please enter the value : 10
Please enter the value : 11
Please enter the value : 12
Please enter the value : 13
Please enter the value : 14
The sum of even no. in this list = 60

Question 5.
Write a program that reverse a list using a loop?
Answer:
def reverse(list):
list.reverse( )
return list
list = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
print(reverse(list))
Output:
15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10
Question 6.
Write a program to insert a value in a list at the specified location?
Answer:
vowel = [‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘u’]
vowel.insert(3, ‘o’)
print(‘updated list’, vowel)
Output:
updated list [‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’]

Question 7.
Write a program that creates a list of numbers from 1 to 50 that are either divisible by 3 or divisible by 6?
Answer:
n = [ ]
s = [ ]
for x in range(1, 51):
n.append(x)
for x in range(1, 51):
if(x%3 == 0) or (x % 6 == 0):
s.append(x)
print(“The numbers divisible by 3 or 6 is “, s)
Output:
The numbers divisible by 3 or 6 is
[3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48]
Question 8.
Write a program to create a list of numbers in the range 1 to 20. Then delete all the numbers from the list that are divisible by 3?
Answer:
num = [ ]
for x in range(1, 21):
num.append(x)
print(“The list of numbers from 1 to 20 =”, num)
for index, i in enumerate(num):
if(i % 3 == 0)
del num[index]
print(“The list after deleting numbers”, num)
Output:
The list of numbers from 1 to 20 = [1,2,3,4… 20]
The list after deleting numbers[1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 19, 20]

Question 9.
Write a program that counts the number of times a value appears in the list. Use a loop to do the same?
Answer:
a = [ ]
n = int(input”Enter number of elements :”))
for i in range(l, n+1):
b = int(input(“Enter element”))
a.append(b)
k = 0
num = int(input(“Enter the number to be counted : “))
for j in a:
if(j == num):
k = k+1
print(“Number of times”, num, “appears is”, k)
Output:
Enter number of elements : 4
Enter element: 23
Enter element: 45
Enter element: 23
Enter element: 67
Enter the number to be counted : 23
Number of times 23 appears is 2

Question 10.
Write a program that prints the maximum and minimum value in a dictionary?
Answer:
my_dict = {‘x’: 500, ‘y’: 5874, ‘z’: 560}
val = my_dict.values( )
print(‘max value’, max(val))
print(‘min value’, min(val))
Output:
max value 5874
min value 500
Samacheer kalvi 12th Computer Science Lists, Tuples, Sets and Dictionary Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
A list in python is denoted by ………………………..
(a) [ ]
(b) { }
(c) <>
(d) #
Answer:
(a) [ ]
Question 2.
A ………………………… is a sequence data type like strings.
(a) List
(b) Tuples
(c) Set
(d) Dictionary
Answer:
(a) List

Question 3.
Each value of a list is called as –
(a) Set
(b) Dictionary
(c) Element
(d) Strings
Answer:
(c) Element
Question 4.
The position of an element is indexed with numbers beginning with …………………………….
(a) n
(b) n-1
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer:
(c) 0

Question 5.
(1) mylist[ ] – (i) tuple
(2) mylist[10,[2,4,6]] – (ii) Empty tuple
(3) t=(23,56,89) – (iii) Nested list
(4) lis=( ) – (iv) empty list
(a) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(i), 4-(ii)
(b) 1-(i), 2-(ii), 3-(iii), 4-(iv)
(c) 1-(iv), 2-(ii), 3-(i), 4-(iii)
(d) 1-(i), 2-(iii), 3-(iv), 4-(ii)
Answer:
(a) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(i), 4-(ii)

Question 6.
………………………… is used to access an element in a list
(a) element
(b) i
(c) index
(d) tuple
Answer:
(c) index
Question 7.
Index value can be positive or negative in the list.
True / false
Answer:
True
Question 8.
To access the list elements in reverse order, ……………………. value have to be given
(a) 0
(b) positive
(c) imaginery
(d) negative
Answer:
(d) negative

Question 9.
………………………. are used to access all elements from a list.
(a) If
(b) loop
(c) array
(d) tuple
Answer:
(b) loop
Question 10.
Find the Output:
marks = [10, 23, 41, 75]
i = -1
while i >= – 4:
print(marks[i])
i = i + – 1
(o) 1 2 3 4
(b) 10, 23, 41, 75
(c) 75, 41, 23, 10
(d) 0, 41, 23, 0
Answer:
(c) 75, 41, 23, 10

Question 11.
…………………….. operator is used to change the list of elements
(a) =
(b) +
(c) +=
(d) *=
Answer:
(a) =
Question 12.
In changing list elements, …………………………. is the upper limit of this range.
(a) Index from
(b) Index to
(c) Index with
(d) Index
Answer:
(b) Index to

Question 13.
If the range is specified as [1 : 5], it will update the elements from …………………………..
(a) 2 to 4
(b) 1 to 5
(c) 1 to 4
(d) 2 to 5
Answer:
(c) 1 to 4
Question 14.
……………………….. function is used to add a single element in the list.
Answer:
append( )
Question 15.
Write the output,
list = [34, 45, 48]
list.append(90)
(a) [34, 45, 48, 90]
(b) [90, 34, 45, 48]
(c) [34, 90, 45, 48]
(d) [34, 45, 90, 48]
Answer:
(a) [34, 45, 48, 90]

Question 16.
list = [34, 45, 48]
list.extend([71, 32, 29]) results in ………………………….
Answer:
[35, 45, 48, 71, 32, 29]
Question 17.
………………………… function is used to insert an element at any position of a list.
Answer:
insert( )
Question 18.
Find the correct statement from the following
(a) when new element is inserted in the list, the existing elements shift one position to the right
(b) when a new element is inserted in the list, the existing element shifts one position to the left.
Answer:
(a) when new element is inserted in the list, the existing elements shift one position to the right

Question 19.
How many ways of deleting the elements from a list are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 20.
The two ways of deleting elements from a list are ……………………….. and …………………………
Answer:
del and remove( )
Question 21.
Which function is used to delete elements of a list if its index is unknown?
(a) del
(b) delete
(c) remove( )
(d) backspace
Answer:
(c) remove( )

Question 22.
Which statement is used to delete known elements?
(a) del
(b) delete
(c) remove
(d) rem
Answer:
(a) del
Question 23.
………………………… statement deletes the entire list.
Answer:
del

Question 24.
…………………….. function deletes the element using the given index value.
Answer:
pop( )
Question 25.
When you try to print the list which is already cleared, ……………………….. is display without any elements
Answer:
[ ] or empty square bracket
Question 26.
…………………………… function is used to generate a series of values in python
(a) range
(b) series
(c) Fill series
(d) Auto fill
Answer:
(a) range

Question 27.
The range( ) function has ………………………. arguments.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 28.
Which is an optional argument in range( ) function …………………………..
(a) start value
(b) end value
(c) step value
(d) default
Answer:
(c) step value
Question 29.
The ……………………… function is used to create list in python
Answer:
list( )

Question 30.
……………………… is a simplest way of creating sequence of elements that satisfy a certain conditions returns copy of the list.
Answer:
List comprehension
Question 31.
……………….. returns copy of the list
Answer:
copy( )
Question 32.
x = mylist = [36, 12, 12]
x = mylist.count(12)
print(x) gives the vlaue as
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 2

Question 33.
………………….. returns the index value of the first recurring element.
Answer:
index( )
Question 34.
How many arguments are there in the sort( ) function?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 35.
……………………… consists of a number of values separated by comma and enclosed within parenthesis
(a) list
(b) tuples
(c) dictionary
(d) sets
Answer:
(b) tuples

Question 36.
The term ………………………. in latin represents an abstraction of the sequence of numbers.
(a) list
(b) tuples
(c) set
(d) dictionary
Answer:
(b) tuples
Question 37.
Identify the wrong statement from the following:
(a) The elements of the tuple are enclosed by parenthesis.
(b) The elements of a tuple can be even defined without parenthesis
(c) The list elements have to be given in square brackets
(d) Iterating list is faster than tuples.
Answer:
(d) Iterating list is faster than tuples.

Question 38.
The …………………….. function is used to create tuples from a list.
Answer:
tuple( )
Question 39.
Creating a tuple with one element is called ……………………….. tuple.
Answer:
Singleton
Question 40.
Find the wrong tuple.
(a) mytup = (10)
(b) mytup = (10)
(c) print(tup[: ])
(d) tup(10, 20)
Answer:
(d) tup(10, 20)

Question 41.
To delete an entire tuple, …………………….. command is used.
(a) del
(b) delete
(c) clear
(d) remove
Answer:
(a) del
Question 42.
Which operator is used to join two tuples?
(a) –
(b) _
(c) +
(d) +:
Answer:
(c) +

Question 43.
…………………….. assignment is a powerful feature in python.
Answer:
Tuple
Question 44.
(x, y) = (3**2, 15%2)
print(x,y) gives the answer
(a) 6 1
(b) 6 7
(c) 9 1
(d) 9 7
Answer:
(c) 9 1

Question 45.
Which one of the following is the tuple assignment operator?
(a) +=
(b) =
(c) ==
(d) *=
Answer:
(b) =
Question 46.
How many values can be returned by the functions in python?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) many
Answer:
(d) many

Question 47.
A tuple defined in another tuple is called as ……………………….
Answer:
Nested tuple
Question 48.
…………………………. feature is used to include membership testing and eliminate duplicate elements.
Answer:
Set
Question 49.
A …………………………… is a mutable and an unordered collection of elements without duplicates.
Answer:
Set

Question 50.
Which is true related to sets?
(a) mutable
(b) unordered
(c) No duplicates
(d) All are true
Answer:
(d) All are true
Question 51.
A list or tuples can be converted as set by using …………………………. function?
(a) set
(b) create set
(c) change
(d) alter
Answer:
(a) set

Question 52.
Which operator joins two sets?
(a) +
(b) |
(c) ||
(d) &
Answer:
(b) |
Question 53.
Join is called as ……………………… in sets
(a) union
(b) intersection
(c) difference
(d) symmetric difference
Answer:
(a) union

Question 54.
Identify the intersection operator.
(a) +
(b) –
(c) .
(d) &
Answer:
(d) &
Question 55.
Which operator is used to do difference in set?
(a) +
(b) –
(c) :
(d) &
Answer:
(b) –

Question 56.
Which is the symmetric difference operator?
(a) +
(b) –
(c) ^
(d) &
Answer:
(c) ^
Question 57.
………………………. is used to separate the elements in the dictionary
Answer:
Comma
Question 58.
The key value pairs are enclosed with ……………………………
(a) <>
(b) [ ]
(c) { }
(d) ( )
Answer:
(c) { }

Question 59.
The mixed collection of elements are called as ………………………….
(a) list
(b) tuples
(c) sets
(d) dictionary
Answer:
(d) dictionary
Question 60.
Identify the correct statement.
(a) The dictionary type stores a index along with its element
(b) The dictionary type stores a key along with its element
Answer:
(a) The dictionary type stores a index along with its element

Question 61.
Which part is optional in dictionary comprehension?
(a) If
(b) expression
(c) var
(d) sequences
Answer:
(a) If
Question 62.
Find the statement which is wrong. When you assign a value to the key
(a) it will be appended
(b) it will overwrite the old data
Answer:
(a) it will be appended

Question 63.
Pick odd one with including elements in list.
(a) append( )
(b) extend( )
(c) insert( )
(d) include
Answer:
(d) include
Question 64.
Pick the odd one with deleting elements from a list.
(a) del
(b) remove( )
(c) pop( )
(d) clear
Answer:
(d) clear
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Write note on nested list?
Answer:
Mylist = [ “Welcome”, 3.14, 10, [2, 4, 6] ]
In the above example, Mylist contains another list as an element. Nested list is a list containing another list as an element.

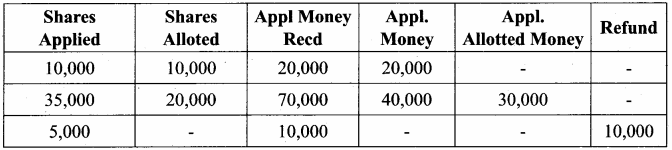
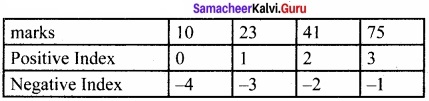
Question 2.
Fill the table
Answer:
marks = [10, 23, 41, 75]
Example
Marks [10, 23, 41, 75]
Question 3.
Give the syntax to access an element from a list?
Answer:
To access an element from a list, write the name of the list, followed by the index of the element enclosed within square brackets.
Syntax:
List_Variable = [El, E2, E3 …………….. En]
print (List_Variable [index ofa element])

Question 4.
What is meant by Reverse Indexing?
Answer:
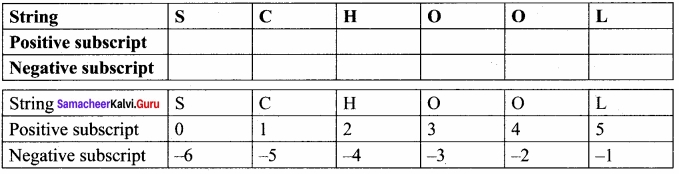
Python enables reverse or negative indexing for the list elements. Thus, python lists index in opposite order. The python sets -1 as the index value for the last element in list and -2 for the preceding element and so on. This is called as Reverse Indexing.
Question 5.
Give the syntax for changing list elements?
Answer:
Syntax:
List_Variable [index of an element] = Value to be changed
List_Variable [index from : index to] = Values to changed
Where, index from is the beginning index of the range; index to is the upper limit of the range which is excluded in the range.

Question 6.
Give the syntax for append, extend and insert?
Answer:
Syntax:
List.append (element to be added)
List, extend ( [elements to be added])
List, insert (position index, element)
Question 7.
Differentiate clear( ) and del in list?
Answer:
The function clear( ) is used to delete all the elements in list, it deletes only the elements and retains the list. Remember that, the del statement deletes entire list.

Question 8.
How will you create a list with series of value?
Answer:
Using the range( ) function, you can create a list with series of values. To convert the result of range( ) function into list, we need one more function called list( ). The list( ) function makes the result of range( ) as a list.
Syntax:
List_Varibale = list (range ( ))
Question 9.
Write note on list comprehensions?
Answer:
List comprehensions:
List comprehension is a simplest way of creating sequence of elements that satisfy a certain condition.
Syntax:
List = [expression for variable in range]

Question 10.
Define singleton tuple?
Answer:
While creating a tuple with a single element, add a comma at the end of the element. In the absence of a comma, Python will consider the element as an ordinary data type; not a tuple. Creating a Tuple with one element is called “Singleton” tuple.
MyTup5 = (10,)
Question 11.
Write note on dictionary comprehensions?
Answer:
In Python, comprehension is another way of creating dictionary. The following is the syntax of creating such dictionary.
Syntax
Diet = { expression for variable in sequence [if condition] }
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
How will you create a list in python? Explain with syntax and examples?
Answer:
In python, a list is simply created by using square bracket. The elements of list should be specified within square brackets. The following syntax explains the creation of list.
Syntax:
Variable = [element – 1, element – 2, element – 3 element – n]
Example:
Marks = [10, 23, 41, 75]

Question 2.
How will you find the length of the list. Give example?
Answer:
The len( ) function in Python is used to find the length of a list, (i.e., the number of elements in a list). Usually, the len( ) function is used to set the upper limit in a loop to read all the elements of a list. If a list contains another list as an element, len( ) returns that inner list as a single element.
Example :Accessing single element
>>> MySubject = [“Tamil”, “English”, “Comp. Science”, “Maths”]
>>> len(MySubject)
4
Question 3.
Give the 3 different syntax formats for deleting the elements from a list?
Answer:
Syntax:
del List [index of an element]
# to delete a particular element del List [index from : index to]
# to delete multiple elements
del List
# to delete entire list
Question 4.
Give the syntax for remove, pop and clear?
Answer:
Syntax:
List.remove(element) # to delete a particular element
List.pop(index of an element)
List, clear( )

Question 5.
Write a program that creates a list of numbers from 1 to 20 that are divisible by 4. Program to create a list of numbers from 1 to 20 that are divisible by 4
Answer:
divBy4=[ ]
for i in range(21):
if (i%4= =0):
divBy4.append(i)
print(divBy4)
Output
[0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20]
Question 6.
Write a program to join two tuple assignment?
Answer:
# Program to join two tuples
Tup 1 = (2,4,6,8,10)
Tup2 = (1,3,5,7,9)
Tup3 = Tup1 + Tup2
print(Tup3)
Output
(2,4,6,8,10,1,3,5,7,9)

Question 7.
Write note on tuple assignment?
Answer:
Tuple assignment is a powerful feature in Python. It allows a tuple variable on the left of the assignment operator to be assigned to the values on the right side of the assignment operator.
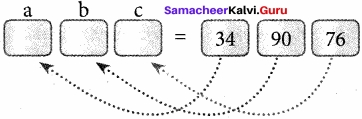
Example
>>> (a, b, c) = (34, 90, 76)
>>> print(a,b,c)
34 90 76
# expression are evaluated before assignment
>>> (x, y, z, p) = (2**2, 5/3+4, 15%2, 34>65)
>>> print(x,y,z,p)
4 5.666666666666667 1 False

Question 8.
How will you create a set in python?
Answer:
A set is created by placing all the elements separated by comma within a pair of curly brackets.
The set( ) function can also used to create sets in Python.
Syntax:
Set Variable = {El, E2, E3 ………………. En}
Example:
>>> S1={1,2,3,’A’,3.14}
>>> print(S1)
{1,2, 3, 3.14, ‘A’}
>>> S2={1,2,2,’A’,3.14}
>>> print(S2)
{1,2,’A’, 3.14}
Question 9.
Write note on dictionaries. Give syntax?
Answer:
A dictionary is a mixed collection of elements. The dictionary type stores a key along with its element. The keys in a Python dictionary is separated by a colon ( : ) while the commas work as a separator for the elements. The key value pairs are enclosed with curly braces { }. Syntax of defining a dictionary:
Dictionary_Name =
{ Key_l: Value_1,
Key_2: Value_2,
……………..
Key_n: Value_n
}
PART – IV
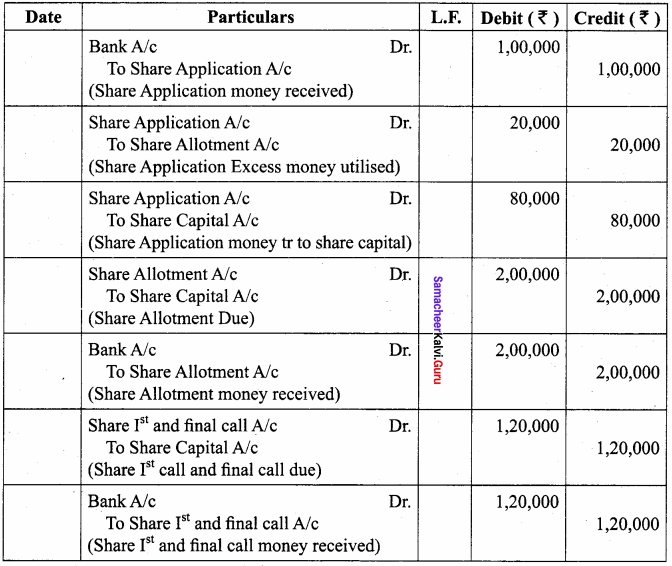
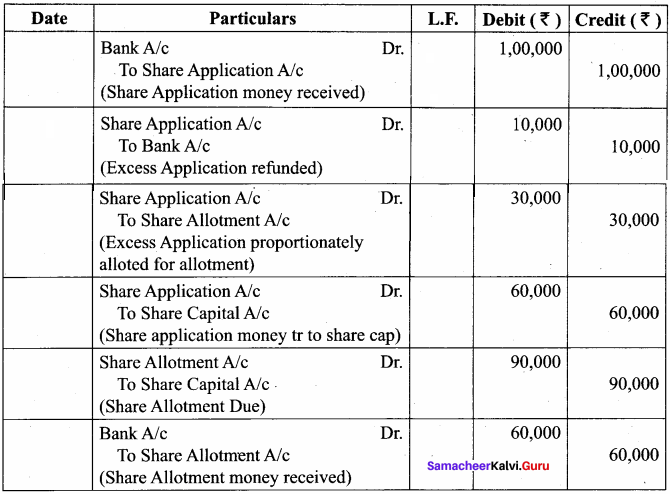
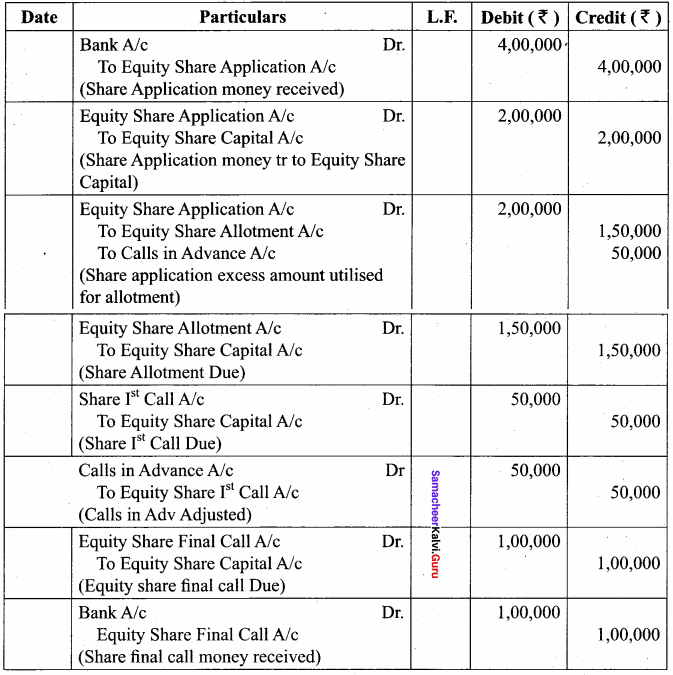
IV. Answer The Following Questions
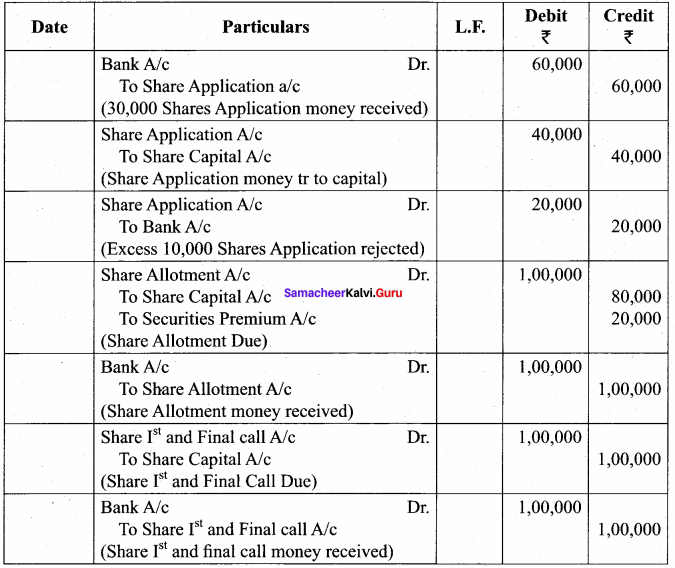
Question 1.
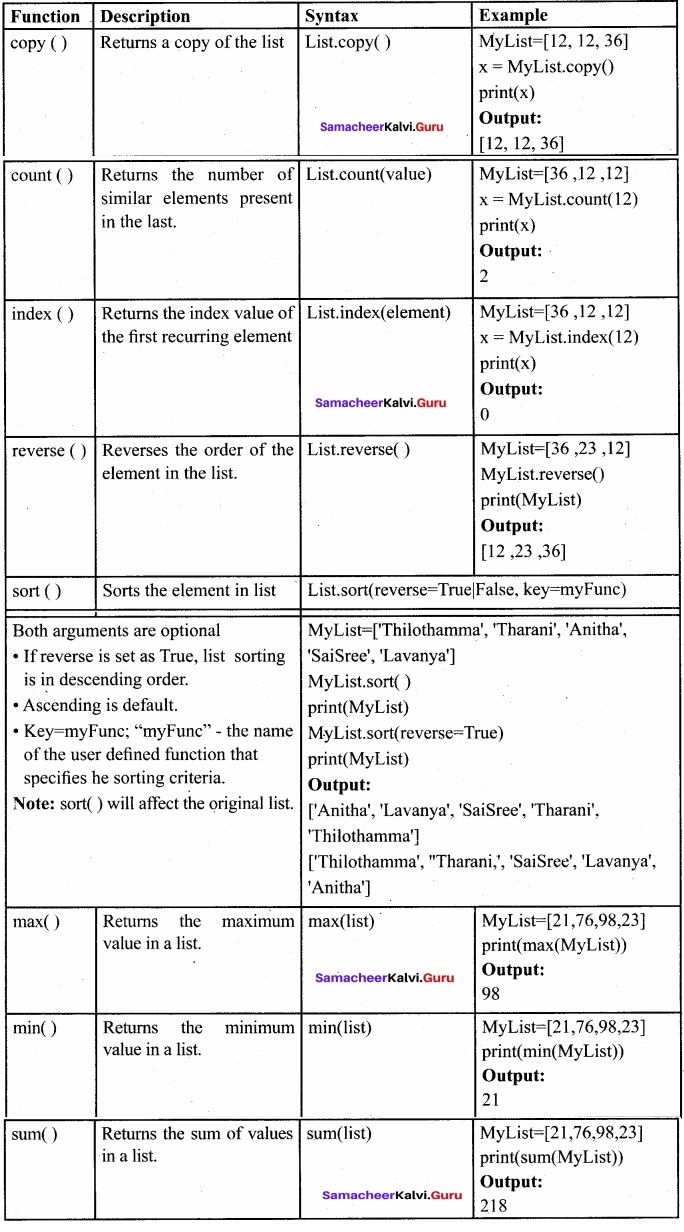
Explain Various Functions in list?
Answer:

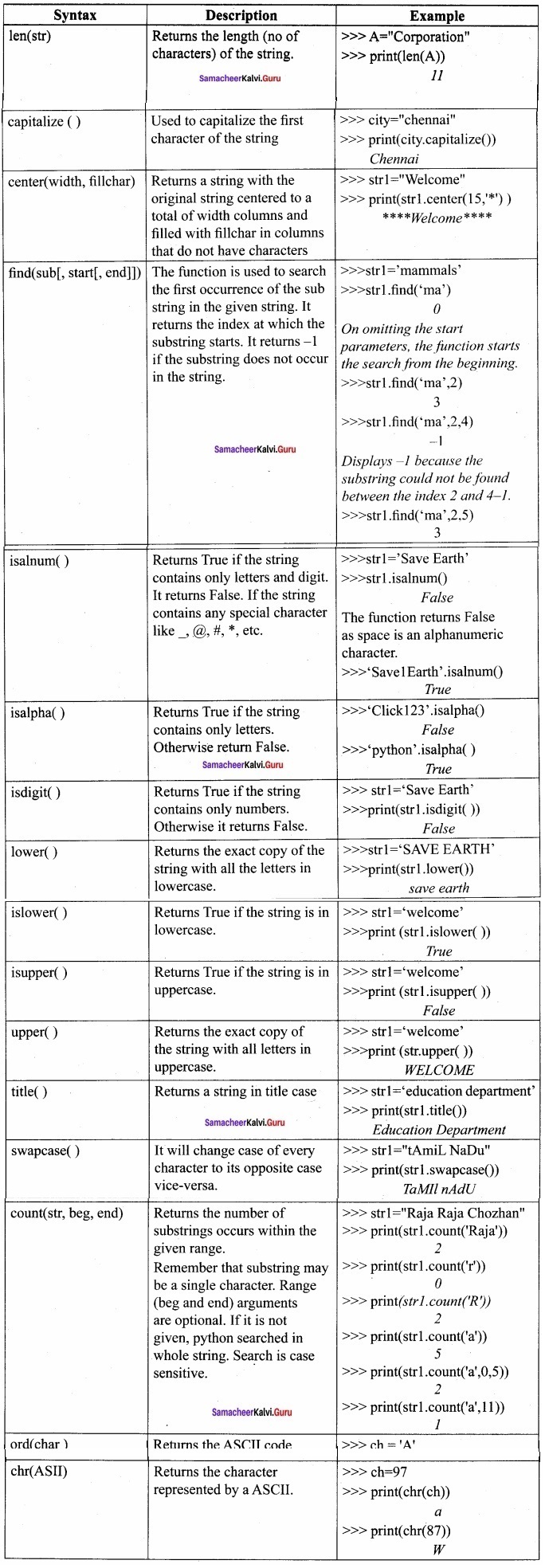
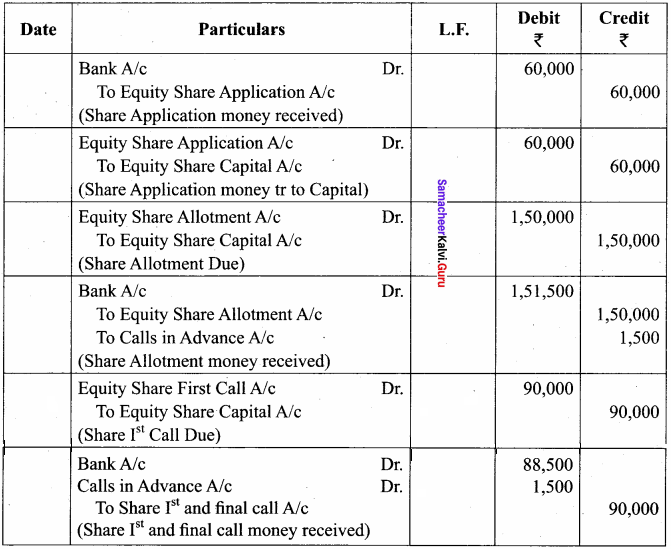
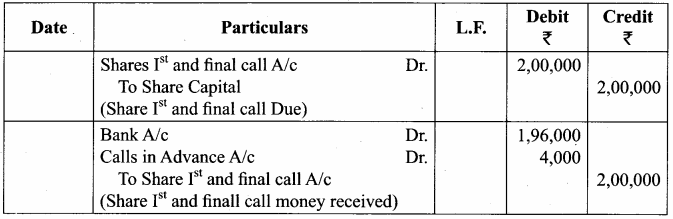
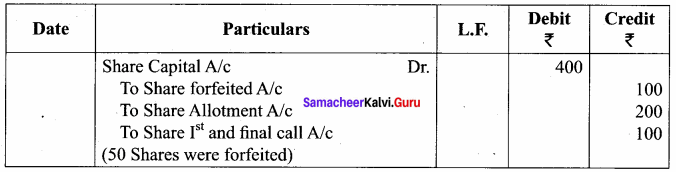
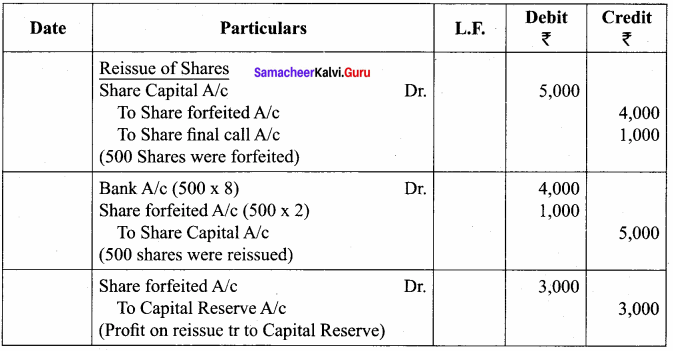
Question 2.
Write a python program using list to read marks of six subjects and to print the marks scored in each subject and show the total marks.
Python program to read marks of six subjects and to print the marks scored in each subject and show the total marks
Answer:
marks=[ ]
subjects=[‘Tamir, ‘English’, ‘Physics’, ‘Chemistry’, ‘Comp. Science’, ‘Maths’]
for i in range(6):
m=int(input(“Enter Mark = “))
marks.append(m)
for j in range(len(marks)):
print(“{ }. { } Mark= { } “.format(jl+,subjects[j],marks[j]))
print(“Total Marks = “, sum(marks))
Output
- Enter Mark = 45
- Enter Mark = 98
- Enter Mark = 76
- Enter Mark = 28
- Enter Mark = 46
- Enter Mark = 15
- Tamil Mark = 45
- English Mark = 98
- Physics Mark = 76
- Chemistry Mark = 28
- Comp. Science Mark = 46
- Maths Mark = 15
- Total Marks = 308

Question 3.
Write a program using list to generate the Fibonacci series and find sum. Program to generate in the Fibonacci series and store it in a list. Then find the sum of all values?
Answer:
a=-1
b=1
n=int(input(“Enter no. of terms: “))
i=0
sum=0
Fibo=[ ]
while i<n:
s = a + b
Fibo.append(s)
sum+=s
a = b
b = s
i+=1
print(“Fibonacci series upto “+ str(n) +” terms is : ” + str(Fibo))
print(“The sum of Fibonacci series: “,sum)
Output
Enter no. of terms: 10
Fibonacci series upto 10 terms is : [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
The sum of Fibonacci series: 88
Question 4.
Write a program to swap two values using tuple assignment
Program to swap two values using tuple assignment
Answer:
a = int(input(“Enter value of A: “))
b = int(input(“Enter value of B: “))
print(“Value of A = “, a, “\n Value of B = “, b)
(a, b) = (b, a)
print(“Value of A = “, a, “\n Value of B = “, b)
Output:
Enter value of A: 54
Enter value of B: 38
Value of A = 54
Value of B = 38
Value of A = 38
Value of B = 54

Question 5.
Write a program using a function that returns the area and circumference of a circle whose radius is passed as an argument two values using tuple assignment. Program using a function that returns the area and circumference of a circle whose radius is passed as an argument. Assign two values using tuple assignment:
Answer:
pi = 3.14
def Circle(r):
return (pi*r*r, 2*pi*r)
radius = float(input(“Enter the Radius! “))
(area, circum) = Circle(radius)
print (“Area of the circle = “, area)
print (“Circumference of the circle = “, circum)
Output:
Enter the Radius: 5
Area of the circle = 78.5
Circumference of the circle = 31.400000000000002