Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 9 Development Experiences in India
Students can Download Economics Chapter 9 Development Experiences in India Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 9 Development Experiences in India
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Development Experiences in India Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is the way of Privatisation?
(a) Disinvestment
(b) Denationalization
(c) Franchising
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 2.
Countries today are to be ______ for their growth.
(a) Dependent
(b) Interdependent
(c) Free trade
(d) Capitalist
Answer:
(b) Interdependent
![]()
Question 3.
The Arguments against LPG is ______
(a) Economic growth
(b) More investment
(c) Disparities among people and regions
(d) Modernization
Answer:
(c) Disparities among people and regions
Question 4.
Expansion of FDI ______
(a) Foreign Private Investment
(b) Foreign Portfolio
(c) Foreign Direct Investment
(d) Forex Private Investment
Answer:
(c) Foreign Direct Investment
Question 5.
India is the largest producer of ______ in the world.
(a) fruits
(b) gold
(c) petrol
(d) diesel
Answer:
(a) fruits
Question 6.
Foreign investment includes ______
(a) FDI only
(b) FPI and FFI
(c) FDI and FPI
(d) FDI and FFI
Answer:
(a) FDI only
Question 7.
The Special Economic Zones policy was announced in ______
(a) April 2000
(b) July 1990
(c) April 1980
(d) July 1970
Answer:
(a) April 2000
Question 8.
Agricultural Produce Market Committee is a ______
(a) Advisory body
(b) Statutory body
(c) Both a and b
(d) none of these above
Answer:
(b) Statutory body
Question 9.
Goods and Services Tax is ______
(a) a multi point tax
(b) having cascading effects
(c) like Value Added Tax
(d) a single point tax with no cascading effects.
Answer:
(d) a single point tax with no cascading effects.
Question 10.
The New Foreign Trade Policy was announced in the year ______
(a) 2000
(b) 2002
(c) 2010
(d) 2015
Answer:
(d) 2015
Question 11.
Financial Sector reforms mainly related to ______
(a) Insurance Sector
(b) Banking Sector
(c) Both a and b
(d) Transport Sector
Answer:
(c) Both a and b
Question 12.
The Goods and Services Tax Act came in to effect on ______
(a) 1st July 2017
(b) 1st July 2016
(c) 1st January 2017
(d) 1st January 2016
Answer:
(a) 1st July 2017
Question 13.
The new economic policy is concerned with the following ______
(a) foreign investment
(b) foreign technology
(c) foreign trade
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 14.
The recommendation of Narashimham Committee Report was submitted in the year ______
(a) 1990
(b) 1991
(c) 1995
(d) 2000
Answer:
(b) 1991
![]()
Question 15.
The farmers have access to credit under Kisan credit card scheme through the following except ______
(a) co-operative banks
(b) RRBs
(c) Public sector banks
(d) private banks
Answer:
(a) co-operative banks
Question 16.
The Raja Chelliah Committee on Trade Policy Reforms suggested the peak rate on import duties at ______
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 60%
(d) 100%
Answer:
(b) 50%
Question 17.
The first ever SEZ in India was set up at
(a) Mumbai
(b) Chennai
(c) Kandla
(d) Cochin
Answer:
(c) Kandla
Question 18.
‘The Hindu Rate of Growth’ coined by Raj Krishna refers to ______
(a) low rate of economic growth
(b) high proportion of Hindu population
(c) Stable GDP
(d) none
Answer:
(a) low rate of economic growth
Question 19.
The highest rate of tax under GST ______ is (as on July, 2017)
(a) 18%
(b) 24%
(c) 28%
(d) 32%
Answer:
(c) 28%
Question 20.
The transfer of ownership from the public sector to the private sector is known as ______
(a) Globalization
(b) Liberalization
(c) Privatization
(d) Nationalization
Answer:
(c) Privatization
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
Why was structural reform implemented in the Indian Economy?
Answer:
- Indian Economy responded to the crisis by introducing a set of policies known as Structural Reforms.
- These policies were aimed at correcting the weaknesses and rigidities in the various sectors of the economy such as industry, trade, fiscal, and agriculture.
Question 22.
State the reasons for implementing LPG.
Answer:
To correct the weaknesses and rigidities in the various sectors of the economy India implemented LPG which is the triple pillar of New Economic Policy.
Question 23.
State the meaning of Privatization.
Answer:
Privatization means the transfer of ownership and management of enterprises from the public sector to the private sector.
Question 24.
Define disinvestment.
Answer:
Disinvestment means selling of government securities of public sector undertakings to other PSUs or private sector or banks.
Question 25.
Write three policy initiatives introduced in 1991 – 1992 to correct the fiscal imbalance.
Answer:
The important policy initiatives introduced in the budget for the year 1991-92 for correcting the fiscal imbalance were:
- Reduction in fertilizer subsidy
- Abolition of subsidy on sugar.
- Disinvestment of a part of the government’s equity holdings in select public sector undertakings.
Question 26.
State the meaning of Special Economic Zones.
Answer:
SEZs is an area in which business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country mainly aiming at increasing trade, investment, and job creation.
Question 27.
State the various components of Central government schemes under post-harvest measures.
Answer:
- Mega food parks, Integrated Cold Chain, Value Addition Preservation, Infrastructure and Modernization of Slaughterhouse.
- Scheme for Quality Assurance, Codex Standards, Research and Development, and Other promotional activities.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 28.
How do you justify the merits of Privatisation?
Answer:
Privatization was necessitated because of the belief that the private sector was not given enough opportunities to earn more money.
![]()
Question 29.
What are the measures taken towards Globalization?
Answer:
- As globalization measures tend to integrate all economies of the world and bringing them all under one umbrella.
- They pave the way for the redistribution of economic power at the world level.
- Well-developed countries are favoured in this process and the welfare of the less- developed countries will be neglected.
- Globalization refers to the integration of the domestic (Indian) economy with the rest of the world.
- Import liberalization through reduction of tariff and non-tariff barriers, opening the doors to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) are some of the measures towards globalization.
Question 30.
Write a note on Foreign investment policy?
Answer:
The major feature of the economic reform opened the gate to foreign investment and foreign technology. Foreign investment including FDI and FPI were allowed.
In 1991, the government announced a specified list of industries wherein automatic permission was granted for FDI. Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) has been set up to negotiate with international firms and approve the foreign direct investment in select areas.
Question 31.
Give a short note on Cold storage.
Answer:
- India is the largest producer of fruits and the second-largest producer of vegetables in the world.
- In spite of that per capita availability of fruits and vegetables is quite low because of post-harvest losses which account for about 25% to 30% of production.
- Besides, the quality of a sizable quantity of produce also deteriorates by the time it reaches the consumer.
- Most of the problems relating to the marketing of fruits and vegetables can be traced to their perishability.
- Perishability is responsible for high marketing costs, market gluts, price fluctuations, and other similar problems.
- In order to overcome this constraint, the Government of India and the Ministry of Agriculture promulgated an order known as “Cold Storage Order, 1964” under section 3 of the Essential Commodities Act., 1955.
Question 32.
Mention the functions of APMC.
Answer:
- To promote public-private partnership in the ambit of agricultural markets.
- To provide market-led extension services to farmers.
- To promote agricultural activities.
- To bring transparency in pricing systems and market transactions.
- To ensure payments to the farmer for the sale on the same day.
- To display data on arrivals and rates from time to time in the market.
Question 33.
List out the features of the new trade policy.
Answer:
The main feature of the new trade policy as it has evolved over the years since 1991 are as follows: Free imports and exports:
- Prior to 1991, in India imports were regulated.
- From 1992, imports were regulated by a limited negative list.
- The trade policy of 1 April 1992 freed imports of almost all intermediate and capital goods. Rationalization of tariff structure and removal of quantitative restrictions:
- The Chelliah Committee’s Report had suggested a drastic reduction in import duties.
- It had suggested a peak rate of 50 percent.
- With a gradual reduction in the tariffs, the 1991-92 budget had reduced the peak rate of import duty from more than 300 percent to 150 percent.
- The process of lowering the customs tariffs was carried further in successive budgets.
The Chelliah Committee’s report had suggested a drastic reduction in import duties. As a first step towards a gradual reduction in the tariffs, the 1991 -92 budget had reduced the peak rate of import duty.
Question 34.
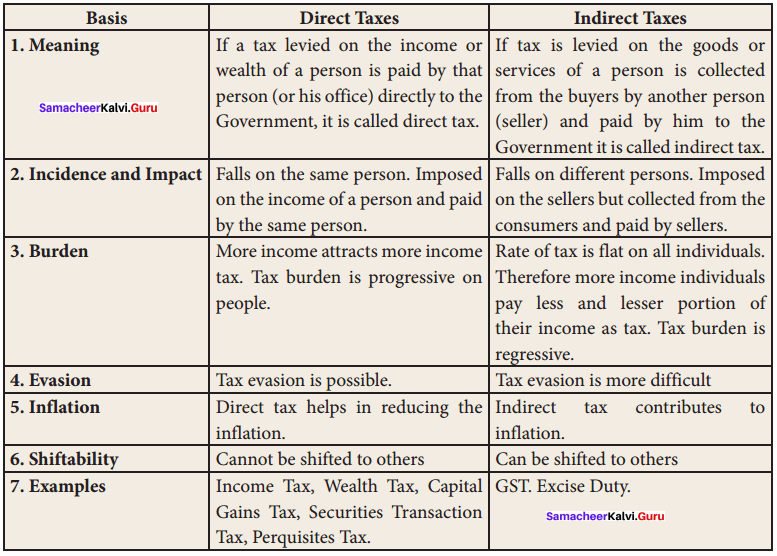
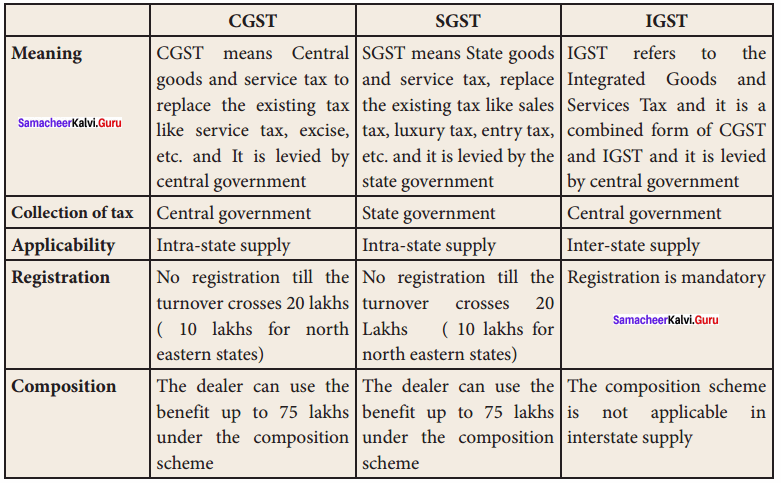
What is GST? Write its advantages.
Answer:
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the manufacture, sale, and consumption of goods as well as services.
Advantages of GST :
- Removing cascading tax effect.
- Single point tax.
- Higher threshold for registration
- Composition scheme for small business.
- The online simpler procedure under GST.
- Defined treatment for e-commerce.
- Increased efficiency in logistics
![]()
Question 35.
Discuss the important initiatives taken by the Government of India towards Industrial Policy?
Answer:
The policy has brought changes in the following aspects of industrial regulation.
- Industrial delicensing.
- De-reservation of the Industrial Sector.
- Public sector policy (dereservation and reform of PSEs).
- Abolition of MRTP Act.
- Foreign Investment policy and foreign technology policy.
Industrial delicensing policy:
- The most important objective of the new Industrial policy of 1991 was the end of the Industrial licensing or the license raj or red-tapism.
- The Industrial licensing policies, private sector firms had to secure licenses to start an Industry.
Dereservation of the Industrial Sector:
- The public sector was given reservation especially in the capital goods and key industries.
- Industrial deregulation, most of the industrial sectors were opened to the private sector as well.
- The new industrial policy, only three sectors viz., atomic energy, mining, and railways will continue as reserved for the public sector.
Reforms related to the Public Sector enterprises:
- Reforms in the public sector were aimed at enhancing the efficiency and competitiveness of the sector.
- The government identified strategic and priority areas for the public sector concentrate.
Abolition of MRTP Act:
- The New Industrial Policy of 1991 has abolished the Monopoly and Restrictive Trade Practices Act 1969.
- In 2010, the Competition Commission has emerged as the watchdog in monitoring competitive practices in the economy.
Foreign Investment Policy:
- Foreign investment including FDI and FPI were allowed.
- In 1991, the government announced a specified list of high-technology and high-investment priority Industries.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) upto 51 percent foreign equity.
- Foreign Investment Promotion Board has been set up to negotiate with International firms and approve Foreign Direct Investment.
Question 36.
Explain the objectives and characteristics of SEZs?
Answer:
- The Special Economic Zones [SEZs] Policy was announced in April 2000.
- The Special Economic Zones Act of 2005, the government has so far notified about 400 such zones in the country.
1. Major objectives of SEZs:
- To enhance foreign investment, especially to attract foreign direct investment [FDI] and thereby increasing GDP.
- To increase shares in Global Export (International Business).
- To generate additional economic activity.
- To create employment opportunities.
- To develop infrastructure facilities.
- To exchange technology in the global market.
2. Main Characteristics of SEZ:
- The geographically demarked area with physical security.
- Administrated by single body authority.
- Streamlined procedures.
- Having separate custom area.
- Governed by more liberal economic laws.
- Greater freedom to the firms located in SEZs.
Question 37.
Describe the salient features of EXIM policy (2015 – 2020)
Answer:
The new EXIM policy has been formulated focusing on increasing in exports Scenario, boosting production, and supporting the concepts like Make in India and Digital India. Salient Features:
- Reduce export obligations by 25% and give a boost to domestic manufacturing supporting the “Make in India” concept.
- As a step to Digital India concept, the online procedure to upload digitally signed document by CA /CS / Cost Accountant are developed and further mobile app for filing tax, stamp duty has been developed.
- Repeated submission of physical copies of documents available on Exporter Importer Profile is not required.
- Export obligation period for export items related to defense, military store, aerospace, and nuclear energy to be 24 months.
- EXIM policy 2015 – 2020 is expected to double the share of India in World Trade from the present level of 3% by the year 2020. This appears to be too ambitious.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Development Experiences in India Additional Questions and Answers
Part-A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
The expansion of FDI is
(a) Foreign comprehensive investment ______
(b) Foreign direct investment
(c) Foreign indirect investment
(d) Foreign private investment
Answer:
(b) Foreign direct investment
Question 2.
India ranked ______ position in Asia’s GDP.
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 3.
The monopoly and Restrictive Trade Practices Act was abolished in ______
(a) 1919
(b) 1971
(c) 1991
(d) 1791
Answer:
(c) 1991
![]()
Question 4.
The crop Insurance scheme was launched on
(a) 2009
(b) 2014
(c) 2016
(d) 2012
Answer:
(c) 2016
Question 5.
The expansion of KCC ______
(a) Kisan Crop Card
(b) Kisan Cash Card
(c) Kisan Credit Card
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Kisan Credit Card
Question 6.
EPZ means ______
(a) Export Pay Zone
(b) Export Policy Zone
(c) Export Processing Zone
(d) Special Economic Zone
Answer:
(c) Export Processing Zone
Question 7.
Goods and Services Tax came into effect on ______
(a) 30,h June 2017
(b) 1st July 2016
(c) 1st July 2017
(d) 1st April 2017
Answer:
(c) 1st July 2017
Question 8.
Fiscal deficit should not exceed ______ percent of GDP
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 3
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
Question 1.
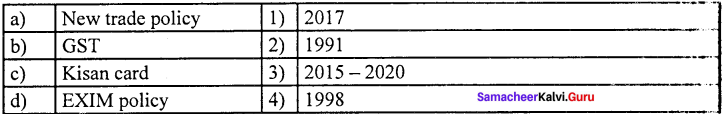
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 1 2 4 3
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Question 2.
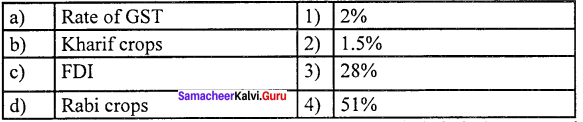
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 3 2 4 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 1 4 2
Answer:
(d) 3 1 4 2
Choose the correct option
Question 3.
New economic policy was introduced in
(a) 2010
(b) 1991
(c) 1884
(d) 1894
Answer:
(b) 1991
Question 4.
Kisan card was introduced in
(a) 2000
(b) 2015
(c) 1998
(d) 2017
Answer:
(c) 1998
![]()
Question 5.
was one of the first in Asia to recognize the effectiveness of the export processing zone
(a) India
(b) China
(c) America
(d) the Soviet Union
Answer:
(a) India
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 6.
Disinvestment means
(a) Selling of government securities
(b) Selling of public sectors
(c) Selling of private securities
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Selling of government securities
Question 7.
was set up to encourage FDI
(a) Domestic investment promotion board
(b) Foreign investment promotion board
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Foreign investment promotion board
Question 8.
The share of India to Asia’s GDP is
(a) 7.50%
(b) 6.50%
(c) 8.50%
(d) 9.50%
Answer:
(c) 8.50%
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 9.
(a) Prime minister’s crop insurance scheme was launched on 2016
(b) New industrial policy was established on 1991
(c) Kisan credit card was introduced by RBI and NABARD
(d) Goods and Services Tax was introduced in 2015
Answer:
(d) Goods and Services Tax was introduced in 2015
Question 10.
(a) New foreign trade policy was introduced on 2015
(b) First ever export processing zone was set up by China
(c) Cold storage order was introduced in 1964.
(d) India’s GDP crossed 2 trillion dollars in 2015-16
Answer:
(b) First ever export processing zone was set up by China
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 11.
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 1 2 4 3
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Question 12.
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 3 2 4 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 1 4 2
Answer:
(c) Chelliah committee (iii) GST
Choose the correct pair
Question 13.
Answer:
(d) Cash reserve ratio (iv) 1991
Question 14.
Answer:
(a) Dr.Raj Krishna (i) Low rate of economic growth
Pick the odd one out
Question 15.
(a) Liberalization
(b) Industrialization
(c) Privatization
(d) Globalization
Answer:
(b) Industrialization
![]()
Question 16.
(a) Crop insurance
(b) Cold storage
(c) Agriculture subsidy reduction
(d) Kisan credit card
Answer:
(c) Agriculture subsidy reduction
Choose the correct statement
Question 17.
(a) China is the largest producer of fruits.
(b) India is the largest producer of vegetables.
(c) Agricultural produce market committee (ADMC) promotes agricultural activities.
(d) Tobacco is a plantation crop
Answer:
(c) Agricultural produce market committee (ADMC) promotes agricultural activities.
Question 18.
(a) Privatization measures discourage the continuance of monopoly.
(b) Disinvestment process was fully implemented
(c) New industrial policy abolished the MRTP act.
(d) Foreign investment includes FDI and FII
Answer:
(c) New industrial policy abolished the MRTP act.
Analyze the reason for the following
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Agriculture in India is highly prone to risks like droughts and floods.
Reason (R): Agriculture is a seasonal activity.
(a) (A) and (R) are true; (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) (A) and (R) are true. (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is true (R) is false.
Answer:
(a) (A) and (R) are true; (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 20.
Assertion (A): GST is a comprehensive indirect tax.
Reason (R): GST is a multi-point tax
(a) (A) is true (R) is false.
(b) (A) is false (R) is true
(c) Both (A) and (R) are true.
(d) Both (A) and (R) are false.
Answer:
(a) (A) is true (R) is false.
Part -B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What is an industrial delicensing policy or Red Tapism?
Answer:
The new industrial policy of 1991 abolished the procedure of securing licenses (Red Tapism) to start an industry which is called an industrial delicensing policy.
Question 2.
What is liberalization?
Answer:
Liberalization refers to the removal of the relaxation of governmental restrictions in all stages in the industry.
Question 3.
What is the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)?
Answer:
SLR refers to the amount that the commercial banks require to maintain in the form of cash or gold or government approved securities before providing credit to the customers. Agricultural Produce Market Committee (APMC) is a statutory body constituted by the state government in order to trade in agricultural or horticultural or livestock production.
Question 5.
Write a note on Kisan Credit Card.
Answer:
A Kisan Credit Card (KCC) is a credit delivery mechanism that is aimed at enabling farmers to have quick and timely access to affordable credit. It was launched in 1998 by RBI and NABARD.
Question 6.
What is globalization?
Answer:
Globalization stands for the consolidation of the various economies of the world.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the agrarian crisis after the economic reforms of 1991.
Answer:
- High input costs
- The cutback in agricultural subsidies
- Reduction of import duties
- The paucity of credit facilities.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
What is a crop insurance scheme?
Answer:
To protect the farmers from natural calamities and ensure their credit eligibility for the next season, the Government of India introduced many agricultural schemes throughout the country.
One of the schemes is the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana which was launched on 18 February 2016. It envisages a uniform premium of 2% for Kharif and 1.5% for Rabi and 5% for commercial and horticultural crops.
Question 2.
State the arguments against LPG.
Answer:
- Liberalization measures favor the unrestricted entry of foreign companies which prevents the growth of the local manufactures.
- Privatization measures favor the continuance of the monopoly power.
- Only the developed countries are favored under globalization but the welfare of (he less developed countries will be neglected.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the major changes in India after 1991.
Answer:
- Foreign exchange reserves started rising.
- There was rapid industrialization.
- The pattern of consumption started improving.
- Infrastructure facilities such as express highways, metro rails, flyovers, and airports started expanding (but the local people were thrown away).
Part -D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 1.
Explain the measures taken in the Ranking system under the new economic policy 1991.
Answer:
- Reduction in statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) and the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) was recommended by the Narasimham Committee Report 1991.
- Interest rate liberalization.
- Greater competition among public, private, and foreign banks and elimination of administrative constraints.
- Liberalization of bank branch licensing policy.
- Banks were given the freedom to relocate branches and open specialized branches.
- Guidelines for opening new private sector banks.
- New accounting norms regarding the classification of assets and provisions of bad debt were introduced.