Students can Download Economics Chapter 6 Distribution Analysis Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Distribution Analysis
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Distribution Analysis Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In Economics, distribution of income is among the
(a) factors of production
(b) individual
(c) firms
(d) traders
Answer:
(a) factors of production
Question 2.
Theory of distribution is popularly known as ………………………..
(a) Theory of product – pricing
(b) Theory of factor – pricing
(c) Theory of wages
(d) Theory of Interest
Answer:
(b) Theory of factor-pricing
![]()
Question 3.
Rent is the reward for the use of
(a) capital
(b) labour
(c) land
(d) organization
Answer:
(c) land
Question 4.
The concept of ‘Quasi – Rent’ is associated with ………………………
(a) Ricardo
(b) Keynes
(c) Walker
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(d) Marshall
Question 5.
The Classical Theory of Rent was propounded by
(a) Ricardo
(b) Keynes
(c) Marshall
(d) Walker
Answer:
(a) Ricardo
Question 6.
‘Original and indestructible powers of the soil’ is the term used by ……………………….
(a) J.S.Mill
(b) Walker
(c) Clark
(d) Ricardo
Answer:
(d) Ricardo
Question 7.
The reward for labour is
(a) rent
(b) wage
(c) profit
(d) interest
Answer:
(b) wage
Question 8.
Money wages are also known as ……………………….
(a) Real wages
(b) Nominal wages
(c) Original wages
(d) Transfer wages
Answer:
(b) Nominal wages
Question 9.
Residual Claimant Theory is propounded by
(a) Keynes
(b) Walker
(c) Hawley
(d) Knight
Answer:
(b) Walker
Question 10.
The reward is given for the use of capital ………………………
(a) Rent
(b) Wage
(c) Interest
(d) Profit
Answer:
(c) Interest
Question 11.
Keynesian Theory of interest is popularly known as
(a) Abstinence Theory
(b) Liquidity Preference Theory
(c) Loanable Funds Theory
(d) Agio Theory
Answer:
(b) Liquidity Preference Theory
![]()
Question 12.
According to the Loanable Funds Theory, supply of loanable funds is equal to …………………………
(a) S + BC + DH + DI
(b) I + DS + DH + BM
(c) S+ DS + BM+ DI
(d) S + BM + DH + DS
Answer:
(a) S + BC + DH + DI
Question 13.
The concept of meeting unexpected expenditure according to Keynes is
(a) Transaction motive
(b) Precautionary motive
(c) Speculative motive
(d) Personal motive
Answer:
(b) Precautionary motive
Question 14.
The distribution of income or wealth of a country among the individuals are ………………………….
(a) Functional distribution
(b) Personal distribution
(c) Goods distribution
(d) Services distribution
Answer:
(b) Personal distribution
Question 15.
Profit is the reward for
(a) land
(b) organization
(c) capital
(d) labour
Answer:
(b) organization
Question 16.
Innovation Theory of profit was given by …………………………..
(a) Hawley
(b) Schumpeter
(c) Keynes
(d) Knight
Answer:
(b) Schumpeter
Question 17.
Quasi-rent arises in
(a) Man-made appliances
(b) Homemade items
(c) Imported items
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Man-made appliances
Question 18.
“Wages as a sum of money are paid under contract by an employer to a worker for service rendered”- Who said this?
(a) Benham
(b) Marshall
(c) Walker
(d) J.S.Mill
Answer:
(a) Benham
Question 19.
Abstinence Theory of Interest was propounded by
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) N.W Senior
(c) Bohm-Bawerk
(d) Knut Wicksell
Answer:
(b) N.W Senior
![]()
Question 20.
Loanable Funds Theory of Interest is called as …………………………
(a) Classical Theory
(b) Modem Theory
(c) Traditional Theory
(d) Neo-Classical Theory
Answer:
(d) Neo-Classical Theory
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
What is meant by distribution?
Answer:
Distribution means division of income among the four factors of production in terms of rent to landlords, wage to labourer, interest to capital and profit to entrepreneurs. The theory of functional distribution deals with how the relative prices of these factors of production are determined. The theory of factor prices is popularly known as the theory of distribution.
Question 22.
Mention the types of distribution?
Answer:
Personal Distribution: Personal Distribution is the distribution of national income among individuals.
Functional Distribution: Functional Distribution means the distribution of income among the four factors of production namely land, labour, capital and organization for their services in the production process.
Question 23.
Define ‘Rent’.
Answer:
Rent is the price or reward given for the use of land or house or a machine to the owner But, in Economics, “Rent” or “Economic Rent” refers to that part of the payment made by a tenant to his landlords for the use of land only.
Question 24.
Distinguish between real and money wages.
Answer:
Real wages :
Wages paid in terms of goods and services. It refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
Money wages :
Nominal wages are referred to as wages paid in terms of money.
Question 25.
What do you mean by interest?
Answer:
Interest is the price paid for the use of capital in any market.
Question 26.
What is profit?
Answer:
Profit is the amount left with the entrepreneur after he has made payments for all the other factors of production.
Question 27.
State the meaning of liquidity preference?
Answer:
- Liquidity preference means the preference of the people to hold wealth in the form of liquid cash rather than in other non – liquid assets like bonds, securities, bills of exchange, land, building, gold etc.
- “Liquidity Preference is the preference to have an amount of cash rather than of claims against others”.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 28.
What are the motives of demand for money?
Answer:
1. Transaction motive :
It relates to the desire of the people to hold cash for the current transactions.
Mt=f (y)
2. Precautionary motive :
It relates to the desire of the people to hold cash to meet unexpected or unforeseen expenditures.
Mp = f (y)
3. Speculative motive :
It relates to the desire of the people to hold cash in order to take advantage of market movements regarding future changes in the price of bonds and securities in the capital market.
Ms = f (i)
![]()
Question 29.
List out the kinds of wages:
Answer:
Wages are divided into four types.
- Nominal Wages or Money Wages: Nominal wages are referred to the wages paid in terms of money.
- Real Wages: Real wages are the wages paid in terms of goods and services. Hence, real wages are the purchasing power of money wages.
- Piece Wages: Wages that are paid on the basis of quantum of work done.
- Time Wages: Wages that are paid on the basis of the amount of time that the worker works.
Question 30.
Distinguish between rent and quasi-rent
Answer:
Rent:
- Rent accrues to land
- The supply of land is fixed forever
- It enters into price
Quasi – rent:
- Quasi-rent accrues to man-made appliances
- The supply of man made appliances is fixed for a short period only
- It does not enter into price.
Question 31.
Briefly explain the Subsistence Theory of Wages?
Answer:
The subsistence theory of wages:
- Subsistence theory of wages is one of the oldest theories of wages.
- According to this theory, wage must be equal to the subsistence level of the labourer and his family.
- Subsistence means the minimum amount of food, clothing and shelter which workers and their family require for existence.
- If workers are paid higher wages than the subsistence level, the workers would be better off and they will have large families.
- Hence, the population would increase.
- When the population increases, the supply of labourer would increase and therefore, wages will come down.
- If wages are lower than the subsistence level, there would be a reduction in population and thereby the supply of labour falls and wages increase to the subsistence level.
Question 32.
State the Dynamic Theory of Profit.
Answer:
- This theory was propounded by the American economist J.B.Clark in 1900.
- Profit is the reward for dynamic changes in society.
- Static society is one where everything is stationary or stagnant and there is no change at all.
- There is no role for an entrepreneur in a static society.
- According to Clark, the following five main changes are taking place in a dynamic society.
- Population is increasing
- Volume of Capital is increasing
- Methods of production are impro ving
- Forms of industrial organization are changing
- The wants of consumer are multiplying
Question 33.
Describe briefly the Innovation Theory of Profit?
Answer:
Innovation Theory of Profit:
- The innovation theory of profit was propounded by Joesph. A.Schumpeter.
- Schumpeter says an entrepreneur is not only an undertaker of a business but also an innovator in the process of production.
- Profit is the reward for “innovation”.
- According to Schumpeter, an innovation may consist of the following:
- Introduction of a new product.
- Introduction of a new method of production.
- Opening up of a new market.
- Discovery of new raw materials
- Reorganization of an industry/firm.
When any one of these innovations is introduced by an entrepreneur, it leads to a reduction in the cost of production and thereby brings profit to an entrepreneur. To obtain profit continuously, the innovator needs to innovate continuously. The real innovators do so. Imitative entrepreneurs cannot innovate.
Question 34.
Write a note on the Risk-bearing Theory of Profit.
Answer:
- Risk bearing theory of profit was propounded by the American economist F.B. Hawley in 1907.
- According to him, profit is the reward of “risk-taking” in business.
- Risk-taking is an essential function of the entrepreneur and is the basis of profits.
- It is a well-known fact that every business involves some risks.
- Since the entrepreneur undertakes the risks, he receives profit.
- If the entrepreneur does not receive the reward, he will not be prepared to undertake the risks.
- Every entrepreneur produces goods in anticipation of demand.
- It is the profit that induces the entrepreneurs to undertake such risks.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 35.
Explain the Marginal Productivity Theory of Distribution.
Answer:
Marginal productivity theory of distribution was developed by Clark, Wicksteed and Walras. This theory explains how the prices of various factors of production are determined. This theory is also known as the “General theory of distribution” or “National dividend theory of distribution”.
Assumptions:
- All the factors of production are homogenous and can be substituted for each other.
- There is perfect competition in both factor and product market.
- There is perfect mobility and full employment of factors of production.
- This theory is applicable only in the long-run.
- The entrepreneurs aim at profit maximization.
- There is no government intervention and no technological change.
Explanation of the theory :
Each factor is rewarded according to its marginal productivity.
Marginal product:
The marginal product of a factor of production means the addition made to the total product by employment of an additional unit of that factor.
Marginal physical product (MPP) :
The MPP of a factor is the increment in the total product obtained by the employment of an additional unit of that factor.
Value of marginal product (VMP):
VMP = MPP x price
Statement of the theory:
- The price of a factor of production depends upon its productivity.
- The price of a factor is determined by and will be equal to the marginal revenue product of that factor.
- Under certain conditions, the price of a factor will be equal to both the average and marginal products of that factor.
Marginal productivity under perfect competition:
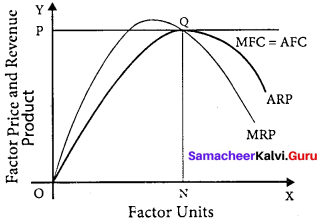
The X-axis represents factor units and Y-axis represents the factor price and revenue product.
MRP – Marginal Revenue Product Curve
ARP – Average Revenue Product Curve
AFC – Average Factor Cost Curve
MFC – Marginal Factor cost Curve
AFC – is horizontal under perfect competition and MFC coincides with it.
When there is perfect competition in the factor market, the firm is in equilibrium only when MFC = MRP
At the point Q by employing ON units of factors and paying OP price (NQ) where MFC = MRP
At Q, MRP = ARP
Price of the factor (NQ) = Marginal revenue
Product (NQ) = Average revenue product (NQ)
There is no exploitation of factors under perfect competition.
Beyond point Q the price paid to the factor is more than the marginal revenue product and average revenue product, so employers do not employ the factors.
![]()
Question 36.
Illustrate the Ricardian Theory of Rent.
Answer:
The classical theory of rent is called the “Ricardian theory of rent”.
Definition:
Rent is that portion of the produce of the earth which is paid to the landlord for the use of the original and indestructible powers of the soil.
Assumptions:
- Land differs infertility.
- The law of diminishing returns operates in agriculture.
- Rent depends upon the fertility and location of the land.
- The theory assumes perfect competition and a long period.
- There is the existence of marginal land or no-rent land.
- The land has certain “Original and indestructible powers”.
- The land is used for cultivation only.
- Most fertile lands are cultivated first.
Statement of the theory with an illustration:
Assume that some people settle on the newly discovered island. People will first cultivate the most fertile ‘A’ grade land. They produce 40 bags of paddy.
Suppose after some time if another group of people settles down on the same island. They cultivate ‘B’ grade land which produces 30 bags of paddy. Suppose yet another group of people settle down there they cultivate ‘C’ grade land. It produces 20 bags of paddy.
This surplus of ‘A’ grade land is now raised to 20 bags (40 – 20) and it is the ‘Economic Rent’ of ‘A’ grade land. The surplus of ‘B’ grade land is 10 bags (30 – 20). In ‘C’ grade land cost of production is equal to the price of its products and it does not yield any rent (20 – 20). Hence ‘C’ grade land is called ‘no-rent land’ or marginal land.
The land which yields rent is called “intra-marginal land”.
Rent indicates the differential advantage of the superior land over the marginal land.
Ricardian Theory’ of Rent :
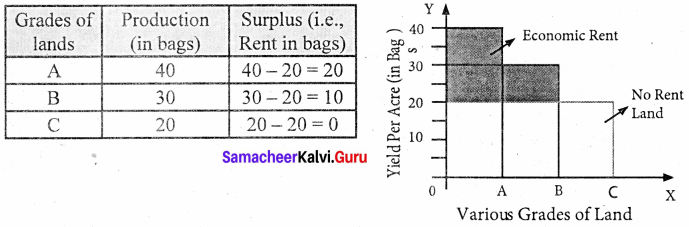
Diagrammatic illustration:
The X-axis represents various grades of land and the Y-axis yield per acre (in bags). OA, AB, and BC are the ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ grade lands respectively.
The ‘C’ grade land is the no-rent land. A and B grade lands are “intra-marginal lands. The economic rent yielded by ‘A’ and ‘B’ grade lands is equal to the shaded area of their respective rectangles.
Criticisms:
- The order of cultivation from most fertile to least fertile lands is historically wrong.
- This theory assumes that rent does not enter into price. But in reality, rent enters into the price.
![]()
Question 37.
Elucidate the Loanable Funds Theory of Interest.
Answer:
- The Loanable Funds Theory, also known as the “Neo-Classical Theory,” was developed by Swedish economists like Wicksell, Bertil, Ohlin, Viner, Gunnar Myrdal, and others.
- According to this theory, interest is the price paid for the use of loanable funds.
- The rate of interest is determined by the equilibrium between the demand for and supply of loanable funds in the credit market.
Demand for Loanable Funds
The demand for loanable funds depends upon the following:
1. Demand for Investment [I]
- The most important factor responsible for the loanable funds is the demand for investment.
- The bulk of the demand for loanable funds comes from business firms which borrow money for purchasing capital goods.
2. Demand for consumption [C]
- The demand for loanable funds comes from individuals who borrow money for consumption purposes also.
3. Demand for Hoarding [H]
- The next demand for loanable funds comes from hoarders. Demand for hoarding money arises because of people’s preference for liquidity, idle cash balances, and so on.
- The demand for C, I, and H varies inversely with the interest rate.
Equilibrium:
The rate of interest is determined by the equilibrium between the total demand for and the total supply of loanable funds.
Supply of loanable funds = S + BC + DH + DI
Demand for loanable funds = I + C + H
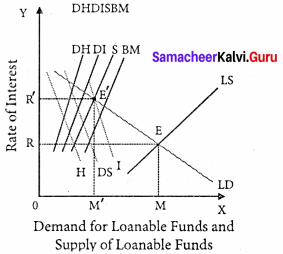
Supply of Loanable funds:
The supply of loanable funds depends upon the following four sources:
1. Savings [S]: Loanable funds comes from savings. According to this theory, savings may be of two types, namely,
- Savings planned by individuals are called “ex-ante-savings ”.
- The unplanned savings are called ‘ex-post savings”.
2. Bank Credit [BC]: Bank credit is another source of loanable funds. Commercial banks create credit and supply loanable funds to the investors.
3. Dishoarding [DH]: Dishoarding means bringing out the hoarded money into use and thus it constitutes a source of supply of loanable funds.
4. Disinvestment: [DI]: Disinvestment is the opposite of investment. Disinvestment means not providing sufficient funds for the depreciation of equipment.
It gives rise to the supply of loanable funds.
All four sources of supply of loanable funds vary directly with the interest rate.
![]()
Question 38.
Explain the Keynesian Theory of Interest.
Answer:
According to Keynes, interest is the reward for parting with liquidity’ for a specified period of time.
Meaning of liquidity preference:
Liquidity preference means the preference of the people to hold wealth in the form of liquid cash rather than in other non-liquid assets.
Motives of demand for money:
The three motives of liquidity preference are.
- The transaction motive Mt = f (y)
- The precautionary motive Mp = f (y)
- The speculative motive Ms = f (i)
Determination of Rate of Interest:
According to Keynes, the rate of interest is determined by the demand for and the supply of money. The demand for money is liquidity preference. The supply of money is determined by the policies of the government and the central bank.
Equilibrium between demand and supply of money:
The equilibrium between liquidity preference and demand for money determine the rate of interest. In short-run, the supply of money is assumed to be constant.
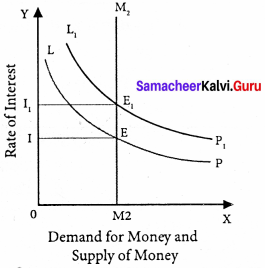
LP is the liquidity preference curve. M2 shows the supply curve of money to satisfy speculative motive. Both curves intersect at the point E which is the equilibrium. Here, rate of interest is I.
If liquidity preference increases from LP to L1 P1 the supply of money remains constant, the rate of interest increase from OI to OI1
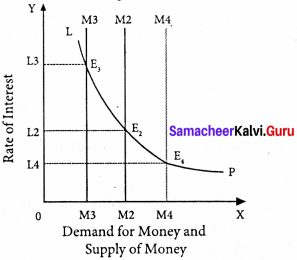
Suppose LP remains constant. If the supply of money is OM2, the interest is OI2 and if the supply of money is reduced from OM2 to OM2, the interest would increase from OM2 to OM4. If the supply of money is increased from OM2 to OM4 the interest would decrease from OI2 to Ol4
Criticisms:
- This theory does not explain the existence of different interest rates prevailing in the market at the same time.
- It explains interest rate only in the short – run.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Distribution Analysis Additional Questions and Answers
Part -A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
Marginal Productivity theory is the …………………….. theory of distribution.
(a) Average
(b) Marginal
(c) Liquidity preference theory
(d) General
Answer:
(d) General
![]()
Question 2.
“Interest is the price paid for the use of capital in any market” is said by_______
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Torrance
(c) Walker
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(d) Marshall
Question 3.
The standard of living of workers in a country depends upon the ……………………… wages.
(a) Real
(b) Effective
(c) Direct
(d) Elastic
Answer:
(a) Real
Question 4.
The author of the agio-theory of interest.
(a) N.W. Senior
(b) Bohm Bawerk
(c) Walker
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(b) Bohm Bawerk
Question 5.
Who propounded the risk-bearing theory of profit?
(a) Bohm – Bawerk
(b) F.B Hawley
(c) Marshall
(d) Walker
Answer:
(b) F.B Hawley
Question 6.
The dynamic theory of profit was propounded by_______
(a) Marshall
(b) J.B.Clark
(c) J.M. Keynes
(d) Walker
Answer:
(b) J.B.Clark
Question 7.
What is meant by MPS?
(a) Marginal production supply
(b) Marginal production sale
(c) Marginal production service
(d) Marginal propensity to save
Answer:
(d) Marginal propensity to save
![]()
Question 8.
Time preference theory was given by_______
(a) John Ray
(b) Bohm Bawerk
(c) F.B. Hawley
(d) Irving Fisher
Answer:
(d) Irving Fisher
Question 9.
The demand for labour is ………………………
(a) Effective demand
(b) Direct demand
(c) Derived demand
(d) Elastic demand
Answer:
(c) Derived demand
Question 10.
_______ is the author of the modern theory of rent
(a) Joan Robinson
(b) Boulding
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
Question 1.
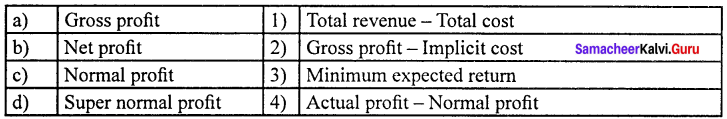
(a) 3 4 2 1
(b) 4 3 1 2
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
(c) 1 2 3 4
Question 2.
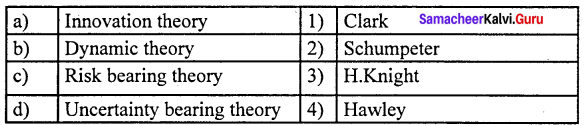
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 1 4 2 3
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 4 1 3 2
Answer:
(a) 2 1 4 3
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 3.
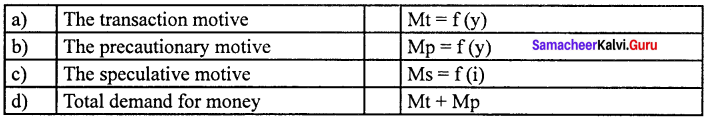
Answer:
(d) Total demand for money (iv) Mt + Mp
Question 4.
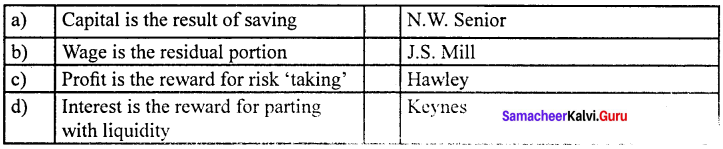
Answer:
(b) Wage is the residual portion (ii), J.S. Mill
Choose the correct statement
Question 5.
(a) The supply of land is fixed forever
(b) Quasi-rent accrues to land
(c) The supply of man-made appliances are fixed
(d) Quasi-rent enters price
Answer:
(a) The supply of land is fixed forever
![]()
Question 6.
(a) Rent is the reward for labour
(b) Profit is the reward for labour
(c) Wages are the reward for labour
(d) Interest is the reward for organization
Answer:
(b) Profit is the reward for labour
Choose the odd one out
Question 7.
(a) Bank credit
(b) Hoarding
(c) Dishoarding
(d) Disinvestment
Answer:
(b) Hoarding
Question 8.
(a) Monopoly profit
(b) Windfall profit
(c) Functional reward
(d) Reward for labourer
Answer:
(d) Reward for labourer
Question 9.
(a) Nominal wages
(b) Real wages
(c) Direct wages
(d) Piece wages
Answer:
(c) Direct wages
![]()
Question 10.
(a) Abstinence theory
(b) Loanable funds theory
(c) Liquidity preference theory
(d) Risk bearing theory
Answer:
(b) Loanable funds theory
Analyze the reason for the following
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : Demand for loanable funds depends on investment, consumption, and hoarding.
Reason (R) : The supply of loanable funds depends on hoarding and investment.
(a) (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(b) (A) and (R) are true, (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is true (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true (R) are false.
Question 12.
Assertion (A) : The rate of interest is determined by the demand for money and the supply of money.
Reason (R) : The demand for money is liquidity preference.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : Only superior land get rent
Reason (R) : Rent arose on account of differences in the fertility of the land.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true
(b) Both (A) and (R) are a false correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is true and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 14.
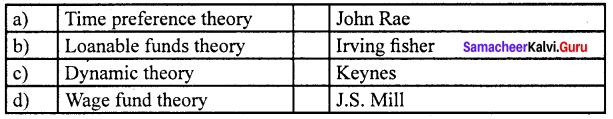
Answer:
(d) Wage fund theory (iv) J.S. Mill
Question 15.
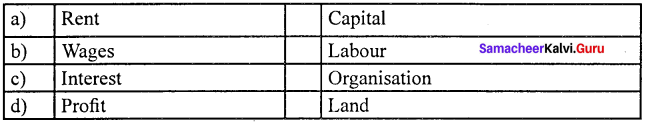
Answer:
(b) Wages (ii) Labour
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 16.
F.A. Walker wrote a book ______ in 1875.
(a) Political economy
(b) Social economy
(c) Principles of economics
(d) Wealth of nations
Answer:
(a) Political economy
![]()
Question 17.
The author of Agio theory of interest______
(a) N.W. Seniors
(b) Bohm-Bawerk
(c) Walker
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(b) Bohm-Bawerk
Question 18.
______ is the produced means of production.
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Capital
(d) Organisation
Answer:
(c) Capital
Choose the best option
Question 19.
The theory of factor prices is popularly known as the theory of
(a) Distribution
(b) Exchange
(c) Wages
(d) Profit
Answer:
(a) Distribution
Question 20.
______ is the author of the modern theory of rent
(a) Joan Robinson
(b) Boulding
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What is the theory of distribution?
Answer:
The theory of factor prices is popularly known as the theory of distribution.
Question 2.
Define VMP?
Answer:
- VMP – means Value of Marginal Product.
- The Value of the Marginal Product is obtained by multiplying the Marginal Physical Product of the factor by the price of the product. Symbolically, VMP = MPP x Price.
Question 3.
Define the Marginal productivity theory of distribution.
Answer:
The theory states that price or the reward for any factor of production is equal to the marginal productivity of that factor.
Question 4.
What is the marginal product? Define marginal physical product ?
Answer:
The addition made to the total product by the employment of an additional unit of that factor.
Question 5.
Define modern theory of rent.
Answer:
Rent is the difference between the actual earnings of a factor of production and its transfer earning.
Rent = Actual earning – Transfer earning
![]()
Question 6.
What is “Wage Fund“.
Answer:
According to Mill, “Every employer will keep a given amount of capital for payment to the workers”. It is known as the “Wage Fund”.
Question 7.
Define Quasi Rent.
Answer:
“Quasi rent is the income derived from machines and other appliances made by man
QR = Total revenue – Total variable cost
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
Explain the types of distribution.
Answer:
1. Personal distribution: It is the distribution of national income among individuals.
2. Functional distribution: It means the distribution of income among the four factors of production for their services in the production process.
Question 2.
Explain the standard of living theory of wages.
Answer:
This theory of wages was developed by Torrance is an improved version of the subsistence theory of wage. According to this theory, the wage is equal to the standard of living of the workers. If the standard of living is high, wages will be high and vice versa. The standard of a living wage means the amount necessary to maintain the labourer in the standard of life to which he is accustomed.
Question 3.
Briefly explain the Abstinence theory or waiting theory?
Answer:
- This theory was propounded by N.W.Senior.
- According to Senior, capital is the result of saving.
- Saving involves “abstinence” or “Sacrifice”
- It is possible to save only if one abstains from present consumption.
- Interest is the reward or compensation paid to the saver (capitalist) for his “abstinence” or “sacrifice”.
- Marshall accepted the Abstinence theory of interest.
- According to him, interest is a reward for waiting.
- Saving involves waiting.
- Therefore, interest is the reward paid to the saver for his “ waiting ”.
Question 4.
State the theories of interest.
Answer:
- Abstinence theory or waiting theory.
- Agio theory or the psychological theory.
- Loanable funds theory or the neoclassical theory.
- Liquidity preference theory or the monetary theory.
Question 5.
What are the four sources of loanable funds?
Answer:
The supply of loanable funds depends upon the following four sources.
- Savings (S)
- Bank Credit (BC)
- Dishoarding (DH)
- Disinvestment (DI)
![]()
Question 6.
What are the kinds of profit?
Answer:
1. Monopoly profit:
Profit earned by the firm because of its monopoly control.
2. Windfall profit:
Some times, profit arises due to changes in the price level. Profit is due to unforeseen factors.
3. Profit as a functional reward:
Just like rent, wage and interest, profit is earned by the entrepreneur for his entrepreneurial function.
Question 7.
State the residual claimant theory of wage.
Answer:
This theory was propounded by the American economist F.A. Walker in 1875, in his book political economy. According to this theory, wage is the residual portion after paying the remuneration of all the other three factors namely land capital and organization.
Criticisms:
- This theory does not explain the role of trade unions can secure higher wages for workers.
- The demand-side of labour in the determination of wages needs to be considered.