Students can Download Economics Chapter 10 Environmental Economics Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 10 Environmental Economics
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Environmental Economics Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
The term environment has been derived from a French word …………………………
(a) Environ
(b) Environs
(c) Environia
(d) Envir
Answer:
(c) Environia
Question 2.
The word biotic means environment
(a) Living
(b) Non – living
(c) Physical
(d) None of the the above
Answer:
(a) Living
![]()
Question 3.
Ecosystem is smallest unit of …………………………
(a) Ionosphere
(b) Lithosphere
(c) Biosphere
(d) Mesosphere
Answer:
(c) Biosphere
Question 4.
Who developed Material Balance Models?
(a) Thomas and Picardy
(b) Non – market goods
(c) Joan Robinson and J.M. Keynes
(d) Joseph Stiglitz and Edward Chamberlin
Answer:
(d) Joseph Stiglitz and Edward Chamberlin
Question 5.
Environmental goods are …………………………
(a) Market goods
(b) Non – market goods
(c) Both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Non – market goods
Question 6.
In a pure public good, consumption is …………………………
(a) Rival
(b) Non – rival
(c) Both
(d) None of the the above
Answer:
(a) Rival
![]()
Question 7.
One of the most important market failures is caused by …………………………
(a) Positive externalities
(b) Negative externalities
(c) Both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Negative externalities
Question 8.
The common source of outdoor air pollution is caused by combustion processes from the following …………………………
(a) Heating and cooking
(b) Traditional stoves
(c) Motor vehicles
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Traditional stoves
Question 9.
The major contributor of Carbon monoxide is …………………………
(a) Automobiles
(b) Industrial process
(c) Stationary fuel combustion
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Automobiles
![]()
Question 10.
Which one of the following causes of global warming?
(a) Earth gravitation force
(b) Oxygen
(c) Centripetal force
(d) Increasing temperature
Answer:
(d) Increasing temperature
Question 11.
Which of the following is responsible for protecting humans from harmful ultraviolet rays?
(a) UY – A
(b) UV – C
(c) Ozone layer
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Ozone layer
Question 12.
Global warming also refers to as …………………………
(a) Ecological change
(b) Climate Change
(c) Atmosphere change
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following is the anticipated effect of Global warming?
(a) Rising sea levels
(b) Changing precipitation
(c) Expansion of deserts
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Changing precipitation
Question 14.
The process of nutrient enrichment is termed as …………………………
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Limiting nutrients
(c) Enrichment
(d) Schistosomiasis
Answer:
(b) Limiting nutrients
Question 15.
Primary cause of Soil pollution is …………………………
(a) Pest control measures
(b) Land reclamation
(c) Agricultural runoff
(d) Chemical fertilizer
Answer:
(d) Chemical fertilizer
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following is main cause for deforestation?
(a) Timber harvesting industry
(b) Natural afforestation
(c) Soil stabilization
(d) Climate stabilization
Answer:
(a) Timber harvesting industry
Question 17.
Electronic waste is commonly referred as …………………………
(a) Solid waste
(b) Composite waste
(c) E – waste
(d) Hospital waste
Answer:
(c) E – waste
Question 18.
Acid rain is one of the consequences of ………………………… Air pollution.
(a) Water Pollution
(b) Land pollution
(c) Noise pollution
(d) Soil Pollution
Answer:
(a) Water Pollution
![]()
Question 19.
Sustainable Development Goals and targets are to be achieved by …………………………
(a) 2020
(b) 2025
(c) 2030
(d)2050
Answer:
(c) 2030
Question 20.
Alkali soils are predominantly located in the ………………………… plains?
(a) Indus – Ganga
(b) North – Indian
(c) Gangetic plains
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 21.
State the meaning of environment?
Answer:
- Meaning of Environmental Economics is a different branch of economics that recognizes the value of both the environment and economic activity and makes choices based on those values.
- The goal is to balance the economic activity and the environmental impacts by taking into account all the costs and benefits.
- In short, Environmental Economics is an area of economics that studies the financial impact of environmental issues and policies.
- Environmental Economics involves theoretical and empirical studies of the economic effects of national or local environmental policies around the world.
![]()
Question 22.
What do you mean by ecosystem?
Answer:
- An ecosystem includes all living things (plants, animals and organisms) in a given area, interacting with each other, and also with their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere).
- Ecosystems are the foundations of the Biosphere and they determine the health of the entire earth system.
Question 23.
Mention the countries where per capita carbondioxide emission is the highest in the world?
Answer:
- United States of America – (USA)
- Europian Union – (EU)
- Japan
- Russian Federation
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Saudi Arabia
- China.
Question 24.
What are environmental goods? Give examples?
Answer:
1. Environmental goods are typically non-market goods, including clear air, clean water, landscape, green transport infrastructure (footpaths, cycle ways, greenways, etc.), public parks, urban parks, rivers, mountains, forests, and beaches.
2. Concerns with environmental goods focus on the effects that the exploitation of ecological systems have on the economy, the well – being of humans and other species, and on the environment.
![]()
Question 25.
What are the remedial measures to control noise pollution?
Answer:
Remedial measures to control Noise Pollution
- Use of noise barriers
- Newer roadway for surface transport
- Traffic control
- Regulating times for heavy vehicles
- Installations of noise barriers in the work place
- Regulation of Loudspeakers
Question 26.
Define Global warming?
Answer:
1. Global warming is the current increase in temperature of the Earth’s surface (both land and water) as well as its atmosphere. Average temperatures around the world have risen by 0.75°C (1.4°F) over the last 100 years. About two thirds of this increase has occurred since 1975.
Carbon dioxide, methane, Chlorofluoro Carbon, nitrous oxides are the green house gases warming the earth’s surface. So it is also called green house effect. The CO2 is the most important of the green house gases contributing to 50% of global warming.
2. Global warming adversely affects agriculture, horticulture and eco system.
![]()
Question 27.
Specify the meaning of seed ball?
Answer:
- A seed ball (or seed bomb) is a seed that has been wrapped in soil materials, usually a mixture of clay and compost, and then dried.
- Essentially, the seed is ‘pre-planted’ and can be sown by depositing the seed ball anywhere suitable for the species, keeping the seed safely until the proper germination window arises.
- Seed balls are an easy and sustainable way to cultivate plants that provide a larger window of time when the sowing can occur.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 28.
Brief the linkage between economy and environment?
Answer:
Linkage between Economy and Environment:
- Man’s life is interconnected with various other living and non-living things.
- The life also depends on social, political, ethical, philosophical and other aspects of economic system.
- In fact, the life of human beings is shaped by his living environment.
- The relationship between the economy and the environment is generally explained in the form of a “Material Balance Model”.
- The model considers the total economic process as a physically balanced flow between inputs and outputs.
- Inputs are bestowed with physical property of energy which is received from the environment.
- The interdependence of economics and environment.
Economy – Environmental Interlinkages Material Balance Model
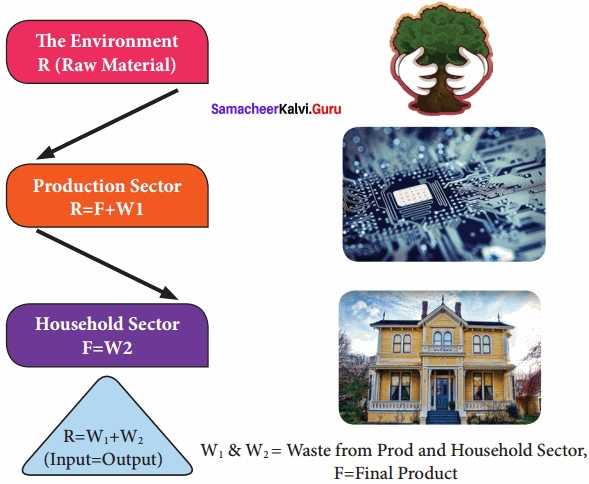
![]()
Question 29.
Specify the meaning of material balance principle?
Answer:
- The relationship between the economy and the environment is generally explained in the form of a “Material Balance Model” developed by AlenKneese and R.V. Ayres.
- The model considers the total economic process as a physically balanced flow between inputs and outputs.
- Inputs are bestowed with physical property of energy which is received from the environment.
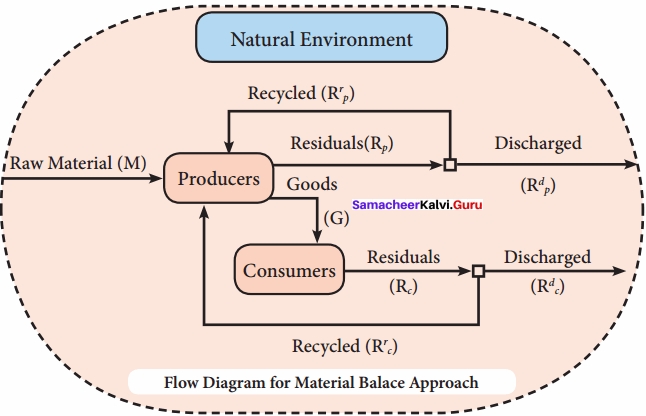
1. The interdependence of economics and environment.
2. The first law of thermodynamics, i.e. the law of conservation of matter and energy, emphasizes that in any production system “what goes in must come out”. This is known as the Material Balance Approach or Material Balance Principle.
3. Moreover, all resources extracted from the environment eventually become unwanted wastes and pollutants. Production of output by firms from inputs resulting in discharge of solid, liquid and gaseous wastes. Similarly, waste results from consumption activities by households.
4. In its simple form the Material Balance Approach can be put in form equation.
M = G – RC – RP + RrP + Rrc = Rdc + Rdc

![]()
Question 30.
Explain different types of air pollution?
Answer:
Types of Air pollution:
1. Indoor Air Pollution:
It refers to toxic contaminants that we encounter in our daily lives in our homes, schools and workplaces. For example, cooking and heating with solid fuels on open fires or traditional stoves results in high levels of indoor air pollution.
2. Outdoor Air Pollution:
It refers to ambient air. The common sources of outdoor air pollution are caused by combustion processes from motor vehicles, solid fuel burning and industry.
Question 31.
What are the causes of water pollution?
Answer:
Causes of Water Pollution:
Water pollution is caused due to several reasons. Here are the few major causes of water
pollution:
(I) Discharge of sewage and waste water:
- Sewage, garbage and liquid waste of households, agricultural runoff and effluents from factories are discharged into lakes and rivers.
- These wastes contain harmful chemicals and toxins which make the water poisonous for aquatic animals and plants.
(II) Dumping of solid wastes:
The dumping of solid wastes and litters in water bodies cause huge problems.
(III) Discharge of industrial wastes:
Industrial waste contains pollutants like asbestos, lead, mercury, grease oil and petrochemicals, which are extremely harmful to both people and environment.
(IV) Oil Spill:
- Sea water gets polluted due to oil spilled from ships and tankers while travelling.
- The spilled oil does not dissolve in water and forms a thick sludge polluting the water.
(V) Acid rain:
- Acid rain is pollution of water caused by air pollution.
- When the acidic particles caused by air pollution in the atmosphere mix with water vapor, it results in acid rain.
(VI) Global warming:
Due to global warming, there is an increase in water temperature as a result aquatic plants and animals are affected.
(VII) Eutrophication:
- Eutrophication is an increased level of nutrients in water bodies.
- This results in bloom of algae in water.
- It also depletes the oxygen in water which negatively affects fish and other aquatic animal population.
![]()
Question 32.
State the meaning of e – waste?
Answer:
1. Electronic waste which is commonly referred as “e-waste” is the new byproduct of the Info Tech society.
2. It is a physical waste in the form of old discarded, end of life electronics.
3. It includes a broad and growing range of electronic devices from large household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, cellular phones, computers and other electronic goods”.
4. Similarly, e-waste can be defined as the result when consumer, business and household devices are disposed or sent for re-cycling (example, television, computers, audio-equipments, VCR, DVD, telephone, Fax, Xerox machines, wireless devices, video games, other household electronic equipments).
Question 33.
What is land pollution? Mention the causes of land pollution?
Answer:
1. The land pollution is defined as, “the degradation of land because of the disposal of waste on the land”. Any substance (solid, liquid or gaseous) that is discharged, emitted or deposited in the environment in such a way that it alters the environment causes land pollution.
Causes of Land Pollution:
(I) Deforestation and soil erosion:
- Deforestation carried out to create dry lands is one of the major concerns.
- Land that is once converted into a dry or barren land, can never be made fertile again, whatever the magnitude of measures to convert it.
(II) Agricultural activities:
- With growing human and pet animal population, demand for food has increased considerably.
- Farmers often use highly toxic fertilizers and pesticides to get rid off insects, fungi and bacteria from their crops.
- However the overuse of these chemicals, results in contamination and poisoning of land.
(III) Mining activities:
During extraction and mining activities, several land spaces are created beneath the surface.
(IV) Landfills:
- Each household produces tones of garbage each year due to changing economic lifestyle of the people.
- Garbage like plastic, paper, cloth, wood and hospital waste get accumulated.
- Items that cannot be recycled become a part of the landfills that cause land pollution.
(V) Industrialization:
- Due to increasing consumerism more industries were developed which led to deforestation.
- Research and development paved the way for modem fertilizers and chemicals that were highly toxic and led to soil contamination.
(VI) Construction activities:
- Due to urbanization, large amount of construction activities are taking place.
- This has resulted in large waste articles like wood, metal, bricks, plastic.
- These are dumped at the outskirts of urban areas that lead to land pollution.
(VII) Nuclear waste:
- The leftover radioactive materials, harmful and toxic chemicals affect human health.
- They are dumped beneath the earth to avoid any casualty.
![]()
Question 33.
Write a note on
(a) Climate change and
(b) Acid rain.
Answer:
(a) Climate Change:
1. The climate change refers to seasonal changes over a long period with respect to the growing accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
2. Recent studies have shown that human activities since the beginning of the industrial revolution, have contributed to an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by as much as 40%, from about 280 parts per million in the pre-industrial period, to 402 parts per million in 2016, which in turn has led to global warming.
3. Several parts of the world have already experienced the warming of coastal waters, high temperatures, a marked change in rainfall patterns, and an increased intensity and frequency of storms. Sea levels and temperatures are expected to be rising.
(b) Acid Rain:
- Acid rain is one of the consequences of air pollution.
- It occurs when emissions from factories, cars or heating boilers contact with the water in the atmosphere.
- These emissions contain nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide which when mixed with water becomes sulfurous acid, nitric acid and sulfuric acid.
- This process also occurs by nature through volcanic eruptions.
- It can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals and infrastructure.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 35.
Briefly explain the relationship between GDP growth and the quality of environment?
Answer:
GDP Growth:
- Ross domestic product is the money value of final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year.
- GDP can determined in 3 ways in all of which should in principle give the same result.
- The real Economic GDP growth rate expressed as percentage that shows the rate of change in a countries GDP.
- The Four supply Factors are natural resources capital goods, human resources and technology.
- GDP is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services.
- The contribution of the nature to GDP as well as depletion of natural resources are not accounted in the present system of National Income.
Quality of Environment:
- Environmental quality is a set of properties and characteristics of the environment either generalized or local as they impinge on human beings and other organisms.
- It is measure of condition of an environment relative to one or more species any human need or purpose.
- Environmental quality has been continuously declining due to capitalistic mode of functioning.
- Environment is a pure public good that can be consumed simultaneously by everyone and from which no one can be excluded.
- A pure public good is one for which consumption is non-revival and from which it is impossible to exclude a consumer.
- The environment directly affects health status and plays a major role in quality of life lived and good health disparties.
![]()
Question 36.
Explain the concepts of externality and its classification?
Answer:
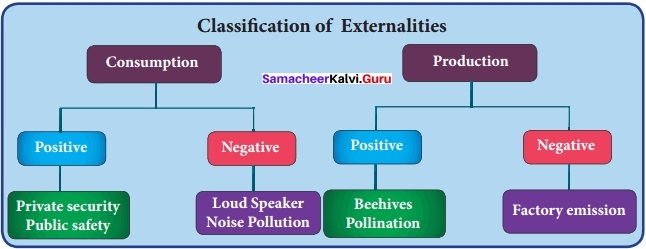
Externalities refer to external effects or spillover effects resulting from the act of production or consumption on the third parties. Externalities arise due to interdependence between economic units.
Positive Consumption Externality:
When some residents of a locality hire a private security agency to patrol their area, the other residents of the area also benefit from better security without bearing cost.
Negative Consumption Externality:
A person smoking cigarette gets may gives satisfaction to that person, but this act causes hardship (dissatisfaction) to the non – smokers who are driven to passive smoking.
Positive Production Externality:
- The ideal location for beehives is orchards (first growing fields).
- While bees make honey, they also help in the pollination of apple blossoms.
- The benefits accrue to both producers (honey as well as apple). This is called reciprocal untraded interdependency.
- Suppose training is given for the workers in a company. If those trained workers leave the. company to join some other company, the later company gets the benefit of skilled workers without incurring the cost of training.
Negative Production Externality:

![]()
Question 37.
Explain the importance of sustainable development and its goals?
Answer:
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
1. It is crucial to harmonize three core elements such as economic growth, social inclusion and environmental protection.
2. A set of 17 goals for the World’s future can be achieved before 2030 with three unanimous principles fixed by United Nations such as Universality, Integration and Transformation.
- End Poverty in all its forms everywhere
- End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
- Ensure inclusive and quality education for all and promote lifelong learning
- Achieve gender equality and empower women.and girls
- Ensure access to water and sanitation for all
- Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modem energy for all.
- Promote inclusive and sustainable economic growth, employment and decent work for all.
- Build resilient infrastructure, promote sustainable industrialization and foster innovation.
- Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Make cities inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
- Ensure sustainable consumption and production pattern
- Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
- Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources
- Sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity loss
- Promote just, peaceful and inclusive societies
- Revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Environmental Economics Additional Questions and Answers
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
“All the conditions, circumstances, and influences surrounding and affecting the development of an organism or group of organisms” is called ………………………..
(a) Environment
(b) Economics
(c) Eco system
(d) Biosphere
Answer:
(a) Environment
Question 2.
The relationship between the Economy and the environment is generally explained in the form of a …………………….. model.
(a) Material Economic
(b) Material Eco
(c) Material balance
(d) Material Environment
Answer:
(c) Material balance
![]()
Question 3.
…………………….. Economics involves theoretical and empirical studies of the Economic effects.
(a) Biosphere
(b) Political
(c) Environment
(d) Philosphical
Answer:
(c) Environment
Question 4.
Environmental externalities are called ……………………..
(a) Externality
(b) Economic externalities
(c) Nagative externalities
(d) Positive externalities
Answer:
(d) Positive externalities
Question 5.
…………………….. is of contaminants environment.
(a) Pollution
(b) Air Pollution
(c) Water pollution
(d) Noise Pollution
Answer:
(a) Pollution
![]()
Question 6.
Vehicles smoke happens to release high amounts of ……………………..
(a) Carbon – di – oxide
(b) Carbon – monoxide
(c) Carbon
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(b) Carbon – monoxide
Question 7.
…………………….. it creates several respiratory and heart ailments along with cancer.
(a) Water pollution
(b) Noise pollution
(c) Air pollution
(d) Land pollution
Answer:
(c) Air pollution
![]()
Question 8.
…………………….. is an increase in water temperature as a result aquatic plants and animals are affected.
(a) Oil spill
(b) Acid rain
(c) Global warming
(d) Eutrophication
Answer:
(c) Global warming
Question 9.
…………………….. is unwanted or excessive sound that can have deleterious effects on human health and environmental quality.
(a) Air pollution
(b) Water pollution
(c) Noise pollution
(d) Land pollution
Answer:
(c) Noise pollution
Question 10.
…………………….. adversely affects agriculture, horticulture and eco system.
(a) Climate change
(b) Global warming
(c) Land pollution
(d) Acid rain
Answer:
(b) Global warming
![]()
Question 11.
Soil pollution is another form of …………………….. pollution.
(a) Land
(b) Fertilizer
(c) Chemical
(d) Medicinal
Answer:
(a) Land
Question 12.
…………………….. is the supplier of the forms of resources.
(a) Farmers
(b) Environment
(c) Chemicals
(d) Fertilizers
Answer:
(b) Environment
Question 13.
…………………….. is led to land pollution.
(a) Forestation
(b) Forest
(c) Fertilizers
(d) Deforestation
Answer:
(d) Deforestation
![]()
Question 14.
Acid rain is one of the consequences of …………………….. pollution.
(a) Land
(b) Air
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Answer:
(a) Land
Question 15.
Atmospheric noise or static is caused by lighting discharges in ……………………..
(a) Thunder storms
(b) Flood
(c) Land slide
(d) Drought
Answer:
(a) Thunder storms
Question 16.
Polluted water is harmful for ……………………..
(a) Industries
(b) Agriculture
(c) Land pollution
(d) Soil pollution
Answer:
(b) Agriculture
![]()
Question 17.
Electronic waste is commonly referred as …………………….. is the new by product of the Info Tech society.
(a) E – waste
(b) Plastic waster
(c) Waste
(d) Rubber waste
Answer:
(a) E – waste
Question 18.
…………………….. is the current increase in temperature of the Earth’s surface as well as its atmosphere.
(a) Globe warming
(b) Global warming
(c) Globe spoiled
(d) Temperature warming
Answer:
(b) Global warming
![]()
Question 19.
…………………….. is an increased level of nutrients in water bodies.
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Global warming
(c) Acid rain
(d) Oil spill
Answer:
(a) Eutrophication
Question 20.
…………………….. is the supplier of all forms of resources like renewable and non – renewable.
(a) Environment
(b) Environmental goods
(c) Environmental quality
(d) Environmental wastes
Answer:
(a) Environment
Question 21.
Heavy machineries located inside big factories and industrial plants also emit pollutants into the ……………………..
(a) Land
(b) Soil
(c) Air
(d) Water
Answer:
(c) Air
![]()
Question 22.
…………………….. causes great damage to human beings, animals and crops.
(a) Natural
(b) Factories
(c) Acid rain
(d) Global warming
Answer:
(c) Acid rain
Question 23.
…………………….. is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
(a) Alternative approach
(b) Environmental protection
(c) Economic growth
(d) Sustainable development
Answer:
(d) Sustainable development
![]()
Question 24.
…………………….. is a system of agricultural production which relies on animal manure, organic waste, crop rotation, legumes and biological pest control.
(a) Organic farming
(b) Land forming
(c) Land pollution
(d) Soil pollution
Answer:
(a) Organic farming
II. Match The following And Choose The Correct Answer By Using Codes Given Below.
Question 1.
A. Causes of air pollution – (i) Solid waste
B. Types of water pollution – (ii) Vehicle exhaust smoke
C. Types of land pollution – (iii) Deforestation
D. Causes of land pollution (iv) Ground water pollution
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iv) B (iii) c (ii) D(i)
(c) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(d) A (iii) B(i) C (iv) D (ii)
Answer:
(c) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
![]()
Question 2.
A. Organic farming – (i) Global warming
B. Effects of noise pollution – (ii) Animal manure
C. Effects of water pollution – (iii) Hearing loss
D. Effects of air pollution – (iv) Death of aquatic animals
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
(d) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D(i)
Answer:
(d) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D(i)
Question 3.
A. World commision – (i) Seawater
B. Organic farming – (ii) Environment and Development
C. Oil spill – (iii) Nutrients in water
D. Eutrophication – (iv) Animal husbandry
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C(i) D (iii)
(c) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
Answer:
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C(i) D (iii)
![]()
Question 4.
A. Alkali soil – (i) High noise
B. Cardio vascular – (ii) Indo gangetic
C. Solid waste – (iii) Toxic chemicals
D. Skin cancer (iv) Rubbish
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D(i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C(i) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
![]()
Question 5.
A. Remedies of land pollution – (i) Sulphur dioxide
B. Acid rain – (ii) Degradation of land
C. Land pollution – (iii) Fossil fuel
D. Power plants – (iv) Usage of plastic
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iii) C(iv) D (i)
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
(d) A (iii) B (iv) C(i) D(ii)
Answer:
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
III. State Whether The Statements Are True or False.
Question 1.
(i) Environmental economics is a different branch of economics that recognizes the value of both the environment and economic activity.
(ii) Environmental Economics involves theoretical and empirical studies of the economic effects.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
![]()
Question 2.
(i) The relationship between the economy and the environment is generally explained in the form of a “Material Balance Model”.
(ii) This model developed by Alenkneese and R.V. Ayres.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 3.
(i) Beneficial externalities are called “Positive externalities”.
(ii) Beneficial externalities are called “Negative externalities”.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
![]()
Question 4.
(i) Surface water includes natural water found on the earth’s surface, like rivers, lakes, lagoons and oceans.
(ii) Hazardous substances coming into contact with this surface water, dissolving or mixing physically with the water can be called surface of land pollution.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 5.
(i) Noise pollution is unwanted or excessive sound that can have deleterious effects on human health and environmental quality.
(ii) Noise pollution is also comes from highway, railway and airplane traffic and from outdoor construction activities.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
IV. Which Of The Following Is Correctly Matched:
Question 1.
(a) Types of noise pollution – Death of aquatic animals
(b) Effects of water pollution – Factory mechinery
(c) Types of water pollution – Respiratory and heart problems
(d) Causes of air pollution – Vehicle exhaust smoke
Answer:
(d) Causes of air pollution – Vehicle exhaust smoke
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Environmental goods – Human beings
(b) Types of pollution – Transport
(c) Human health – Land pollution
(d) Microbiological pollution – Water pollution
Answer:
(d) Microbiological pollution – Water pollution
Question 3.
(a) Global warming – Affects industry
(b) Acid rain – Usage of pesticides
(c) Electronic waste – e – waste
(d) SDGs – Poverty increased
Answer:
(c) Electronic waste – e – waste
![]()
Question 4.
(a) Crackers – Big industry
(b) Soil pollution – Damaged river
(c) Farmers – Use highly toxic fertilizers
(d) Deforestation – Due to urbanisation
Answer:
(c) Farmers – Use highly toxic fertilizers
Question 5.
(a) Seed ball – Providing oxygen
(b) E – waste – Sustainable development
(c) Fertilizers used – Water pollution
(d) Oil spill – Sea water polluted
Answer:
(d) Oil spill – Sea water polluted
V. Which Of The Following Is Not Correctly Matched.
Question 1.
(a) Acid rain – Sulphur dioxide
(b) Agro – Eco system
(c) Negative production – Factory emission
(d) Ozone layer – Major cause of death
Answer:
(d) Ozone layer – Major cause of death
Question 2.
(a) Fossil fuel – Power plants
(b) Forest – Replenish soil
(c) Environmental goods – Pre – planted
(d) Agriculture – Fertilizer
Answer:
(c) Environmental goods – Pre – planted
![]()
Question 3.
(a) Sustainable development – Monitors
(b) Oil spill – Seawater
(c) Water – Land pollution
(d) Tree – Lungs of the Earth
Answer:
(c) Water – Land pollution
Question 4.
(a) Natural pollution – Aquatic and Human illness
(b) Global warming – Increasing temperature
(c) Discharge of sewage – Outdoor air pollution
(d) Organic farming – Deforestation
Answer:
(d) Organic farming – Deforestation
![]()
Question 5.
(a) Acid rain – Land pollution
(b) Soil – Soil contamination
(c) Heavy industries – Land pollution
(d) Environmental goods – Environmental quality
Answer:
(c) Heavy industries – Land pollution
VI. Pick The Odd One Out.
Question 1.
Types of Noise pollution
(a) Atmospheric noise pollution
(b) Industrial noise pollution
(c) Man made noise pollution
(d) Acid rain pollution
Answer:
(d) Acid rain pollution
Question 2.
Causes of Noise pollution
(a) Construction
(b) Motor vehicles
(c) Crackers
(d) Factory machinery
Answer:
(a) Construction
![]()
Question 3.
Types of Land pollution
(a) Solid waste
(b) Cardiovascular effects
(c) Pesticides and fertilizers
(d) Deforestation
Answer:
(b) Cardiovascular effects
Question 4.
Causes of Land Pollution
(a) Deforestation and soil erosin
(b) Agriculture activities spoiled
(c) Fertilizer spoiled
(d) Mining activities spoiled
Answer:
(c) Fertilizer spoiled
![]()
Question 5.
Organic farming
(a) Manure
(b) Biofertilizers
(c) Crop rotation
(d) Solid waste
Answer:
(d) Solid waste
VII. Assertion And Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The natural pollution causes both aquatic and human illness.
Reason (R): Pollution is damage to eco system and aesthetics of our surrounding.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Vehicles smoke happens to release high amounts of carbon monoxide.
Reason (R): Chemicals like carbon-di-oxide are released during the burning process.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Sewage, garbage and liquid waste of households, agriculture runoff and effluents from factories are discharged into lakes and rivers.
Reason (R): These wastes contain useful chemicals and toxins.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Remedial measures to control air pollution is growing more plants and trees.
Reason (R): Remedial measures to control air pollution is establishment of industries in the town and cities.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Soil pollution is another form of water pollution.
Reason (R): The upper layer of the soil is damaged is caused by the over use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 1.
Define “Solid wastes”?
Answer:
Solid Wastes:
- Non-liquid, non-soluble materials, ranging from municipal garbage to industrial wastes that contain complex, and hazardous, substances.
- Solid wastes include sewage sludge, agricultural refuse, demolition wastes, and mining residues.
![]()
Question 2.
What is organic farming?
Answer:
- Organic farming is a system of agricultural production which relies on animal manure, organic waste, crop rotation, legumes and biological pest control.
- It avoids use of synthetic fertilizer, pesticides and livestock additives.
- Organic inputs have certain benefits, such as enriching soil for microbes.
Question 3.
Define “Sustainable Development”?
Answer:
- Sustainable Development is development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- “The alternative approach (to sustainable development) is to focus on natural capital assets and suggest that they should not decline through time.”
Question 4.
Define “Noise pollution”?
Answer:
- Noise pollution is unwanted or excessive sound that can have deleterious effects on human health and environmental quality.
- Noise pollution is commonly generated by many factories.
- It also comes from highway, railway and airplane traffic and from outdoor construction ’ activities.
![]()
Question 5.
Define “Deforestation”?
Answer:
- Humans depend on trees for many things including life.
- Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release Oxygen, which is needed for life.
- Forest helps replenish soils and help retain nutrients being washed away.
- Deforestation is led to land pollution.
Question 6.
What are the types of pollution?
Answer:
Types of Pollution:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Noise pollution
- Land pollution.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Write note on “Remedial Measures to control land pollution?
Answer:
Remedial measures to control Land Pollution:
- Making people aware about the concept of a Reduce, Recycle and Reuse
- Buying biodegradable products
- Minimizing the usage of pesticides
- Shifting cultivation
- Disposing unwanted garbage properly either by burning or by burying under the soil.
- Minimizing the usage of plastics.
![]()
Question 2.
Mention the Remedial Measures to control water pollution?
Answer:
Remedial measures to control Water Pollution:
- Comprehensive water management plan.
- Construction of proper storm drains and settling ponds.
- Maintenance of drain line.
- Effluent and sewage treatment plant.
- Regular monitoring of water and waste water.
- Stringent actions towards illegal dumping of waste into the water bodies.
Question 3.
Explain the types of Noise pollution?
Answer:
Types of Noise Pollution:
(I) Atmospheric Noise:
Atmospheric noise or static is caused by lighting discharges in thunderstorms and other natural electrical disturbances occurring in the atmosphere.
(II) Industrial Noise:
- Industrial noise refers to noise that is created in the factories.
- When sound becomes noise it becomes unwanted.
- Heavy industries like ship building, iron and steel have long been associated with Noise Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL).
(III) Man made Noise:
The main sources of man-made noise pollution are ships, aircraft, seismic exploration, marine construction, drilling and motor boats.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 1.
What are the effects of Land pollution?
Answer:
Effects of Land Pollution:
(I) Soil pollution:
- Soil pollution is another form of land pollution, where the upper layer of the soil is damaged.
- This is caused by the overuse of chemical fertilizers, and pesticides.
- This leads to loss of fertile land.
- Pesticides kill not only pests and also human beings.
(II) Health Impact:
- The land when contaminated with toxic chemicals and pesticides lead to problem of skin cancer and human respiratory system.
- The toxic chemicals can reach our body through foods and vegetables.
(III) Cause for Air pollution:
- Landfills and waste dumping lead to air pollution.
- The abnormal toxic substances spread in the atmosphere cause transmit respiratory diseases among the masses.
(IV) Effect on wildlife:
- The animal kingdom has suffered mostly in the past decades.
- They face a serious threat with regards to loss of habitat and natural environment.
- The constant human activity on land is leaving it polluted, forcing these species to move farther away.
- Sometimes several species are pushed to the verge of extinction or disappear due to no conducive environment.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly explain effects of Noise pollution?
Answer:
Effects of Noise Pollution:
(a) Hearing Loss:
- Chronic exposure to noise may cause noise-induced hearing loss.
- Older people are exposed to significant occupational noise and thereby reduced hearing sensitivity.
(b) Damage Physiological and Psychological health:
- Unwanted noise can damage physiological and psychological health.
- For example, annoyance and aggression, hypertension, and high stress levels.
(c) Cardiovascular effects:
High noise levels can contribute to cardiovascular problems and exposure to blood pressure.
(d) Detrimental effect on animals and aquatic life:
Noise can have a detrimental effect on animals, increasing the risk of death.
(e) Effects on wildlife and aquatic animals:
It creates hormone imbalance, chronic stress, panic and escape behavior and injury.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the causes of Air pollution?
Answer:
Causes of Air Pollution:
(I) Vehicle exhaust smoke:
- Vehicles smoke happens to release high amounts of Carbon monoxide.
- Millions of vehicles are operated every day in cities, each one leaving behind its own carbon footprint on the environment.
(II) Fossil fuel based power plants:
- Fossil fuels also present a wider scale problem when they are burned for energy in power plants.
- Chemicals like sulphur dioxide are released during the burning process, which travel straight into the atmosphere.
- These types of pollutants react with water molecules to yield something known as acid rain.
(III) Exhaust from Industrial Plants and Factories:
Heavy machineries located inside big factories and industrial plants also emit pollutants into the air.
(IV) Construction and Agricultural activities:
- Potential impacts arising from the construction debris would include dust particles and gaseous emissions from the construction sites.
- Likewise, using of ammonia for agriculture is a frequent byproduct that happens to be one of the most dangerous gases affecting air.
(V) Natural Causes:
- Earth is one of the biggest polluters itself, through volcanoes, forest fires, and dust storms.
- They are nature-borne events that dump massive amounts of air pollution into the atmosphere.
(VI) Household activities:
Household activities like cooking, heating and lighting, use of various forms of mosquito repellents, pesticides and chemicals for cleaning at home and use of artificial fragrances are some of the sources that contribute to air pollution.
Question 4.
Explain different sources of E – waste?
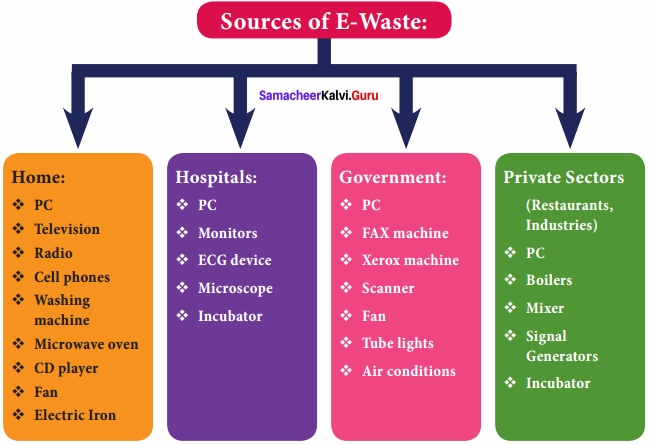
Answer: