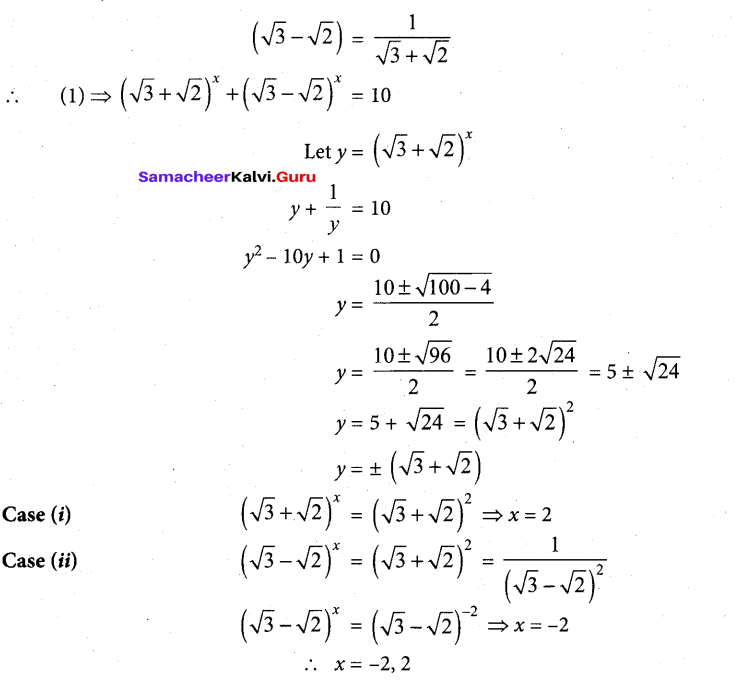
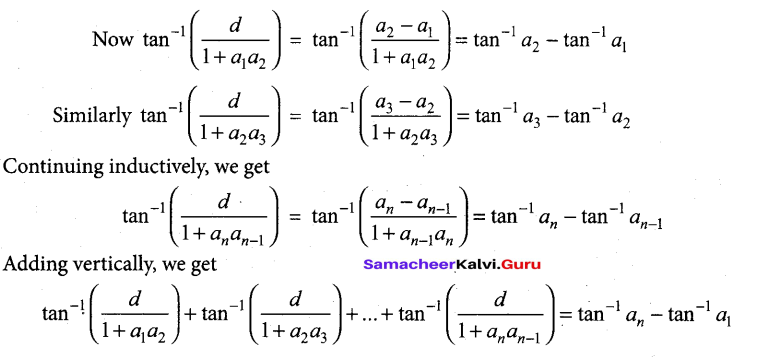
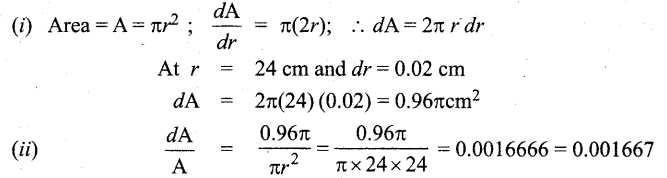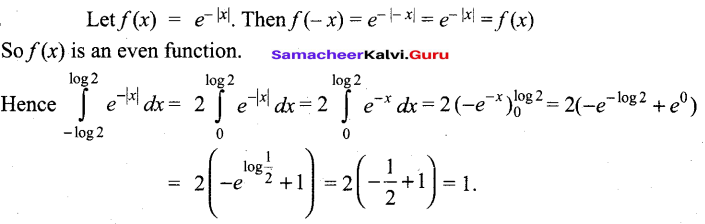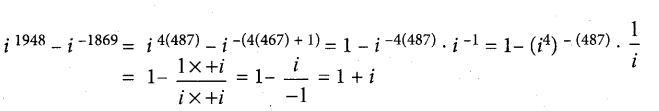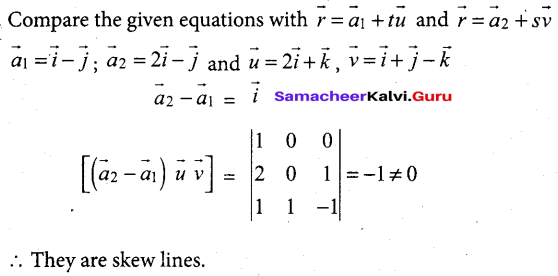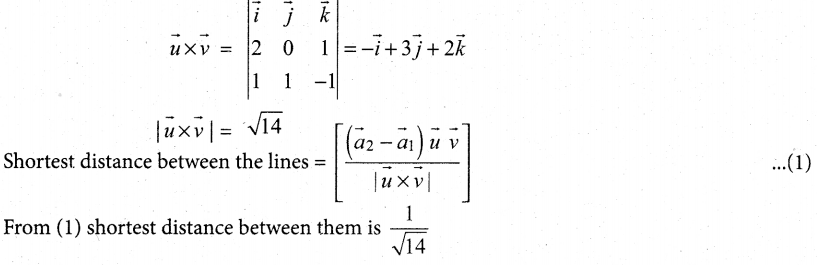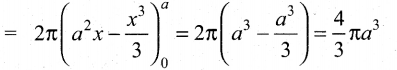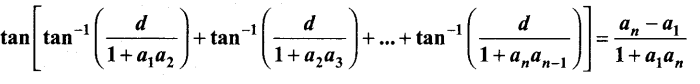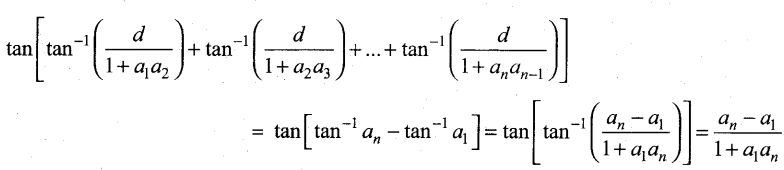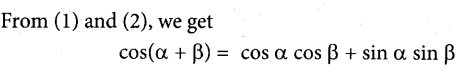Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 9 Electro Chemistry
Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 9 Electro Chemistry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 9 Electro Chemistry
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Chapter 9 Electro Chemistry Textual Evaluation Solved
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The number of electrons that have a total charge of 9650 coulombs is ………..
(a) 6.22 x 1023
(b) 6.022 x 1024
(c) 6.022 x 1022
(d) 6.022 x 10-34
Answer:
(c) 6.022 x 1022
Hint: IF = 96500 C = 1 mole of e– = 6.023 x 1023 e–
9650 C = \(\frac{6.22 \times 10^{23}}{96500} \times 9650\) = 6.022 x 1022
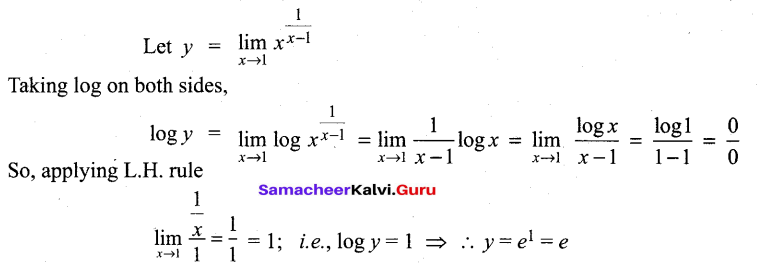
Question 2.
Consider the following half cell reactions:
Mn2+ + 2e– → Mn E° = – 1.18V
Mn2+ → Mn3+ + e– E = – 1.51V
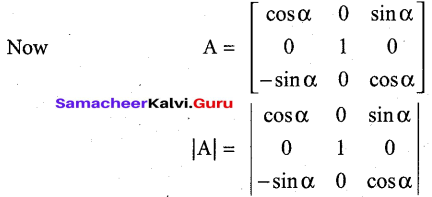
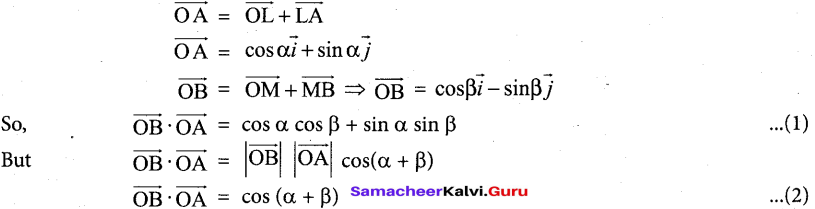
The E for the reaction 3Mn2+ → Mn+2Mn3+, and the possibility of the forward reaction are respectively.
(a) 2.69V and spontaneous
(b) – 2.69 and non spontaneous
(c) 0.33V and Spontaneous
(d) 4.18V and non spontaneous
Answer:
(b) – 2.69 and non spontaneous
Hint: Mn+ + 2e– → Mn(E0red) = 1.18V
2[Mn2+ → Mn3+ + e–] (E0ox) = – 1.51V
3Mn2++ → Mn3+ + 2Mn3+ + (E0cell) = ?
E0red = (E0ox) + (E0cell)
= – 1.51 – 1.18 and non spontaneous
= – 2.69 V
Since E° is – ve ∆G is +ve and the given forward cell reaction is non – spontaneous.
![]()
Question 3.
The button cell used in watches function as follows:
Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) + H2O(1) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2Ag(s) + Zn2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) the half cell potentials are
Ag2O(s) + H2O(1) + 2e– →2Ag(S) + 2OH–(aq) E° = 034V. The cell potential will be
(a) 0.84V
(b) 1.34V
(c) 1.10V
(d) 0.42V
Answer:
(c) 1.10V
Hint: Anodic oxidation: (Reverse the given reaction)
(E0ox ) = 0.76V cathodic reduction
E0cell = (E0ox) + (E0red) = 0.76 + 0.34 = 1.1V
Question 4.
The molar conductivity of a 0.5 mol dm-3 solution of AgNO3 with electrolytic conductivity of 5.76 x 10-3S cm-1at 298 K is ………….
(a) 2.88 S cm2 mo1-1
(b) 11.52 S cm2 mol-1
(c) 0.086 S cm2 mol-1
(d) 28.8 S cm2 mol-1
Answer:
(b) 11.52 S cm2 mol-1
Hint:
A = \(\frac { k }{ M }\) x 10-3 mol-1 m3
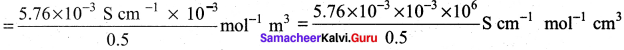
= 11.52 S cm2 mol-1
Question 5.
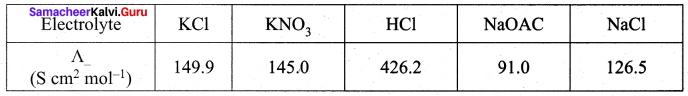
Calculate A0HOAC using appropriate molar conductances of the electrolytes listed above at infinite dilution in water at 25°C.
(a) 517.2
(b) 552.7
(c) 390.7
(d) 217.5
Answer:
(c) 390.7
Hint:
![]()
(426.2 + 91) – (126.5) = 390.7
Question 6.
Faradays constant is defined as
(a) charge carried by I electron
(b) charge carried by one mole of electrons
(c) charge required to deposit one mole of substance
(d) charge carried by 6.22 X 1010 electrons
Answer:
(b) charge carried by one mole of electrons
Hint:
IF = 96500 C = 1 charge of mole of e– = charge of 6.022 x 1023 e–
Question 7.
How many faradays of electricity are required for the following reaction to occur
MnO–4 → Mn2+
(a) 5F
(b) 3F
(C) IF
(d) 7F
Answer:
(a) 5F
Hint:
7MnO–4 + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O
5 moles of electrons i.e., 5F charge is required.
![]()
Question 8.
A current strength of 3.86 A was passed through molten Calcium oxide for 41 minutes and 40 seconds. The mass of Calcium in grams deposited at the cathode is (atomic mass of Ca is 40g / mol and IF = 96500C).
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 8
(d) 6
Answer:
(b) 2
Hint: m = ZIt
41mm 40sec = 2500 seconds
= \(\frac { 40 x 3.86 x 2500 }{ 2 x 96500 }\)
Z = \(\frac { m }{ n x 96500 }\) = \(\frac { 40 }{ 2 x 96500 }\)
= 2g
Question 9.
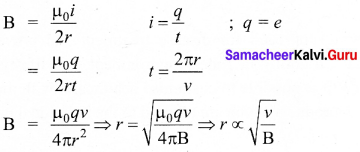
During electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time required to produce 0.1 mol of chlorine gas using a current of 3A is ………..
(a) 55 minutes
(b) 107.2 minutes
(c) 220 minutes
(d) 330 minutes
Answer:
(b) 107.2 minutes
Hint: \(\frac { m }{ ZI }\) (mass of 1 mole of Cl2 gas = 71)
t = \(\frac { m }{ ZI }\) mass of 0.1 mole of Cl2 gas = 7.1 g mol-1)
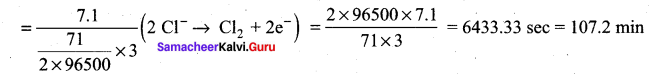
Question 10.
The number of electrons delivered at the cathode during electrolysis by a current of 1 A in 60 seconds is (charge of electron = 1.6 x 10-19C)
(a) 6.22 x 1023
(b) 6.022 x 1020
(c) 3.75 x 1020
(d) 7.48 x 1023
Answer:
(c) 3.75 x 1020
Hint: Q = It
= 1A x 60S
96500 C charge 6.022 x 1023 electrons
60 C charge = \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{96500} \times 960\)
= 3.744 x 1020 electrons
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following electrolytic solution has the least specific conductance?
(a) 2N
(b) 0.002N
(c) 0.02N
(d) 0.2N
Answer:
(b) 0.002N
Hint: In general, specific conductance of an electrolyte decreases with dilution. SO, 0.002N solution has least specific conductance.
Question 12.
While charging lead storage battery
(a) PbSO4 on cathode is reduced to Pb
(b) PbSO4 on anode is oxidised to PbO4
(c) PbSO4 on anode is reduced to Pb
(d) PbSO4 on cathode is oxidised to Pb
Answer:
(c) PbSO4 on anode is reduced to Pb.
Hint: Charging: anode: PbSO4(s) + 2e– → Pb (s) + SO4-2 (aq)
Cathode: PbSO4(s) + 2H2O (1) → PbO2 (s) + SO4-2 (aq) + 2e–
Question 13.
Among the following cells
I. Leclanche cell
II. Nickel – Cadmium cell
III. Lead storage battery
IV. Mercury cell
Primary cells are …………
(a) I and IV
(b) I and III
(c) III and IV
(d) II and III
Answer:
(a) I and IV
Question 14.
Zinc can be coated on iron to produce galvanized iron but the reverse is not possible. It is because
(a) Zinc is lighter than iron
(b) Zinc has lower melting point than iron
(c) Zinc has lower negative electrode potential than iron
(d) Zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron
Answer:
(d) Zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron
Hint: E0Zn+|Zn = – 0.76V and E0Fe2+|Fe = 0.44V. Zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron, iron cannot be coated on zinc.
![]()
Question 15.
Assertion: pure iron when heated in dry air is converted with a layer Of rust.
Reason: Rust has the composition Fe3O4
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(d) both assertion and reason are false.
Hint: Both are false
- Dry air has no reaction with iron
- Rust has the composition Fe2O3 x H2O
Question 16.
In H2 – O2 fuel cell the reaction occur at cathode is ……….
(a) O2(g) + 2H2O (l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq)
(b) H+(aq) + OH–(aq) → H2O (l)
(c) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O (g)
(d) H+ + e– → 1/2 H2
Answer:
(a) O2(g) + 2H2O (l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq)
Question 17.
The equivalent conductance of M/36 solution of a weak monobasic acid is 6mho cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mho cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is ………….
(a) 1.25 x 10-16
(b) 6.25 x 10 -6
(c) 1.25 x 10-4
(d) 6.25 x 10-5
Answer:
(b) 6.25 x 10 -6
Hint: α = \(\frac { 6 }{ 400 }\)
Ka = α2C = \(\frac { 6 }{ 400 }\) x \(\frac { 6 }{ 400 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 36 }\)
= 6.25 x 10-6
![]()
Question 18.
A conductivity cell has been calibrated with a 0.01M, 1:1 electrolytic solution (specific conductance (K = 1.25 x 10-3 S cm-1 ) in the cell and the measured resistance was 800Ω at 250 C. The cell constant is,
(a) 10-1 cm-1
(b) 10-1 cm-1
(c) 1 cm-1
(d) 5.7 x 10-12
Answer:
(c) 1 cm-1
Hint: R = p.\(\frac { 1 }{ A }\)
Cell constant = \(\frac { R }{ ρ }\) = k.R \((\frac { 1 }{ ρ } =k)\) = 1.25 x 10-3 f-1cm-1 x 800Ω = 1cm-1
Question 19.
The conductivity of a saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt AB (1:1 electrolyte) at 298K is 1.85 x 10-5 S m-1. Solubility product of the salt AB at 298K (Λ0m)AB = 14 x 10-3 S m2 mol-1.
(a) 5.7 x 10-2
(b) 1.32 x 1012
(c) 7.5 x 10-12
(d) 1.74 x 10-12
Answer:
(d) 1.74 x 10-12
Question 20.
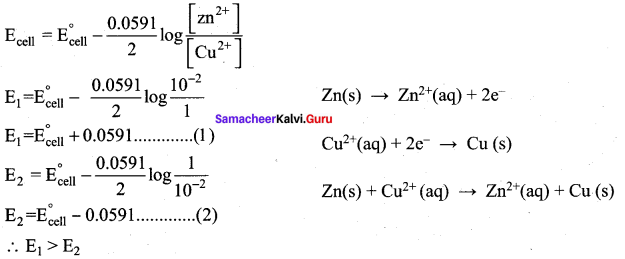
In the electrochemical cell: Zn|ZnSO4 (0.01M)||CuSO4 (1.0M)|Cu , the emf of this Daniel cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that CuSO4 changed to 0.0 1M, the emf changes to E2. From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2?
(a) E1 < E2
(b) E1 > E2
(c) E2 = 0↑E1
(d) E1 = E2
Answer:
(b) E1 > E2
Hint:
Question 21.
Consider the change in oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below:
![]()
Then the species undergoing disproportional is …………..
(a) Br2
(b) BrO4–
(c) BrO3–
(d) HBrO
Answer:
(d) HBrO
Hint:
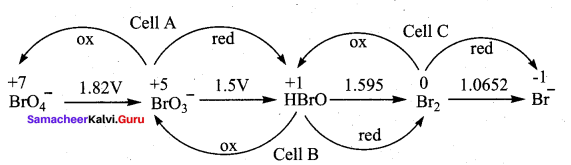
(Ecell)A = – 1.82 + 1.5 = – 0.32V
(Ecell)B = – 1.5 + 1.595 = + 0.095V
(Ecell)C = 1.595 + 1.0652 = – 0.529V
The species undergoing disproportionation is HBrO
Question 22.
For the cell reaction
2Fe3+(aq) + 2I(aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + I2(aq)
EC0cell = 0.24V at 298K. The standard Gibbs energy (∆, G0 ) of the cell reactions is …………
(a) – 46.32 KJ mol-1
(b) – 23.16 KJ mol-1
(c) 46.32 KJ mol-1
(d) 23.16 KJ mor-1
Answer:
(a) – 46.32 KJ mol-1
Question 23.
A certain current liberated 0.504gm of hydrogen in 2 hours. How many grams of copper can be liberated by the same current flowing for the same time in a copper sulphate solution?
(a) 31.75
(b) 15.8
(c) 7.5
(d) 63.5
Answer:
(b) 15.8
![]()
Question 24.
A gas X at 1 atm is bubble through a solution containing a mixture of 1MY– and 1MZ-1 at 25°C . If the reduction potential of Z > Y> X, then
(a) Y will oxidize X and not Z
(b) Y will oxidize Z and not X
(c) Y will oxidize both X and Z
(d) Y will reduce both X and Z
Answer:
(a) Y will oxidize X and not Z
Question 25.
Cell equation: A2+ + 2B– → A2+ + 2B
A2+ + 2e– → AE° = + 0.34V and log10 K = 15.6 at 300K for cell reactions find E° for
B1 + e– → B
(a) 0.80
(b) 1.26
(c) – 0.54
(d) – 10.94
Answer:
(a) 0.80
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry Short Answer
Question 1.
Define anode and cathode
Answer:
- Anode: The electrode at which the oxidation occur is called anode.
- Cathode: The electrode at which the reduction occur is called cathode.
Question 2.
Why does conductivity of a solution decrease on dilution of the solution?
Answer:
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration (on dilution of the solution) both for weak as much as for strong electrolytes. ¡t is because the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current is a solution decreases on dilution.
Question 3.
State Kohlrausch Law. How is it useful to determine the molar conductivity of weak electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Answer:
Kohlrausch’s law:
It is defined as, at infinite dilution the limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivities of its constituent ions.
Determination of the molar conductivity of weak electrolyte at infinite dilution.
It is impossible to determine the molar conductance at infinite dilution for weak electrolytes experimentally. However, the same can be calculated using Kohlraushs Law. For example, the molar conductance of CH3COOH, can be calculated using the experimentally determined molar conductivities of strong electrolytes HCI, NaCI and CH3COONa.
Λ°CH3COONa = λ°Na+ + λ°CH3COONa …….(1)
Λ°HCl = λ°H+ + λ°Cl– ………………(2)
Λ°NaCl = λ°Na+ + λ°Cl– …………….(3)
Equation (1) + Equation (2) – Equation (3) gives,
(Λ°CH3COONa) + (Λ°HCl) – (Λ°NaCl) = λ°H+ + λ°CH3COONa = Λ°CH3COONa
Question 4.
Describe the electrolysis of molten NaCI using inert electrodes.
Answer:
1. The electrolytic cell consists of two iron electrodes dipped in molten sodium chloride and they are connected to an external DC power supply via a key.
2. The electrode which is attached to the negative end of the power supply is called the cathode and the one is which attached to the positive end is called the anode.
3. Once the key is closed, the external DC power supply drives the electrons to the cathode and at the same time
pull the electrons from the anode.
Cell reactions:
Na+ ions are attracted towards cathode, where they combines with the electrons and reduced to liquid sodium.
Cathode (reduction)
Na+(I) + e–Na(1)
E0 = – 2.7 1V
Similarly, Cl– ions are attracted towards anode where they losses their electrons and oxidised to chlorine gas. Anode (oxidation)
2Cl–(1) Cl2(g) + 2e–
E° = – 1 .36V
The overall reaction is,
2Na+(l) + 2Cl–(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl2(g) (g)
E0 = 4.07 V
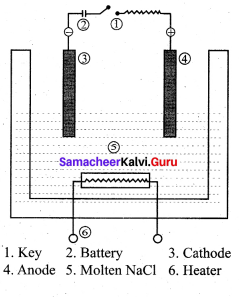
The negative E° value shows that the above reaction is a non-spontaneous one. Hence, we have to supply a voltage greater than 4.07V to cause the electrolysis of molten NaCl. In an electrolytic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction occur at the cathode as in a galvanic cell, but the sign of the electrodes is the reverse i.e., in the electrolytic cell cathode is -ve and the anode is +ve.
![]()
Question 5.
State Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis.
Answer:
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis:
1. First law:
The mass of the substance (M) liberated at an electrode during electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of charge (Q) passed through the cell. M α Q
2. Second law:
When the same quantity of charge is passed through the solutions of different electrolytes, the amount of substances liberated at the respective electrodes are directly proportional to their electrochemical equivalents. M α Z
Question 6.
Describe the construction of Daniel’s cell. Write the cell reaction.
Answer:
The separation of half-reaction is the basis for the construction of Daniel’s cell. It consists of two half cells.
Oxidation half cell:
The metallic zinc strip dips into an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate taken in a beaker.
Reduction half cell:
A copper strip that dips into an aqueous solution of copper sulphate taken in a beaker.
Joining the half cell:
The zinc and copper strips are externally connected using a wire through a switch (k) and a load (example: voltmeter). The electrolytic solution present in the cathodic and anodic compartment are connected using an inverted U tube containing an agar-agar gel mixed with an inert electrolyte such as Kl1, Na2SO4 etc.,
The ions of inert electrolyte do not react with other ions present in the half cells and they are not either oxidized (or) reduced at the electrodes. The solution in the salt bridge Voltmeter cannot get poured out, but through which the ions can move into (or) out of the half cells. When the switch (k) closes the circuit, the electrons flow from zinc strip to copper strip. This is due to the following redox reactions which are taking place at the respective electrodes.
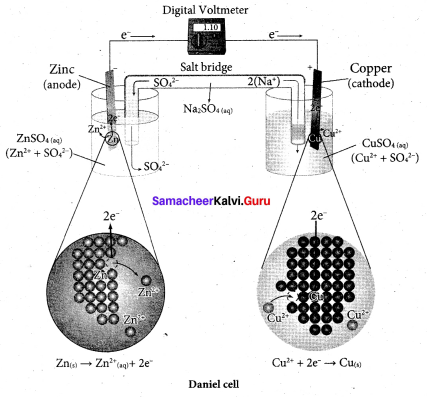
Anodic oxidation:
The electrode at which the oxidation occur is called the anode. In Daniel cell, the oxidation take place at zinc electrode, i.e., zinc is oxidised to Zn2 ions and the electrons. The Zn2 ions enters the solution and the electrons enter the zinc metal, then flow through the external wire and then enter the copper strip. Electrons are liberated at zinc electrode and hence it is negative ( – ve).
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e– (loss of electron-oxidation)
Cathodic reduction:
As discussed earlier, the electrons flow through the circuit from zinc to copper, where the Cu2+ ions in the solution accept the electrons, get reduced to copper and the same get deposited on the electrode. Here, the electrons are consumed and hence it is positive (+ve).
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s) (gain of electron-reduction)
Salt bridge:
The electrolytes present in two half cells are connected using a salt bridge. We have learnt that the anodic oxidation of zinc electrodes results in an increase in the concentration of Zn2+ in solution. i.e., the solution contains more number of Zn2+ ions as compared to SO42- and hence the solution in the anodic compartment would become positively charged.
Similarly, the solution in the cathodic compartment would become negatively charged as the Cu2+ ions are reduced to copper i.e., the cathodic solution contain more number of SO2-4 ions compared to Cu2+.
Completion of circuit:
Electrons flow from the negatively charged zinc anode into the positively charged copper electrode through the external wire, at the same time, anions move towards anode and cations are move towards the cathode compartment. This completes the
circuit.
Consumption of Electrodes:
As the Daniel cell operates, the mass of zinc electrode gradually decreases while the mass of the copper electrode increases and hence the cell will function until the entire metallic zinc electrode is converted in to Zn2+ the entire Cu2+ ions are converted in to metallic copper.
Daniel cell is represented as
Zn(s)|Zn2+(aq)||Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s)
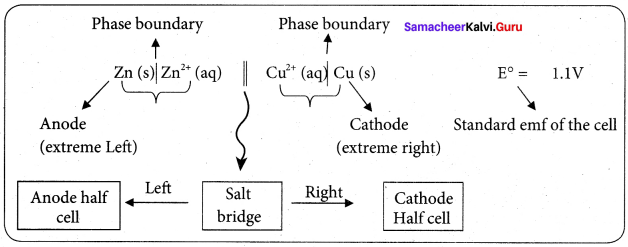
Question 7.
Why is anode in galvanic cell considered to be negative and cathode positive electrode?
Answer:
A galvanic cell works basically in reverse to an electrolytic cell. The anode is the electrode where oxidation takes place, in a galvanic cell, it is the negative electrode, as when oxidation occurs, electrons are left behind on the electrode.
The anode is also the electrode where metal atoms give up their electrons to the metal and go into solution. The electron left behind on it render ¡t effectively negative and the electron flow goes from it through the wire to the cathode.
Positive aqueous ions in the solution are reduced by the incoming electrons on the cathode. This why the cathode is a positive electrode, because positive ions are reduced to metal atoms there.
![]()
Question 8.
The conductivity of a 0.01%M solution of a 1:1 weak electrolyte at 298K is 1.5 x 10-4 S cm-1.
- molar conductivity of the solution
- degree of dissociation and the dissociation constant of the weak electrolyte
Given that
λ0cation = 248.2 S cm2 mol-1
λ0anion = 51.8 S cm2 mol-1
Answer:
1. Molar conductivity
C = 0.01M
k = 1.5 x 10-4 S cm-1
(or)
K = 1.5 x 10-2 S m-1
\(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{\mathrm{C}}\) S m-1 mol-1 m3 = \(\frac{1.5 \times 10^{-2} \times 10^{-3}}{0.01}\) S m2 mol-1
Λm = 1.5 x 10-3 s m-1
2. Degree of dissociation
α = \(\frac{\Lambda_{\mathrm{m}}}{\Lambda_{\infty}^{\circ}}\) (or) α = \(\frac{\Lambda_{\mathrm{m}}}{\Lambda_{\mathrm{m}}^{\circ}}\)
= (248.2 + 51.8)S cm2 mol-1
= 300 S cm2 mol-1
Ka = \(\frac{\alpha^{2} C}{1-\alpha}\)
= \(\frac{(0.05)^{2}(0.01)}{1-0.05}\)
Ka = 2.63 x 10-5
Question 9.
Which of 0.1M HCI and 0.1 M KCI do you expect to have greater molar conductance and why?
Answer:
Compare to 0.1M HCI and 0.1 M KCI, 0.1M HCl has greater molar conductance.
- Molar conductance of 0.1M HCl = 39.132 x 10-3 S m2 mol-1.
- Molar conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 12.896 x 10-3 S m2 mol-1
Because, H+ ion in aqueous solution being smaller size than K+ ion and H+ ion have greater mobility than K ion. When mobility of the ion increases, conductivity of that ions also increases. Hence, 0. 1M HCI solution has greater molar conductance than 0.1 M KCI solution.
Question 10.
Arrange the following solutions in the decreasing order of specific conductance.
- 0.01M KCI
- 0.005M KCI
- 0.1M KCI
- 0.25 M KCI
- 0.5 M KCI
Answer:
0.005M KCl > 0.01M KCI > 0.1M KCI > 0.25KCl > 0.5 KCI.
Specific conductance and concentration of the electrolyte. So if concentration decreases, specific conductance increases.
Question 11.
Why is AC current used instead of DC in measuring the electrolytic conductance?
Answer:
1. AC current to prevent electrolysis of the solution.
2. If we apply DC current to the cell the positive ions will be attracted to the negative plate and the negative ions to the positive plate. This will cause the composition of the electrolyte to change while measuring the equivalent conductance.
3. So DC current through the conductivity cell will lead to the electrolysis of the solution taken in the cell. To avoid such a electrolysis, we have to use AC current for measuring equivalent conductance.
Question 12.
0.1M NaCI solution is placed in two different cells having cell constant 0.5 and 0.25cm-1 respectively. Which of the two will have greater value of specific conductance.
Answer:
The specific conductance values are same. Because the reaction (cation) of cell constant does not change.
![]()
Question 13.
A current of 1 .608A is passed through 250 mL of 0.5M solution of copper sulphate for 50 minutes. Calculate the strength of Cu2+ after electrolysis assuming volume to be constant and the current efficiency is 100%.
Answer:
Given, I = I .608A
t = 50 min (or) 50 x 60 = 3000 S
V = 250 mL
C = 0.5M
η = 100%
The number of Faraday’s of electricity passed through the CuSO4 solution
Q = It
= Q = 1.608 x 3000
Q = 4824C
Number of Faraday’s of electricity = \(\frac { 4824C }{ 96500C }\) = 0.5F
Electrolysis of CuSO4
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
The above equation shows that 2F electricity will deposit 1 mole of Cu2+
0.5F electicity will deposit \(\frac { 1mol }{ 2F }\) x 0.5F = 0.025 mol
Initial number of molar of Cu2+ in 250 ml of solution = \(\frac { 1mol }{ 250mL }\) x 250mL = 0.125 mol
Number of molar of Cu2+ after electrolysis 0.125 – 0.025 = 0.1 mol
Concentration of Cu2+ = \(\frac { 0.1mol }{ 250mL }\) X 1000 mL = 0.4 M
Question 14.
Can Fe3+ oxidises Bromide to bromine under standard conditions?
Given:
![]()
Answer:
Required half cell reaction
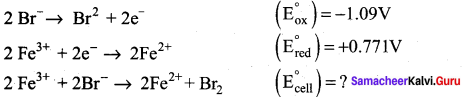
E0cell = (E0ox) + (E0red) = – 1.09 + 0.771 = – 0.319V
We know that ∆G° = – nFE0cell
If E0cell is -ve; ∆G is +ve and the cell reaction is non-spontaneous.
Hence, Fe3+ cannot oxidise Bromide to Bromine.
Question 15.
Is it possible to store copper sulphate in an iron vessel for a long time?
Given:
![]()
Answer:
E0cell = (E0ox) + (E0red) = 0.44 V + 0.34V = 0.78V
These +ve E0cell values shows that iron will oxidise and copper will get reduced i.e., the vessel
will dissolve. Hence it is not possible to store copper sulphate in an iron vessel.
Question 16.
Two metals M1 and M2 have reduction potential values of – xV and + yV respectively. Which will liberate H2 in H2SO4?
Answer:
Metals having negative reduction potential acts as powerful reducing agent. Since M1 has – xV, therefore M1 easily liberate H2 in H2SO4. Metals having higher oxidation potential will liberate H2 from H2SO4. Hence, the metal M1 having + xV, oxidation potential will liberate H2 from H2SO4.
Question 17.
Reduction potential of two metals M1 and M2 are
![]()
Predict which one Is better for coating the surface of iron.
Given:![]()
Answer:
Oxidation potential of M1 is more +ve than the oxidation potential of Fe which indicates that it will prevent iron from rusting.
Question 18.
Calculate the standard emf of the cell: Cd | Cd2+|| Cu2+ | Cu and determine the cell reaction. The standard reduction potentials of Cu2+ | Cu and Cd2+ | Cd are 0.34V and – 0.40 volts respectively. Predict the feasibility of the cell reaction.
Answer:
Cell reactions:
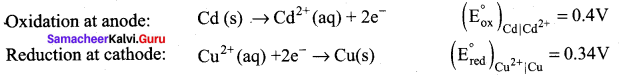
Cd(s) + 2e– Cd2+ + Cu(s)
E0cell = (E0ox) + (E0red) = 0.4 + 0.34
emf is +ve, so ∆G is (-)ve, the reaction is feasible.
Question 19.
In fuel cell H2 and O2 react to produce electricity. In the process, H2 gas is oxidised at the anode and O2 at cathode. If 44.8 litre of H2 at 25°C and also pressure reacts in 10 minutes, what is average current produced? If the entire current is used for electro deposition of Cu from Cu2+, how many grams of Cu deposited?
Answer:
Oxidation at anode:
2H2(g) + 4OH– (aq) → 4H2O (1) + 4e–
1 mole of hydrogen gas produces 2 moles of electrons at 25°C and 1 atm pressure, 1 mole of hydrogen gas occupies = 22.4 litres
∴no. of moles of hydrogen gas produced = \(\frac{1 \mathrm{mole}}{22.4 \text { litres }}\) x 44.8 litres = 2 moles of hydrogen
∴2 of moles of hydrogen produces 4 moles of electro i.e., 4F charge. We know that Q = It
I = \(\frac { Q }{ t }\) = \(\frac{4 \mathrm{F}}{10 \mathrm{mins}}\) = \(\frac { 4×96500 }{ 10x60s }\)
I = 643.33 A
Electro deposition of copper
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
2F charge is required to deposit
1 mole of copper i.e., 63.5 g
If the entire current produced in the fuel cell i.e., 4 F is utilised for electrolysis, then 2 x 63.5 i.e., 127.0 g copper will be deposited at cathode.
![]()
Question 20.
The same amount of electricity was passed through two separate electrolytic cells containing solutions of nickel nitrate and chromium nitrate respectively. If 2.935g of Ni was deposited in the first cell. The amount of Cr deposited in the another cell? Given: molar mass of Nickel and chromium are 58.74 and 52gm-1 respectively.
Answer:
Ni2+ (aq) + 2e– → Ni (s)
Cr2+(aq) + 3e– → Cr(s)
The above reaction indicates that 2F charge is required to deposit 58.7 g of Nickel form nickel nitrate and 3F charge is required to deposit 52g of chromium. Given that 2.935 gram of Nickel is deposited 2F
The amount of charge passed through the cell = \(\frac { 2F }{ 58.7g }\) x 2.935g = 0.1F
If 0. IF charge is passed through chromium nitrate the amount of chromium deposited
= 52g x 0.IF = 1.733g
Question 21.
0.1M copper sulphate solution in which copper electrode is dipped at 25C. Calculate the electrode potential of copper.
![]()
Answer:
Given that
[Cu2+] = 0.1 M
E0Cu2+|Cu = 0.34
Ecell = ?
Cell reaction is Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu (s)
Ecell = E0 – \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log \(\frac{[\mathrm{Cu}]}{\left[\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}\right]}\) = 0.34 – \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ 2 }\) log \(\frac { 1 }{ 0.1 }\)
= 0.34 – 0.0296 = 0.31 V
Question 22.
For the cell Mg(s) | Mg2+(aq) || Ag+ (aq) | Ag (s), calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and maximum work that can be obtained during operation of cell. Given:
![]()
Answer:
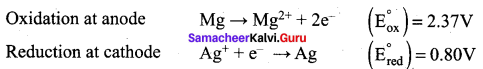
E0cell = (E0ox) + (E0red) = 2.37 + 0.80 = 3.17 V
Overall reaction
Mg + 2Ag+ → Mg2+ + 2Ag
∆G° = -nFE°
= – 2 x 96500 x 3.17
= – 6.118 x 105 J
We know that Wmax = ∆G°
Wmax = + 6.118 x 105 J
Relationship between ∆G° and Keq is,
∆G = – 2.303 RT logKeq
∆G = – 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 log Keq [25°C = 298 K]
log Keq = \(\frac{6.118 \times 10^{5}}{2.303 \times 8.314 \times 298}\) = \(\frac{6.118 \times 10^{5}}{5705.84}\)
log Keq = 107.223
Keq = Antilog (107.223)
Question 23.
8.2 x 1012 litres of water is available in a lake. A power reactor using the electrolysis of water in the lake produces electricity at the rate of 2 x 106 Cs-1 at an appropriate voltage. How many years would it like to completely electrolyse the water in the lake. Assume that there is no loss of water except due to electrolysis.
Answer:
Hydrolysis of water:
At anode: 2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e– …………..(1)
At cathode: 2H2O + 2e– → H2 + 2OH–
Overall reaction: 6H2O → 4H– + 4OH– +2H2 + O2
(or)
Equation (1) + (2) x 2
= 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
According to Faraday’s Law of electrolysis, to electrolyse two mole of Water
(36g ≃ 36 mL. of H2O), 4F charge is required alternatively, when 36 mL of water is electrolysed,
the charge generated = 4 x 96500 C.
When the whole water which is available on the lake is completely electrolysed the amount of charge generated is equal to
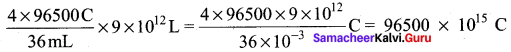
Given that in 1 second, 2 x 106 C is generated therefore, the time required to generate
96500 x 1015 C is = \(\frac{1 \mathrm{S}}{2 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{C}}\) x 96500 x 1015C = 48250 x 109 S
Number of year = \(\frac{48250 \times 10^{9}}{365 \times 24 \times 60 \times 60}\) 1 year = 365 days
= 1.5299 x 106
= 365 x 24 hours
= 365 x 24 x 60 min
= 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 sec
![]()
Question 24.
Derive an expression for Nernst equation.
Answer:
Nernst equation is the one which relates the cell potential and the concentration of the species involved in an electrochemical reaction.
Let us consider an electrochemical cell for which the overall redox reaction is,
Answer:
xA + yB = lC + mD
The reaction quotient Q is,
\(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\)
We know that,
∆G = ∆G0 + RT ln Q
∆G = – nFEcell
∆G0 = -nFE0cell
equation (1) becomes
– nFEcell = -nFE0cell + RT ln Q
Subsitute the Q value in equation (2)
– nFEcell = – nFE0cell + RT ln \(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\). ………..(3)
Divide the whole equation (3) by – nF
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { RT }{ nF }\) ln \(\left(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\right)\)
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { 2.303RT }{ nF }\) log \(\left(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\right)\) ……………(4)
This is called the Nernst equation.
At 25°C (298 K) equation (4) becomes,
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { 2.303×8.314×298 }{ nx96500 }\) log \(\left(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\right)\)
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log \(\left(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{1}[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{m}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{x}}[\mathrm{B}]^{\mathrm{y}}}\right)\)
Question 25.
Write a note on sacrificial protection.
Answer:
In this method, the metallic structure to be protected is made cathode by connecting it with more active metal (anodic metal). So that all the corrosion will concentrate only on the active metal. The artificially made anode thus gradually gets corroded protecting the original metallic structure. Hence this process is otherwise known as sacrificial anodic protection. Al, Zn and Mg are used as sacrificial anodes.
Question 26.
Explain the function of H2 – O2 fuel cell.
Answer:
In this case, hydrogen act as a fuel and oxygen as an oxidant and the electrolyte is aqueous KOH maintained at 200°C and 20 – 40 atm. Porous graphite electrode containing Ni and NiO serves as the inert electrodes. Hydrogen and oxygen gases are bubbled through the anode and cathode, respectively.
Oxidation occurs at the anode:
2H2(g)+ 4OH-(aq) → 4H2O(1) + 4e–
Reduction occurs at the cathode O2(g) + 2 H2O(1) + 4e– → 4 OH– (aq)
The overall reaction is 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(1)
The above reaction is the same as the hydrogen combustion reaction, however, they do not react directly ie., the oxidation and reduction reactions take place separately at the anode and cathode respectively like H2 – O2 fuel cell. Other fuel cell like propane – O2 and methane O2 have also been developed.
Question 27.
Ionic conductance at infinite dilution of Al3+ and SO42- are 189 and 160 mho cm2 equiv-1. Calculate the equivalent and molar conductance of the electrolyte Al2(SO4) at infinite dilution.
Answer:
1. Molar conductance
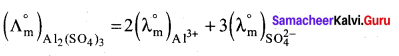
= (2 x 189) + (3 x 160)
= 378 + 480
= 858 mho cm2 mol-1
2. Equivalent conductnace
![]()
= \(\frac { 189 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 160 }{ 2 }\)
= 143 mho cm2 (g equiv)-1
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
Calculate the molar conductance of 0.01M aqueous KCI solution at 25°C . The specific conductance of KCl at 25°C is 14.114 x 10-2 Sm-1.
Answer:
Concentration of KCI solution = 0.01 M.
Specific conductance (K) = 14.114 x 10-2 S m-1
Molar conductance (Λm) = ?
Λm = \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{M}\) = \(\frac{14.114 \times 10^{-2} \times 10^{-3}}{0.01}\)
S m-1 mol-1 m3
Λm = 14.114 x 10-5 x 102 = 14.114 x 10-3 Sm2 mol-1
Question 2.
The resistance of 0.15M solution of an electrolyte is 50. The specific conductance of the solution is 2.4 Sm-1. The resistance of 0.5 N solution of the same electrolyte measured using the same conductivity cell is 480Ω. Find the equivalent conductivity of 0.5 N solution of the electrolyte.
Answer:
Given that R1 = 50Ω
R2 = 480Ω
K1 =2.4Sm-1
K2 = ?
N1 = 0.15N
N2 = 0.5N
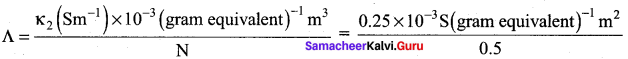
= 5 x 10-4sm2 gram equivalent-1
We know that
\(\frac{\text { Cell constant }}{\mathrm{R}}\)
\(\frac{\kappa_{2}}{\kappa_{1}}\) = \(\frac{R_{1}}{R_{2}}\)
k2 = k1 x \(\frac{R_{1}}{R_{2}}\) = 2.4 Sm-1 x \(\frac{50 \Omega}{480 \Omega}\) = 0.25 Sm-1
Question 3.
The emf of the following cell at 25°C is equal to 0.34v. Calculate the reduction potential of copper electrode.
Pt(s) | H2(g,1atm) | H+ (aq,1M) || Cu2+(aq,1M) | Cu(s)
Answer:
SHE Value is zero
E°cell = E°R – E°L
= 0.34 – 0 = 0.34V
The reduction potential of copper electrode = 0.34V
![]()
Question 4.
Using the calculated emf value of zinc and copper electrode, calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C.
Zn (s) | Zn2+ (aq, 1M) || Cu2+(aq, 1M) | Cu (s)
Answer:
E°cell = E°R – E°L
Ezn/zn2+ = 0.76V
ECu/Cu2+ = 0.76V
E°cell = 0.76 – (- 0.34V)
E°cell = 0.76 – (- 0.34)
E°cell = + 1.1 V
Question 5.
Write the overall redox reaction which takes place in the galvanic cell,
Pt(s) | Fe2+(aq),Fe2+(aq) || MnO–4(aq), H+(aq), Mn2+(aq) || Pt(s)
Answer:
At Anode half cell – 5Fe2+(aq) → 5Fe3+(aq) + 5e–
At cathode half cell – MnO–4(aq) + 8H+(aq) + 5e– → Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(1)
Overall redox reaction – 5Fe2+(aq) + MnO–4(aq) + 8H+(aq) → 5Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(1)
Question 6.
The electrochemical cell reaction of the Daniel cell is
Zn (s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
What is the change in the cell voltage on increasing the ion concentration in the anode compartment by a factor 10?
Answer:
Zn (s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
ln the case E°cell = 1.1V
Reaction quotient Q for the above reaction is, Q = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{Zn}^{2+}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}\right]}\)
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log \(\frac{\left[Z n^{2+}\right]}{\left[C u^{2+}\right]}\)
If suppose concentration of Cu2+ is 1 .OM then the concentration of Zn2+ is 10M (why because,
ion concentration in the anode compartment increased by a 10 factor)
Ecell = 1.1 – \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log \((\frac { 10 }{ 1 })\)
= 1.1 – 0.02955 ……………….(1)
= 1.070 V (cell voltage decreased)
Thus, the initial voltage is greater than E° because Q < 1. As the reaction proceeds, [Zn2+] in the anode compartment increases as the zinc electrode dissolves, while [Cu2+] in the cathode compartment decreases as metallic copper is deposited on the electrode.
During this process, the Q = [Zn2+] [Cu2+] steadily increases and the cell voltage therefore steadily decreases. [Zn2+] will continue to increase in the anode compartment and [Cu2+] will continue to decrease in the cathode compartment. Thus the value of Q will increase further leading to a further
decrease in value.
Question 7.
A solution of a salt of metal was electrolysed for 150 minutes with a current of 0.15 amperes. The mass of the metal deposited at the cathode is 0.783g. calculate the equivalent mass of the metal.
Answer:
Given,
I = 0.15 amperes
t = 150 mins
= t = 15O x 6Osec
= t = 9000sec
Q = It
= Q = 0.15 x 9000 coulombs
= Q = 1350 coulombs
Hence, 135 coulombs of electricity deposit is equal to 0.783g of metal.
96500 coulombs of electricity, \(\frac { 0.783 x 96500 }{ 1350 }\) = 55.97 gm of metal
Hence equivalent mass of the metal is 55.97
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry Example Problems
Question 1.
A conductivity cell has two platinum electrodes separated by a distance 1.5 cm and the cross sectional area of each electrode is 4.5 sq cm. Using this cell, the resistance of 0.5 N electrolytic solution was measured as 15?. Find the specific conductance of the solution.
Solution.
k = \(\frac { 1 }{ 15Ω }\) x \(\frac{1.5 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{m}}{4.5 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{m}^{2}}\) = 2.22S m-1
l = 1.5cm = 1.5 x 102m
A = 4.5 cm2 x (10-4)m2
R = 15Ω
Question 2.
Calculate the molar conductance of 0.025M aqueous solution of calcium chloride at 25°C. The specific conductance of calcium chloride is 12.04 x 102S m3.
Answer:
Molar conductance
Λm = \(\frac{\left(\mathrm{Sm}^{-1}\right) \times 10^{-3}}{\mathrm{M}}\) mol-1 m3
= \(\frac{\left(12.04 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{Sm}^{-1}\right) \times 10^{-3}}{0.025}\) mol-1 m3 = 581 . 6 10-2 S m2 mol1
Question 3.
The resistance of a conductivity cell is measured as 190Ω using 0.1M KCI solution (specific conductance of 0.1M KCI is 1.3 Sm-1). When the same cell is filled with 0.003M sodium chloride solution, the measured resistance is 6.3K?. Both these measurements are made at a particular temperature. Calculate the specific and molar conductance of NaCl solution.
Answer:
Given that
K = 1.3 S m-1 (for 0.1 M KCI solution)
R = 190Ω
\(\left(\frac{l}{A}\right)\) = k.R = (1.3 S m-1) (190?) = 247m-1
k(NaCl) = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{(\mathrm{NaCT})}}\)\(\left(\frac{l}{A}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{6.3 \mathrm{K} \Omega}\) (247m-1)
= 39.2 x 10-3Sm-1
Λm = \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{mol}^{-1} \mathrm{m}^{3}}{\mathrm{M}}\) = \(\frac{39.2 \times 10^{-3}\left(\mathrm{Sm}^{-1}\right) \times 10^{-3}\left(\mathrm{mol}^{-1} \mathrm{m}^{3}\right)}{0.003}\)
Λm = 13.04 x 10-3Sm2 mol-1
Question 4.
The net redox reaction of a galvanic cell is given below
2 Cr (s) + 3Cu2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3Cu(s)
Write the half reactions and describe the cell using cell notation.
Answer:
Anodic oxidation: 2Cr(s) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 6e– …………..(1)
Cathodic reduction: 3Cu2+ + 6e– → 3Cu(s) ………….(2)
Cell Notation is: Cr(s) | CI3+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
Question 5.
Let us calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C using Nernst equation.
Cu (s) | Cu2+(0.25 aq, M) || Fe3+(0.05 aq M) | Fe2+(0.1 aq M) | pt(s)
Answer:
Given: ![]()
Half reactions are
Cu (s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e– ……………(1)
2 Fe3+(aq) + 2e– → 2Fe2+(aq) ……………(2)
the overall reaction is Cu (s) + 2 Fe3+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq), and n = 2
Apply Nernst equation at 25°C
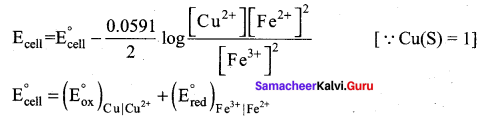
Given standard reduction potetial of Cu2+ | Cu is o.34

Question 6.
A solution of silver nitrate Is electrolysed for 20 minutes with a current of 2 amperes. Calculate the mass of silver deposited at the cathode.
Answer:
Electrochemical reaction at cathode is Ag+ + e– Ag (reduction)
m = ZIt
m = \(\frac{108 \mathrm{gmol}^{-1}}{96500 \mathrm{Cmol}^{-1}} \times 2400 \mathrm{C}\)
m = 2.68 g
z = \(\frac{\text { molarmass of } \mathrm{Ag}}{(96500)}\) = \(\frac{108}{1 \times 96500}\)
I = 2Ag
t = 20 x 60s = 1200s
It = 2A x 1200S = 2400C
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry Additional Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry 1 Marks Questions And Answers
I. Choose the best answer and write it.
Question 1.
Which one of the following is an example of the conductor?
(a) PVC
(b) Bakelite
(c) Aluminium
(d) Rubber
Answer:
(c) Aluminium
Question 2.
Which one of the following can act as an insulator?
(a) Bakelite
(b) Aluminium
(c) Copper
(d) NaCI Solution
Answer:
(a) Bakelite V
Question 3.
Which form of energy is converted to electrical energy in batteries?
(a) tidal energy
(b) Chemical energy
(c) mechanical energy
(d) atomic energy
Answer:
(b) Chemical energy
Question 4.
Electrochemical reactions are generally ………..
(a) Reduction reactions
(b) oxidation reactions
(c) Redox reactions
(d) condensation reactions
Answer:
(c) Redox reactions
Question 5.
Consider the following statements.
Answer:
(i) Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but one form of energy can be converted to another form
(ii) In batteries, electrical energy is converted to chemical energy.
(iii) Electrochemjcal reactions are redox reactions.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) i & ii only
(b) ii only
(c) i only
(d) iii only
Answer:
(b) ii only
Question 6.
Which one of the following represents Ohm’s law?
(a) V = IR
(b) R = \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\)
(c) I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
(d) R = VI
Answer:
(a) V = IR
Question 7.
The unit of resistivity is …………
(a) Ω m-1
(b) Ω m
(c) m-1Ohm2
(d) Ω-1m-1
Answer:
(b) Ω m
![]()
Question 8.
When cell constant is unit, the resistance is known as …………
(a) specific resistance
(b) conductance
(c) specific conductance
(d) equivalent conductance
Answer:
(a) specific resistance
Question 9.
The unit of specific resistance is equal to ………..
(a) Ohm metre
(b) Ohm-1 metre
(c) Ohm-1 metre-1
(d) Ohm
Answer:
(a) Ohm metre
Question 10.
Which is the SI unit of conductance?
(a) Siemen-1 (or) S-1
(b) Siemen (or) S
(c) Sm-1
(d) S-1m-1
Answer:
(b) Siemen (S)
![]()
Question 11.
Which one of the following represents specific conductance (kappa)?
(a) \(\frac { I }{ C }\) . \(\frac { l }{ a }\)
(b) \(\frac { I }{ P }\) . \(\frac { a }{ I }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) . \(\frac{a}{l^{2}}\)
(d) \(\frac { I }{ P }\) . \(\frac { l }{ a }\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac { I }{ P }\) . \(\frac { l }{ a }\)
Question 12.
Which one is the unit of specific conductance?
(a) Ohm m
(b) Ohm-1 m
(c) Ohm m-1
(d) Ohm-1 m-1.
Answer:
(d) Ohm-1m-1
Question 13.
Which one of the following formulas represents equivalent conductance?
(a) \(\frac { I }{ P }\).\(\frac { l }{ a }\)
(b) \(\frac { I }{ P }\).\(\frac { A }{ l }\)
(c) C x \(\frac { l }{ a }\)
(d) \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{N}\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{N}\)
Question 14.
The unit of equivalent conductance is …………
(a) Sm2g equivalenr’
(b) Sm-1
(c) Ohm-1m-1
(d) Ohm m
Answer:
(a) Sm2g equivalent-1
Question 15.
Consider the following statements:
(i) Solvent of higher dielectric constant show very low conductance in solution.
(ii) Conductance is directly proportional to the viscosity of the medium.
(iii) Molar conductance of a solution increases with increase in dilution.
Which of the above statement is / are correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(c) (iii) only
![]()
Question 16.
Consider the following statements:
(i) If the temperature of the electrolytic solution increases, conductance decreases.
(ii) Conductivity increases with the decrease in viscosity.
(iii) Molar conductance of a solution decreases with increase in dilution.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) & (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) & (iii)
Question 17.
Which one of the following is used to measure conductivity of ionic solutions?
(a) metre scale
(b) wheat stone bridge
(c) Dynamo
(d) Ammeter
Answer:
(b) wheat stone bridge
Question 18.
Which of the following is used to calculate the conductivity of strong electrolytes?
(a) Kohlraush’s law
(b) Henderson equation
(c) Debye-Huckel and Onsagar equation
(d) Ostwald’s dilution law
Answer:
(c) Debye-Huckel and Onsagar equation
Question 19.
Which one of the following represents Debye-Huckel and Onsagar equation?
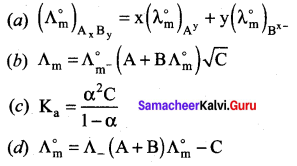
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
The value of A in Debye – Huckel and Onsagar equation is ……….
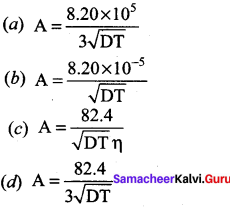
Answer:
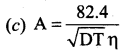
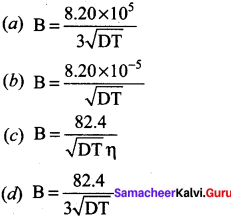
Question 21.
The value of B in Debye Huckel and onsagar equation is …………
Answer:
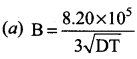
Question 22.
Kohlrausch’s law is applied to calculate
(a) molar conductance at infinite dilution of a weak electrolyte
(b) degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte
(c) solubility of a sparingly soluble salt
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 23.
In which of the following interconversion of electrical energy into chemical energy and vice versa take place?
(a) electrochemical cell
(b) electric cell
(c) Dynamo
(d) AC generator
Answer:
(a) electrochemical cell
Question 24.
Consider the following statements:
(i) In Galvanic cell, chemical energy is’converted into electrical energy.
(ii) In electrolytic cell, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
(iii) In voltaic cell, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) only
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(b) (iii) only
![]()
Question 25.
In Galvanic cell, the Zinc metal strip placed gets ………….
(a) Oxidised
(b) reduced
(c) hydrolysed
(d) condensed
Answer:
(a) Oxidised
Question 26.
Consider the following statements:
(i) In Galvanic cell, Zinc is oxidised to Zn2+ ions and Cu2+ ions are reduced to copper
(ii) In Galvanic cell, Zn2+ ions are reduced to Zinc and copper is oxidised to Cu2+ ions
(iii) In Galvanic cell, Zn and copper both get oxidised.
Which of the above statement is / are correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) only
Question 27.
The salt bridge used in Daniel cell contains
(a) Na2SO4 + NaCl
(b) Agar-Agar gel + Na2SO4
(c) Silica gel + CuSO4
(d) ZnSO4 + CuSO4
Answer:
(b) Agar-Agar gel + Na2SO4
Question 28.
Consider the following statements.
(i) In Daniel cell, when the switch (k) closes the circuit, the electrons flow from Zinc strip to copper strip.
(ii) In Daniel cell, when the switch (k) closes the circuit, the electrons flow from copper strip to Zinc strip
(iii) In Daniel cell, when the Switch (k) opens the circuit, the electrons flow from Zinc to copper.
Which of the above statement is / are correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(a) (i) only
Question 29.
Which one of the following can act as an inert electrode?
(a) Graphite
(b) Copper
(c) Platinum
(d) either a (or) e
Answer:
(a) either a (or) c
Question 30.
The SI unit of cell potential is ………….
(a) Ampere
(b) Ohm
(c) Volt
(d) Ohm-1
Answer:
(c) Volt
![]()
Question 31.
The emf of Daniel cell Zn(s) + Zn2+aq(1m) || Cu2+aq(1m) | Cu(S) iS equal to …………
(a) – 1.107 Volts
(b) 1.107 Volts
(c) 3.4 Volt
(d) 7.6 Volt
Answer:
(b) 1.107 Volts
Question 32.
Which instrument is used to measure potential difference?
(a) Ammeter
(b) Voltmeter
(c) Wheat stone bridge
(d) metre bridge
Answer:
(b) Voltmeter
Question 33.
The value of EMF of standard hydrogen electrode at 25°C is …………
(a) maximum
(b) zero
(c) negative
(d) positive
Answer:
(b) zero
Question 34.
The electrode used in SHE is made of ………….
(a) graphite
(b) copper
(c) platinum
(d) iron
Answer:
(c) Platinum
Question 35.
What is the charge of one electron?
(a) 1.602 x 1019C
(b) 1.6 x 10-19C
(c) 9645C
(d) 96488C
Answer:
(b) 1.6 x 10-19C
Question 36.
The maximum work that can be obtained from a galvanic cell is ………..
(a) + nFE
(b) – nFE
(c) 2F
(d) 96500 F
Answer:
(b) – nFE
Question 37.
For all spontaneous cell reactions, the value of ?G should be ………….
(a) constant
(b) zero
(c) negative
(d) positive
Answer:
(c) negative
![]()
Question 38.
The value of one Faraday is equal to …………..
(a) 96400 C
(b) 96500 C
(c) 1 .602 x 10-19C
(d) 1 .602 x 1019C
Answer:
(b) 96500 C
Question 39.
The relationship between standard free energy change and equilibrium constant is expressed as ………..
(a) ΔG° = -RTInkeq
(b) ΔG = RTlnkeq
(c) ΔG° = \(-\frac{1}{\mathrm{RT} \ln \mathrm{k}_{\mathrm{eq}}}\)
(d) ΔG = RTlogeq
Answer:
(a) ΔG° -RThilc
Question 40.
Which equation relates the cell potential and the concentration of the species involved in an electro chemical reaction?
(a) Henderson equation
(b) Arrhenius equation
(c) Debye Huckel Onsagar equation
(d) Nemst equation
Answer:
(a) Nernst equation
Question 41.
Which one of the following is Nernst equation.
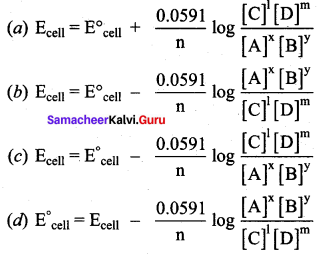
Answer:
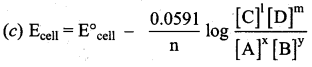
Question 42.
Gibbs free energy can be related to cell emf as follows.
(a) ΔG° = – nFEcell
(b) ΔG° = – nFE°cell
(c) ΔG = nFEcell
(d) ΔG° = nFE°cell
Answer:
(b) ΔG° = – nFE°cell
Question 43.
Which one of the following represents Faraday’s first law?
(a) m = ZIt
(b) m = \(\frac { Z }{ It }\)
(c) m = \(\frac { It }{ Z }\)
(d) Z = mIt
Answer:
(a) m = ZIt
Question 44.
When 1 coulomb of electric current is passed the amount of substance deposited or liberated is known as ………..
(a) equivalent mass
(b) electro chemical equivalent
(c) molar mass
(d) 1 Faraday
Answer:
(b) electro chemical equivalent
Question 45.
The value of electro chemical equivalent is equal to ………..
(a) \(\frac{96500}{\text { Equivalent mass }}\)
(b) \(\frac{96500}{\text { Molar mass }}\)
(c) \(\frac{\text { Molar mass }}{96500}\)
(d) \(\frac{\text { Equivalent mass }}{96500}\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac{\text { Equivalent mass }}{96500}\)
![]()
Question 46.
The mathematical expression of Faraday’s second law is …………
(a) m = ZIt
(b) \(\frac{m_{1}}{E_{1}}=\frac{m_{2}}{E_{2}}=\frac{m_{3}}{E_{3}}\)
(c) \(\frac{m_{1}}{Z_{1}}=\frac{m_{2}}{Z_{2}}=\frac{m_{3}}{Z_{3}}\)
(d) \(Z=\frac{m}{I t}\)
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{m_{1}}{Z_{1}}=\frac{m_{2}}{Z_{2}}=\frac{m_{3}}{Z_{3}}\)
Question 47.
Which one of the following is used in cell phone, dry cell in flashlight?
(a) Zn – Cu battery
(b) Li – ion battery
(c) Ag – Cu battery
(d) Na, NaCI battery
Answer:
(b) Li – ion battery
Question 48.
The primary batteries are ………..
(a) rechargeable
(b) non – rechargeable
(c) reversible
(d) renewable
Answer:
(b) non – rechargeable
Question 49.
Consider the following statements.
(i) The secondary batteries are rechargeable
(ii) Primary batteries are non – rechargeable
(iii) Batteries are used as a source of AC current at a constant voltage.
Which of the above statement is I are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (i) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(b) (iii) only
Question 50.
The anode and cathode used in Leclanche cell are ………… respectively.
(a) Zinc, Graphite rod with MnO2
(b) Graphite rod in MnO2 and Zinc container
(c) Zn container and copper rod
(d) Copper container and Zinc rod
Answer:
(a) Zinc, Graphite rod with MnO2
Question 51.
Which electrolyte is used in Leclanche cell?
(a) ZnSO4 + CuSO4
(b) NH4CI + ZnCl2
(c) NaCI + CuSO4
(d) MnSO4 + MnO2
Answer:
(b) NH4Cl + ZnCl2
Question 52.
Which one of the following is used as cathode in Mercury button cell?
(a) Zinc
(b) Copper
(c) Zinc amalgamated with mercury
(d) HgO mixed with graphite
Answer:
(c) Zinc amalgamated with mercury
Question 53.
Which one of the following is used as anode in Mercury button cell?
(a) HgO mixed with graphite
(b) Zinc amalgamated with mercury
(c) Copper amalgamated with Mercury
(d) HgO mixed with Copper
Answer:
(a) HgO mixed with graphite.
![]()
Question 54.
The value of cell emf of Mercury button cell is ………..
(a) 1.35V
(b) – 076V
(c) 0.34V
(d) 100V
Answer:
(a) 1.35 V
Which one of the following is used in pacemakers, cameras and electronic watches?
(a) Li-ion battery
(b) Leclanche cell
(c) Galvanic cell
(d) Mercurry button cell
Answer:
(d) Mercury button cell
Question 56.
The electrolyte used in Mercury button cell is ………….
(a) Paste of kOH and ZnO
(b) CuSO4 + ZnSO4
(c) NaCl + MgCl2
(d) NH4CI + ZnCl2
Answer:
(a) Paste of kOH and ZnO
Question 57.
Which of the following is an example of secondary batteries?
(a) Mercury button cell
(b) Leclanche cell
(c) Lead storage battery
(d) Daniel cell
Answer:
(c) Lead storage battery
Question 58.
Which of the following act as cathode and anode in Lead storage battery?
(a) Lead plate bearing PbO2, spongy Lead
(b) Spongy lead, lead plate bearing PbO2
(c) Lead Copper
(d) Mercury oxide, PbO
Answer:
(a) Lead plate bearing PbO2, Spongy lead
Question 59.
Which one of the following is used as an electrolyte Lead storage battery?
(a) PbSO4
(b) H2SO4
(c) CuSO4
(d) HNO3
Answer:
(b) H2SO4
![]()
Question 60.
The emf of lead storage battery is …………
(a) +1.1 V
(b) 2.4V
(c) 2V
(d) 11 . 2V
Answer:
(c) 2 V
Question 61.
The Lead storage battery is used in …………
(a) pacemakers
(b) automobiles
(c) electronic watches
(d) flash light
Answer:
(b) automobiles
Question 62.
Which one of the following is used in automobiles, trains and in inverters?
(a) Lithium ion battery
(b) Mercurry button cell
(c) Lead storage battery
(d) Leclanche cell
Answer:
(c) Lead storage battery
![]()
Question 63.
Which one of the following is used as an anode in Lithium ion battery?
(a) Porous graphite
(b) Lithium
(c) CoO2
(d) Copper
Answer:
(a) Porous graphite
Question 64.
which one of the following is used as cathode in Lithium ion battery?
(a) Porous graphite
(b) Lithium
(c) CoO2
(d) Chromium
Answer:
(c) CoO2
Question 65.
Which one of the following is used in cellular phones, Laptop computers and in digital camera?
(a) Mercury button cell
(b) Lithium – ion battery
(c) H2O2 fuel cell
(d) Leclanche cell
Answer:
(b) Lithium – ion battery
Question 66.
Which one of the following is used as an electrolyte in H2O2 fuel cell?
(a) Aqueous CuSO4
(b) Aqueous CoO2
(c) Aqueous KOH
(d) NH4CI + ZnCI2
Answer:
(c) Aqueous KOH
Question 67.
Which one of the following is an example for electrochemical process?
(a) Chrome plating
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Galvanisation
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) All the above
Question 68.
The formula of rust is ………..
(a) Fe2O3
(b) Fe2O3.xH2O
(c) FeO
(d) FeO.xH2O
Answer:
(b) Fe2O3.xH2O
![]()
Question 69.
Which one of the following is / are very important for rusting’?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Water
(c) Both a & b
(d) H2O
Answer:
(c) Both a & b
Question 70.
The electro plating of Zinc over a metal is called …………..
(a) Electrolysis
(b) Redox reaction
(c) Galvanisation
(d) Passivation
Answer:
(c) Galvanisation
Question 71.
Consider the following statements.
(i) The standard reduction potential (E°) is a measure of oxidising tendency of the species.
(ii) The standard oxidation potential (E°) is a measure of oxidising tendency of the species.
(iii) The standard oxidation potential (E°) is a measure of redox tendency of the species.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (ii) & (iii)
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(c) (ii) & (iii)
Question 72.
On the basis of the electrochemical theory of aqueous corrosion, the reaction occuring at the cathode is …………

Answer:
![]()
Hint:
2H+(aq) + 2e– → 2H2
2H+ + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)O2 → H2O
2H+ + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)O2 +2e– → H2O
Balancing the above equation
4H+(aq) + O2 + 4e– → 2H2O
Question 73.
The standard reduction potential for the half reactions are as ………..
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– E° = +0.76V
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–E° = + 041 V.
So for cell reaction F2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Fe is ………….
(a) – 0.35V
(b) +0.35V
(c) +1.17V
(d) – 1.117V
Answer:
(b) +0.35V
Hint:
In the reaction F2+ + Zn° → Zn2+ + Fe°
emf = Ecathode – Eanode
= – 0.41 – (- 0.76)
= – 0.41 + 0.76
emf = + 0.35V
Question 74.
The standard emf for the given cell reaction Zn + Cu2+ → Cu + Zn2+ is 1.10V at 25°C. The emf for the cell reaction when 0.1 M Cu2+ and 0.1 M Zn2+ solutions are used at 25°C is ……….
(a) 1.10V
(b) 0.110V
(c) – 1.10V
(d) – 110V
Answer:
(a) 1.10V
Hint:
Ecell = E°cell – \(\frac { 0.0592 }{ 2 }\) log\(\frac{\left(Z n^{2+}\right)}{\left(C u^{2+}\right)}\)
= 1.10 – \(\frac { 0.0592 }{ 2 }\) log \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 0.1 }\)
= 1.10 – \(\frac { 0.0592 }{ 2 }\) log 1
= 1.10 – \(\frac { 0.0592 }{ 2 }\) x 0
= 1.10V
![]()
Question 75.
Which amount of chlorine gas liberated at anode, if 1 ampere current is passed for 30 minutes from NaCI solution?
(a) 0.66 moles
(b) 0.33 moles
(c) 0.66 g
(d) 0.33 g
Answer:
(c) 0.66 g
Hint:
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Q = It.
Amount of current passed = 1 x 30 x 60 = 1800C
The amount of Cl2 liberated by passing 1800 coulomb of electric charge
= \(\frac{1 \times 1800 \times 71}{2 \times 96500}\)
= 0.66g
Question 76.
When Zinc piece is kept in CuSO4 solution the copper gets precipitated due to standard potential of Zinc is …………
(a) > copper
(b) < copper
(c) > Sulphate
(d) < Sulphate
Answer:
(b) < copper
Hint:
Standard potential of zinc < copper.
Question 77.
Which equation shows the relation between electrode potential (E) standard electrode potential (E°) and concentration of ions in solution is ………..
(a) Kohlrausch’s equation
(b) Nernst equation
(c) Ohm’s equation
(d) Faraday’s equation
Answer:
(b) Nernst equation
Question 78.
The standard electrode potential of SHE at 298K is ………
(a) 0.05 V
(b) 0.01 V
(c) 0.0 V
(d) 0.11 V
Answer:
(c) 0.0 V
Question 79.
The reaction Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn has a standard potential of – 0.76 V. This means
(a) Zn cannot replace hydrogen from acids
(b) Zn is a reducing agent
(c) Zn is an oxidising agent
(d) Zn2+ is a reducing agent
Answer:
(b) Zn is a reducing agent.
Hint:
Since E0Zn2+/Zn is negative, so Zn has a greater tendency to be oxidised than hydrogen. Hence it can act as reducing agent.
Question 80.
K, Ca and Li metals may be arranged in the decreasing order of their standard electrode potentials as ……..
(a) K, Ca, Li
(b) Ca, K, Li
(c) Li, Ca, K
(d) Ca, Li, K
Answer:
(b) Ca, K, Li
![]()
Question 81.
The correct order of chemical reactivity with water according to electrochemical series ………….
(a) K > Mg > Zn > Cu
(b) Mg > Zn > Cu > K
(c) K > Zn > Mg > Cu
(d) Cu > Zn > Mg > K
Answer:
(a) K > Mg > Zn > Cu
Hint:
The standard reduction potential of K+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Cu2+ increases in this order.
Question 82.
For a spontaneous reaction, the ΔG, the equilibrium constant (K) and E°cell will be respectively
(a) ve, > 1, + ve
(b) + ve , > 1, – ve
(c) – ve, < 1, – ve (d) – ve, > 1, – ve
Answer:
(a) – ve, > 1, + ve.
Question 83.
E° values of mg2+/mg is – 2.37 V, Zn2+/ Zn is – 0.76V, and Fe2+ / Fe is – 0.44 V. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Zn will reduce Fe2+
(b) Zn will reduce mg2+
(c) mg oxidises Fe
(d) Zn oxidises Fe
Answer:
(a) Zn will reduce Fe2+
Hint:
E0Zn2+/Zn<E0Fe2+/Fe So Zn will reduce Fe2+. Zinc cannot reduce Mg2+ because
\(\mathbf{E}_{\mathbf{Z n}^{2+} / \mathbf{z n}}^{\circ}>\mathbf{E}_{\mathrm{Mg}^{2+} / \mathrm{Mg}}^{\circ}\) On similar reason mg and Zn cannot oxidise Fe.
Question 84.
In which cell, the free energy of a chemical reaction is directly converted into electricity?
(a) Leclanche cell
(b) Fuel cell
(c) Lead storage battery
(d) Lithium ion battery
Answer:
(b) Fuel cell
Question 85.
Which of the following has the highest electrode potential?
(a) Li
(b) Cu
(c) Au
(d) Al
Answer:
(c)Au
![]()
Question 86.
Consider the following statements.
(i) A salt bridge is used to eliminate liquid junction potential
(ii) The Gibbs free energy change ∆G is related with electro motive force (E) as ∆G = – nFE.
(iii) Nernst equation for a single electrode potential is E = E° – \(\frac { RT }{ nF }\) In \(a_{m} n^{4}\)
(iv) The efficiency of a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell is 23%.
Which of the above statement is / are not correct?
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (iv) only
(d) (i) only
Answer:
(c) (iv) only
Question 87.
The specific conductance of 0.1 N KCl solution at 23°C is 0.012 Ohm-1 cm-1. The resistance of the cell containing the solution at the same temperature was found to be 55 Ohm. The cell constant will be …………
(a) 0.142 cm-1
(b) 0.66 cm-1
(c) 0.9 18 cm-1
(d) 1.12 cm-1
Answer:
(c) 0.66 cm-1
Hint:
k x \(\frac { 1 }{ R }\) x cell constant
Cell constant = k x R
= 0.012 x 55
= 0.66 cm-1
Question 88.
Which of the following reaction is used to make a fuel cell?
(a) Cd(s) + 2Ni(OH)3(s) → CdO(s) + 2Ni (OH) + H2O(1)
(b) Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2 PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1)
(c) 2H2(g) + O(s) + 2H2O(1)
(d) 2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(ag) + 2Fe4(s) + 2H2O(1)
Answer:
(c) 2H2(g) + O(s) + 2H2O(1)
When lead storage battery is charged
(a) PbO2 is dissolved
(b) PbSO4 is deposited on lead electrode
(c) PbSO4 is deposited on lead electrode
![]()
Question 89.
Which colourless gas evolves when NH4CI reacts with Zinc in a dry cell battery?
(a) NH3
(b) N2
(c) H2
(d) Cl2
Answer:
(c) H2
Hint: 2NH4Cl + Zn → 2NH3 + ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
Question 91.
A cell from the following which converts electrical energy into chemical energy?
(b) Electro chemical cell
(d) Lithium – ion battery
(a) dry cell
(c) Electrolytic cell
Answer:
Question 92.
When 9.65 Coulombs of electricity is passed through a solution of silver nitrate (Atomic weight of Ag = 107.85g), the amount of silver deposited is ……………
(a) 10.8 mg
(b) 5.4 mg
(c) 16.2 mg
(d) 21.2 mg
Answer:
(a) 10.8 mg
Hint:
WAg = \(\frac{E_{A g} \times Q}{96500}\) = \(\frac{108 \times 9.65}{96500}\)
= 1.08 x 10-2
Question 93.
What weight of copper will be deposited by passing 2 Faraday’s of electricity through a cupric salt (Atomic weight of Cu = 63.5)
(a) 2.0g
(b) 3.175g
(c) 63.5g
(d) 127.0g
Answer:
(c) 63.5 g
Hint:
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
2 Faraday’s will deposit 1g atom of Cu = 63.5 g
Question 94.
In electrolysis of a fused salt, the weight of the deposit on an electrode will not depend on ….
(a) temperature of the bath
(b) current intensity
(c) electro chemical equivalent of ions
(d) time for electrolysis.
Answer:
(a) temperature of the bath
Question 95.
The mass deposited at an electrode is directly proportional to ………..
(a) atomic weight
(b) equivalent weight
(c) molecular weight
(d) atomic number
Answer:
(b) equivalent weight
![]()
Question 96.
Which solution will show the highest resistance during the passage of current?
(a) 0.05 N NaCl
(b) 2N NaCI
(c) 0.1N NaCI
(d) 1N NaCI
Answer:
(b) 2N NaCl
Question 97.
In a galvanic cell, the electrons flow from
(a) anode to cathode through the solution
(b) cathode to anode through the solution
(c) anode to cathode through the external circuit
(d) cathode to anode through the external circuit
Answer:
(c) anode to cathode through the external circuit
Question 98.
Rusting of iron is catalysed by which of the following?
(a) Fe
(b) O2
(c) Zn
(d) H
Answer:
(d) H
Question 99.
The conductivity of strong electrolyte is ………..
(a) increase on dilution slightly
(b) decrease on dilution
(c) does not change with dilution
(d) depend upon density of electrolyte itself
Answer:
(a) increase on dilutions lightly
Question 100.
Which one is not a conductor of electricity?
(a) NaCl(aqueous)
(b) NaCl(solid)
(c) NaCl(molten)
(d) Ag(metal)
Answer:
(b) NaCl(solid)
Hint:
In solid state, NaCl does not dissociate into ions so it does not conduct electricity.
Question 101.
The molar conductivity is maximum for the solution of concentration
(a) 0.00 1 m
(b) 0.005 m
(c) 0.002 m
(d) 0.004 m
Answer:
(a) 0.001 m
Hint:
molar conductance α \(\frac{1}{\text { molarity }}\)
![]()
Question 102.
Resistance of 0.2 m solution of an electrolyte is 50 Ohm-1. The specific conductance of the solution is 1.3 Sm-1. If resistance of 0.4 m solution of the same electrolyte is 260 Ohm-1, its molar conductivity is ……..
(a) 62.5 Sm2 mol-1
(b) 6250 Sm2 mol-1
(c) 6.25 x 10-4 Sm2 mol-1
(d) 625 x 10-4 Sm2 mol-1
Answer:
(c) 6.25 x 10-4 Sm2 mol-1
Question 103.
Saturated solution of KCI (or) Na2SO4 is used to make salt bridge because
(a) velocity of K+ is greater than that of Cl–
(b) velocity of Cl– is greater than that of K+
(c) velocity of both K+ and Cl-1 are nearly the same
(d) KCI is highly soluble in water.
Answer:
(c) velocity of both K+ and Cl– are nearly the same
Question 104.
Which of the following electrolytic solutions has the least specific conductance?
(a) 0.02 N
(b) 0.2 N
(c) 2 N
(d) 0.002 N
Answer:
(d) 0.002 N
![]()
Question 105.
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to ……….
(a) increase in both the number of ions and ionic mobility of ions
(b) increase in number of ions
(c) increase in ionic mobility of ions
(d) 100% ionization of electrolyte at normal dilution
Answer:
(c) increase in ionic mobility of ions
Question 106.
Li occupies higher position in the electrochcmical series of metals as compared to Cu, since
(a) the standard reduction potential of Li+/Li is lower than that of Cu2+/Cu
(b) the standard reduction potential of Cu2+/Cu is lower than that of Li+/Li
(c) the standard oxidation potential of Li/Li+ is lower than that of Cu/Cu2+
(d) Li is smaller in size as compared to Cu.
Answer:
(a) the standard reduction potential of Li+/Li is lower than that of Cu2+/Cu
Question 107.
The one which decreases with dilution is …………
(a) conductance
(b) specific conductance
(c) equivalent conductance
(d) molar conductance
Answer:
(b) specific conductance
Question 108.
Corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon where the cell reactions are …………..
(a) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and dissolved oxygen in water is reduced to OH–
(b) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and H2O is reduced to O22-
(c) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and H2O is reduced to O2–
(d) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and H2O is reduced to O2
Answer:
(a) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and dissolved oxygen in water is reduced to OH-2
Question 109.
A button cell used in watches functions as following.
Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) + H2O(1) → 2 Ag(s) + Zn2+(aq)+ 2OHsup>-(aq).
If half cell potentials are Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s)
E° = – O.76V
Ag2O(s) + H2O(1) +2e– 2Ag(s) + 2OH–(aq)E0 = 0.34V
The cell potential will be ………..
(a) 1.10V
(b) 0.42V
(c) 0.84V
(d) 1.34V
Answer:
(a) 1.10V
Hint:
Cell potential = Ecathode – Eanode
= 0.34 – (- 0.76)
= 0.34 + 0.76
= 1.10V
Question 110.
Among the following cells Leclanche cell
(I) Nickel – cadmium cell
(II) Lead storage battery
(III) and Mercury Cell
(IV) primary cells are
(a) I & II
(b) I & III
(c) II & III
(d) I & IV
Answer:
(d) I & IV
II. Fill in the blanks.
- ……… is defined as the resistance of an electrolyte confined between two electrodes having unit cross sectional area and separated by a unit distance
- The reciprocal of the specific resistance is called the and represented by the symbol ………
- The SI unit of specific conductance is ………
- The relation between equivalent conductance and the specific conductance is given as ………
- Conductivity increases with the ……… in viscosity.
- A°m values of the weak electrolytes can be determined using ………
- ……… is a device in which a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current.
- ……… is a device that converts electrical energy into chemical energy.
- The salt bridge contains a agar-agar gel mixed with an inert electrolyte such as ………
- The SI unit of cell potential is ………
- The reference electrode SHE has emf of exactly ……… volt
- The value of charge of one electron is equal to ………
- For a spontaneous cell reaction, the should be ………
- ……… is a process in which electrical energy is used to cause a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
- The negative E° values shows that the reactions are ………
- ……… is defined as the amount of a substance deposited or liberated at the electrode by a charge of 1 Coulomb.
- ……… batteries are used in cell phones.
- ……… cell is used in pacemakers, electronic watches and cameras.
- ………battery is used in automobiles.
- Rusting of iron is an ……… process.
Answer:
- Specific resistance (or) Resistivity
- Specific conductance, Kappa(k)
- Sm-1
- Λ = \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{N}\)
- decrease
- Kohlraush’s law
- Galvanic (or) Voltaic cell
- Electrolytic cell
- KCl (or) Na2SO4
- Volt (V)
- zero
- 1.6 x 10-19C
- negative
- Electrolysis
- non – spontaneous
- electro chemical equivalent
- Li-ion
- Mercury button
- Lead storage
- electro chemical
III. Match the following
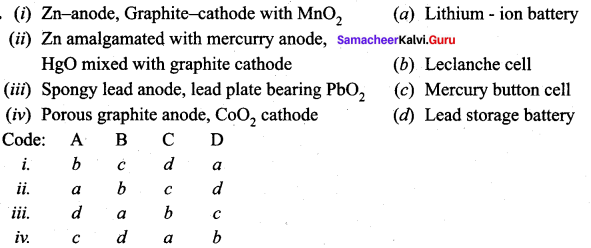
Question 1.

Answer:
i. c d a b
Question 2.

Answer:
ii. c a d b
Question 3.

Answer:
iii. d c a b
Question 4.

Answer:
iv. c a d b
Question 5.
Answer:
i. b c d a
Question 6.

Answer:
i. c a d b
IV. Assertion and reasons.
Question 1.
Assertion(A): If the temperature of the electrolytic solution increases, conductance also increases.
Reason (R): Increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of the ions and decreases the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions and hence conductivity increases.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Assertion(A): Molar conductance of a solution increases with increase in dilution.
Reason (R): For a strong electrolyte, inter ionic forces of attraction decreases with dilution and so conductivity increases. For a weak electrolyte, degree of dissociation increases with dilution and conductivity increases.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A .
(b) A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is not the explanation of A
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Assertion(A): AC current is used in wheatstone bridge arrangement to measure conductivity of ionic solution.
Reason (R): If DC current is used in wheatstone bridge arrangement, it will lead to electrolys is of the solution taken in the cell. So AC current is used to prevent electrolysis.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 4.
Assertion(A): Strong electrolytes have low molar conductivity at high concentration.
Reason (R): For a strong electrolyte, at high concentration, the number of constituent ions of the electrolyte is high and hence the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions is also high
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) A is correct but R is wrong
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 5.
Assertion(A): In Daniel cell, the salt bridge contains an agar-agar gel mixed with an inert electrolyte KCl (or) Na2SO4.
Reason (R): The ions of inert electrolyte do not react with other ions present in half cells and they are not either oxidised or reduced at electrodes.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 6.
Assertion(A): Current stops flowing when Ecell = 0
Reason (R): At Ecell = 0, Equilibrium of the cell reaction is attained.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 7.
Assertion(A): Copper Sulphate can be stored in a Zinc vessel.
Reason (R): Zinc is less reactive than Copper.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 7.
Assertion(A): Copper Sulphate can be stored in a Zinc vessel.
Reason (R): Zinc is less reactive than Copper.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are wrong
Question 8.
Assertion(A): As a lead storage battery gets discharged. density of electrolyte present in it decreases.
Reason (R): Lead and Lead dioxide both react with sulphuric acid to form lead sulphate.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is wrong
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
![]()
Question 9.
Assertion(A): The cell potential of mercury cell is 1.35V which remains constant.
Reason (R): In mercury cell, the electrolyte is a paste of KOH and ZnO.
(a) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct, but R is the correct explanation of A
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 10.
Assertion(A): If an iron rod is dipped in CuSO4 solution, then blue colour of the solution turns red.
Reason (R): Iron is more reactive than copper and so iron displaces copper from CuSO4 solution.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
V. Find the odd one out and give the reasons.
Question 1.
(a) I α V
(b) I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
(c) V = IR
(d) R = \(\frac { I }{ V }\)
Answer:
(d) R is the odd one, and other three represents Ohm’s law
Question 2.
(a) m = Zit
(b) Z = \(\frac { m }{ It }\)
(c) m α It
(c) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1}}{\mathrm{Z}_{1}}$\) = \($\frac{\mathrm{m}_{2}}{\mathrm{Z}_{2}}\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1}}{\mathrm{Z}_{1}}$\) = \($\frac{\mathrm{m}_{2}}{\mathrm{Z}_{2}}\) = is the odd one, all the others are Faraday’s I law but (ci) is Faraday’s ¡I law
Question 3.
(a) Pacemaker
(b) electronic watches
(c) trains
(d) cameras
Answer:
(c) train, Lead storage battery is used in trains, but in all others mercury button cell is used up.
Question 4.
(a) Automobiles
(b) Pacemaker
(c) Train
(d) Inverters
Answer:
(b) Pacemaker. In pacemaker mercury button cell is used whereas in other three, lead storage battery is used up.
![]()
Question 5.
(a) Cellular phone
(b) Laptop
(c) Digital Camera
(d) Electronic watch
Answer:
(d) Electronic watch. ¡n this mercury button cell is used whereas in others Li-ion battery is used up.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry 2 Mark Questions and Answers
VI. Answer the following.
Question 1.
State Ohm’s law.
Answer:
At a constant temperature, the current flowing through the cell (I) is directly proportional to the voltage across the cell (V).
I α V(or) I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
V = IR
Question 2.
Define Resistivity. Give its unit.
p (rho) is called the specific resistance (or) resistivity and it is defined as the resistance of an electrolyte confined between two electrodes having unit cross sectional area and are separated by a unit distance. Unit of resistivity is Ohm metre (Ω m)
Question 3.
Define conductance and give its unit.
Answer:
The reciprocal of the resistance \((\frac { 1 }{ 2 })\) is known as the conductance of an electrolytic solution.
The SI unit of conductance is Ohm-1 (or) Siemen (S)
Question 4.
Define specific conductance. Give its SI unit.
Answer:
The specific conductance is defined as the conductance of a cube of an electrolytic solution of unit dimensions. The SI unit of specific
k = C . \(\frac { l }{ A }\)
conductance is Sm-1
Question 5.
What Is meant by resistance? Give its unit.
Answer:
Resistance is the opposition that a cell offers to the flow of electric current through it.
R α \(\frac { l }{ A }\)
The SI unit of R = Ohm (Ω)
Question 6.
What is molar conductance? Give its SI unit.
Answer:
The conductance of a conductivity cell in which the electrodes are separated by 1m and having V m3 of electrolytic solution that contains 1 moIe of an electrolyte is known as molar conductance.
Λm = k x V
The SI unit of Λm = S m2 mol-1
Question 7.
Define equivalent conductance. Give its SI unit.
Answer:
Equivalent conductance is defined as the conductance of ‘V’ m3 of electrolytic solution containing one gram equivalent of electrolyte in a conductivity cell in which the electrodes are one metre apart.
Λ = \(\frac{\kappa \times 10^{-3}}{N}\)
The SI unit of A = S m2 gm equivalent’
![]()
Question 8.
What are electro chemical cells? Mention its types.
Answer:
Electro chemical cell is a device which inter converts chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. It consists of two separate electrodes which are in contact with an electrolyte solution. Electro chemical cells are classified into two types.
- Galvanic cell and
- Electrolytic cell.
Question 9.
Distinguish between galvanic cell and electrolytic cell.
Answer:
Galvanic Cell
- It is a device in which a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current.
- It converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is commonly known as Battery.
- e.g., Daniel cell, Dry cell.
- A salt bridge is used in this.
Electrolytic cell
- It is a device in which an electric current from an external source drives a non spontaneous reaction
- It converts electrical energy into chemical energy.
- e.g., Electrolysis of molten NaCI.
- Na salt bridge is used.
Question 10.
What is meant by Faraday? How is it calculated?
Answer:
One Faraday is defined as the charge of one mole of electron.
Charge of one electron = 1.6 x 10-19C
Charge of 1 mole of electrons = 6.023 x 1023 x 1.602 x 10-19C
= 6.023 x 1023 x 1.602 x 10-19C
= 96488 C
i.e., IF ≃ 965O0C
Question 11.
Define corrosion. Give one example.
Answer:
The redox process which causes the deterioration of metal is called corrosion. Rusting of iron is an example of corrosion. It is an electro chemical process.
Question 12.
Can you store copper sulphate solution in a zinc pot?
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than copper. Hence, it displaces copper from copper sulphate solution as follows
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu (s) So, we cannot store copper sulphate solution in a zinc pot.
Question 13.
Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Answer:
Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of solution. On dilution the number of ions per unit volume decreases. Hence, the conductivity decrease.
Question 14.
Suggest a way to determine 10m value of water.
![]()
We find out
![]()
Then
![]()
Question 15.
Write the chemistry of recharging the lead storage battery, highlighting all the materials that are involved during recharging? .
A lead storage battery consists of anode made up of lead, cathode made up of grid of lead packed with lead dioxide (PbO2) and 38% solution of sulphuric acid is used as an electrolyte. When the battery is in use, the following reaction take place:
Anode: Pb(s) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e–
Cathode: PbO2(s) + SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e– → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1)
On charging the battery, the reverse reaction takes place, i.e. PbSO4 deposited on the electrode is converted back into Pb and PbO2 and H2SO4 regenerated.
Question 16.
What is meant by cell constant?
Answer:
Cell constant is the ratio of the distance between the electrodes (l) and the area of cross-section (A). It is denoted by 1. Its unit is cm-1. Its SI unit is m-1.
Question 17.
State two advantages of H2 – O2 fuel cell over ordinary cells.
Answer:
- It is highly efficient.
- It is pollution free
![]()
Question 18.
Why Om for CH3COOH cannot be determined experimentally?
Answer:
Molar conductivity of weak electrolytes keeps on increasing with dilution and does not become constant even at very large dilution.
Question 19.
Which will have greater molar conductivity and why?
Answer:
Sol. (A) 1 mol KCI dissolved in 200 cc of the solution.
Sol. (B) 1 mol KCI dissolved in 500 cc of the solution.
Sol. (B) will have greater molar conductivity because
λm = k x V
with dilution K decreases but V increases, so that product will increase more.
Question 20.
Raju and his father were going in a boat in the river. Raju’s father was going to throw away the cell used in watches and hearing aids into the water. Raju prevented him doing so.
- As a student of chemistry, why would you advise Raju’s father not to throw the cell in the water body?
- What is the value associated with the above decision?
Answer:
- The watch cells are made up of mercury. This mercury will pollute the water. Water contaminated with mercury leads to accumulation of mercury in the body of fishes and other aquatic life.
- It helps in keeping the environment safe from pollution due to mercury.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry 3 Mark Questions And Questions
VII.Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Explain about conductivity cell with an example.
Answer:
1. Sodium chloride (or) potassium chloride is dissolved in a solvent like water, the electrolyte is completely dissociated to give its constituent ions (cations and anions).
2. When an electric field is applied to such an electrolytic solution, the ions present in the solution carry charge from one electrode to another. PLattnium electrode and thereby they conduct electricity. electrode
3. The conductivity of the electrolytic solution is measured using a conductivity cell, solution
Question 2.
Explain about the factors affecting electrolytic conductance. Conductivily Cell
Answer:
- If the interionic attraction between the oppositely charged ions ofsolute increases, the conductance will decrease.
- Solvent of high dielectric constant show high conductance in solution.
- Conductance is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the medium. i.e., conductivity increases with the decrease in viscosity.
- If the temperature of the electrolytic solution increases, conductance also increases.
- Molar conductance of a solution increases with increase in dilution. This is because, for a strong electrolyte, inter ionic force of attraction decrease with dilution.
- For a weak electrolyte, degree of dissociation increases with dilution.
Question 3.
Explain about the variation of molar conductivity with concentration by Kohiraush studies?
Answer:
Kohiraush observed that, increase of molar conductance of an electrolytic solution with the increase in dilution. He deduced the following empirical relationship between the molar conductance (Λm) and concentration of the
Λm = Λ0m – k\(\sqrt { c }\)
For strong electrolytes such as KCl, NaCl the plot ΛmVs\(\sqrt { c }\), gives a straight line. It is also observed that the plot is not a linear one for weak electrolyte.
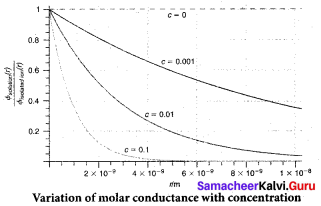
Question 4.
For strong electrolytes the molar conductivity increases on dilution and reaches a maximum value at infinite dilution. Justify this statement.
Answer:
For a strong electrolyte, at high concentration, the number of constituent ions of the electrolyte in a given volume is high and hence the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions is also high. The ions also experienced a viscous drag due to greater solvation. These factors attribute for the low molar conductivity at high concentration.
When the dilution increases, the ions are far apart and the attractive forces decreases. At infinite dilution, the ions are so far apart, the interaction between them becomes insignificant and hence the molar conductivity increases and reaches a maximum value at infinite dilution.
Question 5.
For weak electrolyte, sudden increase In molar conductance with dilution. Prove this statement.
Answer:
For a weak electrolyte, at high concentration the plot is almost parallel to concentration axis with slight increase in conductivity as the dilution increases. When the concentration approaches zero, there is a sudden increase in the molar conductance and the curve is almost parallel to Am axis. This is due to the fact that the dissociation of the weak electrolyte increases with the increase in dilution (Ostwald’s dilution law).
Question 6.
Explain about Debye-Huckel and Onsagar equation.
Answer:
The influence of ion-ion interactions on the conductivity of strong electrolytes was studied by Debye and Huckel.
They considered that each ion is surrounded by an ionic atmosphere of opposite sign, and derived an expression relating the molar conductance of strong electrolytes with the concentration by It was further developed by Onsagar. For a uni – univalent electrolyte the Debye Huckel and Onsagar equation is given below.
Λm = Λ°m (A + B Λ°m) \(\sqrt { c }\)
Where A and B are constants which depend only in the nature of the solvent and temperature.
Question 7.
What are the values of A and B in Debye Huckel and Onsagar equation?
Answer:
Debye Huckel and Onsagar equation is
Λm = Λ°m (A + B Λ°m) \(\sqrt { c }\)
Where
\(\mathrm{A}=\frac{82.4}{\sqrt{\mathrm{DT}} \mathrm{n}}\)
\(B=\frac{8.20 \times 10^{5}}{3 \sqrt{D T}}\)
D = Dielectric constant of the medium
η = Viscosity of the medium
T = Temperature in Kelvin
Question 8.
How will you calculate degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes and dissociation constant using Kohlrausch’s law?
Answer:
1. The degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte can be calculated from the molar conductivity at a given concentration and the molar conductivity in infinite dilution using the formula
2. According to Ostwald’s dilution law Ka = \(\frac{\alpha^{2} C}{1-\alpha}\)
Substituting a value in the above equation
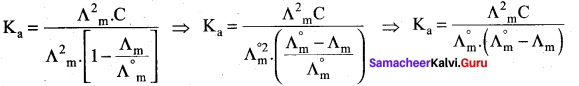
Question 9.
How would you calculate the solubility of sparingly soluble salt using Kohlrausch’s law?
Answer:
1. Substances like AgCl, PbSO4 are sparingly soluble in water. The solubility product can be determined using conductivity experiments.
2. Let us consider AgCl as an example
AgCI(s) → Ag+ + Cl–
Ksp = [Ag+] [Cl–]
3. Let the concentration of [Ag+] be ‘C’ mol L-1.
If [Ag+] = C, then [Cl–] is also equal to C mol L-1.
Ksp = C.C
Ksp = C2.
4. The relationship between molar conductance and equivalent conductance is
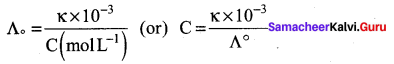
Substitute the concentration value in the relation Ksp = C2
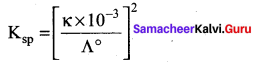
Question 10.
What is the relationship between molar mass and electro chemical equivalent. Derive the equation.
Answer:
1. Consider the following general electro chemical redox reaction
Mn+(aq) + ne– → M(s)
2. We can infer from the above equation that ‘n’ moles of electrons are required to precipitate
3. The quantity of charge required to precipitate 1 mole of Mn+ = Charge of ‘n’ moles of electrons = nF
4. In other words, the mass of the substance deposited by one coulomb of charge. Molar mass (M)
Electro chemical equivalent Mn+ = \(\frac{\text { Molar mass }(\mathrm{M})}{\mathrm{n}(96500)}\)
(or)
Z = \(\frac{\text { Equivalent mass }}{96500}\)
Question 11.
What is meant by standard reduction potential? What is its application?
Answer:
1. The standard reduction potential (E°) is a measure of the oxidising tendency of the species.
2. The greater the E° value means greater is the tendency shown by the species to accept electrons and undergo reduction.
3. So higher the E° values, lesser is the tendency to undergo corrosion.
Question 12.
What is meant by Electro chemical series? Mention the top most and the least placed element in that series.
Answer:
1. The standard aqueous electrode potential at 298 K for various metal-metal ion electrodes are arranged in the decreasing order of their standard reduction potential values is known as electro chemical series.
2. The strongest reducing agent is Li which has E° value as – 3.05 and it is in bottom of the series.
3. The strongest oxidising agent is F which has E° value as + 2.87 is the first element in that series.
Question 13.
Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place
Ni(s) + 2Ag+(0.002 M) —‘ Ni2+(0.160 M) + 2 Ag(s)
Given that E°cell = 1.05 V
Answer:
Applying Nernst equation to the given cell reaction:
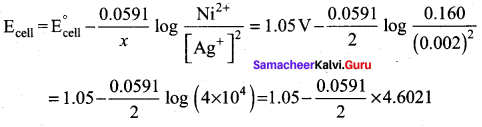
= 1.05 – 0.14 V = 0.91 V
Question 14.
If a current of 0.5 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, then how many electrons would flow through the wire?
Answer:
Q (coulomb) = 1 (ampere) x t(sec)
= 0.5 ampere x 2 x 60 x 60 = 3600C
A flow of IF, i.e., 96500 C is equivalent to the flow of 1 mole of electrons
i.e., 6.023 x 1023electrons
3600 C is equivalent to flow of electrons
= \(\frac{6.02 \times 10^{23}}{96500}\) x 3600 2.246 x 1022 electrons,
Question 15.
What are fuel cells? Write the electrode reactions of a fuel cell which uses the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen?
Answer:
A fuel cell is similar to a galvanic cell, it generates electricity directly by the electrochemical conversion of gaseous or liquid fuels fed into the cell as required.
At anode: H2(g) + 2OH–(aq) → 2H2O(l) + 2e–
At cathode: O2(g) + 2H2O(1) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq)
Overall reaction : 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
Question 16.
Write the cell reaction which occur ¡n the lead storage battery
- When the battery is in use,
- When the battery is charging.
Answer:
1. Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1)
At anode: Pb(s) + SO2-4 → PbSO4(s) + 2e–
At cathod: PbO4(s) + SO2-4(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e– → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1)
2. 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(s) → PbSO4(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
Question 17.
Describe the composition of anode and cathode in a mercury cell. Write the electrode reactions for this cell.
Answer:
Mercury cell: It consists of zinc mercury amalgam as anode, a paste of HgO and Carbon black is used as cathode. The electrolyte is a paste of KOll and ZnO.
At anode: Zn (amalgam) + 2OH– → ZnO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e–
At cathode: HgO(s) + H2O + 2e– → Hg(1) + 2OH–
The net reaction : Zn (amalgam) + HgO(s) → ZnO(s) + Hg(l)
Question 18.
How much copper is deposited on the cathode of an electrolytic cell If a current of 5 ampere is passed through a solution of copper sulphate for 45 minutes?
Answer:
[Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1, IF = 96,500 C mol-1]
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
m = Z xI x t
= \(\frac{63.5}{2 \times 96500}\) x 5amp x 45 x 60 = \(\frac { 857250 }{ 193000 }\) = 4.44g
Question 19.
How much time would it take in minutes to deposit 1.18 g of metallic copper on a metal object when a current of 2.0 A is passed through the electrolytic cell containing Cu2+ ions?
Answer:
[Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1, IF = 96,500 C mol-1]
m = Z x I x t
1.18 = \(\frac{63.5}{2 \times 96500}\)
t = \(\frac{1.18 \times 2 \times 96500}{2 \times 63.5}\)
= 1793.23 sec
= \(\frac { 1793.23 }{ 60 }\) = 29.88 min
![]()
Question 20.
What is a salt bridge? What is it used for?
Answer:
A salt bridge is a U – shaped tube containing concentrated solution of an inert electrolyte like KCl, KNO3, K2SO4, etc., or a solidified solution of an electrolyte such as agar-agar and gelatine. It is used,
- To complete the electrical circuit by allowing ions to flow from one solution to the other without mixing the two solutions.
- To maintain the electrical neutrality of the solutions in the two half cells.
Question 21.
Calculate emf of the following cell of 25°C.
Answer:
Fe | Fe2+(0.001M) || H+(0.01M) | H2(g) (1 bar) pt
E0(Fe2+/Fe) = – 0.44V
E0(H+/H2) = 0.00V
Cell reaction
Fe + 2H+ Fe2+ + H2
E0cell = E0cathode – E0anode
E0cell = 0.44 – \(\frac{0.0591}{2}\) 10 g \(\frac{\left[10^{-3}\right]}{\left[10^{-2}\right]^{2}}\)
= 0.44 – \(\frac{0.0591}{2}\) 10g 10
= 0.44 – \(\frac{0.0591}{2}\)
E0cell = 0.4105V
Question 22.
What is corrosion? CO2 is always present in natural water. Explain its effect (increases, stops or no effect) on rusting of Fe.
Answer:
Corrosion is a process of slowly eating away of the metal due to the attack of atmospheric gases on thc surface of metal resulting into the formation of compounds such as oxides, suiphides, carbonates, suiphates, etc.
Factors affecting corrosion are:
- Reactivity of metal
- Presence of impurities
- Presence of air and moisture
- Strains in metals
- Presence of electrolytes
CO2 increases the rusting of iron because greater the number of W ions, faster the rusting will take place.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Electro Chemistry 5 Marks Question
VIII.Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
How would you measure the conductivity of ionic solutions?
Answer:
1. The conductivity of an electrolytic solution is determined by using a wheatstone bridge arrangement in which one resistance is replaced by a conductivity cell filled with the electrolytic solution of unknown conductivity.
2. In the measurement of specific resistance of a metallic wire, a DC power supply is used. Here AC is used for this measurement to prevent electrolysis. Because DC current through the conductivity cell leads to the electrolysis of the solution taken in the cell.
3. A wheatstone bridge is constituted using known resistances P,Q, a variable resistance S and conductivity cell. An AC source (550 Hz to 5 KHz) is connected between the junctions A and C. A suitable detector is connected between the junctions B and D.
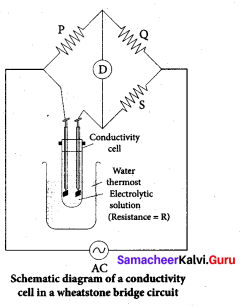
4. The variable resistance S is adjusted until the bridge is balanced and in this canditions, there is no current flow through the detector.
5. Under balanced condition
P/Q = R/S
R = P/Q x S ………..(1)
The resistance of the electrolytic solution (R) is calculated from the known resistance values P, Q and the measured S value using the equation (1).
6. Specific conductance (or) conductivity of an electrolyte can be calculated from the resistance value (R) using the following expression
7. The value of cell constant is usually provided by the cell manufacturer. Alternatively the cell constant may be determined using KCI solution whose concentration and specific conductance are known.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain about SHE (Standard Hydrogen Electrode).
Answer:
1. It is impossible to measure the emf of a single electrode, but we can H2 out H2 measure the potential difference between two electrodes (Ecell) using a voltmeter.
2. To calculate the emf of a single electrode, we need a reference electrode whose emf is known. For that purpose, Standard Hydrogen
Electrode (SHE) is used as the reference electrode.
3. SHE has been assigned an orbitary emf of exactly zero volt.
4. It consists of platinum electrode in contact with 1M HC1 solution and 1 atm hydrogen gas.
5. The hydrogen gas bubbled through the solution at 25°C. SHE can act as cathode as well as an anode.
6. The Half cell reactions are given below:
If SHE is used as a cathode, the reduction reaction is
2H2 + 2e– + H2(g,1 atm) E°= 0 volt
If SHE is used as an anode, the oxidation reaction is
H2(g, 1 atm) 2H+( aq, 1M) + 2e– E° = 0 volt.
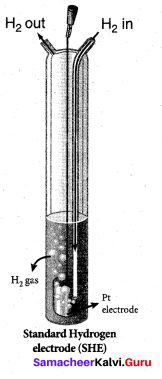
Question 3.
How would you determine the reduction potential of Zn/Zn2+(aq)? (or) How will you calculate the reduction potential of Half cell?
Answer:
1. Consider the zinc electrode dipped in zinc sulphate solution using SHE
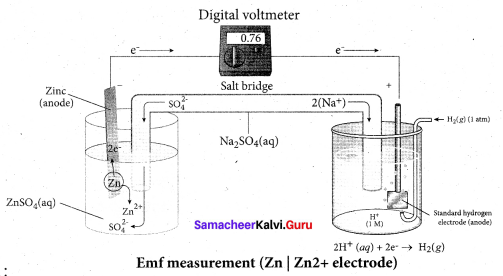
2. Step 1:
The following galvanic cell is constructed using SHE
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq.1M) | H2(g.1atm) | Pt(s)
3. Step 2:
The emf of the above galvanic cell is measured using a voltmeter. In this case the measured emf of the above galvanic cell is 0.76 V
4. Calculation:
We know that.
E°cell = (E°ox)zn|zn2+ + (E°red)SHE
E°cell = 0.76 + 0V
= 0.76 V
This oxidation potential corresponds to the below mentioned half cell reaction which takes place at the cathode
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– (oxidation)
(y) The emf of the reverse reaction will give the reduction potential
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn
(E°red)zn2+|zn = – 0.76V
Question 4.
Derive the relationship between Gibb’s free energy and maximum work obtained from galvanic cell and equilibrium constant.
Answer:
1. In a galvanic cell, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The electrical energy produced by the cell is equal to the product of the total charge of the electrons and emf of the cell which drives these electrons between the electrodes.
2. If ‘n’ is the number of moles of electrons exchanged between the oxidising and reducing
agent in the overall cell reaction, then the electrical energy produced by the cell is given
as below.
Electrical energy = change of ‘n’ moles of electrons x Ecell ……………..(1)
Charge of I mole of electrons = one Faraday = 1F
Charge of n moles of electrons = nF ……………..(2)
3. Electrical energy = nFEcell …………….(3)
This energy is used to do electric work. Therefore the maximum work that can be obtained from a galvanic cell is
Here the – ve sign is introduced to indicate that work is done by the system on the surroundings.
4. Second law of thermodynamics states that the maximum work done by the system is equal to the change in Gibbs free energy of the system
Wmax = ΔG …………..(5)
5. ΔG = – nFEcell (6)
For a spontaneous cell reactions, the AG should be negative. The above expression indicates that Ecell should be positive to get a negative AG value.
6. When all the cell components are in their standard state, the equation (6) becomes
ΔG° = – nFE°cell …………….(7)
7. The standard free energy change is related to the equilibrium constant as per the following equation.
ΔG° = – RT In Keq …………..(8)
Comparing equations (7) and (8)
nFE°cell = RT In Keq …………..(9)
nFE°cell = \(\frac { 2.303RT }{ nF }\) log Keq ………………(10)
Question 5.
Describe about the working principle of Leclanche cell.
Answer:
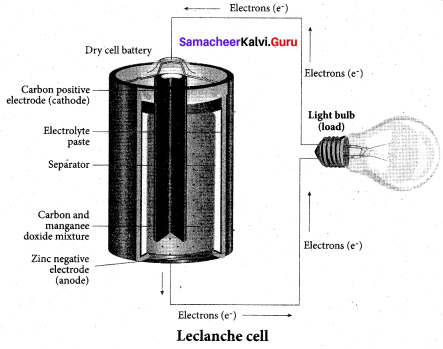
1. Leclanche cell:
Anode: Zinc container
Cathode: Graphite rod in contact with MnO2
Electrolyte: Ammonium chloride and Zinc chloride in water.
emf of the cell = 1.5 V
2. Cell reaction:
Oxidation at anode
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e– ……………(1)
Reduction at cathode
2NH+4 (aq) + 2e– → 2NH3(aq) + H2(aq)
3. The hydrogen gas is oxidised to water by MnO2
H2(g)+ 2MnO2(s) → Mn2O3(s) + H2O(1) ……(3)
Adding equations 1,2,3 the overall redox reaction
Zn(s) + 2NH+4(aq) + 2MnO2(s) → Zn2+(aq) + Mn2O3(s) + H2O(1) + 2NH3 …………….(4)
4. The ammonia produced at the cathode combines with Zn2+ to form a complex ion [Zn (NH3)4]2+(aq). As the reaction proceeds, the concentration of NH4+ will decrease and the aqueous NH3 will increase which lead to the decrease in the emf of the cell.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain about the construction and uses of mercury button cell.
Answer:
1. Mercury button cell:
Anode: Zinc Amalgamated with mercury
Cathode: HgO mixed with graphite
Electrolyte: Paste of KOH and ZnO.
2. Oxidation occurs at anode:
![]()
3. Reduction occurs at cathode
![]()
Hg(s) + 2OH–(aq)
Overall reaction is
Zn(s) + HgO(s) → ZnO(s) + Hg(1)
4. Cell emf: about 1.35 V
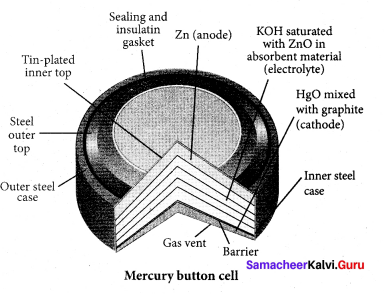
5. Uses:
It has higher capacity and longer life. It is used in pacemakers, electronic watches, cameras.
Question 7.
Describe about lead storage battery construction and its uses.
Answer:
Lead storage battery:
1. Anode – Spongy lead
Cathode – Lead plate bearing PbO2
Electrolyte – 38% by mass of H2SO4 with density 1.2 g/ml
2. Oxidation occurs at the anode
Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2e– ………..(1)
The Pb2+ ions combine with SO42- to form PbSO4 precipitate
Pb2+(aq) + SO42- → PbSO4(s) …………(2)
3. Reduction occurs at the cathode
PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e– → + 2H2O(1) ……….(3)
The Pb2+ ions also combines with SO42- ions to form sulphuric acid to form PbSO4 Precipitate
Pb2+(aq) + SO2-2+ → PbSO ………….(4)
4. The overall reaction is,
(1) + (2) + (3) + (4)
Pb(s) + pbO2(s) + 4H+(s) + 2SO2-4(s) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1)
5. The emf of a single cell is about 2V. Usually six such cells are combined in series to produce 12 volts.
6. The emf of the cell depends on the concentration of H2SO4. As the cell reaction uses SO42- ions, the concentration H2SO4 decreases. When the cell potential falls to about 1.8V, the cell has to be recharged.
7. Recharge of the cell – During recharge process, the role of anode and cathode is reversed and H2SO4 is regenerated. Oxidation occurs at cathode (now anode)
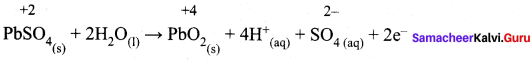
Reduction occurs at anode (now cathode)
PbSO4(s) + 2e– → Pb(s) + SO2-4(sq)
Overall reaction
2 pbSO4(s) + 2H2O(1) → pb(s) + pbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO2-4(aq)
The above reaction is exactly the reverse of redox reaction which takes place while discharging.
8. Uses: Lead storage battery is used in automobiles, trains, inverters.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe about lithium-ion battery and its uses.
Answer:
1. Lithium-ion battery
Anode – Porous graphite
Cathode – Transition metal oxide as CoO2
Electrolyte – Lithium salt in an organic solvent
2. At the anode oxidation occurs
Li(s) → Li+(aq) + e–
At the cathode reduction Occurs.
Li+ + CoO2(s) + e– → Li CoO2(s)
3. Overall reactions
Li(s) + CoO2 → Li CoO2(s)
4. Both electrodes allow Li ions to move in and out of their structures. During discharge the Li ions produced at the anode moves towards cathode through the non-aquaeous electrolyte.
5. When a potential greater than the emf produced by the cell is applied across the electrode, the cell reaction is reversed and now the Li+ ions move from cathode to anode where they become embedded on the porous electrode. This is known as intercalation.
6. Uses: This Li-ion battery is used in cellular phones, Laptop computer and digital camera.
Question 9.
What is corrosion? Explain about the electrochemical mechanism of corrosion.
Answer:
1. The metal is oxidised by oxygen in the presence of moisture. The redox process which causes the deterioration of metal is called corrosion.
2. Corrosion of iron is known as Rusting and it is an electrochemical process.
3. Electrochernical mechanism of corrosion – The formation of rust requires both oxygen and water. Since it is an electrochemical redox process, it requires both an anode and cathode in different places on the iron. The iron surface and a droplet of water on the surface form a tiny galvanic cell.
The region enclosed by water is exposed to low amount of oxygen and it act as anode. The remaining area has high amount of oxygen and it act as cathode. So based on oxygen amount, an electrochem leal cell is formed.
Fe(s) → Fe2+(aq) + 2e–
O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e– → 2H2O(1)
4. At anode:
2Fe(s) → 2Fe2+(aq) + 4e– E° = 1.23V
The electrons move through the iron metal from the anode to the cathode area where the oxygen dissolved in water is reduced to water.
5. At cathode:
The reaction of atmospheric carbondioxide with water gives carbonic acid which furnishes the H+ ions for reduction.
O2(s) + 4H+(g) + 4H+(aq) → 2H2O(1)
E° = 1.23 V
= + 1.67V
6. The electrical circuit is completed by the migration of ions through water droplet. The overall redox reaction is
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) → 2Fe3+(aq) + 2H2O(1).
E°= 0.44+ 1.23
= + 1.67 V
7. The positive emf value indicates that the reaction is spontaneous.
8. The Fe2+ ions are further oxidised to Fe3+ which on further reaction with oxygen to form rust.
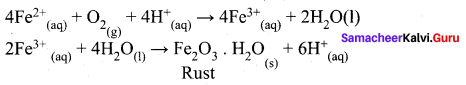
Question 10.
Explain about the various protection methods to prevent corrosion.
1. Coating metal surface by paint
2. Galvanizing – By Coating with another metal such as zinc. Zinc is stronger oxidising agent than iron and hence it can be more easily corroded than iron. i.e., instead of iron, zinc is oxidised.
3. Cathodic protection: In this technique, unlike galvanizing, the entire surface of the metal to be protected need not be covered with a protecting metal instead, metals such as Mg (or) Zn which is corroded more easily than iron can be used as sacrificial anode and the iron material act as cathode. So iron protected but Mg or Zn gets corroded.
4. Passivation – The metal is treated with strong oxidising agent such as Conc. HNO3. As a result, a protective layer is formed on the surface of the metal.
5. Alloy formation – The oxidising tendency of iron can be reduced by forming its alloy with other more anodic metals. Example – Stainless steel, an alloy of Fe and Cr.
Question 11.
(a) Give reasons for the following
- Rusting of iron is quicker in saline water than in ordinary water.
- Aluminium metal cannot be produced by the electrolysis of aqueous solution of aluminium salt.
(b) Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCI solution is 1oo ohms. If the resistance of the sanie cell when filled with 0.02 M KCI solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCI solution. Conductivity of 0.01 M KCI solution is 1.29 S m-1.
Answer:
(a)
1. It is because in saline water, there are inore H4 ions. Greater the number of H4 ions, quicker the rusting will take place.
2. It is because aluminium metal is more reactive than hydrogen and it will react with H2O.
(b)
Cell constant = Conductivity (k) x Resistance (R)
= 1.29 S m-1 x 100Ω
= 1.29 m-1 = 1.29 cm-1
λm = \(\frac { 100k }{ M }\)
k = \(\frac { 1 }{ R }\) x \(\frac { l }{ A }\)
k = \(\frac { 1 }{ 520Ω }\) x 1.29 cm-1, where
k = 2.48 x 10-3S cm-1
λm = \(\frac{100 \times 0.248 \times 10^{-2}}{0.02}\)
= 124 S cm2 mol1
![]()
Question 12.
1. State two advantages of H2 – O2 fuel cell over ordinary cell.
2. Silver is electron deposited on a metallic vessel of total surface area 900 cm2 by passing a current of 0.5 amp for two hours. Calculate the thickness of silver metal deposited. [Given: Density of silver = 10.5 g cm-3 Atomic mass of silver = 108 u. IF = 96500 C mol-1].
Answer:
1.
- It is highly efficient and do not produce pollution.
- The H2O so produced can be used by astronauts for drinking purpose.
2.
m = Z x l x t
m = \(\frac{108}{96500}\) x 0.5 x 2 x 60 x 60
= \(\frac{108 \times 5}{965 \times 10}\) x 2 x 6 x 6 = 4.03g
4.03g = V x d
4.03 g = V x 10.5 g cm-3
V = Area x thickness
v = 4.03
= 900 cm2 x thickness
Thickness = \(\frac{4.03}{10.5}\)
\(\frac{0.338 \mathrm{cm}^{3}}{900 \mathrm{cm}^{2}}\) = 4.26 x 10-4cm
Question 13.
Distinguish between Leclanche cell and Lead storage battery.
Answer:
Leclanche Cell
- It is a primary cell
- It is a non-rechargeable cell
- Anode : Zinc container
Cathode : Graphite rod in contact with MnO2 - Electrolytes: Ammonium chloride and zinc chloride in water
- Emf of the cell = 1.5 V
Lead storage battery
- It is a secondary cell
- It is rechargeable cell
- Anode : Spongy lead
Cathode : Lead plate bearing PbO2 - Electrolytes: 38% by mass of H2SO4 with density 1.2 g/ml
- emf of the cell 2 V.
![]()
Question 14.
Account for the following
- Aluminium undergo slow corrosion than iron.
- H2 – O2 fuel cell ¡s more useful than other cells.
Answer:
1. Aluminium, copper, silver also undergo corrosion but at a slower rate than iron. For eg., let us consider the reduction of Aluminium
Al(s) → Al3+(aq) + 3e–
Al3+ which reacts with oxygen in air to form a protective coating of AI2O3. This coating act as a protective film for the inner surface. So further corrosion is prevented.
2. H2 – O2 fuel cell is more advanced. Because it is highly efficient. it is pollution free. In this, H2 – O2 fuel cell, energy of combustion of fuel is directly converted to electrical energy.
Common Errors
- Units of electrical quantities may get confused.
- Writing cell notation may be difficult.
Rectifications
1.Resistance – R ohm (Ω)
Potential difference – V = Volt
Amount of current – 1 = ampere
Specific resistance (ohm m) (Ω m)
Conductivity = Siemen = S
Specific conductance – k = S m-1
Molar conductance = S m2 mol-1
Equivalent conductance = S m2 gram equivalent-1
Cell constant = m-1
2. Easy way is (AC)
solid I aqueous solution II aqueous solution I soLid