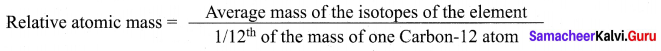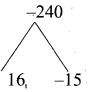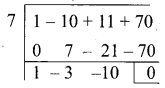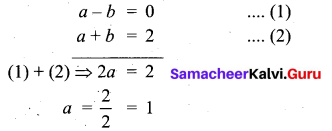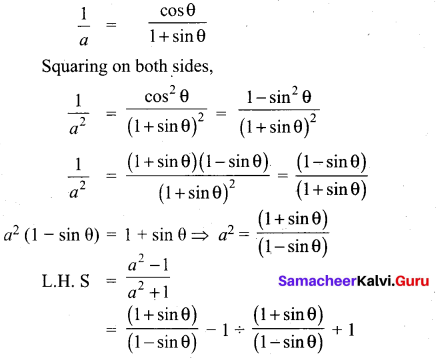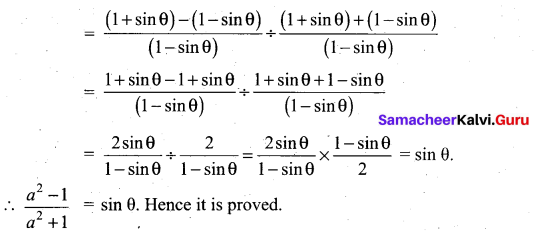Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
Instructions
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Quèstions of one-mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and.writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II àre two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are eight-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 100
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
If there are 10 relations from a set A = {1, 2, 3,4, 5} to a set B, then the number of elements in B is ………….. .
(1) 3
(2) 2
(3) 4
(4) 8
Answer:
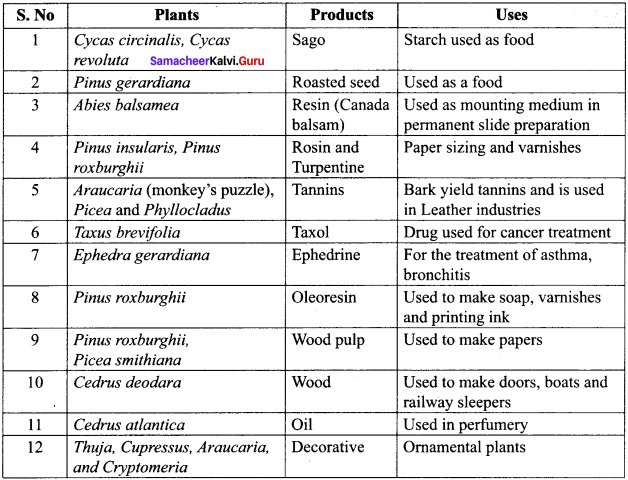
(2) 2
![]()
Question 2.
If g = {(1,1),(2, 3),(3,5),(4,7)} is a function given by g(x) = αx + β then the values of α and β are ………….. .
(1) (-1,2)
(2) (2,-1)
(3) (-1,-2)
(4) (1,2)
Answer:
(2) (2,-1)
Question 3.
If 74k = ………….. (mod 100)
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
Answer:
(1) 1
Question 4.
The next term ot the sequence \(\frac{3}{16}, \frac{1}{8}, \frac{1}{12}, \frac{1}{18}\) is ………….. .
(1) \(\frac{1}{24}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{27}\)
(3) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(4) \(\frac{1}{81}\)
Answer:
(2) \(\frac{1}{27}\)
Question 5.
If (x – 6) is the HCF of x2 – 2x – 24 and x2 – kx – 6 then the value of K is ………….. .
(1) 3
(2) 5
(3) 6
(4) 8
Answer:
(2) 5
Question 6.
Find the matrix X if 2X + \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 7 \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 & 7 \\ 9 & 5 \end{matrix} \right]\) ………….. .
(1) \(\left[ \begin{matrix} -2 & -2 \\ 2 & -1 \end{matrix} \right] \)
(2) \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & 2 \\ 2 & -1 \end{matrix} \right] \)
(3) \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] \)
(4) \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] \)
Answer:
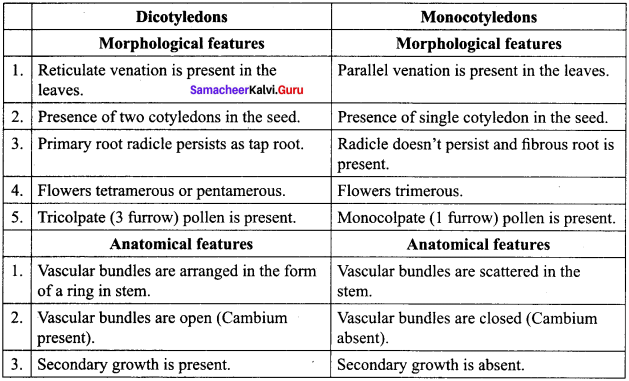
(2) \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & 2 \\ 2 & -1 \end{matrix} \right] \)
![]()
Question 7.
The two tangents from an external points P to a circle with centre at O are PA and PB. If ∠APB = 70° then the value of ∠AOB is ………….. .
(1) 100°
(2) 110°
(3) 120°
(4) 130°
Answer:
(2) 110°
Question 8.
The equation of a line passing through the origin and perpendicular to the line 7x – 3y + 4 = 0 is ………….. .
(1)7x – 3y + 4 = 0
(2) 3x – 7y + 4 = 0
(3) 3x + 7y = 0
(4) 7x – 3y = 0
Answer:
(3) 3x + 7y = 0
Question 9.
If x = a tan θ and y = b sec θ then ………….. .
(1) \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\)
(2) \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\)
(3) \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=0\)
(4) \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}=0\)
Answer:
(1) \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\)
Question 10.
The ratio of the volumes of a cylinder, a cone and a sphere, if each has the same diameter and same height is ………….. .
(1) 1:2:3
(2) 2:1:3
(3) 1:3:2
(4) 3:1:2
Answer:
(4) 3:1:2
![]()
Question 11.
The probability of getting a job for a person is \(\frac { x }{ 3 }\). If the probability of not getting the job is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) then the value of x is ………….. .
(1) 2
(2) 1
(3) 3
(4) 1.5
Answer:
(2) 1
Question 12.
Variance of the first 11 natural numbers is ………….. .
(1) √5
(2) √10
(3) 5√2
(4) 10
Answer:
(4) 10
Question 13.
If α and β are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 then (α + β)2 is ………….. .
(1) \(-\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
(2) \(\frac{c^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
(3) \(\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
(4) \(\frac{b c}{a}\)
Answer:
(3) \(\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
Question 14.
If K(x) = 3x – 9 and L(x) = 7x – 10 then Lok is ………….. .
(1) 21x + 73
(2) -21x + 73
(3) 21x – 73
(4) 22x – 73
Answer:
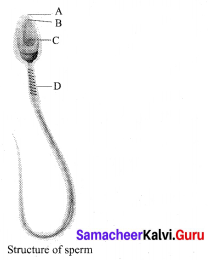
(3) 21x – 73
![]()
PART – II
II. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 × 2 = 20]
Question 15.
Let A = {1,2,3,4,…, 45} and R be the relation defined as “is square of ” on A. Write R as a subset of A × A. Also, find the domain and range of R.
Answer:
A = {1,2,3,4. . . .45} .
The relation is defined as “is square of’
R = {(1, 1) (2, 4) (3, 9) (4, 16) (5, 25) (6, 36)} .
Domain of R = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Range of R = {1,4,9,16,25,36}
Question 16.
If f(x) = 3x – 2, g(x) = 2x + k and if fog = gof, then find the value of k.
Answer:
f(x) = 3x – 2, g(x) = 2x + k
fog(x) = f(g(x)) = f(2x + k) = 3(2x + k) – 2 = 6x + 3k – 2
Thus, fog(x) = 6x + 3k – 2.
gof(x) = g(3x – 2) = 2(3x – 2) + k
Thus, gof(x) = 6x – 4 + k.
Given that fog = gof
Therefore, 6x + 3k – 2 = 6x – 4 + k
6x – 6x + 3k – k = – 4 + 2 ⇒ k = – 1
Question 17.
Find the rational form of the number \(0 . \overline{123}\).
Answer:
Letx = \(0 . \overline{123}\)
= 0.123123123….
= 0.123 + 0.000123 + 000000123 + ….
This is an infinite G.P
Here a = 0.123, r = \(\frac{0.000123}{0.123}\) = 0.001
Sn = \(\frac{a}{1-r}=\frac{0.123}{1-0.001}=\frac{0.123}{0.999}=. \frac{41}{333}\)
![]()
Question 18.
How many consecutive odd integers beginning with 5 will sum to 480?
Answer:
First term (a) = 5
Common difference (d) = 2 (consecutive odd integer)
Sn = 480
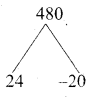
\(\frac { n }{ 2 }\) [2a + (n – 1)d] = 480
\(\frac { n }{ 2 }\) [10 + (n – 1)2] = 480
\(\frac { n }{ 2 }\) [10 + 2n – 2] = 480
\(\frac { n }{ 2 }\) (8 + 2 n) = 480
n( 4 + n) = 480
4n + n2 – 480 = 0
n2 + 4n – 480 = 0
(n + 24) (n – 20) = 0
n + 24 = 0 or n – 20 = 0
n = -24 or n = 20 [number of terms cannot be negative]
∴ Number of consecutive odd integers is 20
Question 19.
Simplify \(\frac{5 t^{3}}{4 t-8} \times \frac{6 t-12}{10 t}\)
Answer:

![]()
Question 20.
Solve the following quadratic equations by factorization method √2x2 + 7x + 5 √2 = 0
Answer:
√2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0
√2x2 + 2x + 5x + 5√2 = 0
√2x(x + √2) + 5(x + √2) = 0
(x + √2) + 5(x + √2) = 0
(x + √2) or 5(x + √2) = 0 (equate the product of factors to zero)
x = -√2 or √2x = -5 x ⇒ x = \(\frac{-5}{\sqrt{2}}\)
The roots are -√2, \(\frac{-5}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Question 21.
Find the value of a, b, c, d from the equation \(\begin{pmatrix} a-b & 2a+c \\ 2a-b & 3c+d \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 5 \\ 0 & 2 \end{pmatrix}\)
Answer:
The given matrices are equal. Thus all corresponding elements are equal.
Therefore, a – b = 1 …(1)
2a + c = 5 …(2)
2a – b = 0 ….(3)
3c + d = 2 …(4)
(3) gives 2a – b = 0 …(4)
2 a = b …(5)
Put 2a = b in equation (1), a – 2a = 1 gives a = -1
Put a = -1 in equation (5), 2(-1) = b gives b = -2 .
Put a = -1 in equation (2), 2(-1) + c = 5 gives c = 7
Put c = 7 in equation (4), 3(7) + d = 2 gives = -19
Therefore, a = -1, b = -2, c = 7, d = -19
![]()
Question 22.
In ∆ABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC If AD = 8x -7 , DB = 5x – 3 , AE = 4x – 3 and EC = 3x – 1, find the value of x.
Answer:
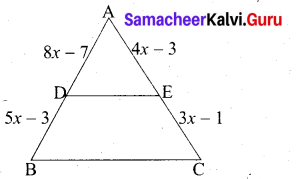
Given AD = 8x – 7; BD = 5x – 3; AE = 4x – 3; EC = 3x – 1
In ∆ABC we have DE || BC
By Basic proportionality theorem
\(\frac{A D}{D B}=\frac{A E}{E C}\)
\(\frac{8 x-7}{5 x-3}=\frac{4 x-3}{3 x-1}\)
(8x – 7) (3x -1) = (4x -3) (5x -3)
24x2 – 8x – 21x + 7 = 20x2 – 12x – 15x + 9
24x2 – 20x2 – 29x + 27x + 7 – 9 = 0
4x2 – 2x – 2 = 0 .
2x2 – x – 1 = 0 (Divided by 2)
2x2 – 2x + x – 1 = 0
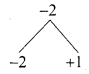
2x(x – 1) + 1 (x – 1) = 0
(x – 1) (2x + 1) = 0
x – 1 = 0 or 2x + 1 = 0
x = 1 or 2x = -1 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (Negative value will be omitted)
The value of x = 1
![]()
Question 23.
The hill in the form of a right triangle has its foot at (19, 3) . The inclination of the hill to the ground is 45°. Find the equation of the hill joining the foot and top.
Answer:
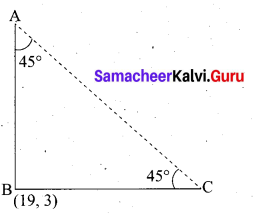
Slope of AB (m) = tan 45° = 1
Equation of the hill joining the foot and the top is 45°
y – y1 = m(x – x1
y – 3 = 1(x – 19)
y – 3 = x – 19
– x + y – 3 + 19 = 0
– x + y + 16 = 0
x – y – 16=0
The required equation is x – y – 16 = 0
Question 24.
Prove that \(\sqrt{\frac{1+\sin \theta}{1-\sin \theta}}\) = sec θ + tan θ
Answer:
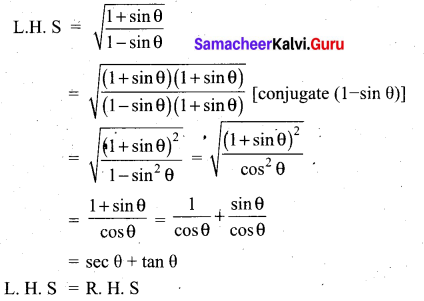
![]()
Question 25.
If the total surface area of a cone of radius 7cm is 704 cm2, then find its slant height.
Answer:
Given that, radius r = 7 cm
Now, total surface area of the cone = πr(l + r)sq. units
T.S.A = 704 cm2
704 = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 7(l + 7)
32 = l + 7 implies l = 25 cm
Therefore, slant height of the cone is 25 cm.
Question 26.
The first term of an A.P is 6 and the common difference is 5. Find the A.P and its general term.
Answer:
Given a = 6, d = 5
General term tn = a + (n – 1) d
= 6 + (n – 1)5
= 6 + 5n – 5
= 5n + 1
The general form of the A.P is a, a + d, a + 2d ………
The A.P. is 6, 11, 16, 21 …. 5n + 1
Question 27.
If θ is an acute angle and tan θ + cot θ = 2 find the value of tan7θ + cot7θ
Answer:
Given tan θ + cot θ = 2
tan θ + \(\frac{1}{\tan \theta}\) = 2
\(\frac{\tan ^{2} \theta+1}{\tan \theta}\) = 2
tan2θ + 1 = 2 tan θ
tan2θ – 2 tan θ + 1 = 0
(tan θ – 1)2 = 0
∴ tanθ – 1 = 0
tanθ = 1
tanθ = tan45 ⇒ θ = 45°
tan7θ + cot7θ = tan745° + cot 745°
= (1)7 + (1)7
= 2
![]()
Question 28.
Cards marked with the numbers 2 to 101 are placed in a box and mixed thoroughly one card is drawn from this box. Find the probability that the number on the card is a number which is a perfect square.
Answer:
Sample space = {2, 3, 4,… 101}
n(s) = 100
Let A be the event of getting perfect square numbers
A= {4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100}
n(A) = 9
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{9}{100}\)
Probability of getting a card marked with a number which is a perfect square is \(\frac{9}{100}\)
PART – III
III. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 × 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Consider the functions f(x) = x2, g(x) = 2x and h(x) = x + 4 Show that (fog)oh = fo(goh)
Answer:
f(x) = x2 ; g(x) = 2x and h(x) = x + 4
(fog) x = f[g(x)]
= f( 2X)
= (2x)2
= 4x2
(fog) oh (x) = fog [h(x)]
= fog(x + 4)
= 4(x + 4)2
= 4[x2 + 8x + 16]
= 4x2 + 32x + 64 ….(1)
goh (x) = g[h(x)]
= g(x + 4)
= 2(x + 4)
= 2x + 8
fo(goh)x = fo[goh(x)}
= f[2x + 8}
= (2x + 8)2
= 4x2 + 32x + 64 ……. (2)
From (1) and (2) we get (fog) oh = fo(goh)
![]()
Question 30.
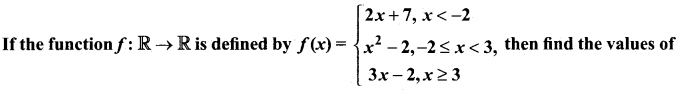
(i) f(4)
(ii) f(-2)
(iii) f(4) + 2f(1)
(iv) \(\frac{f(1)-3 f(4)}{f(-3)}\)
Answer:
The function f is defined by three values in intervals I, II, III as shown by the side
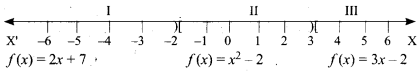
For a given value of x = a, find out the interval at which the point a is located, there after find f(a) using the particular value defined in that interval.
(i) First, we see that, x = 4 lie in the third interval.
Therefore, f(x) = 3x – 2 ; f(4) = 3(4) – 2 = 10
(ii) x = -2 lies in the second interval.
Therefore, f(x) = x2 – 2 ; f(-2) = (-2)2 – 2 = 2
(iii) From (i), f(4) = 10.
To find f(1), first we see that x = 1 lies in the second interval.
Therefore,f(x) = x2 – 2 => f(1) = 12 – 2 = -1
So, f(4) + 2f(1) = 10 + 2 (-1) = 8
(iv) We know that f(1) = -1 and f(4) = 10.
For finding f(-3), we see that x = -3 , lies in the first interval.
Therefore, f(x) = 2x + 7; thus, f(-3) = 2(-3) + 7 = 1
Hence, \(\frac{f(1)-3 f(4)}{f(-3)}=\frac{-1-3(10)}{1}=-31\)
Question 31.
If (m + 1)th term of an A.P. is twice the (n + 1)th> term, then prove that (3m + 1)th term is twice the (m + n + 1)th term.
Answer:
tn = a + (n – 1)d
Given tm+1 = 2 tn+1
a + (m + 1 – 1)d = 2[a + (n + 1 – 1)d]
a + md = 2(a + nd) ⇒ a + md = 2a + 2nd
md – 2nd = a
d(m – 2n) = a ……. (1)
To prove that t3m + 1 = 2(t3m + n + 1)
L.H.S. = t3m + 1
= a + (3m + 1 – 1 )d
= a + 3md
= d(m – 2n) + 3md (from 1)
= md – 2nd + 3md
= 4md – 2nd
= 2d (2m – n)
R.H.S. = 2 (tm + n + 1)
= 2[a + (m + n + 1 – 1) d]
= 2 [a + (m + n)d]
= 2 [d (m – 2n) + md + nd)] (from 1)
= 2 [dm – 2nd + md + nd]
= 2 [2md – nd] = 2d (2m – n)
R.H.S = L.H.S
∴ t(3m + 1)= 2t(m + n + 1)
![]()
Question 32.
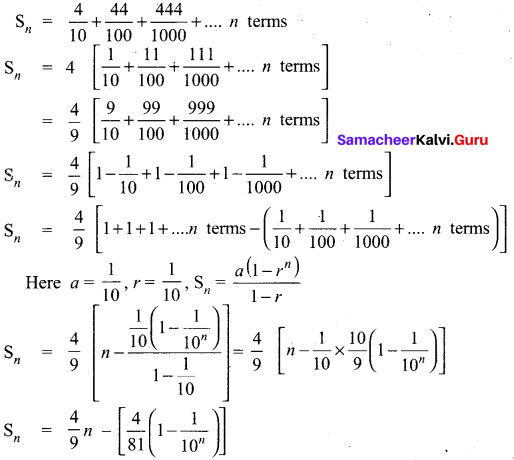
Find the sum to n terms of the series 5 + 55 + 555 + ….
Answer:
The series is neither Arithmetic nor Geometric series. So it can be split into two series and then find the sum.
5 + 55 + 555 + …. + n terms = 5[1 + 11 + 111 + …. + n terms]
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\)[9 + 99 + 999 + …. + « terms]
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\)[(10 – 1) + (100 – 1) + (1000 – 1) + …. + n terms)]
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\)[(10 + 100 + 1000 + …. +n terms) -n]
= \(\frac{5}{9}\left[\frac{10\left(10^{n}-1\right)}{(10-1)}-n\right]=\frac{50\left(10^{n}-1\right)}{81}-\frac{5 n}{9}\)
Question 33.
Vani, her father and her grand father have an average age of 53. One-half of her grand father’s age plus one-third of her father’s age plus one fourth of Vani’s age is 65. If 4 years ago Vani’s grandfather was four times as old as Vani then how old are they all now?
Answer:
Let the age of Vani be”x” years
Vani father age = “y” years
Vani grand father = “z” years
By the given first condition.
\(\frac{x+y+z}{3}=53\)
x + y + z = 159….(1)
By the given 2nd condition.
\(\frac{1}{2} z+\frac{1}{3} y+\frac{1}{4} x=65\)
Multiply by 12
6z + 4y +3x = 780
3x + 4y + 6z = 780 ….(2)
By the given 3rd condition
z – 4 = 4 (x – 4) ⇒ z – 4 = 4x – 16
-4x + z = -16 + 4
4x – z = 12 ….(3)
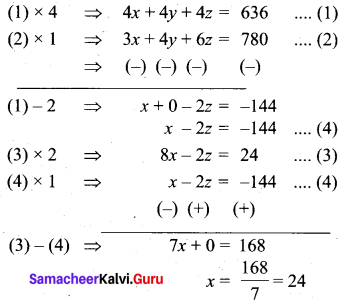
Substitute the value of x = 24 in (3)
4 (24) – z = 12
96 – z = 12
-Z = 12 – 96
z = 84
Substitute the value of
x = 24 and z = 84 in (1)
24 + y + 84 = 159
y + 108 = 159
y = 159 – 108
= 51
Vani age = 24 years
Vani’s father age = 51 years
Vani – grand father age = 84 years
![]()
Question 34.
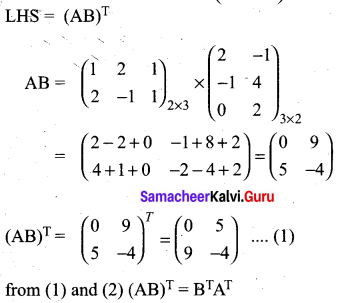
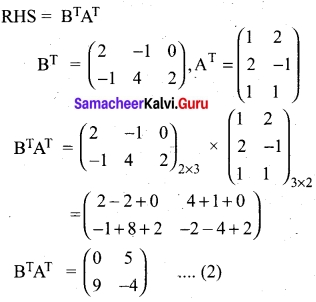
If A = \(\left( \begin{matrix} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & -1 & 1 \end{matrix} \right)\) and B = \(\left( \begin{matrix} 2 & -1 \\ -1 & 4 \\ 0 & 2 \end{matrix} \right)\) show that (AB)T = BTAT
Answer:
Question 35.
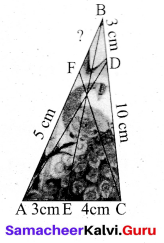
In figure, O is the centre of the circle with radius 5 cm. T is a point such that OT = 13 cm and OT intersects the circle E, if AB is the tangent to the circle at E, find the length of AB.
Answer:
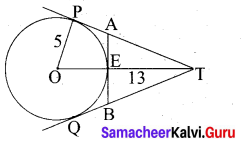
In the right ∆ OTP,
PT2 = OT2 – OP2
= 132 – 52
= 169 – 25 = 144
PT = √144 = 12 cm
Since lengths of tangent drawn from a point to circle are equal.
∴ AP = AE = x .
AT = PT – AP
= (12 – x) cm
Since AB is the tangent to the circle E.
∴ OE ⊥ AB .
∠OEA= 90°
∠AET = 90°
In ∆AET, AT2 = AE2 + ET2
In the right triangle AET,
AT2 = AE2 + ET2
(12 – x)2 = x2 + (13 – 5)2
144 – 24x + x2 = x2 + 64
24x = 80 ⇒ x = \(\frac{80}{24}=\frac{20}{6}=\frac{10}{3}\)
BE = \(\frac{10}{3}\) cm
AB = AE + BE
= \(\frac{10}{3}+\frac{10}{3}=\frac{20}{3}\)
∴ Length of AB = \(\frac{20}{3}\) cm
![]()
Question 36.
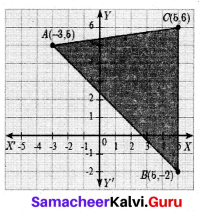
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices are at (-9, 0), (-8, 6), (-1, -2) and (-6,-3)
Answer:
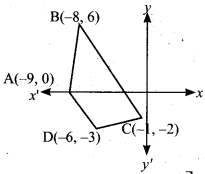
Let the vertices A(-9, 0), B(-8, 6), C(-1, -2) and D(-6, -3)
Plot the vertices in a graph and take them in counter – clock wise order.
Area of the Quadrilateral DCB
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y4 + x4y1) – (x2y1 + x3y2 + x4y3 + x1y4 )]
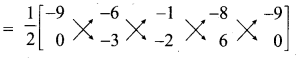
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [27 + 12- 6 + 0 -(0 + 3 + 16 – 54)]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [33 -(-35)]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [33 + 35] = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 68 = 34 sq. units.
Area of the Quadrilateral = 34 sq. units
Question 37.
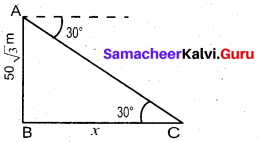
A pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top of the pole observed from a point ‘A’ on the ground is 60° and the angle of depression to the point ‘A’ from the top of the tower is 45°. Find the height of the tower. (√3 = 1.732)
Answer:
Let BC be the height of the tower and CD be the height of the pole.
Let‘A’be the point of observation.
Let BC = x and AB = y.
From the diagram,
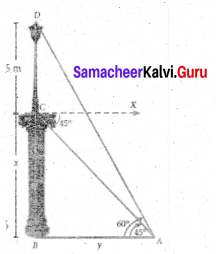
∠BAD = 60° and ∠XCA = 45° = ∠BAC ,
In right triangle ABC, tan 45° = \(\frac{B C}{A B}\)
gives 1 = \(\frac { x }{ y }\) so, x = y …… (1)
In right triangle ABD, tan60° = \(\frac{B D}{A B}=\frac{B C+C D}{A B}\)
gives √3 = \(\) so, √3y = x + 5
we get √3x = x + 5 [From (1)]
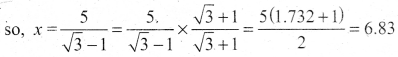
Hence, height of the tower is 6.83 m.
![]()
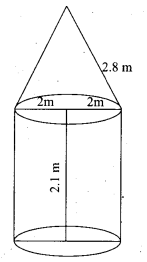
Question 38.
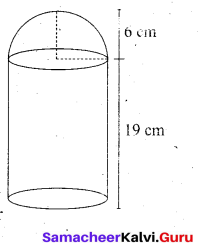
A shuttle cock used for playing badminton has the shape of a frustum of a cone is mounted on a hemisphere. The diameters of the frustum are 5 cm and 2 cm. The height of the entire shuttle cock is 7 cm. Find its external surface area.
Answer:
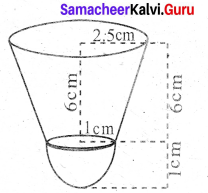
Radius of the lower end of the frustum (r) = 1 cm
Radius of the upper end of the frustum (R) = 2.5 cm
Height of the frustum (h) = 6 cm
Let “l” be the slant height of the frustum
l = \(\sqrt{h^{2}+(\mathrm{R}-r)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{6^{2}+(2.5-1)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+2.25}\) = \(\sqrt{38.25}\)
= 6.18 cm
External surface area of shuttle cock = C.S.Aof the frustum + C.S.Aof a hemisphere
= πl(R + r) + 2 πr2
= π [6.18 (2.5 + 1) + 2 × 12] cm2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\)[6.18 × 3.5 + 2]
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × (21.63 + 2)
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 23.63 cm2 = 74.26 cm2
External surface area = 74.26 cm2
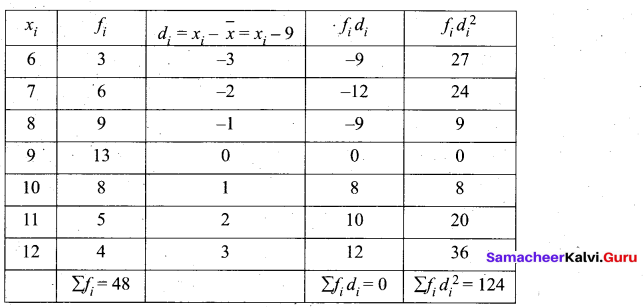
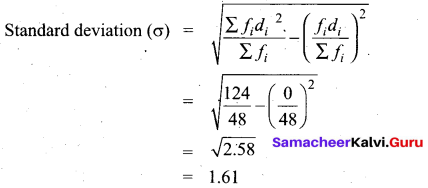
Question 39.
The mean and variance of seven observations are 8 and 16 respectively. If five of these are 2, 4,10,12 and 14, then find the remaining two observations.
Answer:
Let the missing two observation be ‘a’ and ‘b’
Arithmetic mean = 8
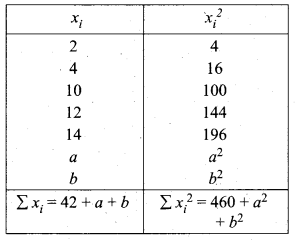
\(\frac{2+4+10+12+14+a+b}{7}\) = 8 ⇒ \(\frac{42+a+b}{7}\) = 8
a + b + 42 = 56
a + b = 56 – 42
a + b = 14 ……… (1)
Variance = 16
Variance = \(\frac{\Sigma x_{i}^{2}}{n}-\left(\frac{\Sigma x_{i}}{n}\right)^{2}\)
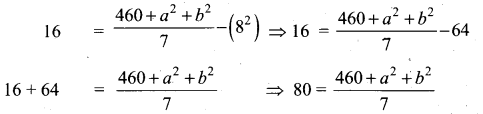
560 – 460 = a2 + b2
a2 + b2 = 100 ⇒ (a + b)2 – 2ab = 100 [a2 + b2 = (a+b)2 – 2 ab]
142 – 2 ab = 100 ⇒ 196 – 2 ab = 100 [a + b = 14(from (1)]
196 – 100 = 2ab
96 = 2ab ⇒ ab = \(\frac{96}{2}\) = 48
∴ b = \(\frac{48}{a}\) …… (2)
Substitute thr value of b = \(\frac{48}{a}\) in (1)
a + \(\frac{48}{a}\) = 14 ⇒ a2 + 48 = 14a
a2 – 14a + 48 = 0 ⇒ (a – 6) (a – 8) = 0
a = 6 or 8
when a = 6
b = \(\frac{48}{a}=\frac{48}{6}=8\) = 8
when a = 8
b = \(\frac{48}{a}=\frac{48}{6}=8\) = 6
∴ Missing observation is 8 and 6 (or) 6 and 8
![]()
Question 40.
From a solid circular cylinder with height 10 cm and radius of the base 6 cm, a right circular cone of the same height and same base is removed. Find (i) the volume of the remaining solid also, find (ii) the whole surface area.
Answer:
Circular cylinder
Radius of the base (r) = 6 cm
Height of the cylinder (h) = 10 cm
Circular Cone
Radius of the base (R) = 6 cm
Height of the cone (H) = 10 cm
(i) Volume of the remaining solid = Volume of the cylinder – Volume of the cone
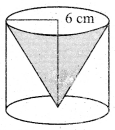
= πr2h – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)πR2H
= π(r2h – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)R2H)
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) [6 × 6 × 10 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) × 6 × 6 × 10] cm2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) [360 – 120] cm3
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 240 cm3
= \(\frac { 5280 }{ 7 }\) cm3 = 754.29 cm3
(ii) Slant height of a cone = \(\sqrt{h^{2}+r^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{10^{2}+6^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{100+36}\)
= \(\sqrt{136}\) = 11.66 cm
Whole surface area of the solid = curved surface area of the cylinder + curved surface area of the cone + base area
= 2 πrh + πRI + πr2
= π[2 × 6 × 10 + 6 × 11.66 + 6 × 6]
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\)[120 + 69.96 + 36] cm2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 225.96 cm2
= \(\frac { 4971.12 }{ 7 }\) cm2
= 710.16 cm2
(i) Volume of the remaining solid = 754.29 cm3
(ii) whole surface area = 710.16 cm2
![]()
Question 41.
If a and p are the roots of the equation 3x2 – 6x + 1=0 form the equation whose roots are 2α + β and 2β + α
Answer:
α and β are the roots of 3x2 – 6x + 1 = 0
α + β = \(\frac { 6 }{ 3 }\) = 2
αβ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
Given the roots are 2α + β; 2β + α
Sum of the roots = 2α + β + 2β + α
= 2(α + β) + (α + β)
= 2(2) + 2
= 6
Product of roots = (2α + β) (2β + α)
= 4αβ + 2α2 + 2β2 + αβ
= 5αβ + 2(α2 + β2)
5αβ + 2[(α + β)2 – 2αβ]
= 5 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + 2 (4 – 2 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\))
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\) + \(2\left(\frac{12-2}{3}\right)\)
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\) + 2 × \(\frac { 10 }{ 3 }\)
= \(\frac{5}{3}+\frac{20}{3}\)
= \(\frac { 25 }{ 3 }\)
The quadratic polynomial is x2 – (sum of the roots)x – product of the roots = 0
x2 – 6x + \(\frac { 25 }{ 3 }\) = 0
3x2 – 18x + 25 = 0
Question 42.
Tw o dice are rolled simultaneously. Find the probability that that sum of the numbers on the faces is neither divisible by 3 nor by 4.
Answer:
Sample space = {(1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (2,6), (3.1) , (3,2), (3,3), (3,4), (3,5), (3,6), (4,1), (4,2), (4,3), (4,4), (4,5), (4,6), (5.1) , (5,2), (5,3), (5,4), (5,5), (5,6), (6,1), (6,2), (6,3), (6,4), (6,5), (6,6)}
n(S) = 36
Let A be the event of getting the sum is divisible by 3 ‘
A = { (1,2) (2,1) (1,5) (5,1) (2,4) (4,2) (3,3) (3,6) (6,3) (4,5) (5,4) (6,6)}
n (A) = 12
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{12}{36}\)
Let B be the event of getting a sum is divisible by 4.
B = {(1,3) (2,2) (2,6) (3,1) (3,5) (4,4) (5,3) (6,2) (6,6)} n (B) = 9
n(B) = 9
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{9}{36}\)
A ∩ B = {(6,6)}
n(A ∩ B) = 1
P(A ∩ B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A} \cap \mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{1}{36}\)
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P (A ∩ B)
\(=\frac{12}{36}+\frac{9}{36}-\frac{1}{36}\)
\(=\frac{12+9-1}{36}=\frac{20}{36}\)
Neither divisible by 3 nor by 4
P(A’ ∩ B’) = P(A ∪ B)’
= 1 – p(A ∪ B) = 1 – \(\frac{20}{36}=\frac{36-20}{36}\)
= \(\frac{16}{36}=\frac{4}{9}\)
![]()
PART-IV
IV. Answer all the questions. [2 × 8 = 16]
Question 43.
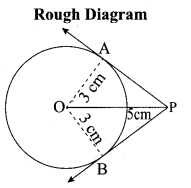
(a) Draw the two tangents from a point which is 10 cm away from the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. Also, measure the lengths of the tangents.
Answer:
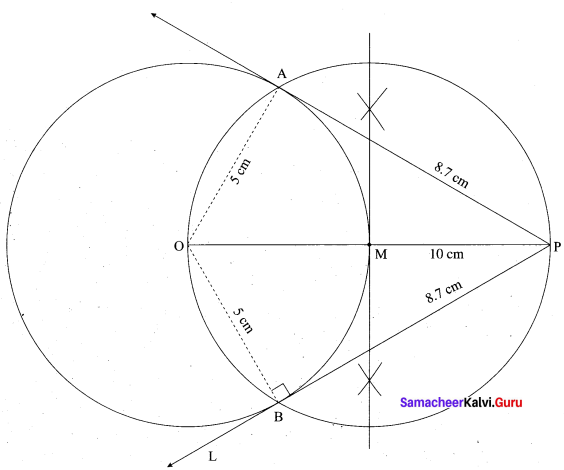
Steps of construction:
- With. O as centre, draw a circle of radius 5 cm.
- Draw a line OP = 10 cm.
- Draw a perpendicular bisector of OP, which cuts OP at M.
- With M as centre and MO as radius draw a circle which cuts previous circle at A and B.
- Join AP and BP. AP and BP are the required tangents.
Verification: In the right ∆ OAP
PA2 = OP2 – OA2
= 102 – 52 = \(\sqrt{100-25}\) = √75 = 8.7 cm.
Length of the tangent is 8.7 cm
![]()
[OR]
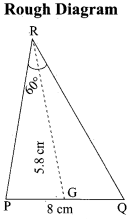
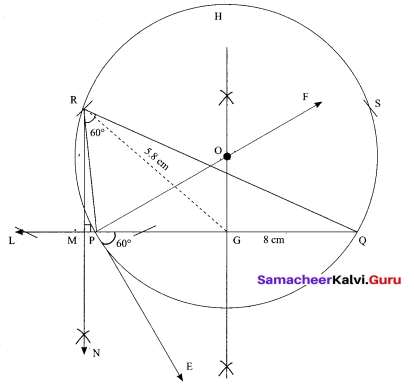
(b) Construct a ∆PQR which the base PQ = 4.5 cm, R = 35° and the median from R to RG is 6 cm.
Answer:
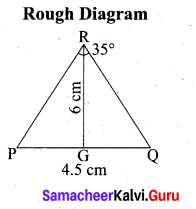
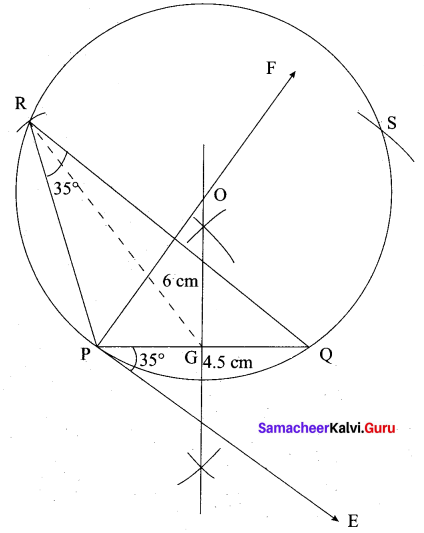
Steps of construction
- Draw a line segment PQ = 4.5 cm
- At P, draw PE such that ∠QPE = 60°
- At P, draw PF such that ∠EPF = 90°
- Draw the perpendicular bisect to PQ, which intersects PF at O and PQ at G.
- With O as centre and OP as radius draw a circle.
- From G mark arcs of radius 5.8 cm on the circle. Mark them at R and S
- Join PR and RQ. PQR is the required triangle.

Question 44.
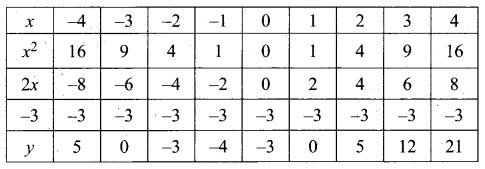
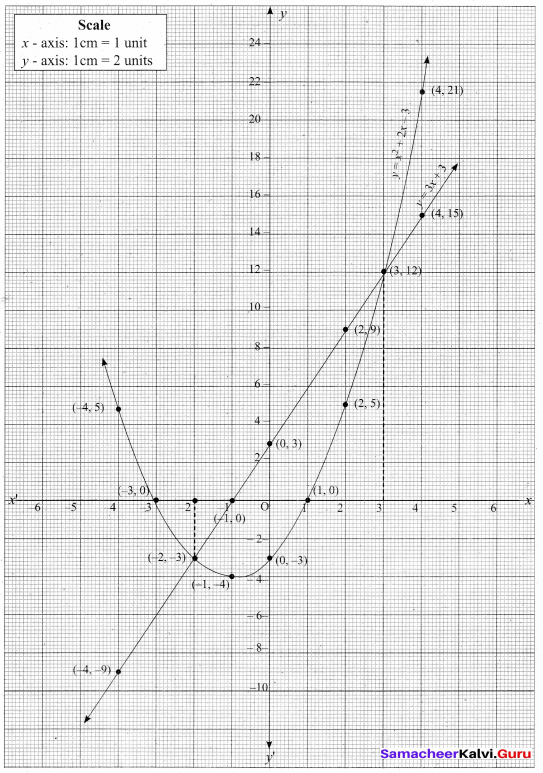
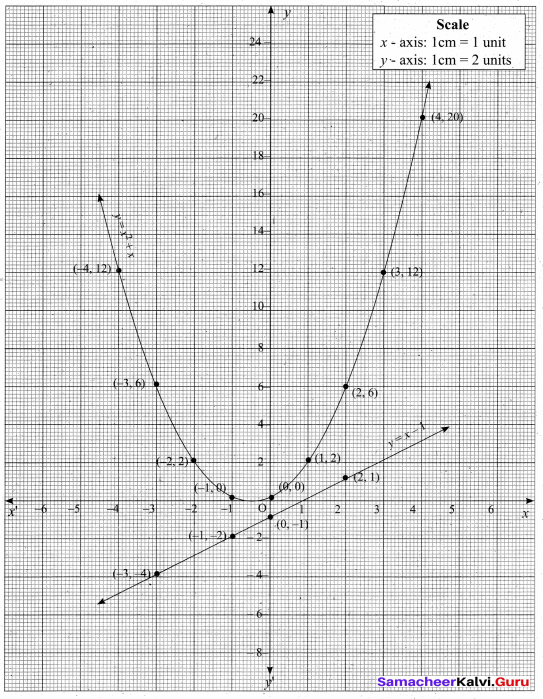
(a) Draw the graph of y = x2 and hence solve x2 – 4x – 5 = 0.
Answer:
Given equations are y = x2 and x2 – 4x – 5 = 0
(i) Assume the values of x from – 4 to 5.

(ii) Plot the points (-4, 16), (- 3, 9), (-2,4), (-1, 1), (0, 0), (1, 1), (2,4), (3, 9), (4, 16), (5, 25).
(iii) Join the points by a smooth curve.
(iv) Solve the given equations
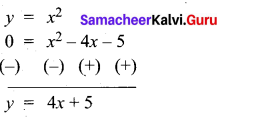
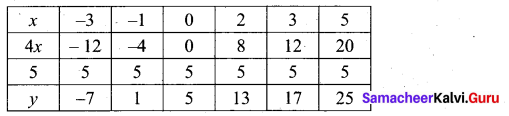
(v) The points of intersection of the line and the parabola are (-1, 1) and (5, 25).
The x-coordinates of the points are -1 and 5.
Thus solution set is {- 1, 5}.
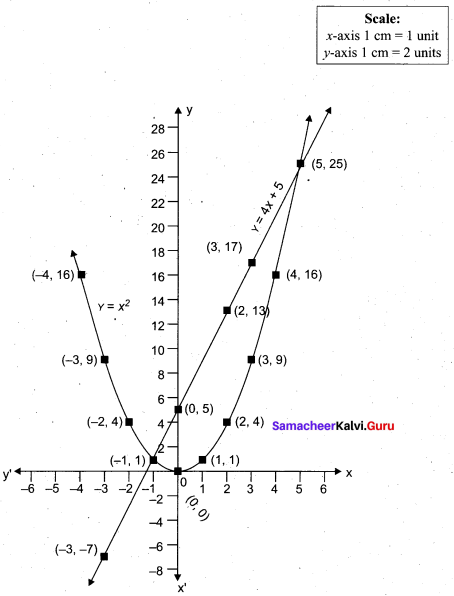
[OR]
![]()
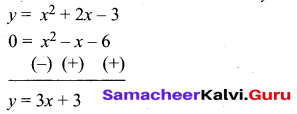
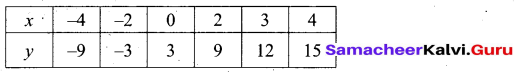
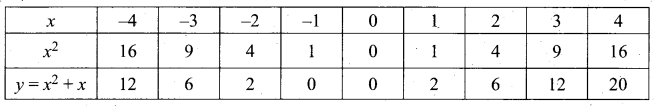
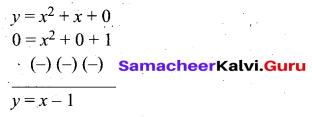
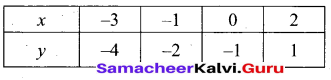
(b) Draw the graph of y – x2 -5x – 6 and hence solve x2 – 5x – 14 = 0
Answer:
Let y = x2 – 5x – 6
(i) Draw the graph of y = x2 – 5x – 6 by preparing the table of values as below.
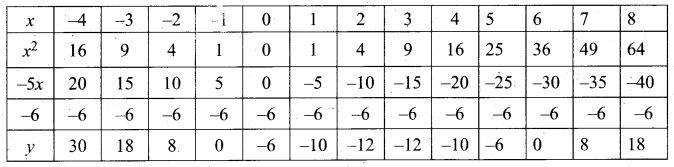
(ii) Plot the points (-3, 18), (-2, 8), (-1, 0), (0, -6), (1, -10), (2, -12), (3, -12), (4, -10), (5, -6), (6, 0) and (7, 8).
(iii) Join the points by a free hand to get smooth curve.
(iv) To solve x2 – 5x – 14 = 0, subtract x2 – 5x – 14 = 0 from y = x2 – 5x – 6.
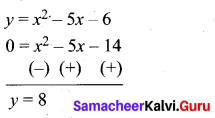
The equation y = 8 represent a straight line draw a straight line through y = 8 intersect the curve at two places. From the two points draw perpendicular line to the X – axis it will intersect at -2 and 7.
The solution is -2 and 7