Students can Download Bio Zoology Chapter 5 Molecular Genetics Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 5 Molecular Genetics
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Molecular Genetics Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Hershey and Chase experiment with bacteriophage showed that
(a) Protein gets into the bacterial cells
(b) DNA is the genetic material
(c) DNA contains radioactive sulphur
(d) Viruses undergo transformation
Answer:
(b) DNA is the genetic material
Question 2.
DNA and RNA are similar with respect to
(a) Thymine as a nitrogen base
(b) A single-stranded helix shape
(c) Nucleotide containing sugars, nitrogen bases and phosphates
(d) The same sequence of nucleotides for the amino acid phenyl alanine
Answer:
(c) Nucleotide containing sugars, nitrogen bases and phosphates
Question 3.
A mRNA molecule is produced by
(a) Replication
(b) Transcription
(c) Duplication
(d) Translation
Answer:
(b) Transcription

Question 4.
The total number of nitrogenous bases in human genome is estimated to be about
(a) 3.5 million
(b) 35000
(c) 35 million
(d) 3.1 billion
Answer:
(d) 3.1 billion
Question 5.
E. coli cell grown on 15N medium are transferred to 14N medium and allowed to grow for two generations. DNA extracted from these cells is ultracentrifuged in a cesium chloride density gradient. What density distribution of DNA would you expect in this experiment?
(a) One high and one low density band
(b) One intermediate density band
(c) One high and one intermediate density band
(d) One low and one intermediate density band
Answer:
(d) One low and one intermediate density band
Question 6.
What is the basis for the difference in the synthesis of the leading and lagging strand of DNA molecules?
(a) Origin of replication occurs only at the 5’ end of the molecules
(b) DNA ligase works only in the 3’ → 5’ direction
(c) DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3 ’ end of the growing stand
(d) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins that work at the 5’ end
Answer:
(d) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins that work at the 5’ end
Question 7.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of event with reference to the central dogma?
(a) Transcription, Translation, Replication
(b) Transcription, Replication, Translation
(c) Duplication, Translation, Transcription
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Answer:
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Question 8.
Which of the following statements about DNA replication is not correct?
(a) Unwinding of DNA molecule occurs as hydrogen bonds break
(b) Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it
(c) Process is known as semi – conservative replication because one old strand is conserved in the new molecule
(d) Complementary base pairs are held together with hydrogen bonds
Answer:
(b) Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it
Question 9.
Which of the following statements is not true about DNA replication in eukaryotes?
(a)) Replication begins at a single origin of replication.
(b) Replication is bidirectional from the origins.
(c) Replication occurs at about 1 million base pairs per minute.
(d) There are numerous different bacterial chromosomes, with replication occurring in each at the same time.
Answer:
(d) There are numerous different bacterial chromosomes, with replication occurring in each at the same time.
Question 10.
The first codon to be deciphered was which codes for
(a) AAA, proline
(b) GGG, alanine
(c) UUU, Phenylalanine
(d) TTT, arginine
Answer:
(c) UUU, Phenylalanine
Question 11.
Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proved __________
(a) Transduction
(b) Transformation
(c) DNA is the genetic material
(d) Semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
Answer:
(d) Semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
Question 12.
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits; the smaller subunit of a ribosome has a binding site for and the larger subunit has two binding sites for two
Answer:
mRNA, tRNA
Question 13.
Anoperonisa:
(a) Protein that suppresses gene expression
(b) Protein that accelerates gene expression
(c) Cluster of structural genes with related function
(d) Gene that switched other genes on or off
Answer:
(d) Gene that switched other genes on or off
Question 14.
When lactose is present in the culture medium:
(a) Transcription of lacy, lac z, lac a genes occurs
(b) Repressor is unable to bind to the operator
(c) Repressor is able to bind to the operator
(d) Both (a) and (b) are correct
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b) are correct
Question 15.
Give reasons: Genetic code is ‘universal’.
Answer:
The genetic code is universal. It means that all known living systems use nucleic acids and the same three base codons (triplet codon) direct the synthesis of protein from amino acids. . For example, the mRNA (UUU) codon codes for phenylalanine in all cells of all organisms. Some exceptions are reported in prokaryotic, mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. However, similarities are more common than differences.
Question 16.
Name the parts marked ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the given transcription unit:
Answer:
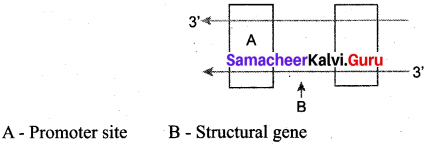
Question 17.
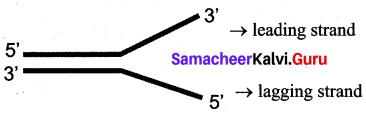
Differentiate – Leading strand and lagging strand
Answer:
- DNA polymerase I Involved DNA repair mechanism
- DNA polymerase II Involved DNA repair mechanism
- DNA polymerase III Involved in DNA replication
Question 18.
Differentiate – Template strand and coding strand.
Answer:
Template Strand: During replication, DNA strand having the polarity 3’ → 5’ act as template strand.
Coding Strand: During replication, DNA strand having the polarity 5’ → 3’ act as coding strand.
Question 19.
Mention any two ways in which single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) identified in the human genome can bring a revolutionary change in biological and medical science.
Answer:
Scientists have identified about 1.4 million locations, where single-base DNA differences (SNPs – Single nucleotide polymorphism – pronounced as ‘snips’) occur in humans. Identification of ‘SNIPS’ is helpful in finding chromosomal locations for disease-associated sequences and tracing human history.

Question 20.
State any three goals of the human genome project.
Answer:
- Identify all the genes (approximately 30000) in human DNA.
- Determine the sequence of the three billion chemical base pairs that make up the human DNA.
- To store this information in databases.
Question 21.
In E.coli, three enzymes 0- galactosidase, permease, and transacetylase are produced in the presence of lactose. Explain why the enzymes are not synthesized in the absence of lactose.
Answer:
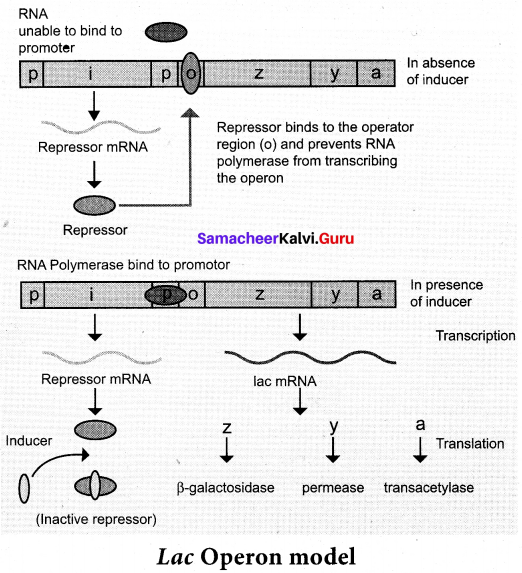
In the absence of lactose, the repressor protein binds to the operator and prevents the transcription of the structural gene by RNA polymerase, hence the enzymes are not produced. However, there will always be a minimal level of lac operon expression even in absence of lactose.
Question 22.
Distinguish between structural gene, a regulatory gene, and operator gene.
Answer:
Structure of the operon: Each operon is a unit of gene expression and regulation and consists of one or more structural genes and an adjacent operator gene that controls the transcriptional, activity of the structural gene.
- The structural gene codes for proteins, rRNA, and tRNA required by the cell.
- Promoters are the signal sequences in DNA that initiate RNA synthesis. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter prior to the initiation of transcription.
- The operators are present between the promoters and structural genes. The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon.
Question 23.
A low level of expression of lac operon occurs at all the time in E-coli. Justify the statement.
Answer:
One of the enzyme synthesized by lac operon is permease which is involved in the transport of lactose into the cells. If the lac operon gets inactivated, permease is not synthesized hence lactose cannot enter the cell. Lactose acts as an inducer, binding to the repressor protein and switch on the operator to initiate gene expression.
Question 24.
Why the human genome project is called a megaproject?
Answer:
The international human genome project was launched in the year 1990. It was a mega project and took 13 years to complete. The human genome is about 25 times larger than the genome of any organism sequenced to date and is the first vertebrate genome to be completed. Human genome is said to have approximately 3 x 109 bp. HGP was closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called bioinformatics.
Question 25.
From their examination of the structure of DNA, What did Watson and Crick infer about the probable mechanism of DNA replication, coding capability and mutation?
Answer:
Inference of Watson and Crick on DNA replication: They concluded that each of the DNA strand in a helix act as template during DNA replication leading to formation of new daughter DNA molecules, which are complementary to parental strand, (i.e., Semi-conservative method of replication) Inference on coding capability: During transcription, the genetic information in the DNA strand is coded to mRNA as complementary bases, (except for uracil in place of thymine in RNA) Inference on mutation: Any changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA leads to the corresponding alteration in amino acid sequence of specific protein thus confirming the validity of genetic code.
Question 26.
Why tRNA is called an adapter molecule?
Answer:
The transfer RNA, (tRNA) molecule of a cell acts as a vehicle that picks up the amino acids scattered through the cytoplasm and also reads specific codes of mRNA molecules. Hence it is called an adapter molecule. This term was postulated by Francis Crick.
Question 27.
What are the three structural differences between RNA and DNA?
Answer:
DNA:
- Sugar is deoxyribose sugar.
- Double-stranded structure.
- Nitrogen bases are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine.
RNA:
- Sugar is ribose sugar.
- Single-stranded molecule.
- Nitrogen bases are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil.
Question 28.
Name the anticodon required to recognize the following codons:
AAU, CGA, UAU, and GCA.
Answer:
UUA, GCU, AUA and CGU.
Question 29.
(a) Identify the figure given below
(b) Redraw the structure as a replicating fork and label the parts
(c) Write the source of energy for this replication and name the enzyme involved in this process.
(d) Mention the differences in the synthesis of protein, based on the polarity of the two template strands.
Answer:
(a) Replication fork
(b)
(c) Deoxy nucleotide, triphosphate acts as an energy source for replication. DNA polymerase is used for replication
(d) mRNA contacting information for protein synthesis will develop from DNA strand having polarity 5’ → 3’
Question 30.
If the coding sequence in a transcription unit is written as follows:
5’ TGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC 3’
Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Answer:
mRNA sequence is 3’ACGUACGUACGUUCGUACGUACGUACG5’
Question 31.
How is the two-stage process of protein synthesis advantageous?
Answer:
The split gene feature of eukaryotic genes is almost entirely absent in prokaryotes. Originally each exon may have coded for a single polypeptide chain with a specific function. Since exon arrangement and intron removal are flexible, the exon coding for these polypeptide subunits act as domains combining in various ways to form new genes. Single genes can produce different functional proteins by arranging their exons in several different ways through alternate splicing patterns, a mechanism known to play an important role in generating both protein and functional diversity in animals. Introns would have arosen before or after the evolution of eukaryotic gene.
If introns arose late how did they enter eukaryotic gene? Introns are mobile DNA sequences that can splice themselves out of, as well as into, specific ‘target sites’ acting like mobile transposon-like elements (that mediate transfer of genes between organisms – Horizontal Gene Transfer – HGT). HGT occurs between lineages of prokaryotic cells, or from prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells and between eukaryotic cells. HGT is now hypothesized to have played a major role in the evolution of life on Earth.
Question 32.
Why did Hershey and Chase use radioactively labelled phosphorous and sulphur only? Would they have got the same result if they use radiolabelled carbon and nitrogen?
Answer:
Generally proteins contain sulphur but not phosphorous and nucleic acid (DNA) contains , phosphorous but not sulphur. Hence Hershey – Chase used radioactive isotopes of sulphur (35S) and phosphorus (32P) to keep separate track of viral protein and nucleic acid in culture medium. The expected result cannot be achieved, if radioactive carbon and nitrogen is used, since these molecules are present in both DNA and proteins.

Question 33.
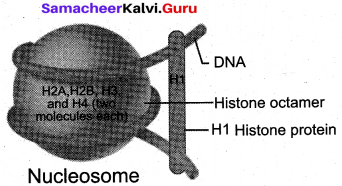
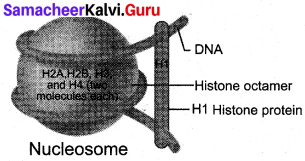
Explain the formation of a nucleosome.
Answer:
Komberg proposed a model for the nucleosome, in which 2 molecules of the four histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are organized to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamere.
The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamere to form a structure called nucleosome. A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix. The histone octameres are in close contact and DNA is coiled on the outside of nucleosome.
Question 34.
It is established that RNA is the first genetic material. Justify giving reasons.
Answer:
Three molecular biologists in the early 1980’s (Leslie Orgel, Francis Brick and Carl Woese) independently proposed the ‘RNA world’ as the first stage in the evolution of life, a stage when RNA catalysed all molecules necessary for survival and replication. The term ‘RNA world’ first used by Walter Gilbert in 1986, hypothesizes RNA as the first genetic on Earth. There is now enough evidence to suggest that essential life processes (such as metabolism, translation and splicing etc.,) evolved around RNA. RNA has the ability to act as both genetic material and catalyst. There are several biochemical reactions in living systems that are catalyzed by RNA. This catalytic RNA is known as a ribozyme. But, RNA being a catalyst was reactive and hence unstable.
This led to the evolution of a more stable form of DNA, with certain chemical modifications. Since DNA is a double-stranded molecule having a complementary strand, it has resisted changes by evolving a process of repair. Some RNA molecules function as gene regulators by binding to DNA and affect gene expression. Some viruses use RNA as genetic material. Andrew Fire and Craig Mellow (recipients of the Nobel Prize in 2006) were of the opinion that RNA is an active ingredient in the chemistry of life.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Molecular Genetics Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
The term‘gene’was coined by ___________
Answer:
Wilhelm Johannsen
Question 2.
Whose experiment finally provided convincing evidence that DNA is the genetic material?
(a) Griffith experiment
(b) Avery, Macleod, and McCarty’s experiment
(c) Hershey-Chase experiment
(d) Urey-Miller’s experiment
Answer:
(c) Hershey-Chase experiment
Question 3.
In Hershey – Chase experiment, the DNA of T2 phase was made radioactive by using ___________
(a) 32P
(b) 32S
(c) 35P
(d) 32S
Answer:
(a) 32P
Question 4.
A nucleoside is composed of ___________
(a) Sugar and Phosphate
(b) Nitrogen base and Phosphate
(c) Sugar and a Nitrogen base
(d) Sugar, Phosphate, and Nitrogenous base
Answer:
(c) Sugar and a Nitrogen base
Question 5.
Identify the incorrect statement
(a) a base is a substance that accepts H+ ion
(b) Both DNA and RNA have four bases
(c) Purines have a single carbon-nitrogen ring
(d) Thymine is unique for DNA
Answer:
(c) Purines have a single carbon-nitrogen ring

Question 6.
Watson and Crick proposed their double helical DNA model based on the X-ray diffraction analysis of ___________
(a) Erwin Chargaff
(b) Meselson and Stahl
(c) Wilkins and Franklin
(d) Griffith
Answer:
(c) Wilkins and Franklin
Question 7.
The term ‘RNA world’ was first used by ___________
Answer:
Walter Gilbert
Question 8.
The distance between two consecutive base pairs in DNA is ___________
(a) 0.34 nm
(b) 3.4 nm
(c) 0.034 nm
(d) 34 nm
Answer:
(a) 0.34 nm
Question 9.
If the length of E. coli DNA is 1.36 mm, the number of base pairs is ___________
(a) 0.36 × 106m
(b) 4 × 106m
(c) 0.34 × 10-9nm
(d) 4 × 10-9m
Answer:
(b) 4 × 106m
Question 10.
Identify the proper sequence in the organisation of the eukaryotic chromosome.
(a) Nucleosome – Solenoid – Chromatid
(b) Chromatid – Nucleosome – Solenoid
(c) Solenoid – chromatin – DNA
(d) Nucleosome – solenoid – genophore
Answer:
(a) Nucleosome – Solenoid – Chromatid
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : Genophore is noticed in prokaryotes.
Reason (R) : Bacteria possess circular DNA without chromatin organization.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R explains A
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Answer:
(c) R explains A
Question 12.
Assertion (A): Heterochromatin is transcriptionally active.
Reason (R): Tightly packed chromatin which stains dark.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R explains A
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Answer:
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : semi-conservative model was proposed by Hershey and Chase.
Reason (R) : The daughter DNA contains only new strands.
(a) Both A and R are incorrect
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R explains A
(d) A is incorrect R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are incorrect
Question 14.
Kornberg enzyme is called as _____
Answer:
DNA polymerase I

Question 15.
Replication of DNA occurs at __________ phase of cell cycle.
(a) M
(b) S
(c) G1
(d) G2
Answer:
(b) S
Question 16.
Semi-conservative model of replication was proved by __________
(a) Hershey and Chase
(b) Griffith
(c) Meselson and Stahl
(d) Macleod and McCarty
Answer:
(c) Meselson and Stahl
Question 17.
How many types of DNA polymerases does a eukaryotic cell possess?
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(d) Five
Question 18.
Identify the incorrect statement
(a) Replication occurs at ori – site of DNA
(b) Deoxy nucleotide triphosphate acts as a substrate
(c) Unwinding of DNA strand is carried out by topoisomerase
(d) DNA polymerase catalyses the polymerization at 3-OH
Answer:
(c) Unwinding of DNA strand is carried out by topoisomerase
Question 19.
The discontinuously synthesized fragments of lagging strand are called ________
Answer:
Okazaki fragments
Question 20.
Retroviruses possess ________ as genetic material.
Answer:
RNA
Question 21.
Which is NOT a part of the transcription unit?
(a) Promoter
(b) Operator
(c) Structural gene
(d) Terminator
Answer:
(b) Operator
Question 22.
Goldberg – Hogness box of eukaryotes is equivalent to ________ of prokaryotes.
Answer:
Pribnow box
Question 23.
Okazaki fragments are joined by the enzyme ________ during DNA replication.
Answer:
DNA ligase
Question 24.

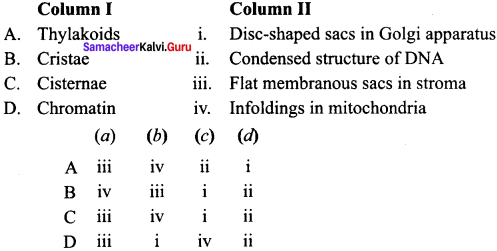
Answer:
(a) A – iv, B – i, C – ii, D – iii
Question 25.
The RNA polymerase of prokaryotes binds with the factor to initiate polymerization.
(a) rho
(b) theta
(c) sigma
(d) psi
Answer:
(c) sigma
Question 26.
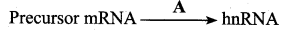
(a) Capping
(b) Tailing
(c) Splicing
(d) Transcribing
Answer:
(c) Splicing

Question 27.
Which of the following feature is absent in prokaryotes?
(a) Prokaryotes possess three major types of RNAs
(b) Structural genes are polycistronic
(c) Initiation process of transcription requires ‘P’ factor
(d) Split gene feature
Answer:
(d) Split gene feature
Question 28.
Which of the following sequence has completely translated?
(i) AGA, UUU, UGU, AGU, UAG
(ii) AUG, UUU, AGA, UAC, UAA
(iii) AAA, UUU, UUG, UGU, UGA
(iv) AUG,AAU,AAC,UAU,UAG
(a) i and ii
(b) ii only
(c) i and iii
(d) ii and iv
Answer:
(d) ii and iv
Question 29.
Capping of mRNA occurs using __________
(a) Poly A residues
(b) Methyl guanosine triphosphate
(c) Deoxy ribonucleotide triphosphate
(d) Ribonucleotide triphosphate
Answer:
(b) Methyl guanosine triphosphate
Question 30.
One of the aspects is not a feature of genetic code?
(a) Specific
(b) Degenerate
(c) Universal
(d) Ambiguous
Answer:
(d) Ambiguous
Question 31.
Which of the triplet codon is not a code of proline?
(i) CCU
(ii) CAU
(iii) CCG
(iv) CAA
(a) i only
(b) ii and iv
(c) iii only
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) ii and iv
Question 32.
Coding sequences found in split genes are called.
(a) Operons
(b) Introns
(c) Exons
(d) Cistron
Answer:
(c) Exons
Question 33.
Which of the following mRNA yields 6 aminoacids after translation?
(i) UCU UAU AGU CGA UGC AGU UGA AAA UUU
(ii) UGA AGA UAG GAG CAU CCC UAC UAU GAU
(iii) GUC UGC UGG GCU GAU UAA AGG AGC AUU
(iv) AUG UAC CAU UGC UGA UGC AGG AGC CCG
Answer:
(i) UCU UAU AGU CGA UGC AGU UGA AAA UUU
Question 34.
The transcription termination factor associated with RNA polymerase in prokaryotes is
(a) θ
(b) σ
(c) ρ
(d) ∑
Answer:
(c) ρ

Question 35.
In a DNA double strand, if guanine is of 30%, what will be the percentage of thymine?
(a) 100%
(b) 20%
(c) 10%
(d) 70%
Answer:
(b) 20%
Question 36.
Identify the triplet pairs that code for Tyrosine
(a) UUU, UUC
(b) UAU, UAU
(c) UGC, UGU
(d) CAU, CAC
Answer:
(b) UAU, UAU
Question 37.

Answer:
A – ii B – i C – iv D – iii
Question 38.
AUG code is for __________
(a) Arginine
(b) Tyrosine
(c) Tryptophan
(d) Methionine
Answer:
(d) Methionine
Question 39.
The sequence of bases in the coding strand of DNA is G A G T T A G C A G G C, then the sequence of codons in the primary transcript is
(a) C U C A U A C G C C C G
(b) C U C A A U C G U C C G
(c) U C A G A U C U G C G C
(d) U U C A A U C G U G C G
Answer:
(b) C U C A A U C G U C C G
Question 40.
The promoter region of eukaryote is __________
(a) TATAA
(b) AUGUT
(c) UUUGA
(d) AAAAU
Answer:
(a) TATAA
Question 41.
Match the following:
(A) AUG – (i) Tyrosine
(B) UGA – (ii) Glycine
(C) UUU – (iii) Methionine
(D) GGG – (iv) Phenylalanine
(a) A – iii B – i C – iv D – ii
(b) A – iii B – ii C – i D – iv
(c) A – iv B – i C – iii D – ii
(d) A – ii B – i C – iv D – iii
Answer:
(d) A – ii B – i C – iv D – iii
Question 42.
__________ number of codons, codes for cystine.
Answer:
Two
Question 43.
In sickle cell anaemia, the __________ codon of β – globin gene is modified.
(a) Eighth
(b) Seventh
(c) Sixth
(d) Nineth
Answer:
(c) Sixth
Question 44.
Pick out the incorrect statement.
(a) tRNA acts as a adapter molecule
(b) Stop codons donot have tRNA’s
(c) Addition of aminoacid leads to hydrolysis of tRNA
(d) tRNA has four major loops
Answer:
(c) Addition of aminoacid leads to hydrolysis of tRNA
Question 45.
Which of the following antibiotic inhibits the interaction between tRNA and mRNA?
(a) Neomycin
(b) Streptomycin
(c) Tetracycline
(d) Chloramphenicol
Answer:
(a) Neomycin
Question 47.
The cluster of genes with related function is called _________
(a) Cistron
(b) Operon
(c) Muton
(d) Recon
Answer:
(b) Operon
Question 48.
Repressor protein of Lac operon binds to __________ of operon.
(a) Promoter region
(b) Operator region
(c) terminator region
(d) inducer region
Answer:
(b) Operator region
Question 49.
Lac Z gene codes for __________
(a) Permease
(b) transacetylase
(c) β -galactosidase
(d) Aminoacyl transferase
Answer:
(c) β -galactosidase

Question 50.
Lac operon model was proposed by __________
Answer:
Jacob and Monod
Question 51.
Approximate count of base pair in human genome is __________
Answer:
3 × 109 bp
Question 52.
Automated DNA sequences are developed by.
Answer:
Frederick Sanger
Question 53.
Which of the chromosome has higher gene density?
(a) Chromosome 20
(b) Chromosome 19
(c) Chromosome 13
(d) Chromosome Y
Answer:
(b) Chromosome 19
Question 54.
Number of genes located in chromosome Y is __________
(a) 2968
(b) 213
(c) 2869
(d) 231
Answer:
(d) 231
Question 55.
How many structural genes are located in lac operon of E.Coli?
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 56.
DNA finger printing technique was developed by
(a) Jacob and Monod
(b) Alec Jeffreys
(c) Frederick Sanger
Answer:
(b) Alec Jeffreys
Question 57.
In DNA fingerprinting, separation of DNA fragments is done by __________
(a) Centrifugation
(b) Electrophoresis
(c) X-ray diffraction
(d) denaturation
Answer:
(b) Electrophoresis
Question 58.
SNP stands for
(a) Single nucleotide Polymorphism
(b) Single Nucleoside Polypeptide
(c) Single nucleotide Polymorphism
(d) Single nucleotide polymer
Answer:
(a) Single nucleotide Polymorphism
Question 59.
Specific sequences of mRNA that are not translated are __________
Answer:
UnTranslated Regions (UTR)
Question 60.
Non-coding or intervening DNA sequence is called __________
Question 61.
_______ Intron is the monomer of DNA.
Answer:
Nucleotide
Question 62.
Which one of the following is wrongly matched?
(a) Transcription – Copying information from DNA to RNA
(b) Translation – Decoding information from mRNA to protein
(c) Replication – Making of DNA copies
(d) Splicing – Joining of exons with introns
Answer:
(d) Splicing – Joining of exons with introns
2- Mark Questions
Question 1.
Who proposed One gene – One enzyme hypothesis? Define it.
Answer:
George Beadle and Edward Tatum proposed One gene – One enzyme hypothesis which states that one gene controls the production of one enzyme.
Question 2.
Differentiate nucleoside from nucleotide.
Answer:
- Nucleoside: Nucleoside subunit is composed of nitrogenous bases linked to a pentose sugar molecule.
- Nucleotide: Nucleotide subunit is composed of nitrogenous bases, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group.
Question 3.
State the key differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
DNA:
- DNA is made of deoxyribose sugar.
- Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine.
RNA:
- RNA is made of ribose sugar.
- Nitrogenous bases of RNA are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil.
Question 4.
Point out the nitrogenous bases of RNA.
Answer:
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil.
Question 5.
What makes the DNA and RNA as acidic molecules?
Answer:
The phosphate functional group (PO4) gives DNA and RNA the property of an acid at physiological pH, hence the name nucleic acid.
Question 6.
Which type of bond is formed
- between a purine and pyrimidine base?
- between the pentose sugar and adjacent nucleotide?
Answer:
- Purine and pyrimidine bases are linked by hydrogen bonds.
- Pentose sugar is linked to adjacent nucleotide by phosphodiester bonds.
Question 7.
DNA acts as genetic material for majority of living organisms and not the RNA. Give reasons to support the statement.
Answer:
- RNA was reactive and hence highly unstable.
- Some RNA molecules acts as gene regulators by binding to DNA and affect gene expression.
- Uracil of RNA is less stable than thymine of DNA.
Question 8.
Name any two viruses whose genetic material is RNA.
Answer:
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
- Bacteriophage 0B
Question 9.
What are the properties that a molecule must possess to act as genetic material?
Answer:
- Self replication
- Information storage
- Stability
- Variation through mutation
Question 10.
How many base pairs are present in one complete turn of DNA helix? What is the distance between two consecutive base pairs?
Answer:
There are ten base pairs in each turn with a distance of 0.34 x 109m between two adjacent base pairs.
Question 11.
What is a genophore?
Answer:
In prokaryotes such as E. coli though they do not have defined nucleus, the DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. DNA (being negatively charged) is held with some proteins (that have positive charges) in a region called the nucleoid. The DNA as a nucleoid is organized into large loops held by protein. DNA of prokaryotes is almost circular and lacks chromatin organization, hence termed genophore.
Question 12.
Whqt is nucleosome? How many base pairs are there in a typical nucleosome?
Answer:
The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamere to form a structure called nucleosome. A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix.
Question 13.
Expand and define NHC
Answer:
- NHC : Non-histone Chromosomal protein.
- In eukaryotes, apart from histone proteins, additional set of proteins are required for packing of chromatin at higher level and are referred as non – histone chromosomal proteins.
Question 14.
Differentiate between Heterochromatin and Euchromatin.
Answer:
Heterochromatin:
- Region of nucleus where the chromatin are loosely packed and stains light are called Heterochromatin.
- Transcriptionally inactive.
Euchromatin:
- Region of nucleus where the chromatin are tightly packed and stains dark are called Euchromatin.
- Transcriptionally active.
Question 15.
Which is the widely accepted model of DNA replication? Who has proved it?
Answer:
Semi-conservative replication model. It was proved by Meselson and Stahl in 1958.
Question 16.
Name the chemical substance which is called by the name
- Kornberg Enzyme
- Ochoa’s enzyme
Answer:
- DNA polymerase I is also known as Komberg enzyme.
- Polynucleotide phosphorylase is also known as Ochoa’s enzyme.
Question 17.
Name the various types of prokaryotic DNA polymerase. State their role in replication process.
Answer:
- DNA Polymerase I Involver in DNA repair mechanism
- DNA Polymerase II Involver in DNA repair mechanism
- DNA Polymerase III Involver in DNA replication
Question 18.
What is the function of Deoxy nucleotide triphosphate in replication?
Answer:
Deoxy nucleotide triphosphate acts as substrate and also provides energy for polymerization reaction.
Question 19.
Given below are some events of eukaryotic replication. Name the enzymes involved in the process.
- Unwinding of DNA
- Joining of Okazaki fragments
- Addition of nucleotides to new strand
- Correcting the repair
Answer:
- Helicase
- DNA ligase
- DNA polymerase
- Nuclease

Question 20.
Differentiate leading strand from lagging strand
Answer:
Leading strand:
- Leading strand has the polarity 3’ → 5’.
- Replication is continuous.
Lagging strand:
- Lagging strand has the polarity 5’ → 3’.
- Replication is discontinuous.
Question 21.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Answer:
The discontinuously synthesized fragments of the lagging strand are called the Okazaki fragments are joined by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question 22.
What is a replication fork?
Answer:
At the point of origin of replication, the helicases and topoisomerases (DNA gyrase) unwind and pull apart the strands, forming a Y-Shaped structure called the replication fork. There are two replication forks at each origin.
Question 23.
Apart from DNA polymerase, name any other four enzymes which were involved in DNA replication of eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
DNA ligase, Topoisomerase (DNA gyrase), Helicase and Nuclease.
Question 24.
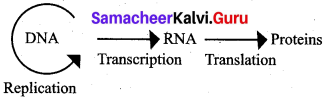
Who proposed the central dogma? Write its concept.
Answer:
Francis Crick proposed the Central dogma in molecular biology which states that genetic information flows as follows:
Question 25.
Define transcription and name the enzyme involved in this process.
Answer:
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA into RNA is termed transcription. This process takes place in presence of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Question 26.
What is TATA box? State its function.
Answer:
In eukaryotes, the promoter has AT-rich regions called TATA box or Goldberg-Hogness box. It acts as a binding site for RNA polymerase.
Question 27.
Structural gene of eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes. How?
Answer:
In eukaryotes, the structural gene is monocistronic coding for only one protein whereas in prokaryotes the structural gene is polycistronic coding for many proteins.
Question 28.
What are the two major components of prokaryotic RNA polymerase? How do they act?
Answer:
Bacterial (prokaryotic) RNA polymerase consists of two major components, the core enzyme and the sigma subunit. The core enzyme (β1, β, and α) is responsible for RNA synthesis ” whereas a sigma subunit is responsible for recognition of the promoter.
Question 29.
Distinguish between exons and introns.
Answer:
- Exons: Expressed sequences (Coding sequences) of an eukaryotic gene
- Introns: Interveining sequences (non-coding sequences) of an eukaryotic gene
Question 30.
Define splicing.
Answer:
The process of removing introns from hnRNA is called splicing.
Question 31.
What is capping and tailing?
Answer:
In capping an unusual nucleotide, methyl guanosine triphosphate is added at the 5’ end of hnRNA, whereas adenylate residues (200-300) (Poly A) are added at the 3’ end in tailing.
Question 32.
If a double stranded DNA has 20% of cytosine, calculate the percentage of adenine in DNA.
Answer:
Cytdsine = 20, hence Guanine = 20
As per ChargafFs rule (A+T) = (G+C) =100
Percent of Thymine + Adenine = 20 + 20 = 100
(T + A) = (20 + 20) =100
(T + A)=100-(20 + 20)
T +A = 100 – 40
T + A = 60
Therefore the percent of Adenine will be 60/2 = 30%.
Question 33.
Mention the dual functions of AUG.
Answer:
AUG has dual functions. It acts as a initiator codon and also codes for the amino acid methionine.
Question 34.
How many codons are involved in termination of translation. Name them.
Answer:
Three codons terminate translation process. They are UAA, UAG and UGA.
Question 35.
Degeneracy of codon – comment.
Answer:
A degenerate code means that more than one triplet codon could code for a specific amino acid. For example, codons GUU, GUC, GUA and GUG code for valine.

Question 36.
Point out the exceptional categories to universality of genetic code.
Answer:
Exceptions to universal nature of genetic code is noticed in prokaryotic mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes.
Question 37.
What are non-sense codons?
Answer:
UGA, UAA and UAG are the non-sense codons, which terminates translation.
Question 38.
Name the triplet codons that code for
- Tyrosine
- Histidine
Answer:
- Tyrosine – UAU, UAC
- Histidine – CAU, CAC
Question 39.
Why hnRNA has to undergo splicing?
Answer:
Since hnRNA contains both coding sequences (exons) and non-coding sequences (introns) it has to undergo splicing to remove introns.
Question 40.
State the role of following codons in translation process
- AUG
- UAA
Answer:
- AUG is the initiator codon and also codes for methionine.
- UAA is a terminator codon.
Question 41.
Given below is mRNA sequence. Mention the aminoacids sequence that is formed after its translation.
Answer:
3’AUGAAAGAUGGGUAA5’
Methionine – Lysine – Aspartic acid – Glycine
Question 42.
Name the four codons that codes valine.
Answer:
GUU, GUC, GUA and GUG.
Question 43.
The base sequence in one of the DNA strand is TAGC ATGAT. Mention the base sequence in its complementary strand.
Answer:
The complementary strand has ATCGTACTA.
Question 44.
Why t-RNA is called as adapter molecule?
Answer:
The transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule of a cell acts as a vehicle that picks up the amino acids scattered through the cytoplasm and also reads specific codes of mRNA molecules. Hence it is called as adapter molecule.
Question 45.
What do you mean by charging of tRNA? Name the enzyme involved in this process.
Answer:
The process of addition of amino acid to tRNA is known as aminoacylation or charging and the resultant product is called aminoacyl- tRNA (charged tRNA). Aminoacylation is catalyzed by an enzyme aminoacyl – tRNA synthetase.
Question 46.
What are UTR’s?
Answer:
mRNA also have some additional sequences that are not translated and are referred to as Untranslated Regions (UTR). UTRs are present at both 5’ end (before start codon) and at 3’ end (after stop codon).
Question 47.
What is S – D sequence?
Answer:
The 5’ end of the mRNA of prokaryotes has a special sequence which precedes the initial AUG start codon of mRNA. This ribosome binding site is called the Shine – Dalgamo sequence or S-D sequence. This sequences base-pairs with a region of the 16Sr RNA of the small ribosomal subunit facilitating initiation.
Question 48.
Define translation unit.
Answer:
A translation unit in mRNA is the sequence of RNA that is flanked by the start codon on 5’ end and stop codon on 3’ end and codes of polypeptide.
Question 49.
Mention the inhibitory role of tetracycline and streptomycin in bacterial translation.
Answer:
Tetracycline inhibits binding between aminoacyl tRNA and mRNA.Streptomycin inhibits initiation of translation and causes misreading.
Question 50.
At what stage, does the gene expression is regulated?
Answer:
Gene expression can be controlled or regulated at transcriptional or translational levels.
Question 51.
What is an operon? Give example.
Answer:
The cluster of genes with related functions is called an operon.
E.g: lac operon in E.coli.
Question 52.
Considering the lac operon of E.coli, name the products of the following genes.
- i gene
- lac Z gene
- lac Y gene
- lac a gene
Answer:
- i gene – repressor protein
- lac Z gene – fS-galactosidase
- Lac Y gene – Permease
- lac a gene – transacetylase
Question 53.
Expand
- ETS
- YAC.
Answer:
- ETS : Expressed Sequence Tags
- YAC : Yeast Artificial Chromosomes
Question 54.
Name the human chromosome that has
- most number of genes
- least number of genes
Answer:
- Chromosome 1 has maximum number of genes (2968 genes)
- Chromosome Y has least genes (231 genes)
Question 55.
What are SNPs? Mention its uses.
Answer:
SNPs : Single nucleotide polymorphism. It helps to find chromosomal locations for disease associated sequences and tracing human history.

Question 56.
Mention any four areas where DNA fingerprinting can be used.
Answer:
- Forensic analysis
- Pedigree analysis
- Conservation of wild life
- Anthropological studies
3 – Mark Questions
Question 57.
Classify nucleic acid based on sugar molecules.
Answer:
There are two types of nucleic acids depending on the type of pentose sugar. Those containing deoxyribose sugar are called Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid (DNA) and those with ribose sugar are known as Ribonucleic Acid (RNA). The only difference between these two sugars is that there is one oxygen atom less in deoxyribose.
Question 58.
Both purines and pyrimidines are nitrogen bases yet they differ. How?
Answer:
Both purines and pyrimidines are nitrogen bases. The purine bases Adenine and Guanine have double carbon – nitrogen ring, whereas cytosine and thymine bases have single carbon nitrogen ring.
Question 59.
How 5’ of DNA differ from its 3’?
Answer:
The 5’ of DNA refers to the carbon in the sugar to which phosphate (P04V) functional group is attached. The 3’ of DNA refers to the carbon in the sugar to which a hydroxyl (OH) group is attached.
Question 60.
State Chargaff’s rule.
Answer:
According to Erwin Chargaff,
- Adenine pairs with Thymine with two hydrogen bonds.
- Guanine pairs with Cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
Question 61.
Chemically DNA is more stable than RNA – Justify.
Answer:
In DNA, the two strands being complementary, if separated (denatured) by heating can come together (renaturation) when appropriate condition is provided. Further 2 OH group present at every nucleotide in RNA is a reactive group that makes RNA liable and easily degradable. RNA is also known to be catalytic and reactive. Hence, DNA is chemically more stable and chemically less reactive when compared to RNA. Presence of thymine instead of uracil in DNA confers additional stability to DNA.
Question 62.
Write in simple about semi-conservative mode of DNA replication.
Answer:
Semi-conservative replication was proposed by Watson and Crick in 1953. This mechanism of replication is based on the DNA model. They suggested that the two polynucleotide strands of DNA molecule unwind and start separating at one end. During this process, covalent hydrogen bonds are broken. The separated single strand then acts as template for the synthesis of a new strand. Subsequently, each daughter double helix carries one polynucleotide strand from the parent molecule that acts as a template and the other strand is newly synthesised and complementary to the parent strand.
Question 63.
Draw a simplified diagram of nucleosome and label it.
Answer:
Question 64.
What is a primer?
Answer:
A primer is a short stretch of RNA. It initiates the formation of new strand. The primer produces 3’-OH end on the sequence of ribonucleotides, to which deoxyribonucleotides are added to form a new strand.
Question 65.
Both strands of DNA are not copied during transcription. Give reason.
Answer:
Both the strands of DNA are not copied during transcription for two reasons.
- If both the strands act as a template, they would code for RNA with different sequences. This in turn would code for proteins with different amino acid sequences. This would result in one segment of DNA coding for two different proteins, hence complicate the genetic information transfer machinery.
- If two RNA molecules were produced simultaneously, double stranded RNA complementary to each other would be formed. This would prevent RNA from being translated into proteins.

Question 66.
What do you mean by a template strand and coding strand?
Answer:
DNA dependent RNA polymerase catalyses the polymerization in only one direction, the strand that has the polarity 3’→ 5’ acts as a template, and is called the template strand. The other strand which has the polarity 5’→ 3’ has a sequence same as RNA (except thymine instead of uracil) and is displaced during transcription. This strand is called coding strand.
Question 67.
Name the factors that are responsible for initiation and termination of transcription in prokaryotes.
Answer:
- Sigma factor is responsible for initiation of transcription.
- Rho factor is responsible for termination of transcription.
Question 68.
Name the major RNA types of prokaryotes and mention their role.
Answer:
In prokaryotes, there are three major types of RNAs: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. All three \ RNAs are needed to synthesize a protein in a cell. The mRNA provides the template, tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code, and rRNAs play structural and catalytic role
during translation.
Question 69.
Define genetic code.
Answer:
The order of base pairs along DNA molecule controls the kind and order of amino acids found in the proteins of an organism. This specific order of base pairs is called genetic code.
Question 70.
Explain Wobble hypothesis.
Answer:
Wobble Hypothesis is proposed by Crick (1966) which states that tRNA anticodon has the ability to wobble at its 5’ end by pairing with even non-complementary base of mRNA codon.’ According to this hypothesis, in codon-anticodon pairing the third base may not be complementary.
The third base of the codon is called wobble base and this position is called wobble position. The actual base pairing occurs at first two positions only. The importance of Wobbling hypothesis is that it reduces the number of tRNAs required for polypeptide synthesis and it overcomes the effect of code degeneracy.
Question 71.
Explain the nature of eukaryotic ribosome.
Answer:
The ribosomes of eukaryotes (80 S) are larger, consisting of 60 S and 40 S sub units. ‘S’ denotes the sedimentation efficient which is expressed as Svedberg unit (S). The larger subunit in eukaryotes consist of a 23 S RNA and 5Sr RNA molecule and 31 ribosomal proteins. The smaller eukaryotic subunit consist of 18Sr RNA component and about 33 proteins.
Question 72.
Expand and define ORF.
Answer:
Any sequence of DNA or RNA, beginning with a start codon and which can be translated into a protein is known as an Open Reading Frame (ORF).
Question 73.
What are the components of initiation complex of prokaryotic translation?
Answer:
Initiation of translation in E. coli begins with the formation of an initiation complex, consisting of the 30S subunits of the ribosome, a messenger RNA and the charged N-formyl methionine tRNA (fmet -1 RNA fmet), three proteinaceous initiation factors (IF 1, IF2, IF3), GTP (Guaniner Tri Phosphate) and Mg 2+.
Question 74.
Explain the components of operon.
Answer:
Structure of the operon: Each operon is a unit of gene expression and regulation and consists
of one or more structural genes and an adjacent operator gene that controls transcriptional
activity of the structural gene.
- The structural gene codes for proteins, rRNA and tRNA required by the cell.
- Promoters are the signal sequences in DNA that initiate RNA synthesis. RNA polymerase I binds to the promoter prior to the initiation of transcription.
- The operators are present between the promoters and structural genes. The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon.
5 – Mark Question
Question 75.
Describe Hershey and Chase experiment. What is concluded by their experiment?
Answer:
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase (1952) conducted experiments on bacteriophages that infect bacteria. Phage T2 is a virus that infects the bacterium Escherichia coli. When phages (virus) are added to bacteria, they adsorb to the outer surface, some material enters the bacterium, and then later each bacterium lyses to release a large number of progeny phage. Hershey and Chase wanted to observe whether it was DNA or protein that entered the bacteria. All nucleic acids contain phosphorus, and contain sulphur (in the amino acid cysteine and methionine). Hershey and Chase designed an experiment using radioactive isotopes of Sulphur (35S) and phosphorus (32P) to keep separate track of the viral protein and nucleic acids during the infection process.
The phages were allowed to infect bacteria in culture medium which containing the radioactive isotopes 35S or 32P. The bacteriophage that grew in the presence of 35S had labelled proteins and bacteriophages grown in the presence of 32P had labelled DNA. The differential labelling thus enabled them to identity DNA and proteins of the phage. Hershey and Chase mixed the labelled phages with unlabeled E. coli and allowed bacteriophages to attack and inject their genetic material. Soon after infection (before lysis of bacteria), the bacterial cells were gently agitated in a blender to loosen the adhering phase particles.
It was observed that only 32P was found associated with bacterial cells and 35S was in the surrounding medium and not in the bacterial cells. When phage progeny was studied for radioactivity, it was found that it carried only 32P and not 35 S. These results clearly indicate that only DNA and not protein coat entered the bacterial cells. Hershey and Chase thus conclusively proved that it was DNA, not protein, which carries the hereditary information from virus to bacteria.

Question 76.
Explain the properties of DNA that makes it an ideal genetic material.
Answer:
1. Self Replication: It should be able to replicate. According to the rule of base pairing and complementarity, both nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) have the ability to direct duplications. Proteins fail to fulfill this criterion.
2. Stability: It should he stable structurally and chemically. The genetic material should be stable enough not to change with different stages of life cycle, age or with change in physiology of the organism. Stability as one of the properties of genetic material was clearly evident in Griffith’s transforming principle. Heat which killed the bacteria did not destroy some of the properties of genetic material. In DNA the two strands being complementary.
if separated (denatured) by heating can come together (renaturation) when appropriate condition is provided. Further 2’ OH group present at every nucleotide in RNA is a reactive group that makes RNA liable and easily degradable. RNA is also known to be catalytic and reactive. Hence, DNA is chemically more stable and chemically less reactive when compared to RNA. Presence of thymine instead of uracil in DNA confers additional stability to DNA.
3. Information storage: It should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’. RNA can directly code for protein synthesis and can easily express the characters. DNA, however depends on RNA for synthesis of proteins. Both DNA and RNA can act as a genetic material, but DNA being more stable stores the genetic information and RNA transfers the genetic information.
4. Variation through mutation: It should be able to mutate. Both DNA and RNA are able to mutate. RNA being unstable mutates at a faster rate. Thus viruses having RNA genome with shorter life span can mutate and evolve faster. The above discussion indicates that both RNA and DNA can function as a genetic material. DNA is more stable, and is preferred for storage of genetic information.
Question 77.
How the DNA is packed in a eukaryotic cell? ft
Answer:
In eukaryotes, organization is more complex. Chromatin is formed by a series of repeating units called nucleosomes. Komberg proposed a model for the nucleosome, in which 2 molecules of the four histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are organized to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamere. The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamere to form a structure called a nucleosome. A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix. The histone octameres are in close contact and DNA is coiled on the outside of the nucleosome. Neighbouring nucleosomes are connected by linker DNA (HI) that is exposed to enzymes.
The DNA makes two complete turns around the histone octameres and the two turns are sealed off by an HI molecule. Chromatin lacking HI has a beads-on-a-string appearance in which DNA inters and leaves the nucleosomes at random places. HI of one nucleosome can interact with 33l of the neighbouring nucleosomes resulting in the further folding of the fibre.
The chrof&atin fiber in interphase nuclei and mitotic chromosomes have a diameter that vary between 200-300 nm and represents inactive chromatin. 30 nm fibre arises from the folding of nucfeosbme, chains into a solenoid structure having six nucleosomes per turn. This structure is stabilized by interaction between different HI molecules. DNA is a solenoid and packed about,%)_folds. The hierarchical nature of chromosome structure is illustrated.
Additional set of proteins are required for packing of chromatin at higher level and are referred to as non-histone chromosomal proteins (NHC). In*,a typical nucleus, some regions of chromatin are Ibosely packed (lightly stained) and are referred to as euchromatin. The chromatin that is,-tightly packed (stained darkly) is called heterochromatin. Euchromatin is transcriptionally active and heterochromatin is transcriptionally inactive.
Question 78.
Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proved the semi-coflBptervation mode of DNA replication. Explain.
Answer:
The mode of DNA replication was determined in 1958 by Meselson and Stahl. They designed an experiment to distinguish between semi-conservative, conservative and dispersive replications. In their experiment, they grew two cultures of E.coli for many generations in separate media. The ‘heavy’ culture was grown in a medium in which the nitrogen source (NH4CI) contained the heavy isotope 15N and the ‘ light’ culture was grown in a medium in which the nitrogen source contained light isotope 14H for many generations. At the end of growth, they observed that the bacterial DNA in the heavy culture contained only 15N and in the light culture only 14N. The heavy DNA could be distinguished from light DNA (15N from 14N) with a technique called Cesium Chloride (CsCl) density gradient centrifugation. In this process, heavy and light DNA extracted from cells in thtytwo cultures settled into two distinct and separate bands (hybrid DNA).
The heavy culture (15N) was then transferred into a medium that had only NH4CI, and took samples at various definite time intervals (20 minutes duration). After the first replication, they extracted DNA and subjected it to density gradient centrifugation. The DNA settled into a band that was intermediate in position between the previously determined heavy and light bands. After the second replication (40 minutes duration), they again extracted DNA samples,and this time found the DNA settling into two bands, one at the light band position and one at intermediate position. These results confirm Watson and Crick’s semi-conservative replication hypothesis.
Question 79.
Give a detailed account of a transcription unit.
Answer:
A transcriptional unit in DNA is defined by three regions, a promoter, the structural gene and a terminator. The promoter is located towards the 5 ’ end. It is a DNA sequence that provides binding site for RNA polymerase. The presence of promoter in a transcription unit, defines the template and coding strands. The terminator region located towards the 3’ end of the coding strand contains a DNA sequence that causes the RNA polymerase to stop transcribing. In eukaryotes the promoter has AT rich regions called TATA box (Goldberg- Hogness box) ‘ and in prokaryotes this region is called Pribnow box.
Besides promoter, eukaryotes also require an enhancer. The two strands of the DNA in the structural gene of a transcription unit have opposite polarity. DNA dependent RNA polymerase catalyses the polymerization in only one direction, the strand that has the polarity 3’→5’ acts as a template, and is called the template strand. The other strand which has the polarity 5’→ 3’ has a sequence same as RNA (except thymine instead of uracil) and is displaced during transcription. This strand is called coding strand
The structural gene may be monocistronic (eukaryotes) or polycistronic (prokaryotes). In eukaryotes, each mRNA carries only a single gene and encodes information for only a single protein and is called monocistronic mRNA. In prokaryotes, clusters of related genes, known as operon, often found next to each other on the chromosome are transcribed together to give a single mRNA and hence are polycistronic.
Question 80.
Explain the transcription process in prokaryotes with the needed diagram.
Answer:
In prokaryotes, there are three major types of RNAs:
mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. All three RNAs are needed to synthesize a protein in a cell. The mRNA provides the template, tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code, and rRNAs play a structural and catalytic role during translation. There is a single DNA-dependent RNA polymerase that catalyses the transcription of all types of RNA. It binds to the promoter and initiates transcription (Initiation).
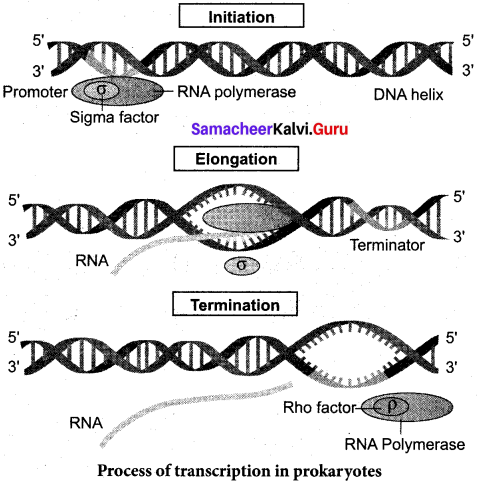
The polymerase binding sites are called promoters. It uses nucleoside triphosphate as substrate and polymerases in a template dependent fashion following the rule of complementarity. After the initiation of transcription, the polymerase continues to elongate the RNA, adding one nucleotide after another to the growing RNA chain. Only a short stretch of RNA remains bound to the enzyme, when the polymerase reaches a terminator at the end of a gene, the, nascent RNA falls off, so also the RNA polymerase. The RNA polymerase is only capable of catalyzing the process of elongation. The RNA polymerase associates transiently with initiation factor sigma (a) and termination factor rho (p) to initiate and terminate the transcription, respectively.
Association of RNA with these factors instructs the RNA polymerase either to initiate or terminate the process of transcription. In bacteria, since the mRNA does not require any processing to become active and also since transcription and translation take place simultaneously in the same compartment since there is no separation of cytosol and nucleus in bacteria), many times the translation can begin much before the mRNA is fully transcribed. This is because the genetic material is not separated from other cell organelles by a nuclear membrane consequently; transcription and translation can be coupled in bacteria.

Question 81.
Write the salient features of genetic code.
Answer:
The salient features of genetic code are as follows:
- The genetic codon is a triplet code and 61 codons code for amino acids and 3 codons do not code for any amino acid and function as a stop codon (Termination).
- The genetic code is universal. It means that all known living systems use nucleic acids and the same three base codons (triplet codon) direct the synthesis of protein from amino acids. For example, the mRNA (UUU) codon codes for phenylalanine in all cells of all organisms. Some exceptions are reported in prokaryotic, mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. However, similarities are more common than differences.
- A non-overlapping codon means that the same letter is not used for two different codons. For instance, the nucleotide sequence GUTJ and GUC represents only two codons.
- It is comma less, which means that the message would be read directly from one end to the other i.e., no punctuation are needed between two codes.
- A degenerate code means that more than one triplet codon could code for a specific amino acid. For example, codons GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG code for valine.
- Non-ambiguous code means that one codon will code for one amino acid.
- The code is always read in a fixed direction i.e. from 5’→3’ direction called polarity.
- AUG has dual functions. It acts as an initiator codon and also codes for the amino acid methionine.
- UAA, UAG (tyrosine) and UGA (tryptophan) codons are designated as termination (stop) codons and also are known as “non-sense” codons.
Question 82.
Mutations in genetic code affect the phenotype. Describe with an example.
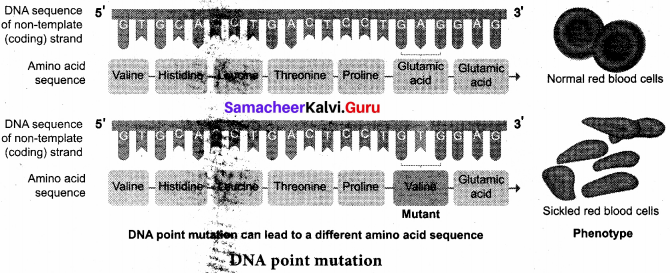
Answer:
The simplest type of mutation at the molecular level is a change in nucleotide that substitutes one base for another. Such changes are known as base substitutions which may occur spontaneously or due to the action of mutagens. A well-studied example is sickle cell anaemia in humans which results from a point mutation of an allele of β-hemoglobin gene (βHb).
A haemoglobin molecule consists of four polypeptide chains of two types, two a chains and two P-chains. Each chain has a heme group on its surface. The heme groups are involved in the binding of oxygen. The jruman blood disease, sickle cell anaemia is due to abnormal haemoglobin. This abnormality in hemoglobin is due to a single base substitution at the sixth codon of the beta globingene from GAG to GTG in p -chain of haemoglobin.
It results in a change of amino acid glufeniic acid to valine at the 6th position of the p -chain. This is the classical example of point mutation that results in the change of amino acids residue glutamic acid to valine. The mutant haemoglobin undergoes polymerisation under oxygen tension causing the change in the shape of the RBC from biconcave to a sickle shaped structure.
Question 83.
Explain the mechanism of AteArperon of the E-coli.
Answer:
The Lac (Lactose) operon: The metabolism of lactose in E.coli requires three enzymes – permease, P-galactosidase (P-gat) and transacetylase. The enzyme permease is needed for entry of lactose into the cell, Pjgglactosidase brings about hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose, while transacety transfers acetyl group from acetyl Co A to P-galactosidase. The lac operon consists of one-regulator gene (T gene refers to inhibitor) promoter sites (p), and operator site (o). Besides these, it has three structural genes namely lac z, y and lac a. The lac ‘z’ gene codes for P-gaiaqtttsidase, lac ‘y’ gene codes for permease and ‘a’ gene codes for transacetylase.
Jacob and Monod proposed the classical model of Lac operon to explain gene expression and regulation in E.coli. In lac a polycistronic structural gene is regulated by a common promoter and regulatory genfc When the cell is using its normal energy source as glucose, the ‘i’ gene transcribes a repressor mRNA and after its translation, a repressor protein is produced. It binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents translation, as a result, P-galactosidase is not produced. In the absence of preferred carbon source such as glucose, if lactose is available as an energy source for the bacteria then lactose enters the cell as a result of permease enzyme. Lactose acts as an inducer and interacts with the repressor to inactivate it.
The repressor protein binds to the operator of the operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon. In the presence of inducer, such as lactose or allolactose, the repressor is inactivated by interaction with the inducer. This allows RNA polymerase to bind to the promotor site and transcribe the operon to produce lac mRNA which enables formation of all the required enzymes needed for lactose metabolism. This regulation of lac operon by the repressor is an example of negative control of transcription initiation.
Question 84.
What are the objectives of Human Genome project?
Answer:
The main goals of Human Genome Project are as follows:
- Identify all the genes (approximately 30000) in human DNA.
- Determine the sequence of the three billion chemical base pairs that makeup the human DNA.
- To store this information in databases.
- Improve tools for data analysis.
- Transfer related technologies to other sectors, such as industries.
- Address the ethical, legal and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project.

Question 85.
Write the salient features of Human Genome Project.
Answer:
- Although human genome contains 3 billion nucleotide bases, the DNA sequences that encode proteins make up only about 5% of the genome.
- An average gene consists of 3000 bases, the largest known human gene being dystrophin with 2.4 million bases.
- The function of 50% of the genome is derived from transposable elements such as LINE and ALU sequence.
- Genes are distributed over 24 chromosomes. Chromosome 19 has the highest gene density. Chromosome 13 and Y chromosome have lowest gene densities.
- The chromosomal organization of human genes shows diversity.
- There may be 35000-40000 genes in the genome and almost 99.9 nucleotide bases are exactly the same in all people.
- Functions for over 50 percent of the discovered genes are unknown.
- Less than 2 percent of the genome codes for proteins.
- Repeated sequences make up very large portion of the human genome. Repetitive sequences have no direct coding functions but they shed light on chromosome structure, dynamics and evolution (genetic diversity).
- Chromosome 1 has 2968 genes, whereas chromosome ’Y’ has 231 genes.
- Scientists have identified about 1.4 million locations, where single-base DNA differences (SNPs – Single nucleotide polymorphism – pronounce as ‘snips’) occur in humans. Identification of ‘SNIPS’ is helpful in finding chromosomal locations for disease-associated sequences and tracing human history.
Question 86.
Describe the principle involved in DNA fingerprinting technique.
Answer:
The DNA fingerprinting technique was first developed by Alec Jeffreys in 1985. The DNA of a person and finger prints are unique. There are 23 pairs of human chromosomes with 1.5 million pairs of genes. It is a well known fact that genes are segments of DNA that differ in the sequence of their nucleotides. Not all segments of DNA code for proteins, some DNA segments have a regulatory function, while others are intervening sequences (introns) and still others are repeated DNA sequences. In DNA fingerprinting, short repetitive nucleotide sequences are specific for a person. These nucleotide sequences are called as variable number tandem repeats (VNTR). The VNTRs of two persons generally show variations and are useful as genetic markers.
DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in the DNA sequence called repetitive DNA because in these sequences, a small stretch of DNA is repeated many times. These repetitive DNA are separated from bulk genomic DNA as different peaks during density gradient centrifugation. The bulk DNA forms a major peak and the other small peaks are referred to as satellite DNA. Depending on base composition (A: T rich or G : C rich), length of segment and number of repetitive units, the satellite DNA is classified into many subcategories such as micro-satellites and mini satellites, etc.
These sequences do not code for any proteins, but they form a large portion of human genome. These sequences show high degree of polymorphism and form the basis of DNA fingerprinting. DNA isolated from blood, hair, skin cells, or other genetic evidences left at the scene of a crime can be compared through VNTR patterns, with the DNA of a criminal suspect to determine guilt or innocence. VNTR patterns are also useful in establishing the identity of a homicide victim, either from DNA found as evidence or from the body itself.

Question 87.
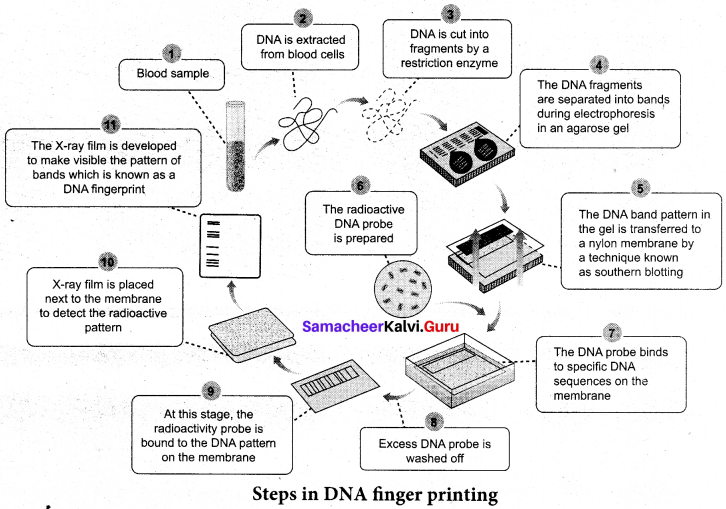
Draw a flow chart depicting the steps of DNA finger printings technique
Answer:
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
An mRNA strand has a series of triplet codons of which the first three codons are given below
(a) AUG
(b) UUU
(c) UGC
(i) Name the amino acid encoded by these triplet codons.
(ii) Mention the DNA sequence from which these triplet codons would have transcribed?
Answer:
(i) AUG codes for Methionine
UUU codes for Phenylalanine
UGC codes for Cysteine
(ii) TAC sequence of DNA is transcribed to AUG
AAA sequence of DNA is transcribed to UUU
ACG sequence of DNA is transcribed to UGC
Question 2.
Given below are the structures of tRNA molecules which are involved in the translation process. In one tRNA, the codon is mentioned but not the amino acid. In another tRNA molecule, the amino acid is named and not the codon. Complete the figure by mentioning the respective amino acids and codons.
Answer:
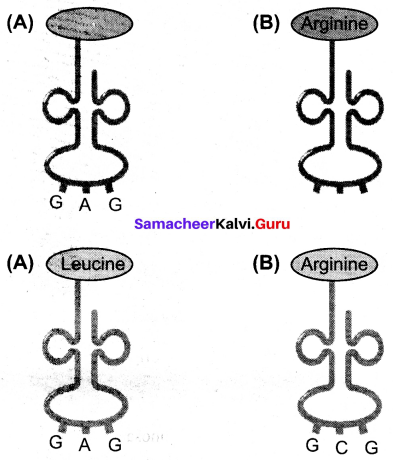
Question 3.
A DNA fragment possesses 32 adenine bases and 32 cytosine bases. How many total numbers of nucleotides does that DNA fragment contain? Explain.
Answer:
128 nucleotides. Adenine always pairs Thymine base. If there are 32 adenine bases then there must be 32 Thymine bases. Similarly cytosine pairs with guanine. If cytosine bases are 32 in number the guanine bases will be equal to cytosine. So it makes a total of 128 nucleotides.

Question 4.
Following is a DNA sequence representing a part of the gene TAC TCG CCC TAT UAA CCC AAA ACC TCT using this derive A.
- The RNA transcript
- The spliced mRNA (consider all the codons with two Aderine bases are introns)
- The total number of amino acids coded by the mRNA
Answer:
- RNA transcript: AUG UGC GGG AUA GGG UUU UGG AGA
- Spliced mRNA: AUG UGC GGG GGG UUU UGG
- 6 amino acids are coded by mRNA
Question 5.
Complete the molecular processes by naming them
- DNA → DNA
- mRNA → Protein
- RNA transcript → mRNA
Answer:
- Replication
- Translation
- Splicing
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()




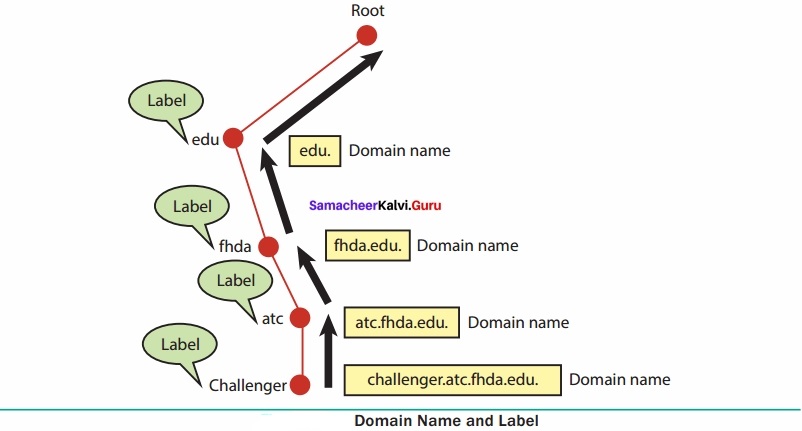
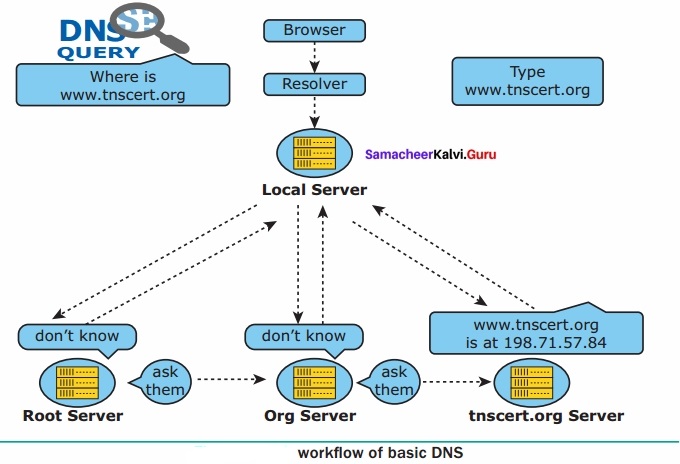
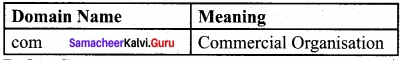
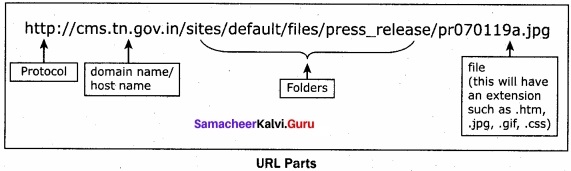
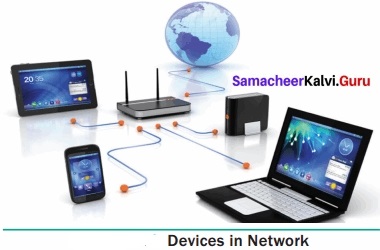
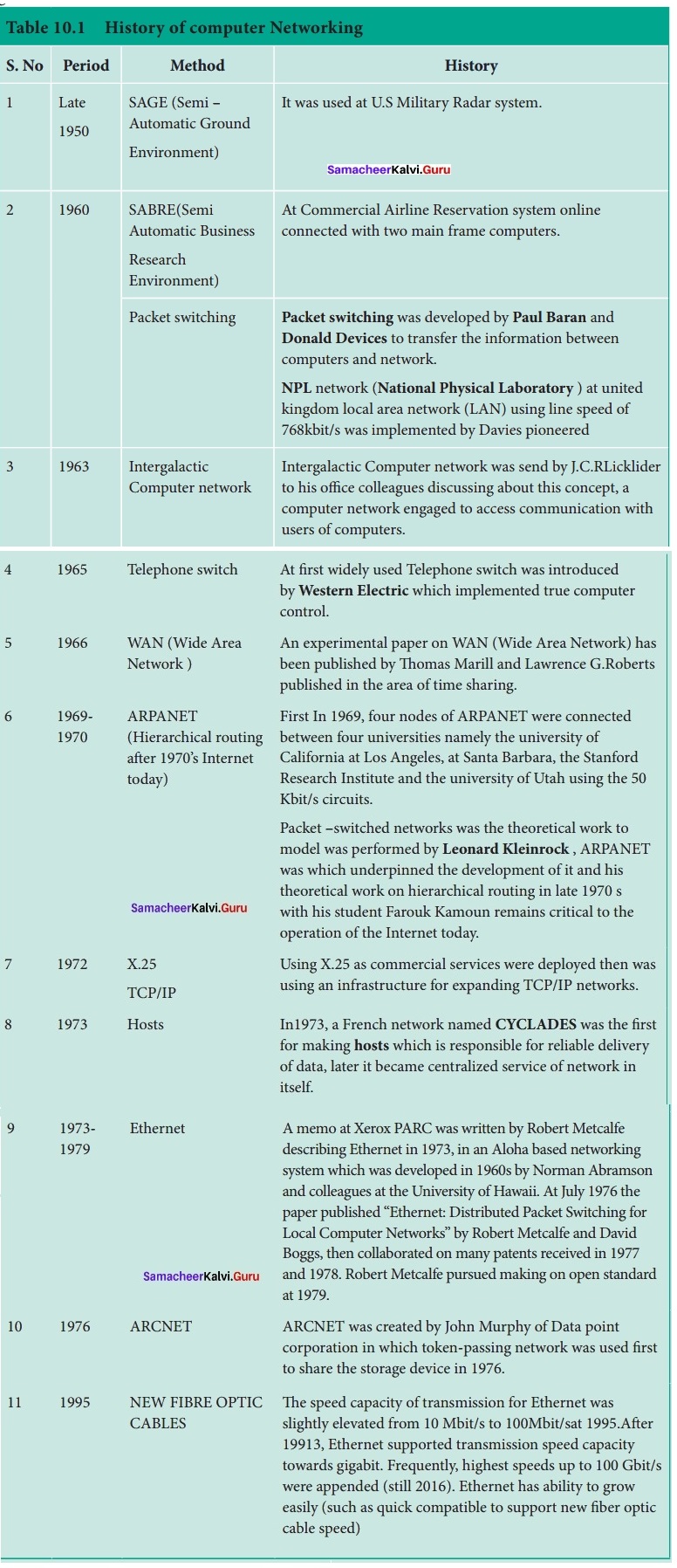 A set of computers connected together for the purpose of sharing resources is called as computer networks. At present, Internet is the most common resource shared everywhere. Some of the shared resources are file server, web camera, speakers, printer, scanner, fax machine etc., Accessing services such as WWW (World Wide Web), Digital audio, Digital video which are shared t use applications, software, and storage servers. All are well-known the term Internet Networks of network is called Internet.
A set of computers connected together for the purpose of sharing resources is called as computer networks. At present, Internet is the most common resource shared everywhere. Some of the shared resources are file server, web camera, speakers, printer, scanner, fax machine etc., Accessing services such as WWW (World Wide Web), Digital audio, Digital video which are shared t use applications, software, and storage servers. All are well-known the term Internet Networks of network is called Internet.