Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 10 Depreciation Accounting
Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 10 Depreciation Accounting Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 10 Depreciation Accounting
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Depreciation Accounting Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Under straight line method, the amount of depreciation is ……………..
(a) Incfeasing every year
(b) Decreasing every year
(c) Constant for all the years
(d) Fluctuating every year
Answer:
(c) Constant for ail the years
Question 2.
If the total charge of depreciation and maintenance cost are considered, the method that provides a uniform charge is ……………..
(a) Straight line method
(b) Diminishing balance method
(c) Annuity method
(d) Insurance policy method
Answer:
(b) Diminishing balance method
Question 3.
Under the written down value method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is ……………..
(a) Uniform in all the years
(b) Decreasing every year
(c) Increasing every year
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Decreasing every year
![]()
Question 4.
Depreciation provided on machinery is debited to ……………..
(a) Depreciation account
(b) Machinery account
(c) Trading account
(d) Provision for depreciation account
Answer:
(a) Depreciation account
Question 5.
Cash received from sale of fixed asset is credited to ……………..
(a) Profit and loss account
(b) Fixed asset account
(c) Depreciation account
(d) Bank account
Answer:
(b) Fixed asset account
Question 6.
Depreciation is provided on ……………….
(a) Fixed assets
(b) Current assets
(c) Outstanding charges
(d) All assets
Answer:
(a) Fixed assets
Question 7.
Depreciation is caused by ……………..
(a) Lapse of time
(b) Usage
(c) Obsolescence
(d) a, b and c
Answer:
(d) a, b and c
Question 8.
Depreciation is the process of ……………..
(a) Allocation of cost of the asset to the period of its useful life
(b) Valuation of assets
(c) Maintenance of an asset in a state of efficiency
(d) Adding value to the asset
Answer:
(a) Allocation of cost of the asset to the period of its useful life
Question 9.
For which of the following assets, the depletion method is adopted for writing off cost of the asset?
(a) Plant and machinery
(b) Mines and quarries
(c) Buildings
(d) Trademark
Answer:
(b) Mines and quarries
Question 10.
A depreciable asset may suffer obsolescence due to ……………..
(a) Passage of time
(b) Wear and tear
(c) Technological changes
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Technological changes
![]()
Question 11.
Which method shall be efficient, if repairs and maintenance cost of an asset increases as it grows older?
(a) Straight line method
(b) Reducing balance method
(c) Sinking fund method
(d) Annuity method
Answer:
(b) Reducing balance method
Question 12.
Depreciation is to be calculated from the date when ……………..
(a) Asset is put to use
(b) Purchase order is made
(c) Asset is received at business premises
(d) Invoice of assets is received
Answer:
(a) Asset is put to use
Question 13.
If the rate of depreciation is same, then the amount of depreciation under straight line method vis – a – vis written down value method will be
(a) Equal in all years
(b) Equal in the first year but higher in subsequent years
(c) Equal in the first year but lower in subsequent years
(d) Lower in the first year but equal in subsequent years
Answer:
(b) Equal in the first year but higher in subsequent years
Question 14.
Residual value of an asset means the amount that it can fetch on sale at the of its useful life.
(a) Beginning
(b) End
(c) Middle
(d) None
Answer:
(b) End
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by depreciation?
Answer:
The process of allocation of the relevant cost of a fixed asset over its useful life is known as depreciation. It is an allocation of cost against the benefits derived from a fixed asset during an accounting period.
Question 2.
List out the various methods of depreciation.
Answer:
- Straight line method or fixed instalment method or Original cost method.
- Written down value method or Diminishing balance method or Reducing balance method.
- Sum of years digits method.
- Machine hour rate method.
- Depletion method.
- Annuity method.
- Revaluation method.
- Sinking fund method.
- Insurance Policy method.
Question 3.
Give the formula to find out the amount and rate of depreciation under straight line method of depreciation.
Answer:
1. Amount of depreciation per year = 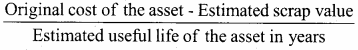
2. Rate of depreciation = ![]()
Question 4.
What is annuity method?
Answer:
Under this method, not only the original cost of the asset but also the amount of interest on the investment is taken into account while computing depreciation. The idea of considering interest is that if the investment is made in any other asset instead of the relevant fixed asset, it . would have earned a certain rate of interest. To calculate the amount of depreciation, annuity factor is used. Annuity factor can be found out from the annuity table or by using formula. Amount of depreciation is computed as follows:
Amount of depreciation = Annuity factor x original cost of the asset.
![]()
Question 5.
What is sinking fund method?
Answer:
This method is adopted especially when it is desired not merely to write off an asset but also to provide enough funds to replace an asset at the end of its working life. Under this method, the amount charged as depreciation is transferred to depreciation fund and invested outside the business. The investment is made in safe securities which offer a certain rate of interest. Interest is received annually and reinvested every year along with the amount of annual depreciation. On the expiry of the life of the asset, the investments are sold and the sale proceeds are used for replacement of the asset. This method of depreciation is suitable for assets of higher value. This method is also known as depreciation fund method.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the objectives of providing depreciation?
Answer:
- To find out the true profit or loss
- To present the true and fair view of financial position
- To facilitate replacement of fixed assets
- To avail tax benefits
- To comply with legal requirements
Question 2.
What are the causes for depreciation?
Answer:
- Wear and tear
- Efflux of time
- Obsolescence
- Inadequacy for the purpose
- Lack of maintenance
- Abnormal factors
Question 3.
State the advantages and limitations of straight line method of depreciation.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to understand
- Equality of depreciation burden
- Assets can be completely written off
- Suitable for the assets having fixed working life
Limitations:
- Ignores the actual use of the asset
- Ignores the interest factor
- Total charge on the assets will be more when the asset becomes older
- Difficulty in the determination of scrap value
![]()
Question 4.
State the advantages and limitations of written down value method of depreciation.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Equal charge against income
- Logical method
Limitations:
- Assets cannot be completely written off
- Ignores the interest factor
- Difficulty in determining the rate of depreciation
- Ignores the actual use of the asset
Question 5.
Distinguish between straight line method and written down value method of providing depreciation.
Answer:
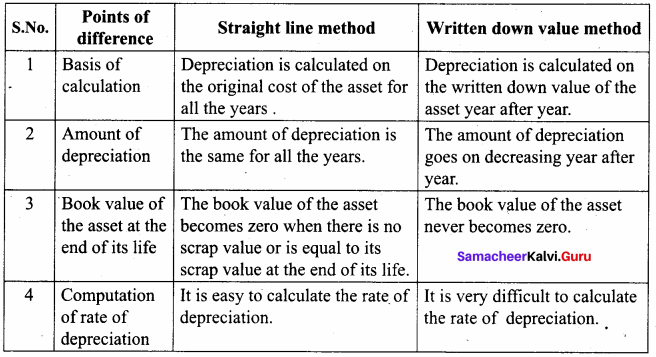
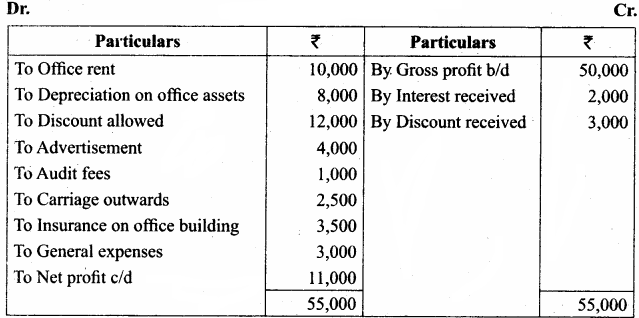
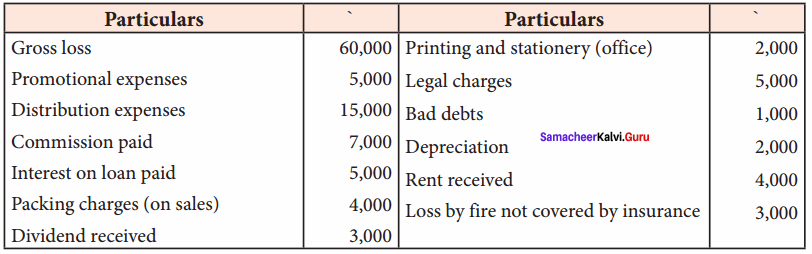
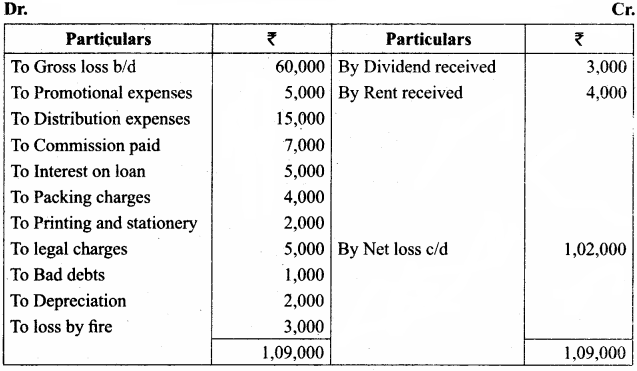
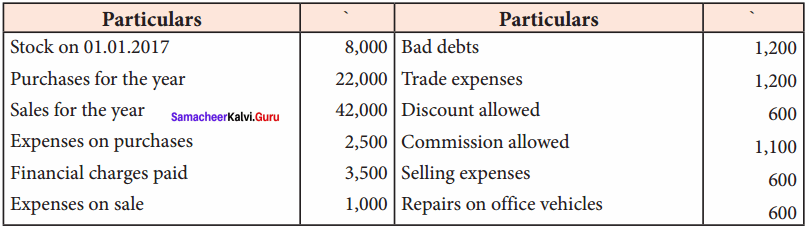
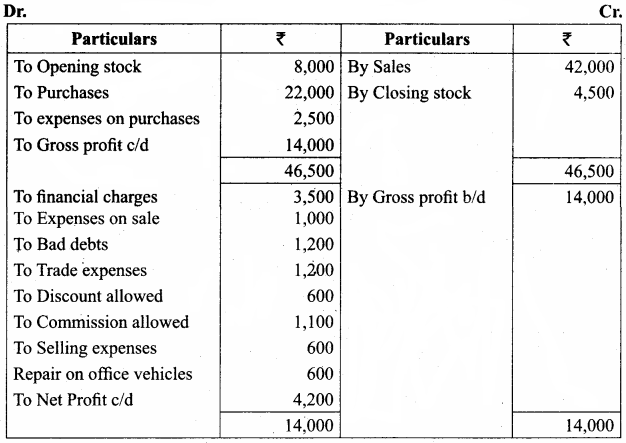
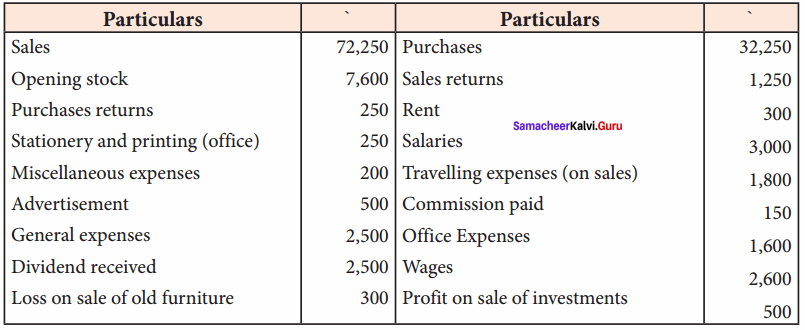
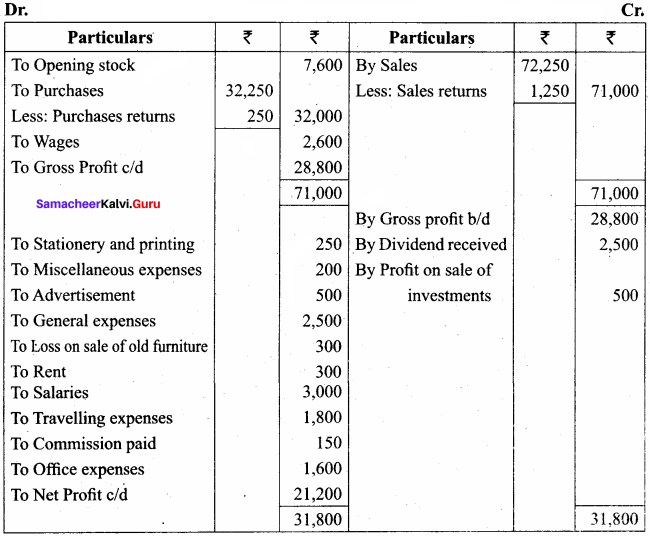
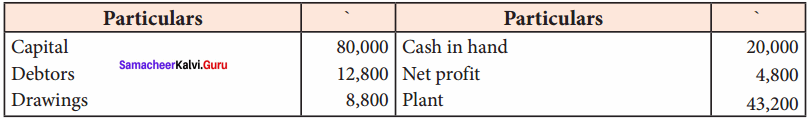
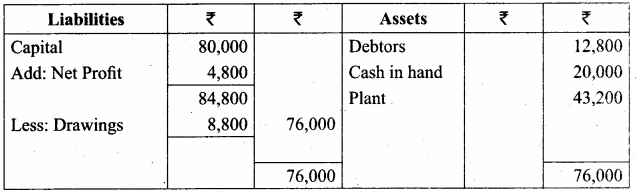
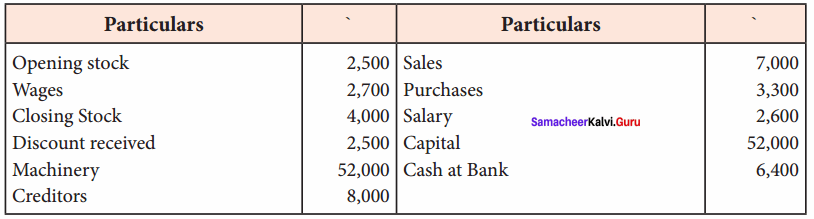
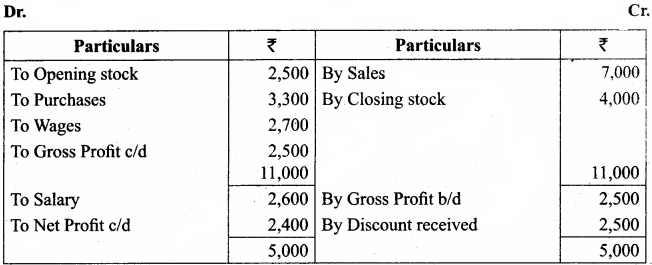
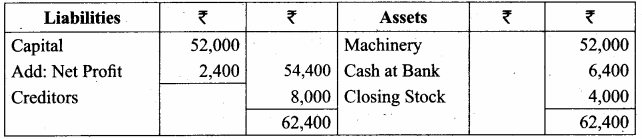
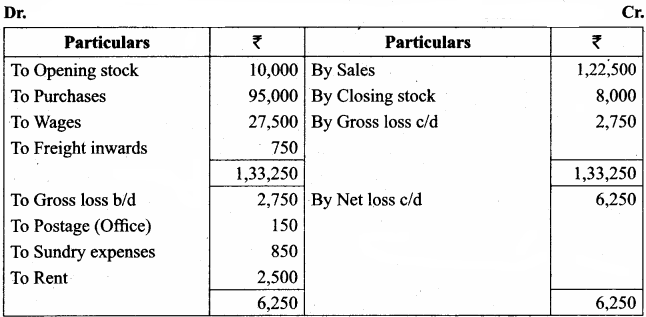
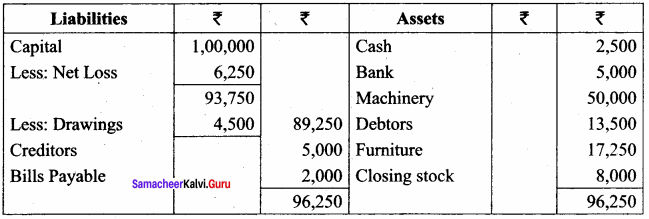
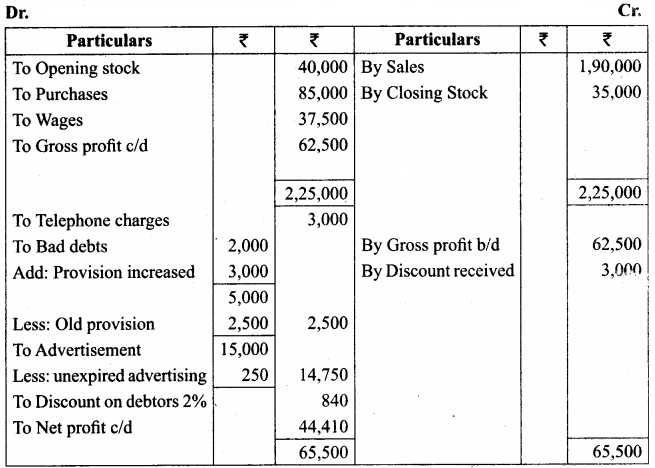
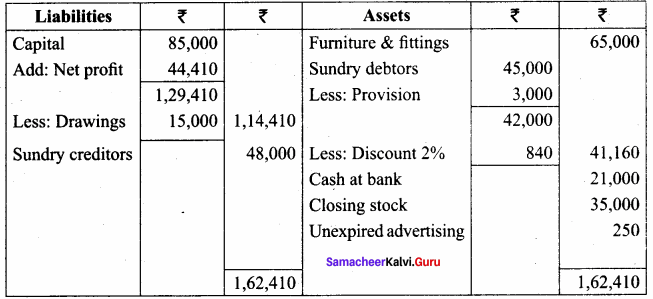
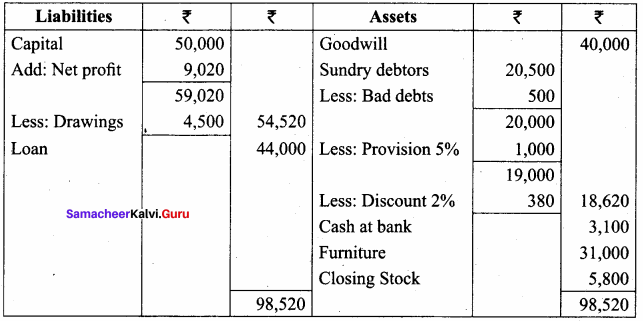
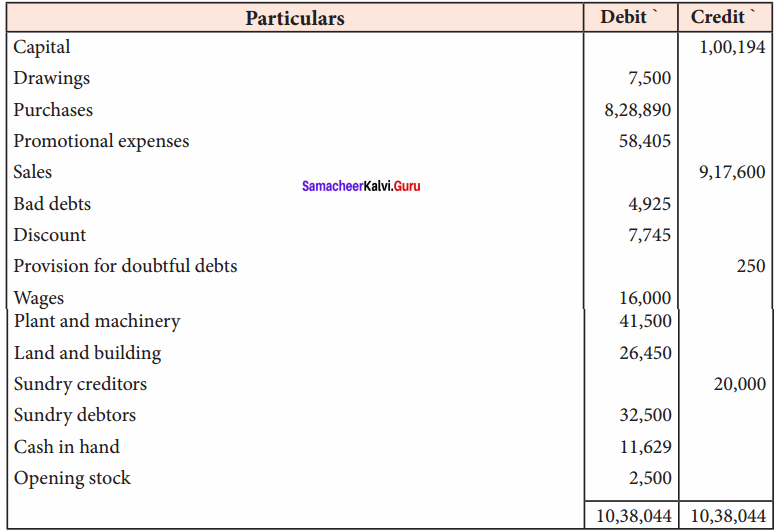
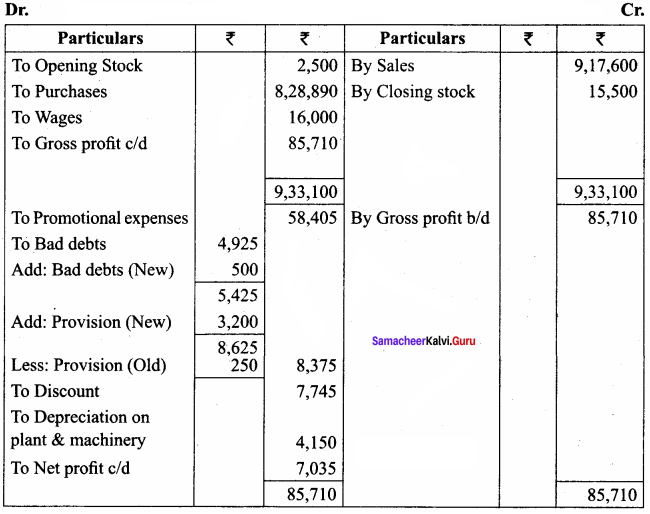
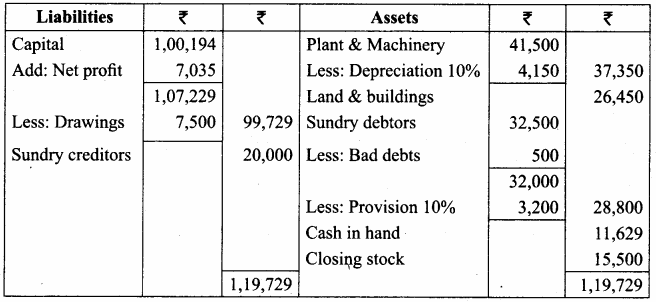
IV. Exercises
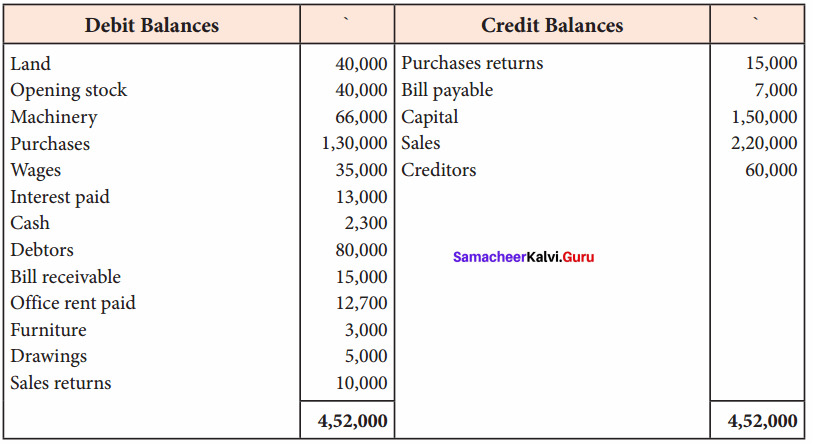
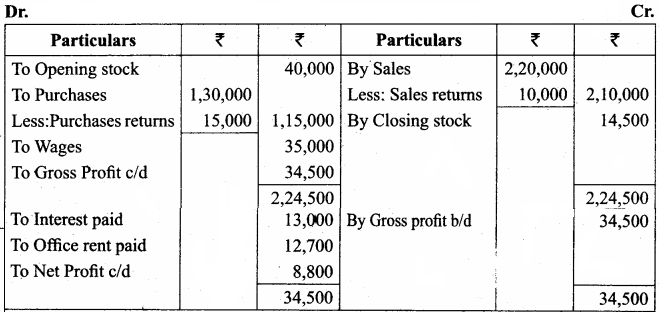
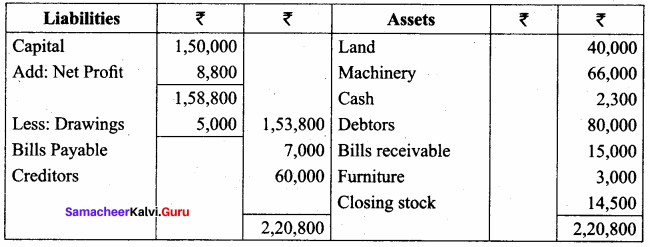
Straight line method:
Question 1.
A firm purchased a plant for ₹ 40,000. Erection charges amounted to ₹ 2,000. Effective life of the plant is 5 years. Calculate the amount of depreciation per year under straight line method.
Answer:
Calculation of amount of depreciation
Amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = Purchase of plant + Erection charges = ₹ 40,000 + ₹ 2,000 = ₹ 42,000
Estimated life = 5 years = \(\frac{₹ 42000-0}{5 \text { years }}\) = ₹ 8,400/-
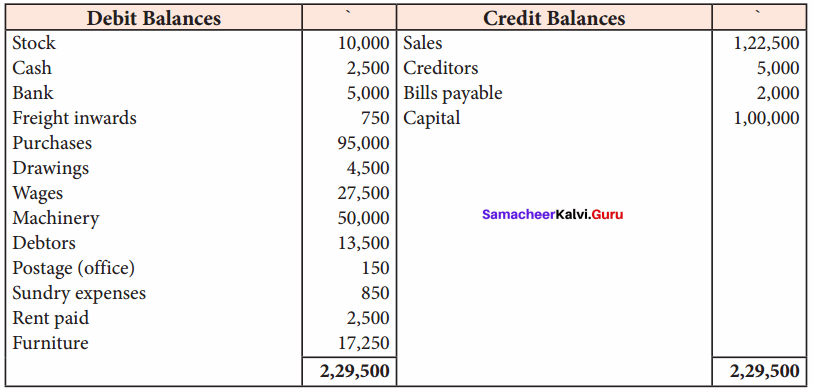
Question 2.
A company purchased a building for ₹ 50,000. The useful life of the building is 10 years and the residual value is ₹ 2,000. Find out the amount and rate of depreciation under straight line method.
Answer:
(1) Calculation of amount of depreciation:
Amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = ₹ 50,000
residual value = ₹ 2,000
Estimated life = 10 years
\(\frac{50,000-2,000}{10 \text { years }}\) = \(\frac { 48,000 }{ 10 }\) = ₹ 4,800/-
(2) Calculation of rate of depreciation:
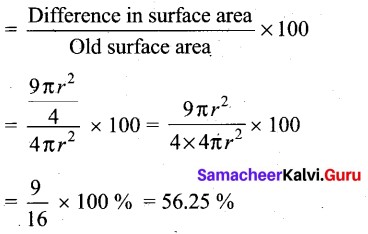
rate of depreciation = ![]() = \(\frac { 48,000 }{ 50,000 }\) x 100 = 9.6%
= \(\frac { 48,000 }{ 50,000 }\) x 100 = 9.6%
Question 3.
Furniture was purchased for ₹ 60,000 on 1-7-2016. It is expected to last for 5 years. Estimated scrap at the end of five years is ₹ 4,000. Find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method.
Answer:
(1) Amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = ₹ 60,000
Scrap value = ₹ 4,000
Estimated life = 5 years
= \(\frac{60,000-4,000}{5 \text { years }}\) = \(\frac { 56,000 }{ 5 }\) = ₹ 11,200/-
Question 4.
Calculate the rate of depreciation under straight line method from the following information: Purchased a second hand machinery on 1.1.2018 for ₹ 38,000 On 1.1.2018 spent ₹ 12,000 on its repairs
Expected useful life of machine is 4 years
Estimated residual value ₹ 6,000
Answer:
Original cost – residual value
(1) Calculation of amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = Purchase of machinery + repair charges = 38,000 + 12,000 = 50,000
Residual value = 6,000
Estimated life = 4 years = \(\frac{50,000-6,000}{4 \text { years }}\) = ₹ 11,000/-
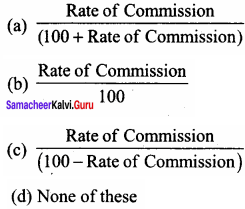
(2) Rate of depreciation = ![]()
= \(\frac { 11,000 }{ 50,000 }\) x 100 = 22 %
Question 5.
Calculate the rate of depreciation under straight line method.
Purchase price of a machine ₹ 80,000
Expenses to be capitalised ₹ 20,000
Estimated residual value ₹ 4,000
Expected useful life ₹ 4 years
Answer:
Original cost – residual value = ![]()
Original cost = Machine purchased + capitalised expenses
80,000 + 20,000 = 1,00,000
Residual value = 4,000
Estimated life = 4 years
= \(\frac{1,00,000-4,000}{4 \text { years }}\) = \(\frac { 96,000 }{ 4 }\) = ₹ 24,000/-
Question 6.
Machinery was purchased on 1st January 2015 for ₹ 4,00,000. ₹ 15,000 was spent on its erection and ₹ 10,000 on its freight charges. Depreciation is charged at 10% per annum on straight line method. The books are closed on 31st March each year. Calculate the amount of depreciation on machinery for the first two years.
Answer:
Calculation of depreciation:
Original cost = Machinery purchased + erection charges + freight charges
= 4,00,000 + 15,000 + 10 ,000
= 4,25,000
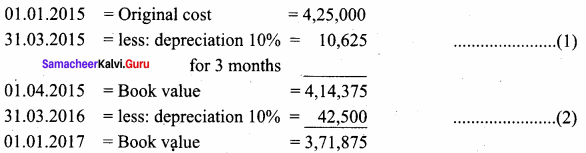
First year depreciation = ₹ 10,625
Second year depreciation = ₹ 42,500
Question 7.
An asset is purchased on 1.1.2016 for ₹ 25,000. Depreciation is to be provided annually according to straight line method. The useful life of the asset is 10 years and its residual value is ₹ 1,000. Accounts are closed on 31st December every year. You are required to find out the rate of depreciation and give journal entries for first two years.
Answer:
Amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = ₹ 25,000
Residual value = ₹ 1,000
Estimated life = 10 years
= \(\frac{25,000-1,000}{10 \text { years }}\) = \(\frac { 24,000 }{ 10 }\) = ₹ 24,000/-
(2) Rate of depreciation = ![]()
= \(\frac { 2,400 }{ 25,000 }\) x 100 = 9.6%
Journal Entries for first two years
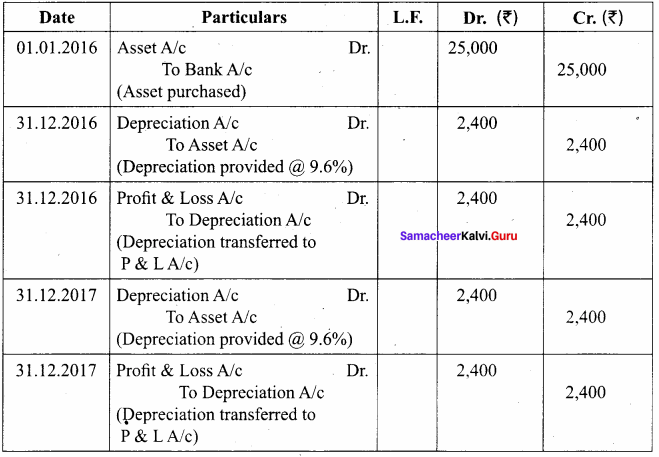
Question 8.
From the following particulars, give journal entries for 2 years and prepare machinery account under straight line method of providing depreciation:
Machinery was purchased on 1.1.2016
Price of the machine ₹ 36,000
Freight charges ₹ 2,500
Installation charges ₹ 1,500
Life of the machine 5 years
Answer:
Calculation of Asset of depreciation:
Amount of depreciation = ![]()
Original cost = Price of the machine + Freight charges + Installation charges
= 36,000 + 2,500 + 1,500 = ₹ 40,000
= \(\frac { 40,000 – 0 }{ 5 years }\) = ₹ 8,000
Journal Entries for 2 years
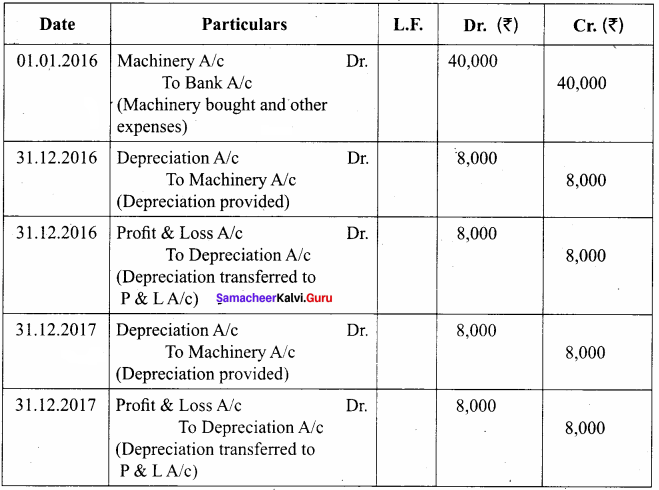
Machinery
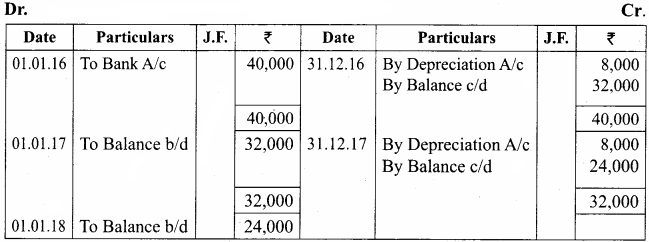
Question 9.
A manufacturing company purchased on 1st April, 2010, a plant and machinery for ₹ 4,50,000 and spent ₹ 50,000 on its installation. After having used it for three years, it was sold for ₹ 3,85,000. Depreciation is to be provided every year at the rate of 15% per annum on the fixed instalment method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Calculate profit or loss on sale of machinery.
Answer:
Calculation of Profit or Loss on sale of Machinery
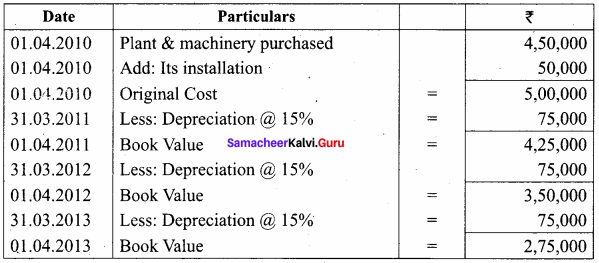
Note: If the selling price is more than the book value is called profit.
Selling price – Book value = Profit 3,85,000 – 2,75,000 = 1,10,000
Profit on sale of Machinery is = ₹ 1,10,000.
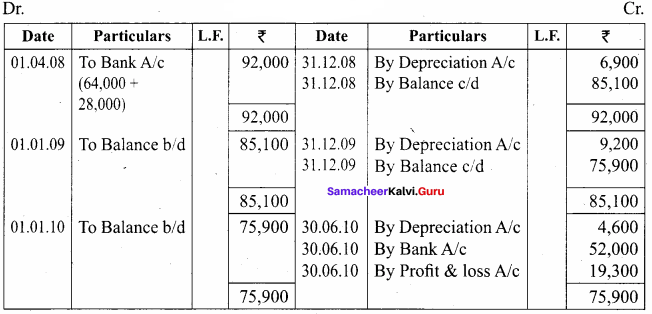
Question 10.
On 1st April 2008, Sudha and Company purchased machinery for ₹ 64,000. To instal the machinery expenses incurred was ₹ 28,000. Depreciate machinery 10% p.a. under straight line method. On 30th June, 2010 the worn out machinery was sold for ₹ 52,000. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Show machinery account.
Answer:
Workings:
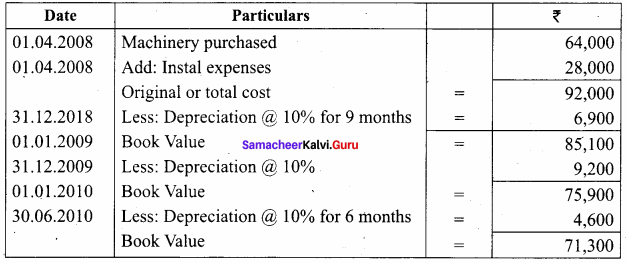
If Book value is more than the selling price it is called loss.
Book value – selling price = loss
71,300 – 52,000 = 19,300
Loss on sale of machinery is = 19,300
Machinery
Question 11.
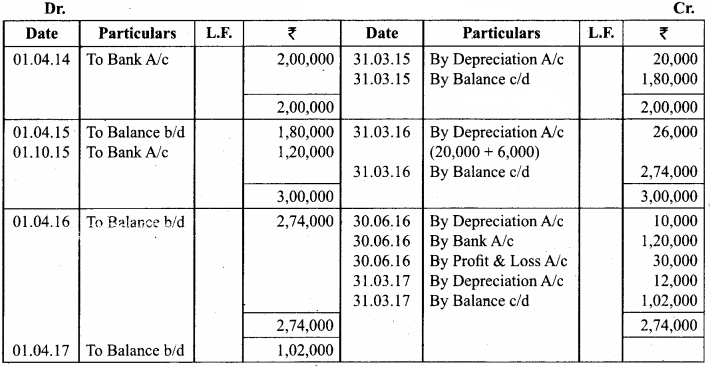
Ragul purchased machinery on April 1, 2014 for ₹ 2,00,000. On 1st October 2015, a new machine costing ₹ 1,20,000 was purchased. On 30th September 2016, the machinery purchased on April 1, 2014 was sold for ₹ 1,20,000. Books of accounts are closed on 31st March and depreciation is to be provided at 10% p.a. on straight line method. Prepare machinery account and depreciation account for the years 2014 – 15 to 2016 – 17.
Answer:
Workings
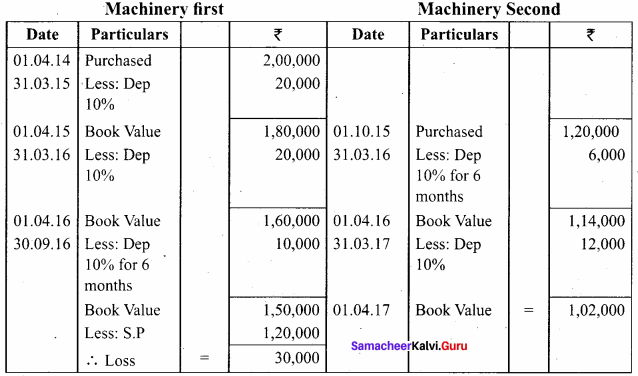
Machinery
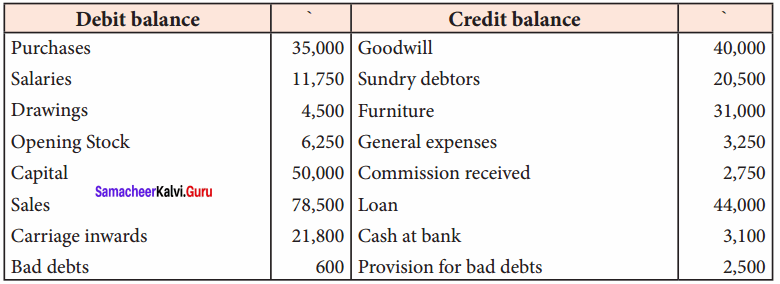
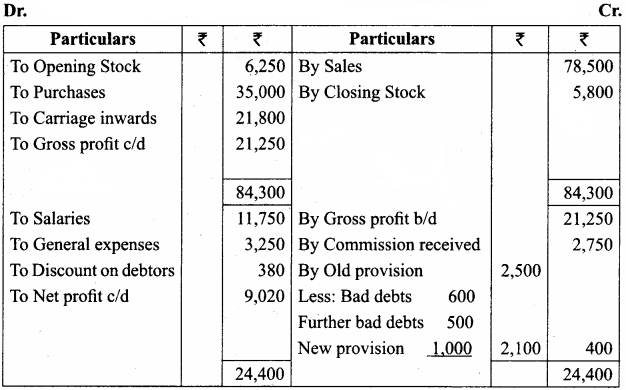
Written down value method
Question 12.
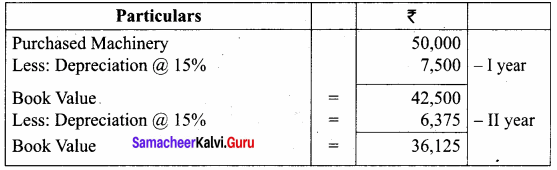
An asset is purchased for ₹ 50,000. The rate of depreciation is 15% p.a. Calculate the annual depreciation for the first two years under diminishing balance method.
Answer:
Workings: Calculation of depreciation of Machinery
Question 13.
A boiler was purchased on 1st January 2015 from abroad for ₹ 10,000. Shipping and forwarding charges amounted to ₹ 2,000. Import duty ₹ 7,000 and expenses of installation amounted to ₹ 1,000. Calculate depreciation for the first 3 years @10% p.a. on diminishing balance method assuming that the accounts are closed 31st December each year.
Answer:
Calculation of amount of depreciation on diminishing balance method:
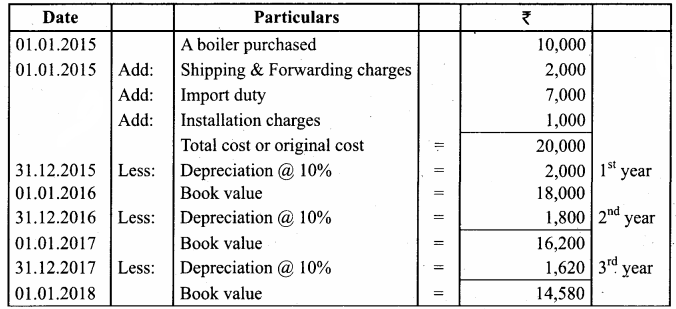
2015 Depreciation ₹ 2,000
2016 Depreciation ₹ 1,800
2017 Depreciation ₹ 1,620
Question 14.
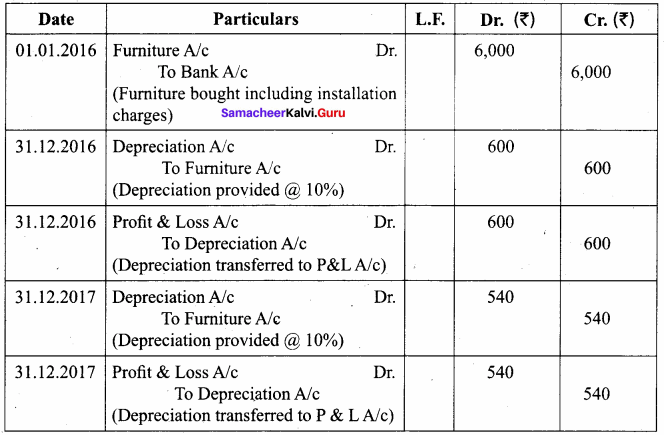
A furniture costing ₹ 5,000 was purchased on 1.1.2016, the installation charges being ₹ 1,000. The furniture is to be depreciated @ 10% p.a. on the diminishing balance method. Pass journal entries for the first two years.
Answer:
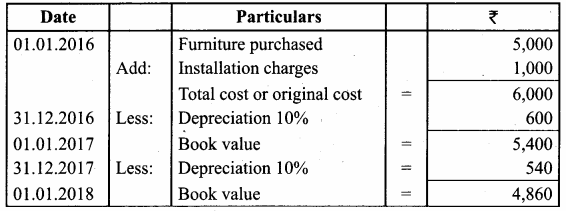
Journal Entries
Question 15.
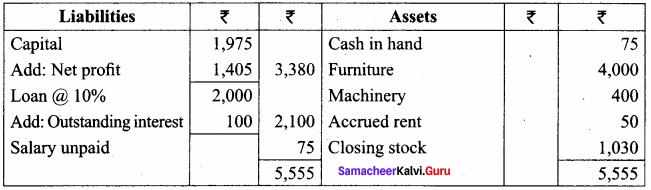
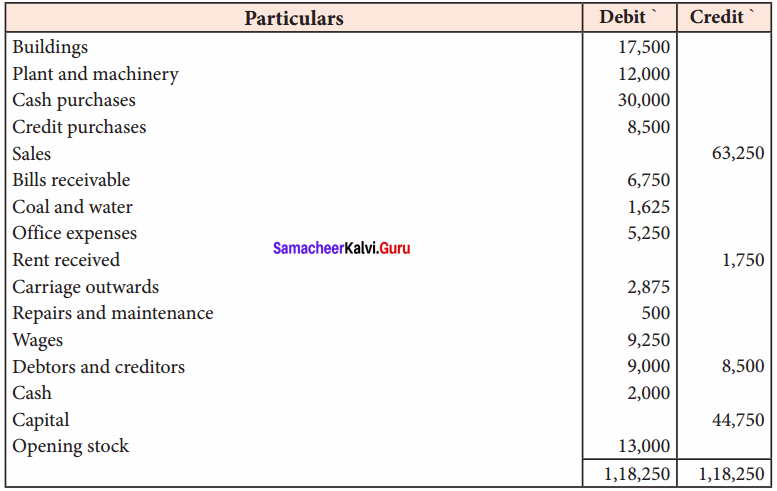
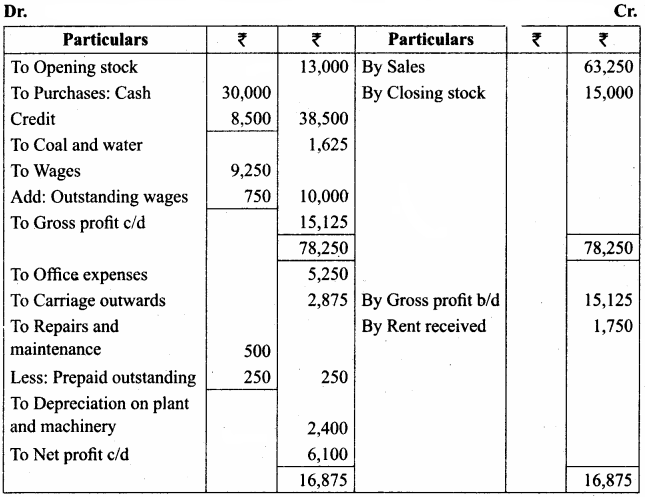
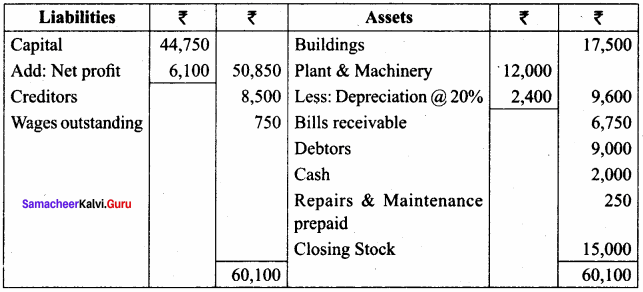
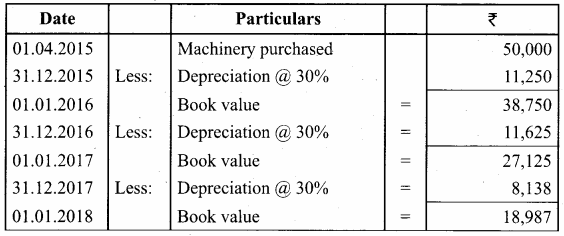
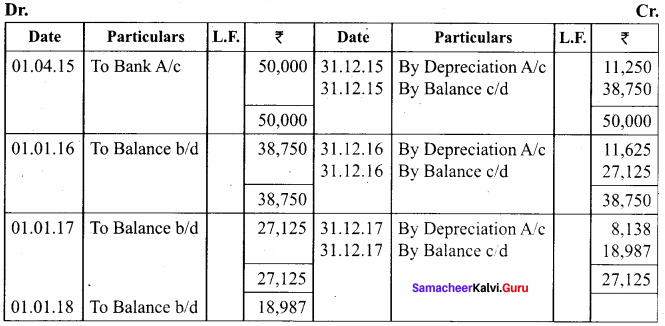
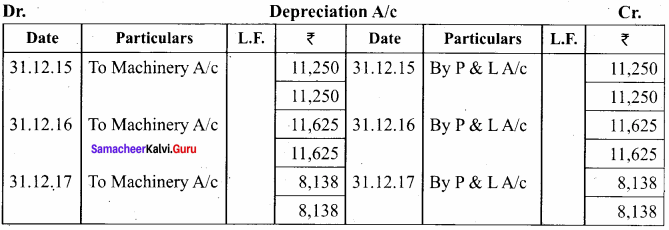
A firm acquired a machine on 1st April 2015 at a cost of ₹ 50,000. Its life is 6 years. The firm writes off depreciation @ 30% p.a. on the diminishing balance method. The firm closes its books on 31st December every year. Show the machinery account and depreciation account for three years starting from 1st April 2015.
Answer:
Workings:
Machinery
Depreciation A/c
Question 16.
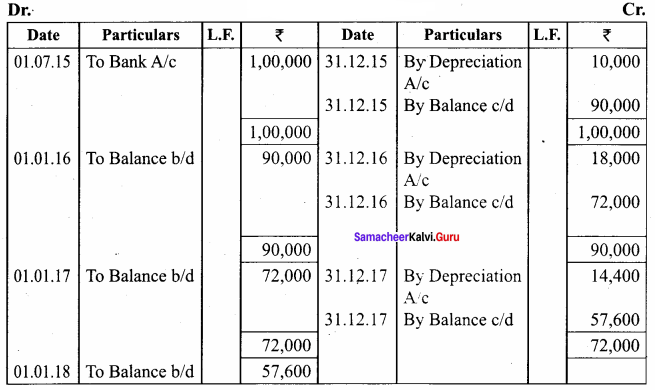
A firm purchased a machine for ₹ 1,00,000 on 1-7-2015. Depreciation is written off at 20% on reducing balance method. The firm closes its books on 31st December each year. Show the machinery account upto 31-12-2017.
Answer:
Workings:
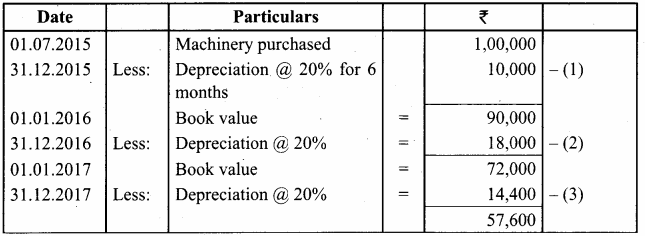
MachineryA/c
Question 17.
On 1st October 2014, a truck was purchased for ₹ 8,00,000 by Laxmi Transports Ltd. Depreciation was provided @ 15% p.a. under diminishing balance method. On 31st March 2017, the above truck was sold for ₹ 5,00,000. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Find out the profit or loss made on the sale of the truck.
Answer:
Calculation of Profit or loss on sale of truck:
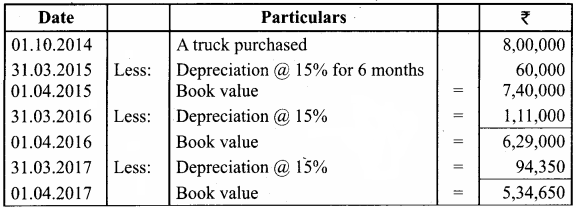
Note: If Book value is more than the selling price it is called loss:
Book value – selling price = Loss
5,34,650 – 5,00,000 = 34,650
∴ Loss on sale of truck = ₹ 34,650
Question 18.
On 1st January 2015, a second hand machine was purchased for ₹ 58,000 and ₹ 2,000 was spent on its repairs. On 1st July 2017, it was sold for ₹ 28,600. Prepare the machinery account for the years 2015 to 2017 under written down value method by assuming the rate of depreciation as 10% p.a. and the accounts are closed on 31st December every year.
Answer:
Calculation of profit or loss on sale of machinery
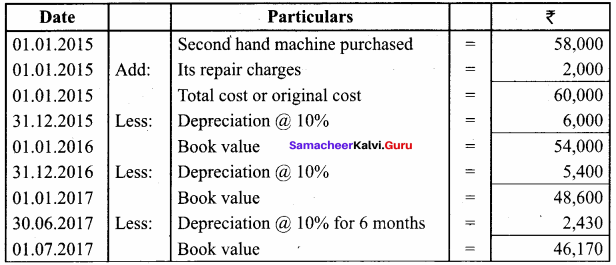
Note: If Book value is more than the selling price it is called loss.
Book value – selling price = loss
46,170 – 28,600 = 17,570
∴ Loss on sale of machinery = ₹ 17,570
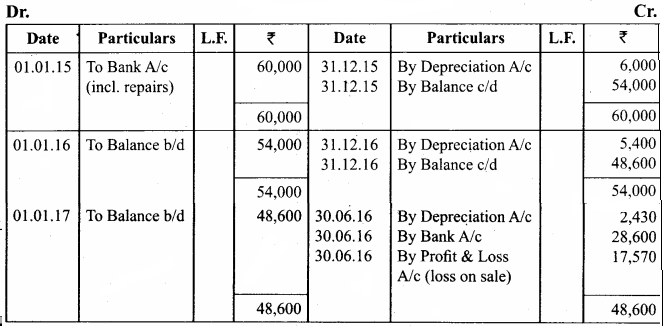
Question 19.
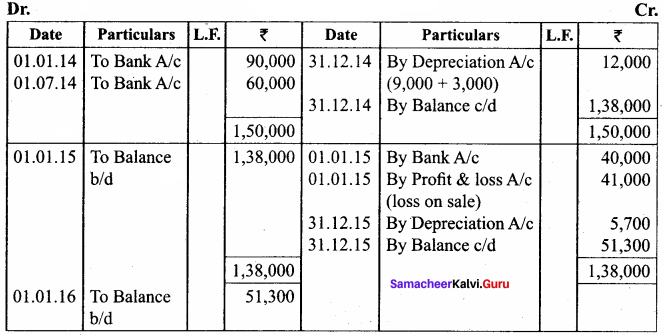
Raj & Co purchased a machine on 1st January 2014 for ₹ 90,000. On 1st July 2014, they purchased another machine for ₹ 60,000. On 1st January 2015, they sold the machine purchased on 1st January 2014 for ₹ 40,000. It was decided that the machine be depreciated at 10% per annum on diminishing balance method. Accounts are closed on 31st December every year. Show the machinery account for the years 2014 and 2015.
Answer:
Workings
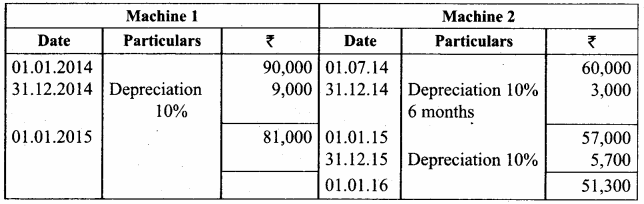
Note: If Book value is more than the selling price is called loss.
Book value – selling price = loss
81,000 – 40,000 = 41,000
Machinery
Textbook Case Study Solved
Question a.
Lucky & Co’s income statement shows a loss of ₹ 3,000. The owner thinks that there is no need to provide for depreciation as the company has made a loss. He also suggests his accountant to change the method of depreciation for the next year so as to avoid the loss. But, the accountant is hesitant to make the necessary changes suggested by his owner.
Now, discuss on the following points:
Question 1.
Do you agree on the point that there is no need to charge depreciation when the company has made a loss?
Answer:
No, I don’t agree on the point that there is no need to charge depreciation when the company has made a loss. We have to charge depreciation whether profit or loss, otherwise we cannot find out the actual profit or loss.
Question 2.
Why does the accountant hesitate to make the changes suggested by his owner?
Answer:
The accountant hesitates to make the changes suggested by his owner because it will differ the profit or loss for the business. The depreciation is a necessary one, so it must be deducted every year.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the accounting principles not followed if the accountant agrees to his owner’s suggestion?
Answer:
If the accountant agrees to his owner’s suggestion, they will not follow double entry system.
Question 4.
Do you think charging depreciation could be the only reason for the company’s loss?
Answer:
No, charging depreciation could not be the only reason for the company’s loss, because the business activities are subject to change but the depreciation is compulsory when the business is running.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Depreciation Accounting Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Depreciation is the gradual and permanent decrease in the value of an asset from any cause ……………….
(a) Owen
(b) Wheeler
(c) Spicer and Pegler
(d) R.N. Carter
Answer:
(d) R.N. Carter
Question 2.
Certain assets whether used or not become potentially less useful with the passage of time ……………….
(a) Efflux of time
(b) Lack of maintenance
(c) Abnormal factors
(d) Wear and tear
Answer:
(a) Efflux of time
Question 3.
The normal use of a tangible asset results in physical deterioration which is called ……………….
(a) Wear and tear
(b) Abnormal factors
(c) Obsolescence
(d) Efflux of time
Answer:
(a) Wear and tear
![]()
Question 4.
Allocation of acquisition cost of intangible fixed assets such as goodwill is called ……………….
(a) Abnormal factors
(b) Wear and tear
(c) Amortization
(d) Obsolescence
Answer:
(c) Amortization
Question 5.
………………. is also known as residual value.
(a) Book value
(b) Scrap value
(c) Amortization
(d) Wear and tear
Answer:
(b) Scrap value
Question 6.
The following formula is used to complete the rate of depreciation under 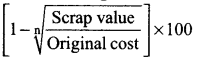 ……………….
……………….
(a) Written down value method
(b) Straight line method
(c) Machine hour rate method
(d) Annuity method
Answer:
(a) Written down value method
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State R.N. Carter’s definition of depreciation.
Answer:
According to R.N. Carter, “Depreciation is the gradual and permanent decrease in the value of an asset from any cause”.
Question 2.
What is wear and tear?
Answer:
The normal use of a tangible asset results in physical deterioration which is called wear and tear. When there is wear and tear, the value of the asset decreases proportionately.
Question 3.
What is obsolescence?
Answer:
It is a reduction in the value of assets as a result of the availability of updated alternative assets. This happens due to new inventions and innovations.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Straight line method?
Answer:
Under this method, a fixed percentage on the original cost of the asset is charged every year by way of depreciation. Hence it is called original cost method. As the amount of depreciation remains equal in all years over the useful life of an asset, it is also called as fixed instalment method.
Question 5.
What is written down value method?
Answer:
Under this method, depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage on the written down value of the asset every year. Hence, it is called written down value method.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on sum of years of digits method.
Answer:
This method is similar to the diminishing balance method. The amount of depreciation goes on decreasing year after year in proportion to the unexpired life of the asset. This method is suitable for those assets having more profitability of obsolescence and increased repair charges as the assets grow older. Under this method, amount of depreciation per year is calculated by multiplying the cost of the asset and the number of remaining years of life and dividing it by the sum of the digits of all years of life of the asset.
Question 2.
What is machine hour rate method?
Answer:
Under this method, depreciation per machine hour is calculated. The cost of the machinery after deducting the residual value, if any, is divided by the estimated working hours of the machine to find the depreciation per hour. The actual depreciation for any given period depends upon the working hours during that year. The special feature of this method is that depreciation is found directly in proportion to the actual use of the asset. Under this method life of the asset is estimated in hours and not in years.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Depletion method?
Answer:
Depletion means exhaustion of natural resources. That is depletion means quantitative reduction in the content of assets. This is applicable to those assets that get exhausted due to extraction and exploitation. Examples: mines and oil fields, etc. Under this method, depreciation rate is calculated on the basis of the estimated quantities of the output during the whole life of the asset.