Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 11 Network Examples and Protocols Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 11 Network Examples and Protocols
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Network Examples and Protocols Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
The ……………………… “the Net,” is a worldwide system of computer networks
(a) Internet
(b) mobile
(c) communication
(d) protocol
Answer:
(a) Internet
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following will be easy the way to uses Internet technology and the public telecommunication system to securely share business’s information with suppliers, vendors, partners and customers.
(a) Extranet
(b) Intranet
(c) arpanet
(d) arcnet
Answer:
(a) Extranet
Question 3.
Match the following and choose the correct Answer:wer
(i) HTTP -The core protocol of the World Wide Web.
(ii) FTP- enables a client to send and receive complete files from a server.
(iii) SMTP – Provide e-mail services.
(iv) DNS- Refer to other host computers by using names rather than numbers.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
(c) (iii), (iv), (i), (ii)
(d) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
![]()
Question 4.
Communication over …………………………… is be made up of voice, data, images and text messages.
(a) Social media
(b) mobile network
(c) whatsapp
(d) software
Answer:
(b) mobile network
Question 5.
Wi-Fi stands for ……………………………
(a) Wireless Fidelity
(b) wired fidelity
(c) wired optic fibre
(d) wireless optic fibre
Answer:
(a) Wireless Fidelity
![]()
Question 6.
A TCP/IP network with access restricted to members of an organization
(a) LAN
(b) MAN
(c) WAN
(d) Intranet
Answer:
(d) Intranet
Question 7.
RFID stands for …………………………
(a) Radio Free identification
(b) real Frequency identity
(c) Radio Frequency indicators
(d) Radio Frequency Identification.
Answer:
(d) Radio Frequency Identification.
![]()
Question 8.
It guarantees the sending of data is successful and which checks error on operation at OSI layer is ………………………………
(a) Application layer
(b) Network layer
(c) Transport Layer
(d) Physical layer
Answer:
(c) Transport Layer
Question 9.
Which one of the following will secure data on trAnswer:missions?
(a) HTTPS
(b) HTTP
(c) FTP
(d) SMTP
Answer:
(a) HTTPS
![]()
Question 10.
………………………… provides e-mail service.
(a) DNS
(b) TCP
(c) FTP
(d) SMTP
Answer:
(d) SMTP
Question 11.
………………………… refer to other host computers by using names rather than numbers.
(a) DNS
(b) TCP
(c) FTP
(d) SMTP
Answer:
(a) DNS
![]()
Question 12.
TCP/IP is a combination of two protocols:
(i) TrAnswer:mission Control Protocol (TCP)
(ii) Internet Protocol (IP)
(iii) Selection Protocol (SP)
(iv) Captial Protocol (CP)
(a) (i), (ii)
(b) (i), (iii)
(c) (iii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii)
PART – II
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
Define Intranet?
Answer:
INTRANET:
- It is a private network within an enterprise to share company data and computing resources between the employees.
- It may consist of many interlinked local area networks.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the uses of mobile networks?
Answer:
The common application of mobile networks is mobile phones, tablets, etc.. In past, wireless communications largely used circuit switching to carry only voice over a network, but now currently both data and voice are being trAnswer:mitted over both circuit via switched networks and packet-switched networks.
Question 3.
List out the benefits of WiFi/
Answer:
- It provides mobility.
- It provides connection to Internet.
- Flexibility of LAN.
- Ensures connectivity.
- It allows places that are remote to benefit from connectivity.
- Low cost, high benefit.
![]()
Question 4.
How many types of RFID System available and what are they?
Answer:
Two types of RFID Systems:
1. Active RFID system:
the tag has its own power source. These systems used for larger distances and to track high value goods like vehicles.
2. Passive RFID system:
the tag gets power through power from a reader antenna to the tag „ antenna. They are used for shorter range trAnswer:mission.
![]()
Question 5.
Expand HTTP, HTTPS, FTP?
Answer:
- HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- HTTPS – Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
- FTP – File Transfer Protocol
PART – III
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
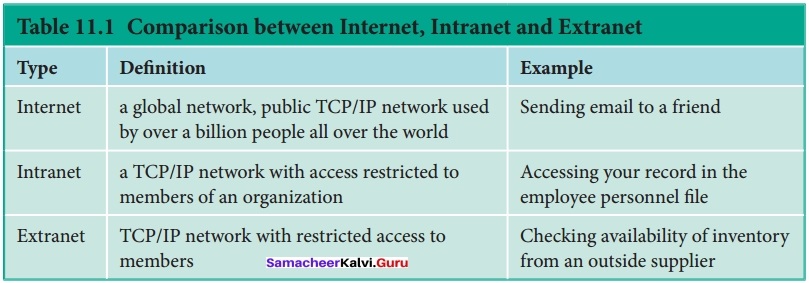
Compare Internet, Intranet and Extranet?
Answer:
Question 2.
List out the components of a RFID enabled system?
Answer:
Main Components of a RFID System
- A RFID tag: It has silicon microchip attached to a small antenna and mounted on a substrate.
- A reader: It has a scanner with antennas to trAnswer:mit and receive signals, used for communication.
- A Controller: It is the host computer with a Microprocessor which receives the reader input and process the data.
![]()
Question 3.
Write short notes on HTTP, HTTPS, FTP?
Answer:
- HTTP – A protocol used between a web client and a web server protects non-secure data trAnswer:missions. The core protocol of the World Wide Web.
- HTTPS – A protocol used between a web client and a web server permits secure data trAnswer:missions.
- FTP – Used between computers for sending and receiving data. Enables a client to send and receive complete files from a server.
Question 4.
What are the layers available in TCP/IP Reference Model?
Answer:
There are four total layers of TCP/IP protocol, each of which is listed below with a brief description.
- Network Access Layer – concerned with building packets.
- Internet Layer – describes how packets are to be delivered.
- Transport Layer – ensure the proper transfer mission of data.
- Application Layer – application network processes. These processes include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
![]()
Question 5.
Expand ARP, ICMP, SMTP and DNS?
Answer:
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Transfer mission Control Protocol (TCP)
- Simple Mail TrAnswer:fer Protocol (SMTP)
- Domain Name System (DNS).
PART – IV
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain about Internet, Intranet and Extranet?
Internet/Intranet/Extranet
INTERNET:
Answer:
- The Internet, “the Net,” is a worldwide system of computer networks.
- A network of networks where the users at any one computer can, if they have permission, get information from any other computer.
- The Internet is a network of global connections – comprising private, public, business, academic and government networks – linked by guided, wireless and fiber-optic technologies.
- It was perceived by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. government in 1969 and was first recognized as the ARPANet.
- The unique aim was to generate a network that would permit users of a research computer from one university to “talk to” research computers on other universities.
- The Internet denotes to the global communication system, including infrastructure and hardware, whereas the web is one of the services interconnected over the Internet.
INTRANET:
- It is a private network within an enterprise to share company data and computing resources between the employees.
- It may consist of many interlinked local area networks.
- It includes connections through one or more gateway (connects two networks using different protocols together known as protocol convertor) computers to outside Internet.
EXTRANET:
It is a private network that uses Internet technology and the public – telecommunication system to securely share business’s information with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other businesses.
![]()
Question 2.
Discuss about OSI model with its layers?
Answer:
OSI Model:
Open System Interconnection (OSI) model was found in the year 1934, general framework that enables network protocols along with software and systems to be developed based on general set of guidelines. It describes the standards for the inter-computer communication.
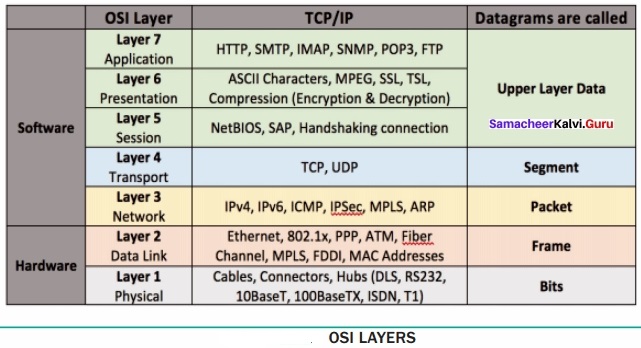
OSI Layers:
(i) Physical Layer:
This is the 1st layer, it defines the electrical and physical specifications for devices.
(ii) Data Link Layer:
It is the 2nd layer and it guarantees that the data trAnswer:mitted are free of errors. This layer has simple protocols like “802.3 for Ethernet” and “802.11 for Wi-Fi”.
(iii) Network Layer:
It is the 3rd layer determining the path of the data packets. At this layer, routing of data packets is found using IP Addressing.
(iv) Transport Layer:
It is the 4th layer that guarantees the trAnswer:portation/sending of data is successful. It includes the error checking operation.
(v) Session Layer:
It is the 5th layer, identifies the established system session between different network entities. It controls dialogues between computers. For instance, while accessing a system remotely, session is created between your computer and the remote system.
(vi) Presentation Layer:
It is the 6th layer that does the trAnswer:lation of data to the next layer (Prepare the data to the Application Layer). Encryption and decryption protocols occur in this layer such as, Secure Socket Layer (SSL).
(vii) Application Layer:
It is the 7th layer, which acts as the user interface platform comprising of software within the system.
![]()
Question 3.
Difference between TCP/IP and OSI Reference Model?
Answer:
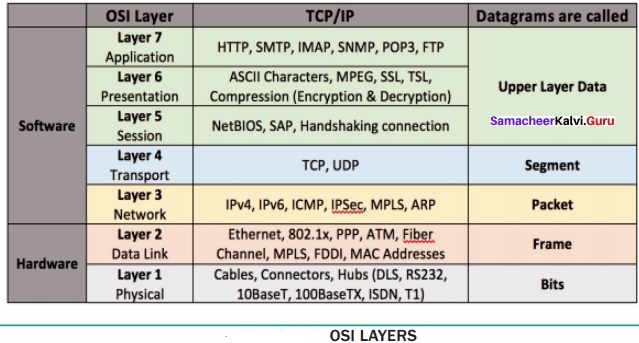
TCP/Ip:
- TCP/IP stands for Transmission control protocol/Intemet protocol
- TCP/IP has 4 layers
- TCP/IP are set of rulers/protocols defined for communication over the network
- TCP/IP is a client-server model
- It follows top to bottom approach
OSI:
- OSI means open system interconnect
- OSI has 7 layers
- OSI is a model based on the concept of layering
- OSI is a conceptual model
- It follows bottom-up approach
![]()
Question 4.
Explain about the development, merits and demerits in Mobile networks?
Merits of Mobile Networks:
- Higher efficiency.
- Increased ability to communicate in and out of the workspace.
- Greater access to modem apps and services.
- Improved networking capabilities.
- Quality and flexibility of services.
- Rapid developments in cloud technologies.
Demerits of Mobile Networks:
- Cost
- Vulnerable to security risks.
- Additional training is needed to use new technology.
- Cyber crime
Development:
The generations of mobile networks are as follows.
- First Generation(lG) 1981- NMT launch
- Second Generation(2G) 1991-GSM Launch
- Second to Third Generation Bridge (2.5)2000 – GPRS launch
- Third Generation! 3G) 2003- first UK 3G launch
- Fourth Generation (4G) 2007
- Fifth Generation (5G) 2019+
1. First Generation (1G) 1981 – NMT launch:
- During the initial periods the mobile systems were based on analog trAnswer:mission.
- NMT stands for Nordic Mobile Telephone communication.
- And a very poor voice quality.
2. Second Generation(2G) 1991-GSM Launch:
- Later the second generation of mobile systems were placed on digital trAnswer:mission with GSM.
- GSM stands for (Global System for Mobile communication) was most popular standard which is used in second generation, using 900MHz and 1800MHz for the frequency bands.
- The transfer mission used as TMDA stands for (Time Division Multiple Access) and CDMA One stands for (Code Division Multiple’Access) method to increase the amount of information trAnswer:ported on the network
3. Second to Third Generation Bridge (2.5)2000 – GPRS launch:
- GPRS was introduced here GPRS stands for (General Packet Radio Service). GPRS is a data service which enables mobile devices to send and receive messages, picture messages and e-mails.
- GSM data transfer mission rates typically reached 9.6kbit/s.
4. Third Generation( 3G) 2003- first UK 3G launch:
1. This generation of mobile systems merges different mobile technology standards, and uses higher frequency bands for transfer mission and Code Division Multiple Access to delivery data rates of up to 2Mbit/s supports multimedia services (MMS: voice, video and data).
2. Data transfer mission used a WCDMA. WCDMA stands for (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access).
3. Few 3G suppliers use ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) for their ‘over the air’ network with in MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) or IP for theirs backbone network.
5. Fourth Generation (4G) 2007:
1. 4G is at the research stage. 4G was based on an adhoc networking model where there was no need for a fixed infrastructure operation.
2. Adhoc networking requires global mobility features (e.g. Mobile IP) and connectivity to a global IPv6 network to support an IP address for each mobile device.
3. Logically roaming in assorted IP networks (for example: 802.11 WLAN, GPRS and UMTS) were be possible with higher data rates, from 2Mbit/s to 10-100Mbit/s, offering reduced delays and newly services.
6. Fifth Generation (5G) 2019+:
1. 5G is the stage succeeds the 4G (LTE/ WiMAx), 3G(umts) and 2G(GSM) syetems.
2. 5G targets to performance the high data rate, reduced latency, energy saving, cost reduction, higher system, capacity, and massive device connectivity.
3. The ITU IMT – 2020 provides speeds up to 20 gigabits per second it has been demonstrated with millimeter waves of 15 gigahertz and higher frequency.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Network Examples and Protocols Additional Question and Answer
I. Choose the Best Answer
Question 1.
Internet Protocol delivers packets from source to destination through
(a) TCP
(b) datagram
(c) packets header
(d) http
Answer:
(c) packets header
![]()
Question 2.
IP connectionless datagram service was developed in the year
(a) 1972
(b) 1974
(c) 1976
(d) 1978
Answer:
(b) 1974
Question 3.
IP connectionless datagram service was developed by
(i) Vint cerf
(ii) Bob FrAnswer:ton
(iii) Bob Kahnin
(iv) Dan Bricklin
(a) i, ii
(b) ii, iii
(c) ii, iv
(d) i, iii
Answer:
(d) i, iii
![]()
Question 4.
TCP/IP stands for …………………………..
Answer:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
Question 5.
Which protocols have to do end-to-end process of secure on time and manage data or communication.
(a) Physical
(b) TCP
(c) Network
(d) ARPC
Answer:
(c) Network
Question 6.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) HTTP
(b) SFTL
(c) SSL
(d) SNMP
Answer:
(d) SNMP
![]()
Question 7.
Find the Network management protocol from the following
(a) ICMP
(b) HTTP
(c) TCP/IP
(d) SFTP
Answer:
(a) ICMP
Question 8.
Find the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Network Communication Protocol – HTTP, TCP/IP
(b) Network Security Protocol – ICMP
(c) Network Management Protocol – SNMP
Answer:
(b) Network Security Protocol – ICMP
![]()
Question 9.
ARPANET was first recognized in the year
(a) 1964
(b) 1956
(c) 1972
(d) 1969
Answer:
(d) 1969
Question 10.
The ……………………….. is one of the services interconnected over the Internet.
Answer:
web
![]()
Question 11.
Gateway connects two networks using different protocols together known as …………………………..
Answer:
Protocol Converter
Question 12.
Find the correct statement from the following.
I. Internet or things refers to the digital interconnection of everyday objects with the Internet
II. Extranet is a private network within an enterprise to share company data and computing resources between the employees.
(a) I-True, II-False
(b) I-False, II-True
(c) I, II-True
(d) I, II-False
Answer:
(a) I-True, II-False
![]()
Question 13.
Sending e-mail to a friend is an example for ………………………..
(a) Internet
(b) Intranet
(c) Extranet
(d) IP address
Answer:
(a) Internet
Question 14.
A …………………………. as it is made up of a large number of signal areas called cells.
(a) Mobile Network
(b) Cellular Network
(c) Both a & b
(d) Chatting
Answer:
(c) Both a & b
![]()
Question 15.
The NMT launch comes ………………………….. generation of mobile networks
(a) 1G
(b) 2G
(c) 3G
(d) 4G
Answer:
(a) 1G
Question 16.
Expand NMT.
(a) North Mobile Telephone
(b) Nordic Mobile Telephone
(c) Nordic Movement Telephone
(d) Nurture Mobile Telephone
Answer:
(b) Nordic Mobile Telephone
![]()
Question 17.
Match the following:
(i) 1G – (I) GSM
(ii) 2G – (II) UMTS
(iii) 3G – (III) GPRS
(iv) 2-3G Bridge – (IV) NMT
(a) IV I II III
(b) I II III IV
(c) IV III II I
(d) II I IV III
Answer:
(a) IV I II III
Question 18.
GSM means ……………………………… communication.
Answer:
Global System for Mobile
Question 19.
SIM means …………………………. technology.
Answer:
Subscriber Identity Module
![]()
Question 20.
TMDA means …………………………
Answer:
Time Division Multiple Access
Question 21.
CMDA stands for
(a) Code Divide Multiple Access
(b) Code Divide Mobile Access
(c) Code Division Multiple Access
(d) Code Division Mobile Access
Answer:
(c) Code Division Multiple Access
![]()
Question 22.
GPRS stands for ………………………
Answer:
General Packet Radio Service
Question 23.
Expand EDGE
(a) Extra Data rates for Global Evolution
(b) Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution
(c) Entry Data rates for Global Evolution
(d) Extra Dual rate for Global Evolution
Answer:
(b) Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution
![]()
Question 24.
UMTS stands for …………………………..
Answer:
Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems
Question 25.
WCDMA stands for …………………………
Answer:
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
Question 26.
ATM stands for ………………………….
Answer:
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
![]()
Question 27.
First Generation (1G) was developed in the year …………………………
(a) 1980
(b) 1983
(c) 1982
(d) 1981
Answer:
(d) 1981
Question 28.
Find the wrongly matched pair.
(a) First Generation – 1981
(b) Second Generation – 1991
(c) Third Generation – 2004
(d) Fourth Generation – 2007
Answer:
(c) Third Generation – 2004
![]()
Question 29.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) 1G
(b) 2G
(c) 2.5G
(d) 3.5G
Answer:
(d) 3.5G
Question 30.
Analog trAnswer:mission have taken place in …………………………
(a) 1G
(b) 2G
(c) 3G
(d) 4G
Answer:
(a) 1G
![]()
Question 31.
Which technology is used to authenticate a user for identification and billing purposes and to encrypt the data to prevent listen without permission.
(a) GSM
(b) NMT
(c) CDMA
(d) SIM
Answer:
(d) SIM
Question 32.
Which method increased the amount of information trAnswer:ported on the network?
(I) SIM
(II) NMT
(III) TDMA
(IV) CDMA
(a) I, II
(b) II, III
(c) III, IV
(d) IV, I
Answer:
(c) III, IV
![]()
Question 33.
General Packet Radio Service was introduced in
(a) 1G
(b) 2G
(c) 2.5G
(d) 3G
Answer:
(c) 2.5G
Question 34.
……………………………… is a data service which enables mobile devices to send and receive messages, picture messages and e-mails.
(a) GPS
(b) GPRS
(c) CDMA
(d) SIM
Answer:
(b) GPRS
![]()
Question 35.
What is the data trAnswer:mission rate of GSM?
(a) 9.6 kb/s
(b) 11.2 kb/s
(c) 12.3 kb/s
(d) 8.5 kb/s
Answer:
(a) 9.6 kb/s
Question 36.
MMS is the combination of …………………………
(I) Image, Voice, Video
(II) Voice, Video, Speed
(III) Voice, Video, Data
(IV) Speed, Data, Image
(a) III
(b) II
(c) I
(d) IV
Answer:
(a) III
![]()
Question 37.
The data trAnswer:mission used by 3G is ……………………………
(a) TDMA
(b) CDMA
(c) EDGE
(d) WCDMA
Answer:
(d) WCDMA
Question 38.
MPLS means ……………………….
Answer:
Multiprotocol Label Switching
Question 39.
Few 3G suppliers use ATM for their ……………………………. network with in MPLS or IP for their network.
Answer:
Over the Air
![]()
Question 40.
Which generation of mobile network is considered as a research stage?
(a) 1G
(b) 2G
(c) 3G
(d) 4G
Answer:
(d) 4G
Question 41.
Li-Fi is the short form of …………………………..
(a) Light Fidelity
(b) LAN Fidelity
(c) Light Fix
(d) Low Frequency
Answer:
(a) Light Fidelity
![]()
Question 42.
The term Li-Fi was first used by …………………………..
Answer:
Harald Haas
Question 43.
How many phases of 5G are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 44.
The two phases of 5G are ………………………….
(I) Release-14
(II) Release-15
(III) Release-16
(IV) Release-17
(a) I, II
(b) II, III
(c) I, III
(d) III, IV
Answer:
(b) II, III
![]()
Question 45.
ITU stands for ……………………………..
Answer:
International Telecommunication Union
Question 46.
Which is used for radio wares to read and capture information stored on a tag attached to an object?
(a) RF
(b) RFID
(c) Li-Fi
(d) Wi-Fi
Answer:
(b) RFID
Question 47.
How many parts are there in RFID tags are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
![]()
Question 48.
RFID has a ……………………… and a ……………………….. or a ……………………………..
Answer:
reader, tag and label
Question 49.
Ffow many types of RFID tags are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 50.
How many components of a RFID system are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
![]()
Question 51.
………………………… is a scanner with antennas to trAnswer:mit and receive signals used for communication
(a) RFID tag
(b) Reader
(c) Controller
(d) Em-ware
Answer:
(b) Reader
Question 52.
Find the statement which is true.
(а) Active RFID System – larger distances
(b) Active RFID System – shorter range transfer mission
Answer:
(а) Active RFID System – larger distances
![]()
Question 53.
Which method is used in passive RFID system?
(a) TCP
(b) UDP
(c) Induction coupling
(d) Direct coupling
Answer:
(c) Induction coupling
Question 54.
OSI model means ……………………………..
Answer:
Open System Interconnection
Question 55.
OSI model was found in the year
(a) 1927
(b) 1932
(c) 1935
(d) 1934
Answer:
(d) 1934
![]()
Question 56.
Which one describes the standards for the inter-computer communication?
(a) OSI
(b) BSI
(c) DSI
(d) LSI
Answer:
(a) OSI
Question 57.
How many OSI layers are there?
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 7
![]()
Question 58.
The protocols for Ethernet in datalink layer is ………………………….
(a) 8.023
(b) 80.23
(c) 802.3
(d) 8023
Answer:
(c) 802.3
Question 59.
Which is the third layer in the OSI model?
(a) Datalink
(b) Physical
(c) port
(d) Network
Answer:
(d) Network
Question 60.
In which layer, routing of data packets is found using IP addressing?
(a) Data link
(b) Network
(c) port
(d) Physical
Answer:
(b) Network
![]()
Question 61.
SSL stands for ………………………
Answer:
Secure Socket Layer
Question 62.
Match the following
(i) Physical Layer – (I) controls dialogues between computer
(ii) Network Layer – (II) Specifications for devices
(iii) TrAnswer:port Layer – (III) data packets
(iv) Session Layer – (IV) error checking
(v) Application Layer – (V) Encryption, Decryption
(a) II, III, IV, I, V, VI
(b) I, II, III, IV, VI, VI
(c) VI, V, IV, III, II, I
(d) III, IV, V, VI, II, I
Answer:
(a) II, III, IV, I, V, VI
Question 63.
Which protocol is accountable for guaranteeing the trustworthy trAnswer:mission of data?
(a) TCP
(b) IP
(c) HTTP
(d) SMTP
Answer:
(a) TCP
![]()
Question 64.
google.com is the ………………………. for Google.
Answer:
domian name
Question 65.
How many different layers of TCP/IP are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 66.
FTP stands for …………………………
(a) File Transfer Protocol
(b) File Transmission Protocol
(c) File Transport Protocol
(d) File Type Protocol
Answer:
(a) File Transfer Protocol
![]()
Question 67.
HTTP stands for …………………………..
(a) High Text Transmission Protocol
(b) Hyper Text Transmission Protocol
(c) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
(d) Height Typed Transfer Protocol
Answer:
(c) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Question 68.
SMTP stands for …………………………………
(a) Single Mail Transfer Protocol
(b) Single Message Transfer Protocol
(c) Simple Mail Text Protocol
(d) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Answer:
(d) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
![]()
Question 69.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) FTP
(b) RFID
(c) HTTP
(d) SMTP
Answer:
(b) RFID
Question 70.
Which one of the following is not a network protocol.
(a) SSL
(b) ARP
(c) TCPI
(d) FTP
Answer:
(c) TCPI
Question 71.
HTTPs stands for …………………………..
Answer:
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure
Question 72.
ARP stands for ………………………….
Answer:
Address Resoloution Protocol
![]()
Question 73.
Expand MAC
(a) Mega Access Code
(b) Multiple Access Code
(c) Medium Access Code
(d) Medium Access Control
Answer:
MEdium Access Control
Question 74.
Which one of the following is a hardware identification number that uniquely identifies each device on a network?
(a) MIC
(b) MAC
(c) MOC
(d) MUC
Answer:
(b) MAC
Question 75.
ICMP stands for ………………………….
Answer:
Internet Control Message Protocol
Question 76.
IGMP stands for …………………………..
Answer:
Internet Group Management Protocol
Question 77.
Which is used to send group communication messages to multiple IP addresses?
(a) ICMP
(b) IGMP
(c) IDMP
(d) IKMP
Answer:
(b) IGMP
![]()
Question 78.
The two main protocols mainly used in the trAnswer:port layers are
(I) TCP
(II) UDP
(III) UTP
(IV) ATP
(V) STP
(a) I, II
(b) III, IV
(c) II, V
(d) IV, V
Answer:
(a) I, II
Question 79.
UDP stands for …………………………….
Answer:
User Daragram Protocol
![]()
Question 80.
DNS meAnswer: ………………………..
Answer:
Domian Name System.
I. Short Answer
Question 1.
Write note on Extranet?
Answer:
EXTRANET:
It is a private network that uses Internet technology and the public telecommunication system to securely share business’s information with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other businesses.
![]()
Question 2.
Mention the various generations of Mobile networks?
Answer:
The generations of mobile networks are as follows.
- First Generation(lG) 1981- NMT launch
- Second Generation(2G) 1991-GSM Launch
- Second to Third Generation Bridge (2.5)2000 – GPRS launch ,
- Third Generation( 3G) 2003- UK 3G launch
- Fourth Generation (4G) 2007
- Fifth Generation (5G) 2019+
Question 3.
What is meant by Li-Fi?
Answer:
Li-Fi is a wireless technology which uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for data transmission Li-Fi is the short form of Light Fidelity.
![]()
Question 4.
Define Wi-Fi?
Answer:
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity. It is a wireless network technology that permits computers and alternative devices to be connected to every alternative into a local area network and to the net without wires and cables.
Question 5.
Write note on Network protocols?
Answer:
Network protocols is that the usual procedures, rules, formal standards and policies comprised of formats which allocates communication between more than one device Which connected to the network.
II. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Explain the types of Networking protocols?
Answer:
The broad types of networking protocols, including:
- Network communication protocols is that the Basic data communication protocols which specific as HTTP and TCP/IP.
- Network security protocols is that which implement security over network communications and include HTTP, SFTP and SSL.
- Network management protocols will Provide network governance and maintenance and include ICMP and SNMP.
![]()
Question 2.
Define Internet of things?
Answer:
Internet of Things refers to the digital interconnection of everyday objects (home applicances, wearable devices or automobiles) with the Internet. The ‘thing’ in refers to an objects that have been assigned an IP address and have the ability to collect and transfer data over a network without manual assistance or intervention.
Question 3.
Write about Mobile Networks?
Answer:
Mobile Networks:
A mobile network or cellular network as it is made up of a large number of signal areas called cells. These cells join to form a large coverage area. Communication over mobile network is be made up of voice, data, images and text messages.
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate Wi-Fi?
Answer:
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity. It is a wireless network technology that permits computers and alternative devices to be connected to every alternative into a local area network and to the net without wires and cables.
Question 5.
Write note on Network protocols?
Answer:
Network protocols is that the usual procedures, rules, formal standards and policies comprised of formats which allocates communication between more than one device Which connected to the network.
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Explain the types of Networking protocols?
Answer:
The broad types of networking protocols, including:
- Network communication protocols is that the Basic data communication protocols which specific as HTTP and TCP/IP.
- Network security protocols is that which implement security over network communications and include HTTP, SFTP and SSL.
- Network management protocols will Provide network governance and maintenance and include ICMP and SNMP.
![]()
Question 2.
Define Internet of things?
Answer:
Internet of Things refers to the digital interconnection of everyday objects (home applicances, wearable devices or automobiles) with the Internet. The ‘thing’ in IoT refers to an objects that have been assigned an IP address and have the ability to collect and trAnswer:fer data over a network without manual assistance or intervention.
Question 3.
Write about Mobile Networks?
Answer:
Mobile Networks:
A mobile network or cellular network as it is made up of a large number of signal areas called cells. These cells join to form a large coverage area. Communication over mobile network is be made up of voice, data, images and text messages.
Question 4.
Differentiate Wi-Fi and Li-Fi?
Answer:
Wi-Fi:
- Wireless Fidelity
- Wi-Fi uses radio frequencies for data transmission.
Li-Fi:
- Li-Fi is a wireless technology which uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for data transmission.
- Li-Fi is the short form of Light Fidelity.
![]()
Question 5.
What is RFID?
Answer:
- RFID stands for Radio -Frequency Identification (RFID).
- RFID used for radio waves to read and capture information stored on a tag attached to an object. Tag can be read from several feet away and does not need to be in direct-line-of-sight of the reader to be tracked.
- RFID has been made up of two parts a reader and a tag or a label.
- RFID tags are installed with a transmitter and receiver.
Question 6.
List out the two types of RFID tags?
Answer:
Two types of RFID tags were Active RFID and Passive RFID systems.
- Passive RFID tag will be used the reader radio wave energy to really its stored information back to the reader.
- Battery powered RFID tag is installed with small battery that powers the broadcast of information
![]()
Question 7.
Write note on Network Interface Layer?
Answer:
Network Interface Layer:
- It is the bottom most level layer.
- It is comparable to that of the Open System Interconnection Physical and Data Link layers.
- Different TCP/IP protocols are being used at this layer, Ethernet and Token Ring for local area networks and protocols such as X.25, Frame Relay, and ATM for wide area networks.
- It is assumed to be an unreliable layer.
Question 8.
Write note on Application Layer?
Answer:
The Application layer of the TCP/IP model is similar to the Session, Presentation, and Application layers of the OSI Reference Model. The most popular Application layer protocols are:
(i) Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP):
The core protocol of the World Wide Web.
(ii) File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
enables a client to send and receive complete files from a server.
(iii) Telnet:
connect to another computer on the Internet.
(iv) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP):
Provide e-mail services.
(v) Domain Name System (DNS):
Refer to other host computers by using names rather than numbers
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain any 5 applications of Internet Intranet and Extranet?
Answer:
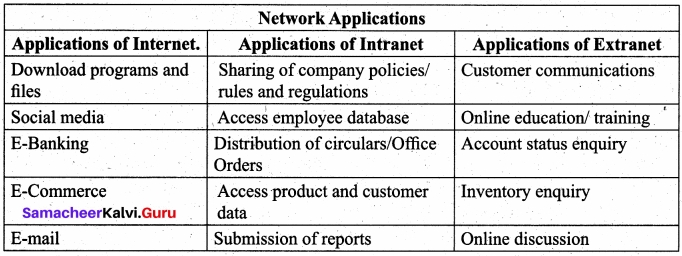
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the working of Passive and Active RFID systems with diagram?
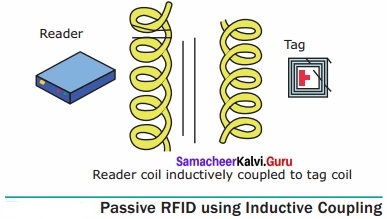
Working of Passive RFID System
A Passive RFID system using Induction coupling method:
Answer:
The RFID tag gets power from the reader through the inductive coupling method.
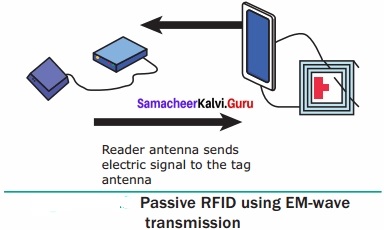
A Passive RFID system using EM wave propagation method:
The reader antenna trAnswer:mits the electromagnetic waves that are received by the antenna.
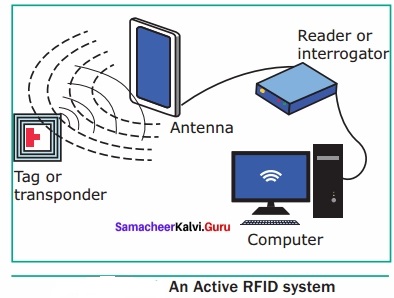
Working Of Active RFID System
The reader sends signal to the tag using an antenna.
Question 3.
Discuss in detail about TCP/IP protocols?
Answer:
TCP/IP:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, TCP/IP is a set of protocols which governs communications among all computers on the Internet. TCP/IP protocol tells how information should be packaged, sent, and received, as well as how to get to its destination.
TCP WORKING: TCP/IP is a combination of two protocols: TrAnswer:mission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP). The Internet Protocol typically specifies he logistics of the packets that are sent out over networks; it specifies the packets which have to go, where to go and how to get there. The TrAnswer:mission Control Protocol is accountable for guaranteeing the trustworthy trAnswer:mission of data. It sees that the packets for errors and submits the requests for re-trAnswer:missions incase any of them are missing’.
Frequent TCP/IP Protocols
- HTTP – It is used between a web client and a web server and it guarantees non-secure data trAnswer:missions.
- HTTPS – It is used between a web client and a web server ensures secure data trAnswer:missions.
- FTP – It is used between computers for sending and receiving file.
Domain Names and TCP/IP Addresses
The address for any website is not as easy as to remember, domain name are used instead. For example, 216.58.216.164 is one of the IP address for Google and google.com is the domain name.
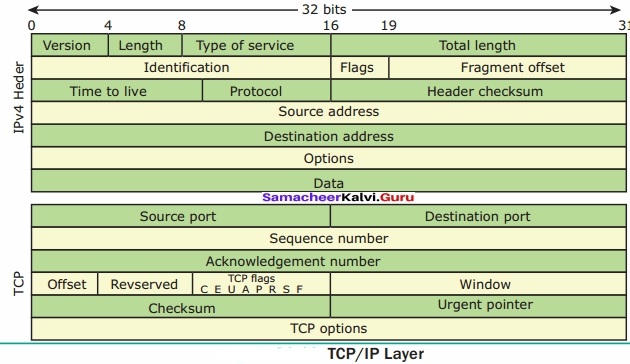
The Different Layers of TCP/IP
There are four total layers of TCP/IP protocol, each of which is listed below with a brief description.
- Network Access Layer – concerned with building packets.
- Internet Layer – describes how packets are to be delivered.
- Transport Layer – ensure the proper transmission of data.
- Application Layer – application network processes. These processes include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Hypertext TrAnswer:fer Protocol (HTTP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the important protocols present in
- Network layer
- Transport Layer
Answer:
1. Network Layer:
It is the layer where data is addressed, packaged, and routed among networks. The important Internet protocols that operate at the Network layer are:
2. Internet Protocol (IP):
Routable protocol which uses IP addresses to deliver packets. It is an unreliable protocol, does not guarantee delivery of information.
3. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP):
Resolves IP addresses to MAC (Medium Access Control) addresses. (A MAC address is a hardware identification number that uniquely identifies each device on a network.)i.e., to map IP network addresses to the hardware addresses.
4. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP):
Used by network devices to send error messages and operational information. Example: A host or router might not be reached or a requested service is not presented.
5. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP):
It is a communication protocol used by hosts and routers to send Multicast (group Communication) messages to multiple IP addresses at once.
6. port Layer:
The sessions are recognized and data packets are swapped between hosts in this layer. Two main protocols established at this layer are:
7. Mission Control Protocol (TCP):
Provides reliable connection oriented trAnswer:mission between two hosts. It ensures delivery of packets between the hosts.
8. User Datagram Protocol (UDP):
Provides connectionless, unreliable, one-to-one or one- to-many delivery.