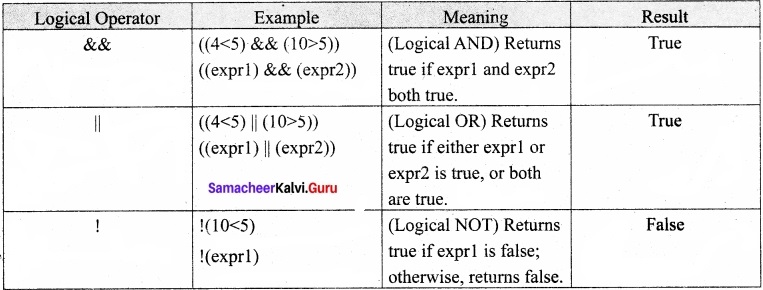
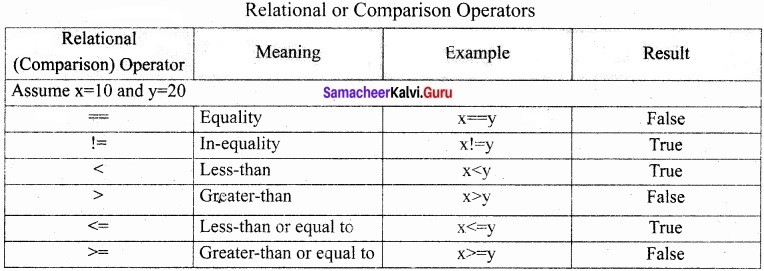
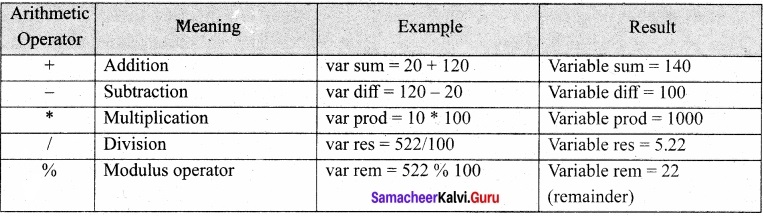
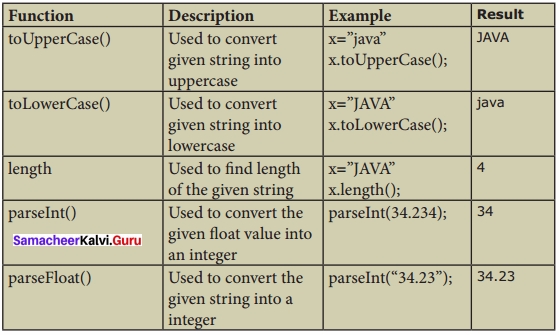
Tamil Nadu 12th Economics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Economics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Economics Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Economics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3.00 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART -1
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 x 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Who is regarded as the “Father of Modem Macro Economics”?
(a) Adam Smith
(b) J.M. Keynes
(c) Ranger Frisch
(d) Karl Marks
Answer:
(b) J.M. Keynes
Question 2.
The Financial year in India is………..
(a) April 1st to March 31st
(b) March 1st to April 30th
(c) March 1st to March 16th
(d) Jan 1st to Dec 31st
Answer:
(a) April 1st to March 31st
Question 3.
The concept, National Income was first introduced by ………..
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) J.M. Keynes
(c) Richardo
(d) Simon Kuznets
Answer:
(d) Simon Kuznets
![]()
Question 4.
In disguised unemployment, the marginal productivity of labour is…………
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) positive
Answer:
(a) 0
Question 5.
The sum of MPC and MPS is………
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 0.1
(d) 1.1
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 6.
If the MPC is 0.5, the multiplier is………..
(a) 2
(b) 1/2
(c) 0.2
(d) 20
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 7.
The headquarters of Reserve Bank of India is located at……….
(a) Delhi
(b) Chennai
(c) Mumbai
(d) Banglore
Answer:
(c) Mumbai
Question 8.
The new currency symbol (T) in India was designed by………
(a) L. Sivakumar
(b) T. Udaya Chandran
(c) D. Udayakumar
(d) Amartya Kumar Sen
Answer:
(c) D. Udayakumar
Question 9.
“Repo rate (RR)” meAnswer:………..
(a) Rate at which the commercial banks are willing to lend to RBI
(b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
(c) Exchange rate of foreign bank
(d) Growth rate of the economy
Answer:
(b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
Question 10.
Export – Import bank was established in………..
(a) June 1982
(b) April 1982
(c) May 1982
(d) March 1982
Answer:
(d) March 1982
Question 11.
Exchange rates are determined in………
(a) Monetary economy
(b) Stock market
(c) Foreign exchange market
(d) Capital market
Answer:
(c) Foreign exchange market
Question 12.
IBRD is otherwise called as………..
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) World bank
(c) ASEAN
(d) International finance corporations
Answer:
(b) World bank
Question 13.
International monetary fund has its headquarters at………
(a) Washington DC
(b) New York
(c) Vienna
(d) Geneva
Answer:
(a) Washington DC
Question 14.
Which of the following is not a tax under union list?
(a) Personal Income Tax
(b) Corporation Tax
(c) Agricultural Income Tax
(d) Excise duty
Answer:
(d) Excise duty
Question 15.
The true statements of the following………
(i) The 14th Finance commission is headed by C. Rangarajan
(ii) The recommendations of this commission will come into effect from April 1, 2015, is /are
(a) i only is correct
(b) ii only is correct
(c) both are correct
(d) none of the above is correct
Answer:
(d) none of the above is correct
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following is the main cause for deforestation?
(a) Timber harvesting industry
(b) Natural afforestation
(c) Soil stabilization
(d) Climate stabilization
Answer:
(a) Timber harvesting industry
Question 17.
Which is responsible for protecting people from harmful ultra violet rays?
(a) UV -A
(b) UV – C
(c) Ozone layer
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Ozone layer
Question 18.
Arrange the following in chronological order……….
(i) People’s Plan
(ii) Bombay Plan
(iii) Jawaharlal Nehru Plan
(iv) Vishveshwarya Plan
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
(c) (i), (ii), (iv), (iii)
(d) (ii), (i), (iv), (iii)
Answer:
(b) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
Question 19.
Choose the correct answer for the given assertion and reason.
Assertion (A): The deficiency of capital, in turn leads to low levels of productivity and back to low income.
Reason (R): The low level of saving leads to low investment and to deficiency of capital.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A are R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 20.
If both variables X and Y increase or decrease simultaneously, then the coefficient of correlation will be
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) Positive
PART – II
Answer any seven questions. Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Define the term inflation.
Inflation refers to steady increase in general price level. Estimating the general price level by constructing various price index numbers such as wholesale Price. Index, Consumer Price Index, efc, are needed.
Question 22.
What is GDP deflator?
Answer:
GDP deflator is an index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP. It is a price index which is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP for the same year and multiplying it by 100.
GDP deflator = \(\frac{Nominal GDP}{Real GDP}\) x 100
Question 23.
What is investment functions?Answer:
The investment function refers to investment -interest rate relationship. There is a functional and inverse relationship between rate of interest and investment. The investment function slopes downward.
I = f(r)
1= Investment (Dependent variable)
r = Rate of interest (Independent variable)
Question 24.
Write a note on stagflation.
Answer:
Stagflation is a combination of stagnant economic growth, high unemployment and high inflation.
Question 25.
Distinguish between CRR and SLR.
Answer:
| S.No. | CRR | SLR |
| 1. | The Central Bank controls credit by changing the Cash Reserves Ratio. | Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) is the amount which a bank has to maintain in the form of cash, gold or approved securities. |
| 2. | Commercial Banks have excessive cash reserves on the basis of which they are creating too much of credit, this will be harmful for the larger interest of the economy. | The quantum is specified as some percentage of the total demand and time liabilities. |
| 3. | So it will raise the cash reserve ratio which the Commercial Banks are required to maintain with the Central Bank. | The liabilities of the bank which are payable on demand anytime, and those liabilities which are accruing in one month’s time due to maturity. |
Question 26.
What is meant by Balance of Payment?
Answer:
- BoP is a systematic record of a country’s economic and financial transactions with the rest of the world over a period of time.
- When a payment is received from a foreign country, it is a credit transaction while a payment to a foreign country is a debit transaction.
- The principal items shown on the credit side are exports of goods and services, transfer receipts in the form of gift etc., from foreigners, borrowing from abroad, foreign direct investment and official sale of reserve assets including gold to foreign countries and international agencies.
- The principal items on the debit side include imports of goods and services, transfer payments to foreigners, lending to foreign countries, investments by residents in foreign countries and official purchase of reserve assets or gold from foreign countries and international agencies.
![]()
Question 27.
Write the meaning of special drawing rights.
Answer:
Special Drawing Rights (SDRs):
- The Fund has succeeded in establishing a scheme of Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) which is otherwise called ‘Paper Gold’.
- They are a form of international reserves created by the IMF in 1969 to solve the problem of international liquidity.
- They are allocated to the IMF members in proportion to their Fund quotas.
- SDRs are used as a means of payment by Fund members to meet balance of payments deficits and their total reserve position with the Fund.
- Thus SDRs act both as an international unit of account and a means of payment.
- All transactions by the Fund in the form of loans and their repayments, its liquid reserves, . its capital, etc., are expressed in the SDR.
Question 28.
Differentiate between tax and fee.
Answer:
| S.No. | Tax | Fee |
| 1 | A tax is a compulsory payment made to the government. | Fees are another important source of revenue for the government. |
| 2 | People on whom a tax is imposed must pay the tax. | A fee is charged by public authorities for rendering a service to the citizens. |
| 3 | There is no quid pro quo between a taxpayer and public authorities. This means that the tax payer cannot claim any specific benefit against the payment of a tax. | The government provides certain services and charges certain fees for them. For example, fees are charged for issuing of passports, driving licenses, etc. |
Question 29.
Define regression.
Answer:
- The term ‘Regression’ was first coined and used in 1877 by Francis Galton while studying the relationship between the height of fathers and sons.
- The average height of children born of parents of a given height tended to move or “regress” toward the average height in the population as a whole.
- Gabon’s law of universal regression was confirmed by his friend Karl Pearson, who collected more than a thousand records of heights of members of family groups.
- The literal meaning of the word “regression” is “Stepping back towards the average”.
Question 30.
What is pollution and write the types of pollution?
Answer:
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that causes adverse change, in the form of killing of life, toxicity of environment, damage to ecosystem and aesthetics of our surrounding.
Types of Pollution
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Noise pollution
- Land pollution
PART – III
Answer any seven questions. Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
List out the uses of National Income.
The following are some of the concepts used in measuring national income.
GDP:
GDP is the total market value of final goods and services produced within the country during a year. This is calculated at market prices and is known as GDP at market prices. Thus GDP by expenditure method at market prices = C + I + G + (X – M)
Where C – Consumption goods;
I – Investment goods;
G – Government purchases;
(X – M) is net export which can be positive or negative.
Net National Product (NNP) (at Market price):
Net National Product refers to the value of the net output of the economy during the year. NNP is obtained by deducting the value of depreciation, or replacement allowance of the capital assets from the GNP. It is expressed as,
NNP = GNP – depreciation allowance.
NNP at Factor cost:
NNP refers to the market value of output. NNP at factor cost is the total of income payment made to factors of production.
Personal Income:
Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all sources before payment of direct taxes in a year.
Per Capita Income:
The average income of a person of a country in a particular year is called Per Capita Income. Per capita income is obtained by dividing national income by population.
Per Capita income = \(\frac{National income}{population}\)
Disposable Income:
- Disposable Income is also known as Disposable personal income.
- It is the individuals income after the payment of income tax.
- This is the amount available for households for consumption.
Real Income:
Nominal income is national income expressed in terms of a general price level of a particular year in other words, real income is the buying power of nominal income.
GDP deflator:
GDP deflator is an index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP. It is a price index which is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP for the same year and multiplying it by 100.
![]()
Question 32.
Explain Keynes theory in the form of flow chart.
Answer:
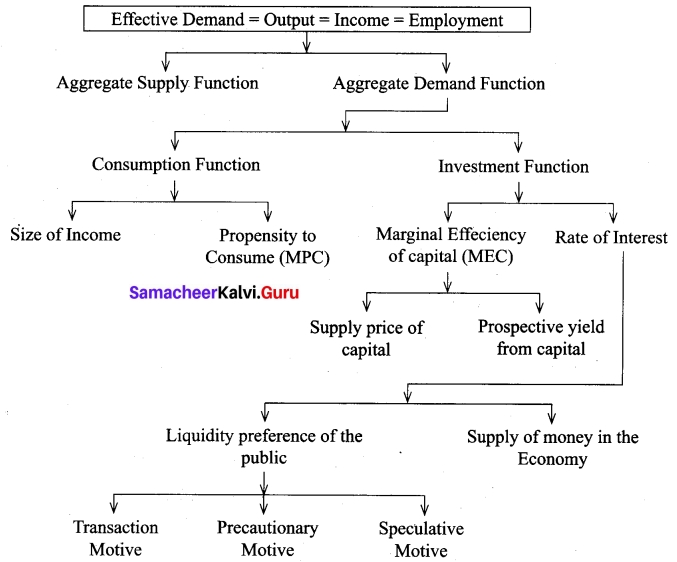
Question 33.
Complete the table.
| Income | Consumption | Savings |
| 0 | 20 | |
| 60 | -10 | |
| 120 | 0 | |
| 10 | ||
| .240 | 220 |
Answer:
| Income | Consumption | Savings |
| 0 | 20 | -20 |
| 60 | 70 | -10 |
| 120 | 120 | 0 |
| 180 | 170 | 10 |
| .240 | 220 | 20 |
Question 34.
What are the functions of NABARD?
Functions of NABARD:
NABARD has inherited its apex role from RBI i.e, it is performing all the functions performed by RBI with regard to agricultural credit.
(i) NABARD acts as a refinancing institution for all kinds of production and investment credit to agriculture, small-scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts and rural crafts and real artisans and other allied economic activities with a view to promoting integrated rural development.
(ii) NABARD gives long-term loans (upto 20 Years) to State Government to enable them to subscribe to the share capital of co-operative credit societies.
(iii) NABARD gives long-term loans to any institution approved by the Central Government or contribute to the share capital or invests in securities of any institution concerned with agriculture and rural development.
(iv) NABARD has the responsibility of co-ordinating the activities of Central and State Governments, the Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog) and other all India and State level institutions entrusted with the development of small scale industries, village and cottage industries, rural crafts, industries in the tiny and decentralized sectors, etc.
(v) It maintains a Research and Development Fund to promote research in agriculture and rural development.
Question 35.
What are the import quotas?
Answer:
Import Control: Imports may be controlled by
- imposing or enhancing import duties
- restricting imports through import quotas
- licensing and even prohibiting altogether the import of certain non-essential items. But this would encourage smuggling.
Question 36.
Multilateral Agreement – Comment.
Answer:
Multilateral trade agreement: It is a multi national legal or trade agreements between countries. It is an agreement between more than two countries but not many. The various agreements implemented by the WTO such as TRIPS, TRIMS, GATS, AoA, MFA have been discussed.
Question 37.
Point out any three differences between direct and indirect taxes.
Answer:
| S.No. | Direct Tax | Indirect Tax |
| 1 | Progressive | Regressive |
| 2 | Falls on the same person. | Falls on different persons. |
| 3 | Cannot be shifted. | Can be shifted |
Question 38.
List out the functions of NITIAAYOG.
Answer:
Functions of NITI Aayog:
- Cooperative and Competitive Federalism: To enable the States to have active participation in the formulation of national policy.
- Shared National Agenda: To evolve a shared vision of national development priorities and strategies with the active involvement of States.
- Decentralized Planning: To restructure the planning process into a bottom-up model.
- Vision and Scenario Planning: To design medium and long-term strategic frameworks towards India’s future.
- Network of Expertise: To mainstream external ideas and expertise into government policies and programmes through a collective participation.
- Harmonization: To facilitate harmonization of actions across different layers of government, especially when involving cross-cutting and overlapping issues across multiple sectors; through communication, coordination, collaboration and convergence amongst all the stakeholders.
- Conflict Resolution: To provide platform for mutual consensus to inter-sectoral, inter¬departmental, inter-state as well as centre-state issues for all speedy execution of the government programmes.
- Coordinating Interface with the World: It will act nodal point to harness global expertise and resources coming from International organizations for India’s developmental process.
- Internal Consultancy: It provides internal consultancy to Central and State governments on policy and programmes.
- Capacity Building: It enables to provide capacity building and technology up-gradation across government, benchmarking with latest global trends and providing managerial and technical know-how.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: It will monitor the implementation of policies and progammes and evaluate the impacts.
Question 39.
What are the determinants of money supply?
Answer:
Determinants of Money Supply:
- Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR): It is the ratio of money held by the public in currency to that they hold in bank deposits. .
- Reserve deposit Ratio (RDR): Reserve Money consists of two things (a) vault cash in banks and (b) deposits of commercial banks with RBI.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): It is the fraction of the deposits the banks must keep with RBI.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): It is the fraction of the total demand and time deposits of the commercial banks is the form of specified liquid assets.
![]()
Question 40.
Mention the limitations of Macro Economics.
Answer:
Macro economics suffers from certain limitations. They are:
- There is a danger of excessive generalisation of the economy as a whole.
- It assumes homogeneity among the individual units.
- There is a fallacy of composition. What is good of an individual need not be good for nation and vice versa. And, what is good for a country is not good for another country and at another time.
- Many non-economic factors determine economic activities; but they do not find place in the usual macroeconomic books.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41 (a).
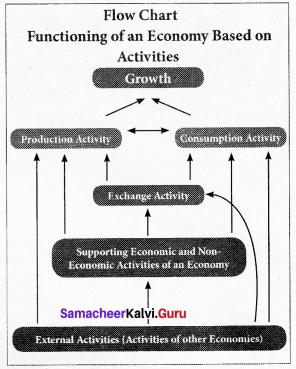
Illustrate the functioning of an economy based on its activities.
Answer:
An economy is referred to any system or area where economic activities are carried out. Each economy has its own character. Accordingly, the functions or activities also vary. The functioning of an economy by its activities is explained in flow chart.
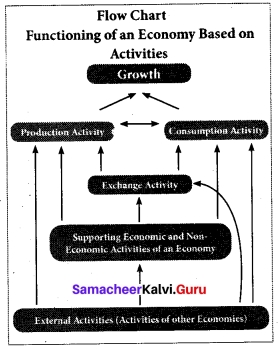
- In an economy, the fundamental economic activities are production and consumption.
- These two activities are supported by several other activities.
- The ultimate aim of these activities is to achieve growth. The ‘exchange activity’ supports the production and consumption activities. These activities are influenced by several economic and non-economic activities.
- The major economic activities include transportation, banking, advertising, planning, government policy and others.
- The major non-economic activities are environment, health, education, entertainment, governance, regulations etc.
- In addition to these supporting activities, external activities from other economies such as import, export, international relations, emigration, immigration, foreign investment, foreign exchange earnings, etc. also influence the entire functioning of the economy.
[OR]
(b) Calculate the Karl Person Correlation co-efficient for the following data.

Answer:
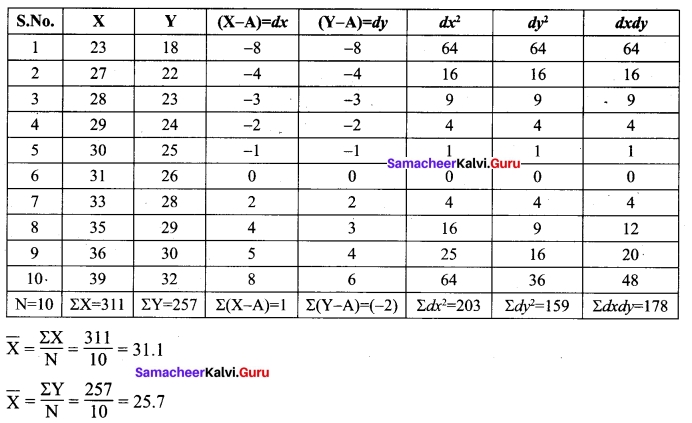
Take the assumed values A = 31 & B = 26
Therefore dx = X – A ⇒ X – 31 and
dy = Y – A ⇒ Y – 26

r = 0.9956 (or) 0.9955
= (0.9955)
Question 42 (a).
Discuss the economic determinants of economic development.
Answer:
Determinants of Economic Development:
Economic development is not determined by any single factor. Economic development depends on Economic, Social, Political and Religious factors.
Economic and Non-Economic Factors:
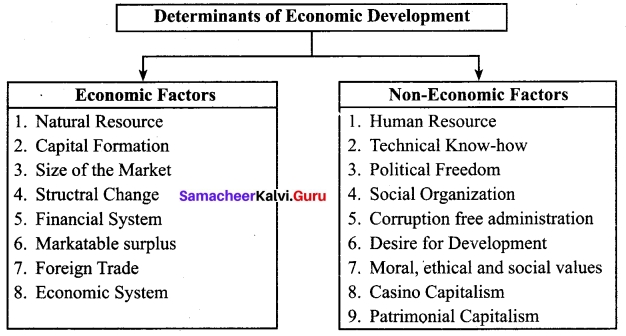
Economic Factors:
1. Natural Resource: The principal factor affecting the development of an economy is the availability of natural resources. The existence of natural resources in abundance is essential for development.
2. Capital Formation: Capital formation is the main key to economic growth. Capital formation refers to the net addition to the existing stock of capital goods which are either tangible like plants and machinery or intangible like health, education and research.
3. Size of the Market: Large size of the market would stimulate production, increase employment and raise the National per capita income. That is why developed countries expand their market to other countries through WTO.
4. Structural Change: Structural change refers to change in the occupational structure of the economy. Any economy of the country is generally divided into three basic sectors: Primary sector such as agricultural, animal husbandry, forestry, etc; Secondary sector such as industrial production, constructions and Tertiary sector such as trade, banking and commerce.
5. Financial System: Financial system implies the existence of an efficient and organized banking system in the country.
6. Marketable Surplus: Marketable surplus refers to the total amount of farm output cultivated by farmers over and above their family consumption needs. This is a surplus that can be sold in the market for earning income.
7. Foreign Trade: The country which enjoys favorable balance of trade and terms of trade is always developed. It has huge forex reserves and stable exchange rate.
8. Economic System: The countries which adopt free market mechanism (laissez faire) enjoy better growth rate compared to controlled economies.
Non-Economic Factors:
‘Economic Development has much to do with human endowments, social attitudes, political conditions and historical accidents. Capital is a necessary but not a sufficient condition of progress.’
1. Human Resources: Human resource is named as human capital because of its power to increase productivity and thereby national income. There is a circular relationship between human development and economic growth. A healthy, educated and skilled labour force is the most important productive asset. Human capital formation is the process of increasing knowledge, skills and the productive capacity of people.
2. Technical Know-how: As the scientific and technological knowledge advances, more and more sophisticated techniques steadily raise the productivity levels in all sectors.
3. Political Freedom: The process of development is linked with the political freedom.
4. Social Organization: People show interest in the development activity only when they feel that the fruits of development will be fairly distributed.
5. Corruption free administration: Corruption is a negative factor in the growth process. Unless the countries root-out corruption in their administrative system, the crony capitalists and traders will continue to exploit national resources.
6. Desire for development: The pace of economic growth in any country depends to a great extent on people’s desire for development.
7. Moral, ethical and social values: These determine the efficiency of the market, according to Douglas C. North. If people are not honest, market cannot function.
8. Casino Capitalism: If People spend larger proportion of their income and time on entertainment liquor and other illegal activities, productive activities may suffer, according to Thomas Piketty.
9. Patrimonial Capitalism: If the assets are simply passed on to children from their parents, the children would not work hard, because the children do not know the value of the assets.
![]()
[OR]
(b) Critically explain say’s law of market.
Answer:
Criticisms of Say’s Law:
The following are the criticisms against Say’s law:
- According to Keynes, supply does not create its demand. It is not applicable where demand does not increase as much as production increases.
- Automatic adjustment process will not remove unemployment. Unemployment can be removed by increase in the rate of investment.
- Money is not neutral. Individuals hold money for unforeseen contingencies while businessmen keep cash reserve for future activities.
- Say’s law is based on the proposition that supply creates its own demand and there is no over production. Keynes said that over production is possible.
- Keynes regards full employment as a special case because there is under – employment in capitalist economies.
- The need for state intervention arises in the case of general over production and mass unemployment.
Question 43 (a).
Explain the importance of National Income analysis.
Answer:
Importance of National Income Analysis:
National income is of great importance for the economy of a country. Nowadays the national income is regarded as accounts of the economy, which are known as social accounts. It enables us
- To know the relative importance of the various sectors of the economy and their contribution towards national income; from the calculation of national income, we could find how income is produced, how it is distributed, how much is spent, saved or taxed.
- To formulate the national policies such as monetary policy, fiscal policy and other policies; the proper measures can be adopted to bring the economy to the right path with the help of collecting national income data.
- To formulate planning and evaluate plan progress; it is essential that the data pertaining to a country’s gross income, output, saving and consumption from different sources should be available for economic planning.
- To build economic models both in short – run and long – run.
- To make international comparison, inter – regional comparison and inter – temporal comparison of growth of the economy during different periods.
- To know a country’s per capita income which reflects the economic welfare of the country (Provided income is equally distributed)
- To know the distribution of income for various factors of production in the country.
- To arrive at many macro economic variables namely, Tax – GDP ratio, Current Account Deficit – GDP ratio, Fiscal Deficit – GDP ratio, Debt – GDP ratio etc.
[OR]
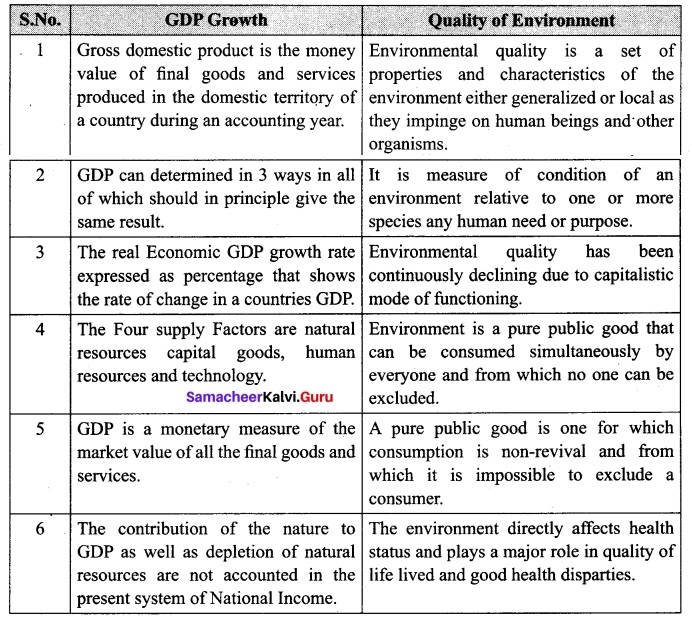
(b) Briefly explain the relationship between GDP growth and the quality of environment.
Answer:
Question 44 (a).
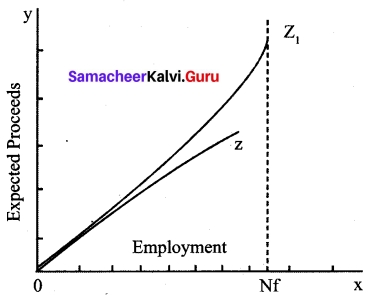
Illustrate the working of multiplier.
Answer:
Working of Multiplier:
- Suppose the Government undertakes investment expenditure equal to Rs 100 crore on some public works, by way of wages, price of materials etc.
- Thus income of labourers and suppliers of materials increases by Rs 100 crore. Suppose the MPC is 0.8 that is 80 %.
- A sum of Rs 80 crores is spent on consumption (A sum of Rs 20 Crores is saved).
- As a result, suppliers of goods get an income of Rs 80 crores.
- They intum spend Rs 64 crores (80% of Rs 80 cr).
- In this manner consumption expenditure and increase in income act in a chain like maimer.
The final result is ΔY = 100 + 100 × 4/5 + 100 × [4/5]² + 100 × [4/5]³ or,
ΔY = 100 + 100 × 0.8 + 100 × (0.8)² + 100 × (0.8)³
= 100+ 80 + 64+ 51.2… = 500
that is 100 × 1/1 = 4/5
100 × 1/1/5
100 × 5 = Rs 500 crores
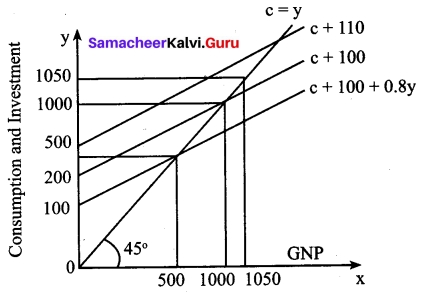
For instance if C = 100 + 0.8Y, I = 100,
Then Y = 100 + 0.8Y + 100
0. 2Y = 200
Y = 200/0.2 = 1000 → Point B
If I is increased to 110, then
0. 2Y = 210
Y = 210/0.2 = 1050 → Point D
For Rs 10 increase in I, Y has increased by Rs 50. This is due to multiplier effect.
At point A, Y = C = 500
C = 100 + 0.8 (500) = 500; S = 0
At point B, Y = 1000
C = 100 + 0.8 (1000) = 900; S = 100 = I
At point D, Y = 1050
C = 100 + 0.8 (1050) = 940; S = 110 = I
When I is increased by 10, Y increases by 50.
This is multiplier effect (K = 5)
K = \(\frac{1}{0.2}\)
[OR]
(b) Bring out the components of balance of payments accounts.
Answer:
Components of BOPs:
The credit and debit items are shown vertically in the BOP account of a country. Horizontally, they are divided into three categories, i.e.,
- The current account,
- The capital account and
- The official settlements account or official reserve assets account.
1. The Current Account: It includes all international trade transactions of goods and services, international service transactions (i.e. tourism, transportation and royalty fees) and international unilateral transfers (i.e. gifts and foreign aid).
2. The Capital Account: Financial transactions consisting of direct investment and purchases of interest-bearing financial instruments, non-interest bearing demand deposits and gold fall under the capital account.
3. The Official Reserve Assets Account: Official reserve transactions consist of movements of international reserves by governments and official agencies to accommodate imbalances arising from the current and capital accounts.
The official reserve assets of a country include its gold stock, holdings of its convertible foreign currencies and Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and its net position in the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

![]()
Question 45 (a).
Explain in detail the measures to control inflation.
Answer:
Measures to Control Inflation
Keynes and Milton Friedman together suggested three measures to prevent and control of inflation.
- Monetary measures,
- Fiscal measures (J.M. Keynes) and
- Other measures.
1. Monetary Measures: These measures are adopted by the Central Bank of the country. They are (i) Increase in Bankrate (ii) Sale of Government Securities in the Open Market (iii) Higher Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) (iv) Consumer Credit Control and (v) Higher margin requirements (vi) Higher Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
2. Fiscal Measures: Fiscal policy is now recognized as an important instrument to tackle an inflationary situation. The major anti-inflationary fiscal measures are the following: Reduction of Government Expenditure, Public Borrowing and Enhancing taxation.
3. Other Measures: These measures can be divided broadly into short-term and long-term measures.
i) Short-term measures can be in regard to public distribution of scarce essential commodities through fair price shops (Rationing). In India whenever shortage of basic goods has been felt, the government has resorted to import so that inflation may not get triggered.
ii) Long-term measures will require accelerating economic growth especially of the wage goods which have a direct bearing on the general price and the cost of living. Some restrictions on present consumption may help in improving saving and investment which may be necessary for accelerating the rate of economic growth in the long run.
[OR]
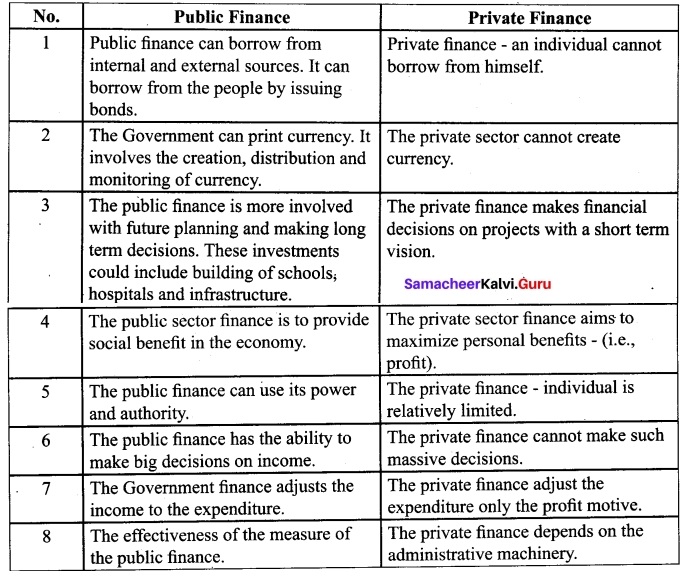
(b) Distinguish between Public Finance and Private Finance.
Answer:
Question 46 (a).
Describe the functions of RBI.
Answer:
Functions of Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India):
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India’s central banking institution, which controls the monetary policy of the Indian rupee.
1. Monetary Authority: It controls the supply of money in the economy to stabilize exchange rate, maintain healthy balance of payment, attain financial stability, control inflation, strengthen banking system.
2. The issuer of currency: The objective is to maintain the currency and credit system of the country. It is the sole authority to issue currency. It also takes action to control the circulation of fake currency.
3. The issuer of Banking License: As per Sec 22 of Banking Regulation Act, every bank has to obtain a banking license from RBI to conduct banking business in India.
4. Banker to the Government: It acts as banker both to the central and the state governments. It provides short-term credit. It manages all new issues of government loans, servicing the government debt outstanding and nurturing the market for government securities. It advises the government on banking and financial subjects.
5. Banker’s Bank: RBI is the bank of all banks in India as it provides loan to banks, accept the deposit of banks, and re-discount the bills of banks.
6. Lender of last resort: The banks can borrow from the RBI by keeping eligible securities as collateral at the time of need or crisis, when there is no other source.
7. Act as clearing house: For settlement of banking transactions, RBI manages 14 clearing houses. It facilitates the exchange of instruments and processing of payment instructions.
8. Custodian of foreign exchange reserves: It acts as a custodian of FOREX. It administers and enforces the provision of Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999. RBI buys and sells foreign currency to maintain the exchange rate of Indian rupee v/s foreign currencies.
9. Regulator of Economy: It controls the money supply in the system, monitors different key indicators like GDP, Inflation, etc.
10. Managing Government securities: RBI administers investments in institutions when they invest specified minimum proportions of their total assets/liabilities in government securities.
11. Regulator and Supervisor of Payment and Settlement Systems: The Payment and Settlement Systems Act of 2007 (PSS Act) gives RBI oversight authority for the payment and settlement systems in the country. RBI focuses on the development and functioning of safe, secure and efficient payment and settlement mechanisms.
12. Developmental Role: This role includes the development of the quality banking system in India and ensuring that credit is available to the productive sectors of the economy. It provides a wide range of promotional functions to support national objectives. It also includes establishing institutions designed to build the country’s financial infrastructure. It also helps in expanding access to affordable financial services and promoting financial education and literacy.
13. Publisher of monetary data and other data: RBI maintains and provides all essential banking and other economic data, formulating and critically evaluating the economic policies in India. RBI collects, collates and publishes data regularly.
14. Exchange manager and controller: RBI represents India as a member of the International Monetary Fund [IMF], Most of the commercial banks are authorized dealers of RBI.
15. Banking Ombudsman Scheme: RBI introduced the Banking Ombudsman Scheme in 1995. Under this scheme, the complainants can file their complaints in any form, including online and can also appeal to the Ombudsman against the awards and the other decisions of the Banks.
16. Banking Codes and Standards Board of India: To measure the performance of banks against Codes and standards based on established global practices, the RBI has set up the Banking Codes and Standards Board of India (BCSBI).
[OR]
(b) Write a note on
(i) SAARC
(ii) BRICS
Answer:
(i) South Asian Association For Regional Co-Operation (SAARC):
- The South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation (SAARC) is an organisation of South Asian nations, which was established on 8 December 1985 for the promotion of economic and social progress, cultural development within the South Asia region and also for friendship and co-operation with other developing countries.
- The SAARC Group (SAARC) comprises of Bangaladesh, Bhutan, India, The Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- In April 2007, Afghanistan became its eighth member.
- The basic aim of the organisation is to accelerate the process of economic and social development of member states through joint action in the agreed areas of cooperation.
- The SAARC Secretariat was established in Kathmandu (Nepal) on 16th January 1987.
- The first SAARC summit was held at Dhaka in the year 1985.
- SAARC meets once in two years. Recently, the 20th SAARC summit was hosted by Srilanka in 2018.
(ii) BRICS:
- BRICS is the acronym for an association of five major emerging national economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Since 2009, the BRICS nations have met annually at formal summits.
- South Africa hosted the 10th BRICS summit in July 2018.
- The agenda for BRICS summit 2018 includes Inclusive growth, Trade issues, Global governance, Shared Prosperity, International peace and security.
- It’s headquarters is at Shanghai, China.
- The New Development Bank (NDB) formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank was established by BRICS States.
- The first BRICS summit was held at Moscow and South Africa hosted the Tenth Conference at Johanesberg in July 2018.
- India had an opportunity of hosting fourth and Eighth summits in 2009 and 2016 respectively.
- The BRICS countries make up 21 percent of global GDP. They have increased their share of global GDP threefold in the past 15 years.
- The BRICS are home to 43 percent of the world’s population.
- The BRICS countries have combined foreign reserves of an estimated $4.4 trillion.
![]()
Question 47 (a).
Describe the phases of trade cycle.
Answer:
Phases of Trade Cycle
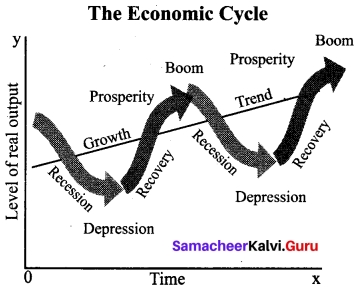
The four different phases of trade cycle is referred to as
- Boom
- Recession
- Depression and
- Recovery. These are illustrated in the figure.
Phases of Trade Cycle
1. Boom or Prosperity Phase:
- The full employment and the movement of the economy beyond full employment is characterized as boom period.
- During this period, there is hectic activity in economy.
- Money wages rise, profits increase and interest rates go up.
- The demand for bank credit increases and there is all-round optimism.
2. Recession:
- the turning point from boom condition is called recession.
- This happens at higher rate, than what was earlier.
- Generally, the failure of a company or bank bursts the boom and brings a phase of recession.
- Investments are drastically reduced, production comes down and income and profits decline.
- There is panic in the stock market and business activities show signs of dullness.
- Liquidity preference of the people rises and money market becomes tight.
3. Depression:
- During depression the level of economic activity becomes extremely low.
- Firms incur losses and closure of business becomes a common feature and the ultimate result is unemployment.
- Interest prices, profits and wages are low. The agricultural class and wage earners would be worst hit.
- Banking institutions will be reluctant to advance loans to businessmen.
- Depression is the worst phase of the business cycle.
- Extreme point of depression is called as “trough”, because it is a deep point in business cycle.
4. Recovery:
- After a period of depression, recovery sets in.
- This is the turning point from depression to revival towards upswing.
- It begins with the revival of demand for capital goods.
- Autonomous investments boost the activity.
- The demand slowly picks up and in due course the activity is directed towards the upswing with more production, profit, income, wages and employment.
- Recovery may be initiated by innovation or investment or by government expenditure
(autonomous investment).
![]()
[OR]
(b) What are the reasons for the recent growth in public expenditure?
Answer:
Causes for the Increase in Government Expenditure:
The modem state is a welfare state. In a welfare state, the government has to perform several functions viz Social, economic and political. These activities are the cause for increasing public expenditure.
(i) Population Growth:
- During the past 67 years of planning, the population of India has increased from 36.1 crore in 1951, to 121 crore in 2011.
- The growth in population requires massive investment in health and education, law and order, etc.
- Young population requires increasing expenditure on education &. youth services, whereas the aging population requires transfer payments like old age pension, social security & health facilities.
(ii) Defence Expenditure:
- There has been enormous increase in defence expenditure in India during planning period.
- The defence expenditure has been increasing tremendously due to modernisation of defence equipment.
- The defence expenditure of the government was Rs 10,874 crores in 1990-91 which increased significantly to Rs 2,95,511 crores in 2018-19.
(iii) Government Subsidies:
- The Government of India has been providing subsidies on a number of items such as food, fertilizers, interest on priority sector lending, exports, education, etc.
- Because of the massive amounts of subsidies, the public expenditure has increased manifold.
(iv) Debt Servicing:
The government has been borrowing heavily both from the internal and external sources, As a result, the government has to make huge amounts of repayment towards debt servicing.
(v) Development Projects:
- The government has been undertaking various development projects such as irrigation, iron and steel, heavy machinery, power, telecommunications, etc.
- The development projects involve huge investment.
(vi) Urbanisation:
- There has been an increase in urbanization.
- In 1950-51 about 17% of the population was urban based.
- Now the urban population has increased to about 43%.
- There are more than 54 cities above one million population.
- The increase in urbanization requires heavy expenditure on law and order, education and civic amenities.
(vii) Industrialisation:
- Setting up of basic and heavy industries involves a huge capital and long gestation period.
- It is the government which starts such industries in a planned economy.
- The under developed countries need a strong of infrastructure like transport, communication, power, fuel, etc.
(viii) Increase in grants in aid to state and union territories:
There has been tremendous increase in grant-in-aid to state and union territories to meet natural disasters.