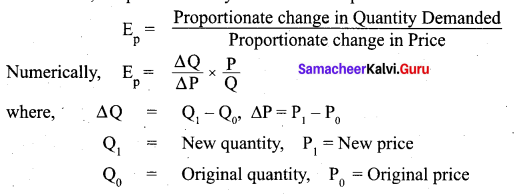
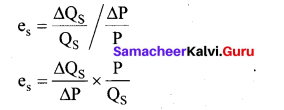
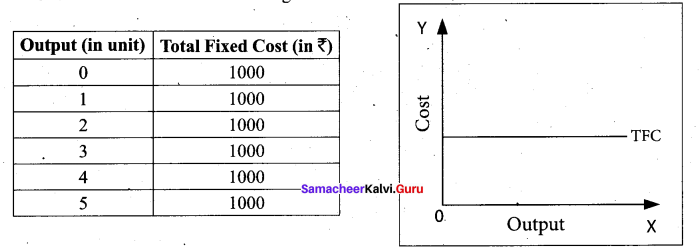
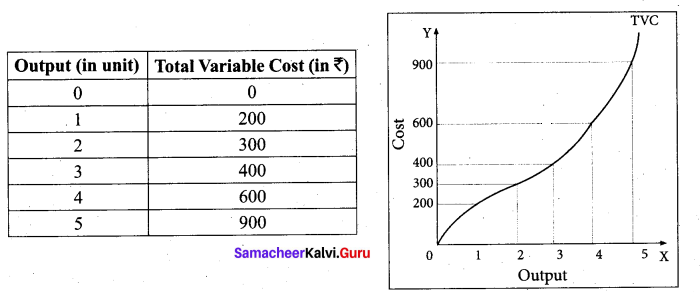
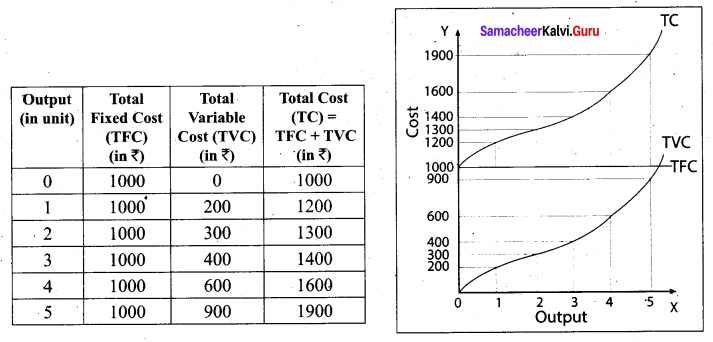
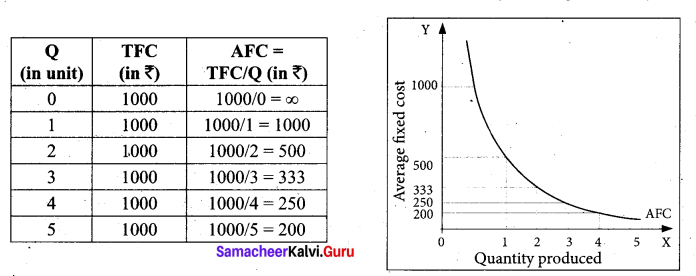
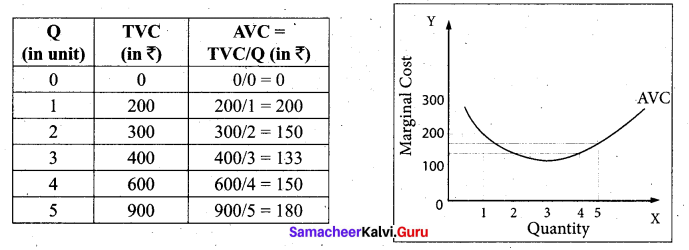
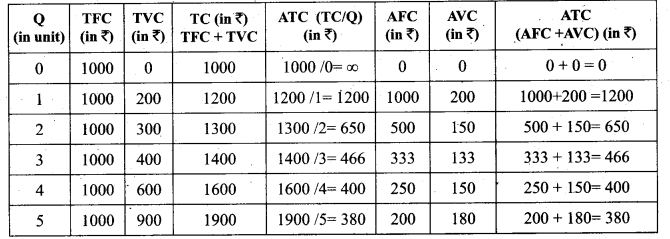
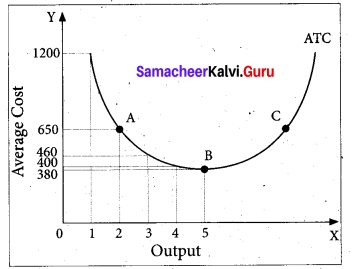
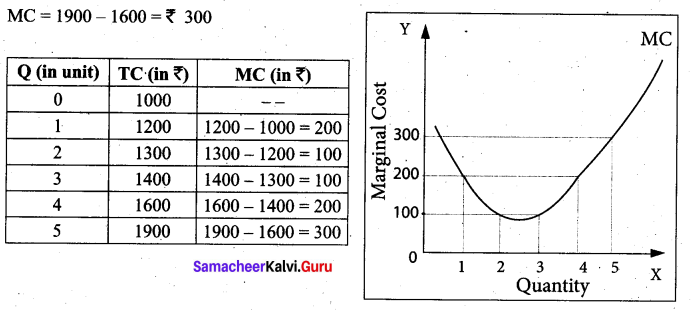
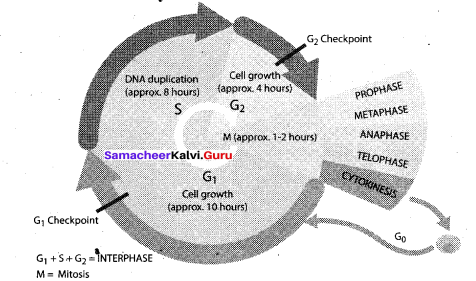
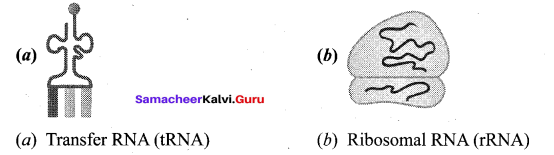
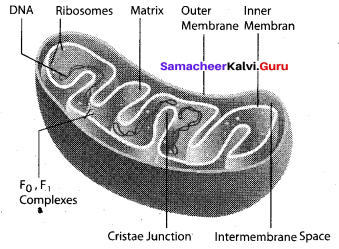
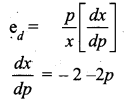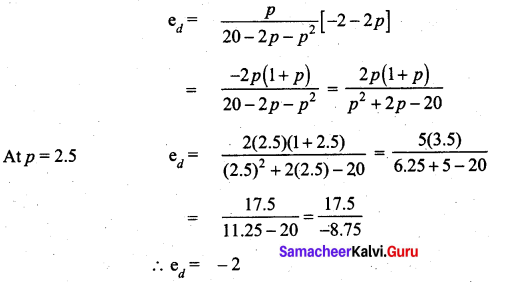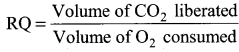Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer . - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Opening statement of affairs is usually prepared to find out the _________.
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
(b) Capital at the end of the year
(c) Profit made during the year
(d) Loss occurred during the year
Answer:
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
Question 2.
The excess of assets over liabilities is ________.
(a) Loss
(b) Cash
(c) Capital
(d) Profit
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 3.
Balance of Receipts and payments account indicates the ________.
(a) Loss incurred during the period
(b) Excess of income over expenditure of the period
(c) Total cash payments during the period
(d) Cash and bank balance as on the date
Answer:
(d) Cash and bank balance as on the date
Question 4.
Income and expenditure account is a ________.
(a) Nominal A/c
(b) Real A/c
(c) Personal A/c
(d) Representative personal account
Answer:
(a) Nominal A/c
![]()
Question 5.
As per the Indian Partnership Act 1932, the rate of interest allowed to an loan advanced by partners is ______.
(a) 8% p.a.
(b) 12%p.a.
(c) 5%p.a.
(d) 6% p.a.
Answer:
(d) 6% p.a.
Question 6.
Which of the following is shown in profit and loss appropriation account _______.
(a) Office expenses
(b) Salary of staff
(c) Partners salary
(d) Interest on bank loan
Answer:
(c) Partners salary
Question 7.
The average rate of return of similar concerns is considered as _______.
(a) Average profit
(b) Normal rate of return
(c) Expected rate of return
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Normal rate of return
Question 8.
Which of the following is true?
(a) Super profit = Total profit/Number of years
(b) Super profit = weighted profit/Number of years
(c) Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit
(d) Super profit = Average profit x years of purchase
Answer:
(c) Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit.
Question 9.
The profit or loss on revaluation of assets and liabilities is transferred to capital account of ________.
(a) The old partners
(b) The new partners
(c) All the partners
(d) The sacrificing partners
Answer:
(a) The old partners
![]()
Question 10.
If the old profit sharing ratio is more than the new profit sharing ratio of a partner, the difference is called ______.
(a) Capital ratio
(b) Sacrificing ratio
(c) Gaining ratio
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Sacrificing ratio
Question 11.
On retirement of a partner, general reserve is transferred to the _______.
(a) Capital account of all the partners
(b) Revaluation A/c
(c) Capital account of the continuing partners
(d) Memorandum of revaluation account
Answer:
(a) Capital account of all the partners
Question 12.
On revaluation, the increase in liabilities leads to __________.
(a) Gain
(b) Loss
(c) profit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Loss
Question 13.
At the time of forfeiture, share capital account is debited with ________.
(a) Face Value
(b) Nominal Value
(c) Paid up amount
(d) Called up amount
Answer:
(d) Called up amount
![]()
Question 14.
After the forfeited shares are reissued, the balance in the forfeited shares account should be transferred to ________.
(a) General reserve A/c
(b) Capital reserve A/c
(c) Securities premium A/c
(d) Surplus A/c
Answer:
(b) Capital reserve A/c
Question 15.
Which of the following tools of financial statement analysis is suitable when data relating to several years are to be analyzed _______.
(a) Cash flow statement
(b) Common size statement
(c) Comparative statement
(d) Trend analysis
Answer:
(d) Trend analysis
Question 16.
The financial statements do not exhibit _______.
(a) Non-monetary data
(b) Past-data
(c) Short term data
(d) Long-term data
Answer:
(a) Non-monetary data
Question 17.
Current assets excluding inventory and prepaid expenses is called ________.
(a) Reserves
(b) Tangible assets
(c) Funds
(d) Quick assets
Answer:
(d) Quick assets
![]()
Question 18.
Debt-equity ratio is a measure of ________.
(a) Short-term solvency
(b) Long-term solvency
(c) Profitability
(d) Efficiency
Answer:
(b) Long-term solvency
Question 19.
Which sub-menu displays groups, ledgers and voucher types in tally?
(a) Inventory vouchers
(b) Accounting vouchers
(c) Company info
(d) Account info
Answer:
(d) Account info
Question 20.
What are the predefined ledgers in tally?
(i) cash (ii) Profit and loss A/c (iii) Capital A/c
(a) only (i)
(b) only (ii)
(c) Both (i) and (ii)
(d) Both (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(c) Both (i) and (ii)
Part – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
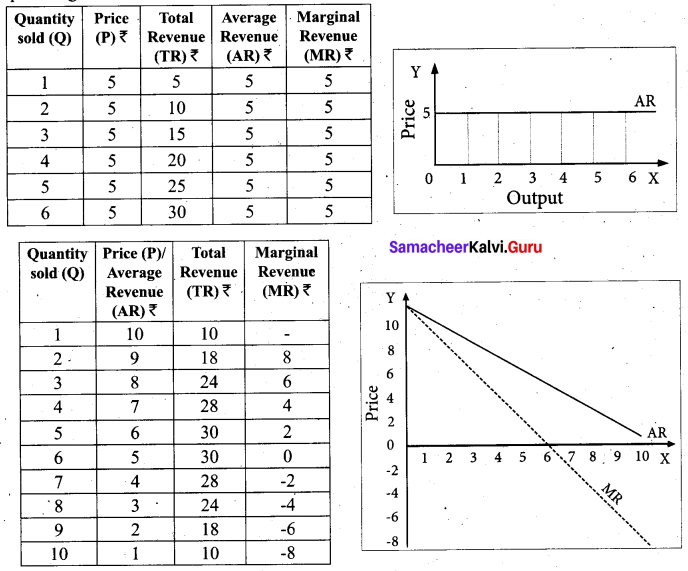
Question 21.
Define single entry system.
Answer:
According to Kolher, “Single entry system is a system of book-keeping in which as a rule, only records of cash and personal accounts are maintained. It is always incomplete double entry system varying with circumstances”.
![]()
Question 22.
From the following receipts and payments and the additional information given, Calculate amount of subscription to be shown in income and expenditure a/c for year ended 31.12.18.
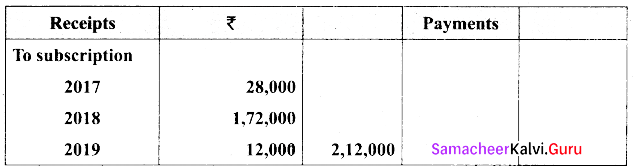
Additional information :
Subscription outstanding for 2018 ₹ 8,000.
Answer:

Question 23.
Define partnership.
Answer:
According to section 4 of the Indian Partnership Act 1932, partnership is defined as, “the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried by all or any of them acting for all”.
Question 24.
The Profits and losses of a firm for the last four years were as follows:
2015 – ₹ 20,000
2016 – ₹ 25,000
2017 – ₹ 3,000 (Loss)
2018 – ₹ 18,000
you are required to calculate goodwill on the basis of 5 years purchase of average profit of last 4 years.
Answer:
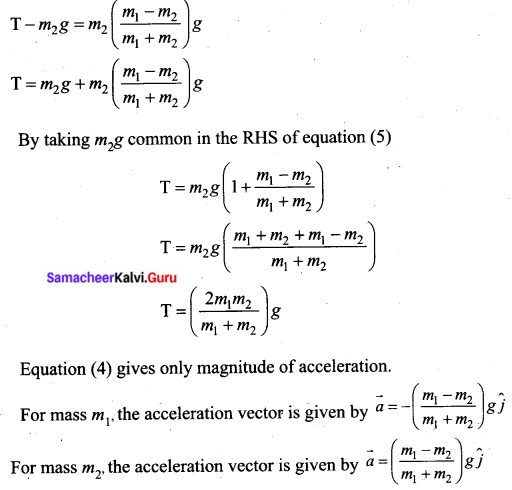
Goodwill = Average profit × No. of years of purchase
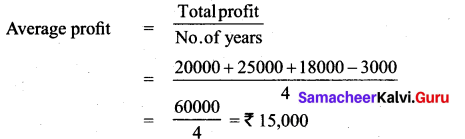
Goodwill= Average profit × No. of years purchase
= ₹ 15,000 × 5
= ₹ 75,000
Question 25.
A and B are partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio 5:3. They admit C on 1.1.2018. On that date, balance sheet showed accumulated profit of? 80,000 on the liabilities side. Give the journal entry.
Answer:

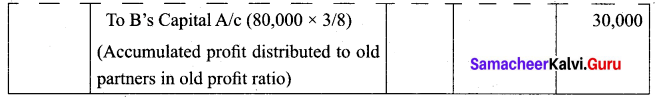
![]()
Question 26.
What is the journal entry to be passed to transfer the amount due to the deceased partner to the executor of the deceased partner?
Answer:
To transfer the amount due to the deceased partner to the executor or legal representative of the deceased partner.
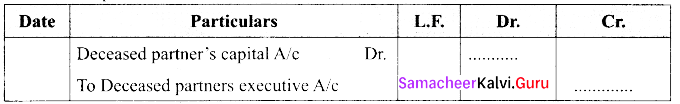
Question 27.
What is meant by calls-in-arrear?
Answer:
When a share holder fails to pay the amount due on allotment or on calls, the amount remaining unpaid is known as calls-in-arrear. In other words, the amount called up but not paid is calls-in-arrears.
Question 28.
Calculate gross profit ratio from the following: revenue from operations ₹ 5,00,000; cost of revenue from operations ₹ 4,20,000; and purchases ₹ 3,60,000.
Answer:
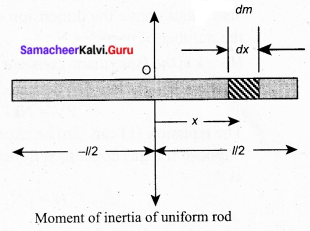
Gross profit Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Gross profit }}{\text { Revenue from operations }} \times 100\)
Gross profit Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
₹ 5,00,000 – ₹ 4,20,000
= ₹ 80,000
Gross profit ratio = \(\frac{80000}{500000} \times 100\)
= 16%
Question 29.
Calculate Quick Ratio from the following information: Current assets – 8,00,000; Current liabilities- ₹ 4,00,000; Inventories ₹ 1,40,000; and prepaid expenses ₹ 60,000.
Answer:
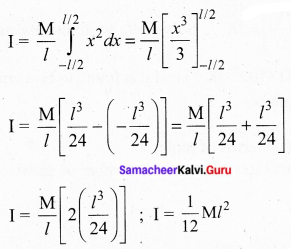
Quick Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Quick Assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
Quick assets = Current assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
= ₹ 8,00,000 – (1,40,000 – 60,000)
= ₹ 6,00,000
∴ Quick ratio = \(\frac{600000}{400000}\) = 6:4 = 3:2 = 1.5:1
![]()
Question 30.
What is computerised accounting system?
Answer:
- Computerised accounting system refers to the system of accounting maintenance using computer.
- It involves the processing of accounting transactions through the use of computer in order to maintain and produce accounting records and reports.
Part – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 31 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
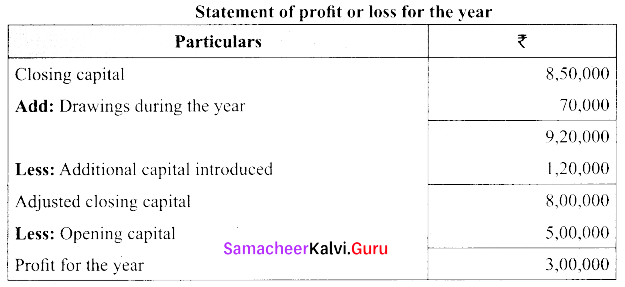
Question 31.
From the following particulars, ascertain profit or loss.
Capital at beginning – ₹ 5,00,000
Capital at end – ₹ 8,50,000
Additional capital – ₹ 1,20,000
Drawing during the year – ₹ 70,000
Answer:
Question 32.
From the following information of club, show the amount of match expenses in financial statements of the club for the year ended 31.03.2016.
Matches expenses 31.03.16 – ₹ 30,000
Match fund – ₹ 17,000
Donations for match fund (31.03.16) – ₹ 9,000
Proceeds from the sale of match tickets – ₹ 3,000
Answer:
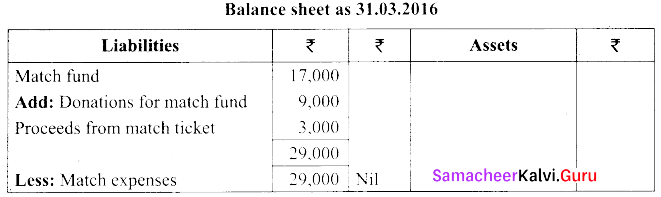
Note:
Match expenses of ₹ 30,000 out of which ₹ 29,000 are met through match fund as per the availability of fund remaining. ₹ 1,000 is debited to income and expenditure A/c.
![]()
Question 33.
Prakash and Supriya were partners who share profit and losses in the ratio 5:3. Capital ₹ 3,00,000 for Prakash ₹ 2,00,000 for Supriya. On 1st April 2018, Prakash introduced additional capital ₹ 60,000 on 1st July 2018. Supriya introduced additional capital ₹ 30,000 during the year. Calculate the interest on capital at 6% p.a.
Answer:
Calculation of interest on capital
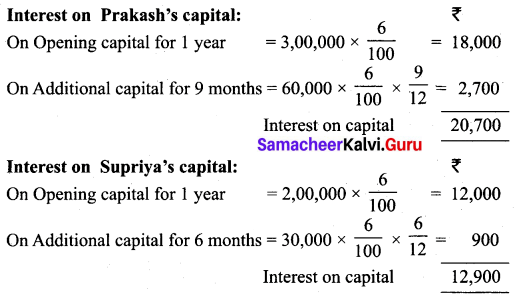
Note:
Date of additional capital introduced by Supriya is not given. Interest on additional capital is calculated for an average period of 6 months.
Question 34.
From the following information relating to a partnership firm, find out the value of its goodwill based on 3 years purchase of average profits of last 4 years.
a) Profits of the year 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018 are ₹ 10,000, ₹ 12,500; ₹ 12,000 and ₹ 11,500, respectively.
b) The business was looked after by a partner and fair remuneration amount to ₹ 1,500 per year. This amount was not considered in the calculation of the above profit.
Answer:
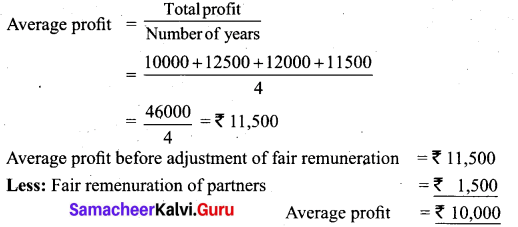
Goodwill = Average profit × No. of years of purchase
= 10,000 × 3
Goodwill = ₹ 30,000
Question 35.
A, B and C are partners sharing profit and losses with ratio of 5:3:2. As from 1st April 2017, D is admitted into the partnership and new profit sharing ratio of 4:3:2:1.
(i) Increase the value of premises by ₹ 60,000
(ii) Depreciate stock by ₹ 5,000; furniture by ₹ 2,000 and machinery by ₹ 2,500.
(iii) Provide an outstanding liability of ₹ 500. Pass journal entries.
Answer:
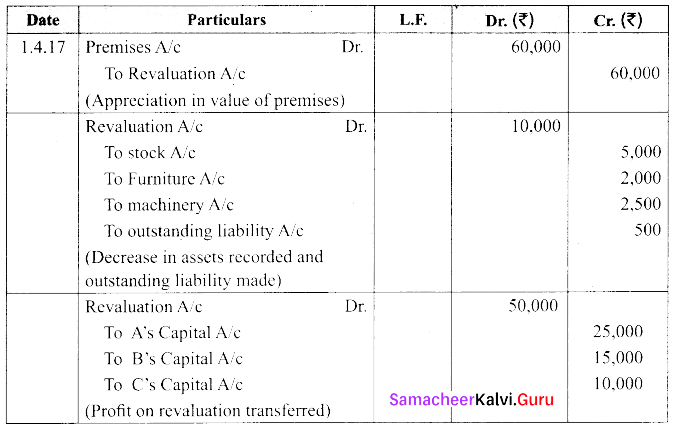
![]()
Question 36.
Kavitha, Kumudha and Lalitha are partners with profit shares ratio of 5:3:3. Kumudha retires from the firm on 31.12.18. On the date of retirement her capital account shows a credit balance of ₹ 2,00,000. Pass journal entries.
(i) The amount due is paid off immediately
(ii) The amount due is not paid immediately
(iii) ₹ 70,000 is paid and balance in future
Answer:
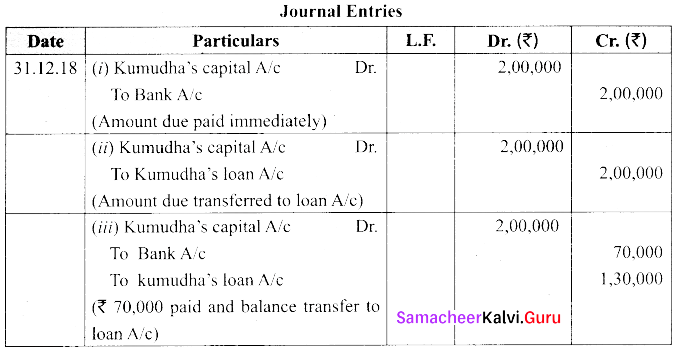
Question 37.
The directors of a company forfeited 200 equity shares of ₹ 10 each fully called up on which final call of ₹ 2/- has not been paid. The shares were reissued upon payment of ₹ 1,500. Journalise the above transaction.
Answer:
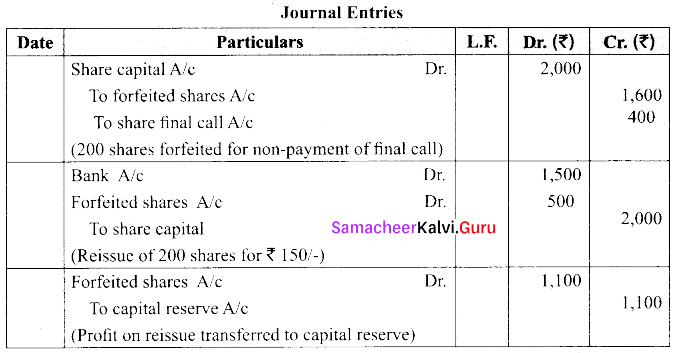
Question 38.
From the following particulars, prepare comparative income statement of Arul Ltd.

Answer:
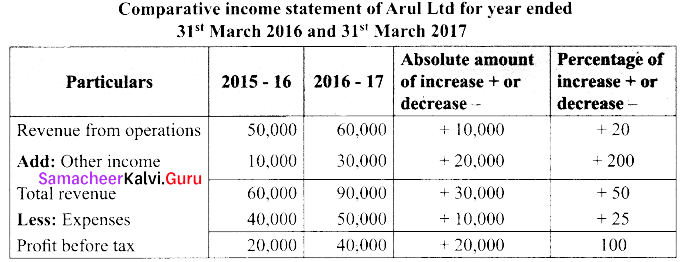
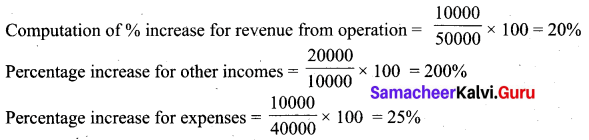
![]()
Question 39.
From the following particulars, calculate current ratio, and liquid ratio.
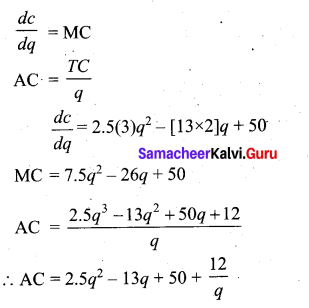
Cash Rs – 18,000; Bills payable – 27,000; Bank O/D – 5,000; Debtors Rs – 1,42,000; creditors – 1,20,000; Stock Rs – 1,80,000; outstanding expenses – 15,000.
Answer:
(a) Current Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}\)
Current Assets = Cash + Debtor + Stock
= 18,000+ 1,42,000+ 1,80,000
= ₹ 3,40,000
Current liabilities = Bills payable + Creditors + Outstanding expenses
= 27,000+ 1,20,000+ 15,000+ 5,000
= ₹ 1,67,000
(b) Liquid ratio = \(\frac{\text { Liquid Assets }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}\)
Liquid Assets = Current Assets – Closing stock
= 3,00,000 – 1,80,000 = ₹ 1,60,000
∴ Liquid ratio = \(\frac{160000}{167000}\) = 96 : 1
Question 40.
What are the pre-defined ledgers available in Tally ERP.9?
Answer:
In Tally, to record transactions, the transactions are to be identified with the related ledger accounts.
In tally ERP.9, there are two types of pre-defined ledgers.
(i) Cash:
Under the group cash in hand, this ledger is created. You can enter the opening balance as on the books beginning from.
(ii) Profit and loss account:
This ledger is created under the group primary. In this ledger, previous year’s profit or loss is entered as the opening balance of this ledger.
To create ledger,
Gateway of Tally → Masters → Accounts Info → Ledgers → Single Ledger → Create.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
(a) Raju does not keep proper books of accounts. Following details are taken from his records.
| Particulars | 1.1.2018 | 31.12.2018 |
| Cash at Bank | 80,000 | 90,000 |
| Stock of goods | 1,80,000 | 1,40,000 |
| Debtors | 90,000 | 2,00,000 |
| Creditors | 1,30,000 | 1,95,000 |
| Bank Loan | 60,000 | 60,000 |
| Bills payable | 80,000 | 45,000 |
| Machinery | 1,70,000 | 1,70,000 |
He introduced further capital of ₹ 50,000 withdrew ₹ 2500/- per month. Prepare statement of profit or loss with the above information.
Answer:
Calculation of opening capital:
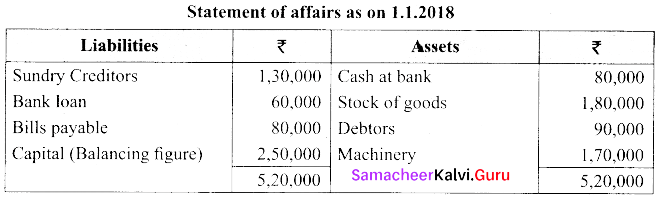
Calculation of closing capital:
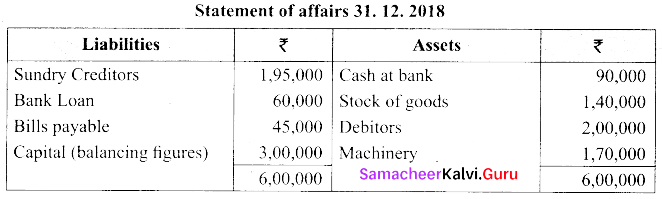
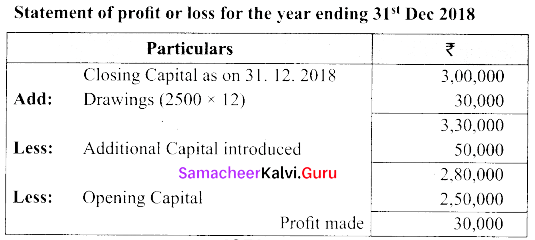
[OR]
(b) From the following particulars, calculate total sales
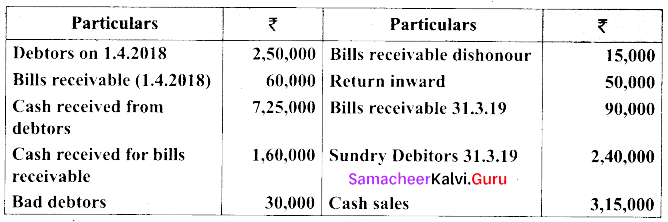
Answer:
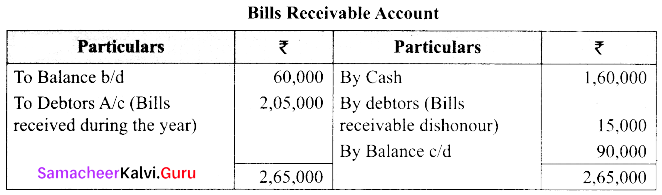
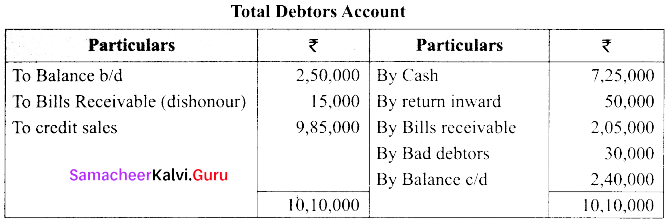
Total sales = Cash sales + Credit sales
= ₹ 3,15,000 + ₹ 9,85,000
= ₹ 13,00,000
![]()
Question 42.
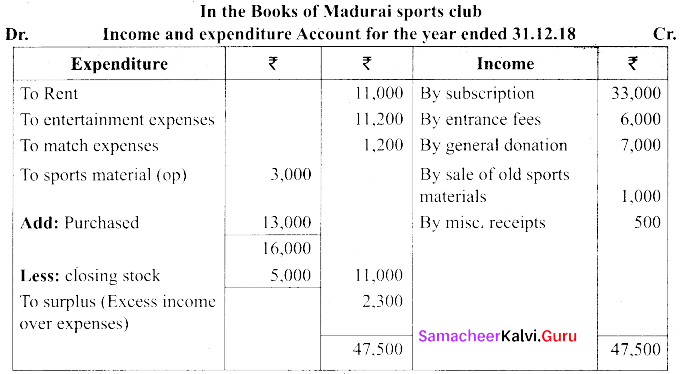
(a) From the following receipts and payments account information given below of Madurai sports club, prepare income and expenditure account for the year ended 31.12.18 and balance sheet.
Answer:
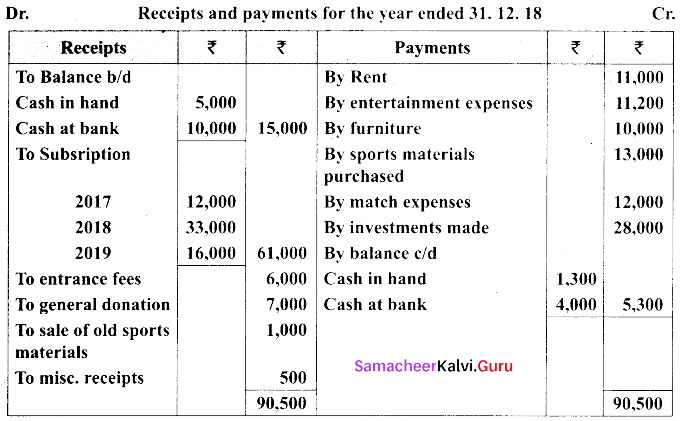
Additional informations:
(i) Capital fund as on 1st January 2018, ₹ 30,000
(ii) Opening stock of sports materials ₹ 3,000 and closing stock of sports material ₹ 5,000
Answer:
[OR]
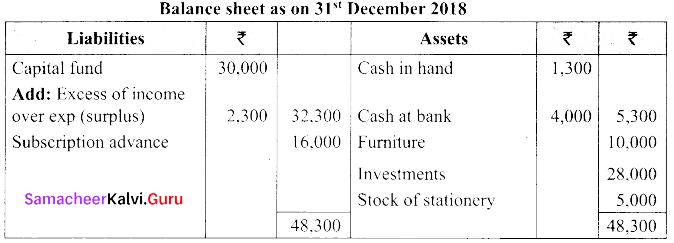
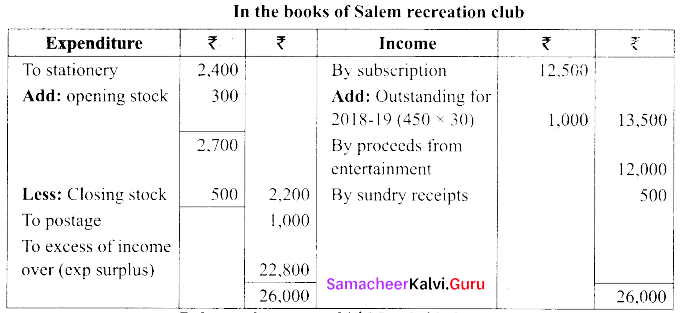
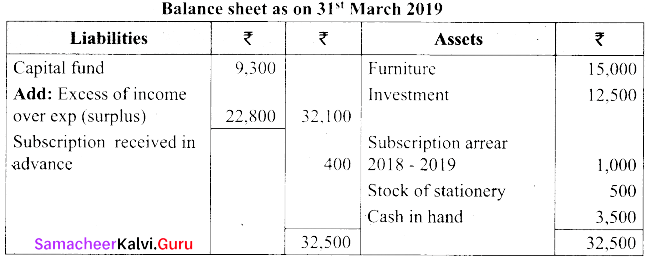
(b) Following is the receipts and payments A/c of Salem recreation club for the year ended 31st March 2019.
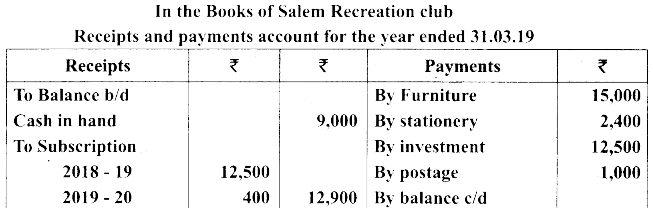

Additional Information:
(i) There are 450 members each paying annual subscription of ₹ 30
(ii) Stock of stationery on 31st March 2018, ₹ 300 and 31st March 2019, ₹ 500
(iii) Capital fund as on 1st April 2018 was ₹ 9,300
Prepare income and expenditure A/c for the year ended 31st March 2019 and balance sheet as on that date.
Answer:
![]()
Question 43.
(a) Santhosh is a partner in a partnership firm. As per deed, interest on drawing is charged at 6% p.a. During the year ended 31st Dec 2018, he withdrew as follows:

Calculate the amount of interest on drawing by using product method.
Answer:
Calculation of interest on drawings under product method.
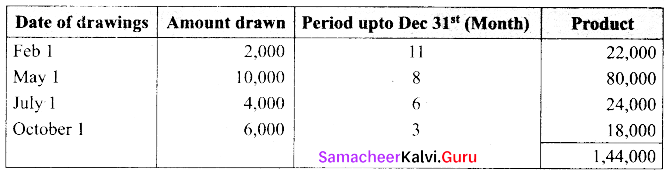
Interest on drawings = Sum of product × Rate of interest x \(\frac{1}{12}\)
= ₹ 1,44,000 × \(\frac{6}{100} \times \frac{1}{12}\)
= ₹ 720
[OR]
(b) Calculate the value of goodwill at 5 years purchase of super profits from the following information:
(a) Capital employed: ₹ 60,000
(b) Normal rate of profit: 20%
(c) Net profit for 5 years: 2014 – 1,00,000; 2015 – 50,000; 2016 – 70,000; 2017 – 54,000; 2018 – 10,000.
(d) Fair remuneration to the partners ₹ 3,600 p. a.
Answer:
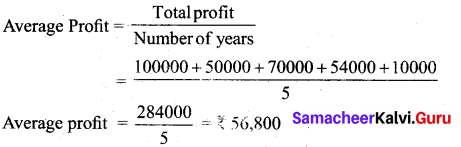

Normal profit = Capital employed × Normal rate of returns
= ₹ 60,000 × \(\frac{20}{100}\)
= ₹ 12,000
Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit
= ₹ 53,200 – 12,000
= ₹ 41,200
Goodwill = Super profit × Numbers of years of purchase
= ₹ 41,200 × 5
= ₹ 2,06,000
Question 44.
(a) Find out the value of goodwill by capitalizing super profit
a) Normal rate of return 10%
b) Profits for the last four years are ₹ 30,000; ₹ 40,000; ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 45,000
c) A non-recurring income of ₹ 3,000 is included in the above mentioned profit of ₹ 30,000
d) Average capital employed is ₹ 3,00,000.
Answer:
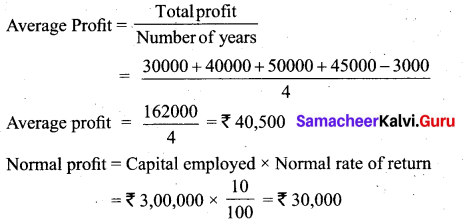
Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit
= ₹ 40,500 – ₹ 30,000
= ₹ 10,500
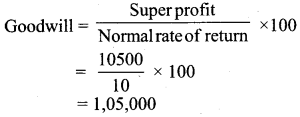
[OR]
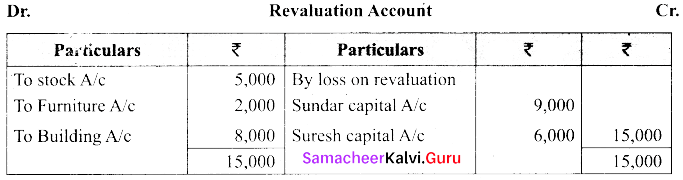
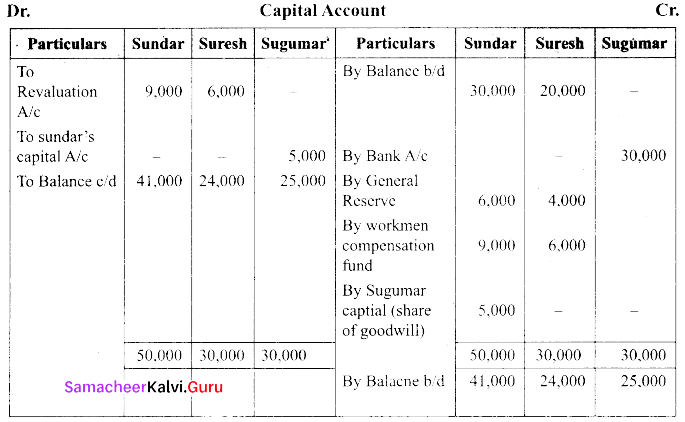
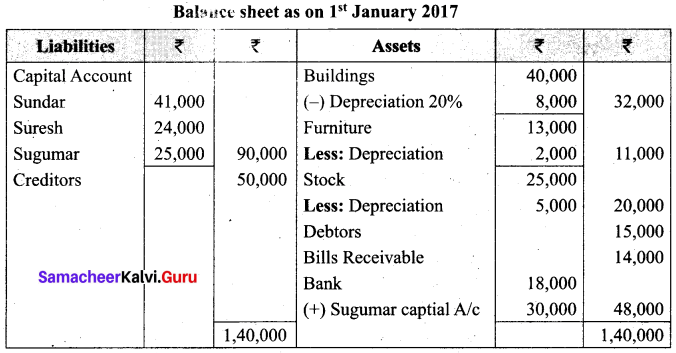
(b) Sundar and Suresh are partners sharing profit ratio of 3:2. Their balance sheet as on 1st January 2017 was as follows:
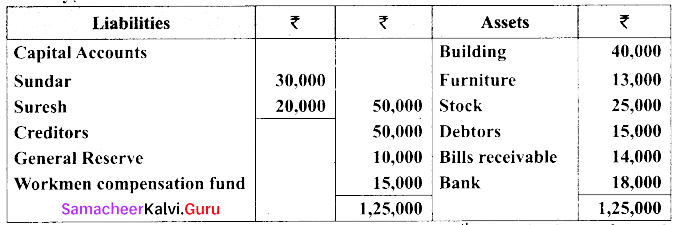
They decided to admit Sugumar into partnership for 1/4th share in the profit on the following terms:
(a) Sugumar has to bring in ₹ 30,000 as capital. His share of goodwill is valued at ₹ 5,000. He could not bring cash toward goodwill
(b) That the stock be valued at ₹ 20,000
(c) That the furniture be depreciated by ₹ 2,000.
(d) That the value of building be depreciated by 20%.
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet.
Answer:
![]()
Question 45.
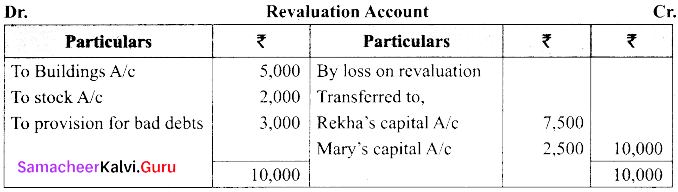
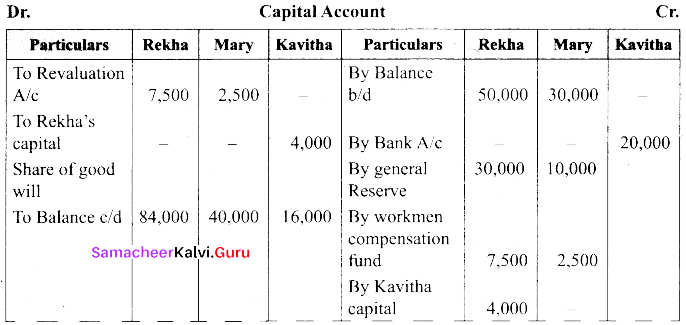
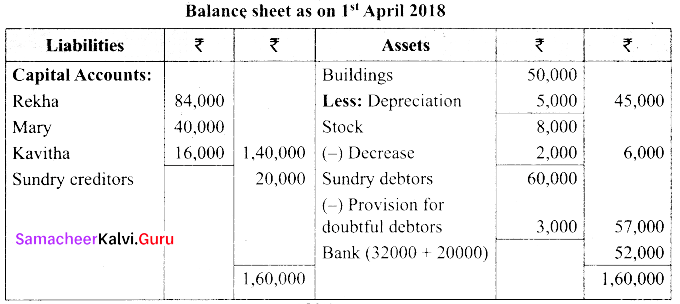
(a) The balance sheet of Rekha and Mary on 31st March 2018.
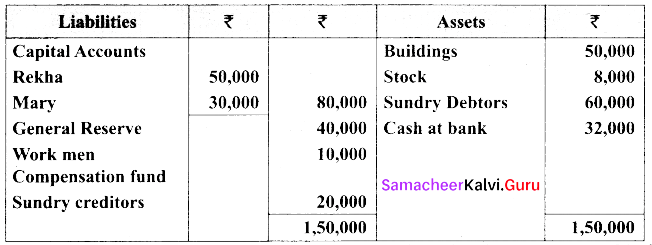
Their profit sharing ratio is 3:1. They agreed to admit kavitha into the partnership firm for 1/4th share of profits which she entirely gets from Rekha.
(i) Kavitha has to bring ₹ 20,000 as capital. Her share of goodwill is valued at 4,000. She could not bring cash towards goodwill.
(ii) Depreciate building by 10%
(iii) Stock to be valued at ₹ 6,000
(iv) Create provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on debtors
Prepare necessary ledger accounts and balance sheet after admission.
Answer:

[OR]
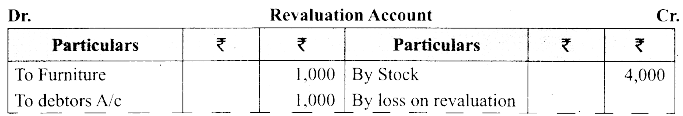
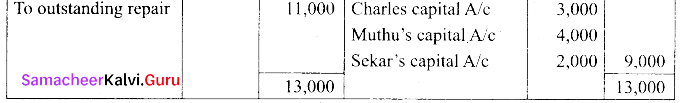
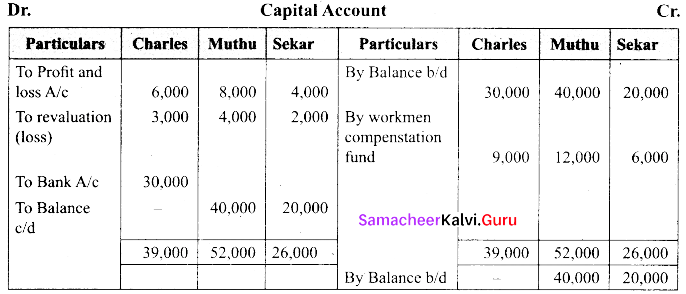
(b) Charles, Muthu and Sekar are partners sharing profits in the ratio 3:4:2. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2018 is as under.
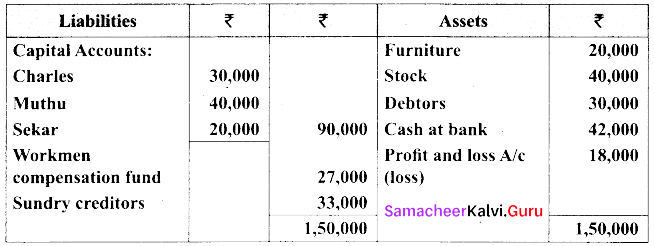
On 1.1.2019 Charles retired from the partnership firm on the following arrangements.
(i) Stock to be appreciated by 10%
(ii) Furniture to be depreciated by 5%
(iii) To provide ₹ 1,000 for bad debtors.
(iv) There is an outstanding repair of ₹ 11,000 not yet recorded
(v) The final amount due to Charles was paid.
Prepare revaluation account, capital account and the balance sheet of a firm after retirement.
Answer:
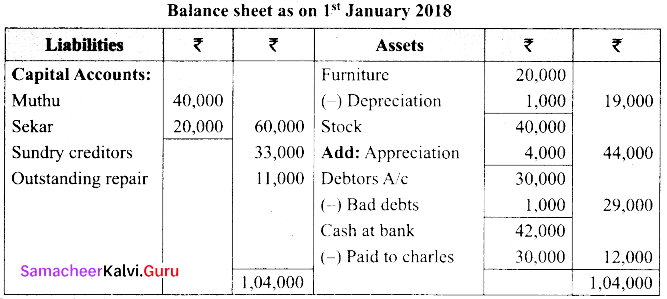
![]()
Question 46.
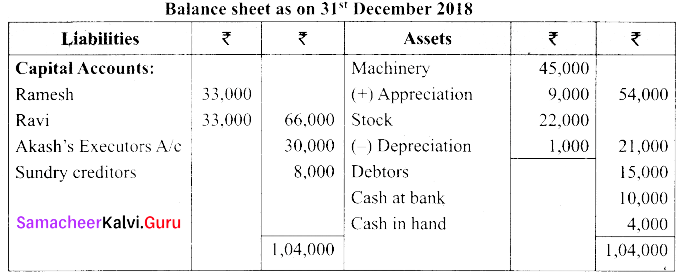
(a) Ramesh, Ravi and Akash are partners who share profits and losses in their capital ratio. Their balance sheet as on 31.12.2017 is as follows.
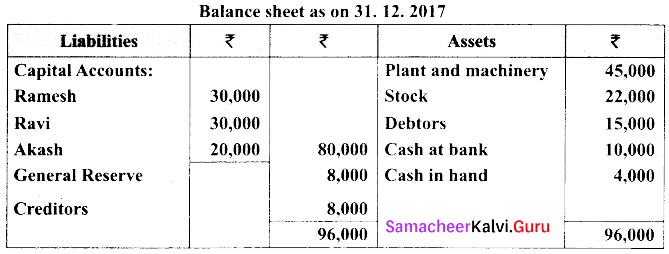
Akash died on 31. 03. 2018. On the death of Akash the following adjustments are made.
(i) Plant and machinery is to be valued at ₹ 54,000.
(ii) Stock to be depreciated by ₹ 1,000.
(iii) Goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹ 24,000.
(iv) Share of profit from the closing of the last financial years to the death of average of the three completed years profit before death. Profit for 2015, 2016 and 2017 were ₹ 66,000; ₹ 60,000 & ₹ 66,000 respectively.
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet.
Answer:
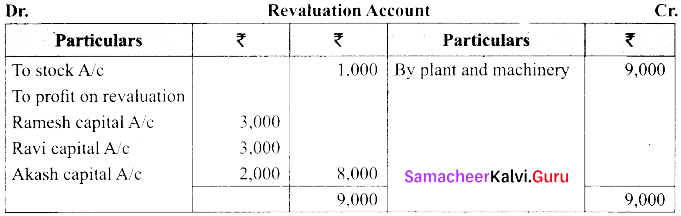
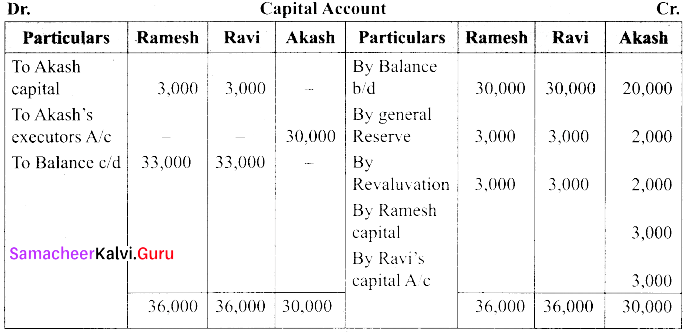
[OR]
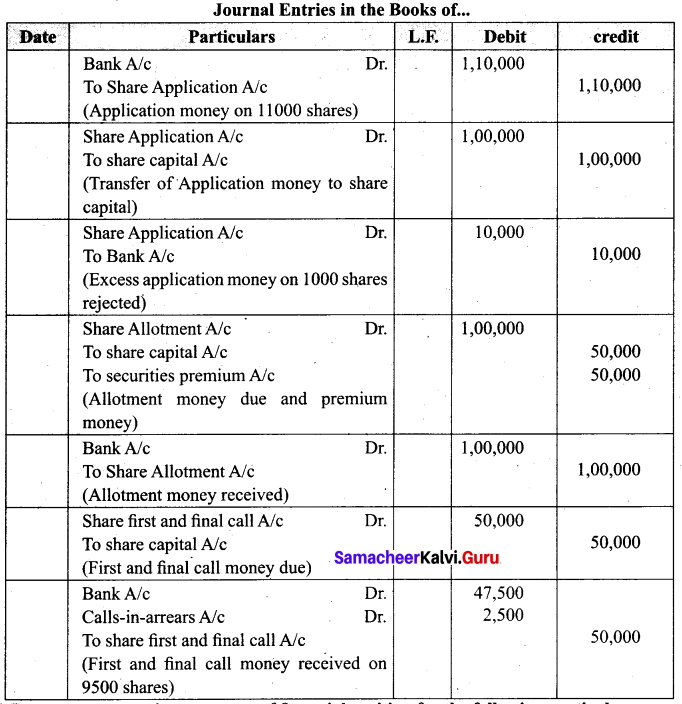
(b) A company issued 10,000 shares of ₹ 20 each a premium of ₹ 5 per share payable ₹ 10/- on application. ₹ 10 on Allotment (including premium) ₹ 5/- on first and final call. The company received 11,000 shares, excess application money was rejected. All money due were received except the final call money on 500 shares. Pass journal entries.
Answer:
![]()
Question 47.
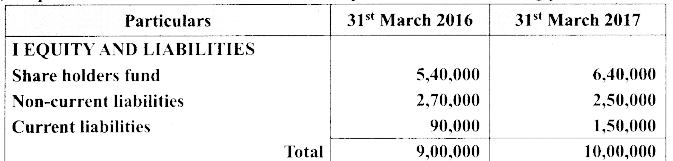
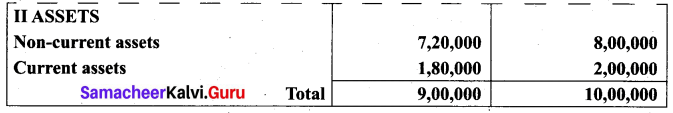
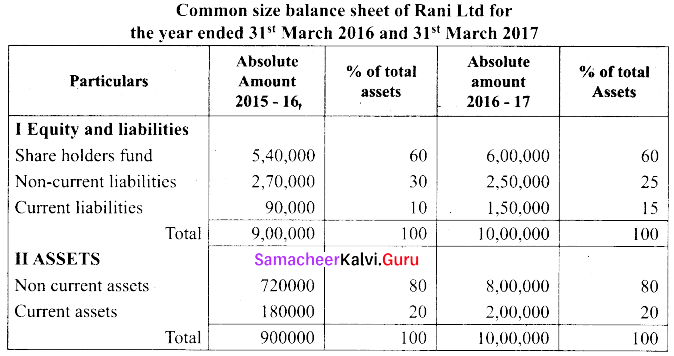
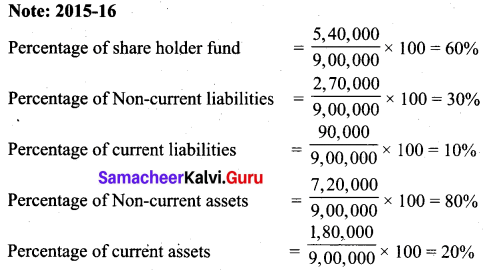
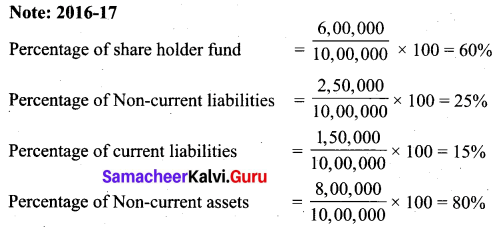
(a) Prepare common size statement of financial position for the following particulars.
Answer:

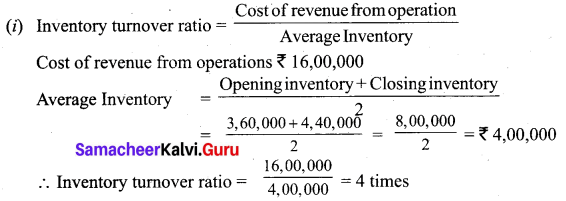
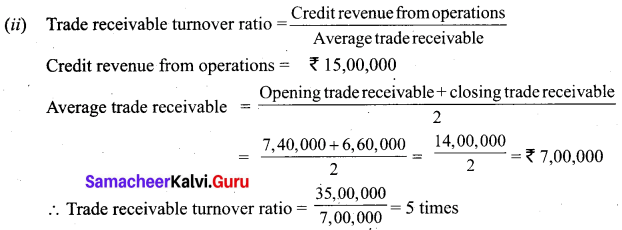
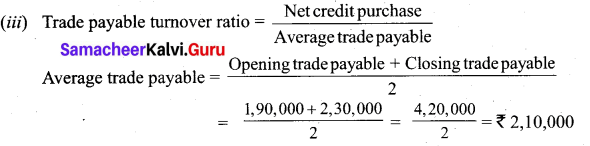
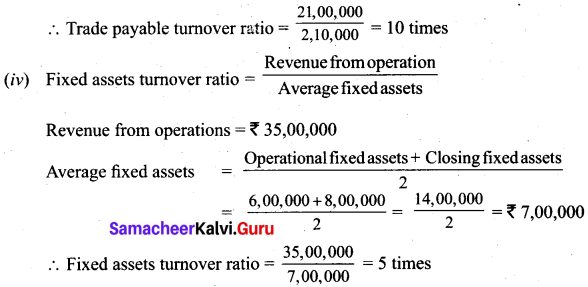
(b) Calculate turnover ratios from the following information from ‘A’ Ltd.
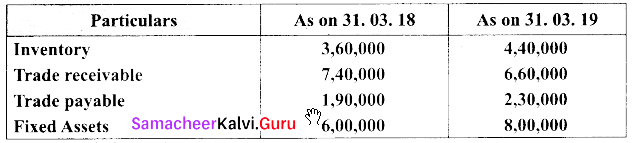
Additional information:
Revenue from operation for the year 35,00,000
Purchases for the year 21,00,000
Cost of revenue from operations 16,00,000
Assume that sales and purchases are for credit.
Answer: