Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Model Question Paper 5
Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Model Question Paper 5 Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Model Question Paper 5
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the sections in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers I to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding – option code.
- Part II has got four sections. The questions are of two marks each. Question numbers 15 to 18 in Section I and Question numbers 19 to 22 in Section II are to be answered in about one or two sentences each. Question numbers 23 to 28 in Section III and IV are to be answered as directed.
- Question numbers 29 to 45 in Part III are of five marks each and have been divided in five sections. These are to be answered as directed.
- Question numbers 46 and 47 in Part IV are of eight marks each. Question number 47 has four questions of two marks each. These are to be answered as directed.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. [14 x 1= 14]
Choose the most suitable answer and write the code with the corresponding answer.
Choose the appropriate synonyms for the italicised words.
Question 1.
The mother seagull swooped upwards.
(a) leap
(b) rush
(c) move very quickly
(d) ascend
Answer:
(a) leap
Question 2.
The attic has always been favourite with children.
(a) loft
(b) terrace
(c) apartment
(d) Strong Room
Answer:
(a) loft
Question 3.
It is a 55-foot sailing vessel built indigenously in India.
(a) fully
(b) collectively
(c) innately
(d) specially
Answer:
(c) innately
Choose the appropriate antonym for the italicised words.
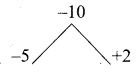
Question 4.
She screamed back mockingly.
(a) disrespectfully
(b) ridiculously
(c) jeeringly
(d) respectfully
Answer:
(d) respectfully
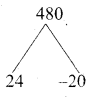
![]()
Question 5.
We don’t have to use any means of repulsion.
(a) attraction
(b) distaste
(c) hate
(d) horror
Answer:
(a) attraction
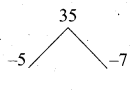
Question 6.
I indulged in banking.
(a) took part
(b) participated
(c) abstained
(d) yielded
Answer:
(c) abstained
Question 7.
Choose the correct plural form of alga from the following:
(a) algum
(b) algi
(c) algae
(d) algas
Answer:
(c) algae
Question 8.
Form a derivative by adding the right suffix to the word – document.
(a) -ory
(b) -ise
(c) -ation
(d) -ly
Answer:
(c) -ation
Question 9.
Choose the correct expansion of the abbreviation SIM.
(a) Subscriber Information Module
(b) Subscriber Identification Module
(c) Student Identification Module
(d) School Identification Module
Answer:
(b) Subscriber Identification Module
Question 10.
Complete the following sentence with the most appropriate phrasal verb given below:
The crew …………………….. of water and food before they could complete their expedition.
(a) ran on
(b) ran about
(c) ran in
(d) ran out
Answer:
(d) ran out
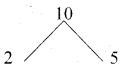
![]()
Question 11.
Choose the suitable option to pair it with the word ‘ watch ’ to form a compound word.
(a) hall
(b) house
(c) man
(d) clock
Answer:
(c) man
Question 12.
Fill in the blank with the most appropriate preposition given below:
Mulan heard this ………….. her tent.
(a) by
(b) from
(c) at
(d) for
Answer:
(b) from
Question 13.
Complete the following sentence using the most appropriate tense form of the verb given below:
After he ………………. his lunch, he went across to the window.
(a) will finish
(b) finish
(c) was finishing
(d) had finished
Answer:
(d) had finished
Question 14.
Choose the most appropriate linker from the given four alternatives.he is ninety years old, he is in the pink of health.
(a) When
(b) Since
(c) Even though
(d) yet
Answer:
(c) Even though
PART – II [10 x 2 = 20]
Section -1
Answer any THREE of the following questions in a sentence or two, [3 x 2 = 6]
Question 15.
Mention the special features of INSV Tarini.
Answer:
Indian Naval Ship Vessel Tarini commissioned to the Indian Navy service on 18th February, 2017, is the second sailboat of the Indian Navy. It is a 55-foot sailing vessel built indigenously in India by M/s Aquarius Shipyard Pvt. Ltd, located in Goa. After undergoing extensive sea trials, she was commissioned to the Indian Navy service.
![]()
Question 16.
What prompted the seagull to fly finally?
Answer:
The seagull was quite hungry and yearned for food. When he saw a piece of fish in the beak of his mother, the sight was quite tempting for him. He was maddened at the sight of the food and suddenly dived at the fish forgetting that he didn’t know how to fly. Thus the young seagull was prompted to fly finally into space.
Question 17.
What was the daily routine of Mr. Sanyal?
Answer:
Sanyal would come every day to Nagen’s Tea Shop, sit at a comer table, have tea and biscuits, pay for the same and leave before it got dark. This was his regular duty after his wife and only son passed away a year ago.
Question 18.
What were the various things that tempted Franz to spend his day outdoors?
Answer
Franz found the warm and bright day to be a temptation to spend his day outdoors. The birds were chirping at the edge of woods. The Pmssian soldiers were drilling in the open field at the back of sawmill. He felt he could gladl> spend life outdoors. Above all, Franz was not prepared for the test on participles.
Section – II
Read the following sets of poetic lines and answer any THREE of the following.
[3 x 2 = 6]
Question 19.
“Let us learn to walk with a smile and a song,
No matter if things do sometimes go wrong;”
(a) What does the poet want everyone to learn?
(b) What should we do when things go wrong?
Answer:
(a) The poetess expects everyone to learn to walk with a smile and a song even when things go wrong.
(b) Even when things go wrong, we need to feel happy and be cheerful.
Question 20.
“She’s a lioness; don’t mess with her.
She ’ll not spare you if you ’re a prankster. ”
(a) How is a woman described here?
(b) Who is a prankster?
Answer:
(a) A woman is described as lionesses whom others should be afraid to play with.
(b) A prankster is a mischievous or malicious person who plays tricks on others.
![]()
Question 21.
“Not a flower could he see,
Not a leaf on a tree.”
(a) Who does ‘he’ refer to?
(b) Mention the season when he could not see a flower or a leaf on a tree.
Answer:
(a) ‘He’ refers to the Cricket.
(b) The season was winter. So he could not see a flower or a leaf on the tree.
Question 22.
“Beside the house sits a tree It never grows leaves.”
(а) What is found near the house?
(b) Why does it never grow leaves?
Answer:
(a) Near the house is found a tree with no leaves.
(b) It never grows leaves because it is eerie.
Section – III
Answer any THREE of the following. [3 x 2 = 6]
Question 23.
Rewrite the following sentence to the other voice.
Answer:
Please assemble in the ground.
You are requested to assemble in the ground.
Question 24.
Rewrite using indirect speech.
Answer:
“Where are we going, sir?” asked the aero-coachman.
The aero-coachman asked the passenger where they were going.
Question 25.
Punctuate the following sentence.
Answer:
Wherefore said miranda did they not that hour destroy us
“Wherefore,” said Miranda, “did they not that hour destroy us?”
Question 26.
Transform the following sentence into a simple sentence.
Answer:
As Catherin is a voracious reader, she buys a lot of books.
Being a voracious reader. Catherin buys a lot of books.
![]()
Question 27.
Rearrange the words in the correct order to make meaningful sentences:
(a) he saw / When / in the / platform/ the train / he rushed.
(b) as /I/ healthy / are you / am / as.
(a) He rushed, when he saw the train in the platform.
Or
(a) When he saw the train in the platform he rushed.
(b) I am as healthy as you are.
Section – IV
Answer the following question:
Question 28.
A stranger wants to visit the library. Write the steps to guide him to reach him destination.
Answer
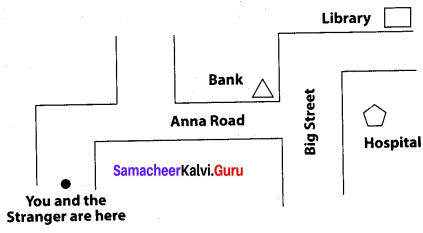
- Go straight and take the first right on Anna Road.
- Proceed further and take the second left after the bank on Big street.
- You will find the Library on the left after you take the right turn.
Section -I
Part – III [10 x 5 = 50]
Answer any TWO of the following in utmost 10 lines. [2 x 5 = 10]
Question 29.
Describe the struggles undergone by the young seagull to overcome its fear of flying.
Answer:
The Young Seagull was afraid to fly and was alone on his ledge. He was more frightened than his siblings. His attempts failed. He had taken a little run forward and tried to flap his wings. But that was all he could do. He felt that his wings would not support him. He failed to muster up the courage and fly. His parents taunted, scolded and threatened him to leave him starving at the ledge unless he flew away. But nothing could make him fly.
The seagull helplessly watched his parents flying with his brothers and sisters. The whole family went on taunting him for his cowardice. Only his mother was looking at him. She had picked a piece of fish and was flying across to him with it. He leaned out eagerly. The mother was very near to him with the fish in her beak. Maddened by hunger, he dived at the fish. With a loud scream, he fell outwards and downwards into space. A terror seized him.
His heart stood still. His mother swooped past him. He answered her with another scream. He saw his two brothers and sister flying around him. The seagull completely forgot that he was not able to fly. He let himself free to dive, soar and curve at will. He was shrieking shrilly. He saw a green sea beneath him. He was tired and weak with hunger. His feet sank into the green sea and his belly touched it. He sank no farther. Now, his family was praising him and their beaks were offering him scraps of fish. He had made his first flight.
“Flying is learning how to throw yourself to the ground and miss.”
Question 30.
‘Technology is a boon to the disabled’. Justify.
Answer:
The differently abled, Alisha and David’s life has been transformed because of Technology. It is a boon to the disabled. Assistive technology is designed to help people with disabilities. Typing was impossible, but now Dragon Dictate helps the disabled to speak for words to be printed on screen. Technology can control a computer screen even with Eye Gaze.
Technology is vital to be free and independent. For verbal communication, Liberator Communication Device, with eye movements to communicate verbally is used. It has a Bluetooth adaptor and took a couple of weeks to learn using it. Communicating with people was very difficult before. An ACTIV controller also in the headrest of a mobility chair is used to control TV, Blu-Ray and music players.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication is also the product of technological advancements and a boon to the disabled. EC02 linked to an interactive whiteboard is used to teach PE lessons. Technology also helps control the Play Station, MP3, electric wheelchair and ECO point Eye Gaze to communicate, access the computer. Thus/Technology is a boon to the disabled’.
“Technology’ is not just a tool. It can give learners a voice
that they may not have had before.”
![]()
Question 31.
How did Watson help his friend to arrest the criminal?
Answer:
Dr. Watson is called by Mrs. Hudson to tend Holmes, who is apparently dying of a rare tropical disease, Tarpaunli fever, contracted while he was on a case at Rotherhithe. Holmes forbids Watson to go near him because the illness is highly infectious. Although Watson wishes to examine Holmes himself or send for a specialist, Holmes demands that Watson wait several hours before seeking help.
While Watson waits, he examines several objects in Holmes’s room. Holmes is angered when Watson touches things on his table stating his dislike for people fidgeting his things. At six o’clock, Holmes asks Watson to turn the gaslight on, but only half-full. He then instructs Watson to bring Mr. Culverton Smith from 13 Lower Burke Street to see Holmes but to make sure that Watson returns to Baker Street before Smith arrives. Watson goes to Smith’s address. Although Smith refuses to see anyone, Watson forces his way in. Once Watson explains his duty on behalf of Sherlock Holmes, Smith’s assertiveness changes significantly. Smith agrees to come to Baker Street within half an hour.
Watson excuses himself, saying that he has another appointment, and returns to Baker Street before Smith’s arrival. Believing that they are alone, Smith is frank with Holmes. It soon appears, to the hiding Watson’s horror, that Holmes has been sickened by the same illness that killed Smith’s nephew Victor. At the fend, Holmes calls for Watson to come out from behind the screen, to present himself as another witness to the conversation. Holmes explains his illness was feigned as a trick to induce Smith to confess to his nephew’s murder. Starving himself for three days and claiming to be suffering from a deadly infectious disease was to keep Watson from examining him and discovering the ruse, since, as he clarifies, he has every respect for his friend’s medical skills.
‘A detectives perspective traps the criminal.’
Question 32.
‘Man does change with time’-What were the various changes that came about in Aditya?
Answer:
Man does change with time. According to Sanyal, Aditya was a boy who could never compete him in scholastic or non-scholastic activities. He was a liar and an envious personality. But, years later Aditya no longer is the same personality. He is more matured and responsible. His childish nature makes him feel guilty for stealing the medal that belonged to Sanyal. Aditya now wanted to restore Sanyal, his lost happiness. Knowing about his financial constraints, he decides to give him the cost of the silver medal. He drives with a firm determination to his ancestral house. When he reaches, he rushes to the attic. Aditya gets on top of a packing case
and pushes his hand inside the ventilator, upsetting a sparrow’s nest. However, he heaves a sigh of relief when he gets what he had been looking for. He goes straight to the Jeweller to determine the current rate of the medal in the market. All these surely show a remarkable change in him. Even when Sanyal behaves rudely, Aditya is courteous and friendly. His only intention is penitence. He is so mature that he even understands and justifies the grievances Sanyal had in his heart. When Sanyal prefers the medal, without second thoughts he restores it to Sanyal whole-heartedly.
“Change is universal.”
![]()
Section – II
Answer any TWO of the following in utmost 10 lines. [2 x 5 = 10]
Question 33.
How is mystery depicted in the poem ‘The House on Elm Street’.
Answer:
Nadia Bush the poetess talks about a house that stood alone in an isolated place on Elm Street. No one knows what happens inside that house and it is very mysterious. Even by looking from outside, one can easily say that it has a vast space but at the same time it is bare to the bone meaning there is no one living inside the mysterious house or no basic necessities inside the house on Elm Street.
Generally at night, the house looks like it is alive with people in if Lights are switched on and off. It gives a feel that someone is inside the house. When Nadia sees such a situation, she is tempted to go inside the house to just take a look and see what is actually happening inside the house. However, Nadia the poetess is frightened and never dares to do so. Every day the poetess, drives past the house. The house seems to look a bit brighter.
The very thought of this mysterious house plays with your mind since it is just one house of this kind in the area around. Next to the house, is also a tree with no leaves the whole year round. It doesn’t grow tall nor does it shrink in size. The tree too is mysterious like the house since it has no leaves in any of the seasons to make wonder how a tree could survive without any leaves or without any growth. Every day, the house also begins to fade making it all the more mysterious.
“The best secrets are the most twisted.”
Question 34.
Compare and contrast the attitude of the ant and the cricket.
Answer:
The poem, ‘The Ant and the Cricket’ is about a careless cricket and a hardworking ant. We all know that ants are hardworking creatures but on the other hand, the Cricket is portrayed as a lazy being. He made no efforts to plan for the future. Thus, the cricket is shown as a young and silly creature because he sang all through summer and spring with no worries in the world for winter that was to come. But when winter arrived, he began to complain that he would die of starvation and hunger.
He found that his cupboard was empty with no piece of bread to eat. He neither found a leaf, nor a flower. Everything was covered with snow. Therefore, the cricket cried and moaned as he perceived his bad future. Finally, deprived of hunger and starvation, being all wet and cold, the cricket journeyed to the house of the stingy ant. Becoming bold by nature, he begged for food and shelter. But the Ant is wise, foresees its needs for winter and prudently turned down the foolish Cricket. The Ant clearly stated that Ants neither borrow nor lend.
So the Ant is shown as a straightforward and outspoken personality. Perhaps the cricket here is portrayed as a person who makes false promises and the Ant is portrayed to be a strong personality not carried away by the false promises of one. Therefore the Ant could never be exploited though it was humble enough to admit it to be a servant and friend of the Cricket. The Cricket was surely careless and reckless against the Ant who was judicious, discrete and level-headed.
“Accept responsibility for your life. Know that it is
you who will get you where you want to go, no one else”
Question 35.
Read the following stanza and answer the questions given below.
“The weather is always too hot or cold;
Summer and winter alike they scold.
Nothing goes right with the folks you meet Down on the gloomy Complaining street.’’
(i) Pick out the rhyming words from the above lines.
(ii) Write the rhyme scheme of the given stanza.
(iii) Identify the figure of speech employed in the fourth line of the given stanza.
(iv) Pick out the alliterating words.
Answer:
(i) The rhyming words are cold-scold and meet-street.
(ii) The rhyme scheme of the poem is aabb.
(iii) The figure of speech employed in the fourth line of the given stanza is Personification.
(iv) There aren’t any consonant sounds repeated in the words in a line. However the vowel ‘ sounds in and alike are repeated in the second line.
Question 36.
Paraphrase the following stanza.
We can pull and haul and push and lift and drive,
We can print and plough and weave and heat and light,
We can run and race and swim and fly and dive,
We can see and hear and count and read and write!
Answer:
In this stanza, the machines elucidate how they can serve human race by doing all the possible human activities mastered by them. They say they can do various tasks such as pulling, carrying, pushing, lifting, driving, printing, ploughing, weaving, heating, lighting, running, racing, swimming, flying, diving, seeing, hearing, counting, reading and writing.
Section – III
Answer any ONE of the following: [1 x 5 = 5]
Question 37.
Rearrange the following sentences in coherent order.
(i) Using his powers, Prospero released the good spirits from large bodies of trees.
(ii) Prospero and Miranda came to an island and lived in a cave.
(iii) He raised a violent storm in the sea to wreck the ship of his enemies.
(iv) The king of Naples and Antonio the false brother, repented the injustice they had done to Prospero.
(v) He ordered Ariel to torment the inmates of the ship.
Answer:
Rearranged number sequence: (ii), (i), (iii), (v), (iv)
(ii) Prospero and Miranda came to an island and lived in a cave.
(i) Using his powers, Prospero released the good spirits from large bodies of trees.
(iii) He raised a violent storm in the sea to wreck the ship of his enemies.
(v) He ordered Ariel to torment the inmates of the ship.
(iv) The king of Naples and Antonio the false brother, repented the injustice they had done to Prospero.
![]()
Question 38.
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
Answer
The country Shining was governed by a despotic leader who though a warrior, had a great and cowardly shrinking from anything suggestive of failing health and strength. This caused him to send out a cruel proclamation. The entire province was given strict orders to immediately put to death all aged people. Those were barbarous days, and the custom of abandoning old people to die was not uncommon.
The poor farmer loved his aged mother with tender reverence, and the order filled his heart with sorrow. But no one ever thought twice about obeying the mandate of the governor, so with many deep and hopeless sighs, the youth prepared for what at that time was considered the kindest mode of death.
(i) Who governed Shining?
(ii) What was the cowardly act of the governor?
(iii) What proclamation did the governor send out?
(iv) How did the poor farmer treat his mother?
(v) Did the people obey the governor’s order?
Answer:
(i) Shining was governed by a despotic leader.
(ii) The governor had a great and cowardly shrinking from anything suggestive of failing health and strength.
(iii) The governor sent out a cruel proclamation in the entire province giving strict orders to immediately put to death all aged people.
(iv) The poor farmer loved his aged mother with tender reverence.
(v) Yes, the people obeyed the governor’s order.
Section – IV
Answer any FOUR of the following. [4 x 5 = 20]
Question 39.
Prepare an attractive advertisement using the hints given below.
Home appliances – Aadi Sale – 20-50% – Special Combo Offers – Aadhi & Co., Raja Street, Chennai, Chennai.
Answer:

Question 40.
Write a letter to the manager of a famous daily, ordering subscription for your school library.
Answer:
From
The Librarian
Indira Gandhi Hr. Sec. School,
Rajajipuram Chennai – 600 087
12.11.2020
To
The Higgin Bothams,
Anna Salai,
Chennai-600 002 Respected Sir,
Sub: Annual subscription for daily.
I would like to place an order for the annual subscription of three English dailies and one Tamil daily to our School from the 1st of January 2020.
| The Hindu | 3 copies | @ 435/- each p.a. | 1305.00 |
| The Times of India | 3 copies | @ 365/- each p.a. | 1095.00 |
| The New Indian Express | 3 copies | @ 425/- each p.a. | 1275.00 |
| Thina Thanthi | 3 copies | @ 175/- each p.a. | 525.00 |
| 4200.00 | |||
Please find enclosed the Annual subscription amount for all the four dailies which amount to Rs. 3780/- (Rupees Three Thousand Seven Hundred and Eighty Only) after deducting the usual 10% discount that you give us.
Thank you very much for your continued support to our institution.
Yours sincerely,
Mrs. Anand – Librarian
Address on the envelope:
The Higgin Bothams,
Anna Salai,
Chennai-600 002
![]()
Question 41.
You are Adhira / Athiran, school pupil leader of GHSS, Trichy. Prepare a notice on behalf of your school inviting the grandparents of the students to celebrate World Elders’ Day in your school auditorium on the 20th of next month.
Answer:
|
Government Higher Secondary School, Trichy On behalf of the school, I invite every’ grandparent of the students in this school to be a part of the World Elder’s Day. We will be celebrating World Elder’s Day in our school auditorium on the 20th of February, 2020. Please bring in your grandparents to school at 10 a.m. Lots of fun-filled activities await your grandparents. The programme will end with a buffet arranged by the management of the school to honour them. Adhira/Athiran School Pupil Leader |
Question 42.
Look at the following picture and express your views an it in about five sentences
Answer:

Though we pray for rain, it’s such a sad state to see people stranded when an area gets flooded. There is about three feet water and people are moving out to safer places. Fathers carry their sons and daughters over the shoulders in order to keep them safe. If there is proper drainage system and proper maintenance by the Corporation, we can surely avoid such disasters. In certain states, natural disaster such as flooding is a frequently witnessed problem.
Question 43.
Make notes or write a summary of the following passage.
Answer:
There are many different kinds of books that are published each year. These are the new’ titles available for us to read. Besides these, there are books that have been published through the years. Together, there are millions of books available throughout the world in as many languages as are spoken by people. There are different genres in which books are published. There are fiction and non-fiction categories in books, and each of these categories has many different genres of books.
The academic books we study at school belong to the text book category. We smdy them to complete our syllabus and pass the examinations at the end of each academic session. There are other books that we read for our pleasure and enrichment. We read story books of different types. There are comedy, horror, detective and thriller stories in prose, plays and poetry forms. Books are our best friends.
Notes
Title: Books Galore
Dif. Kinds A Books
(i) New Titles;
(ii) Publd Every Yr;
(iii) Publd Thru’ The Yrs;
(iv) Publd Thru’out the World;
(v) Publd In Many Langs
Dif. Genres Of Books
(i) Fiction;
(ii) Non-Fiction Categs
Academic Books – Text Book Categy.
For Study – Pres. Syl.
Pass Exams – End A Academic Session.
Books For Pleasure &Enrichment
Books Of Different Types
Comedy, Horror, Detective & Thriller Stories
Various Forms
(i) Prose
(ii) Plays; &
(iii) Poetry Forms Conclusion: Books are our best friends.
Abbreviations used: Dif. – different; A -of; publd.- published; yr=year; thru’- through; langs.- languages; pres. – prscribed; syl-syllabus; & – and
Summary
Title: Books Galore
Rough Draft
There are different kinds of books published every year for us to read. Together, there are millions of books-avaiable throughout the world in many languages. There are different genres such as fiction and non friction categories. The academic books we study at school belong to the text book category. We study them to be tested at the end of each academic session. We read story books for pleasure and enrichment/Here-areaymiedy, horror, detective and thriller stories in prose, plays and poetry forms. Books are our best friends .
Fair Draft:
Title: Books Galore
Millions of books are published every year in different languages. There are different genres such as fiction and non-fiction. The academic books, belong to the text book category. We study them to be tested at the end of the academic year. We read various types of story books for pleasure. Books are our best friends.
No. of words written in the summary: 55
![]()
Question 44.
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
(а) You may speak politely to the elders.
(b) This is the boy whom won the race
(c) He come late to school every day.
(d) Though he was hungry hut he did not eat.
(e) Is this a book that you wanted to buy.
Answer
(a) You must speak politely to the elders.
(b) This is the boy who won the race
(c) He comes late to school every day.
(d) Though he was hungry he did not eat.
(e) Is this the book that you wanted to buy.
Section – V
Quote from memory. [1 x 5 = 5]
Question 45.
Let me but live ……………. back in fear.
Answer:
Let me but live my life from year to year,
With forward face and unreluctant soul;
Not hurrying to, nor turning from the goal; .
Not mourning for the things that disappear
In the dim past, nor holding back in fear
Part – IV
Write a paragraph of about 150 words by developing the following hints. [2 x 8 = 16]
Question 46.
(а) Many years ago – China – the emperor ordered – one man from -family – join army
– Mulan heard -told father – she join army – father objected – she is a girl – Mulan – fathers robes cuts her hair – convinced father – she has learnt – Kung Fu – no one will find – she is a girl. – Mulan left – village – fought bravely – war – given top position – very soon – fever swept – the army -Mulan – sick – doctor examines – finds the truth – spreads the news in the army – everyone objects – to follow a girl leader – Mulan stood tall – gave command – soldiers – followed her – attacked enemies – won the battle- emperor glad – offered Mulan positions – court – Mulan refused – went back – village – royal – gifts.
Answer:
The Story of Mulan portrays the legendary Chinese warrior Hua Mulan. This old Chinese folktale is about the story of the young Chinese maiden who leams that her wizened, old and frail father is to be called up into the army in order to fight the invading Huns by the Chinese Emperor. When the Huns invade China, one man from every family is called to arms. She hears of the order that every family must send one man to the army while washing clothes.
Mulan’s father, who is frail and aged decides to fight for his country though it is clear that he will not survive an enemy encounter. He decides to go to war but is prevented by her daughter with her outrageous decision. Knowing her father’s frail state, she decides to disguise herself and join in his place without second thoughts. In the army, Mulan proves to be a brave soldier who is later put in charge of other soldiers. Her battles goes so well that more soldiers are added. After a few years, Mulan becomes the General of the entire army. Suddenly, bad fever swept through the army. Many soldiers including Mulan become a prey. The arrival of the doctor brings to light the hidden truth.
![]()
Many soldiers disapprove such a thought, though some soldiers see the winning chances. Just then a soldier announces the surprise attack by the enemies. With no time to debate, the soldiers spring to action at the command of the General who hears this from inside her tent. She gets dressed and though not strong, she stands tall. She instructs the soldiers to attack knowing very well her strategic planning that all her soldiers acknowledge and win the battle. It was such a big victory that the enemy gave up, at last. The war was over, and China was saved! The Emperor forgives Mulan and was glad that Mulan had ended the long war. He wanted Mulan to stay with him in the palace and be an advisor but as she chose to go to her family, the emperor gave her six horses and six fine swords so that her people will know that he thinks of her.
[OR]
(b) Holland – land – below sea level – dikes protected the country – everyone did best to -protect – Holland – Years ago – boy Peter – lived Holland – His father – attended – dykes gates – opened- closed dikes – one day – Peter Mother – gave cakes to Peter – to be given – old blind friend of Peter – across the dike Peter happily left home – Peter visited – old man – returned near by the dike – heard water trickling – stopped to see – small hole – dike – called for help – in vain -he put his little finger – throughout the
night – slept near the dike – morning – found by passer by – alerted the people – Peter and Holland -saved.
Answer:
Peter is a little boy who lived in Holland. His father took care of the dikes called sluices so that ships could pass out of Holland’s canals into the sea. On a beautiful day in Autumn, Peter was asked to go and give cakes to his blind friend who lived on the other side of the dike by his mother. After about an hour he returned home, but the climate had changed. It was raining and the water in the channel was rising. All of a sudden he heard the sound of dribbling water and he wondered from where the sound came. He then saw a small hole in the dike.
He knew what that meant and due to the pressure of the water the hole would not stay the same. He feared danger. He climbed onto the dike and put his finger in the hole and hoped for someone to come to his help and cried out aloud. His mother mistook him to have stayed back with his blind friend and retired to bed. The boy was sure that he had to stay awake the entire night and keep his finger in the hole to arrest the water from flooding Holland.
The water in the canal was rising and if he would remove his finger from the hole in the sluice, the water would gush through and make the hole bigger and bigger. The town would obviously flood. When dawn broke, a man going to work heard the sound of Peter groaning and wondered what the little boy was up to. He was shocked at his reply but understood the danger and called for help. People came in with shovel and mended the hole. Peter was carried home and they all hailed him as the brave boy who saved Holland from drowning.
![]()
Question 47.
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
Kung Fu – ‘kung’ meaning ‘energy’ and ‘fu’ meaning ‘time’ – is a Chinese martial art whose recorded history dates back to around 525 CE, during the Liang dynasty. The man credited with introducing martial arts to China is said to be an Indian monk known as Bodhidarma.
Many people have a misconception that Chinese Kung Fu is about fighting and killing. It is actually based on Chinese philosophy and is about improving wisdom and intelligence. Taoist philosophy is deeply rooted in and had a profound influence on the culture of Chinese martial arts.
The five traditional animal styles of Shaolin Kung Fu are the dragon, the snake, the tiger, the leopard and the crane. The union of the five animal forms clearly displayed the efficacy of both hard and soft movements, of both internal and external energy – this form of Chinese martial arts was known as Shaolin Kung Fu, named after the temple in which it was developed.
Questions.
(a) Which country does the martial art Kung Fu belong to?
(b) What is the meaning of the term “Kung Fu”?
(c) Write any two martial arts of India?
(d) What are the five animal styles followed in Shaolin Kung Fu?
Answer:
(a) The martial art Kung Fu belongs to the country China.
(b) The term ‘kung’ means ‘energy’ and ‘fu’ means ‘time’.
(c) Kalari and Silambam are two martial arts in India.
(d) The five traditional animal styles of Shaolin Kung Fu are the dragon, the snake, the tiger, the leopard and the crane.
[OR]
Read the following poem and answer the questions given below:
If you can’t be a pine on the top of the hill,
Be a scrub in the valley – but be
The best little scrub by the side of the rill;
Be a bush, if you can’t be a tree.
If you can’t be a bush, be a bit of the grass,
And some highway happier make;
If you can’t be a muskie, then just be a bass- But the liveliest bass in the lake!
We can’t all be captains, we’ve got to be crew,
There’s something for all of us here.
There’s big work to do and there’s lesser to do
And the task we must do is the near.
If you can’t be a highway, then just be a trail,
If you can’t be the sun, be a star;
It isn’t by size that you win or you fail- Be the best of whatever you are!
Questions.
(a) Where does the best scrub grow?
(b) What makes a highway traveller happy?
(c) Does size matter? Give reason.
(d) What is the underlying theme of the poem?
Answer:
(a) The best scrub grows by the side of a rill.
(b) The green grass on the sides of a highway makes a highway traveller happy.
(c) No, size doesn’t matter because its winning and being the best in whatever you do that matters.
(d) Be your best in all that you try to do and accomplish in life.