Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and Writing the option code and the Corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 4 in Part II are two-marks questions. This also is answered in about one or list sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Identify the Archaebacterium.
(a) Acetobacter
(b) Erwinia
(c) Treponema
(d) Methanobacterium
Answer:
(d) Methanobacterium
![]()
Question 2.
Endosperm in gymnosperm is formed ……………….
(a) at the time of fertilization
(b) before fertilization
(c) after fertilization
(d) along with the development of embryo
Answer:
(b) before fertilization
Question 3.
A true fruit is the one, where
(a) only ovary of the flower develops into fruit
(b) ovary and calyx of the flower develops into fruit
(c) ovary, calyx and thalamus of the flower develops into fruit
(d) all floral whorls of the flower develops into fruit
Answer:
(a) only ovary of the flower develops into fruit
Question 4.
Which of the following electron opaque chemical is used in Electron microscope?
(a) Strontium
(b) Deuterium
(c) Palladium
(d) Uranium
Answer:
(c) Palladium
![]()
Question 5.
In S phase of the cell cycle………………..
(a) Amount of DNA doubles in each cell
(b) Amount of DNA remains same in each cell
(c) Chromosome number is increased
(d) Amount of DNA is reduced to half in each cell
Answer:
(a) Amount of DNA doubles in each cell
Question 6.
Rolling & unrolling of leaves due to whether change are controlled by………………..
(a) Sensory cells
(b) Motor cells
(c) Subsidory cells
(d) Trichomes
Answer:
(b) Motor cells
Question 7.
The inhibitory effect of oxygen in photosynthesis was first discovered by ……………………….
(a) Warburg
(b) Van Helmont
(c) Dutrochet
(d) Desaussure
Answer:
(a) Warburg
![]()
Question 8.
The most widely occuring cytokinin in plants is ………………
(a) Iso propyl adenine
(b) Iso pentenyl adenine
(c) Indole propionic acid
(d) Iso propionic adenine
Answer:
(b) Iso pentenyl adenine
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Define bacteria and bacteriology.
Answer:
Bacteria are prokaryotic, unicellular, ubiquitous, microscopic organisms. The study of bacteria is called bacteriology.
Question 10.
Why do we use the term ‘form genera’ for fossil plants?
Answer:
The term ‘form genera’ is used to name the fossil plants because the whole plant is not recovered as fossils instead organs or parts of the extinct plants are obtained in fragments.
Question 11.
Where does the inflorescence axis arise in cauliflorous type of inflorescence?
Answer:
In cauliflorous type, inflorescence developed directly from a woody trunk.
Example: Theobroma cocoa.
Question 12.
Compare pinnate (or) unicostate venation and palmate (or) multicostate venation.
Answer:
Pinnate (or) unicostate venation
In pinnate (or) unicostate there is only one prominent midrib.
Palmate (or) multicostate venation
In palmate (or) multicostate there are many midribs running parallel to each other.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw and label (a) Branchysclereids (b) Osteoclereids
Answer:
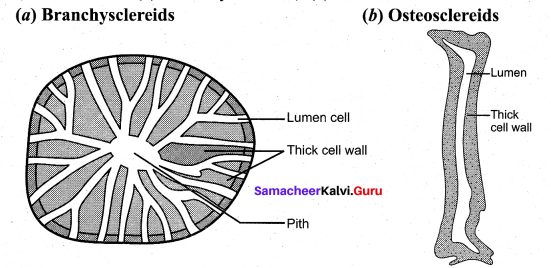
Question 14.
Nitrogen is a Macronutrient – Justify.
Answer:
Nitrogen (N) is required by the plants in greatest amount. It is an essential component of proteins, nucleic acids, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, alkaloids, chlorophyll and cytochrome.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
How the vascular plants dominate the Earth?
Answer:
The success and dominance of vascular plants is due to the development of,
- Extensive root system.
- Efficient conducting tissues.
- Cuticle to prevent desiccation.
- Stomata for effective gaseous exchange.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the three different types of trailers with an example.
Types of Trailers:
- Prostrate (Procumbent): A stem that grows flat on the ground, e.g., Evolvulus alsinoides, Indigofera prostrata.
- Decumbent: A stem that grows flat but becomes erect during reproductive stage. e.g., Portulaca, Tridax, Lindenbergia.
- Diffuse: A trailing stem with spreading branches, e.g., Boerhaavia diffusa, Merremia tridentata.
Question 17.
Name any three synthetic auxins.
Answer:
- 2,4-Dichloro Phenoxy Acetic Acid (2,4-D)
- 2,4,5-Trichloro Phenoxy Acetic Acid (2,4,5-T)
- Napthalene Acetic Acid (NAA)
Question 18.
Compare the Gynoecium of Pisum sativum and Datura metal.
Answer:
Gynoecium of Pisum sativum :
- Mono Carpellary
- Unilocular
- Ovules on marginal placentation
- Feathery stigma
Gynoecium of Datura metal :
- Bicarpellary
- Tetralocular
- Ovules on axile placentation
- Bilobed stigma
Question 19.
Draw the diagram representing oxygen evolving complex.
Answer:
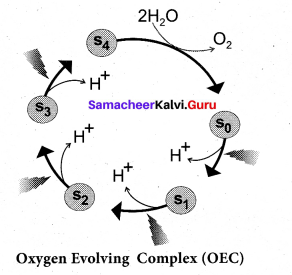
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Tabulate the differences between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
Answer:
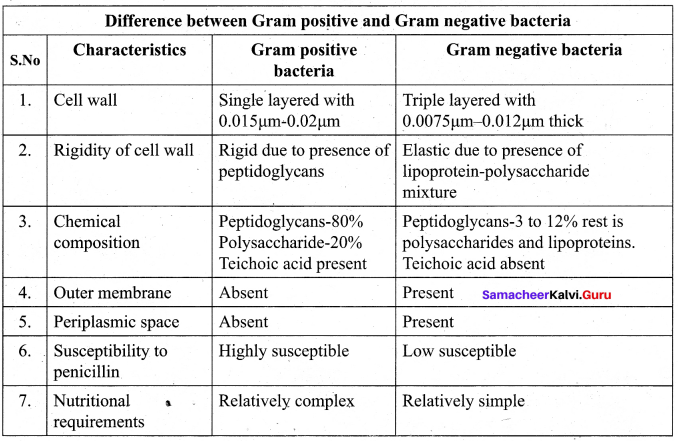

[OR]
Explain Allium cepa in botanical terms. Draw floral diagram.
Answer:
Botanical description of Allium, cepa:
- Habit: Perennial herb with bulb.
- Root: Fibrous adventitious root system
- Stem: Underground bulb
- Leaf: A cluster of radical leaves emerges from the underground bulb, cylindrical and fleshy having sheathy leaf bases with parallel venation.
- Inflorescence: Scapigerous i.e. the inflorescence axis (peduncle) arising from the ground
bearing a cluster of flowers at its apex. Pedicels are of equal length, arising from the apex of the peduncle which brings all flowers at the same level. - Flower: Small, white, bracteate, ebrcteolate, pedicellate, complete, trimerous, actinomorphic and hypogynous, Flowers are protandrous.
- Perianth: Tepals 6, white, arranged in two whorls of three each, syntepalous showing valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens 6, arranged in two whorls of three each, epitepalous, apostamenous free and opposite to tepals. Anthers dithecous, basifixed, introse and dehiscing longitudinally.
- Gynoecium: Tricarpellary and syncarpous. Ovary superior, trilocular with two ovules in
each locule on axile placentation. Style simple, slender with simple stigma. - Fruit: A loculicidal capsule.
- Seed: Endospennous
- Floral Formula:
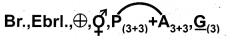
Question 21.
Differentiate between C3 & C4 plants.
Answer:
Differences between C3 and C4 plants
C3 Plants:
- CO2 fixation takes place in mesophyll cells only.
- CO2 acceptor is RUBP only.
- First product is 3C- PGA.
- Kranz anatomy is not present.
- Granum is present in mesophyll cells.
- Normal Chloroplast.
- Optimum temperature 20° to 25°C.
- Fixation of CO2 at 50 ppm.
- Less efficient due to higher photorespiration. ,
- RUBP carboxylase enzyme used for fixation.
- 18 ATPs used to synthesize one glucose.
- Efficient at low CO2.
- Example: Paddy, Wheat, Potato and so on. –
C4 Plants :
- CO2 fixation takes place mesophyll and bundle sheath.
- PEP in mesophyll and RUBP in bundle sheath cells.
- First product is 4C- OAA.
- Kranz anatomy is present.
- Granum present in mesophyll cells and absent in bundle sheath.
- Dimorphic chloroplast.
- Optimum temperature 30° to 45°C.
- Fixation of CO2 even less than 10 ppm.
- More efficient due to less photorespiration.
- PEP carboxylase and RUBP carboxylase used.
- Consumes 30 ATPs to produce one glucose.
- Efficient at higher CO2.
- Example: Sugar cane, Maize, Sorghum, Amaranthus and so on.
[OR]
Classify and explain the plants based on photoperiodism.
Answer:
- Long day plants: The plants that require long critical day length for flowering are called long day plants or short night plants. Example: Pea, Barley and Oats.
- Short long day plants: These are long day plants but should be exposed to short day lengths during early period of growth for flowering. Example: Wheat and Rye.
- Short day plants: The plants that require a short critical day length for flowering are called short day plants or long night plants. Example: Tobacco, Cocklebur, Soybean, Rice and Chrysanthemum.
- Long short day plants: These are actually short-day plants but they have to be exposed to long days during their early periods of growth for flowering. Example: Some species of Bryophyllum and Night jasmine.
- Intermediate day plants: These require a photoperiod between long day and short day for flowering. Example: Sugarcane and Coleus.
- Day neutral plants: There are a number of plants which can flower in all possible photoperiods. They are also called photo neutrals or indeterminate plants. Example: Potato. Rhododendron, Tomato and Cotton.
![]()
Bio-Zoology[Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [1 × 8 = 8]
Question 1.
True species are ………………….
(a) Interbreeding
(b) Sharing the same niche
(c) Feeding on the same food
(d) Reproductively isolated
Answer:
(d) Reproductively isolated
Question 2.
Which of the following snakes is non-poisonous?
(a) Cobra
(b) Krait
(c) Viper
(d) Python
Answer:
(d) Python
![]()
Question 3.
Match the List I and List II:

(a) 1 – (iv) 2 – (i), 3 – (ii), 4 – (Hi)
(b) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
(c) 1 – (iv), 2 – (ii), 3 – (i), 4 – (iii)
(d) 1 – (ii), 2 – (iv), 3 – (iii), 4 – (i)
Answer:
Question 4.
JMV stands for …………….
(a) Juxta medullary nephrons
(b) Juxta memory nephrons
(c) Juxta medullary neuron
(d) Juxta memory neuron
Answer:
(a) Juxta medullary nephrons
Question 5.
Which of the following is an correct statement?
(a) Tuberculosis is a condition in which the pleura becomes inflammed.
(b) Pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that occurs in the lungs.
(c) Asthma is an infectious disease caused due to mycobacterium tuberculosis.
(d) Lung cancer is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes.
Answer:
(b) Pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that occurs in the lungs.
Question 6.
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Axial skeleton contains 80 bones.
(b) Appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones.
(c) Skull contains 28 bones.
(d) Vertebral column contains 26 bones in adults.
Answer:
(c) Skull contains 28 bones
Question 7.
Visual area is located in …………….
(a) Occipital lobe
(b) Parietal lobe
(c) Frontal lobe
(d) Temporal lobe
Answer:
(a) Occipital lobe
![]()
Question 8.
It is the parathyroid gland.
(a) Decreases blood Ca+2 level
(b) Increases blood Ca+2 level
(c) Promotes collagen synthesis by osteoblasts
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Decreases blood Ca+2 level
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 x 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What is cladogram?
Answer:
A tree diagram which represents the evolutionary relationship among organisms in known as cladogram.
Question 10.
Distinguish between radiate and bilateria.
Answer:
Radiata
- These include radially symmetrical animals.
- These are diploblastic eg. Cnidarians, Ctenophores
Bilateria :
- These include bilaterally symmetrical animals.
- These are triploblastic eg. flat-worms.
Question 11.
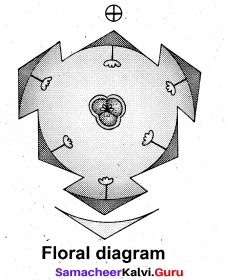
Draw the diagram of Balanoglossus and label the parts.
Answer:
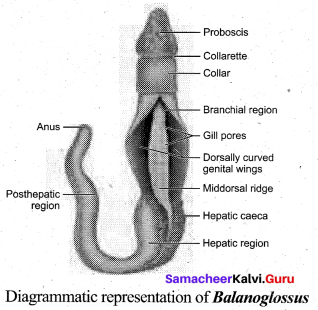
Question 12.
What are the components of food?
Answer:
The components of food are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, fibre and water.
![]()
Question 13.
What is Osmotic regulation?
Answer:
Osmotic regulation is the control of tissue osmotic pressure which acts as a driving force for movement of water across biololgical membranes.
Question 14.
What is periosteum?
Answer:
The external surface of the bone is covered by a double layered membrane called periosteum.
![]()
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What are the three domains of life?
Answer:
Three domain classification was proposed by Carl Woese (1977) and his co-workers. They classified organisms based on the difference in 16s rRNA genes. This adds the taxon domain higher than the kingdom. In this system, prokaryotes are divided into two domains-bacteria and Arachaea. All eukaryotes are placed under the domain Eukarya. Archae appears to have common features with Eukarya. Archaea differ from bacteria in cell wall composition and differ from bacteria and eukaryotes in membrane composition and rRNA types.
Question 16.
Define typhlosole.
Answer:
The dorsal wall of the ftitestine of earthworm is folded into the cavity as the typhlosole.
This fold contains blood vessels and increases the absorptive area of the intestine.
Question 17.
Differentiate parazoa and eumetazoa.
Parazoa :
These include multicellular animals whose cells are loosely arranged without the formation of tissues or organs, e.g. sponges
Eumetazoa :
These include multicellular animals with well defined tissues, organs and organ systems.
![]()
Question 18.
Draw the diagram and label the parts of neuron.
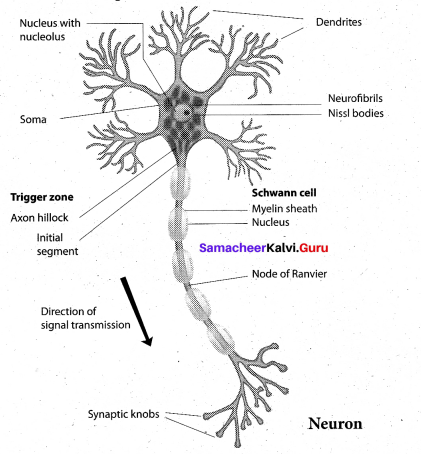
Question 19.
What are the different types of silk worms?
Answer:
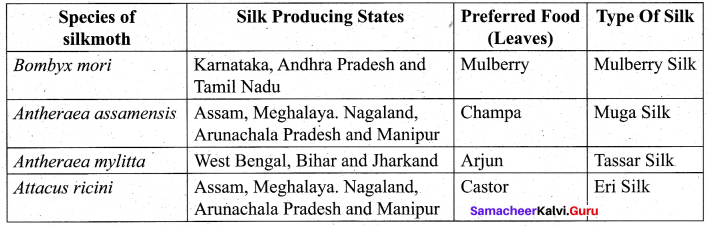
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Describe class Mammalia.
Answer:
(L. Mamma – Breast)
They are found in a variety of habitats.Their body is covered by hair, a unique feature of mammals. Some of them are adapted to fly or live in water. Presence of mammary glands is the most unique feature of mammals. They have two pairs of limbs adapted for walking, running, climbing, burrowing, swimming and flying.
Their skin is glandular in nature, consisting of sweat glands, scent glands and sebaceous glands.Exoskeleton includes homy epidermal horns, spines, scales, claws, nails, hooves and bony dermal plates. Teeth are thecodont,heterodont and diphyodont. External ears or pinnae are present.
The heart is four chambered and possess a left systematic arch. Mature RBCs are circular, biconcave and non nucleated. Mammals have a large brain when compared to other animals They show greatest intelligence among all animals. Their kidneys are metanephric and are ureotelic. All are homeothermic, sexes are separate and fertilization is internal.
Examples: Oviparous- Ornithorhynchus (Platypus), Viviparous- Macropus (Kangaroo), Pteropus (Flying fox), Macaca (Monkey), Cams (Dog), Felis (Cat), Elephas (Elephant), Equus (Horse), Delphinus (Common dolphin) Balaenoptera (Blue whale), Panthera tigris (Tiger), Panther leo (Lion), Homo sapiens (Human), Bos (Cattle).
[OR]
Explain the disorders of the respiratory system of Man.
Answer:
Respiratory system is highly affected by environmental, occupational, personal and social factors. These factors may be responsible for a number of respiratory disorders. Some of the disorders are discussed here.
Asthma-It is characterized by narrowing and inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles and difficulty in breathing.Common allergens for asthma are dust, drugs, pollen grains, certain food items like fish, prawn and certain fruits etc.
Emphysema- Emphysema is chronic breathlessness caused by gradual breakdown of the thin walls of the alveoli decreasing the total surface area of a gaseous exchange, i.e., widening of the alveoli is called emphysema. The major cause for this disease is cigarette smoking, which reduces the respiratory surface of the alveolar walls.
Bronchitis-The bronchi when it gets inflated due to pollution smoke and cigarette smoking, causes bronchitis. The symptoms are cough, shortness of breath and sputum in the lungs.
Pneumonia-Inflammation of the lungs due to infection caused by bacteria or virus is called pneumonia. The common symptoms are sputum production, nasal congestion, shortness of breath, sore throat, etc.
Tuberculosis-Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculate. This infection mainly occurs in the lungs and bones. Collection of fluid between the lungs and the chest wall is the main complication of this disease.
Occupational respiratory disorders-The disorders due to one’s occupation of working in industries like grinding or stone breaking, construction sites, cotton industries, etc. Dust produced affects the respiratory tracts.
Long exposure can give rise to inflammation leading to fibrosis. Silicosis and asbestosis are occupational respiratory diseases resulting from inhalation of particle of silica from sand grinding and asbestos unto the respiratory tract. Workers, working in such industries must wear protective masks.
Question 21.
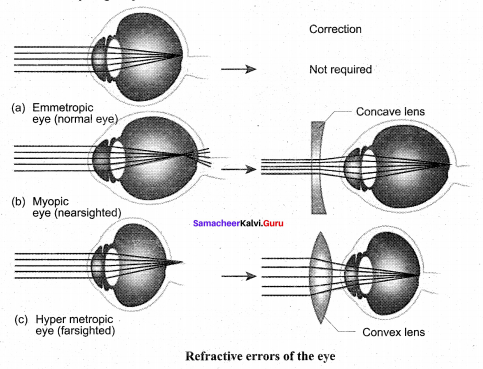
Explain the Refractive errors of eye or defects of human eye.
Answer:
Refractive errors of eye :
Myopia (near sightedness): The affected person can see the nearby objects but not the distant objects. This condition may result due to an elongated eyeball or thickened lens; so that the image of distant object is formed in front of the yellow spot. This error can be corrected using concave lens that diverge the entering light rays and focuses it on the retina.
Hypermetropia (long sightedness): The affected person can see only the distant objects clearly but not the objects nearby.This condition results due to a shortened eyeball and thin lens; so the image of closest object is converged behind the retina. This defect can be _ overcome by using convex lens that converge the entering light rays on the retina.
Presbyopia: Due to aging, the lens loses elasticity and the power of accommodation. Convex lenses are used to correct this defect.
Astigmatism is due to the rough (irregular) curvature of cornea or lens.Cylindrical glasses are used to correct this error.
Cataract: Due to the changes in nature of protein, the lens becomes opaque. It can be corrected by surgical procedures.
[OR]
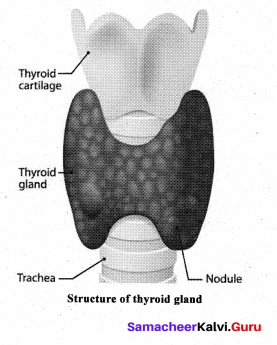
![]()
Briefly explain the structure of thyroid gland.
Answer:
The butterfly shaped thyroid gland is a bilobed gland located below the laryns on each side of upper trachea. It is the largest endocrine gland in the body. Its two lateral lobes are connected by a median tissue mass called isthmus. Each lobe is made up of many lobules.
The lobules consist of follicles called acini. Each acinus is lined with glandular, cuboidal or squamous epithelial cells. The lumen of acinus is filled with colloid, a thick glycoprotein mixture consisting of thyroglobulin molecules.
Hormones of the thyroid gland are often called the major metabolic hormones. The follicular cells of thyroid gland secrete two hormones namely tri-iodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine or tetra- iodothyronine (T4). The parafollicular cells or ‘C’ cells of thyroid gland secrete a hormone called thyrocalcitonin. Iodine is essential for the normal synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Thyroid releasing hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the adenohypophysis to secrete TSH, which intum stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones show a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary.