You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Civics Solutions Chapter 1 Forms of Government and Democracy
Forms of Government and Democracy Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
A system of government in which one person reigns supreme, usually a king or queen, is called ……..
(a) autocracy
(b) monarchy
(c) democracy
(d) republic
Answer:
(b) monarchy
![]()
Question 2.
A system of government by one person with absolute power.
(a) Aristocracy
(b) Theocracy
(c) Democracy
(d) Autocracy
Answer:
(d) Autocracy
Question 3.
When a country is governed by a few privileged, the form of government is called ……
(a) Aristocracy
(b) Parliamentary
(c) Democracy
(d) Republic
Answer:
(a) Aristocracy
Question 4.
Former Soviet Union is an example for ……
(a) aristocracy
(b) theocracy
(c) oligarchy
(d) republic
Answer:
(c) oligarchy
Question 5.
Select the odd one ……
(a) India
(b) USA
(c) France
(d) Vatican
Answer:
(d) Vatican
![]()
Question 6.
Abraham Lincoln was the President of the
(a) USA
(b) UK
(c) USSR
(d) India
Answer:
(a) USA
Question 7.
Kudavolai system was followed by ……….
(a) Gheras
(b) Pandyas
(c) Cholas
(d) Kalabhras
Answer:
(c) Cholas
Question 8.
Direct Democracy in olden times existed ………
(a) In the republics of ancient India
(b) Among the USA
(c) In the city-state of ancient Athens
(d) Among the UK
Answer:
(c) In the city-state of ancient Athens
Question 9.
In which country has democracy originated? .
(a) India
(b) Switzerland
(c) USA
(d) Athens
Answer:
(d) Athens
Question 10.
From which language was the term “Democracy” derived?
(a) Greek
(b) Latin
(c) Persian
(d) Arabic
Answer:
(a) Greek
![]()
Question 11.
In democracy the final authority rests with ………
(a) The Parliament
(b) The People
(c) The council of Ministers
(d) The President
Answer:
(b) The People
Question 12.
Which one of the country has Presidential form of government?
(a) India
(b) Britain
(c) Canada
(d) USA
Answer:
(d) USA
Question 13.
The largest democratic country in the world is ……..
(a) Canada
(b) India
(c) USA
(d) China
Answer:
(b) India
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Direct democracy is practised in Switzerland.
Reason (R): People directly participates in decision making.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 15.
Assertion (A): India has parliamentary form of democracy.
Reason (R): Indian parliament comprises two houses.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 16.
The meaning of Franchise is ………
(a) Right to elect
(b) Right to vote for the poor
(c) Right to vote
(d) Right to vote for the rich
Answer:
(c) Right to vote
![]()
Question 17.
The grant of universal franchise creates ………….
(a) Social equality
(b) Economic equality
(c) Political equality
(d) Legal equality
Answer:
(c) Political equality
Question 18.
Prime Minister of India is appointed by …….
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) Rajya Sabha
(c) Speaker
(d) President
Answer:
(d) President
Question 19.
The President of India can nominate ……….
(a) 12 members to Lok Sabha
(b) 2 members of Rajya Sabha
(c) 12 members to Rajya Sabha
(d) 14 members of Rajya Sabha
Answer:
(c) 12 members to Rajya Sabha
Question 20.
The First general elections after independence in India were held in …………
(a) 1948
(b) 1952
(c) 1957
(d) 1947
Answer:
(b) 1952
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The Constitution of India was finally adopted on ………
- The two types of democracy are …….. and ……….
- An example of direct democracy is ………
- India has a …….. form of democracy.
- ……. was the first Prime Minister of independent India.
- The first general elections were held in British India in the year …….
- The Parliament House in India was designed by …… and ……….
Answers:
- 26th November 1949
- Direct and Indirect
- Switzerland
- Parliamentary
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- 1920
- Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker
III. Match the following.

Answers:
1. (d)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (c)
IV. Give short answers.
Question 1.
Give Abraham Lincoln’s definition of democracy.
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln defines democracy as a government of the people, by the people, and for the people.
Question 2.
Mention the forms of democracy.
Answer:
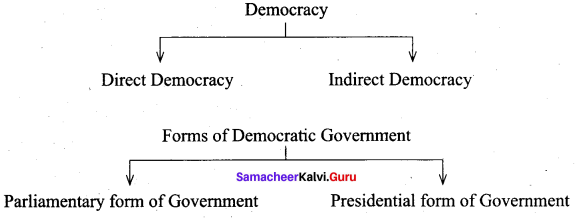
Question 3.
Distinguish between direct and indirect democracy.
Answer:
| Direct democracy | Indirect democracy |
| When the people themselves directly express their will on public affairs, the type of government is called pure or direct democracy. e.g., Ancient Greek city-states, Switzerland |
When the people express their will on public affairs, through their elected representatives, the type of government is called indirect or representative democracy. e.g., The prevailing system of democracy in India, USA and UK |
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What are the challenges to democracy? Explain.
Answer:
- The promise of democracy is far from realized anywhere in the world
- Democracy does not have a challenger, but it does not mean that it does not face any challenge.
- Major challenges to Indian Democracy are
- Illiteracy
- Poverty
- Gender Discrimination
- Regionalism
- Casteism, Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism
- Corruption
- Criminalisation of Politics and Political violence
- Democracy is the dominant form of government in the Contemporary world.
- It does not face a serious challenger or rival
- In the last hundred years, there was an expansion of democracy all over the world.
- Challenges can be faced with the Cooperation of the people in the country.
Question 2.
Explain the conditions necessary for the success of democracy in India.
Answer:
- Empowerment of the poor and illiterates to enjoy the goodness of democracy.
- Willingness among the elected people not to misuse their powerful position and public wealth.
- Eradication of social evils and dangers from which democracy suffers.
- An impartial and efficient press to form public opinion.
- Presence of strong public opinion.
- Feeling of tolerance and communal harmony among the people.
- Awareness among the people of the fundamental rights that they are entitled to enjoy.
- Conscious check and vigilance on the working of the elected representatives.
- Powerful and responsible opposition.
![]()
Question 3.
What is your opinion about democracy in India?
Answer:
- Democracy in India has been appreciated worldwide.
- It is an example of Democracy which is remarkable in many aspects
- It is the largest electorate in history, a huge range of parties and a parliamentary system.
- But we do not really have broad consensus on large scale reforms and plans to improve the whole country.
- We are a big nation with huge population
- There are problems, constraints in the implementation of programs and policies for the benefit of the people.
- But which system does not have problems?
- Democracy gives us right to express our views:
- Solutions found through democratic means are better and long-lasting
- We have a wonderful law, Right to Information Act, use it judiciously to propagate our moves.
- If the necessary conditions for the success of Democracy are fulfilled, there will be smooth functioning of Democracy in the country.
VI. Project and Activity.
Question 1.
Discuss in the class what is a universal adult franchise? Why is it important?
Answer:
- The teacher arranges a discussion session.
- The students will be divided into two groups to discuss on the above content.
Universal Adult Franchise: The Article 326 of the Indian Constitution grants universal adult suffrage, according to which every adult citizen is entitled to cast his/her vote in all state elections unless that citizen is convicted of certain criminal offences (or) deemed unsound of mind.
Why is it important?
- It has nothing to do with economic growth or staying ahead, of the competition. Under this system a government is elected that is accountable to the people it governs.
- Because every vote counts, issues in society receive their appropriate weight in terms of importance and urgency. ,
Question 2.
“Democracy is the power of the majority which respects minority.” Discuss.
Answer:
- Democracy requires, minority rights equally as it does majority rule.
- Indeed, as democracy is understood today the minority’s rights must be protected no matter how alienated a minority is from the majority society. Otherwise, the minority rights lose their meaning.
![]()
Question 3.
Conduct a mock election in your class.
Answer:
Election activities in the classroom
- Campaigning
- Voting Booth
- Voter Registration form
- Campaign posters
- Cast your Ballot
- Reward your voters
- Tally up the votes
- Graph the votes.
- Before beginning, think of issues, students enjoy voting on, make up copies of a short voter registration form for each student.
- Have a ballot box.
- After the election issue is chosen you will need to make up a ballot for each student.
Question 4.
A group discussion on the merits and demerits of democracy of India in the classroom.
Answer:
Merits and Demerits of Democracy:
Merits
- Responsible and accountable government.
- Equality and fraternity.
- Sense of responsibility among common people.
- Local self-government.
- Development and prosperity for all.
- Popular sovereignty.
- Sense of cooperation and fraternal feeling
Demerits
- Indirect or representative nature of democracy.
- Lack of interest in the democratic process and hence lower turnout in elections.
- Instability in governance due to fractured mandate.
- Delay in decision – making process.
VII. HOTS
Question 1.
Will you have the right to equality under a dictatorship? What would be the attitude regarding public opinion in such a country?
Answer:
- A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power
- This power is used in an oppressive manner.
- A state which is ruled by a dictator is called a dictatorship.
- Under small type of government, public opinions have no place. Opinions are suppressed.
- There is no freedom of expression or freedom of right.
![]()
Question 2.
How does democracy lead to a peaceful and a harmonious life among the citizens? Explain.
Answer:
Democracy safeguards the fundamental rights which are defined as basic human freedoms which every Indian citizen has the right to enjoy for proper and harmonious development of personality. The students can refer and download from the Internet.
VIII. Life Skills
Select a group of countries, Research each country and tell what type of government it has: Aristocracy, Monarchy, Autocracy, Oligarchy, Theocracy, Democracy, Republic. Then, provide characteristics of this country that helped you determine the type of government.
| Country name | Type of Government | Characteristics of the country’s government |
The teacher can assign this as a Project & Group Activity for the students.
Forms of Government and Democracy Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
A system of government by one person with absolute power is ……
(a) Autocracy
(b) Aristocracy
(c) Monarchy
(d) Oligarchy
Answer:
(a) Autocracy
Question 2.
Democracy as a government of the people, by the people and for the people defined by ……..
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Abraham Lincoln
(d) Herbert Baker
Answer:
(c) Abraham Lincoln
Question 3.
Democracy began ………. years ago.
(a) 2000
(b) 2500
(c) 3000
(d) 3200
Answer:
(b) 2500
![]()
Question 4.
Kudavolai system was a very notable and unique feature of the village administration of …….
(a) Cheras
(b) Cholas
(c) Pandyas
(d) Pallavas
Answer:
(b) Cholas
Question 5.
This is the dominant form of government in the contemporary world.
(a) Oligarchy
(b) Monarchy
(c) Theocracy
(d) Democracy
Answer:
(d) Democracy
Question 6.
Assertion (A): The term ‘democracy’ is derived from two Greek words demos meaning people and create meaning power.
Reason (R): Literally democracy means “the power of the people”.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true (A) explains (R)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 7.
Assertion (A): India has a parliamentary form of democracy.
Reason (R): The Indian Parliament comprises the elected representatives of people.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true (A) explains (R)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
![]()
Question 8.
Indian citizen above years of age can exercise the right to vote in India.
(a) 16
(b) 17
(c) 18
(d) 19
Answer:
(c) 18
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The modern world prefers ……….
- The democratic institutions existed in India as early as the …….. period.
- An example of Indirect Democracy is ……….
- India has a …….. government with elected representatives at the federal, state, and local levels.
- The two houses of our Parliament are ………. and ………
- A group of people living in the same place having particular characteristics in common is ………
Answers:
- Democracy
- Vedic
- India
- Democracy Quasi Federal
- Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
- Community
III. Match the following.

Answers:
1. (d)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (c)
IV. Give short answers.
Question 1.
What do you mean by “Republic”?
Answer:
A state in which supreme power is held by the people and their elected representatives and which has an elected (or) nominated President rather than a Monarch. e.g., India, Australia.
Question 2.
What is Democracy?
Answer:
- Democracy is a form of government that allows people to choose their rulers.
- Only leaders elected by the people should rule the country.
- People have the freedom to express views, freedom to organise and freedom to protest.
Question 3.
Mention the salient features of Democracy.
Answer:
- Elected representatives of people and final decision-making power to the representatives.
- Free and fair elections.
- Universal adult franchise with each vote having equal value.
- Fundamental rights and protection of individual freedom.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Though democracy in India has been appreciated worldwide for its working there is still a lot of scope for improvement – Discuss.
Answer:
Though democracy in India has been appreciated worldwide for its work, there is still a lot of scope for improvement. The above-mentioned steps must be taken to ensure the smooth functioning of democracy in the country.
Indian democracy can be successful and vibrant only when its citizens imbibe and reflect in their behavior the basic democratic values like equality, freedom, social justice, accountability, and respect for all. Their mindset, thinking and behavior are expected to be in tune with the essential conditions of democracy. They have to appreciate the opportunities for their desired roles like participation, making the system accountable, fulfilling obligations, and playing proactive roles to actualize the goals of democracy.