You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 19 Plant Physiology
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Plant Physiology Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
A big tree falls in a forest but its roots are still in contact with the soil. The branches of this
fallen tree straight up. This happens in response to ……………………
(a) water and light
(b) water and minerals
(c) gravity and water
(d) light and gravity
Answer:
(d) light and gravity
Question 2.
The tropic movement that helps the climbing vines to find suitable support is ……………………..
(a) phototropism
(b) geotropism
(c) thigmotropism
(d) chemotropism
Answer:
(c) thigmotropism
![]()
Question 3.
The chemical reaction occurs during photosynthesis is ……………………….
(a) CO2 is reduced and water is oxidized
(b) water is reduced and CO2 is oxidized
(c) both CO2 and water are oxidized
(d) both CO2 and water are produced
Answer:
(a) CO2 is reduced and water is oxidized
Question 4.
The bending of root of a plant in response to water is called ……………………….
(a) Thigmonasty
(b) Phototropism
(c) Hydrotropism
(d) Photonasty
Answer:
(c) Hydrotropism
Question 5.
A growing seedling is kept in the dark room. A burning candle is placed near it for a few days. The tip part of the seedling bends towards the burning candle. This is an example of ……………….
(a) chemotropism
(b) thigmotropism
(c) phototropism
(d) geotropism
Answer:
(c) phototropism
Question 6.
The root of the plant is …………….
(i) positively phototropic but negatively geotropic
(ii) positively geotropic but negatively phototropic
(iii) negatively phototropic but positively hydrotropic
(iv) negatively hydrotropic but positively phototropic
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii)
![]()
Question 7.
The non-directional movement of a plant part in response to temperature is called ………………
(a) thermotropism
(b) term nasty
(c) chemotropism
(d) thigmonasty
Answer:
(b) term nasty
Question 8.
Chlorophyllin a leaf is required for ……………………..
(a) photosynthesis
(b) transpiration
(c) tropic movement
(d) nastic movement
Answer:
(a) photosynthesis
Question 9.
A plant is kept in a dark room for about 24 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis in order to ……………….
(a) remove chlorophyll from the leaf
(b) remove starch from the leaves
(c) ensure that photosynthesis occurred
(d) to prove transpiration
Answer:
(b) remove starch from the leaves
Question 10.
Transpiration takes place through …………….
(a) fruit
(b) seed
(c) flower
(d) stomata
Answer:
(d) stomata
II. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statement.
- The response of a plant part to the chemical stimulus is called phototropism – False.
Correct Statement: The response of a plant part to the chemical stimulus is called chemotropism. - The shoot is positively phototropic and negatively geotropic – True
- When the weather is hot water evaporates lesser which is due to the opening of stomata – False.
Correct Statement: When the weather is hot, water evaporates faster which is due to the opening of stomata. - Photosynthesis produces glucose and carbon dioxide – False.
Correct Statement: Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen. - Photosynthesis is important in releasing oxygen to keep the atmosphere in balance – True
- Plants lose water when the stomata on leaves are closed – False.
Correct Statement: Plants lose water when the stomata on leaves are opened.
III. Fill in the blanks.
- The shoot system grows upward in response to ……………..
- …………….. is positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
- The green pigment present in the plant is ………………
- The solar tracking of sunflower in accordance with the path of the sun is due to …………………
- The response of a plant part towards gravity is ………………..
- Plants take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis but need ……………. for their living.
Answer:
- negative geotropism.
- Root
- chlorophyll
- tropism
- geotropism
- oxygen
IV. (a) Match column A with column B
| Column A | Column B | |
| 1. | Roots growing downwards into the soil | (a) Positive phototropism |
| 2. | Shoots growing towards the light | (b) Negative geotropism |
| 3. | Shoots growing upward | (c) Negative phototropism |
| 4. | Roots growing downwards away from light | (id) Positive geotropism |
Answer:
- (d) Positive geotropism
- (a) Positive phototropism
- (b) Negative geotropism
- (c) Negative phototropism
(b)
| S.No. | Column A | Column B | Column C |
| 1. | Photonasty | Response to temperature | Tulipa sp |
| 2. | Thigmonasty | Response to light | Mimosa pudica |
| 3. | Thermonasty | Response to touch | Moon flower |
Answer:
| S.No. | Column A | Column B | Column C |
| 1. | Photonasty | Response to light | Moon flower |
| 2. | Thigmonasty | Response to touch | Mimosa pudica |
| 3. | Thermonasty | Response to temperature | Tulipa sp |
V. Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
What is nastic movement?
Answer:
Nastic movements are the non-directional response of a plant or part of a plant to stimulus.
![]()
Question 2.
Name the plant part
- Which bends in the direction of gravity but away from the light.
- Which bends towards light but away from the force of gravity.
Answer:
- Roots
- Stem.
Question 3.
Differentiate phototropism from photo nasty.
Answer:
| Phototropism | Photonasty |
| The unidirectional movement of a plant part to light stimulus is called phototropism. It is slow and irreversible. | The non-directional movement of a plant part in response to light is called photo nasty. It is immediate, temporary and reversible. |
Question 4.
Photosynthesis converts energy X into energy Y.
(a) What are X and Y?
Answer:
X is light energy. Y is chemical energy. During photosynthesis, the light energy is converted into chemical energy.
(b) Green plants are autotrophic in their mode of nutrition. Why?
Answer:
Green plants are autotrophic in their mode of nutrition because they prepare their food, through a process called photosynthesis by using water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and sunlight.
Question 5.
Define transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapour into the atmosphere through stomata in leaves and stems.
Question 6.
Name the cell that surrounds the stoma.
Answer:
Each stomata is surrounded by guard cells.
VI. Short answer questions.
Question 1.
Give the technical terms for the following:
Answer:
(a) Growth dependent movement in plants.
Trophic movements
(b) Growth independent movement in plants.
Nastic Movements.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the movement seen in Pneumatophores of Avicennia.
Answer:
Negatively Geotropic movement.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks:
Answer:
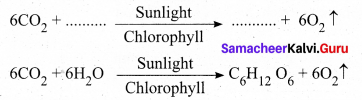
Question 4.
What is chlorophyll?
Answer:
Green pigments present in leaves.
Question 5.
Name the part of a plant which shows positive geotropism. Why?
Answer:
- Roots show positive geotropism.
- Roots are the part of a plant which are responsible for anchoring the plant firmly in the soil and helping them to hold the soil.
- Further, the roots are responsible for absorbing water and mineral salts from the soil and sending it to the leaves to help in photosynthesis and growth of the plant.
- Hence the roots grow deep down into the soil and are positively geotropic.
Question 6.
What is the difference between movement of flower in sunflower plant and closing of the leaves in the Mimosa pudical?
Answer:
The stem of sunflower follows the path of sun from dawn to dusk (from east to west) due to light stimulus. But at night, it moves from west to east. The leaves of mimosa pudica closes on touching stimulus.
Question 7.
Suppose you have a rose plant growing in a pot, how will you demonstrate transpiration in it?
Answer:
Transpiration is the plant can be demonstrated as follows :
- A plastic bag must be tied ovesr the leaf and the plant must be placed in sun fight.
- After some time, we can see water condensing inside the plastic bag. This has been let out by the leaves and is called transpiration.
- Tiny microscopic holes called stomata are present in the leaves.
- The stomatal opening are guarded to guard cells.
- The transpiration of water through the stomata are regulated by the opening and closing of stomatal opening by the guard cells.
![]()
Question 8.
In the given photosynthetic experiment, what will happen to the leaf closed with black paper in starch test? Why?
Answer:

The part of leaf closed with black paper does not turn blue – black, when it is tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch. The leaf closed with black paper did not receive the sunlight and was unable to manufacture starch.
Question 9.
Mention the differences between stomatal and lenticular transpiration.
Answer:
| Stomatal Transpiration | Lenticular Transpiration | |
| 1. | Loss of water in the form of water vapour through minute pore called stomata. | Loss of water in the form of water vapour through lenticels. |
| 2. | Stomata are confined to epidermis of green shoot and leaves. | Lenticels are confined in woody stem and fruits. |
| 3. | It amounts for 90% to 95% of the water transpired from leaves. | It amounts for 1% to 5% of the total water loss by the plants. |
Question 10.
To which directional stimuli do (a) roots respond (b) shoots respond?
Answer:
(a) Roots respond positively geostrophic and negatively phototrophic.
(b) Shoots respond negatively geostrophic and positively phototrophic.
VII. Long answer questions:
Question 1.
Differentiate between tropic and nastic movements
Answer:
| Trophic Movements | Nastic Movements |
| Unidirectional response to the stimulus | Non-directional response to the stimulus |
| Growth dependent movements | Growth independent movements |
| More or less permanent and irreversible | Temporary and reversible |
| Found in all plants | Found only in a few specialized plants |
| Slow action | Immediate action |
![]()
Question 2.
How will you differentiate the different types of transpiration?
Answer:
Transpiration in the plant can be differentiated by the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant body is called as transpiration. The leaves have ” tiny, microscopic pores called stomata. Water evaporates through these stomata. Each stomata is surrounded by guard cells. These guard cells help in regulating the rate of transpiration by opening and closing of stomata.
There are three types of transpiration :
- Stomatal transpiration: Loss of water from plants through stomata. It accounts for 90-95% of the water transpired from leaves.
- Cuticular transpiration: Loss of water in plants through the cuticle.
- Lenticular transpiration: Loss of water from plants as vapour through the lenticels.
The lenticels are tiny openings that protrude from the barks in woody stems and twigs as well as in other plant organs.
Activity
Question 1.
A glass trough is taken and is filled with sand. A flowerpot containing water plugged at the bottom is kept at the centre of the glass trough. Soaked pea or bean seeds are placed around the pot in the sand. What do you observe aft er 6 or 7 days? Record your observation.
Answer:
Experiment to demonstrate Hydrotropism:
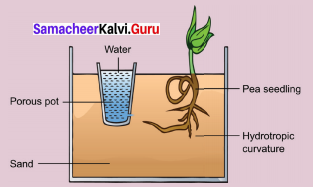
Take a glass trough and fill it with sand. Keep a Pea seedling at the centre. A porous pot with water is kept at the Trough, as shown in the diagram. Keep it for six or seven days. The Radicle has grown towards the porous pot and moisture, instead of growing vertically downward. It proves that primary root is positively Hydrotrophic and that hydrotropism is stronger than Geotropism.
Question 2.
Take pea seeds soaked in water overnight. Wait for the pea seeds to germinate. Once the seedling has grown put it in a box with an opening for light on one side. After few hours, you can clearly see how the stem has bent and grown towards the light.
Answer:
Take pea seeds soaked in water.overnight. Wait for the pea seeds to germinate. Once the seedling has grown put it in a box with an opening for light on one side. After a few days, we can clearly see that the stem has bent and grown towards the light. This experiment demonstrates Phototropism.
Question 3.
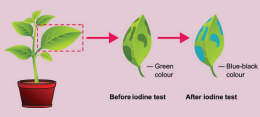
Variegated leaf is plucked from Coleus plant kept in sunlight. It is de-starched by keeping in dark room for 24 hours. The picture of this leaf is draw n and the patches of cholorphyll on the leaf are marked. After immersing the leaf in boiling water follow ed by alcohol it is tested for starch using iodine solution. Record your observation.
Answer:
Experiment to show that Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis:
Aim: To show that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
We need Coleus (croton) plant with variegated leaves, boiling water, alcohol and iodine solution.
Take coleus (croton) plant with variegated leaves. Destarch the leaves of the plant, by keeping the plant in dark room for 24 hours. Then keep the plant in the sunlight for four to six hours for photosynthesis. Pluck a leaf and draw the picture of the leaf. Mark the patches of chlorophyll on the leaf. After immersing the leaf in boiling water and then in alcohol, it is tested for starch with iodine solution. The patches of the leaf with chlorophyll turn blue – black. The other portions remain colourless. This experiment shows that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 4.
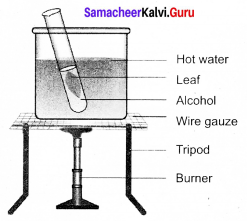
A potted plant is placed in a dark room for about 2 days to de-starch its leaves. One of its leaves is covered with the thin strip of black paper as shown in the picture, make sure that the leaf is covered on both sides.

The potted plant is kept in bright sunlight for 4 to 6 hours. The selected covered leaf is plucked and the black paper is removed.
The leaf is immersed in boiling water for a few minutes and then in alcohol to remove chlorophyll. The leaf is now tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch. The covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black whereas the uncovered part of the leaf turns blue-black colour.
Why are the changes in colour noted in the covered and uncovered part of the leaf?
Answer:
Experiment to that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis:
Aim: To show that sunlight is necessary’ for photosynthesis.
Material required: potted plant, black paper, boiling water, alcohol and iodine solution.
Procedure:
A potted plant is placed in a darkroom for about 2 days to de-starch its leaves. One of its leaves is covered with the thin strip of black paper as shown in the picture, make sure that the leaf is covered on both sides.
The potted plant is kept in bright sunlight for 4 to 6 hours. The selected covered leaf is plucked and the black paper is removed. The leaf is immersed in boiling water for a few minutes and then in alcohol to remove chlorophyll. The leaf is now tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch. The covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black whereas the uncovered part of the leaf turns blue-black colour. The covered part of the leaf which did not receive the sunlight was unable to synthesize starch. Hence it does not turn blue-black colour. But the uncovered part of the leaf which received sunlight was able to synthesise starch and so it turns blue-black in colour.
Question 5.
If you tie a plastic bag over a leaf and place the plant in light, you will be able to see water condensing inside the plastic bag. The water is let out by the leaves. Why does this occur?

Answer:
Experiment:
If you tie a plastic bag over a leaf and place the plant in light, you will be able to see water condensing inside the plastic bag. The water is let out by the leaves.
The leaves have tiny, microscopic holes called stomata. Water evaporates through these stomata. Each stomata is surrounded by guard cells. These guard cells help in regulating the rate of transpiration by opening and closing of stomata.
Typically, only 0.1 percent of water taken up by the plant is used by the plant for producing carbohydrates. That is, if a plant absorbs one litre of water, only one millilitre will be used to produce carbohydrate. The remaining 999 millilitres evaporates from the leaf.
You will be able to see how much water a plant releases in the air.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Plant Physiology Additional Questions
I. Choose the Correct Answer.
Question 1.
In response to light, the Auxin the cells of a stem. So that the plant bends towards
the light.
(a) condenses
(b) solidifies
(c) moves
(d) elongates
Answer:
(d) elongates
Question 2.
The end products of Photosynthesis is ………….. , which will be converted into …………….
(a) Nitrogen, Amino acids
(b) Glucose, Starch
(c) Vitamins, Minerals
(d) Fats, Fatty acids
Answer:
(b) Glucose, Starch
Question 3.
The green leaves, in the presence of light, which manufacture Starch, after removing the
chlorophyll, if Iodine is added, the leaves turn into
(a) Blue-black
(b) Blue orange
(c) Black White
(d) Blue-violet
Answer:
(a) Blue-black
![]()
Question 4.
During respiration plants inhale …………. and exhale ……………
(a) Nitrogen and Oxygen
(b) Oxygen and Hydrogen
(c) Oxygen and Carbon dioxide
(d) Carbon dioxide and Oxygen
Answer:
(c) Oxygen and Carbon dioxide
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The plants respond to gravity and are termed as ……………..
- One of the plant hormones is ………………
- ………….. is evolved during photosynthesis.
- The dead plants and animals are decomposed by ………………..
- The first leaf of monocot plants is called ……………….
- The plumule is covered by a protective sheath called …………………
- The other name for Geotropism is …………………
- The other name for Thigmonasty is …………………
- The process of ………….. will not take place in green plants at night.
- During fertilization, pollen tube grows down the Style, in response to the sugars, in the style is
an example of …………………
Answer:
- geotropism
- Auxin
- Oxygen
- microorganisms
- Cotyledon
- Coleoptile
- Gravitropism
- Seismonasty
- Photosynthesis
- Chemotropism
III. Match the column “A” with Column “B”.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Embryonic shoot | (a) Micronutrients |
| 2. Minerals needed in substantial quantities | (b) Plants |
| 3. Tiny holes in leaves | (c) Plumule |
| 4. Primary producers | (d) Macronutrients |
| 5. Minerals needed in minute | (e) Stomata quantities. |
Answer:
- (c) Plumule
- (d) Macronutrients
- (e) Stomata
- (b) Plants
- (a) Micronutrients
IV. Answer the following.
Question 1.
Name the four important things needed by plants for photosynthesis.
Answer:
- Chlorophyll
- Water
- Carbon dioxide
- Sunlight
![]()
Question 2.
Why is transpiration a necessary evil?
Answer:
- Creates a pull in leaf.
- Creates a pull in stem.
- Creates an absorption force in roots to take more water.
So the minerals are supplied continuously. - Regulates the temperature of the plant.
Question 3.
What is a food chain?
Answer:
The link in the cycle of relationship between plants, animals and micro organisms are called Food chain.
Question 4.
How are Photosynthesis by plants and gas exchange by animals interrelated?
Answer:
The oxygen released by the plants is inhaled by the animals. Animals exhale Carbon dioxide, which is taken up by the green plants for photosynthesis. Thus the photosynthesis by plants and the gas exchanges by animals are interrelated.
Question 5.
What are Nastic movements?
Answer:
When the movements are not directed towards stimuli it is called Nastic movements.
Question 6.
Match the following with the types of Nastic movements in plants

Answer:
- (c) Touch
- (d) Darkness
- (a) Temperature
- (b) Change in light intensity
Question 7.
What is Tropism?
Answer:
Tropism is a growing movement and the direction of which is determined by the direction of the
stimulus.
![]()
Question 8.
Match the following with the types of Tropisms in plants.
Answer:

Answer:
- (d) Phototropism
- (e) Geotropism
- (a) Hydrotropism
- (b) Thigmotropism
- (c) Chemotropism
Question 9.
What are the differences between Trophic and Nastic movements?
Answer:
| Trophic Movements | Nastic Movements |
| Unidirectional response to the stimulus | Non-directional response to the stimulus |
| Growth dependent movements | Growth independent movements |
| More or less permanent and irreversible | Temporary and reversible |
| Found in all plants | Found only in a few specialized plants |
| Slow action | Immediate action |