You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 17 Animal Kingdom
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Animal Kingdom Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Find the group having only marine members.
(a) Mollusca
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Porifera
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 2.
Mesoglea is present in …………………
(a) Porifera
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Annelida
(d) Arthropoda
Answer:
(b) Coelenterata
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the following pairs is not a poikilothermic animal?
(a) Fishes and Amphibians
(b) Amphibians and Aves
(c) Ayes and Mammals
(d) Reptiles and mammals
Answer:
(a) Fishes and Amphibians
Question 4.
Identify the animal having a four-chambered heart ………………..
(a) Lizard
(b) Snake
(c) Crocodile
(d) Calotes
Answer:
(c) Crocodile
Question 5.
The animal without skull is …………………….
(a) Acrania
(b) Acephalia
(c) Apteria
(d) Acoelomate
Answer:
(a) Acrania
Question 6.
Hermaphrodite organisms are …………………….
(a) Hydra, Tapeworm, Earthworm, Amphioxus
(b) Hydra, Tapeworm, Earthworm, Ascidian
(c) Hydra, Tapeworm, Earthworm, Balanoglossus
(d) Hydra, Tapeworm, Ascaris, Earthworm
Answer:
(d) Hydra, Tape worm, Ascaris, Earthworm
Question 7.
Poikilothermic organisms are ……………………….
(a) Fish, Frog, Lizard, Man
(b) Fish, Frog, Lizard, Cow
(c) Fish, Frog, Lizard, Snake
(d) Fish, Frog, Lizard, Crow
Answer:
(c) Fish, Frog, Lizard, Snake
![]()
Question 8.
Air sacs and pneumatic bones are seen in ……………………….
(a) fish
(b) frog
(c) bird
(d) bat
Answer:
(c) bird
Question 9.
An excretory organ of tapeworm is ………………………
(a) Flame cells
(b) Nephridia
(c) Body surface
(d) Solenocytes
Answer:
(a) Flame cells
Question 10.
Water vascular system is found in ……………………….
(a) hydra
(b) earthworm
(c) starfish
(d) Ascaris
Answer:
(c) starfish
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The skeletal framework of Porifera is ……………………….
- Ctenidia are respiratory organs in ……………………
- Skates are ……………… fishes.
- The larvae of an amphibian is …………………..
- …………….. are jawless vertebrates.
- ………………… is the unique characteristic feature of mammal.
- Spiny anteater is an example for ……………… mammal.
Answer:
- spicules
- Octopus
- Cartilaginous
- tadpole
- Cyclostomes
- Placenta
- egg-laying
III. State whether true or false. If false write the correct statement.
- Canal system is seen in coelenterates – False
Correct statement: Canal system is seen in Porifera. - Hermaphrodite animals have both male and female sex organs – True
- Trachea are the respiratory organ of Annelida – False
Correct Statement: Trachea are the respiratory organ of Arthropoda. - Bipinnaria is the larva of Mollusca – False
Correct statement: Bipinnaria is the larva of Echinodermata - Balanoglossus is a ciliary feeder – True
- Fishes have two chambered heart – True
- Skin of reptilians are smooth and moist – False
Correct statement: Their body is covered with homy epidermal scales. - Wings of birds are the modified forelimbs – True
- Female mammals have mammary glands True.
IV. Match the following.
| Phylum | Examples |
| 1. Coelenterata | (a) Snail |
| 2. Platyhelminthes | (b) selfish |
| 3. Echinodermata | (c) Tapeworm |
| 4. Mollusca | (d) Hydra |
Answer:
- (d) Hydra
- (c) Tapeworm
- (b) selfish
- (a) Snail
V. Answers in brief.
Question 1.
Define taxonomy.
Answer:
Taxonomy is the science of classification which makes the study of a wide variety of organisms easier and helps us to understand the relationship among different groups of animals.
![]()
Question 2.
What is nematocyst?
The stinging cells present at tentacles of aquatic animals like jellyfish, hydra, etc in phylum Coelenterata is called nematocyst (cnidoblast)
Question 3.
Why coelenterates are called diploblastic animals?
Answer:
The body wall of coelenterates is diploblastic with two layers, namely outer ectoderm and inner endoderm separated by a non-cellular jelly-like substance called mesoglea. Due to the presence of two layers in the body wall, they are said to be diploblastic animals.
Question 4.
List the respiratory organs of amphibians.
Answer:
The respiratory organs of amphibians are gills, lungs, skin and pharyngeal region.
Question 5.
How does locomotion take place in starfish?
Answer:
Locomotion in starfish is affected by tube feet.
![]()
Question 6.
Are Jelly fish and star fish similar to fishes? Give reasons.
Answer:
No. Jellyfish and starfish are not similar to fishes because jellyfish belong to Cnidarians. Star fish belongs to Echinodermata. Fishes belong to the class Pisces.
Question 7.
Why are frogs said to be amphibians?
Answer:
They are the first vertebrates to live on land with dual adaptation to living in aquatic and land environments. This double life is expressed as amphibious.
VI. Short answer questions.
Question 1.
Give an account on phylum Annelida.
Answer:
- The animals in phylum annelida are segmented worms.
- Example: Earth worms, Leeches and a group of marine worms.
- Segmented body shows metamerism which means the property of having repeated homologous organs in each segment.
- The animals possess body cavity called coelom.
- Some organisms show movable bristles called setae.
- They have no legs and no hard skeleton.
- The body is covered by moist outer cuticle.
- A thick multi-layered structure, outside the epidermis provides protection.
- They have a central nervous system with a brain.
- Metabolic wastes are removed by Nephridia.
Question 2.
Differentiate between flatworms and roundworms.
Answer:
| Flatworms | Roundworms |
| The flatworms come under phylum Platyhelminthes. | The roundworms come under phylum Nematoda |
| Flatworms have a dorsoventrally flattened body. | Roundworms have cylindrical body with tapering at one end. |
| Flatworms do not have cuticle. | Roundworms have an outer covering called cuticle. |
| Flatworms are parasitic in nature. | Roundworms live either on water or in soil. |
Question 3.
Outline the flow charts of Phylum Chordata.
Answer:
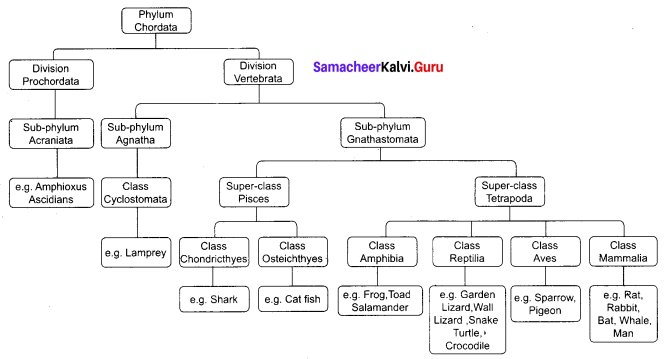
Question 4.
List five characteristic features of fishes.
Answer:
- Fishes are poikilothermic (cold-blooded), aquatic vertebrates with jaws.
- The streamlined body is divisible into the head, trunk, and tail.
- Locomotion is by paired and median fins.
- The body has a covering of scales.
- Respiration is through gills.
- The heart is two-chambered with an auricle and a ventricle.
- There are two main types of fishes.
- Cartilaginous fishes, with a skeleton made of cartilages e.g. Sharks, Skates.
- Bony fishes with a skeleton made of bones e.g. Carps, Mullets.
![]()
Question 5.
Comment on the aquatic and terrestrial habits of amphibians.
Answer:
- The transition from aquatic to terrestrial living is clearly indicated in Amphibian.
- They are the first vertebrates to live on land.
- Amphibians have dual adaptation to living in aquatic and land environments.
- The double life is called amphibious.
- In frogs, the hind limbs have webbed feet.
- The skin is moist and glandular usually without scale.
- Respiration is by gills, lungs, skin and pharyngeal region.
- The heart has three chambers, with two auricles and a single ventricle.
- Fertilization is external.
- The larva is a tadpole, which is metamorphosed into an adult.
Question 6.
How are the limbs of the birds adapted for avian life?
Answer:
- Forelimbs of birds are modified into wings with feathers for flight.
- The hind limbs are adapted for walking perching or swimming.
VII. Long Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Describe the characteristic features of different Prochordates.
Answer:
Prochordates are the forerunners of Vertebrates. They do not have a cranium or skull. So they are called Acrania. The classification is based on the nature of the notochord. The following are the three subphyla of protochordate.
(a) Hemichordates:
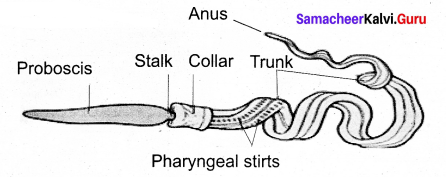
Eg- Balanoglossus.
The organism lack notochord and are without backbones. They are tuberculous forms. The body is soft, vermiform, unsegmented, bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. The notochord is persistent as the stomochord in the anterior region.
(b) Cephalochordates:
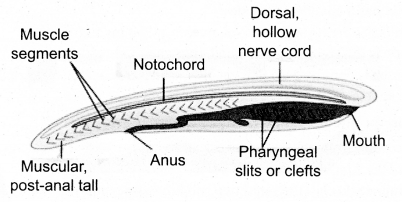
Eg- Amphioxus
The notochord extends forward beyond the brain. Small fish like marine chordates with i unpaired dorsal fins.
(c) Urochordates:

Eg- Ascidians
The notochord is confined to the tail region of the larva. In adults, they degenerate and are in sessile forms. The body is enveloped by a tunic or test.
![]()
Question 2.
Give an account on phylum Arthropoda.
Answer:
- Arthropoda is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom.
- They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate animals.
- The body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen.
- Each segment bears paired jointed legs.
- Exoskeleton is made of chitin and is shed periodically as the animal grows.
- The casting off and regrowing of exoskeleton is called moulting.
- Body cavity is filled with haemolymph(blood).
- The blood does not flow in blood vessels and circulates throughout the body (open circulatory system).
- Respiration is through body surface,gills or trachea (air tubes).
- Excretion occurs by malphigian tubules or green glands Sexes are separate,
e.g., Prawn, Crab, Cockroach, Millipedes, Centipedes, spider, scorpions.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Animal Kingdom Additional Questions
I. Fill in the blanks.
- In a binomial classification of animal and plant, the first name is ………… and the second is ……………..
- The bacteria cells have no …………….
- The two major categories of life are …………. and ……………
- ……….. refers to a fluid-filled cavity inside the body.
- Kingdom animals are classified into two sub kingdom namely ………….. and ……………
- In phylum Porifera, the organisms have many pores in their body called ………….. and for circulation of water.
- In Phylum Coelenterate, the organisms exist in two different body namely a ………….. and a ……………..
- The most common larva in phylum Mollusca is ……………….
- The most common larva in phylum Echinodermata is ……………….
- Dairy farming is referred to as ……………….
Answer:
- Genus, Species
- Nucleus
- Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes
- Coelom
- Invertebrata, Vertebrata
- Ostia, Osculum
- Polyp, Medusa
- Trochophore
- Bipinnaria Larva
- White Revolution
II. Write true or false for the following statement and write the correct statement for the false statements.
- Amoebic dysentery is caused by plasmodium – False.
Correct Statement: Amoebic dysentery is caused by protozoa entamoeba histolytica. - The first systematic approach to the classification of living organisms was done by Carl Linnaeus – True
- Sponges do not have any true tissues – True
- In phylum Arthropoda, the organisms have jointed legs – True
- In phylum Mollusca, the body of organisms is divided into head, thorax, and abdomen – False.
Correct Statement: In phylum Mollusca, the body of organisms is divided into head, muscular foot and the visceral mass.
III. Write any three common characteristic features of the following phyla of invertebrates and classes of vertebrates.
- Protozoa:
- Single-celled eukaryotes.
- Locomotion is done by pseudopodia.
- The nutrition is either autotrophic or heterotrophic.
- Platyhelminthes:
- This Phylum includes flatworms.
- Excretion and osmoregulation occur through flame cells.
- These worms are hermaphrodites having both male and female reproductive organs in a single individual.
- Mollusca:
- Soft-bodied animals without segmentation.
- The body is covered by a mantle and a shell.
- Respiration is carried through gills or lungs or both.
- Class Reptilia:
- The body is covered by an exoskeleton of homy epidermal scales.
- The respiration is by lungs.
- The heart is three-chambered, except crocodile, which has four chambers.-
- Class Mammalia:
- They have epidermal hairs, sweat, sebaceous and scent glands.
- The mammary glands are the modified integumentary glands.
- The external ear or pinna is present in most of mammals.
IV. Write the binomial name for the following common names of animals.
| S. No. | Common Name | Binomial Name |
| 1. | Amoeba | Amoeba proteus |
| 2. | Cockroach | Periplaneta americana |
| 3. | Roundworm | Ascaris lumbricoides |
| 4. | Frog | Rana hexadactyla |
| 5. | Crow | Corvus splendens |
| 6. | Dog | Canis familiaris |
| 7. | Cat | Felis felis |
| 8. | Man | Homo sapiens |
V. Write the names of any two organisms for the following each phylum and the classes.
| S. No. | Phylum Classes | Two Organisms |
| 1 | Protozoa | Amoeba, Euglena |
| 2 | Porifera | Spongilla, Sea sponge |
| 3 | Coelenterata | Jellyfish, Hydra |
| 4 | Platyhelminthes | Liver fluke, Tapeworm |
| 5 | Nematoda | Ascaris lumbricoides, wuchereria boncrofti |
| 6 | Annelida | Earthworm, Leech. |
| 7 | Arthropoda | Cockroach, Centipede |
| 8 | Mollusca | Octopus, Snail |
| 9 | Echinodermata | Starfish, Sea urchin |
| 10 | Pisces | Fishes, Sharks |
| 11 | Amphibia | Frogs, Toads |
| 12 | Reptilia | Lizard, Crocodile |
| 13 | Aves | Dove, Duck |
| 14 | Mammalia | Elephant, Goat |
VI. Write the number of chambers of the heart in the following classes of vertebrates.
| S. No. | Classes of Vertebrates | Number of Chambers |
| 1 | Class Pisces | Two chambers |
| 2 | Class Amphibia | Three chambers |
| 3 | Class Reptilia | Three chambers, except crocodile (4 chambers) |
| 4 | Class Aves | Four chambers |
| 5 | Class Mammalia | Four chambers |