Students can Download Commerce Chapter 10 Reserve Bank of India Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 10 Reserve Bank of India
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Reserve Bank of India Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which bank has the power to issue bank notes?
(a) Central bank
(b) Commercial bank
(c) Co – operative banks
(d) Foreign banks
Answer:
(a) Central bank
Question 2.
The Central bank of India is …………….
(a) PNB
(b) SBI
(c) ICICI
(d) RBI
Answer:
(d) RBI
Question 3.
The Reserve Bank of India commenced its operations from April 1,
(a) 1936
(b) 1935
(c) 1934
(d) 1933
Answer:
(b) 1935
![]()
Question 4.
Bankers are not only dealers of money but also leaders in …………….
(a) Economic development
(b) Trade development
(c) Industry development
(d) Service development
Answer:
(a) Economic development
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a function of a central bank?
(a) Guiding and regulating the banking system of a country
(b) Deal with the general public
(c) Acts essentially as a Government banker
(d) Maintains deposit accounts of all other banks
Answer:
(b) Deal with the general public
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the services included in Service businesses?
Answer:
Educational, Medical, Hospital, Banking, Warehousing, and Insurance are some of the services included in the Service business.
Question 2.
Write the meaning of ‘Bank’.
Answer:
In simple words, a bank is an institution, which deals in money and credit. The Bank normally refers to Commercial Bank.
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly explain about Central Bank.
Answer:
Every nation has one central bank. It is owned by the Government of the country. A Central bank is set up as an autonomous or quasi-autonomous body. Stability and growth of the country’s economy are the main goals of a Central bank.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention the importance of banking services.
Answer:
Banking Service is known as the nerve centre of industry and commerce in a nation. It plays a vital role by providing the money required for their regular functioning and development.
Question 2.
Explain the origin of RBI.
Answer:
The Imperial Bank of India carried out the note issue and other functions of the central bank. In 1926 the Hilton-Young Commission or the Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance (J. M. Keynes and Sir Ernest Cable were its members) made recommendations to create a central bank. As a result the RBI Act 1934 was passed and RBI launched in operations from April 1, 1935. RBI was established with a share capital of Rs. 5 crores divided into shares of Rs. 100 each fully paid up. The Head office of the RBI is situated in Mumbai.
Question 3.
Who are the persons involved in RBI administration?
Answer:
The RBI is governed by a Central Board of Directors. The 21 member board is appointed by the Government of India. It consists of;
- One governor and four deputy governors appointed for a period of four years.
- Ten directors from various fields
- Two Government officials
- Four directors – one each from local boards.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Classify the various functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer:
The functions of RBI can be grouped under three heads.
They are as follows:
Leadership and Supervisory Functions India’s Representative in World Financial Institutions In order to maintain consistency and harmony with international banking standards the RBI is associated with Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS, Switzerland) since 1997.
RBI represents the Government of India in the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD i.e. World Bank) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in which India is a member since December 27, 1945.
1. Regulator and Supervisor of Indian Banking System
The broad guidelines for all banking operations in the country are formulated by the RBI. The RBI has the power to issue licenses, control, and supervise commercial banks under the RBI Act, 1934 and the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. It conducts inspection of the commercial banks and calls for returns and other necessary information from them.
2. Monetary Authority
The RBI formulates, implements, and monitors the monetary policy of the country in order to maintain price stability, controlling inflationary trends and economic growth
3. Closely Monitoring Economic Parameters
Broad economic parameters such as employment level, price levels, and production levels, trade cycles, foreign investment flows, the balance of payments, financial markets, etc., are closely monitored by the RBI in order to achieve economic stability and growth. The Board of Financial Supervision (a committee of the Central Board of Directors) of the RBI meets at least once a month (at times every day) to closely monitor all these current developments in the country.
4. Promptly Responding to New Challenges
Whenever challenges arose before Indian Banking System, RBI promptly attends them by issuing Master Circulars and by organizing committees to analyse, review and strengthen Indian Banking. A wealth of information can be found in every Master Circular or committee report. Example: Gopalakrishnan Committee on “Information security, Electronic Banking”, April 2010
B. Traditional Functions
1. Banker and Financial Advisor to the Government
The RBI accepts money into the Central and State Governments’ accounts and makes payments on their behalf. It manages Government debt and is responsible for the issue of new loans. It advises the government on the quantum, timing, and terms of new loans. Inter-Government and interdepartmental account adjustments are carried out by the RBI.
2. Monopoly of Note Issue
The RBI is the sole authority for the printing and issue of all currency notes in India except one rupee note. It is the duty of the RBI to ensure that a sufficient number of good quality currency notes is available to the public. It exchanges currency and coins not fit for circulation. One rupee note and all coins are issued by the Ministry of Finance. Currency notes are printed at Nasik, Dewas, Salboni, Mysore, and Hoshangabad. (Currency notes are never printed outside India).
3. Banker’s Bank
The relationship between RBI and other banks in the country is just like the relationship of a commercial bank with its customers. The RBI maintains the current accounts of all commercial banks in the country. All scheduled banks should deposit a percentage of cash reserve with RBI. All banks can receive loans from RBI by red is counting of bills and against approved securities.
4. Controller of Credit and Liquidity
Controlling the credit money in circulation and the interest rate in the country is a major function of RBI. For this purpose, the RBI uses quantitative and qualitative methods of credit control. Ensuring the availability of sufficient cash and credit (liquidity) for business transactions and investment purposes in the economy is the responsibility of RBI.
5. Lender of the Last Resort:
In times of emergency, any bank in India can approach RBI for financial assistance. RBI provides them credit. When other sources of getting credit arc exhausted, all banks can obtain loan from RBI, and hence it is called lender of last resort.
6. Clearing House Services:
RBI acts as a clearinghouse and maintains a clearing system for all commercial banks in India. The aggregate amount of cheques presented by a bank on other banks represents the claim by that bank on other banks. Similar claims are made by all the banks on every other bank in the clearing.
A net settlement is arrived at the clearinghouse and accordingly the debit or credit entry is made in their current accounts. Though the RBI maintains the clearinghouse system only 14 clearing houses are owned by the RBI, 840 are managed by SBI, and 6 by nationalized banks (total 860).
7. Promotional Functions
The RBI performs a wide range of promotional functions to support national objectives.
Nurturing Banking Habits among the Public:
It is the responsibility of RBI to maintain public confidence in the banking system. It protects the depositors’ interest and aims at providing cost-effective banking services
8.Grievance Settlement Measures:
RBI has appointed 20 (up to 2017)Banking Ombudsman in 20 state capitals. The banking Ombudsman Scheme is a speedy and inexpensive forum for the resolution of customer complaints relating to certain services rendered by banks in India.
9. Agricultural Development:
The agriculture industry is specified as a priority sector by the RBI. The loans of all scheduled banks should consist of a percentage of loans to the priority sector. It works in close association with NABARD to develop agriculture in India.
10.Promotion of Small Scale Industries:
Micro Small and Medium Enterprises are included in the priority sector. All scheduled banks are required to open separate branches to specialise in the financing of these industries.
11.Facilitates Foreign Trade:
The RBI has simplified the rules for credit to exporters, through which they can now get long term advance from banks.
12. Supports Cooperative Sector:
It helps cooperative banks by relaxing rules and providing indirect financing. The rupee symbol was changed from Rs. to “ ‘ ” by the Government of India on July 15, 2010. This became necessary since other countries Indonesia, Mauritius, Nepal,
13.Custodian of Foreign Exchange Reserves:
The RBI maintains a reserve of gold and foreign currencies. When foreign exchange reserves are inadequate for meeting the balance of payments problem, it borrows from the International Monetary Fund (IMF). It also administers exchange control of the country and enforces the provisions of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999. Development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India is also the function of RBI.
14.Maintenance of Foreign Exchange Rate:
The RBI manages the exchange value of the rupee in order to facilitate India’s foreign trade and payments. It ensures that normal short-term fluctuations in the trade do not affect the exchange rate.
15.Collection and Publication of Authentic Data:
It has also been entrusted with the task of collection and compilation of statistical information relating to banking and other financial sectors of the economy. RBI monthly bulletin, annual report, and various committee reports contain treasures of authentic data.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the organizational structure of RBI.
Answer:
The head office of the RBI is situated in Mumbai. This central office has 33 departments in 2017. It has four zonal offices in Mumbai, Delhi, Calcutta, and Chennai functioning under local boards with deputy governors as their heads. It also has 19 regional offices and 11 sub-offices (2017). The RBI is governed by a central board of directors. The 21 member board is appointed by the Government of India. It consists of:
- One Governor and four deputy governors appointed for a period of four years,
- Ten Directors from various fields
- Two Government officials
- Four Directors – one each from local boards.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Cooperative Organisation Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
The head office of the RBI is situated in …………….
(a) Calcutta
(b) Mumbai
(c) Delhi
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(b) Mumbai
Question 2.
IBRD is otherwise called…………….
(a) IMF
(b) World Bank
(c) SBI
(d) RBI
Answer:
(b) World Bank
Question 3.
When did India become a member of IBRD and IMF?
(a) 1946
(b) 1947
(c) 1945
(d) 1946
Answer:
(c) 1945
![]()
Question 4.
Banking Regulation Act, …………….
(a) 1947
(b) 1949
(c) 1945
(d) 1946
Answer:
(b) 1949
Question 5.
Currency notes are printed at …………….
(a) Nasik
(b) Mumbai
(c) Delhi
(d) Kolkatta
Answer:
(a) Nasik
Question 6.
When did India carry out demonetization?
(a) Nov 8, 1996
(b) Nov 8, 2016
(c) Nov 8, 2006
(d) Nov 8, 2017
Answer:
(b) Nov 8, 2016
Question 7.
Among global currencies, the Indian rupee is given the code ……………….
(a) INR
(b) Rs.
(c) NRI
(d) IRN
Answer:
(a) INR
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)?
Answer:
It is the ratio of money and money equivalents kept within the bank in proportion to the total Time and Demand Liabilities with them.
![]()
Question 2.
What is Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)?
Answer:
It is the ratio of cash reserves with the RBI kept by Scheduled banks in proportion to the total Time and Demand Liabilities with them.
For Future Learning
Question 1.
Know the Central Banks of Some other Countries.
Answer:
The Central Bank of Russia is the Bank of Russia
The Central Bank of Sri Lanka is the Central Bank of Sri Lanka
- The Central Bank of the USA is Federal Reserve tori The Fed
- The Central Bank of Pakistan is The State Bank of Pakistan
Question 2.
Mention the names of Central Banks in three other countries.
Answer:
- Australia – Reserve Bank of Australia
- Algeria – Bank of Algeria
- Canada – Bank of Canada
Case Study
Question 1.
Taka up a recent newspaper clipping about RBI such as the measures taken to reduce NPA. etc.
Answer:
The non – performing asset (NPA) situation has been one of the contentious issues in the country over the last few years. Even though demonstration has been an issue Recently, the issue of NPAs has been at the foremost of the banking fraternity’s concerns in the last year. In the Context of an ordinance issued by the government to provide more independence to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), it is important to understand what can really be done, considering that RBI has more powers to address this issue. The question for the RBI now is “How will it solve the problem?”. While experts have commented on various measures, it would also be prudent to look across the border to China to see how to deal with this.
- The first was to reduce risks by strengthening banks and spearheading reforms to the state-owned enterprises (SOEs) by reducing their level of debt.
- The second important measure was enacting laws that allowed the creation of assets management companies, equity participation, and most important asset-based securitization.
- The third key measure that China took was to ensure the government had the financial loss of the debt “discounted” and debts equity swaps were allowed in case of growth opportunity.
- The fourth measure they took was producing incentives like tax breaks, exemption from administrative fees, and transparent evaluation norms.
- To conclude, it is important to look after some of the key measures taken by other countries to address the NPA issue.
- India should leam from it, especially in the context of valuations, securitization, and a more targeted NPA redressal mechanism. Sri Ram Balasubramanian is an economist First Published: Wednesday, May 10, 2017
![]()
Question 2.
Arrange for a group discussion on customer grievances and the cases settled by Banking Ombudsman offices.
Answer:
Banking Ombudsman offices:
The Banking Ombudsman scheme-, 1995 was notified by RBI on June 14, 1995, in terms of the power confessed on the Bank by Section 35 A of the Banking Regulations Act 1949 (10 of 1949) to provide for a system of redressal of grievances against banks. The scheme sought to establish a system of expeditions and inexpensive resolutions of customer complaints. The scheme is operation since 1995 and was revised during the year 2002. The scheme is being executed by Banking Ombudsman appointed by RBI at 15 centers covering the entire country.
Question 3.
Visit the RBI website www.rbi.org.in to read and have a discussion on any annual report, etc.
Answer:
Name of the complaints received by the Banking Ombudsman
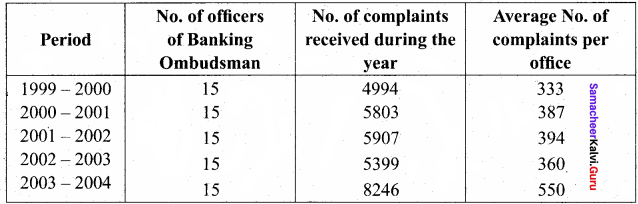
Awards issued by the Banking Ombudsman
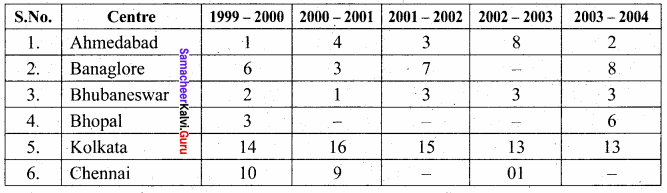
and so on …. till 15 centers.