You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 16 Applied Chemistry
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Applied Chemistry Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
One Nanometre is ………………
(a) 10– 7 metre
(b) 10– 8 metre
(c) 10– 6 metre
(d) 10– 9 metre
Answer:
(d) 10– 9 metre
Question 2.
The antibiotic Penicillin is obtained from …………………
(a) plant
(b) microorganism
(c) animal
(d) sunlight
Answer:
(b) microorganism
![]()
Question 3.
1 % solution of Iodoform is used as ……………..
(a) antipyretic
(b) antimalarial
(c) antiseptic
(d) antacid
Answer:
(c) antiseptic
Question 4.
The cathode of an electrochemical reaction involves …………….
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) neutralisation
(d) catenation
Answer:
(b) reduction
Question 5.
The age of a dead animal can be determined by using an isotope of ………………..
(a) carbon
(b) iodine
(c) phosphorous
(d) oxygen
Answer:
(a) carbon
Question 6.
Which of the following does not contain natural dyes?
(a) Potato
(b) Beetroot
(c) Carrot
(d) Turmeric
Answer:
(a) Potato
![]()
Question 7.
This type of food protect us from deficiency diseases.
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Vitamins
(c) Proteins
(d) Fats
Answer:
(b) Vitamins
Question 8.
Radiochemistry deals with ……………….
(a) oxidants
(b) batteries
(c) isotopes
(d) nanoparticles
Answer:
(c) isotopes
Question 9.
The groups responsible for the colour of an organic compound is called ………………….
(a) isotopes
(b) auxochrome
(c) chromogen
(d) chromophore
Answer:
(d) chromophore
Question 10.
Chlorinated hydrocarbons are used as ……………..
(a) fertilizers
(b) pesticides
(c) food colourants
(d) preservatives
Answer:
(b) pesticides
II. Fill in the blanks.
- ……………. is an electrochemical cell which converts electrical energy into chemical change (Reaction).
- Painkiller drugs are called ……………..
- Aspirin is an …………….
- …………. , …………….. and …………… are macronutrients required for plant growth.
- ……………. is a chemical used in fingerprint analysis.
Answer:
- Electrolytic cell
- Analgesic
- Analgesics
- Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Potassium
- Ninhydrin
III. Match the following.
| S.No. | A | B |
| 1. | Antipyretics | (a) Large surface area |
| 2. | Corrosion prevention | (b) Iodine-131 |
| 3. | Hyperthyroidism | (c) Fever |
| 4. | Nanoparticle | (.d) Cancer cell identification |
| 5. | Nanorobotics | (e) Electroplating |
Answer:
- (c) Fever
- (e) Electroplating
- (b) Iodine – 131
- (a) Large surface area
- (d) Cancer cell identification
IV. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
What is Chemotherapy?
Answer:
Treatment of certain diseases by destroying the invading organism without damaging the cells of the host, by the use of certain organic compounds is known as Chemotherapy.
![]()
Question 2.
What is called Anaesthetics? How are they classified?
Answer:
The drugs which cause loss of sensation are called Anaesthetics.
Classification: Anaesthetics are classified according to the area of application as,
- General Anaesthetics,
- Local Anaesthetics.
Question 3.
What is the need for chemical fertilizers in crop fields?
Answer:
Chemical fertilizers provide the essential micro and macronutrients for crop growth that may not be sufficiently available in the soil.
Question 4.
What is Forensic chemistry related to?
Answer:
Forensic chemistry is related to the application of scientific principles, techniques, and methods to the investigation of crime.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the types of dyes based on their method of application.
Answer:
1. Acid Dyes
- These are acidic in nature.
- They are used for dyeing animal fibres and synthetic fibres.
- These can be used for protein fibre such as wool and silk.
Example: Picric acid, Naphthol yellow-s
2. Basic Dyes:
- These are basic dyes containing basic group (- NH2, NHR, -NR2).
- They are used for dyeing animal fibres and plant fibres.
(Example: Crystal violet, Methylene Blue).
3. Mordant dyes (or) Indirect Dyes :
- These dyes have a poor affinity for cotton fabrics and hence do not dye directly.
- They require pretreatment of the fibre with a mordant.
- Mordant is a substance which can be fixed to the fibre and then can be combined with the dye to form an insoluble complex called lake. Salts of aluminium, chromium and iron are used as mordants.
Example: Alizarin.
4. Direct Dyes:
- They have high affinity for cotton, rayon and other cellulose fibre.
- So they are applied directly as they fix firmly on the fabric.
Example: Congo red.
5. Vat Dyes:
- It can be used only on cotton and, not on silk and wool.
- This dyeing is a continuous process and is carried out in a large vessel called vat.
- So it is called a Vat dye.
Example: Indigo
Question 2.
Name various food additives and explain their functions.
Answer:
| Type of additive | The function of the additive | Example |
| Preservatives | They protect food from spoilage by microorganisms in storage. | Vinegar, Sodium benzoate, benzoic acid, sodium nitrite |
| Colourants | They give pleasant colours to food | Carotenoids, Anthocyanin, Curcumin |
| Artificial Sweeteners | They add sweet taste to food | Saccharin, Cyclamate |
| Flavor enhancers | They are used to enhance the flavor of food items | Monosodium glutamate, Calcium diglutamate |
| Antioxidants | They prevent the oxidation of food. They protect us against cardiovascular disease. | Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Carotene |
VI. HOTS
Question 1.
Batteries that are used in the mobile phones can be recharged. Likewise, can you recharge the batteries used in watches? Justify your answer.
Answer:
A primary cell cannot be recharged. Watch batteries have a primary cell. In a primary cell, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy when current is drawn from it.
Whereas mobile phones use secondary cells. In secondary cells, electrical energy is converted to chemical energy when current is passed through it and chemical energy is converted to electrical energy when current is drawn from it.
![]()
Question 2.
Sudha met with a fire accident. What kind of drug(s), she must take?
Answer:
- Antibiotic ointments must be used to treat the bums.
- Analgesic tablets can be taken to relieve pain.
- Antiseptic creams can be given to prevent infection.
Question 3.
The soil pH of cropland is 5. What kind of fertilizers should be used in that land?
Answer:
Organic fertilizer like compost can be used to maintain pH of soil at 6.5, which is ideal for soil and to moderate the acidity.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Applied Chemistry Additional Questions
I. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
Explain the structure of an electrolytic cell.
Answer:
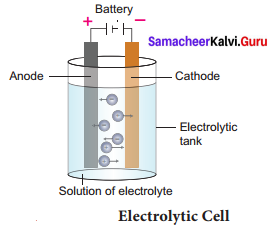
- It is an electrochemical cell which converts electrical energy into chemical energy i.e. in electrolytic cells, electricity is used to bring about chemical reactions.
- Here, both anode and cathode are in contact with Anode same electrolyte and thus the half-cells are not separated. As seen in galvanic cells, the electrolytic cell also involves redox reaction. We get electricity from galvanic cells. But electrolytic cells use electricity.
- In electrolytic cells, when electricity is passed to the electrolyte, it dissociates into its constituent ions. These ions undergo redox reactions forming the respective elements. This phenomenon is called Electrolysis. So electrolysis is a process by which an electrolyte is decomposed into its constituent elements by passing electricity through its aqueous solution or fused (molten) state.
![]()
Question 2.
How does galvanic cells produce electricity?
Answer:
In a galvanic cell, at anode oxidation takes place which releases electrons. These electrons are attracted by the cathode and hence the electrons flowing from anode to cathode are gained in the reduction reaction. As long as the redox reaction proceeds, there is a flow of electrons and hence electricity.
Question 3.
What are drugs? What are their characteristics?
Answer:
The chemicals used for treating diseases are termed as drug.
Characteristics of drugs: A drug must possess the following;
- It should not be toxic
- It should not cause any side effects.
- It should not affect the receptor tissue
- It should not affect the normal physiological activities
- It should be effective in its action.
Question 4.
Write the applications of Nanochemistry.
Answer:
Some applications of Nanochemistry are:
- The metallic nanoparticles can be used as very active catalysts.
- Chemical sensors from nanoparticles and nanowires enhance the sensitivity and sensor selectivity.
- Nanocoatings and nanocomposites are found useful in making a variety of products such as sports equipment, bicycles and automobiles etc.
- These are used as novel UV-blocking coatings on glass bottles which protect beverages from being damaged by sunlight.
- Nanotechnology is being applied in the production of synthetic skin and implant surgery.
- Nanomaterials that conduct electricity are being used in electronics as minute conductors to produce circuits for microchips.
- Nanomaterials have extensive applications in the preparation of cosmetics, deodorants and sunscreen lotion and they are used to improve moisturizers without making them too oily.
- Nanoparticle substances are incorporated in fabrics to prevent the growth of bacteria.
- Biomedical devices like drug infusion pumps, microneedles and glucometers are made from nanomaterials.
- Nanochemistry is used in making space, defence and aeronautical devices
![]()
Question 5.
What are the applications of Radiochemistry?
Answer:
Important applications of radioisotopes are as under –
- Radiocarbon dating – its a method by which the age of fossil wood or animal is determined using C-14 isotope.
- Study of chemical reactions – the nature of some chemical reactions can be studied by mixing a radioisotope with a non-radioactive isotope of the reactants. The radioisotope used for this purpose is radiotracer.
- Diagnosis – Radioisotope is found very useful to diagnose and understand many diseases.
Question 6.
Write a note on Natural dyes.
Answer:
Many natural dyes have been known from a long time. These are obtained from vegetable sources.
- Henna: It is a reddish-brown dye obtained from plant Lawsonia inermis (Tamil: Maruthondri). A paste of these leaves is used as a hair dye and also for colouring palms.
- Turmeric: It is the traditional natural cosmetic in India. It is obtained from the plant Curcuma. longa. It also acts as an antiseptic. Turmeric is mostly used in India for colouring food.
![]()
Question 7.
What is electroplating? Why is it done?
Answer:
The process of depositing a thin layer of one metal over another metal by the process of electrolysis is called electroplating.
It is done to protect the metal from corrosion. For example, metals like iron are electroplated with tin, nickel, or chromium to protect them from rusting.